Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of Dried Yerba Mate and Its Different Infusions
2.2. Bioactive Properties of Different Yerba Mate Infusions
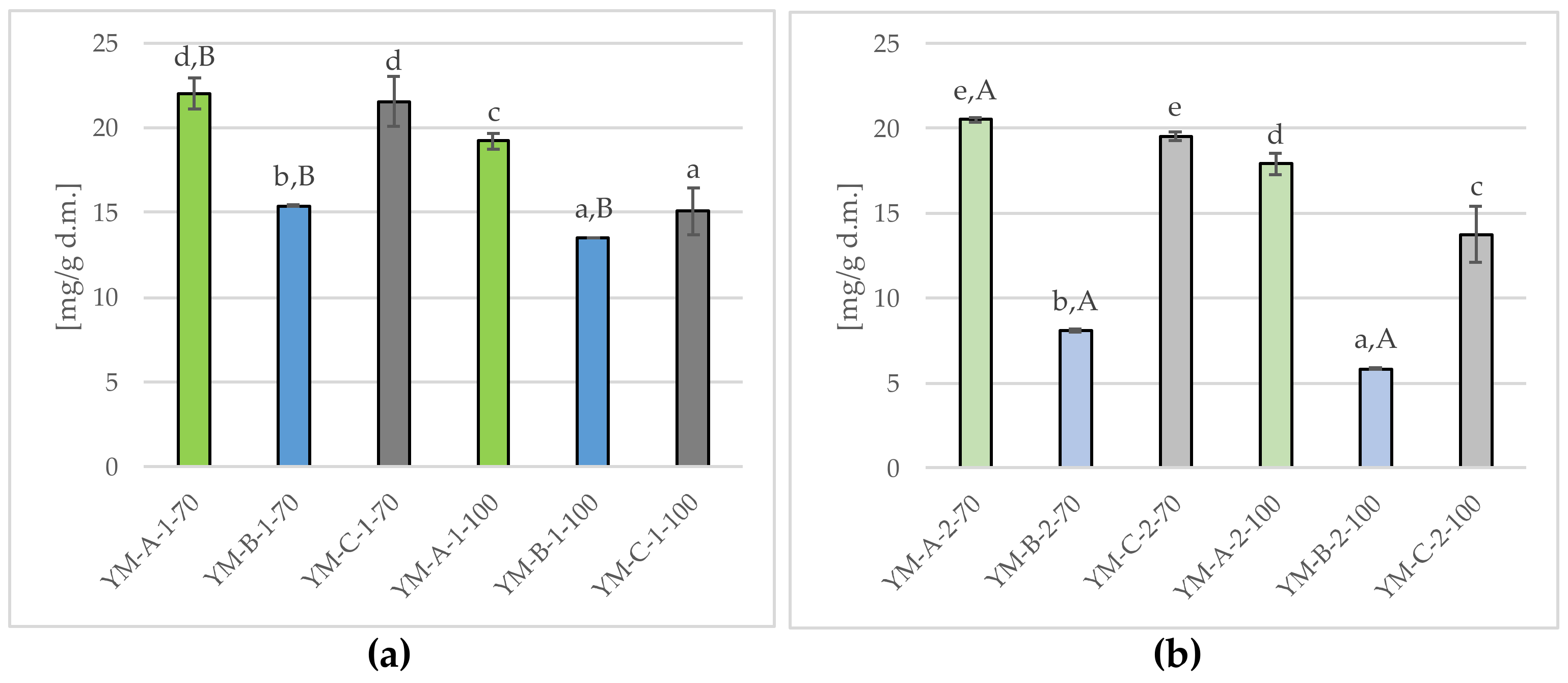
2.2.1. Tannins
2.2.2. Caffeine
2.2.3. Carotenoids
2.2.4. Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids
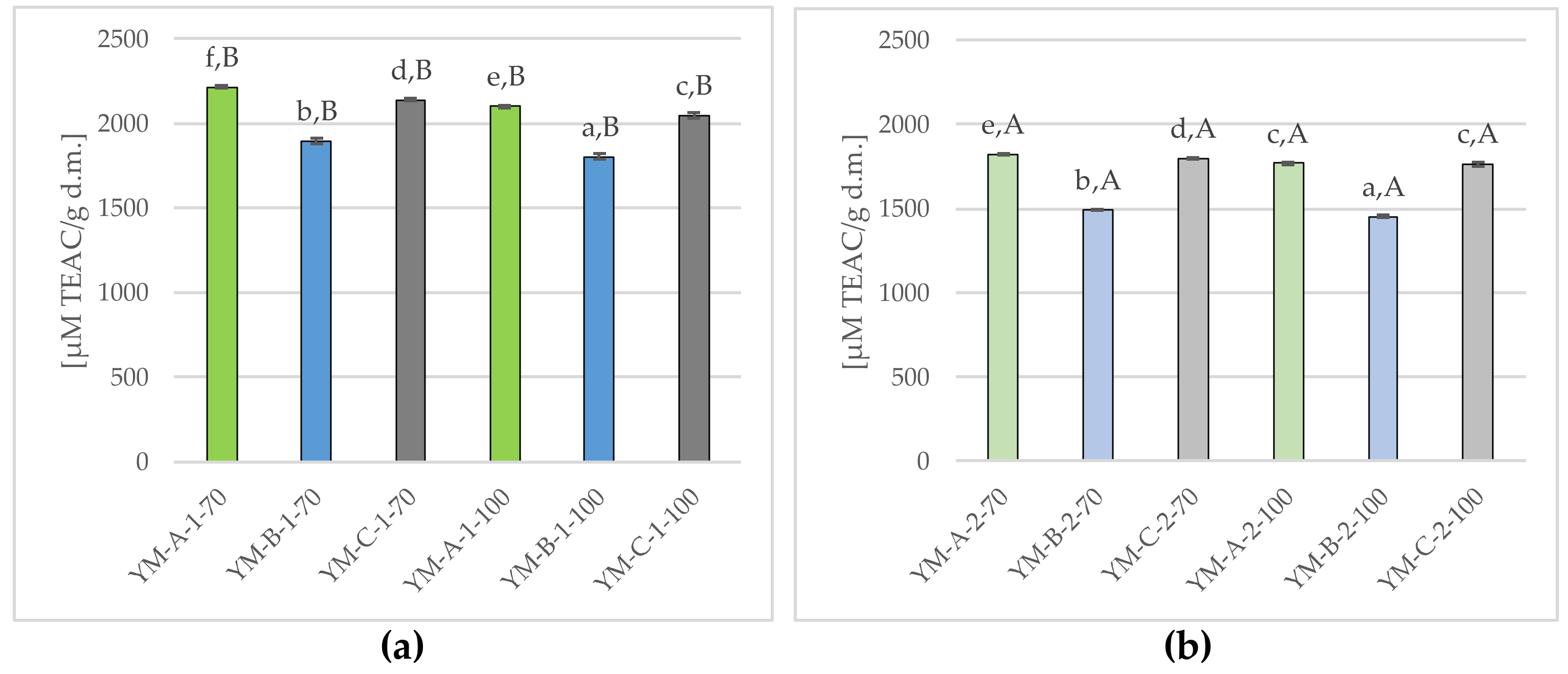
2.2.5. Total Polyphenols
2.2.6. Antioxidant Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Dry Matter (d.m.), Moisture Content (%) and Water Activity (aw) in Dried Yerba Mate
3.2.2. Color Parameters in the CIE LAB (L*a*b*) Color Space and Color Functions in Yerba Mate
3.2.3. pH, Soluble Solids Content (°Brix) and Osmolality in Yerba Mate Infusions
3.2.4. Tannin Content in Yerba Mate
3.2.5. Selectwed Bioactive Compounds Identified by HPLC in Yerba Mate
Carotenoids in Yerba Mate
Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids and Caffein in Yerba Mate
3.2.6. Total Polyphenol Content in Yerba Mate
3.2.7. Antioxidant Activity in Yerba Mate
3.2.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heck, C.I.; De Mejia, E.G. Yerba mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis): A comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawron-Gzella, A.; Chanaj-Kaczmarek, J.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Yerba mate-a long but current history. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croge, C.P.; Cuquel, F.L.; Pintro, P.T.M. Yerba mate: Cultivation systems, processing and chemical composition. A review. Sci. Agric. 2020, 78, e20190259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, M.; Corke, H. Health benefits of bioactive compounds from the genus ilex, a source of traditional caffeinated beverages. Nutrients 2018, 5, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berté, K.A.S.; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B.; Hoffmann-Ribani, R.; Maccari-Junior, A. Chapter 15. Antioxidant Activity of Maté Tea and Effects of Processing. In Processing and Impact on Antioxidants in Beverages; Preedy, V., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, E.L., Jr.; Morand, C. Interest of mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) as a new natural functional food to preserve human cardiovascular health—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutomski, P.; Goździewska, M.; Florek-Łuszczki, M. Health properties of Yerba Mate. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambero, A.; Ribeiro, M.L. The positive effects of yerba maté (Ilex paraguariensis). Nutrients 2015, 7, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuelho, C.H.F.; Bonilha, I.d.F.; do Canto, G.S.; Manfron, M.P. Recent advances in the bioactive properties of yerba. Rev. Cuba. Farm. 2015, 49, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Da Veiga, D.T.A.; Bringhenti, R.; Copes, R.; Tatsch, E.; Moresco, R.N.; Comim, F.V.; Premaor, M. Protective effect of yerba mate intake on the cardiovascular system: A post hoc analysis study in postmenopausal women. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soledad, R.G.L.; Gisel, L.C.; Norailys, L.; Humberto, L.; Fernando, D.A.; Gabriel, H.F. Yerba mate modulates tumor fells functions involved in metastatis in breast cancer models. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 750197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska, K.; Wróblewski, H.; Zajączkowska, M.; Wójtowicz, B.; Zimna, A.; Zygmunt-Siembida, E.; Piecewicz-Szczęsna, H. The correlation between Yerba Mate and cancer—A review. Qual. Sport 2023, 12, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.S.; Schumacher-Schuh, A.F.; Altmann, V.; de Mello Rieder, C.R. A Case–control study of the effects of chimarrão (Ilex paraguariensis) and coffee on Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 10, 619535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłopotek, N.; Dmowski, P. Economic and quality determinants of yerba mate, tea and coffee consumption. Sci. J. Gdyn. Marit. Univ. 2022, 121, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, K.P.; Harte, F.M.; Davidson, P.M.; Stevart, C.N., Jr.; Zivanovic, S. Composition and bioactive properties of yerba mate. Rev. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 72, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, M.; Santos, E.; Kassuya, C.; Salvador, M. Chimarrão, terere and mate-tea in legitimate technology modes of preparation and consume: A comparative study of chemical composition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety properties of the mostly consumed beverages of Ilex paraguariensis St.H. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 28, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.M.; Gabira, M.M.; Tomasi, J.d.C.; Amano, E.; Nogueira, A.C.; Wendling, I. Bioactive compounds and leaf anatomy of yerba mate morphotypes. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2022, 57, e02441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmowski, P.; Śmiechowska, M.; Deja, B. Influence of the tea brewing conditions on the content of tannins and chosen parameters of colour. Sci. J. Gdyn. Marit. Univ. 2011, 65, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Frizon, C.N.T.; Nisgoski, S. Color parameters to predict moisture and tannin bontent in Yerba Mate process. Wood Sci. Technol. Floresta Ambient. 2020, 27, e201800982020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerga, J.; Reta, M.; Lanri, M.C. Polyphenol input to the antioxidant activity of yerba mate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 45, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorini, A.; Damin, F.M.; de Oliviera, D.N.; Criziel, R.L.; Godoy, H.T.; Galli, V.; Meinhart, A.D. Characterization and quantification of bioactive compounds from Ilex paraguariensis residue by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS from plants cultivated under different cultivation systems. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1599–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, T.F.F.; Meinhart, A.D.; de Souza, T.C.L.; Cunha, E.C.E.; de Moraes, M.R.; Lorini, A.; Teixeira Filho, T.J.; Godoy, H.T. Impact of water temperature of chimarrão on phenolic compounds extraction. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rząsa-Duran, E.; Kryczyk-Poprawa, A.; Drabicki, D.; Podkowa, A.; Sułkowska-Ziaja, K.; Szewczyk, A.; Kała, K.; Opoka, W.; Zięba, P.; Fidurski, M.; et al. Yerba mate as a source of elements and bioactive compounds with antioxidant activity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, T.F.F.; Meinhart, A.D.; de Souza, T.C.L.; Cunha, E.C.E.; de Moraes, M.R.; Godoy, H.T. Chlorogenic acids and flavonoid extraction during the preparation of yerba mate based beverages. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Lecumberri, E. LC/MS characterization of phenolic constituents of mate (Ilex paraguariensis, St. Hil.) and its antioxidant activity compared to commonly consumed beverages. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mejía, E.G.; Song, Y.S.; Heck, C.I.; Ramírez-Mares, M. Yerba mate tea (Ilex Pparaguariensis): Phenolics, antioxidant capacity and in vitro inhibition of colon cancer cell proliferation. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujic, N.; Lepojevic, Z.; Srdjenovic, B.; Vladic, J.; Sudji, J. Effects of different extraction methods and conditions on the phenolic composition of mate tea extracts. Molecules 2012, 17, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerman, E.E.; Rice, M.E.; Ritchard, N.T. Mechanisms of protein precipitation for two tannins, pentagalloyl glucose and epicatechin 16 (4 → 8) catechin (procyanidin). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2590–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Wei, C.; Huang, C.W.; Lin, Y. Tannins and human health: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 421–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.; Mbugua, D.M.; Pell, A.N. Analysis of condensed tannins: A review. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2001, 91, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radebe, N.; Rode, K.; Pizzi, A.; Giovando, S.; Pasch, H. MALDI-TOF-CID for the microstructre elucidation of polymeric hydrolysable tannins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 97107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatogawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Shimomura, H.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Hirai, Y. Antibacterial activity of hydrolyzable tannins derived from medicinal plants against Helicobacter pylori. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiori, G.M.L.; Fachin, A.L.; Correa, V.S.C.; Bertoni, B.W.; Giuliatti, S.; Amui, S.F.; Franca, S.D.C.; Pereira, A.M.S. Antimicrobial activity and rates of tannins in Stryphnodendron adstringens Mart. accessions collected in the Brazilian Cerrado. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, L.Y.; Lu, Y.; Mc Nabb, W.C.; Waghorn, G.C.; Ulyatt, M.J. Proanthocyanidins from Lotus pedunculatus. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabbert, N.E. Complexation of condensed tannins with metal ions. Plant Polyphen. 1992, 59, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniawska, E.; Baj, T. Chapter 10—Tannins. In Pharmacognosy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 199–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, M.L. Explaining the French paradox. J. R. Soc. Promot. Health 1995, 115, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaki, V.M.; Lise, C.C.; Oldoni, T.L.C.; de Lima, V.A.; Secco, H., Jr.; Mitterer-Daltoé, M.L. Ultra-refined yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil) as a potential naturally colored food ingredient. Sci. Agric. 2022, 80, e20220054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, M.C.A.; Martins, C.A.; Pozebon, D.; Dressler, V.L.; Ferrão, M.F. Classification of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) according to the country of origin based on element concentrations. Microchem. J. 2014, 117, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proch, J.; Różewska, A.; Orłowska, A.; Niedzielski, P. Influence of brewing method on the content of selected elements in yerba mate (Ilex paraguarensis) infusions. Foods 2023, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proch, J.; Orłowska, A.; Niedzielski, P. Elemental and speciation analyses of different brands of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis). Foods 2021, 10, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guédon, Y.; Costes, E.; Rakocevic, M. Modulation of the yerba-mate metamer production phenology by the cultivation system and the climatic factors. Ecol. Modell. 2018, 384, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valduga, A.T.; Gonçalves, I.L.; Dartora, N.; Mielniczki-Pereira, A.A.; de Souza, L.M. Phytochemical profile of morphologically selected yerba-mate progenies. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2016, 40, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.H.P.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Barros, L.; Calhelha, R.C.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Peralta, R.M.; Bracht, A.; Matsushita, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phytochemicals and bioactive properties of Ilex paraguariensis: An in-vitro comparative study between the whole plant, leaves and stems. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum-Silva, C.H.; Chaves, V.C.; Schenkel, E.P.; Coelho, G.C.; Reginatto, F.H. The influence of leaf age on methylxanthines, total phenolic content, and free radical scavenging capacity of Ilex paraguariensis aqueous extracts. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.H.M.; Ishimoto, E.Y.; Marques, M.O.M.; Ferri, A.F.; Torres, E.A.F.S. Essential oil and antioxidant activity of green mate and mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) infusions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalko, M.E.; Alzamora, S.M. Color, chlorophyll, caffeine, and water content variation during yerba mate processing. Dry Technol. 