Enhanced Chromium (VI) Removal by Micron-Scale Zero-Valent Iron Pretreated with Aluminum Chloride under Aerobic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
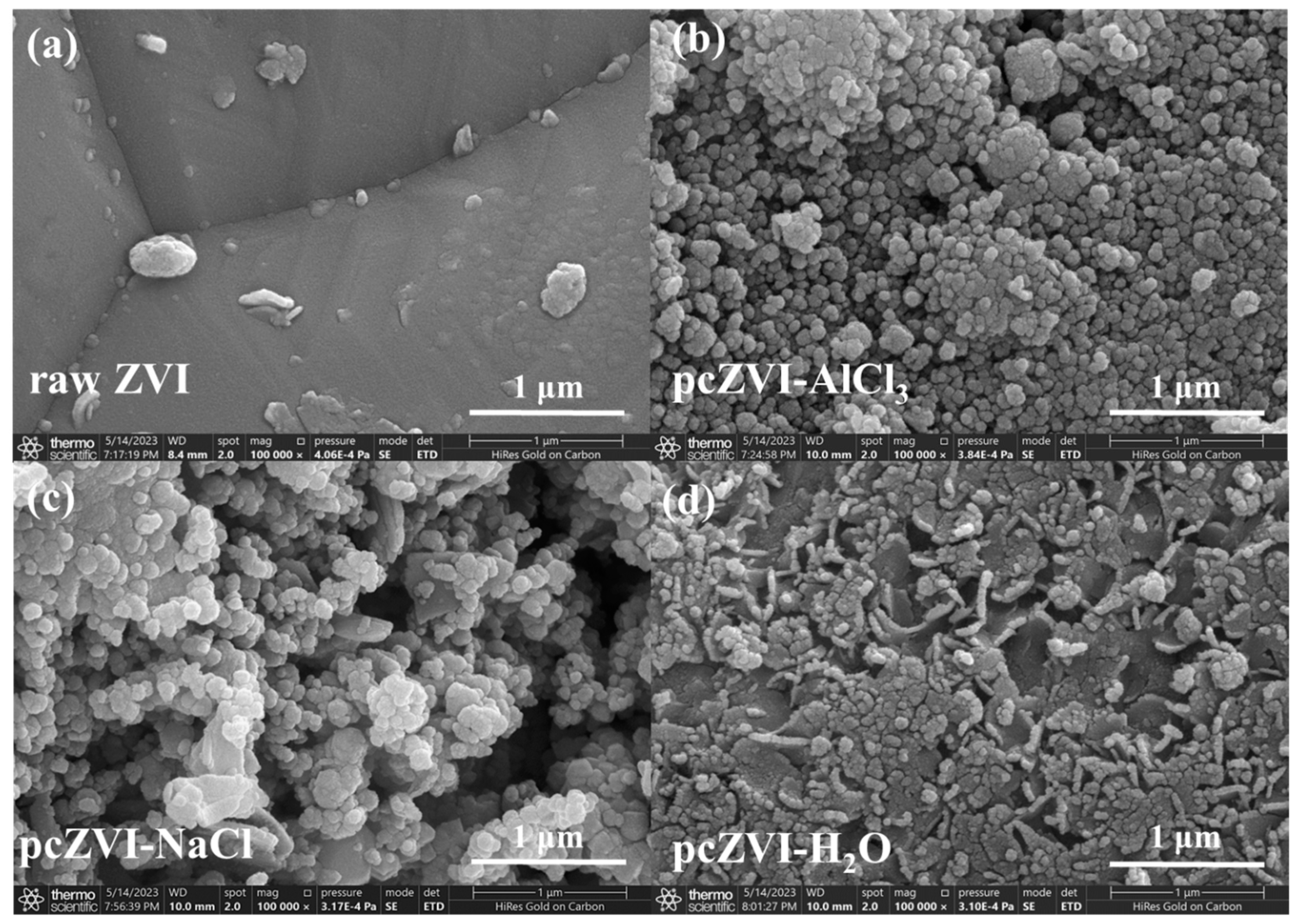
2.1. ZVI Pre-Corrosion Optimization and Characterization
2.1.1. ZVI Preconditioning Process Optimization via Batch Experiments
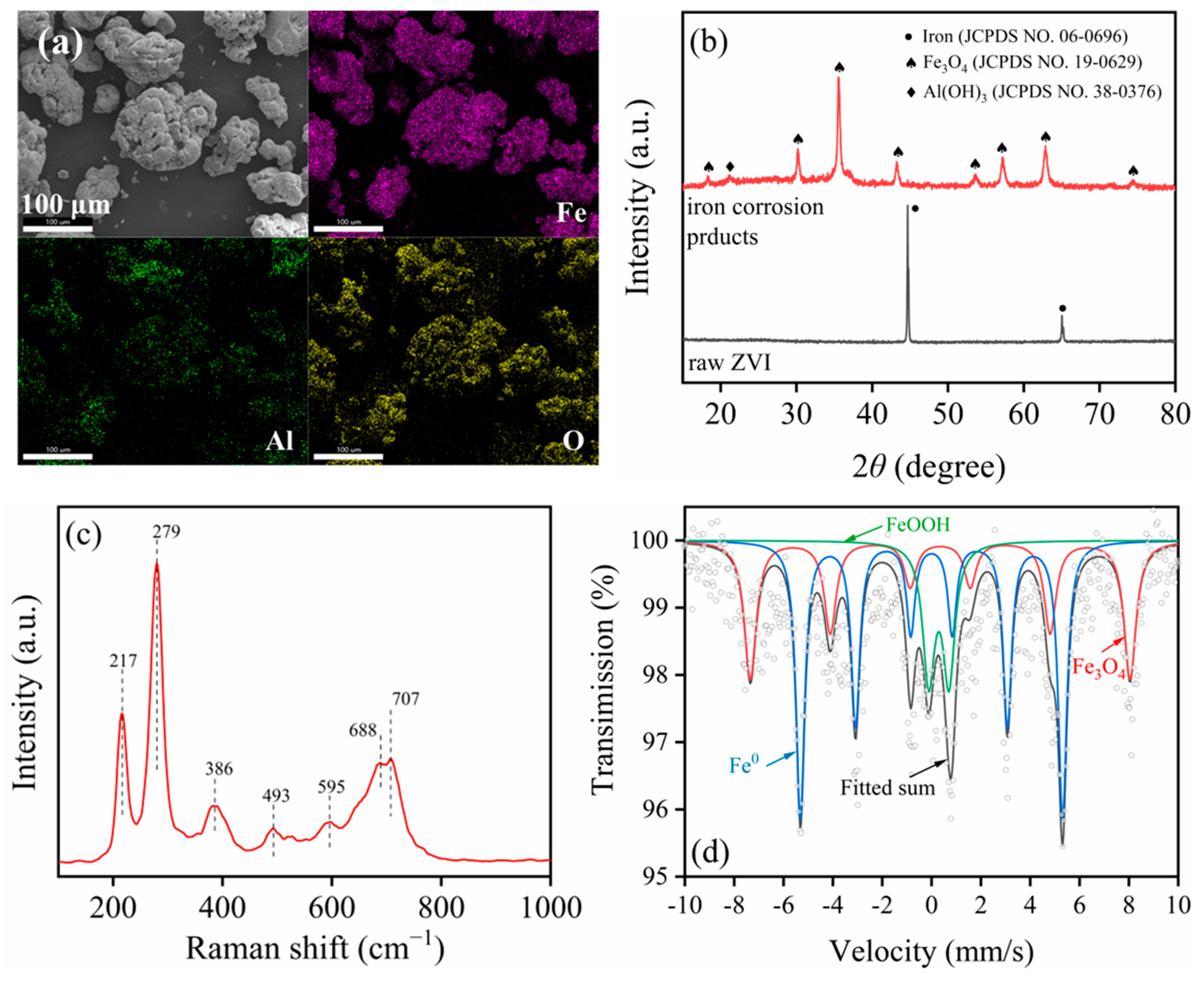
2.1.2. Corrosion Product Characterization
2.2. The Role of Al3+ and Cl− in ZVI Pre-Corrosion
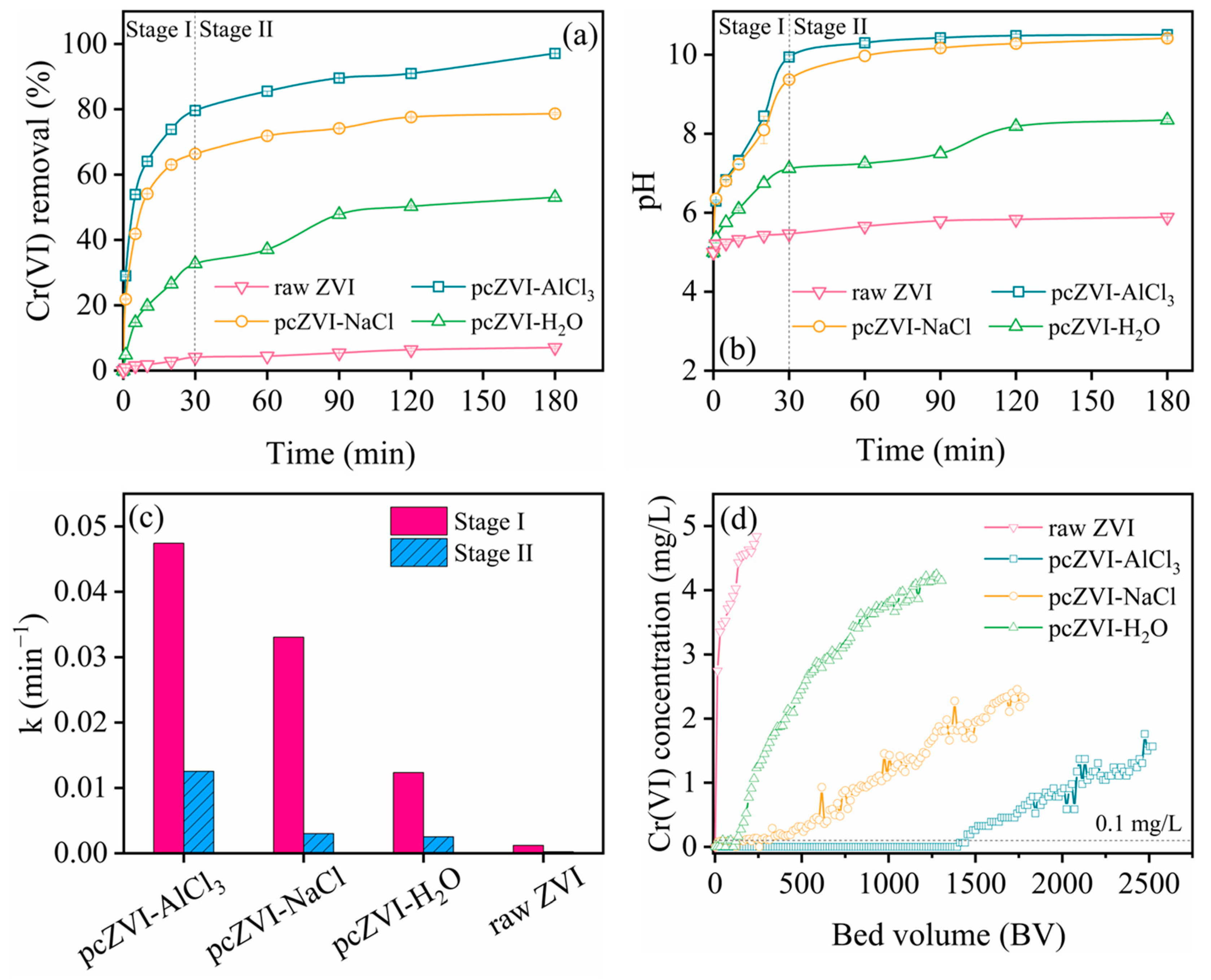
2.2.1. Cr(VI) Removal by ZVI Pretreatment with Different Solutions
2.2.2. Column Experiment Comparison and Longevity Evaluation
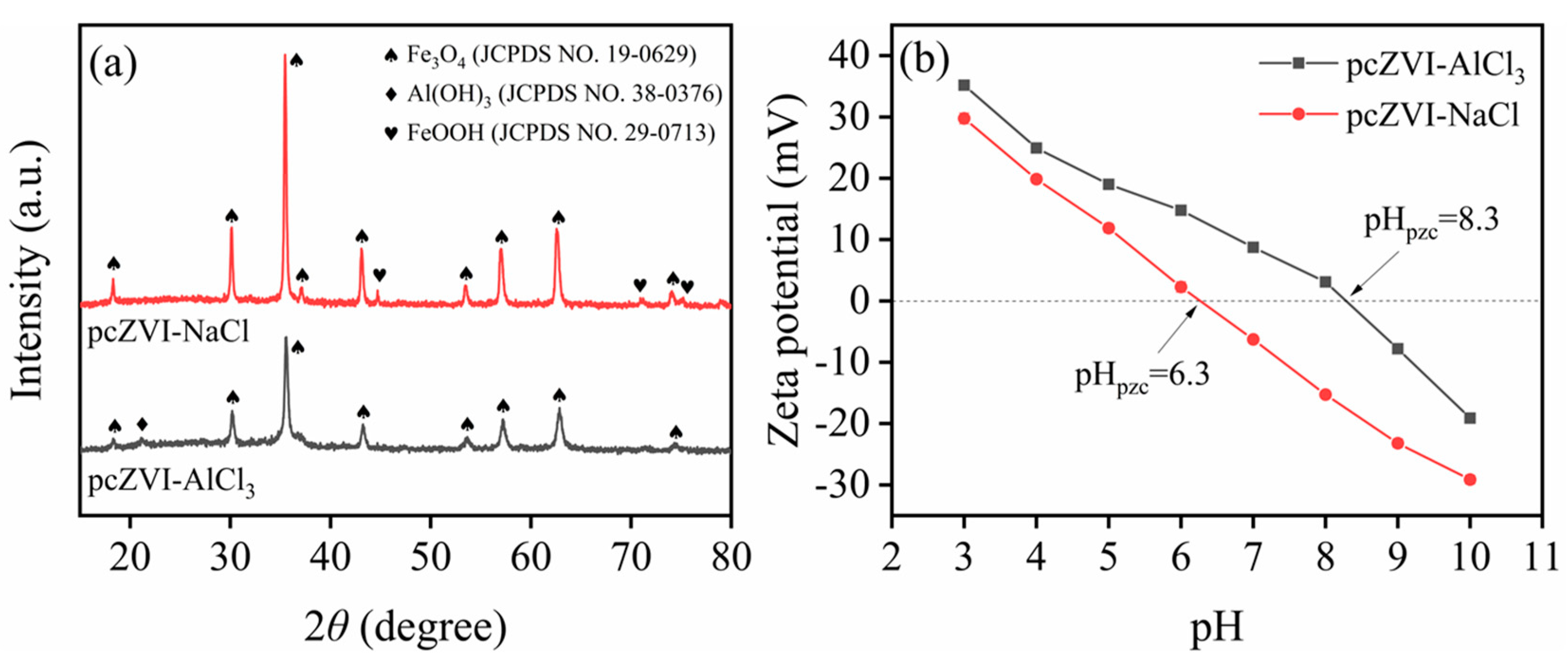
2.2.3. SEM-EDS, XRD, and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.3. The Contribution of Corrosion Products in pcZVI-AlCl3
2.3.1. The Comparison of Cr(VI) Removal in Different Systems
2.3.2. Tafel Analysis
2.4. Effect of Solution Chemistry on Cr(VI) Removal
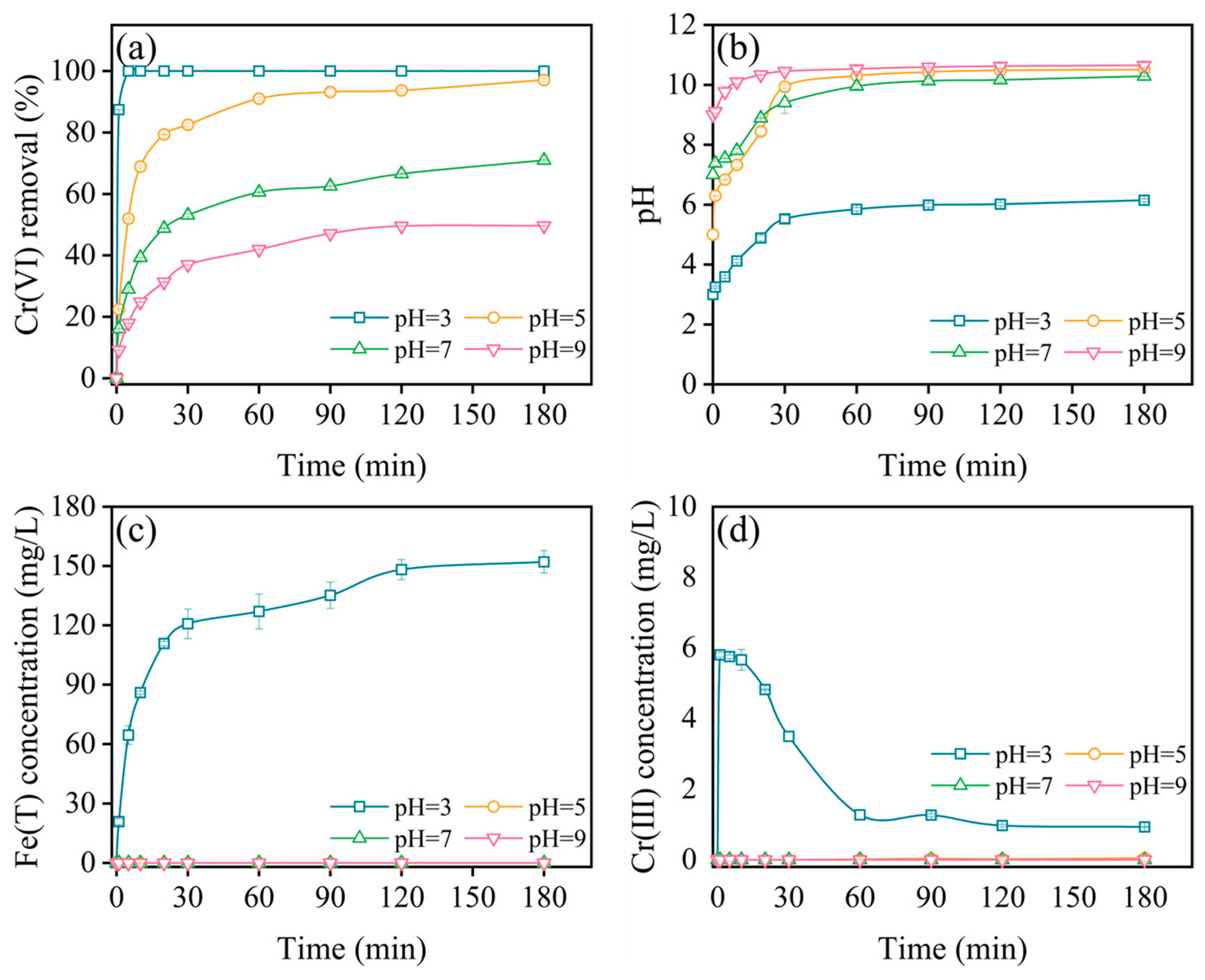
2.4.1. Effect of Initial pH
2.4.2. Matrix Effects
2.5. Mechanisms
2.5.1. SEM-EDS and XRD
2.5.2. Zeta Potential
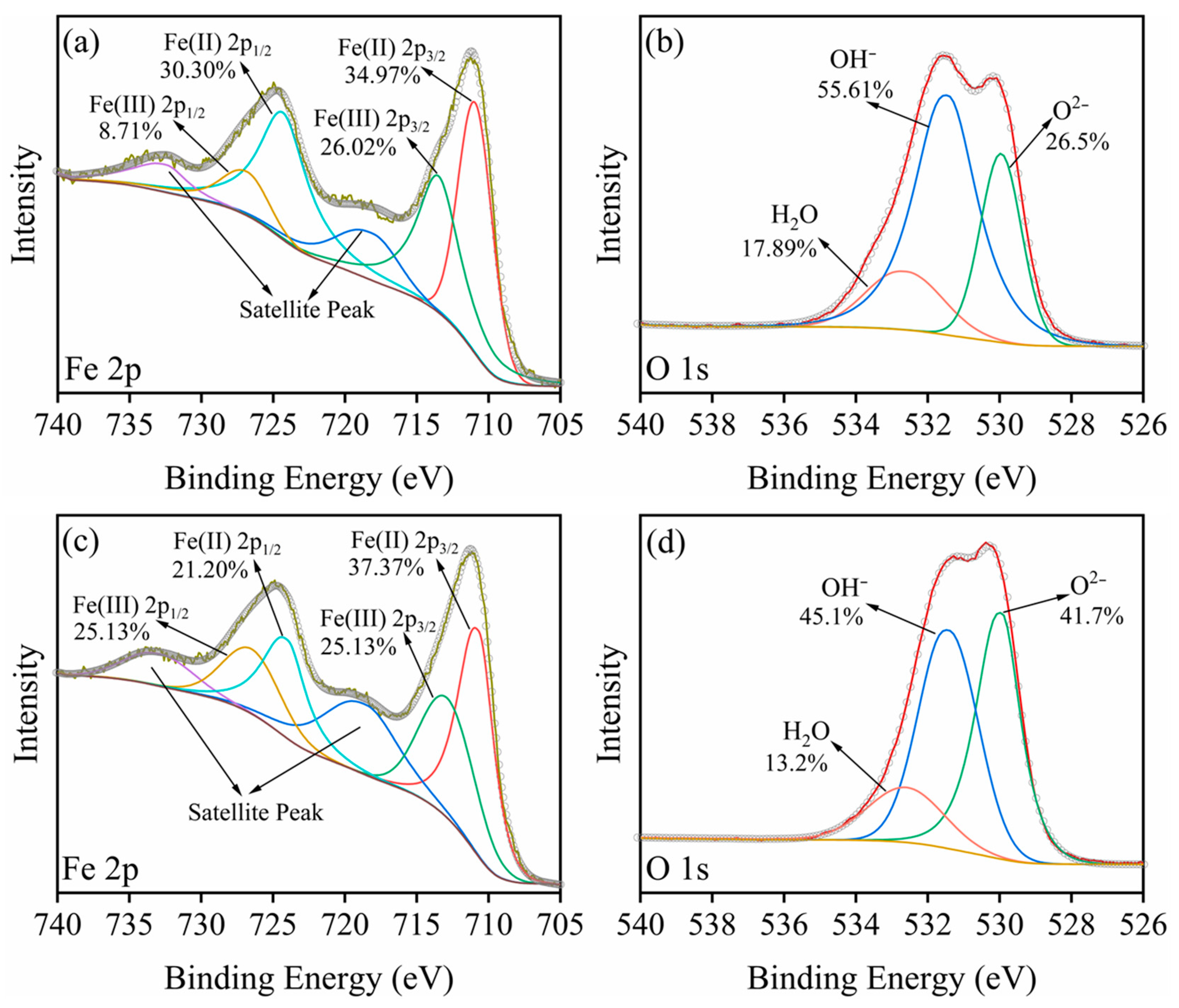
2.5.3. XPS
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation and Optimization of pcZVI-AlCl3
3.3. Batch Experiments
3.4. Characterization of Preconditioned ZVI and Corrosion Products
3.5. Continuous Flow Experiments
