Halogenated Boroxine K2[B3O3F4OH] Modulates Metabolic Phenotype and Autophagy in Human Bladder Carcinoma 5637 Cell Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxic Effects of HB on BC Cells
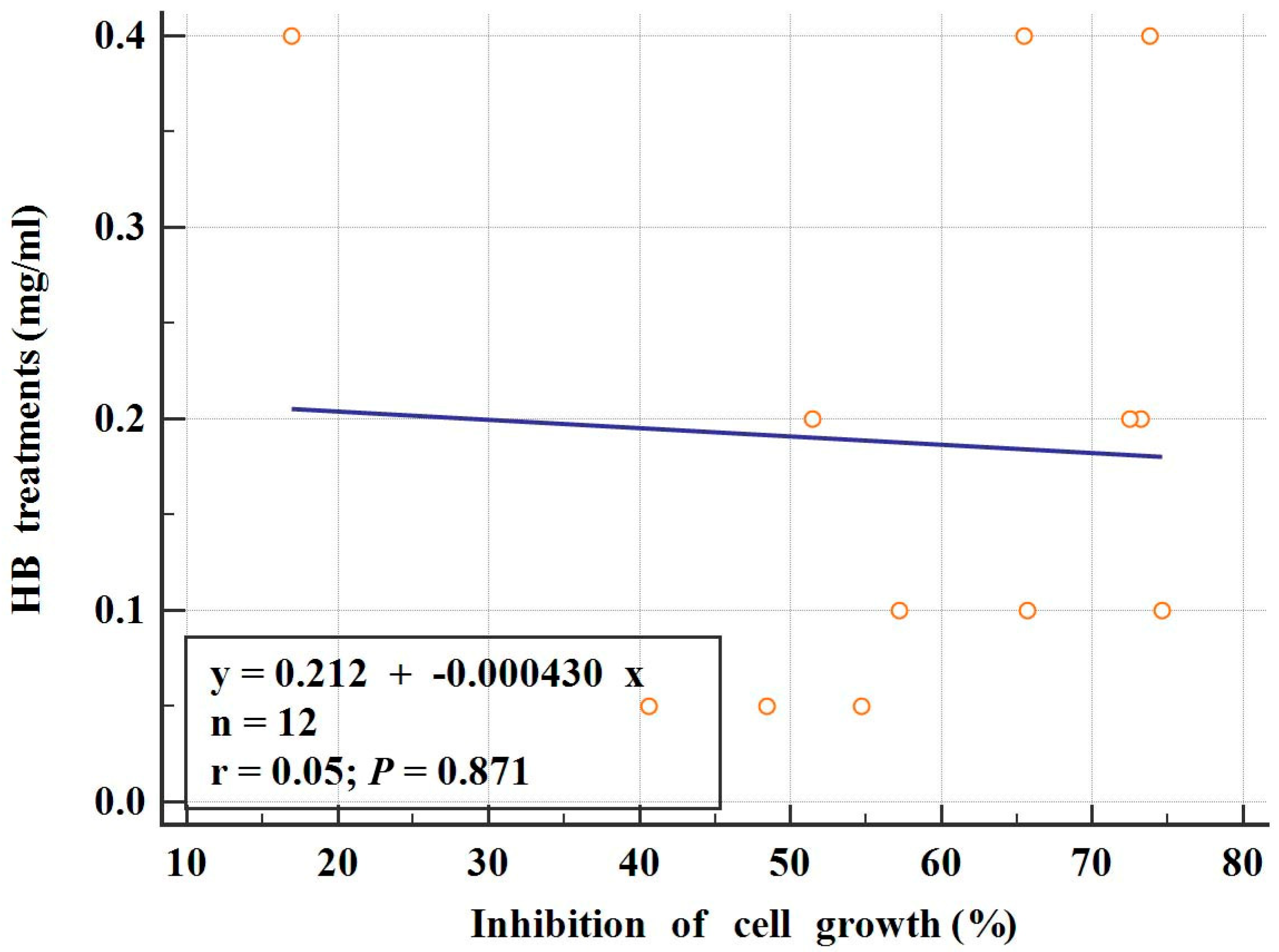
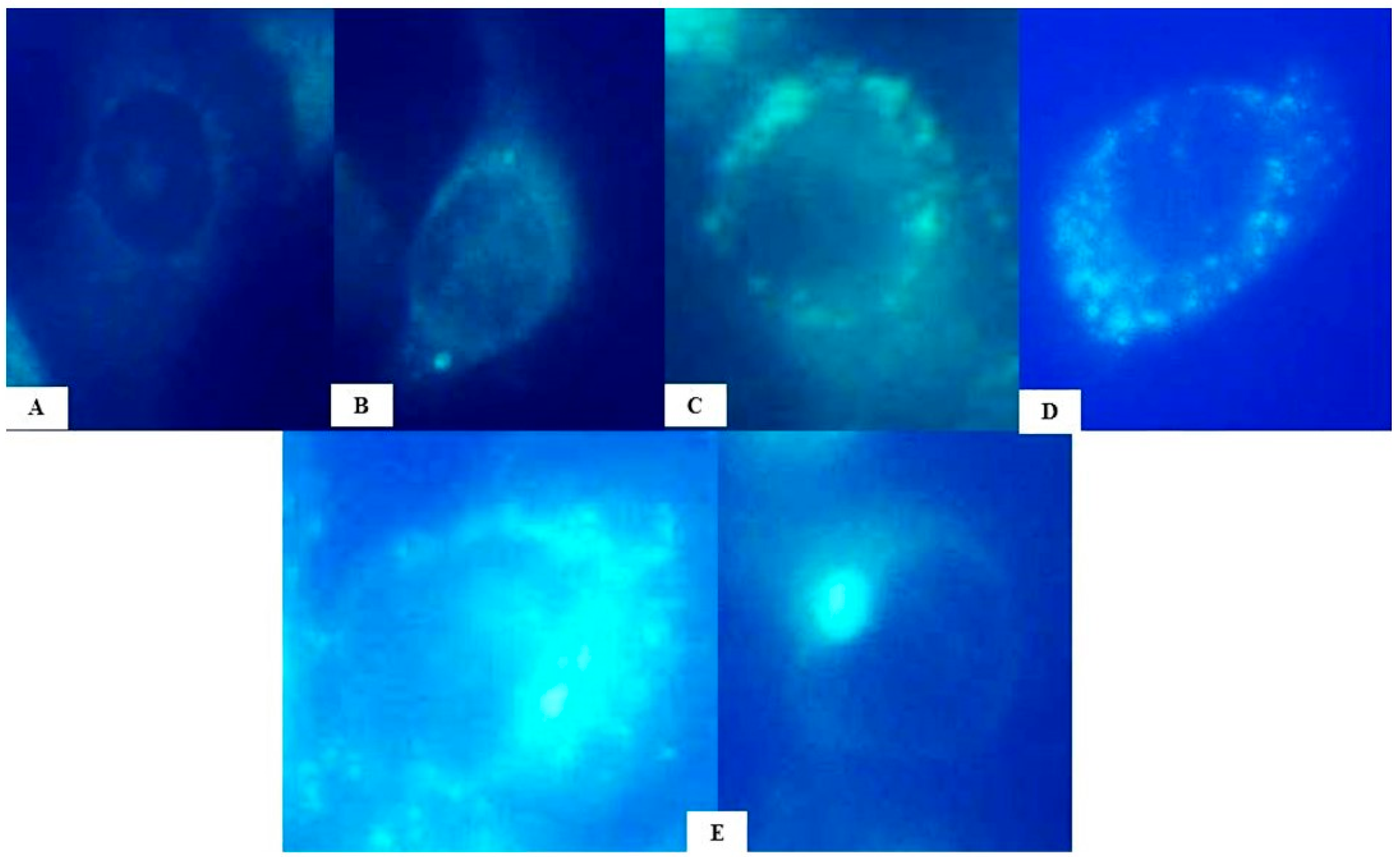
2.2. Evaluation of Autophagy Induction by HB
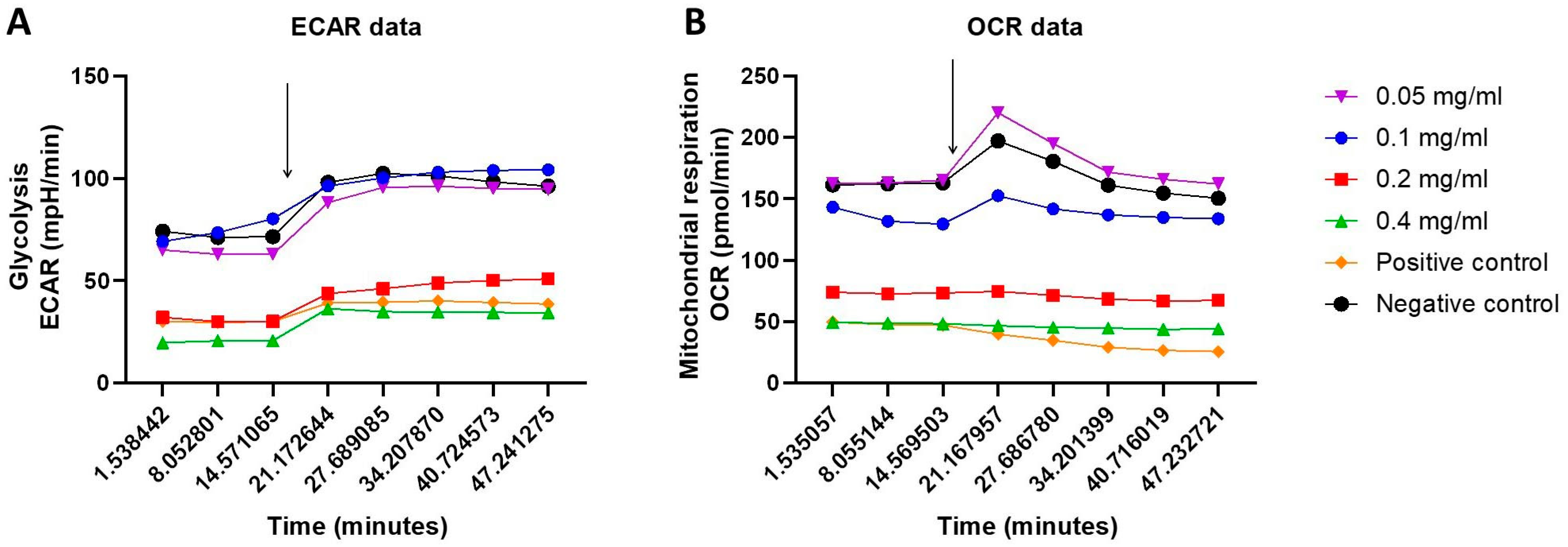
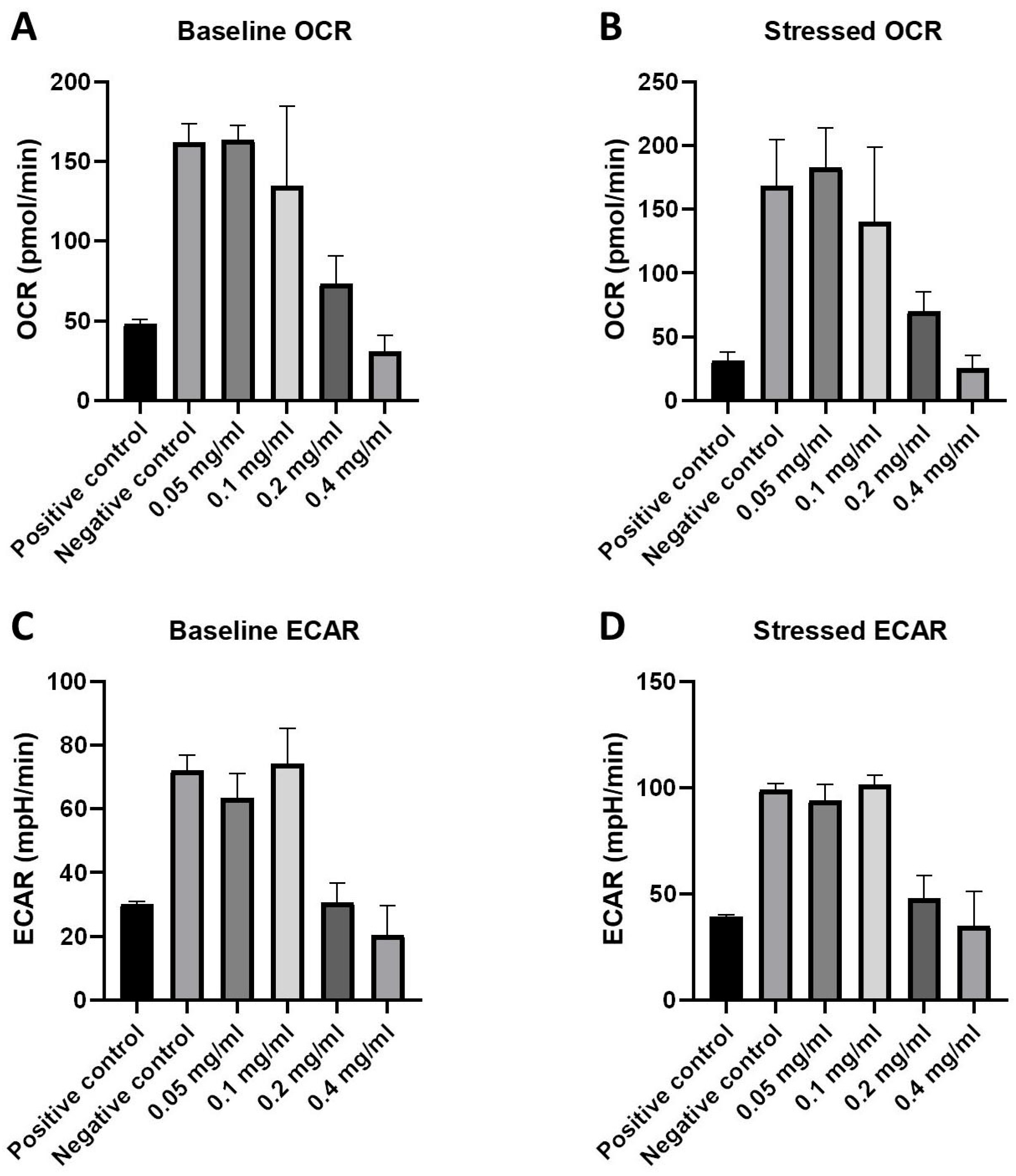
2.3. Cellular Energy Phenotype and the Investigation of Metabolic Switching: OCR and ECAR Rates in Response to HB Treatment—Nts
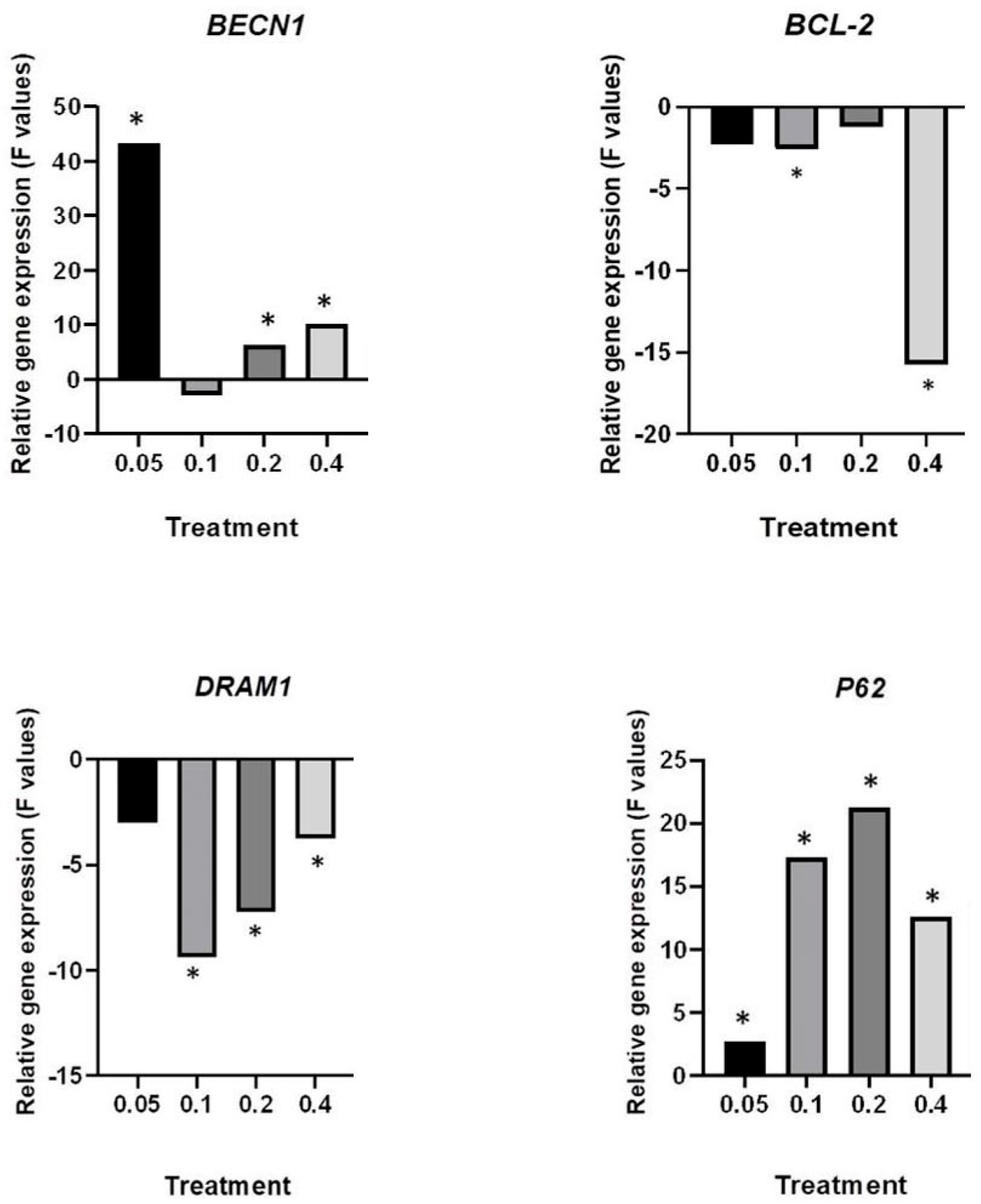
2.4. Deregulation of Autophagy-Associate Genes by HB
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Dipotassium Trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate, K2[B3O3F4OH], Halogenated Boroxine (HB)—Synthesis and Solution Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture Treatment
4.3. Alamar Blue Assay
4.4. Autophagy Detection
4.5. Oxygen Consumption Rate and Extracellular Acidification Rate
4.6. q-PCR and Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levine, B.; Klionsky, D.J. Development by self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Mathew, R.; Fan, J.; Strohecker, A.M.; Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Kamphorst, J.J.; Chen, G.; Lemons, J.M.; Karantza, V.; et al. Activated Ras requires autophagy to maintain oxidative metabolism and tumourigenesis. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, J.F.; Wen, S.I.; Yang, S.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Chen, H.E.; Chou, K.Y.; Hwang, T.I. Inhibition of High Basal Level of Autophagy Induces Apoptosis in Human Bladder Cancer Cells. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; White, E.P.; Mehnert, J.M. Coordinate autophagy and mTOR pathway inhibition enhances cell death in melanoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.H.; Piao, S.; Wang, D.; McAfee, Q.W.; Nathanson, K.L.; Lum, J.J.; Li, L.Z.; Amaravadi, R.K. Measurements of tumour cell autophagy predict invasiveness, resistance to chemotherapy, and survival in melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3478–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, J.; Levine, B.; Debnath, J. Autophagy and cancer metabolism. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 542, 25–57. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, S.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Znaor, A.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Bladder Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Global Overview and Recent Trends. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, H.; Habuchi, T.; Watanabe, J.; Teramukai, S.; Tada, H.; Ono, Y.; Ohshima, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Hirao, Y.; Fukushima, M.; et al. Clinical outcome of a large-scale multi-institutional retrospective study for locally advanced bladder cancer: A survey including 1131 patients treated during 1990–2000 in Japan. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, P.; Silvestri, I.; Gradilone, A.; Scarpa, S.; Morrone, S.; Gandini, O.; Gianni, W.; Frati, L.; Agliano, A.M. Gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in 5637 cell line: An in-vitro model for high-risk superficial bladder cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2007, 18, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, K.M.; Little, A.F.; Swart, J.M.; Kastrinakis, W.V.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Hess, D.T.; Libertino, J.A.; Summerhayes, I.C. Human bladder carcinoma cell lines as indicators of oncogenic change relevant to urothelial neoplastic progression. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Ryan, K.M. p53 and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaad, K.; Tsuruta, A.; Selak, M.A.; Vidal, M.N.C.; Nakano, K.; Bartrons, R.; Gottlieb, E.; Vousden, K.H. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 2006, 126, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyard, T.; Waltzer, W.C.; Waltzer, D.; Romanov, V. Metabolic alterations in bladder cancer: Applications for cancer imaging. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 341, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.B.; Yang, K.; Xie, Y.Q.; Lin, Y.W.; Mao, Q.Q.; Xie, L.P. Silencing of mutant p53 by siRNA induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Chen, H.E.; Chou, K.Y.; Hwang, T.I. Cisplatin induces protective autophagy through activation of BECN1 in human bladder cancer cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 1517–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, T. Emerging strategies for the improvement of chemotherapy in bladder cancer: Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 39, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaborators Group. Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data from Randomised Controlled Trials. Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G. Boronic Acids; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Galić, B. Boroxine Composition for Removal of Skin Changes. U.S. Patent US8278289, 2 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Galić, B. Removal of Skin Changes. European Patent EP1996514, 31 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haverić, S.; Haverić, A.; Bajrović, K.; Galić, B.; Maksimović, M. Effects of dipotassium trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate (K2(B3O3F4OH)) on genetic material and inhibition of cell division in human cell cultures. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžić, M.; Haverić, S.; Haverić, A.; Galić, B. Inhibitory effects of delphinidin and luteolin on genotoxicity induced by K2(B3O3F4OH) in human lymphocytes in vitro. Biologia 2015, 70, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverić, S.; Hadžić, M.; Haverić, A.; Mijanović, M.; Hadžiselimović, R.; Galić, B. Genotoxicity Evaluation of Dipotassium-Trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate, K2(B3O3F4OH), in Human Lymphocyte Cultures and Mice Reticulocytes. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016, 59, e16160195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojskić, L.; Haverić, S.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Hadžić, M.; Haverić, A.; Galić, Z.; Galić, B.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Miloš, M. Effects of dipotassium-trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate, K2(B3O3F4OH), on cell viability and gene expression of common human cancer drug targets in a melanoma cell line. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžić, M.; Haverić, S.; Haverić, A.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Galić, B.; Ramić, J.; Pojskić, L. Bioflavonoids protect cells against halogenated boroxine-induced genotoxic damage by upregulation of hTERT expression. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2019, 74, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojić, J.; Herenda, S.; Bešić, Z.; Miloš, M.; Galić, B. Advantages of an Electrochemical Method Compared to the Spectrophotometric Kinetic Study of Peroxidase Inhibition by Boroxine Derivative. Molecules 2017, 22, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamović, S.; Galić, B.; Miloš, M. A study of the inhibition of catalase by dipotassium trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate K2[B3O3F4OH]. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herenda, S.; Ostojić, J.; Hasković, E.; Hasković, D.; Miloš, M.; Galić, B. Electrochemical Investigation of the Influence of K2[B3O3F4OH] on the Activity of Immobilized Superoxide Dismutase. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 3279–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullo, D.; Miloš, M.; Galić, B.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Dipotassium trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate K2[B3O3F4OH], is a potent inhibitor of human carbonic anhydrases. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elez-Burnjaković, N.; Pojskić, L.; Haverić, A.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Omanović, M.H.; Ramić, J.; Smajlović, A.; Maksimović, M.; Haverić, S. New in vitro findings about halogenated boroxine cytotoxicity and deregulation of cell death-related genes in GR-M melanoma cells. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2023, 74, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, S.; Stojković, R.; Maksimović, M.; Galić, B.; Miloš, M. Impact of calcium ion on cytotoxic effect of the boroxine derivative, K2(B3O3F4OH). J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, S.; Stojković, R.; Galić, Z.; Galić, B.; Ostojić, J.; Marasović, M.; Miloš, M. In vitro and in vivo antitumour activity of the halogenated boroxine dipotassium-trioxohydroxytetrafluorotriborate (K2(B3O3F4OH)). J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverić, A.; Durmić-Pašić, A.; Alić, A.; Mujezinović, I.; Smajlović, A.; Ostojić, J.; Ahatović, A.; Hadžić, M.; Prašović, S.; Haverić, S.; et al. Biochemical and histomorphological findings in Swiss Wistar rats treated with potential boron-containing therapeutic—K2(B3O3F4OH). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverić, A.; Haverić, S.; Hadžić, M.; Ezić, J.; Ćetković, T.; Galić, B. Moderate Toxicity of Potential Boron-containing Therapeutic, Dipotassium-trioxohydroxytetrafl uorotriborate—K2(B3O3F4OH) in Rats and Mice. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 59, e21384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Phan, E.; Saračević, O.; Burnett, M.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Haverić, A.; Galić, B. In vitro study of the anti-proliferative effects of dipotassium-trioxohydroxytetra fluorotriborate on the H520 non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Genet. Appl. 2017, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gwangwa, M.V.; Joubert, A.M.; Visagie, M.H. Crosstalk between the Warburg effect, redox regulation and autophagy induction in tumourigenesis. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2018, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerke, A.; Sweep, F.C.; Geurts-Moespot, A.; Bussink, J.; Span, P.N. Therapeutic targeting of autophagy in cancer. Part I: Molecular pathways controlling autophagy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Park, J.H.; Jung, K.H.; Levine, H.; Kaipparettu, B.A. Elucidating the Metabolic Plasticity of Cancer: Mitochondrial Reprogramming and Hybrid Metabolic States. Cells 2018, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Qi, L.; Wu, J.C.; Qin, Z.H. DRAM1 Regulates Autophagy Flux through Lysosomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galavotti, S.; Bartesaghi, S.; Faccenda, D.; Shaked-Rabi, M.; Sanzone, S.; McEvoy, A.; Dinsdale, D.; Condorelli, F.; Brandner, S.; Campanella, M.; et al. The autophagy-associated factors DRAM1 and p62 regulate cell migration and invasion in glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, S.; Manjithaya, R. A reversible autophagy inhibitor blocks autophagosome-lysosome fusion by preventing Stx17 loading onto autophagosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ding, J.; Wu, Y. Resveratrol induces apoptosis of bladder cancer cells via miR21 regulation of the Akt/Bcl2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžić, M.; Pojskić, L.