DSC, TGA-FTIR and FTIR Assisted by Chemometric Factor Analysis and PXRD in Assessing the Incompatibility of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol Hydrochloride with Pharmaceutical Excipients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DSC Study with FA Calculation
2.2. TGA-FTIR Experiments
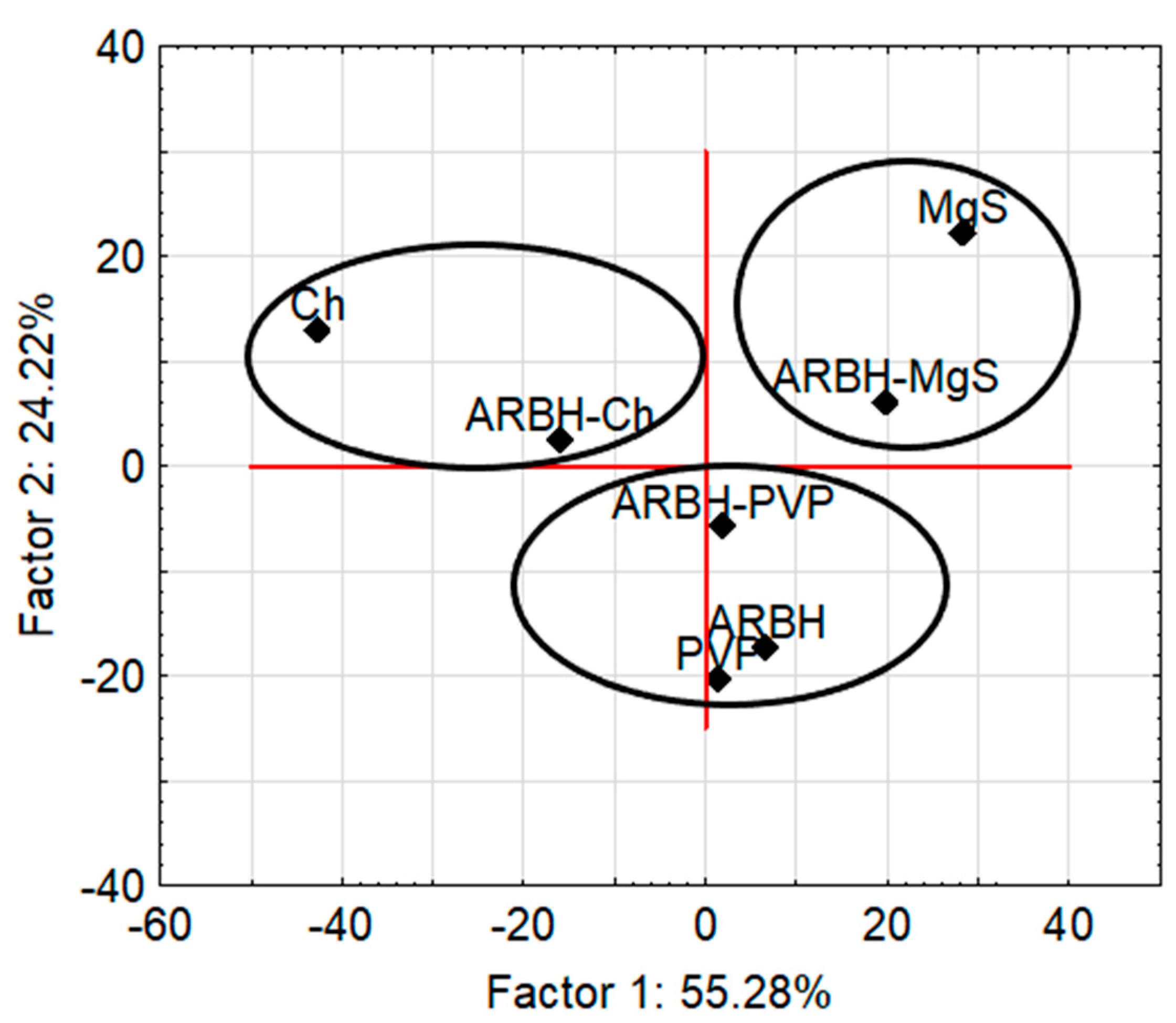
2.3. FTIR Results with FA Calculation
2.4. PXRD Study
2.5. Intrinsic Dissolution Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Arbidol Hydrochloride Mixtures
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. Thermogravimetry Coupled with FTIR Spectroscopy (TG-FTIR)
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.6. Chemometric Factor Analysis (FA)
3.7. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.8. Intrinsic Dissolution Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, T.; Chen, C.; Yang, G.; Zha, T.; Lu, J.; Xue, Y. Arbidol monotherapy is superior to lopinavir/ritonavir in treating COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, E21–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hong, Z.; Xia, J. Arbidol combined with LPV/r versus LPV/r alone against Corona Virus Disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study. J. Infect. 2020, 81, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manin, A.N.; Surov, A.O.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Crystal structures, thermal analysis, and dissolution behavior of new solid forms of the antiviral drug arbidol with dicarboxylic acids. Crystals 2015, 5, 650–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; et al. The anti-influenza virus drug, arbidol is an efficient inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushkov, R.G. Arbidol antiviral, immunostimulant, interferon inducer. Drug Future 1992, 17, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, R.; Bhandari, S. Drug-excipient compatibility screening. Role of thermoanalytical and spectroscopic techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyeye, M.C.; Brittain, H.G. Preformulation in Solid Dosage form