Microfluidic Preparation of pH-Responsive Microsphere Fibers and Their Controlled Drug Release Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
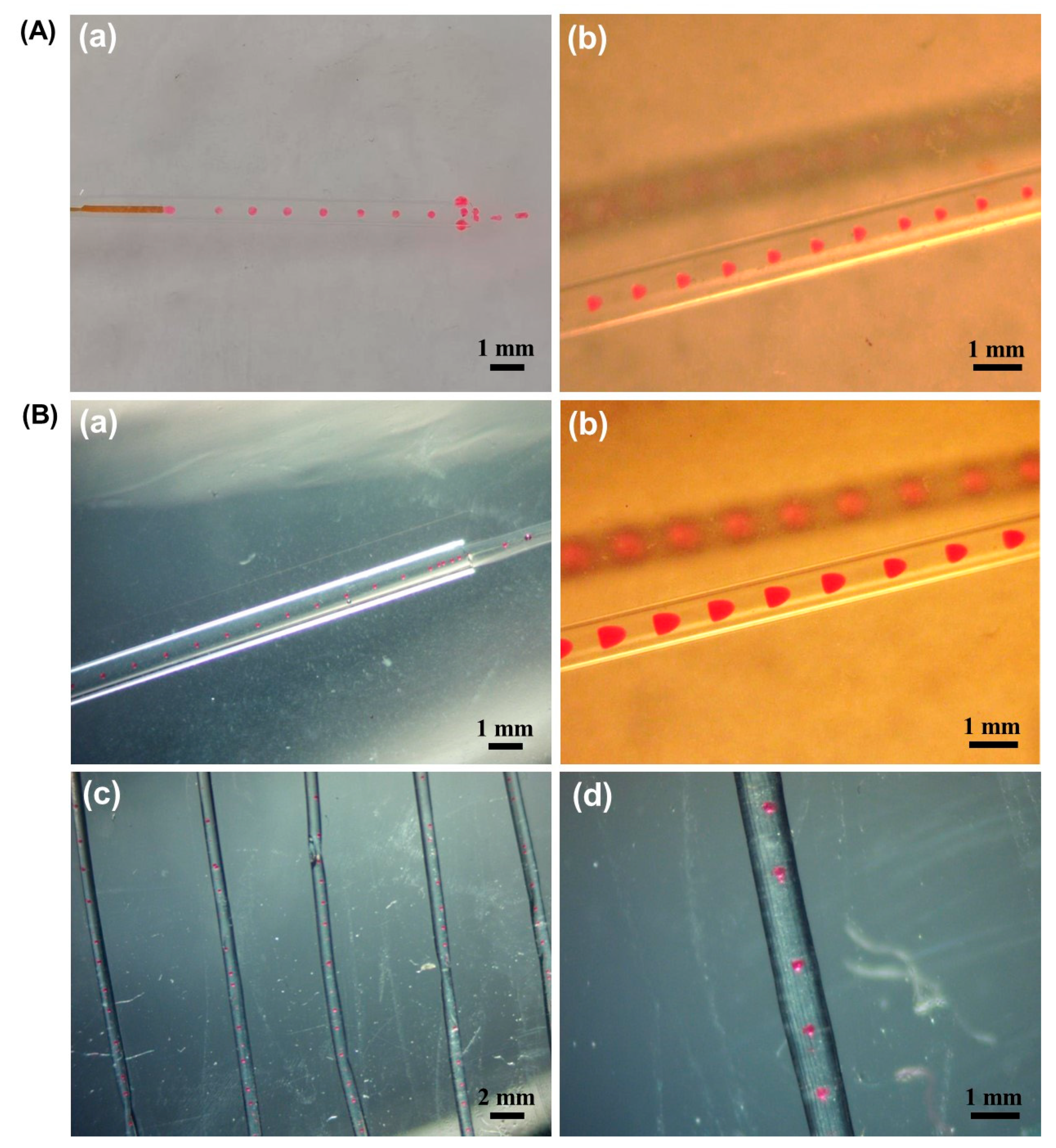
2.1. O/W (Oil-in-Water Emulsions) Droplet Formation
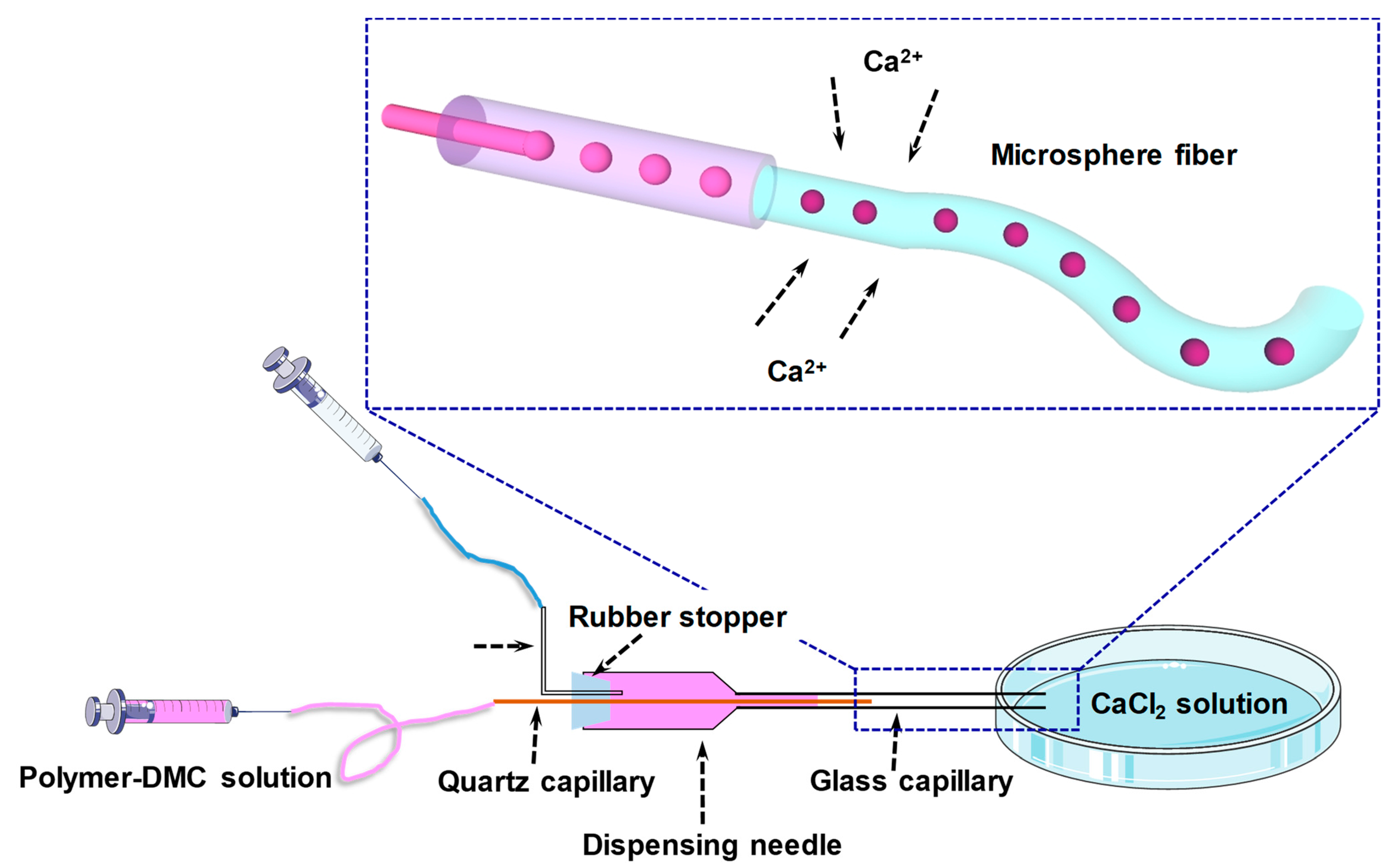
2.2. Microsphere Fiber Formation
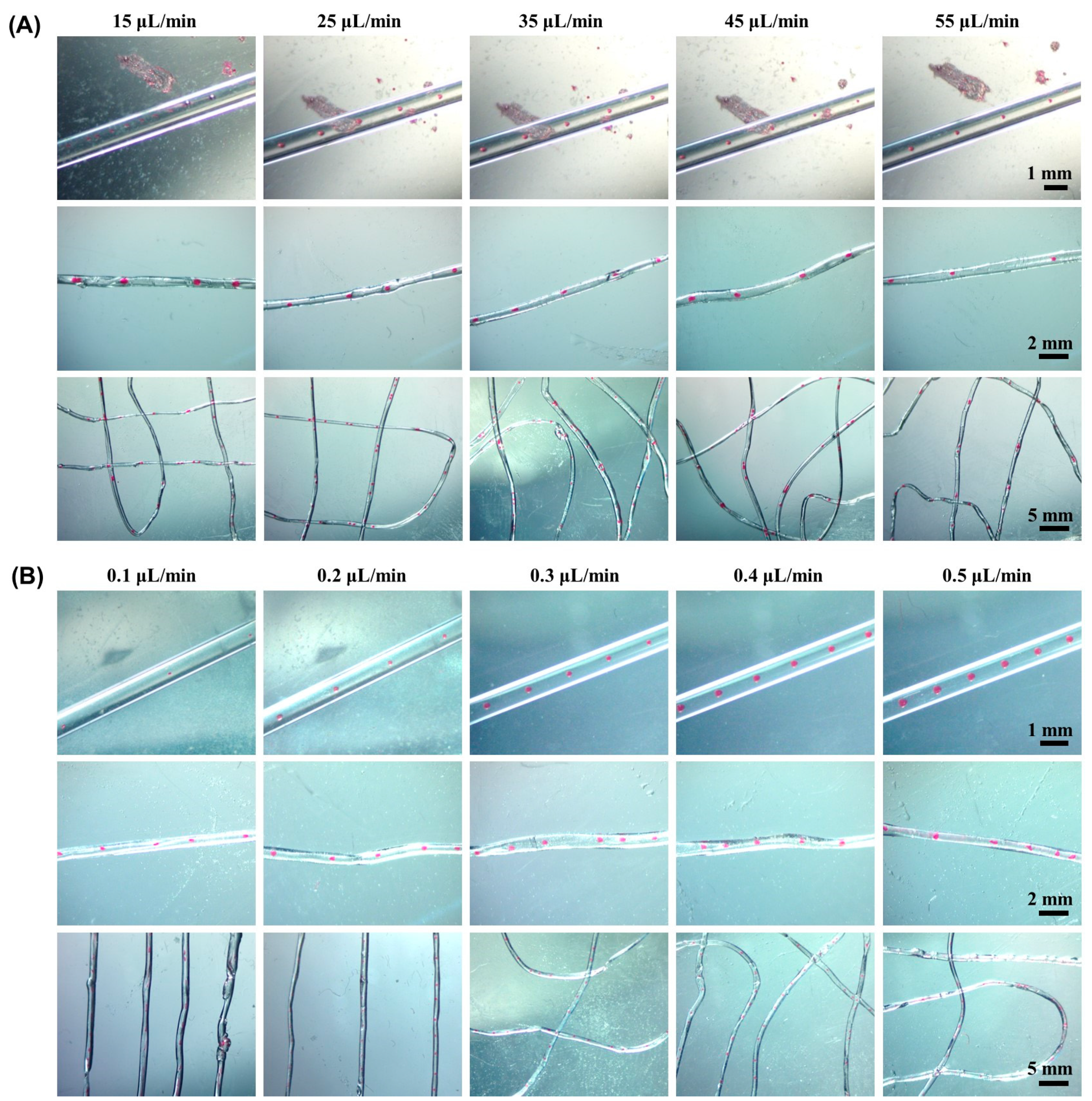
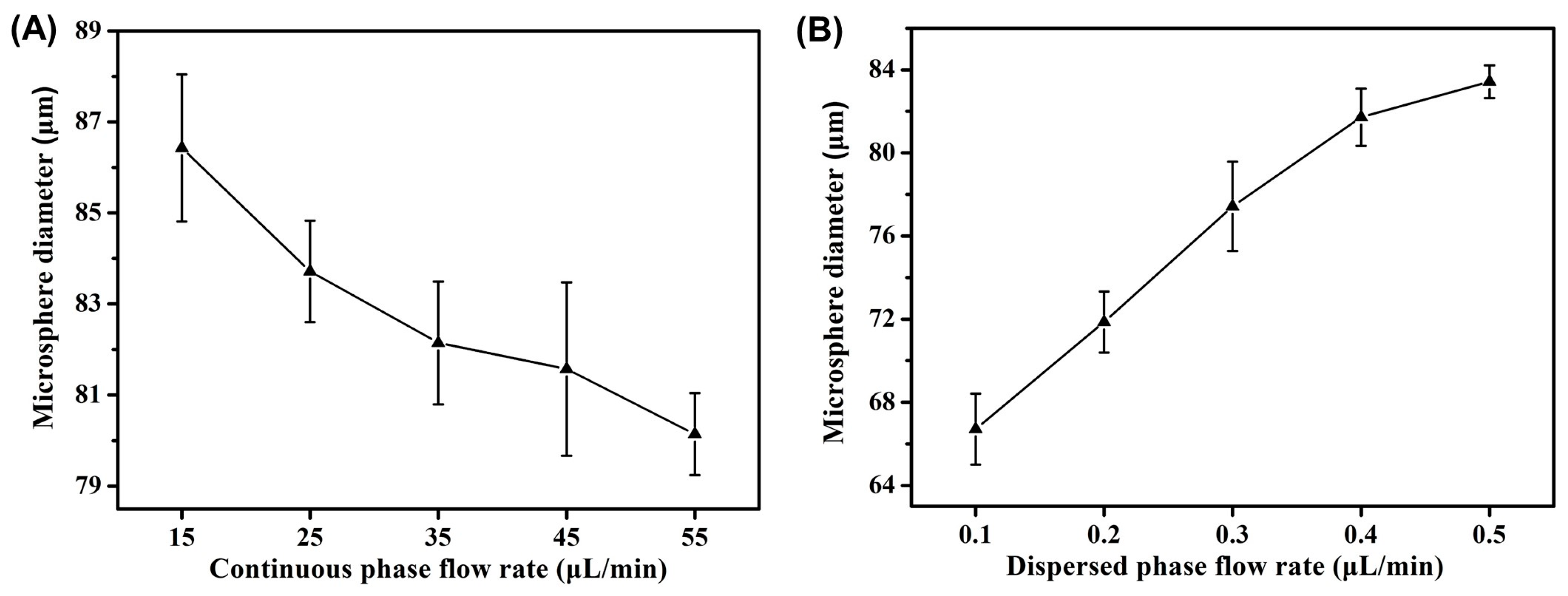
2.3. Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology of Microsphere Fibers
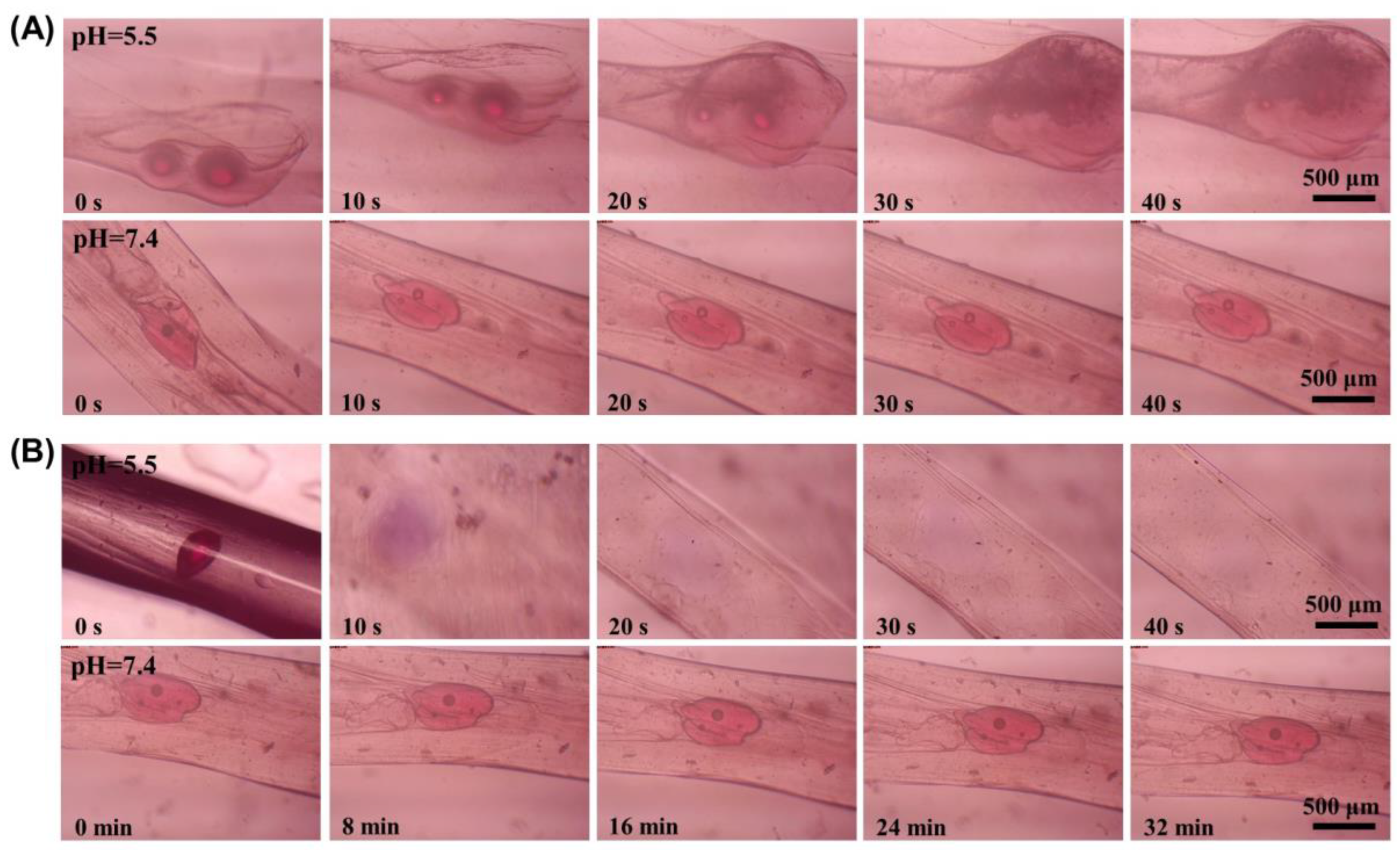
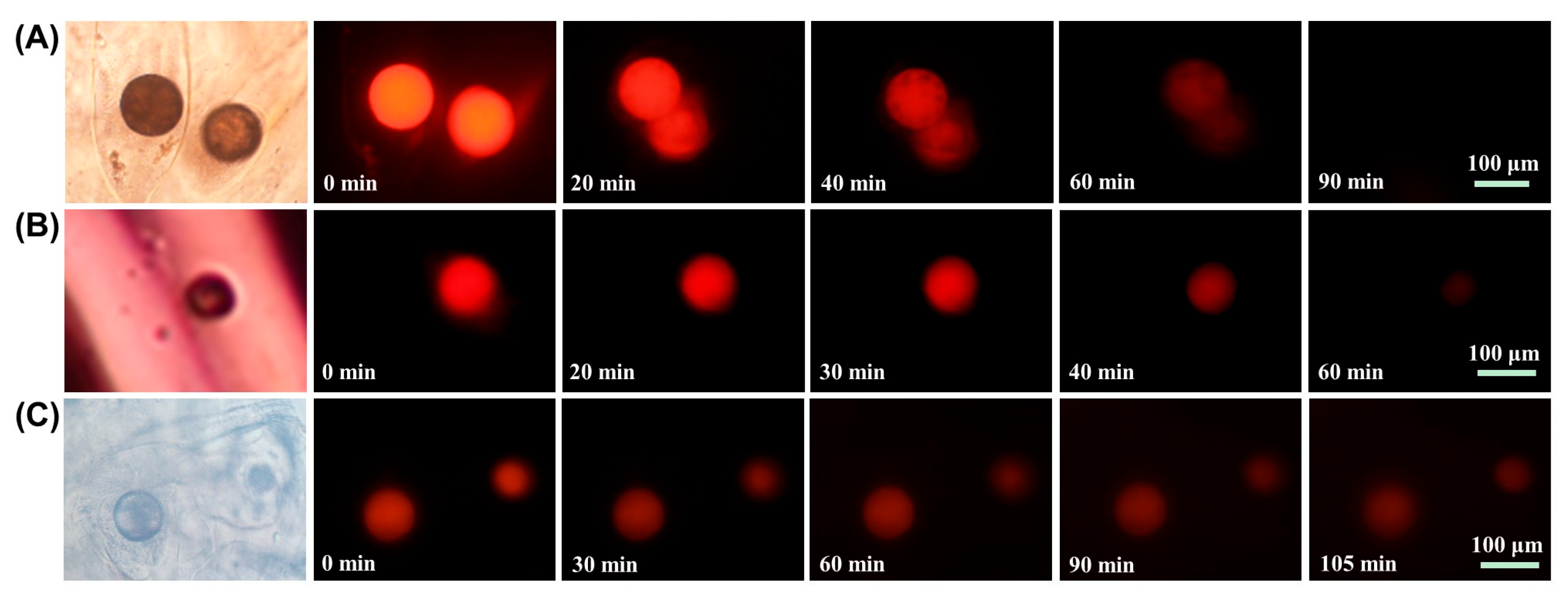
2.4. pH Responsive Properties of Microsphere Fibers
2.5. Controlled Drug Release Properties of Microsphere Fibers
2.6. Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Construction of Coaxial Capillary Microfluidic Device and Preparation of Hydrogel Fibers
4.2. Preparation of Dispersed Phase Solution
4.3. Continuous Phase Solution Preparation
4.4. Composite Fiber Preparation
4.5. Microsphere Degradation at Different pH Conditions
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Microsphere Degradation and Drug Release of Composite Fibers in Cell Environment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuo, W.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Z.; Habib, S.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, N.; Su, S.; Zhu, J. Synthesis of sodium alginate/polyacrylamide photochromic hydrogels with quadruple crosslinked networks. J. Mat. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6952–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qu, K.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; et al. Oxidized sodium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogels adhesive for promoting wheat growth. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Q.; Han, S. Fabrication and performance of novel multifunctional sodium alginate/polyvinylpyrrolidone hydrogels. Chemosphere 2024, 348, 140758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Khan, A.; Afzal, Z.; Umer, M.F.; Khan, J.; Khan, G.M. Formulation development and characterization of cefazolin nanoparticles-loaded cross-linked films of sodium alginate and pectin as wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.X.; Cheng, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Ji, X.; Guo, J.; Lu, Y.H. An eco-friendly antheraea pernyi silk gland protein/sodium alginate multiple network hydrogel as potential drug release systems. Gels 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Lai, G.; Li, Y.; Zeng, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, G.; Li, L.; Wu, L. Photo-crosslinked adhesive hydrogel loaded with extracellular vesicles promoting hemostasis and liver regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1170212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Ahn, G. Alginate-based nanomaterials: Fabrication techniques, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raus, R.A.; Nawawi, W.M.F.W.; Nasaruddin, R.R. Alginate and alginate composites for biomedical applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 280–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, A.; Jakubowska, E.; Wojtylko, M.; Jadach, B.; Gackowski, M.; Gadzinski, P.; Napierala, O.; Ravliv, Y.; Osmalek, T. Alginate-based materials loaded with nanoparticles in wound healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, A.; Neamtu, B.; Zahan, M.; Iancu, G.M.; Bacila, C.; Miresan, V. Current trends in advanced alginate-based wound dressings for chronic wounds. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Molla, M.T.H.; Malitha, M.D.; Chandra, D.; Abul Bashar, M.; Biswas, T.K.; Sultana, M.A.; Ahsan, M.S. Modified alginate-based soft tissue adhesive: Synthesis, characterization, and application in the treatment of in vivo wound closure. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2023, 127, 103515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, B. Highly water-absorptive and antibacterial hydrogel dressings for rapid postoperative detumescence. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 845345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parani, M.; Lokhande, G.; Singh, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. Engineered nanomaterials for infection control and healing acute and chronic wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10049–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.Y.; Mun, C.H.; Kang, E.; No, D.Y.; Ju, J.; Lee, S.H. One-stop microfiber spinning and fabrication of a fibrous cell-encapsulated scaffold on a single microfluidic platform. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 024108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addario, G.; Eussen, D.; Djudjaj, S.; Boor, P.; Moroni, L.; Mota, C. 3D printed tubulointerstitium chip as an in vitro testing platform. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, e2300440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Buyana, B. Alginate in wound dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Ren, K.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S. Alginate: Microbial production, functionalization, and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Alginate: Enhancement strategies for advanced applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Alginate-based micro- and nanosystems for targeted cancer therapy. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadte, P.; Rademacher, F.; Andresen, G.; Hellfritzsch, M.; Qiu, H.; Maschkowitz, G.; Glaeser, R.; Heinemann, N.; Druecke, D.; Fickenscher, H.; et al. 3D-printed wound dressing platform for protein administration based on alginate and zinc oxide tetrapods. Nano Converg. 2023, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, M.; Singh Chandel, A.K.; Malek, N.I.; Dholakiya, B.Z. Preparation of sodium alginate/Cur-PLA hydrogel beads for curcumin encapsulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 254, 128005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xia, X.; Liu, J.; Hou, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y.; He, F.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Cartilage-inspired self-assembly glycopeptide hydrogels for cartilage regeneration via ROS scavenging. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 32, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Pan, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Zang, R. Structures, properties, and bioengineering applications of alginates and hyaluronic acid. Polymers 2023, 15, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.; Dev, A.; Das, S.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kumar, A.; Thakur, V.K.; Han, S.S. Curcumin-loaded alginate hydrogels for cancer therapy and wound healing applications: A review. Int. J Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abka-Khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, properties and applications of alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Geze, A.; Wouessidjewe, D.