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Haverić, A.; Ramić, J.; Galić, B.; Haverić, S. Novel boron-containing compound, halogenated boroxine, induces selective cytotoxicity through apoptosis triggering in UT-7 leukemia. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, R.; Treskova, I.; Vrzalova, J.; Svobodova, S.; Topolcan, O.; Fuchsova, R.; Rousarova, M.; Treska, V.; Kydlicek, T. Evaluation of IGF1 serum levels in malignant melanoma and healthy subjects. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 5217–5220. [Google Scholar]
- Weroha, S.J.; Haluska, P. IGF-1 receptor inhibitors in clinical trials-early lessons. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.M.; Codogno, P. Autophagic cell death: Loch Ness monster or endangered species? Autophagy 2011, 7, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpour, M.; Esclatine, A.; Beau, I.; Codogno, P. Autophagy in health and disease. 1. Regulation and significance of autophagy: An overview. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.; Renna, M.; Park, S.J.; Menzies, F.M.; Ricketts, T.; Fullgrabe, J.; Ashkenazi, A.; Frake, R.A.; Lombarte, A.C.; Bento, C.F.; et al. Contact inhibition controls cell survival and proliferation via YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, C.; Yofu, S.; Kiriyama, K.; Sutoh, K.; Saito, T.; Kishi, S.; Gunji, M.; Inoue, Y.; Sugi, M.; Shioda, S.; et al. High concentration of extracellular nucleotides suppresses cell growth via delayed cell cycle progression in cancer and noncancer cell lines. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Reference Sequence (Fasta Acc Number) | Primers |
|---|---|---|
| BECN1 | NM_003766.5 | Forward: CTCCCGAGGTGAAGAGCATC |