2001, 19, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, D.C.; Nunes, D.S.; Granto, D. Optimization of phenolics and flavonoids extraction conditions and antioxidant activity of roasted yerba-mate leaves (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil., Aquifoliaceae) using response surface methodology. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2013, 86, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmowski, P.; Post, L. Influence of the multiplicity yerba mate brewing on the antioxidant activity of the beverages. Sci. J. Gdyn. Marit. Univ. 2018, 104, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczyński, P.; Viapiana, A.; Wesołowski, M. Comparison of infusions from black and green teas (Camellia sinensis L. Kuntze) and Erva-mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St-Hil) based on the content of essentials elements, secondary metabolites, and antioxidant activity. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceni, G.C.; Baldissera, E.M.; Primo, M.S.; Antunes, O.A.C.; Dariva, C.; Oliveira, J.V.; Oliveira, D. Influence of application of microwave energy on quality parameters of mate tea leaves (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hill.). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Scipioni, G.P.; Argüello, B.V.; Schmalko, M.E. The effect of Mg2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ pre-treatment on the color of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) leaves. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhart, A.D.; Bizzotto, C.S.; Ballus, C.A.; Rybka, A.C.P.; Sobrinho, M.R.; Cerro-Quintana, R.S.; Teixeira-Filho, J.; Godoy, H.T. Methylxanthines and phenolics content extracted during the consumption of mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil) beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskan, M. Kinetics of colour change of kiwifruits during hot air and microwave drying. J. Food Eng. 2001, 48, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskan, M. Production of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice concentrate by various heating methods: Colour degradation and kinetics. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, O.; Bozoglu, T.F. (Eds.) Chapter 5. Factors affecting microbial growth in foods. Food Microbiology: Principles into Practice. In Section 2: Microbial Sources and Factors Affecting Microorganisms; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarraz, P.; Servente, L.; Kuster, F.; Duarte, L.; Garau, M.; Desirello, M.; Perlas, A. Preoperative fasting for the infusion of “yerba mate”: A randomized clinical trial with ultrasound evaluation of gastric contents. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 72, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunkes, L.B.F.; Hashizume, L.N. Evaluation of the pH and titratable acidity of teas commercially available in Brazilian market. Rev. Gaúcha Odontol. 2014, 62, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.Z.; Pilatti-Riccio, D.; Da Costa, E.S.; Micheletto, Y.M.S.; Quast, E.; Dos Santos, G.H.F. Phytochemical composition of extracts from yerba mate chimarrão. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, D.L.; Hopkins, W.G. Effects of hypotonic and isotonic sports drinks on endurance performance and physiology. Sport Sci. 2010, 14, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gisolfi, C.V.; Summers, R.W.; Lambert, G.P.; Xia, T. Effect of beverage osmolality on intestinal fluid absorption during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 1595–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, F.; Olivares, M.; Hertrampf, E.; Walter, T. Factors which modify the nutritional state of iron: Tannin content of herbal teas. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 1994, 44, 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Jyotismita, K.; Chandan, R.; Arindam, R. Determination of tannin content by titrimetric method from different types of tea. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Valduga, A.T.; Gonçalves, I.L.; Borges, A.C.P.; Mielniczki-Pereira, A.A.; Picolo, A.P. Cytotoxic/antioxidant activity and sensorial acceptance of yerba-mate development by oxidation process. Acta Sci. Technol. 2016, 38, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpo, A.C.; Rosa, H.; Lima, M.E.; Pazzini, C.E.F.; de Camargo, V.B.; Bassante, F.E.M.; Puntel, R.; Ávila, D.S.; Mendez, A.; Folmer, V. Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hill.)-based beverages: How successive extraction influences the extract composition and its capacity to chelate iron and scavenge free radicals. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszewski, B.; Jakóbiak, A.; Jasiczek, A.; Wieczorek, B.; Niemczuk, D. Influence of brewing parameters on caffeine content in Yerba Mate infusions. Bromatol. I Chem. Toksykol. 2012, 45, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Loranty, A.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Bennett, R.N. Identification, quantification and availability of carotenoids and chlorophylls in fruit, herb and medicinal teas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, T.F.F.; Dillenburg Meinhart, A.; Pereira Coutinho, J.; de Souza, T.C.L.; Cunha, E.C.E.; de Moraes, M.R.; Godoy, H.T. Content of lutein in aqueous extracts of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil). Int. Food Res. 2016, 82, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewes, F.R.; Brackmann, A.; Schultz, E.E.; Machado, E.P.; Ludwig, V.; Dos Santos, L.F. Controlled atmosphere maintains native and cultivated yerba mate quality during shelf life after long-term storage. Bragantia 2016, 75, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, R.; Baeza, G.; Sarriá, B.; Bravo, L. Improved LC-MSn characterization of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and flavonols in different commercial mate (Ilex paraguariensis) brands. Quantification of polyphenols, methylxanthines, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vasconcellos, A.C.; Frazzon, J.; Zapata Noreña, C.P. Phenolic compounds present in Yerba Mate potentially increase human health: A critical review. Plant. Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovezan-Borges, A.C.; Valério-Júnior, C.; Gonçalves, I.L.; Mielniczki-Pereira, A.A.; Valduga, A.T. Antioxidant potential of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil.) extracts in Saccharomyces cerevisae deficient in oxidant defense genes. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminet, G.; Baroni, M.V.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Naranjo, R.D.D.P. Antioxidant properties and phenolic composition of “Composed Yerba Mate”. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4711–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, C.A.B.; Trugo, L.C.; Miranda, L.S.D.M.; Salvador, E. Stability of 5-caffeoylquinic acid under different conditions of heating. Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladino, L.; Teixeira, A.S.; Reta, M.; García, A.D.M.; Navarro, A.S.; Martino, M.N. Major phenolics in yerba mate extracts (Ilex paraguariensis) and their contribution to the total antioxidant capacity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 4, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, A.A.F.; Alberti, A.; Bona, E.; Bortolini, D.G.; Benvenutti, L.; Bach, F.; Demiate, I.M.; Nogueira, A. A multivariate approach to differentiate yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) commercialized in the southern Brazil on the basis of phenolics, methylxanthines and in vitro antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, V.G.; Brumovsky, L.A.; Fretes, R.M.; Boado, S.L. A novel procedure to measure the antioxidant capacity of yerba maté extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 32, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- PN-EN 12143:2000; Determination of the Content of Soluble Substances—Refractometric Method. Polish Committee for Standardization, Department of Standardization Publishing:: Warsaw, Poland, 2000.
