Optimizing Antimony Speciation Analysis via Frontal Chromatography–ICP-MS to Explore the Release of PET Additives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
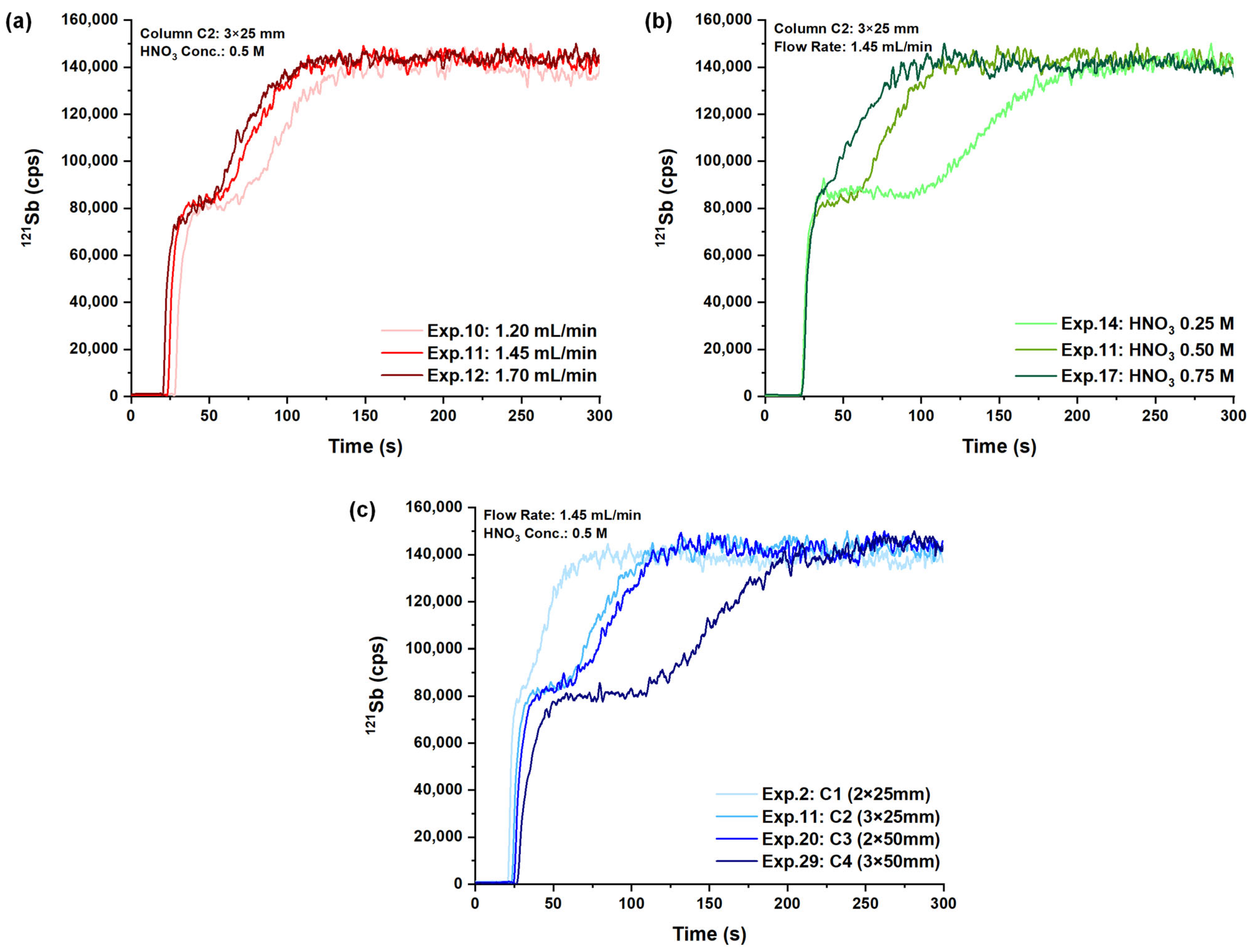
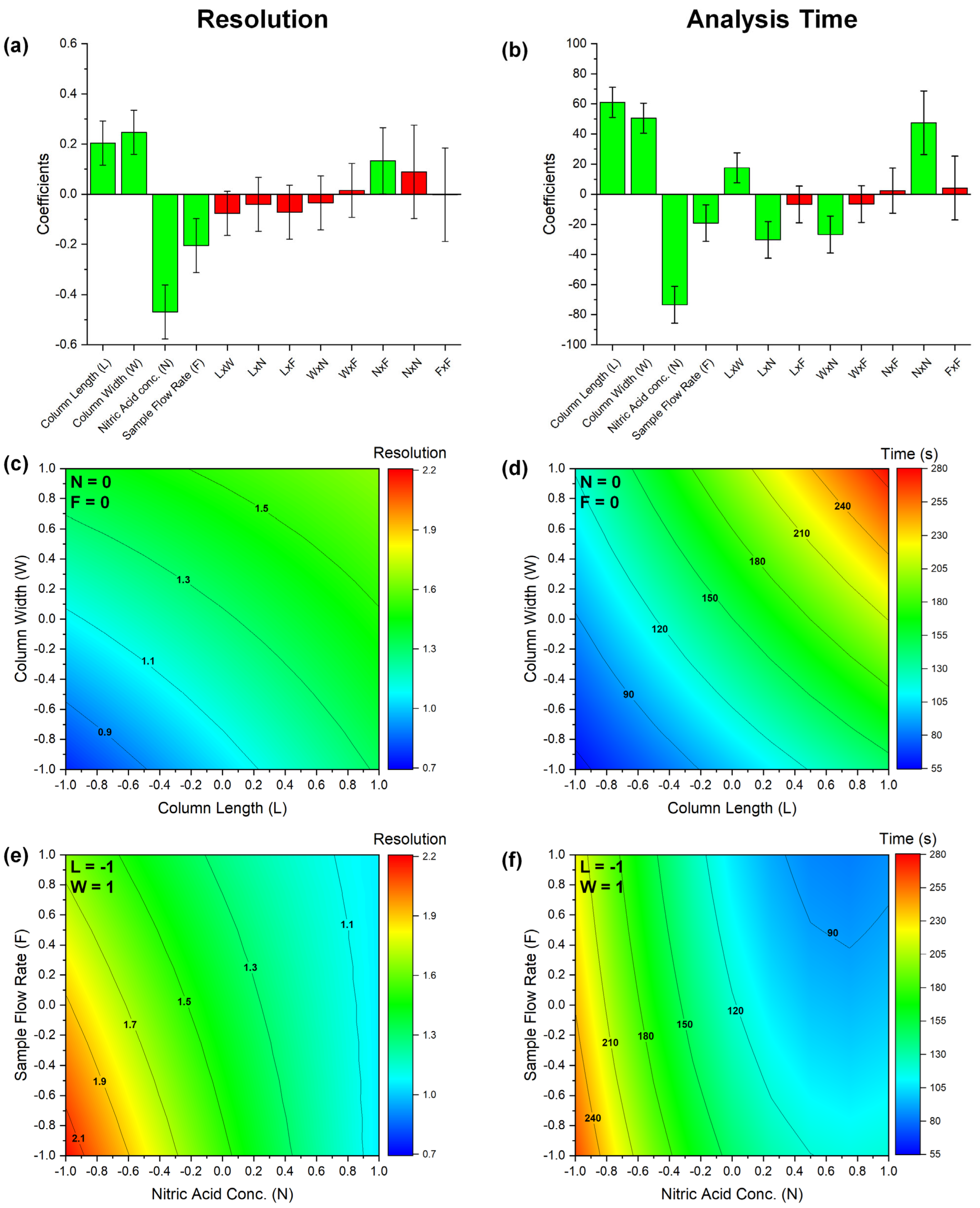
2.1. Analytical Method Optimization
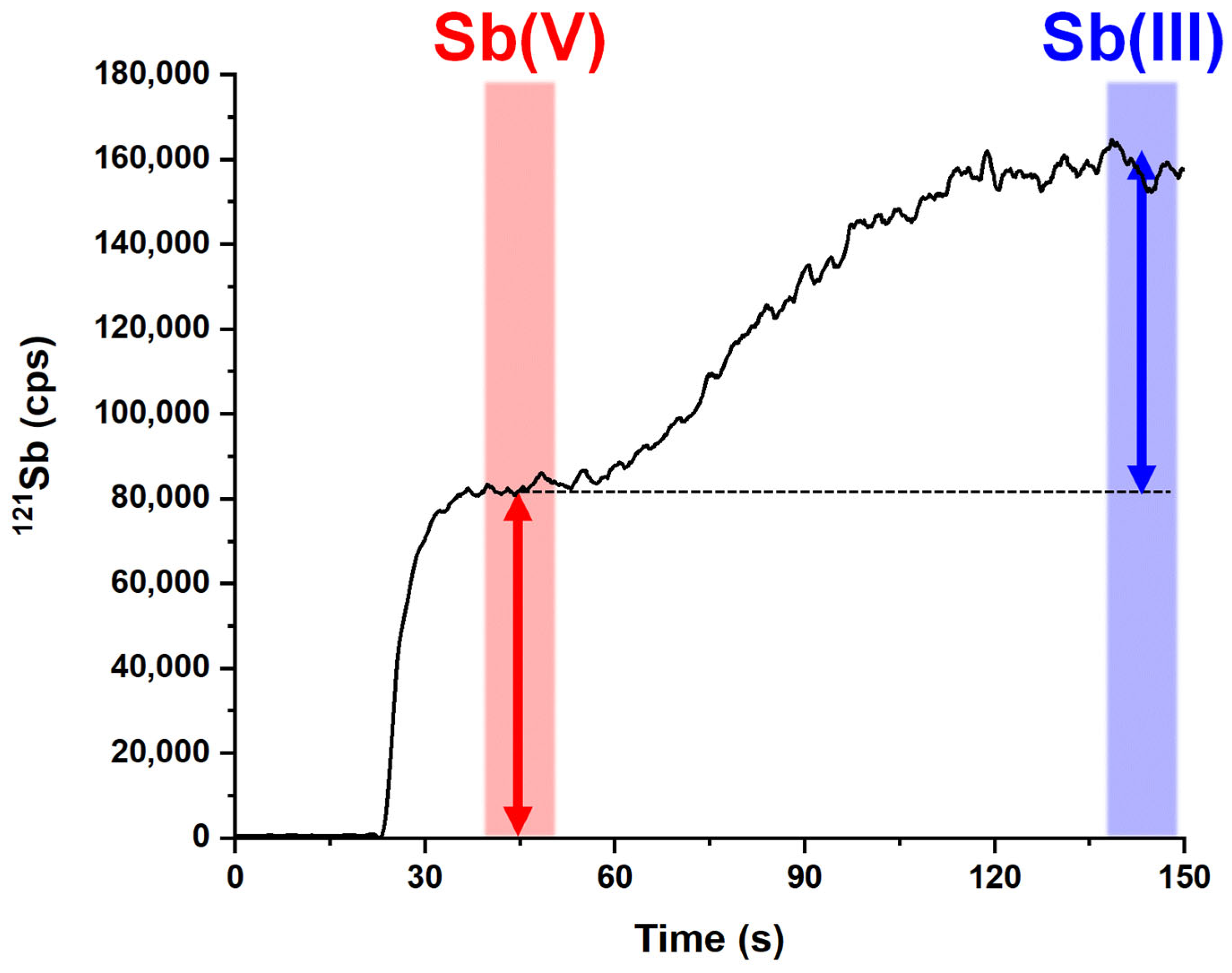
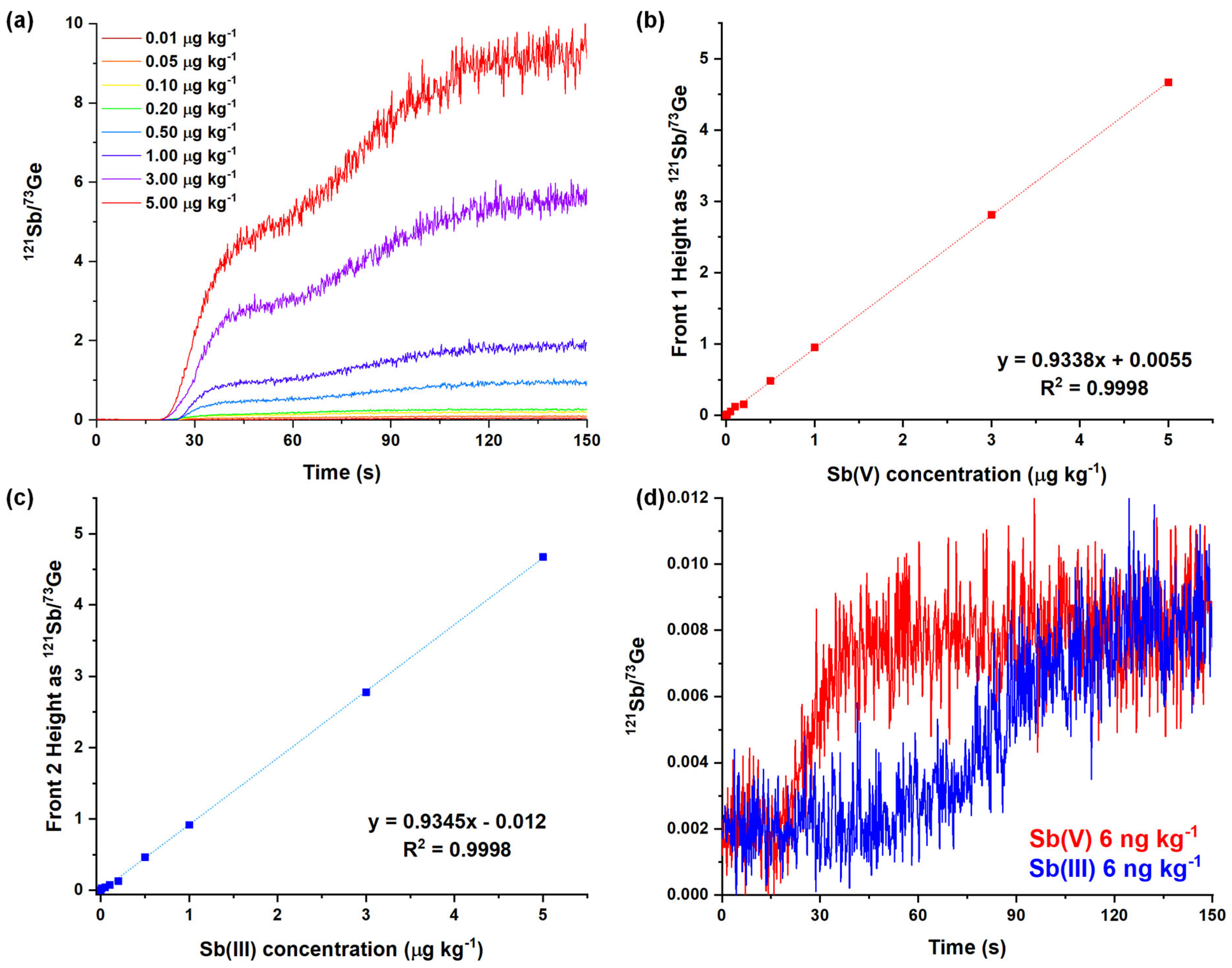