Development; Informa, Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, D.Q.M.; Reading, M. Thermal Analysis of Pharmaceuticals; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Kuang, C.; Zhang, X. Preparation and evaluation of taste masked oral suspension of arbidol hydrochloride. Asian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, B.; Wesolowski, M. Compatibility studies of hydrocortisone with excipients using thermogravimetric analysis supported by multivariate statistical analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S.P.; Nethercott, M.J.; Mays, C.J.; Winquist, N.T.; Arthur, D.; Calahan, J.L.; Sethi, M.; Pardue, D.S.; Kim, J.; Amidon, G.; et al. Characterization of synthesized and commercial forms of magnesium stearate using differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, powder x-ray diffraction, and solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haware, R.V.; Vinjamuri, B.P.; Sarkar, A.; Stefik, M.; Stagner, W.C. Deciphering magnesium stearate thermotropic behavior. Inter. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Ansari, M.N.; Ezzeldin, E.; Khalil, N.Y.; Ali, R. Improving the solubilization and bioavailability of arbidol hydrochloride by the preparation of binary and ternary β-cyclodextrin complexes with Poloxamer 188. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson Education: Essex, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Chi, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T. The delivery of arbidol by salt engineering: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Černá, M.; Barros, A.S.; Nunes, A.; Rocha, S.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Čopíková, J.; Coimbra, M.A. Use of FT-IR spectroscopy as a tool for the analysis of polysaccharide food additives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 51, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačuráková, M.; Wilson, R.H. Developments in mid-infrared FT-IR spectroscopy of selected carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireles, L.K.; Wu, M.R.; Saadeh, N.; Yahia, L.; Sacher, E. Physicochemical characterization of polyvinyl pyrrolidone: A tale of two polyvinyl pyrrolidones. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30461–30467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nep, E.I.; Conway, B.R. Preformulation studies on grewia gum as a formulation excipient. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 108, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Quinn, M.E. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.; Kumar, R.; Lal Sahu, P.; Nath Singh, G. Physicochemical characterization and compatibility study of roflumilast with various pharmaceutical excipients. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1627–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, B.; Wesolowski, M. FTIR and TG analyses coupled with factor analysis in a compatibility study of acetazolamide with excipients. Spectrochim. Acta 2019, 208, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinan, Å.; Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAc Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Pharmacopeia, USP 39, NF 34. Rockville 2015, 1179, 4992–4994.
- Ibraheem, B.; Wagner, K.G. Influence of high pressure compaction on solubility and intrinsic dissolution of ibuprofen binary mixtures employing standard excipients. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

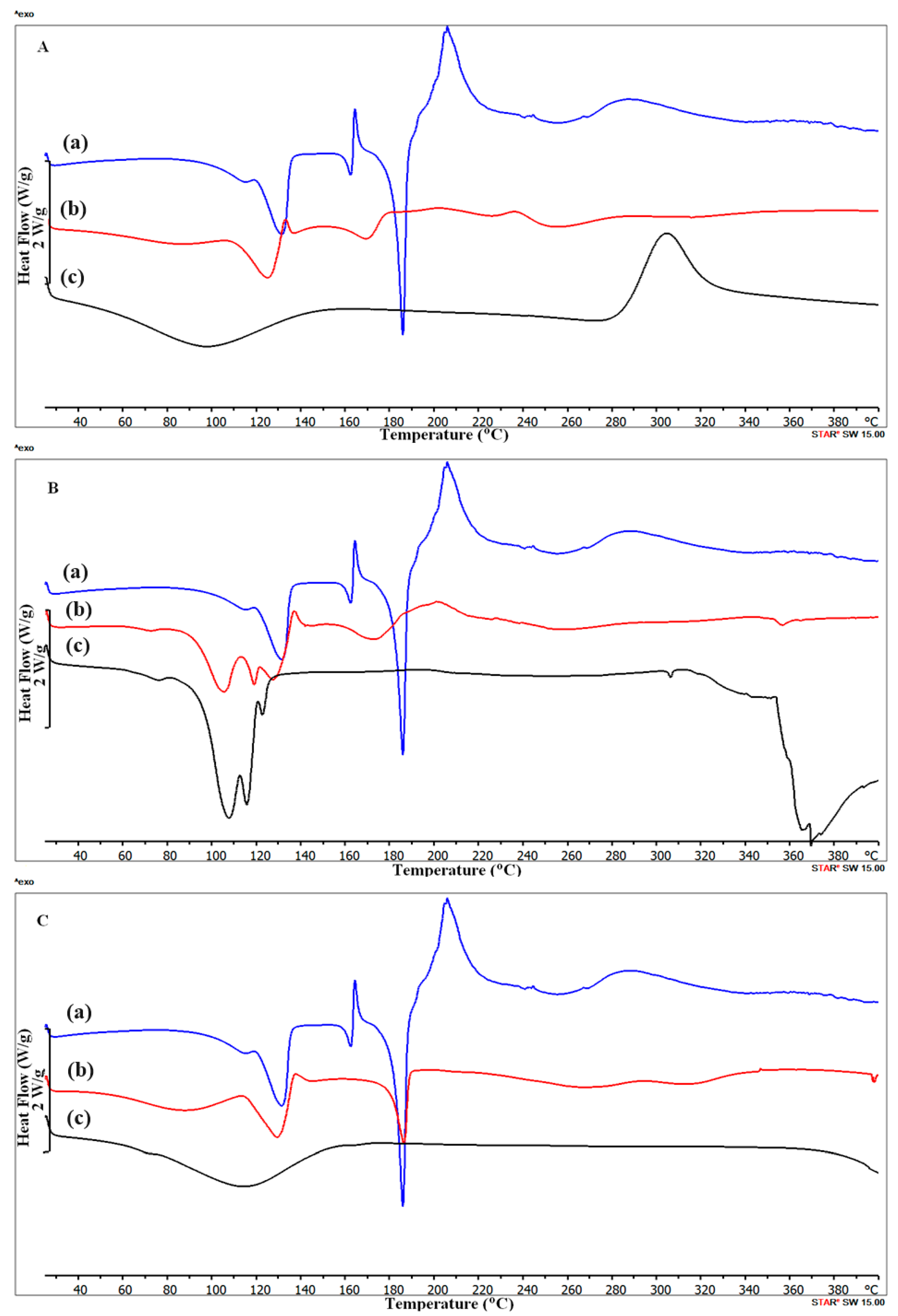



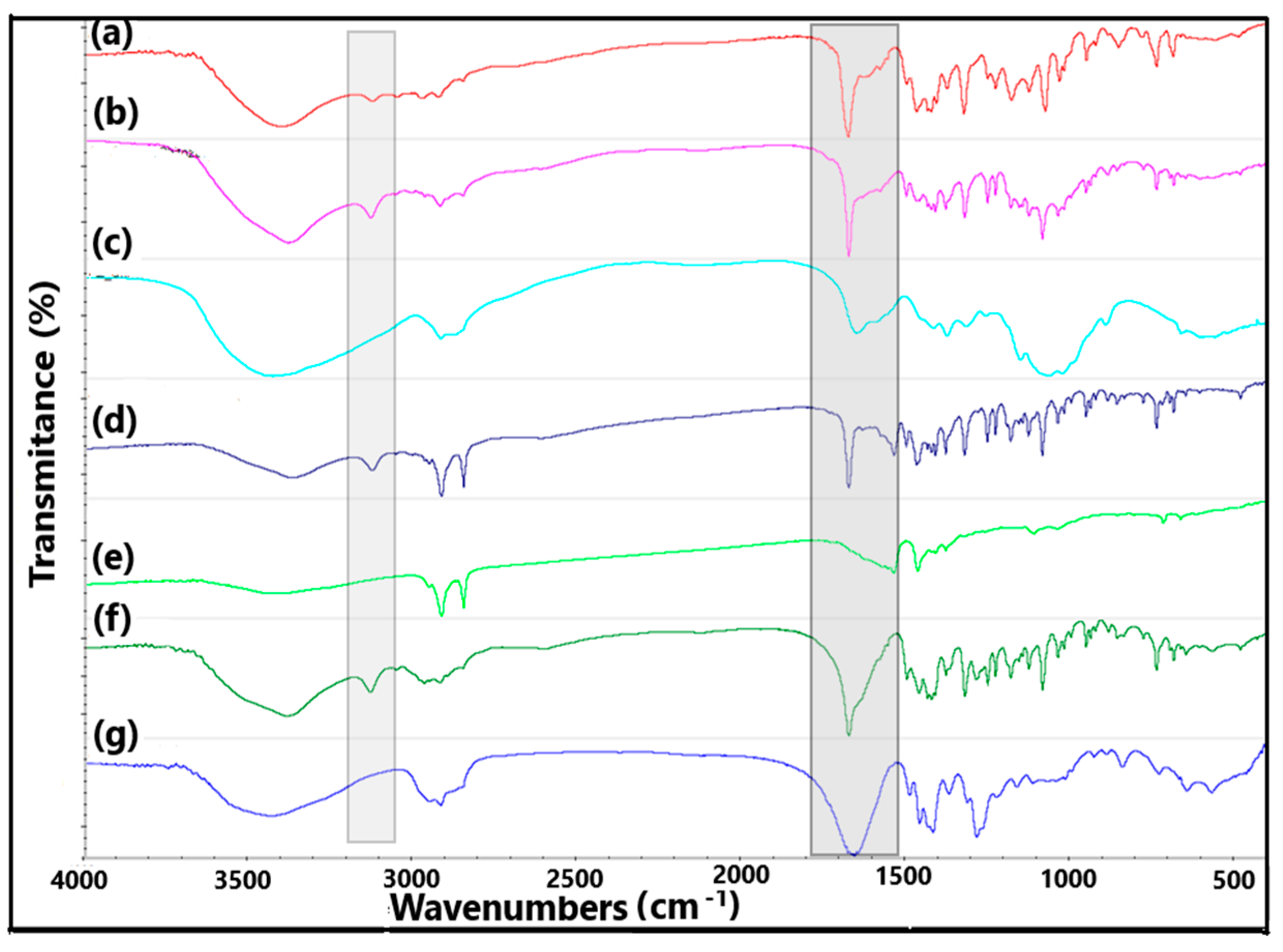


| Substance | T Onest (°C) | T Peak(s) (°C) | Enthalpy (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arbidol hydrochloride | 113.89 | 114.46; 131.48 | −125.93 |
| 156.67 | 162.27; 164.29 | −25.47; 16.28 | |
| 180.37 | 185.77 | −186.18 | |
| 198.08 | 205.79 | 108.79 | |
| 273.88 | 287.97 | 45.86 | |
| Chitosan | 92.72 | 93.78 | −280.91 |
| 194.93 | 273.02 | −112.89 | |
| 286.44 | 305.21 | 250.18 | |
| Magnesium stearate | 64.84 | 75.75; 107.37; 115.73; | −321.22 |
| 304.23 | 122.64 | −42.51 | |
| 358.78 | 255.17; 306.24; 368.6 | ||
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 | 48.0 | 91.3 | −292.1 |
| Arbidol Hydrochloride Mixed with | DSC and FTIR with Aid of FA Approach |
|---|---|
| Chitosan | Incompatibility |