- Ciszewska, R.; Przeszlakowska, N.; Sykut, A.; Szynal, J. A Guide to Practicing Plant Biochemistry; Agricultural University in Lublin: Lublin, Poland, 1975; pp. 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hallmann, E.; Sabała, P. Organic and conventional herbs quality reflected by their antioxidant compounds concentration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A., Jr. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Moisture (%) | Water Activity (aw) | L* (Lightness) | a* (Greenness) | b* (Yellowness) | BI (Browning Index) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YM-A | 5.58 ± 0.04 b | 0.38 ± 0.00 b | 48.78 ± 5.04 b | −0.58 ± 0.17 c | 34.87 ± 3.48 b | 110.93 ± 6.10 b |
| YM-B | 5.86 ± 0.04 c | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 37.63 ± 1.63 a | −1.45 ± 0.14 b | 27.95 ± 1.30 a | 115.64 ± 2.12 b |
| YM-C | 5.05 ± 0.02 a | 0.38 ± 0.00 b | 74.00 ± 3.31 c | −2.25 ± 0.38 a | 32.52 ± 1.84 b | 52.91 ± 2.28 a |
| Sample | L* (Lightness) | a* (Redness) | b* (Yellowness) | BI (Browning Index) | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YM-A-1-70 | 32.30 ± 0.10 b | 12.10 ± 0.40 b | 39.95 ± 0.15 b | 360.26 ± 0.31 e | 21.41 ± 0.28 b |
| YM-B-1-70 | 43.80 ± 1.70 e | 9.35 ± 0.15 a | 45.10 ± 0.60 e | 235.74 ± 12.72 a | 21.22 ± 0.90 ab |
| YM-C-1-70 | 38.30 ± 0.40 d | 15.40 ± 0.30 de | 44.75 ± 0.35 e | 316.68 ± 2.24 d | 41.66 ± 0.37 d |
| YM-A-1-100 | 30.60 ± 0.20 a | 15.72 ± 0.19 e | 34.05 ± 0.25 a | 290.60 ± 8.19 b | 24.43 ± 0.26 c |
| YM-B-1-100 | 36.15 ± 0.65 c | 14.68 ± 0.63 cd | 40.75 ± 0.05 c | 293.85 ± 10.22 bc | 20.66 ± 0.48 a |
| YM-C-1-100 | 37.60 ± 0.30 d | 14.18 ± 0.60 c | 43.45 ± 0.25 d | 308.39 ± 9.45 cd | 41.41 ± 0.44 d |
| Sample | L* (Lightness) | a* (Redness) | b* (Yellowness) | BI (Browning Index) | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YM-A-2-70 | 60.00 ± 0.20 c | −1.88 ± 0.13 c | 43.60 ± 0.40 b | 112.06 ± 0.93 b | 14.28 ± 0.41 a |
| YM-B-2-70 | 57.30 ± 1.60 b | −2.55 ± 0.15 b | 39.15 ± 0.35 a | 100.32 ± 5.72 a | 22.68 ± 1,21 d |
| YM-C-2-70 | 55.05 ± 0.25 a | −1.38 ± 0.13 d | 45.10 ± 0.70 c | 138.62 ± 2.57 c | 22.77 ± 0.17 d |
| YM-A-2-100 | 57.15 ± 0.35 b | −0.58 ± 0.08 e | 49.15 ± 0.35 d | 152.87 ± 3.65 d | 16.56 ± 0.12 b |
| YM-B-2-100 | 57.65 ± 0.85 b | −0.70 ± 0.05 e | 48.65 ± 0.15 d | 147.45 ± 3.07 d | 28.81 ± 0.70 e |
| YM-C-2-100 | 58.15 ± 0.65 b | −2.85 ± 0.05 a | 39.85 ± 0.40 a | 100.23 ± 0.21 a | 17.48 ± 0.42 c |
| Sample | pH | °Brix (%) | Osmolality (mOsm/kg•H2O) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YM-A-1-70 | 5.56 ± 0.03 d | 2.07 ± 0.06 ab | 47.33 ± 0.58 b |
| YM-B-1-70 | 5.41 ± 0.01 b | 2.07 ± 0.06 ab | 46.33 ± 0.58 ab |
| YM-C-1-70 | 5.39 ± 0.01 ab | 2.07 ± 0.06 ab | 45.33 ± 0.58 a |
| YM-A-1-100 | 5.52 ± 0.01 c | 2.17 ± 0.06 b | 55.33 ± 0.58 d |
| YM-B-1-100 | 5.38 ± 0.00 a | 2.07 ± 0.06 ab | 51.00 ± 1.00 c |
| YM-C-1-100 | 5.39 ± 0.00 ab | 2.03 ± 0.06 a | 51.33 ± 0.58 c |
