Anti-Obesity Activities of the Compounds from Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Chemical Profiling of the Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibitory Activity against Adipocyte Differentiation
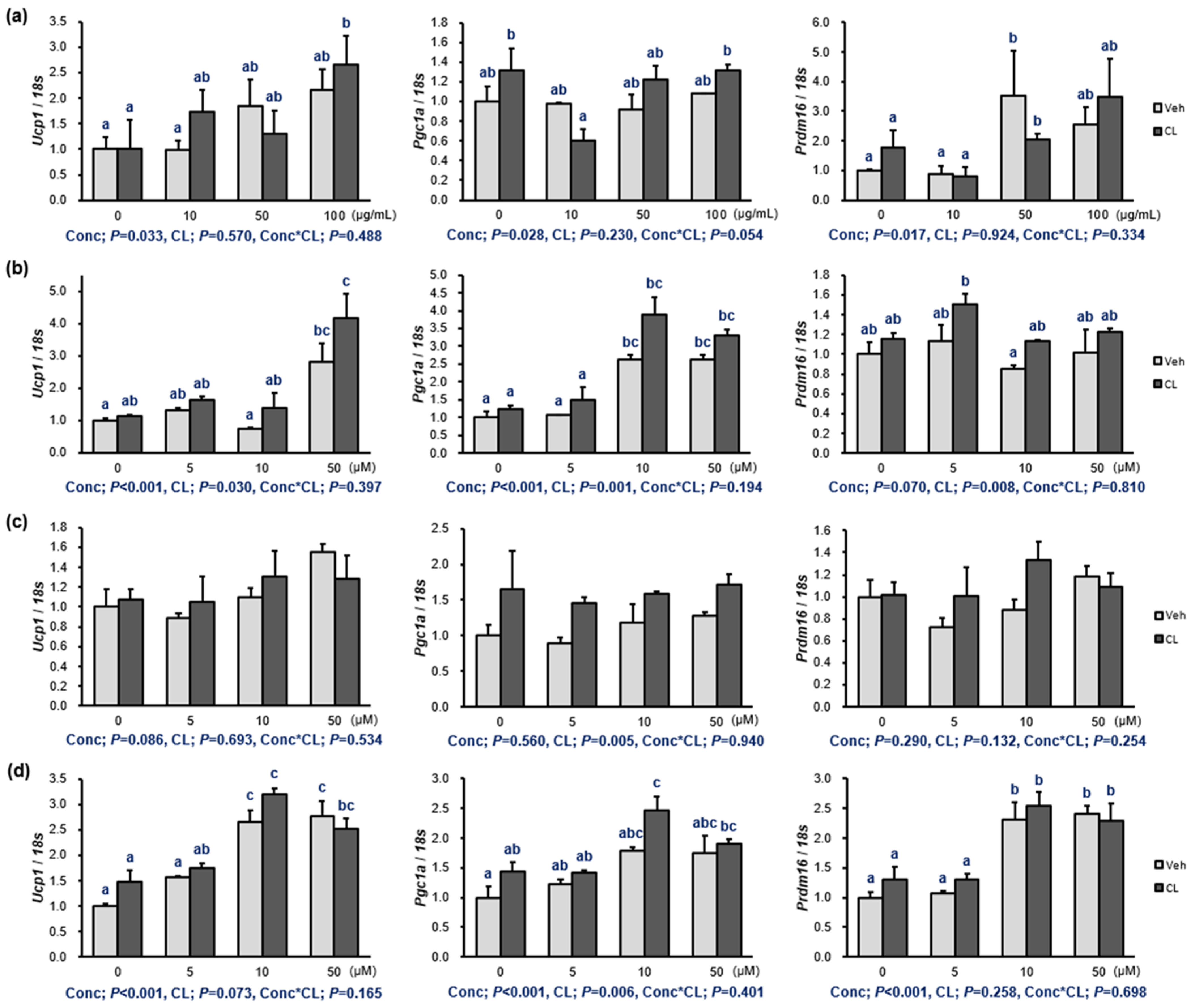
2.2. Thermogenesis of the Extract and 1–3
2.3. Feature-Based Molecular Networking of the Extract
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Sample Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Anti-Adipogenic and Thermogenic Gene Expression
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.6.1. UHPLC and MS/MS Conditions
4.6.2. Feature-Based Molecular Networking
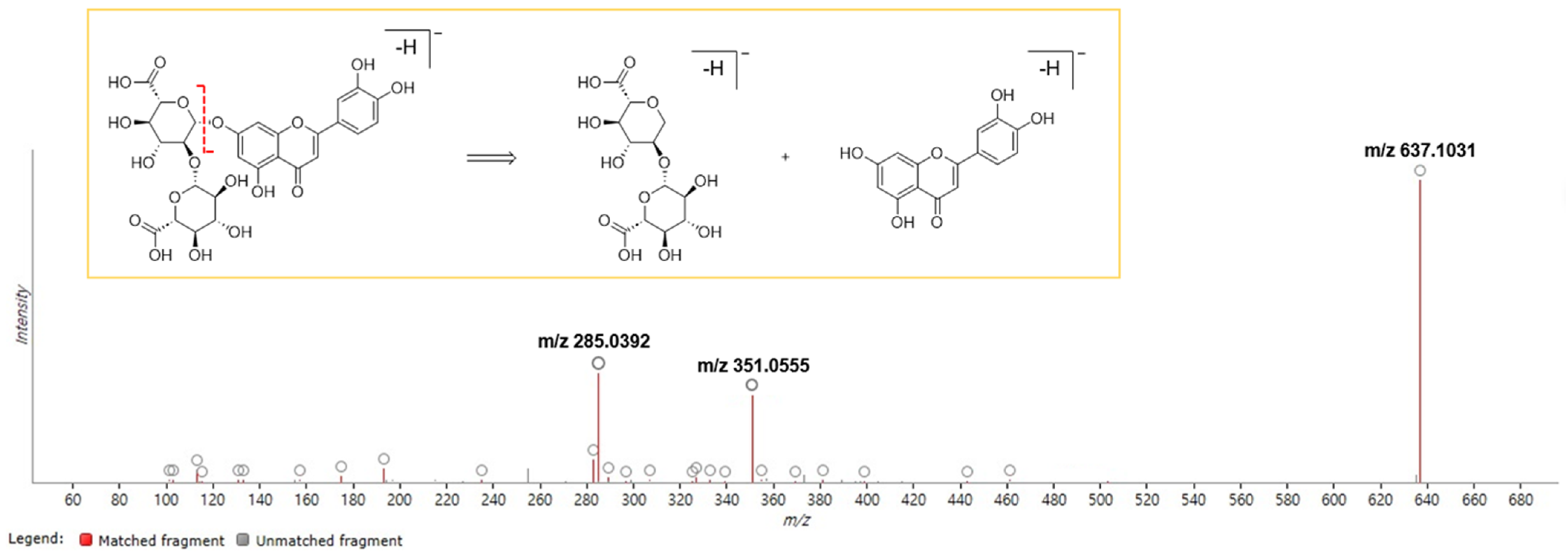
4.6.3. Identification of Chemical Markers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-N.; Kang, M.-C.; Kang, N.; Kim, S.-Y.; Hyun, C.-G.; Roh, S.W.; Ko, E.-Y.; Cho, K.; Jung, W.-K.; Ahn, G. 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzaldehyde, a potential anti-obesity treatment, suppressed adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells and fat accumulation induced by high-fat diet in C57BL/6 mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Yang, M.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L. PRDM16 regulating adipocyte transformation and thermogenesis: A promising therapeutic target for obesity and diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 870250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textbook Compilation Committee of Korean Pharmacognosy. Pharmacognosy, 2nd ed.; Dong-Myeung Press: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2001; pp. 522–523. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Dong, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, M.; Sun, Z.; Luo, H. Perilla frutescens: A traditional medicine and food homologous plant. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Perilla frutescens: A rich source of pharmacological active compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.J.; Cha, Y.S. Antiobesity effects of purple perilla (Perilla frutescens var. acuta) on adipocyte differentiation and mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Kwon, E.-Y. Effects of the Perilla frutescens var. acuta Kudo ethanol extract (PFE) on the improvement of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat diet. J. Korean Soc. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2020, 49, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, I.; Han, S.; Jung, H.J.; Noh, S.G.; Chung, H.Y.; Koo, Y.K.; Shin, S.; Seo, E.K. Anti-inflammatory activity of the constituents from the leaves of Perilla frutescens var. acuta. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.C.; Lane, M.D. Adipose development: From stem cell to adipocyte. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 40, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Lastra, C.A.D.L.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Aviram, M.; Calhau, C.; Cassano, A.; D’Archivio, M.; Faria, A.; Favé, G.; Fogliano, V. Polyphenols and human health: A prospectus. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Contreras, M.d.M. Phenolic compounds as natural and multifunctional anti-obesity agents: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1212–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, Y.; Nelson, M.C.; Ong, E.S.; Jones, Y.Z.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Chien, K.R.; Koder, A.; Evans, R.M. PPAR-γ is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Sarraf, P.; Troy, A.E.; Bradwin, G.; Moore, K.; Milstone, D.S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Mortensen, R.M. PPAR-γ is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, M.; Lin, F.; MacDougald, O.; Vasseur-Cognet, M. Control of adipocyte differentiation by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha). Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1996, 20, S91–S96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rui, Y.; Tong, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, G.; Qin, L.; Wan, Z. Rosmarinic acid suppresses adipogenesis, lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-α secretion in macrophages, and inflammatory mediators in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1330096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothias, L.-F.; Petras, D.; Schmid, R.; Dührkop, K.; Rainer, J.; Sarvepalli, A.; Protsyuk, I.; Ernst, M.; Tsugawa, H.; Fleischauer, M. Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell death and inflammation during obesity: “Know my methods, WAT (son)”. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Ajuwon, K.M. Lipopolysaccharide alters thermogenic and inflammatory genes in white adipose tissue in mice fed diets with distinct 18-carbon fatty-acid composition. Lipids 2018, 53, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M.; Halaas, J.; Ravussin, E.; Pratley, R.; Lee, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, H.; Kim, S.; Lallone, R.; Ranganathan, S. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

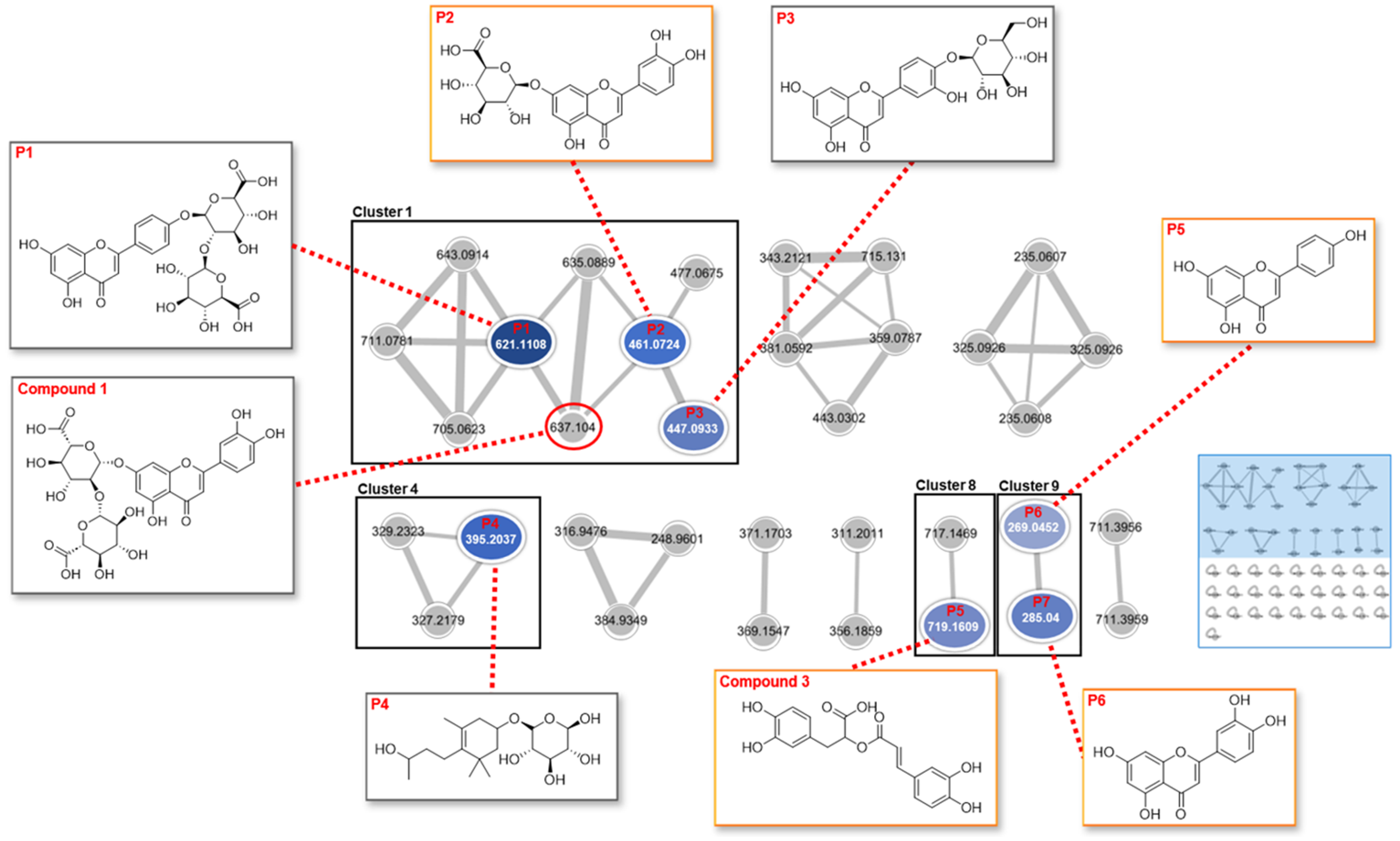
| tR (min) | m/z | Adduct | Cosine Score | Mass Error (ppm) | Compound Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7.68 | 719.1609 | 2M-H | 0.86 | 1.53 | Rosmarinic acid |