2.2. Analytical Performances of the Optimized Method
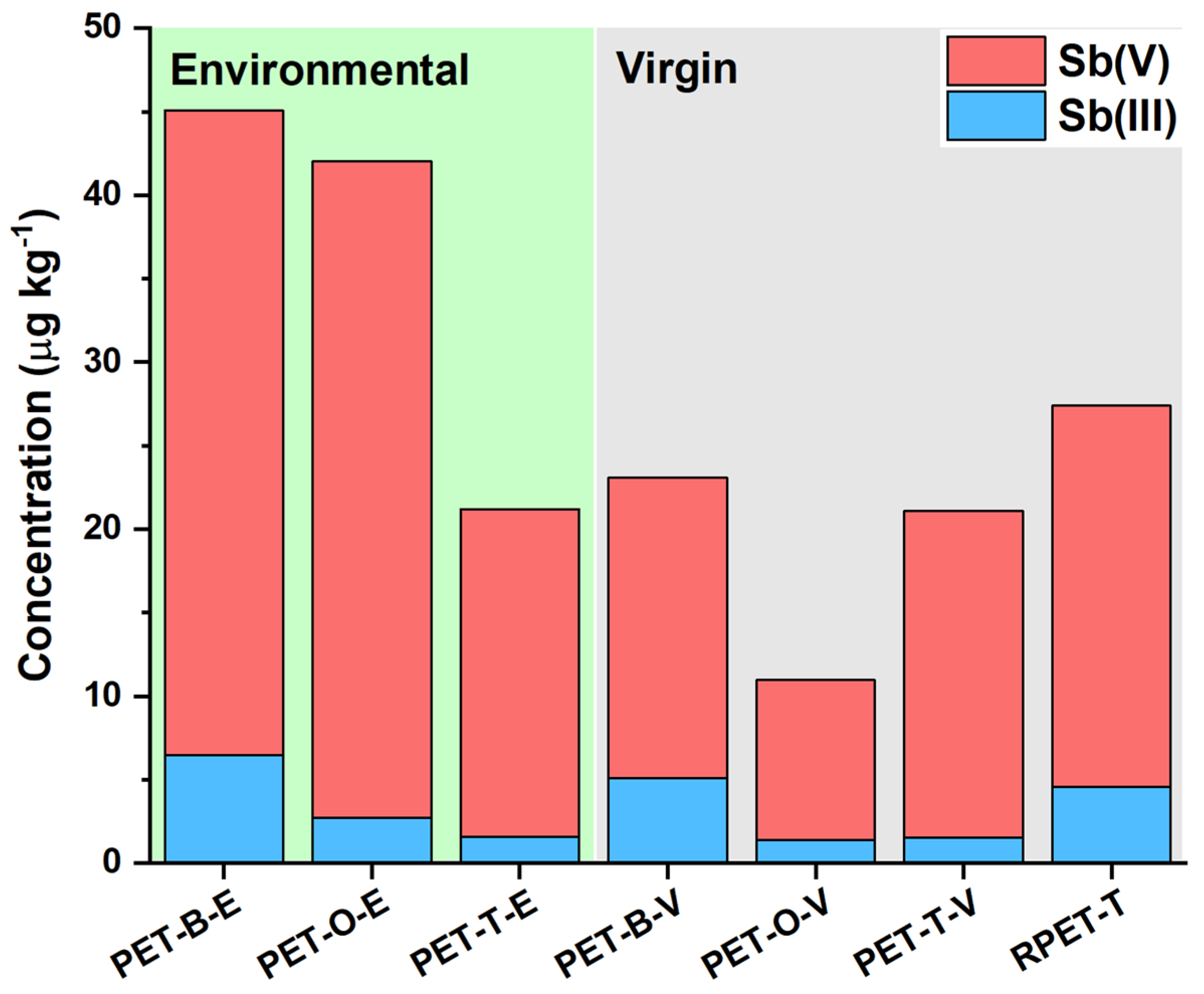
2.3. Application to PET Leaching Solutions
2.4. Evaluation of the Greenness of the Analytical Protocol
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Instrumental Setup and Analytical Procedure
3.3. Sb(III) and Sb(V) Analysis in Plastic Samples
3.4. Microwave-Assisted Acid Digestion of Plastic Samples for Total Sb Determination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.; Wang, N.; Long, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Pervaiz, A.; Shan, J. Antimony speciation in the environment: Recent advances in understanding the biogeochemical processes and ecological effects. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 14–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, M.; Williams, P.A.; Belzile, N. Antimony in the environment: Knowns and unknowns. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 57, 125–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Fu, Z. Antimony pollution in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, M.; Hennebert, P.; Okkenhaug, G.; Turner, A. Occurrence and fate of antimony in plastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishad, P.A.; Bhaskarapillai, A. Antimony, a pollutant of emerging concern: A review on industrial sources and remediation technologies. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, S.; Chakravarty, J. Antimony Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 4267–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, 2019, 1–62.