3.6. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Wu, X.; Dai, M.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A.; Raza, S.; Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Naz, I. The sequestration of aqueous Cr(VI) by zero valent iron-based materials: From synthesis to practical application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, B.; Yin, W.; Gu, J.; Liang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, J. Enhanced hexavalent chromium removal by activated carbon modified with micro-sized goethite using a facile impregnation method. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Tang, B. Adsorption and redox conversion behaviors of Cr(VI) on goethite/carbon microspheres and akaganeite/carbon microspheres composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Tang, T.; Xing, Q.; Peng, C.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, X.; Zou, J.; Min, X.; et al. Mechanism investigation of anoxic Cr(VI) removal by nano zero-valent iron based on XPS analysis in time scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Mallik, A.K.; Moktadir, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.M. Progress in surface-modified silicas for Cr (VI) adsorption: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Gan, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, J.; Fang, L.; Wei, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, B. A novel negatively charged nanofiltration membrane with improved and stable rejection of Cr (VI) and phosphate under different pH conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, P.; Chang, C. The state of the art review on photocatalytic Cr (VI) reduction over MOFs-based photocatalysts: From batch experiment to continuous operation. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J. Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.M.; Jegede, T.O.; Hulse, V.A.; Elgrishi, N. Electrochemical reduction of Cr (VI) in water: Lessons learned from fundamental studies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1642–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, B.; He, C.; Borthwick, A.G. The role of natural Fe (II)-bearing minerals in chemoautotrophic chromium (VI) bio-reduction in groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, L.; Liang, C.; Zheng, T.; Dong, X.; Chen, M. Enhanced Cr(VI) reduction by zero-valent iron and ferroferric oxide wet ball milling: Synergy of electron storage and electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, G.; Li, P.; Gu, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, C. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from groundwater by Fe0-H2O system with bio-amended iron corrosion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, H.; Zhang, K.; Penn, C.J.; Zhang, H. Phosphate removal by low-cost industrial byproduct iron shavings: Efficacy and longevity. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Duan, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, S. Elemental sulfur generated in situ from Fe(III) and sulfide promotes sulfidation of microscale zero-valent iron for superior Cr(VI) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.; Ye, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Pei, X.; Li, Q.; et al. One-step strategy for efficient Cr(VI) removal via phytate modified zero- valent iron: Accelerated electron transfer and enhanced coordination effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, C.; Liang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, C. Cr(VI) removal by micron-scale iron-carbon composite induced by ball milling: The role of activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 389, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Sheu, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sun, Y.; Kao, C. Application of iron/aluminum bimetallic nanoparticle system for chromium-contaminated groundwater remediation. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, F. Insight into core-shell dependent anoxic Cr(VI) removal with Fe@Fe2O3 nanowires: Indispensable role of surface bound Fe(II). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. Improved longevity of nanoscale zero-valent iron with a magnesium hydroxide coating shell for the removal of Cr(VI) in sand columns. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Guo, X.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Leng, S.; Ullah, S.; Ayalew, Z.M. Rapid and long-effective removal of phosphate from water by zero-valent iron in combination with hypochlorite (ZVI/NaClO). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Jia, H.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B. Enhanced removal of Se(VI) from water via pre-corrosion of zero-valent iron using H2O2/HCl: Effect of solution chemistry and mechanism investigation. Water Res. 2018, 133, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Y. A simple and novel method to enhance As (V) removal by zero valent iron and activated iron media through air injection at intervals. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleiman, N.; Deluchat, V.; Wazne, M.; Mallet, M.; Courtin-Nomade, A.; Kazpard, V.; Baudu, M. Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using zero valent iron (ZVI): Influence of solution composition and ZVI aging. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 514, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Shan, C.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, B. Effects of brining on the corrosion of ZVI and its subsequent As(III/V) and Se(IV/VI) removal from water. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Hu, X. Corrosion behaviors and kinetics of nanoscale zero-valent iron in water: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 135, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, M.; Mortimer, R.J.G.; Pan, G. Enhanced Phosphorus Locking by Novel Lanthanum/Aluminum-Hydroxide Composite: Implications for Eutrophication Control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3418–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gai, W.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Z. Surface modified zero-valent aluminum for Cr(VI) removal at neutral pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Guan, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Tratnyek, P.G. Coupled effects of aging and weak magnetic fields on sequestration of selenite by zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6326–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Comins, J.D.; Cukrowski, I. The growth of the passive film on iron in 0.05 M NaOH studied in situ by Raman micro-spectroscopy and electrochemical polarisation. Part I: Near-resonance enhancement of the Raman spectra of iron oxide and oxyhydroxide compounds. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Li, A.; Xu, J.A.; Chen, R.J.; Yamanaka, T. High-pressure phase transition in Al(OH)3: Raman and X-ray observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3083–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Transformation and composition evolution of nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) synthesized by borohydride reduction in static water. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Ding, Z.; Pang, J. Rapid removal of aqueous Cr(VI) and the removal mechanism using ZVI/Fe3O4/Fe2+ system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 85, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Ye, Y.; Kang, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, C.; Xu, Z. Enhanced phosphate removal by zeolite loaded with Mg–Al–La ternary (hydr)oxides from aqueous solutions: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Bao, J.; Lu, C.; Werner, D. Reductive sequestration of chromate by hierarchical FeS@Fe0 particles. Water Res. 2016, 102, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, I.M.; Lam, C.S.; Lai, K.C. Hardness and carbonate effects on the reactivity of zero-valent iron for Cr (VI) removal. Water Res. 2006, 40, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Gorski, C.A. Role of Carbonate in Thermodynamic Relationships Describing Pollutant Reduction Kinetics by Iron Oxide-Bound Fe2+. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10109–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Fang, L.; Fortner, J.D.; Guan, X.; Lo, I.M. Highly efficient and selective phosphate removal from wastewater by magnetically recoverable La(OH)3/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Water Res. 2017, 126, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Luo, M.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, B. Highly efficient remediation of groundwater co-contaminated with Cr(VI) and nitrate by using nano-Fe/Pd bimetal-loaded zeolite: Process product and interaction mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Pi, Y. Enhanced remediation of Cr (VI)-contaminated groundwater by coupling electrokinetics with ZVI/Fe3O4/AC-based permeable reactive barrier. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Fu, F.; Tang, B. Coexistence or aggression? Insight into the influence of phosphate on Cr(VI) adsorption onto aluminum-substituted ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancourt, D.G.; Ping, J.Y. Voigt-based methods for arbitrary-shape static hyperfine parameter distributions in Mössbauer spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1991, 58, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wu, B.; Lo, I.M.C. Development of Fe0/Fe3O4 composites with tunable properties facilitated by Fe2+ for phosphate removal from river water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbols | Meanings |
|---|---|
| ZVI (Fe0) | Zero-valent iron |
| pcZVI-AlCl3 | ZVI pretreated with AlCl3 solution |