| Magnesium stearate | Incompatibility |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 | Compatibility |
| Formulation | Stability of the Tablet in 0.1 M HCl | Amount of Arbidol Hydrochloride Released after 60 min |
|---|---|---|
| Arbidol hydrohloride | disintegration after 5 min | - |
| Arbidol hydrochloride with chitosan | >60 min | ~40% |
| Arbidol hydrochloride with magnesium stearate | >60 min | ~20% |
| Arbidol hydrochloride with polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 | disintegration after 1 min | - |
| Factors Variance (%) | Methods | |
|---|---|---|
| DSC | FTIR | |
| Factor 1 | 69.13 | 55.28 |
| Factor 2 | 15.09 | 24.22 |
| Factor 3 | 8.55 | 10.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojek, B.; Bartyzel, A.; Sawicki, W.; Plenis, A. DSC, TGA-FTIR and FTIR Assisted by Chemometric Factor Analysis and PXRD in Assessing the Incompatibility of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol Hydrochloride with Pharmaceutical Excipients. Molecules 2024, 29, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010264
Rojek B, Bartyzel A, Sawicki W, Plenis A. DSC, TGA-FTIR and FTIR Assisted by Chemometric Factor Analysis and PXRD in Assessing the Incompatibility of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol Hydrochloride with Pharmaceutical Excipients. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010264
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojek, Barbara, Agata Bartyzel, Wiesław Sawicki, and Alina Plenis. 2024. "DSC, TGA-FTIR and FTIR Assisted by Chemometric Factor Analysis and PXRD in Assessing the Incompatibility of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol Hydrochloride with Pharmaceutical Excipients" Molecules 29, no. 1: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010264
APA StyleRojek, B., Bartyzel, A., Sawicki, W., & Plenis, A. (2024). DSC, TGA-FTIR and FTIR Assisted by Chemometric Factor Analysis and PXRD in Assessing the Incompatibility of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol Hydrochloride with Pharmaceutical Excipients. Molecules, 29(1), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010264







