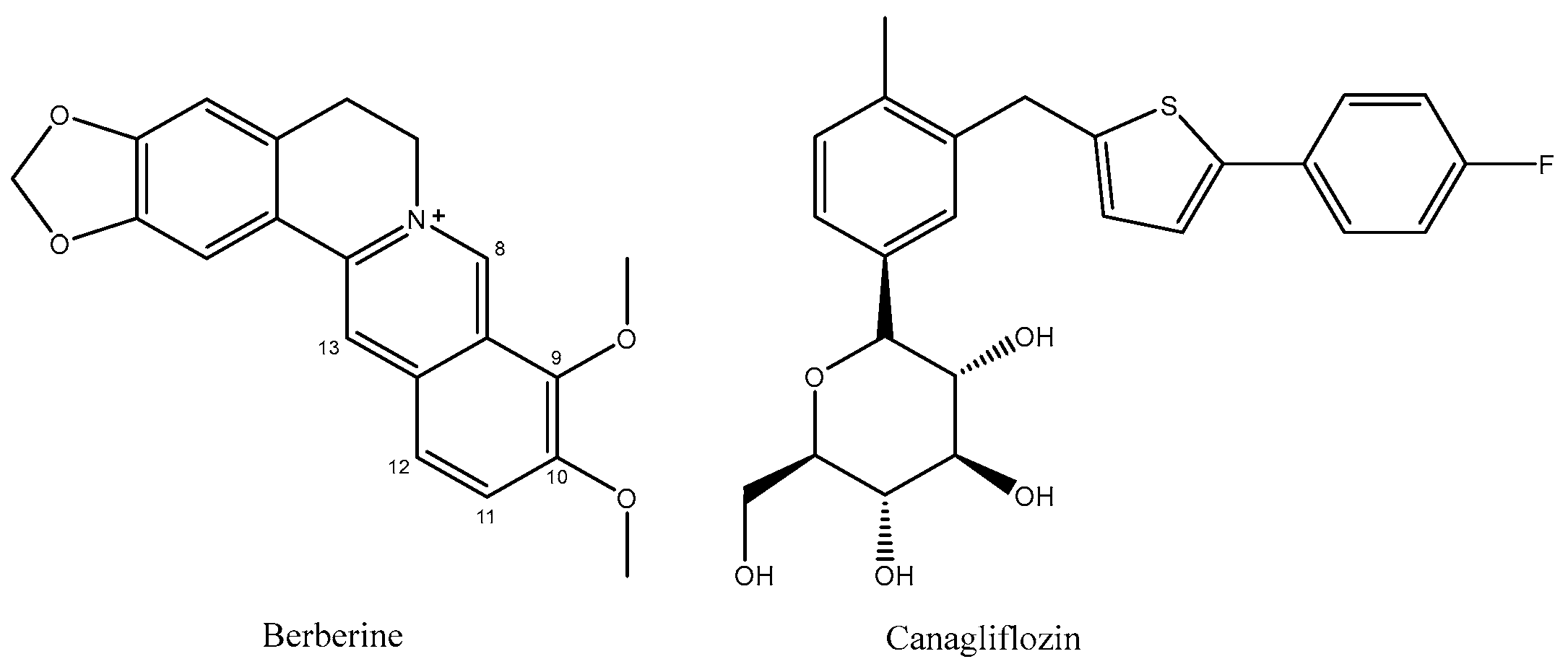
Synthesis of New Derivatives of Berberine Canagliflozin and Study of Their Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
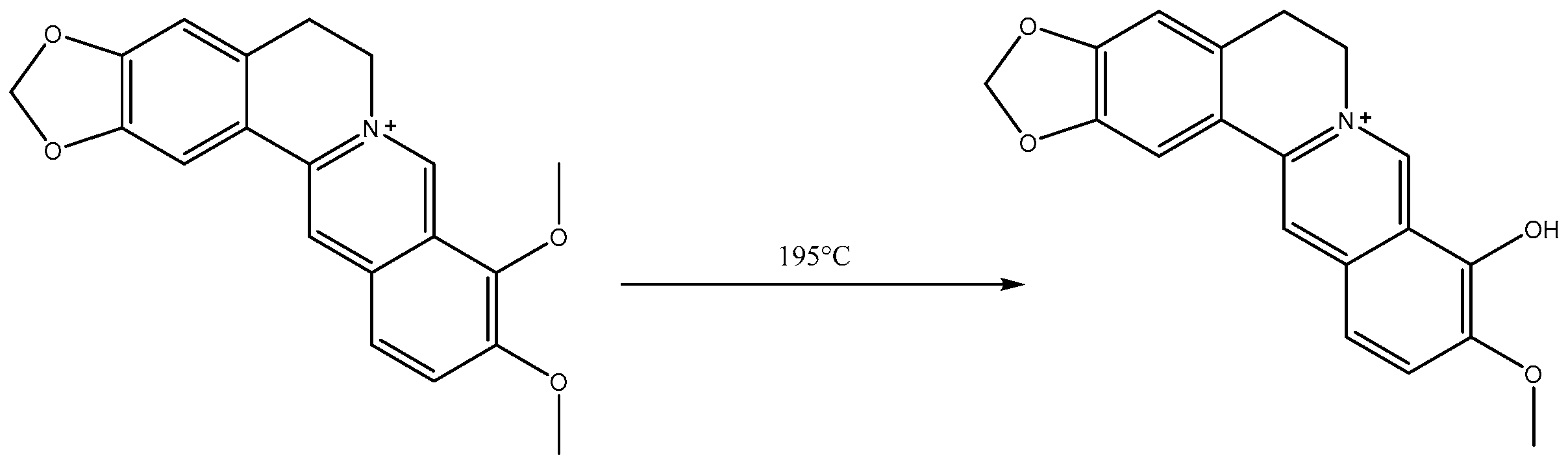
2.1. Analysis of Berberrubine
2.2. Analysis of Br-C
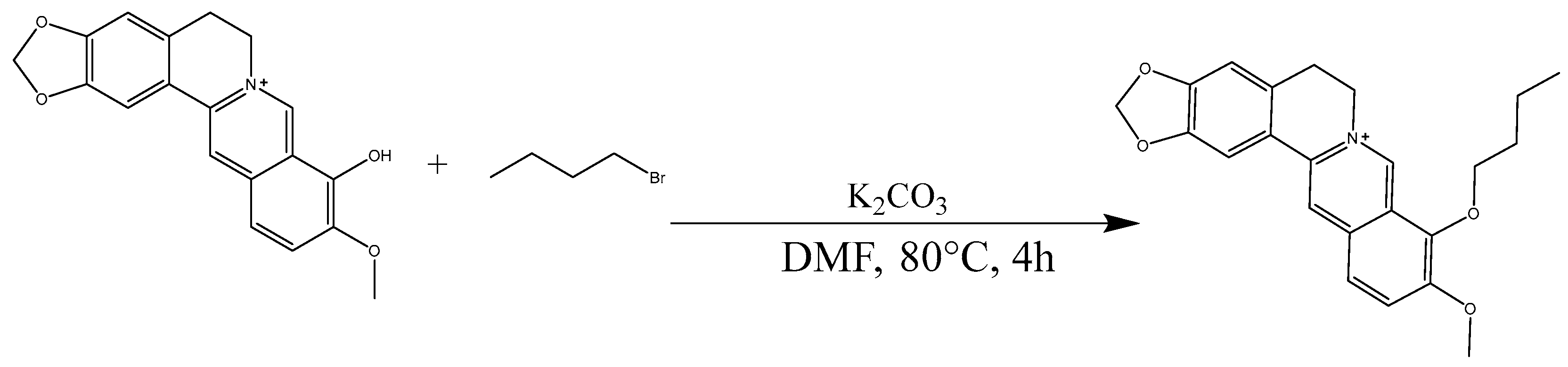
2.3. Analysis of B9OC
2.4. Analysis of B9OBU
2.5. MIC80 of B9OC, BBR, CAN, B + C, and B9OBU against E. coli, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa
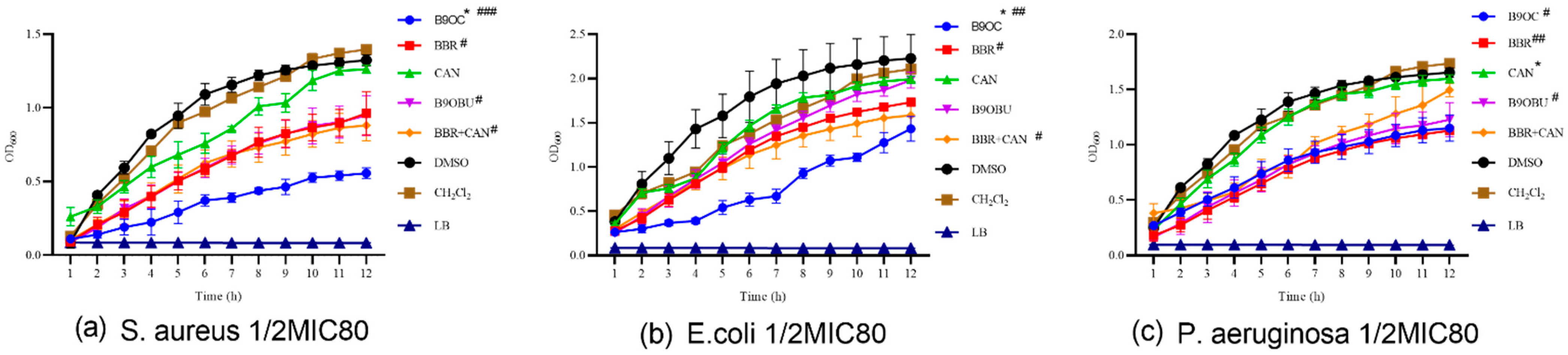
2.6. Effects of B9OC on E. Coli, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa Growth
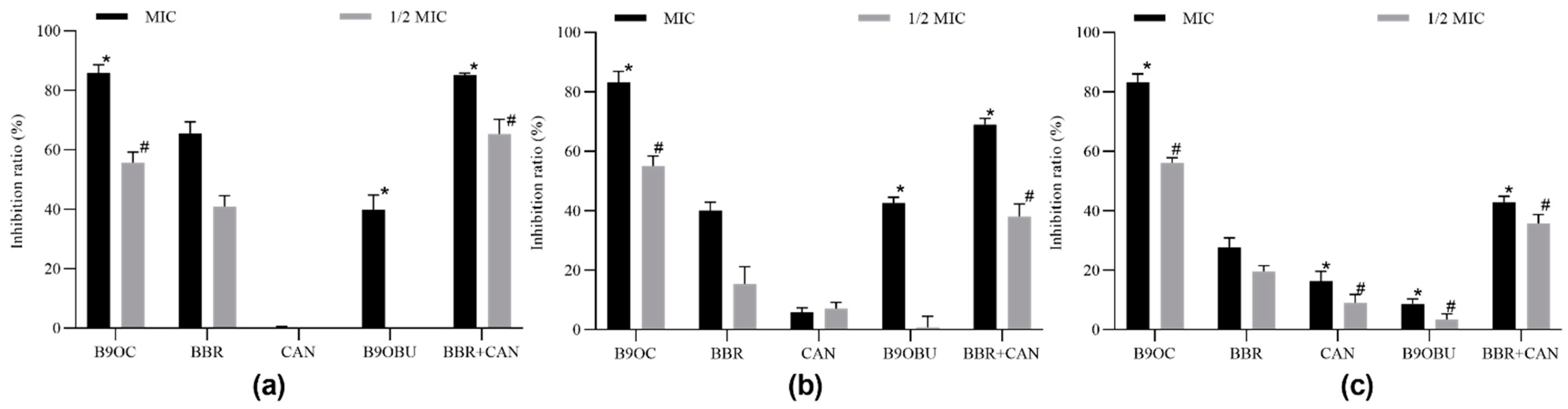
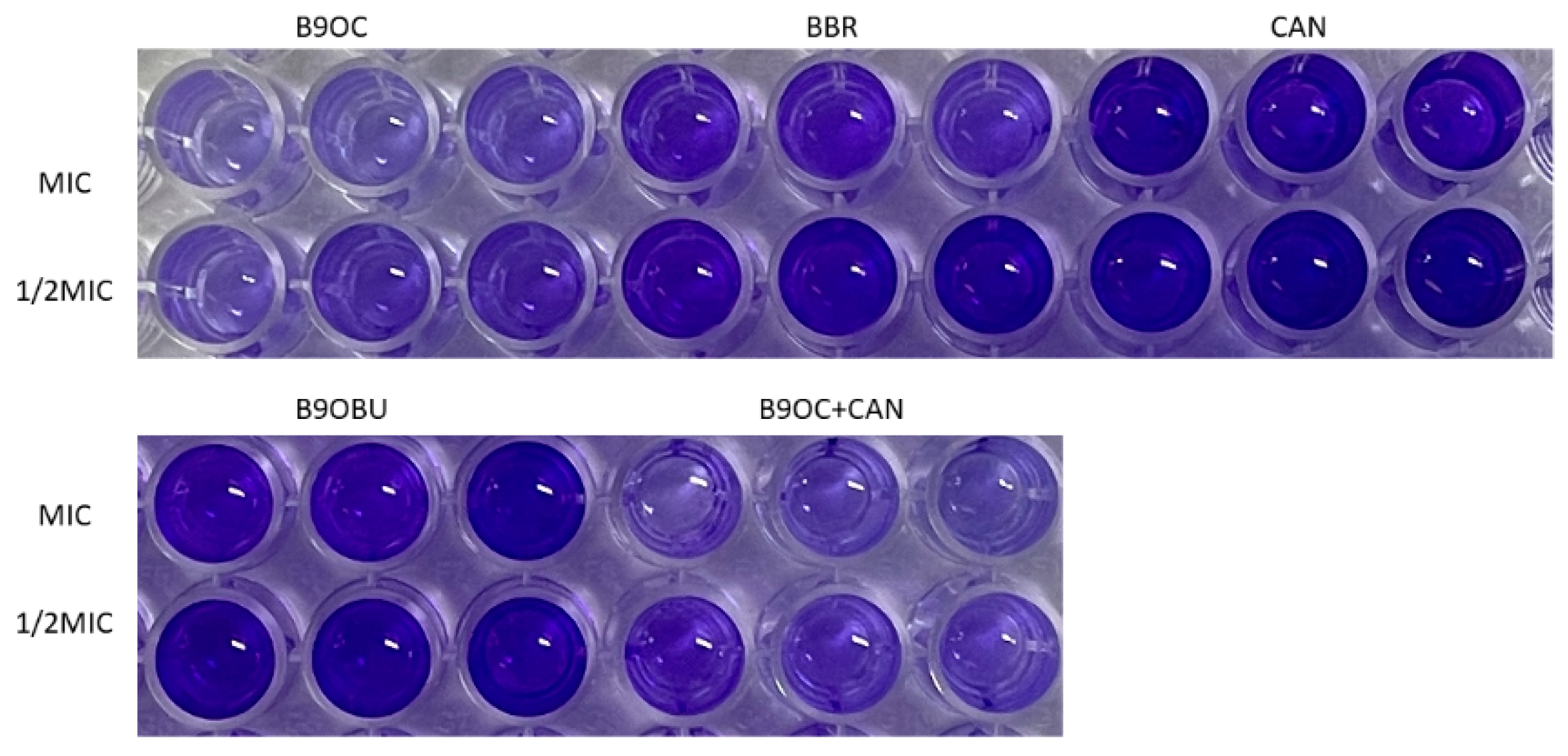
2.7. Antibiofilm Activity of B9OC
2.8. Sds-Page Analysis
2.9. The Morphology of Bacteria Observed by FESEM
2.10. ADMET of B9OC
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Instruments and Compounds
3.3. Synthesis of Berberrubine
3.4. Synthesis of Canagliflozin Bromide (Br-C)
3.5. Synthesis of 9-Berberrubine-(9→6′)-O-canagliflozin Derivative (B9OC)
3.6. Synthesis of Berberine 9 Oxybutyl Derivative (B9OBU)
3.7. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations 80 (MIC80)
3.8. Growth Curve
3.9. Biofilm Growth
3.10. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
3.11. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
3.12. ADMET Prediction Based on Computer Aided Prediction