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Biocompatible double-membrane hydrogels from cationic cellulose nanocrystals and anionic alginate as complexing drugs codelivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6880–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Benavente, L.P.; Chitto, M.; Wychowaniec, J.K.; Post, V.; D’Este, M.; Constant, C.; Zeiter, S.; Feng, W.; Moreno, M.G.; et al. Alginate microbeads and hydrogels delivering meropenem and bacteriophages to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa fracture-related infections. J. Control. Release 2023, 364, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennifer, A.; Senthilvelan, P.; Sethuraman, S.; Sundaramurthi, D. Key advances of carboxymethyl cellulose in tissue engineering & 3D bioprinting applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117561. [Google Scholar]
- Allafchian, A.; Hosseini, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M. Electrospinning of PVA-carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers for flufenamic acid drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.; Repanas, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Glasmacher, B.; NarendraKumar, U.; Manjubala, I. PEO-CMC blend nanofibers fabrication by electrospinning for soft tissue engineering applications. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. SERS-fluorescence dual-mode pH-sensing method based on Janus microparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39699–39707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.Y.H.; Lee, C.S.; Pichika, M.R.; Cheng, S.F.; Lam, K.Y. PH Responsive polyurethane for the advancement of biomedical and drug delivery. Polymers 2022, 14, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Kuang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zheng, D.