| Reverse: GGGGGATGAATCTGCGAGAG | ||
| P62/SQSTM | NM_003900.5 | Forward: CCGTGAAGGCCTACCTTCTG |
| Reverse: TCCTCGTCACTGGAAAAGGC | ||
| BCL-2 | NM_000633.3 | Forward: GGGGTCATGTGTGTGGAGAG |
| Reverse: GAAATCAAACAGAGGCCGCA | ||
| DRAM1 | NM_018370.3 | Forward: TTGGTGCAGCCACGATGTAT |
| Reverse: ACACCACAGACAAAGGCCAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elez-Burnjaković, N.; Pojskić, L.; Haverić, A.; Lojo-Kadrić, N.; Hadžić Omanović, M.; Smajlović, A.; Kalaydjiev, S.; Maksimović, M.; Joksimović, B.; Haverić, S. Halogenated Boroxine K2[B3O3F4OH] Modulates Metabolic Phenotype and Autophagy in Human Bladder Carcinoma 5637 Cell Line. Molecules 2024, 29, 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122919
Elez-Burnjaković N, Pojskić L, Haverić A, Lojo-Kadrić N, Hadžić Omanović M, Smajlović A, Kalaydjiev S, Maksimović M, Joksimović B, Haverić S. Halogenated Boroxine K2[B3O3F4OH] Modulates Metabolic Phenotype and Autophagy in Human Bladder Carcinoma 5637 Cell Line. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122919
Chicago/Turabian StyleElez-Burnjaković, Nikolina, Lejla Pojskić, Anja Haverić, Naida Lojo-Kadrić, Maida Hadžić Omanović, Ajla Smajlović, Svetoslav Kalaydjiev, Milka Maksimović, Bojan Joksimović, and Sanin Haverić. 2024. "Halogenated Boroxine K2[B3O3F4OH] Modulates Metabolic Phenotype and Autophagy in Human Bladder Carcinoma 5637 Cell Line" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122919
APA StyleElez-Burnjaković, N., Pojskić, L., Haverić, A., Lojo-Kadrić, N., Hadžić Omanović, M., Smajlović, A., Kalaydjiev, S., Maksimović, M., Joksimović, B., & Haverić, S. (2024). Halogenated Boroxine K2[B3O3F4OH] Modulates Metabolic Phenotype and Autophagy in Human Bladder Carcinoma 5637 Cell Line. Molecules, 29(12), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122919