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, D.; Hao, J.; Fan, D. Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.J.; Vernieri, C.; Foiani, M.; Jiang, J.D. Berberine in the treatment of metabolism-related chronic diseases: A drug cloud (dCloud) effect to target multifactorial disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, M.; Shabbir, A.; Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H.; Shah, M.A. Neuroprotective potential of berberine in modulating Alzheimer’s disease via multiple signaling pathways. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Sun, W.; Gu, W.; Cao, W.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, H.; et al. Berberine on the Prevention and Management of Cardiometabolic Disease: Clinical Applications and Mechanisms of Action. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Khalil, A.A.; Imran, M.; Shah, Z.A.; Emran, T.B.; Mitra, S.; Khan, Z.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; et al. Berberine as a Potential Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.M.; Jiang, X.; Ouyang, X.X.; Zhang, Y.O.; Xie, W.D. Berberine enhances antidiabetic effects and attenuates untoward effects of canagliflozin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Che, S.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Xie, W. Synthesis of Berberine and Canagliflozin Chimera and Investigation into New Antibacterial Activity and Mechanisms. Molecules 2022, 27, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lü, Y.; Yue, C. Development and Research Progress of Anti-Drug Resistant Bacteria Drugs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5575–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, C.P.F.; Rebelo, J.S.; Dionisio, F.; Nogueira, T. Multi-Drug Resistance in Bacterial Genomes—A Comprehensive Bioinformatic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, F.; Dai, J.; Yang, L.X. New Development of Novel Berberine Derivatives against Bacteria. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, T.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.N.; Yu, L.F.; Liu, T.; Tang, J.; Yi, Z.; Yang, C.G.; Xue, W.; et al. The synthesis and antistaphylococcal activity of 9,13-disubstituted berberine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wu, L.L.; Li, Q.; Hu, Q.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, K.; Jiang, J.Q. Novel berberine derivatives: Design, synthesis, antimicrobial effects, and molecular docking studies. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, M.; He, F.; Zou, M.; Peng, J.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, D. Berberine Derivatives with Different Pharmacological Activities via Structural Modifications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1424–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Long, S.; Zhang, S.; Tan, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z. Synthesis and antioxidant activities of berberine 9-O-benzoic acid derivatives. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17611–17621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liao, S.