| Sample | pH | °Brix (%) | Osmolality (mOsm/kg•H2O) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YM-A-2-70 | 5.72 ± 0.01 e | 0.83 ± 0.15 c | 18.33 ± 0.58 d |
| YM-B-2-70 | 5.54 ± 0.01 c | 0.60 ± 0.00 a | 12.33 ± 0.58 b |
| YM-C-2-70 | 5.48 ± 0.00 a | 0.70 ± 0.00 ab | 11.67 ± 0.58 a |
| YM-A-2-100 | 5.61 ± 0.02 d | 0.77 ± 0.06 bc | 14.67 ± 0.58 c |
| YM-B-2-100 | 5.51 ± 0.01 b | 0.70 ± 0.00 ab | 14.33 ± 0.58 c |
| YM-C-2-100 | 5.50 ± 0.00 b | 0.70 ± 0.00 ab | 12.67 ± 0.58 b |
| Bioactive Compounds (mg/g d.m.) | YM-A-1-70 | YM-B-1-70 | YM-C-1-70 | YM-A-1-100 | YM-B-1-100 | YM-C-1-100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 0.45 ± 0.00 a | 2.25 ± 0.03 c | 2.45 ± 0.08 d | 0.47 ± 0.00 a | 0.55 ± 0.02 b | 2.40 ± 0.01 d |
| Chlorogenic acid | 25.64 ± 0.36 c | 24.47 ± 0.03 b | 27.05 ± 0.86 d | 24.15 ± 0.16 b | 7.94 ± 0.12 a | 25.30 ± 0.43 c |
| Caffeic acid | 3.82 ± 0.08 b | 35.86 ± 2.54 a | 0.62 ± 0.03 a | 3.68 ± 0.04 b | 23.11 ± 0.56 c | 0.43 ± 0.04 a |
| p-coumaric acid | 38.15 ± 0.04 e | 32.20 ± 0.39 b | 36.81 ± 0.14 d | 38.56 ± 0.29 e | 12.86 ± 0.86 a | 34.01 ± 0.44 c |
| Ferulic acid | 1.87 ± 0.02 c | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | 0.36 ± 0.00 a | 1.64 ± 0.02 b | 3.31 ± 0.09 d | 0.30 ± 0.01 a |
| Salicylic acid | 1.98 ± 0.02 d | 0.51 ± 0.06 a | 0.69 ± 0.02 b | 0.56 ± 0.01 a | 0.91 ± 0.05 c | 0.56 ± 0.00 a |
| t-cinnamic acid | 7.03 ± 0.08 c | 7.48 ± 0.03 e | 7.30 ± 0.07 d | 2.77 ± 0.01 a | 8.43 ± 0.09 f | 6.08 ± 0.05 b |
| Total phenolic acids * | 78.95 ± 0.49 f | 67.58 ± 0.82 b | 75.29 ± 0.92 e | 71.83 ± 0.18 d | 57.10 ± 0.61 a | 69.09 ± 0.45 c |
| Rutoside-3-O-quercetin | 2.60 ± 0.04 e | 2.11 ± 0.07 d | 2.02 ± 0.01 c | 1.18 ± 0.04 b | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 a |
| Glycoside-3-O-quercetin | 4.08 ± 0.07 e | 3.19 ± 0.03 c | 3.54 ± 0.03 d | 1.40 ± 0.07 a | 1.87 ± 0.02 b | 1.90 ± 0.03 b |
| Myricetin | 0.94 ± 0.01 d | 0.75 ± 0.01 b | 0.90 ± 0.01 c | 1.64 ± 0.02 e | 0.65 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.00 a |
| Apigenin | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.54 ± 0.02 c | 0.70 ± 0.01 d | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.09 ± 0.00 ab | 0.09 ± 0.00 b |
| Total flavonoids * | 7.71 ± 0.09 e | 6.59 ± 0.12 c | 7.16 ± 0.06 d | 4.28 ± 0.05 b | 3.54 ± 0.03 a | 3.56 ± 0.03 a |
| Lutein # | 8.49 ± 0.03 c | 8.02 ± 0.07 a | 8.19 ± 0.03 b | 8.40 ± 0.04 c | 7.99 ± 0.05 a | 8.27 ± 0.08 b |
| α-carotene # | 3.50 ± 0.01 c | 3.37 ± 0.01 a | 3.46 ± 0.01 b | 3.48 ± 0.02 bc | 3.36 ± 0.01 a | 3.47 ± 0.01 b |
| β-carotene # | 1.10 ± 0.05 b | 0.81 ± 0.05 a | 1.27 ± 0.08 bc | 1.70 ± 0.04 d | 1.32 ± 0.04 c | 1.19 ± 0.23 bc |
| Total carotenoids *# | 13.09 ± 0.07 c | 12.20 ± 0.08 a | 12.92 ± 0.04 c | 13.58 ± 0.08 d | 12.67 ± 0.08 b | 12.93 ± 0.28 c |