| P1 | 6.55 | 621.1108 | M-H | 0.76 | 1.28 | Apigenin-4′-O-[(β-D-glucuronosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucuronide] |
| P2 | 6.92 | 461.0724 | M-H | 0.85 | 1.32 | Luteolin-7-O-D-glucuronide |
| P3 | 6.46 | 447.0933 | M-H | 0.87 | 0.68 | Luteolin-4′-O-glucoside |
| P4 | 9.94 | 395.2037 | M+Na-2H | 0.71 | 9.34 | Tsangane L-3-glucoside |
| P5 | 9.39 | 269.0452 | M-H | 0.84 | 1.81 | Apigenin |
| P6 | 8.61 | 285.0400 | M-H | 0.88 | 0.00 | Luteolin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youn, I.; Piao, D.; Park, J.; Ock, S.A.; Han, S.; Han, A.-R.; Shin, S.; Seo, E.K. Anti-Obesity Activities of the Compounds from Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Chemical Profiling of the Extract. Molecules 2024, 29, 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112465
Youn I, Piao D, Park J, Ock SA, Han S, Han A-R, Shin S, Seo EK. Anti-Obesity Activities of the Compounds from Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Chemical Profiling of the Extract. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112465
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoun, Isoo, Donglan Piao, Jisu Park, Seung A Ock, Sujin Han, Ah-Reum Han, Sunhye Shin, and Eun Kyoung Seo. 2024. "Anti-Obesity Activities of the Compounds from Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Chemical Profiling of the Extract" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112465
APA StyleYoun, I., Piao, D., Park, J., Ock, S. A., Han, S., Han, A.-R., Shin, S., & Seo, E. K. (2024). Anti-Obesity Activities of the Compounds from Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Chemical Profiling of the Extract. Molecules, 29(11), 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112465