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Evaluations of 1,3,5-Triazine Derivatives of Metformin Cyclization with Berberine and Magnolol in the Presence of Sodium Methylate. Molecules 2017, 22, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Hai, L.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 12-(substituted aminomethyl) berberrubine derivatives as anti-diabetics. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1762–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhao, X.Q.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.H.; Zeng, Q.X.; Li, Y.H.; Song, D.Q. Synthesis and Evolution of Berberine Derivatives as a New Class of Antiviral Agents against Enterovirus 71 through the MEK/ERK Pathway and Autophagy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolova, K.; Hrabinova, M.; Hepnarova, V.; Kucera, T.; Kobrlova, T.; Benkova, M.; Janockova, J.; Dolezal, R.; Prchal, L.; Benek, O.; et al. Discovery of novel berberine derivatives with balanced cholinesterase and prolyl oligopeptidase inhibition profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvanshi, R.; Jamwal, A.; Nandi, U.; Bharate, S.B. Multitargeted C9-substituted ester and ether derivatives of berberrubine for Alzheimer’s disease: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, metabolic stability, and pharmacokinetics. Drug Dev. Res. 2023, 84, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Ho, J.H.; Tsai, L.C.; Yang, F.Y.; Yang, L.L.; Kuo, C.D.; Chen, L.G.; Liu, Y.W.; Wu, J.Y. Synthesis and In Vitro Photocytotoxicity of 9-/13-Lipophilic Substituted Berberine Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.H.; Bai, L.P.; Qin, Y.; Pang, J.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Cai, Z.; Xu, Z.L.; Jiang, Z.H. Spacer length and attaching position-dependent binding of synthesized protoberberine dimers to double-stranded DNA. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 4670–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Available online: https://smart.servier.com (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Kamei, J.; Yamamoto, S. Complicated urinary tract infections with diabetes mellitus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugent, M.L.; Hulyalkar, N.V.; Nguyen, V.H.; Zimmern, P.E.; De Nisco, N.J. Advances in Understanding the Human Urinary Microbiome and Its Potential Role in Urinary Tract Infection. mBio 2020, 11, e00218-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, T.; Shen, S.; Fang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Tang, H. Urinary tract and genital infections in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, I.C.; Bronskill, S.E.; Campitelli, M.A.; Guan, J.; Stall, N.M.; Lam, K.; McCarthy, L.M.; Gruneir, A.; Rochon, P.A. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of genital mycotic and urinary tract infection: A population-based study of older women and men with diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakde, P.; Redkar, N.N.; Yelale, A. Urinary Tract Infection in Elderly: Clinical Profile and Outcome. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2018, 66, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Fiayyaz, F.; Sabir, S.; Khurshid, M. Diabetes-associated infections: Development of antimicrobial resistance and possible treatment strategies. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
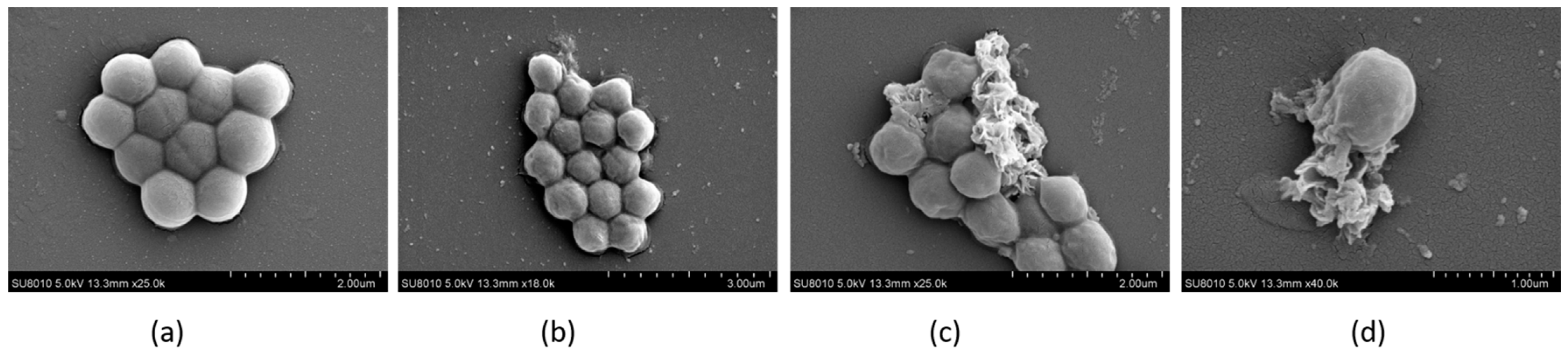


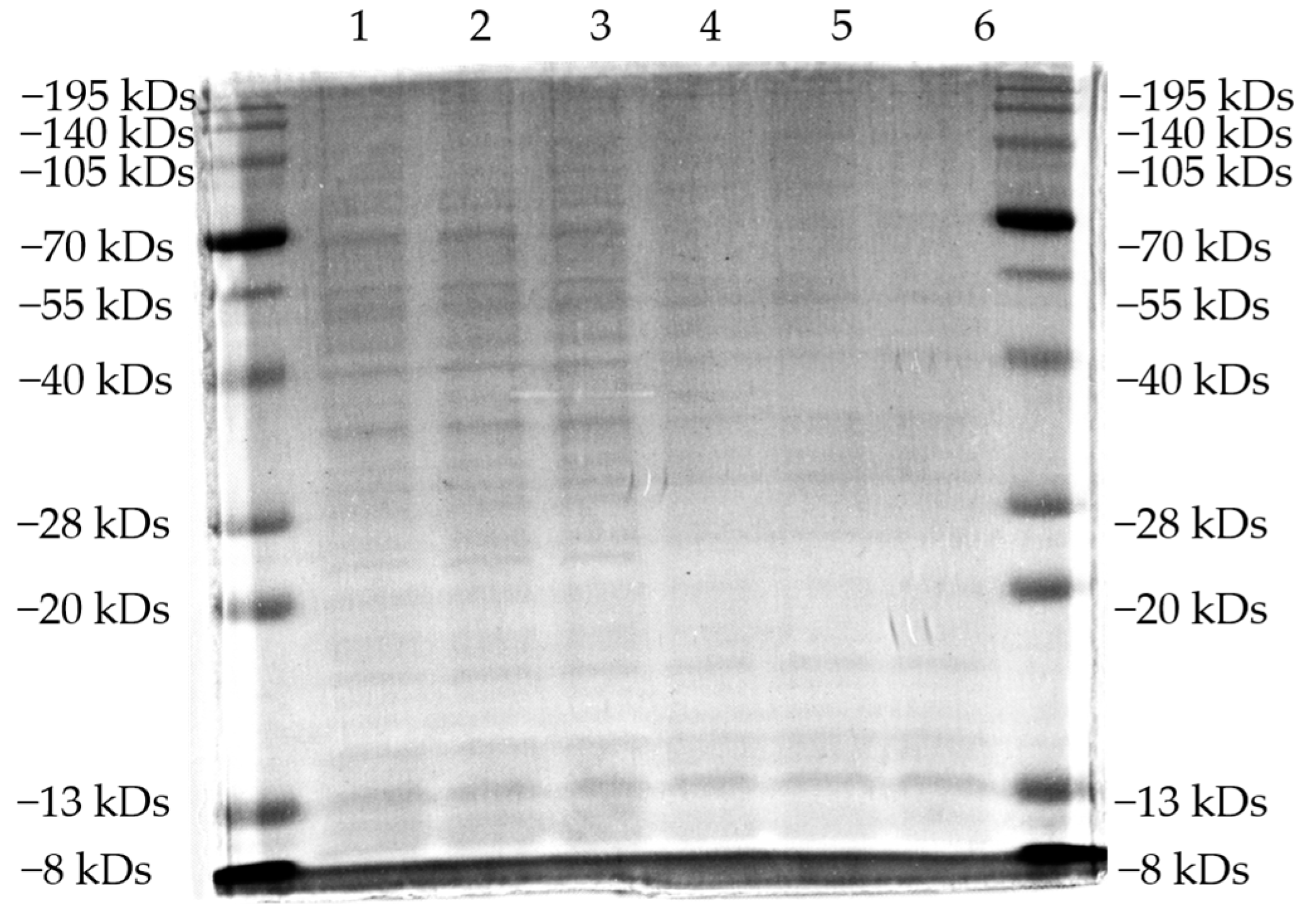





| Bacterial Strain | Drug | MIC80 (mM) | MIC80 (mM) 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| B9OC | 0.035 **,#,$$ | 0.029~0.042 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | BBR | 0.188 | 0.164~0.218 |
| 0485U | BBR + CAN | 0.063 | 0.049~0.085 |
| B9OBU | 0.591 | 0.501~0.707 | |
| CAN | 2.377 | 2.076~2.749 | |
| BC | 0.380 | 0.320~0.440 | |
| B9OC | 0.285 **,##,$$ | 0.239~0.343 | |
| Escherichia coli | BBR | 0.982 | 0.828~1.174 |
| 0335U | BBR + CAN | 0.435 | 0.367~0.529 |
| B9OBU | 2.241 | 1.952~2.539 | |
| CAN | 1.876 | 1.614~2.201 | |
| BC | 0.390 | 0.350~0.430 | |
| B9OC | 0.331 ##,$$ | 0.300~0.367 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | BBR | 0.665 | 0.575~0.781 |
| BNCC125486 | BBR + CAN | 0.251 | 0.221~0.289 |
| B9OBU | 1.283 | 1.204~1.349 | |
| CAN | NI | NI | |
| BC | 0.220 | 0.180~0.260 |