| Bioactive Compounds (mg/g d.m.) | YM-A-2-70 | YM-B-2-70 | YM-C-2-70 | YM-A-2-100 | YM-B-2-100 | YM-C-2-100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 2.44 ± 0.09 e | 0.43 ± 0.00 a | 0.89 ± 0.02 b | 0.87 ± 0.01 b | 1.23 ± 0.04 c | 1.46 ± 0.09 d |
| Chlorogenic acid | 3.28 ± 0.11 a | 15.24 ± 0.45 e | 5.47 ± 0.07 b | 7.89 ± 0.08 d | 6.64 ± 0.04 c | 5.62 ± 0.13 b |
| Caffeic acid | 30.90 ± 0.22 f | 12.81 ± 0.07 c | 12.21 ± 0.34 b | 22.63 ± 0.07 d | 2.41 ± 0.02 a | 24.40 ± 0.14 e |
| p-coumaric acid | 8.93 ± 0.10 a | 19.92 ± 0.12 d | 39.80 ± 0.20 e | 14.67 ± 0.16 b | 16.92 ± 0.11 c | 8.87 ± 0.10 a |
| Ferulic acid | 4.25 ± 0.49 c | 5.33 ± 0.06 d | 3.67 ± 0.05 b | 3.23 ± 0.01 a | 4.14 ± 0.06 c | 5.33 ± 0.02 d |
| Salicylic acid | 2.62 ± 0.13 d | 1.57 ± 0.05 c | 0.48 ± 0.00 a | 0.95 ± 0.04 b | 1.47 ± 0.03 c | 3.08 ± 0.01 e |
| t-cinnamic acid | 13.50 ± 0.29 f | 1.73 ± 0.04 a | 2.71 ± 0.01 b | 9.06 ± 0.05 d | 7.51 ± 0.25 c | 9.95 ± 0.05 e |
| Total phenolic acids * | 65.91 ± 0.62 e | 57.03 ± 0.46 b | 65.23 ± 0.18 d | 59.31 ± 0.01 c | 40.32 ± 0.21 a | 58.71 ± 0.37 c |
| Rutoside-3-O-quercetin | 1.25 ± 0.02 a | 1.60 ± 0.03 b | 2.01 ± 0.01 c | 1.58 ± 0.02 b | 1.55 ± 0.04 b | 1.58 ± 0.04 b |
| Glycoside-3-O-quercetin | 1.51 ± 0.02 d | 0.99 ± 0.01 b | 1.07 ± 0.01 c | 0.90 ± 0.02 a | 1.00 ± 0.03 b | 0.93 ± 0.03 a |
| Myricetin | 2.34 ± 0.00 f | 0.50 ± 0.01 b | 0.68 ± 0.00 d | 0.84 ± 0.01 e | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 c |
| Apigenin | 0.08 ± 0.00 b | 0.08 ± 0.00 ab | 0.13 ± 0.00 c | 0.07 ± 0.02 ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 c |
| Total flavonoids * | 5.18 ± 0.03 e | 3.16 ± 0.04 b | 3.89 ± 0.00 d | 3.38 ± 0.03 c | 3.06 ± 0.03 a | 3.18 ± 0.04 b |
| Lutein # | 9.25 ± 0.05 cd | 8.11 ± 0.07 a | 8.60 ± 0.05 b | 9.49 ± 0.15 d | 8.20 ± 0.28 a | 9.11 ± 0.05 c |
| α-carotene # | 3.23 ± 0.02 bc | 3.15 ± 0.01 a | 3.33 ± 0.01 d | 3.26 ± 0.01 c | 3.21 ± 0.03 b | 3.22 ± 0.02 b |
| β-carotene # | 0.65 ± 0.00 c | 0.58 ± 0.01 b | 0.82 ± 0.02 e | 0.69 ± 0.03 d | 0.52 ± 0.03 a | 0.59 ± 0.03 b |
| Total carotenoids *# | 13.14 ± 0.05 c | 11.84 ± 0.08 a | 12.75 ± 0.03 b | 13.44 ± 0.17 d | 11.93 ± 0.30 a | 12.93 ± 0.02 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najman, K.; Rajewski, R.; Sadowska, A.; Hallmann, E.; Buczak, K. Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions. Molecules 2024, 29, 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112590
Najman K, Rajewski R, Sadowska A, Hallmann E, Buczak K. Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112590
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajman, Katarzyna, Rafał Rajewski, Anna Sadowska, Ewelina Hallmann, and Krzysztof Buczak. 2024. "Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112590
APA StyleNajman, K., Rajewski, R., Sadowska, A., Hallmann, E., & Buczak, K. (2024). Changes in the Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Yerba Mate Depending on the Brewing Conditions. Molecules, 29(11), 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112590