-W.; Song, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Ingenious pH-sensitive dextran/mesoporous silica nanoparticles based drug delivery systems for controlled intracellular drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Park, K.M.; Park, K.D. PLGA microparticle-embedded thermosensitive hydrogels for sustained release of hydrophobic drugs. Biomed. Mater. 2007, 2, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Song, M.; Cui, J.; Wei, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J. Kneading-dough-inspired quickly dispersing of hydrophobic particles into aqueous solutions for designing functional hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFail, A.J.; Edington, H.D.; Matthews, S.; Lee, W.C.C.; Marra, K.G. Controlled release of bioactive doxorubicin from microspheres embedded within gelatin scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 79A, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Huo, Y.; Ci, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Bai, B.; Hao, J.; Hu, G.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; et al. Biomimetic porous hydrogel scaffolds enabled vascular ingrowth and osteogenic differentiation for vascularized tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygili, E.; Kaya, E.; Ilhan-Ayisigi, E.; Saglam-Metiner, P.; Alarcin, E.; Kazan, A.; Girgic, E.; Kim, Y.W.; Gunes, K.; Eren-Ozcan, G.G.; et al. An alginate-poly(acrylamide) hydrogel with TGF-β3 loaded nanoparticles for cartilage repair: Biodegradability, biocompatibility and protein adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, S.; Montembault, A.; Ladaviere, C. Chitosan hydrogels incorporating colloids for sustained drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, Z.; Nourbakhsh, M.S.; Kiani, S.; Heydari, Y.; Ashtiani, M.K.; Daemi, H.; Baharvand, H. Co-delivery of minocycline and paclitaxel from injectable hydrogel for treatment of spinal cord injury. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garakani, S.S.; Davachi, S.M.; Bagher, Z.; Esfahani, A.H.; Jenabi, N.; Atoufi, Z.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Rashedi, H.; Jalessi, M. Fabrication of chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone hydrogel scaffolds containing PLGA microparticles loaded with dexamethasone for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Microfluidic Preparation of pH-Responsive Microsphere Fibers and Their Controlled Drug Release Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010193
Wang N, Wei Y, Hu Y, Sun X, Wang X. Microfluidic Preparation of pH-Responsive Microsphere Fibers and Their Controlled Drug Release Properties. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Yixuan Wei, Yanrong Hu, Xiaoting Sun, and Xiaohong Wang. 2024. "Microfluidic Preparation of pH-Responsive Microsphere Fibers and Their Controlled Drug Release Properties" Molecules 29, no. 1: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010193
APA StyleWang, N., Wei, Y., Hu, Y., Sun, X., & Wang, X. (2024). Microfluidic Preparation of pH-Responsive Microsphere Fibers and Their Controlled Drug Release Properties. Molecules, 29(1), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010193