| Absorption Properties | Metabolism Properties | Distribution Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermodynamic Solubility, Log (S, mol/L) | −3.09 | HLM-CLint (μL/min/mg) | 67.214 | Plasma Protein Binding(human) | 0.97 |
| ESOL_Kinetic, Log (S, mol/L) | −4.42 | MLM-CLint (μL/min/mg) | 415.94 | Blood–Brain barrier Permeability (BBBP) Probability | 0.26 |
| Pampa | 4.85 | RLM-CLint (μL/min/mg) | 89.628 | Blood–Brain Ratio | −0.62 |
| MDCK | 3.43 | CYP Induction Probability | 0.269 | ||
| Caco-2 Permeability (10−6, apical to basolateral) | 3.39 | CYP Inhibition Probability (1A2) | 0.48 | Excretion Properties | |
| P-gp Substrate Probability | 0.96 | CYP Inhibition Probability (2C19) | 0.899 | Human Clearance | 0.401 |
| P-gp Inhibition Probability | 0.55 | CYP Inhibition Probability (2C9) | 0.931 | ||
| Human Intestinal Absorption (HIA) Probability | 0.15 | CYP Inhibition Probability (2D6) | 0.76 | ||
| Oral Bioavailability (human) | 0.47 | CYP Inhibition Probability (3A4) | 0.589 | ||
| Toxicity Properties | hERG Inhibition Probability | 0.124 | |||
| hERG Inhibition probability_cls10 | 0.614 | Phospholipidosis | 0.771 | ||
| hERG Inhibition probability_cls50 | 0.998 | Reproductive Toxicity | 0.997 | ||
| Ames Toxicity Probability | 0.319 | NR-AR | 0.032 | ||
| Hek293 Toxicity Probability | 0.952 | NR-AR-LBD | 0.048 | ||
| Hepatic Toxicity Probability | 0.967 | NR-AhR | 0.325 | ||
| Eye Corrosion | 0 | NR-Aromatase | 0.369 | ||
| Log (LD50) | 2.915 | NR-ER | 0.144 | ||
| Phototoxicity | 0.259 | NR-ER-LBD | 0.066 | ||