- Bolan, N.; Kumar, M.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, L.; Kumar, S.; Keerthanan, S.; Hoang, S.A.; El-Naggar, A.; Vithanage, M.; et al. Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagas, M.R.; Wang, A.; Dorman, D.C.; Hall, A.L.; Pi, J.; Sergi, C.M.; Symanski, E.; Ward, E.M.; Arrandale, V.H.; Azuma, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of cobalt, antimony compounds, and weapons-grade tungsten alloy. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. IARC Monographs—Volume 131; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Filella, M. Antimony and PET bottles: Checking facts. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyataka, P.H.M.; Marangoni Júnior, L.; Brito, A.C.A.; Pallone, J.A.L. Migration of antimony from polyethylene terephthalate bottles to mineral water: Comparison between test conditions proposed by Brazil and the European Union. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 126, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerassimidou, S.; Lanska, P.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Lovat, E.; Vanzetto, S.; Geueke, B.; Groh, K.J.; Muncke, J.; Maffini, M.; Martin, O.V.; et al. Unpacking the complexity of the PET drink bottles value chain: A chemicals perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyataka, P.H.M.; Dantas, S.T.; Albino, A.C.; Pallone, J.A.L. Antimony Assessment in PET Bottles for Soft Drink. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukur, A.; Sharp, L.; Stern, B.; Tizaoui, C.; Benkreira, H. PET bottle use patterns and antimony migration into bottled water and soft drinks: The case of British and Nigerian bottles. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welle, F.; Franz, R. Migration of antimony from PET bottles into beverages: Determination of the activation energy of diffusion and migration modelling compared with literature data. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneado, S.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, Á. Antimony in Polyethylene Terephthalate-Bottled Beverages: The Migration Puzzle. Molecules 2023, 28, 7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneado, S.; Hernández-Nataren, E.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A. Migration of antimony from polyethylene terephthalate used in mineral water bottles. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sakuma, K.; Itai, T.; Zheng, G.; Mitsunobu, S. Speciation of Antimony in PET Bottles Produced in Japan and China by X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9045–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in the packaging industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, G.; Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Pozzi, A.; Bellasi, A.; Bettinetti, R.; Carnati, S.; Nizzetto, L. Unfolding the interaction between microplastics and (trace) elements in water: A critical review. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, G.; Kalčíková, G.; Allan, I.J.; Hurley, R.; Rødland, E.; Spanu, D.; Nizzetto, L. Microplastic aging processes: Environmental relevance and analytical implications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 172, 117566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, R.; Harrington, C.F.; Hill, S.J.; Madrid, Y.; Tyson, J.F. Atomic spectrometry update: Review of advances in elemental speciation. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2023, 38, 1339–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Ferreira, S.L.; dos Anjos, J.P.; Assis Felix, C.S.; da Silva Junior, M.M.; Palacio, E.; Cerda, V. Speciation analysis of antimony in environmental samples employing atomic fluorescence spectrometry—Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, A.; Beltrán, R.; Recamales, M.A.F.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L. Optimization of an HPLC-HG-AFS method for screening Sb(V), Sb(III), and Me3SbBr2 in water samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Emons, H. Potential of high performance liquid chromatography coupled to flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of inorganic and organic antimony compounds. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2000, 15, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Andrade, I.; Regidor-Alfageme, E.; Durazo, A.; Field, J.A.; Umlauf, K.