| pcZVI-NaCl | ZVI pretreated with NaCl solution |
| pcZVI-H2O | ZVI pretreated with DI water |
| Cr(IV) | Hexavalent chromium |
| Cr(III) | Trivalent chromium |
| Fe(T) | Total iron |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| pHpzc | pH point of zero charge |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning electron microscopy with X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction spectrometer |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, X.; Li, R.; Wan, J.; Zhong, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, Y. Enhanced Chromium (VI) Removal by Micron-Scale Zero-Valent Iron Pretreated with Aluminum Chloride under Aerobic Conditions. Molecules 2024, 29, 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102350
Long X, Li R, Wan J, Zhong Z, Ye Y, Yang J, Luo J, Xia J, Liu Y. Enhanced Chromium (VI) Removal by Micron-Scale Zero-Valent Iron Pretreated with Aluminum Chloride under Aerobic Conditions. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Xuejun, Rui Li, Jun Wan, Zhenxing Zhong, Yuxuan Ye, Jiazhi Yang, Jun Luo, Jin Xia, and Yaomeng Liu. 2024. "Enhanced Chromium (VI) Removal by Micron-Scale Zero-Valent Iron Pretreated with Aluminum Chloride under Aerobic Conditions" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102350
APA StyleLong, X., Li, R., Wan, J., Zhong, Z., Ye, Y., Yang, J., Luo, J., Xia, J., & Liu, Y. (2024). Enhanced Chromium (VI) Removal by Micron-Scale Zero-Valent Iron Pretreated with Aluminum Chloride under Aerobic Conditions. Molecules, 29(10), 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102350