| Tubulin Inhibition | 1 | NR-PPAR-gamma | 0.119 | ||
| Eye Irritation | 0 | SR-ARE | 0.613 | ||
| DILI | 0.928 | SR-ATAD5 | 0.073 | ||
| Genotoxicity | 0.99 | SR-HSE | 0.244 | ||
| Carcinogenicity | 0.227 | SR-MMP | 0.688 | ||
| Mutagenicity | 0.001 | SR-p53 | 0.431 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Hou, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wei, H. Synthesis of New Derivatives of Berberine Canagliflozin and Study of Their Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism. Molecules 2024, 29, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010273
Li J, Hou X, Xiao J, Zhu L, Deng Y, Li Z, Zhao Z, Luo Z, Wei H. Synthesis of New Derivatives of Berberine Canagliflozin and Study of Their Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinsheng, Xueli Hou, Jinlong Xiao, Li Zhu, Yujie Deng, Ziyi Li, Zijian Zhao, Zhenghong Luo, and Hao Wei. 2024. "Synthesis of New Derivatives of Berberine Canagliflozin and Study of Their Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism" Molecules 29, no. 1: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010273
APA StyleLi, J., Hou, X., Xiao, J., Zhu, L., Deng, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, Z., Luo, Z., & Wei, H. (2024). Synthesis of New Derivatives of Berberine Canagliflozin and Study of Their Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism. Molecules, 29(1), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010273