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. LC-ICP-OES method for antimony speciation analysis in liquid samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M.; Grygoyć, K. Spatial and temporal variability of metal(loid)s concentration as well as simultaneous determination of five arsenic and antimony species using HPLC-ICP-MS technique in the study of water and bottom sediments of the shallow, lowland, dam reservoir in Pola. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12358–12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M. Antimony, Arsenic and Chromium Speciation Studies in Biała Przemsza River (Upper Silesia, Poland) Water by HPLC-ICP-MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4739–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanella, M.C.; Beone, G.M. Determination of Sb(III) and Sb(V) by HPLC—Online isotopic dilution—ICP MS. MethodsX 2016, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cidu, R.; Biddau, R.; Dore, E. Determination of traces of Sb(III) using ASV in Sb-rich water samples affected by mining. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 854, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, P.; Nagaosa, Y. Determination of antimony(III) and (V) in natural water by cathodic stripping voltammetry with in-situ plated bismuth film electrode. Microchim. Acta 2009, 166, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Renedo, O.; Martinez, M. Simultaneous determination of antimony(III) and antimony(V) by UV–vis spectroscopy and partial least squares method (PLS). Talanta 2005, 68, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Morita, Y.; Sakuragawa, A.; Isozaki, A. Inorganic speciation of As(III, V), Se(IV, VI) and Sb(III, V) in natural water with GF-AAS using solid phase extraction technology. Talanta 2007, 72, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garboś, S.; Bulska, E.; Hulanicki, A.; Fijałek, Z.; Sołtyk, K. Determination of total antimony and antimony(V) by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after selective separation of antimony(III) by solvent extraction with N-benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylamine. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2000, 55, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, J.K.; de Andrade, C.K.; Felsner, M.L.; Quináia, S.P.; dos Anjos, V.E. Pre-concentration and speciation of inorganic antimony in bottled water and natural water by cloud point extraction with Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daus, B.; Hansen, H.R. Analysis of antimony species—Lessons learnt from more than two decades of environmental research. Environ. Chem. 2016, 13, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, W.A.; Krikowa, F.; Foster, S.D.; Ellwood, M.J.; Bennett, W.W. Antimony measurements in environmental matrices: Seven considerations. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Fantinuoli, S.; Binda, G.; Rampazzi, L.; Monticelli, D.; Recchia, S. Streamlining antimony speciation analysis in natural waters with frontal chromatography-ICP-MS. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2023, 207, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Rampazzi, L.; Dossi, C.; Recchia, S. Introducing Frontal Chromatography–Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry as a Fast Method for Speciation Analysis: The Case of Inorganic Arsenic. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13810–13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Butti, L.; Boldrocchi, G.; Bettinetti, R.; Recchia, S.; Monticelli, D. Selective organomercury determination by ICP-MS made easy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Butti, L.; Recchia, S.; Dossi, C.; Monticelli, D. A high-throughput, straightforward procedure for biomonitoring organomercury species in human hair. Talanta 2024, 270, 125612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Binda, G.; Dossi, C.; Rampazzi, L.; Recchia, S. One-minute highly selective Cr(VI) determination at ultra-trace levels: An ICP-MS method based on the on-line trapping of Cr(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzl, T.; Haedrich, J.; Schaechtele, A.; Robouch, P.; Stroka, J. Guidance Document on the Estimation of LOD and LOQ for Measurements in the Field of Contaminants in Feed and Food; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carnati, S.; Pozzi, A.; Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Bettinetti, R.; Boldrocchi, G.; Nizzetto, L.; Binda, G. Assessing sources and fractions of metals associated with environmental plastics: A case study in Lake Como (Italy). Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 1746–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenenberg, J.E.; Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Van Zomeren, A.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Comans, R.N.J. Evaluation of the Single Dilute (0.43 M) Nitric Acid Extraction to Determine Geochemically Reactive Elements in Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Cao, W.; Zheng, L. Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, G.; Carnati, S.; Spanu, D.; Bellasi, A.; Hurley, R.; Bettinetti, R.; Monticelli, D.; Pozzi, A.; Nizzetto, L. Selection of the optimal extraction protocol to investigate the interaction between trace elements and environmental plastic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Pan, X. Effects of aging on environmental behavior of plastic additives: Migration, leaching, and ecotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.A.; Jiang, S.J.; Sahayam, A.C. Determination of antimony compounds in waters and juices using ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, D.; Castelletti, A.; Civati, D.; Recchia, S.; Dossi, C. How to Efficiently Produce Ultrapure Acids. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 5180610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, D.; Butti, L.; Boldrocchi, G.; Bettinetti, R.; Monticelli, D. High-throughput, Multi-batch System for the Efficient Microwave Digestion of Biological Samples. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Boldrocchi, G.; Pozzi, A.; Bettinetti, R. What Are Lake Beaches Made of? An Assessment of Plastic Beach Litter on the Shores of Como Bay (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Level | Column Length (mm) | Column Width (mm) | HNO3 Concentration (M) | Sample Flow Rate (mL min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 25 | 2 | 0.25 | 1.2 |
| 0 | - | - | 0.5 | 1.45 |
| 1 | 50 | 3 | 0.75 | 1.7 |
| Sample | Total Sb Bulk Content | Leached Sb(V) | Leached Sb(III) | Leached Total Sb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET-B-E | (311 ± 14) mg kg−1 | (39 ± 5) μg kg−1 | (6.5 ± 0.9) μg kg−1 | (45 ± 5) μg kg−1 |
| PET-O-E | (279 ± 46) mg kg−1 | (39 ± 4) μg kg−1 | (2.7 ± 0.3) μg kg−1 | (42 ± 3) μg kg−1 |
| PET-T-E | (263 ± 50) mg kg−1 | (20 ± 1) μg kg−1 | (1.6 ± 0.4) μg kg−1 | (21 ± 1) μg kg−1 |
| PET-B-V | (340 ± 18) mg kg−1 | (18 ± 4) μg kg−1 | (5.1 ± 2.3) μg kg−1 | (23 ± 6) μg kg−1 |
| PET-O-V | (202 ± 8) mg kg−1 | (10 ± 1) μg kg−1 | (1.4 ± 0.6) μg kg−1 | (11 ± 2) μg kg−1 |
| PET-T-V | (261 ± 3) mg kg−1 | (20 ± 3) μg kg−1 | (1.6 ± 0.8) μg kg−1 | (21 ± 4) μg kg−1 |
| RPET-T | (265 ± 1) mg kg−1 | (23 ± 3) μg kg−1 | (4.6 ± 1.9) μg kg−1 | (27 ± 5) μg kg−1 |
| Sample Label | Polymer Type | Color | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET-B-E | PET | Blue | Environmental Plastic |
| PET-O-E | PET | Orange | Environmental Plastic |
| PET-T-E | PET | Transparent | Environmental Plastic |
| PET-B-V | PET | Blue | Virgin Plastic |
| PET-O-V | PET | Orange | Virgin Plastic |
| PET-T-V | PET | Transparent | Virgin Plastic |
| RPET-T-V | Recycled PET | Transparent | Virgin Plastic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López, A.R.; Binda, G.; Roncoroni, G.; Recchia, S.; Monticelli, D.; Spanu, D. Optimizing Antimony Speciation Analysis via Frontal Chromatography–ICP-MS to Explore the Release of PET Additives. Molecules 2024, 29, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122870
López AR, Binda G, Roncoroni G, Recchia S, Monticelli D, Spanu D. Optimizing Antimony Speciation Analysis via Frontal Chromatography–ICP-MS to Explore the Release of PET Additives. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122870
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Alejandro R., Gilberto Binda, Gianluca Roncoroni, Sandro Recchia, Damiano Monticelli, and Davide Spanu. 2024. "Optimizing Antimony Speciation Analysis via Frontal Chromatography–ICP-MS to Explore the Release of PET Additives" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122870
APA StyleLópez, A. R., Binda, G., Roncoroni, G., Recchia, S., Monticelli, D., & Spanu, D. (2024). Optimizing Antimony Speciation Analysis via Frontal Chromatography–ICP-MS to Explore the Release of PET Additives. Molecules, 29(12), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122870








