The RNA Helicase Ded1 from Yeast Is Associated with the Signal Recognition Particle and Is Regulated by SRP21
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ded1 Associated with SRP Factors In Vivo
2.1.1. Ded1 Crosslinks to SCR1 RNA
2.1.2. Ded1 Associated with SRP Proteins on Sucrose Gradients
2.1.3. Ded1 Stably Associated with SCR1 RNA and SRP Proteins in Extracts
2.2. Ded1 Was Genetically Linked to SRP Proteins
2.2.1. Multicopy Suppression of Ded1 Mutant
2.2.2. Constitutive and Null Expression of Ded1 and SRP Proteins
2.2.3. Ded1 Multicopy Suppression of SRP Protein Depletions
2.3. In Situ Localization of Ded1 and SRP Proteins
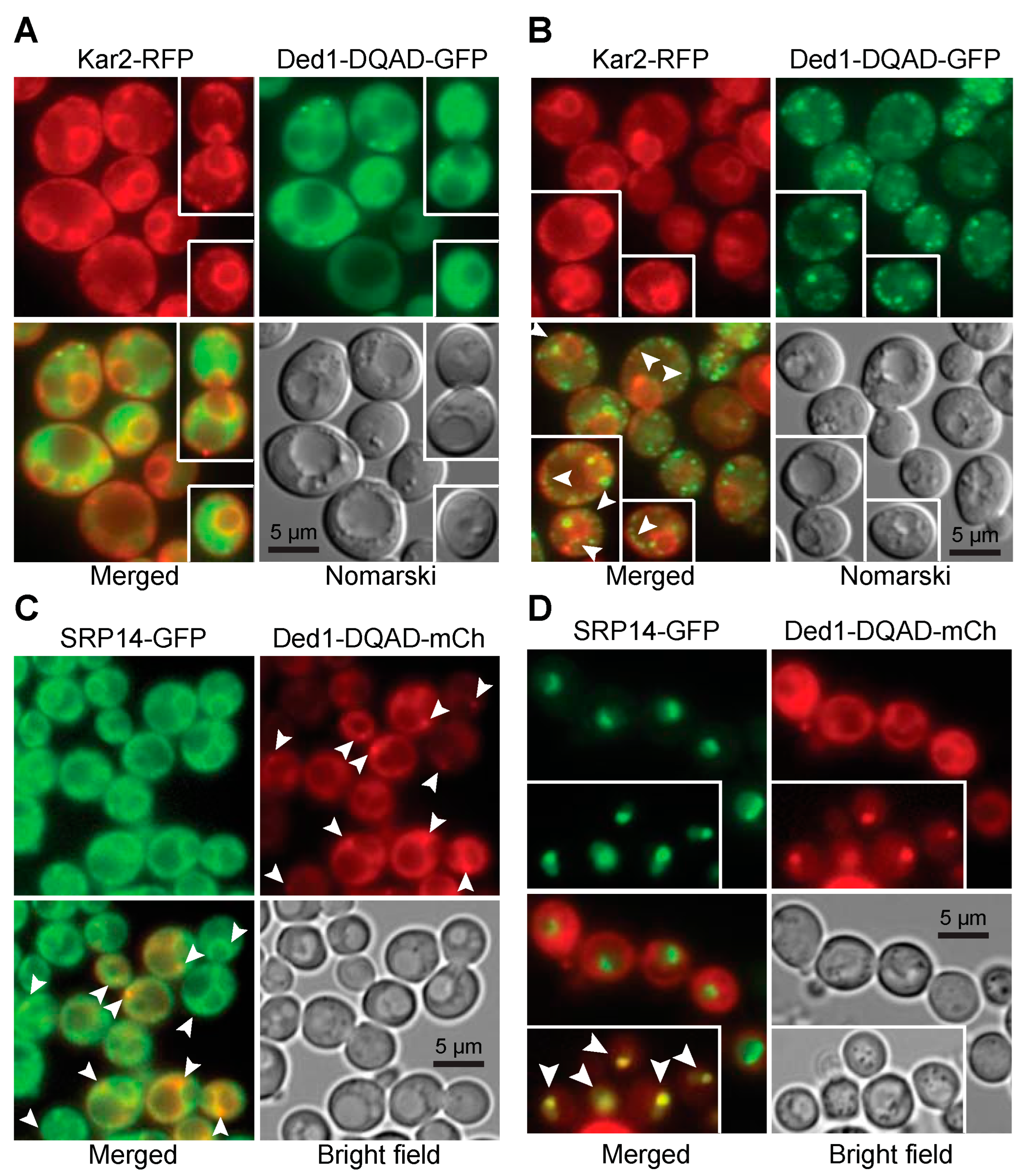
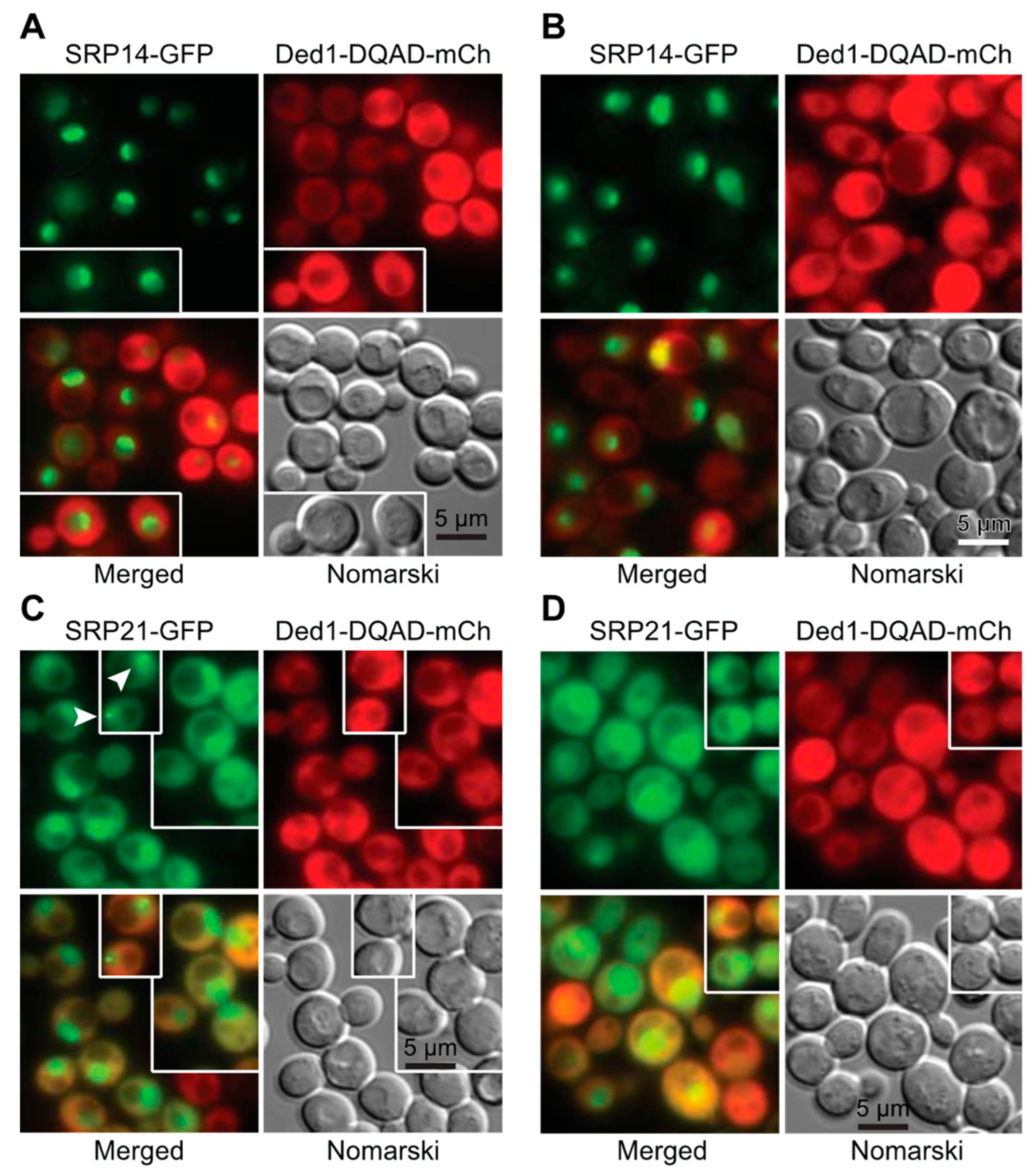
2.3.1. Ded1 Was in Cellular Foci Associated with the Endoplasmic Reticulum
2.3.2. Overexpressed SRP Proteins Accumulated in the Nucleus and Nucleolus
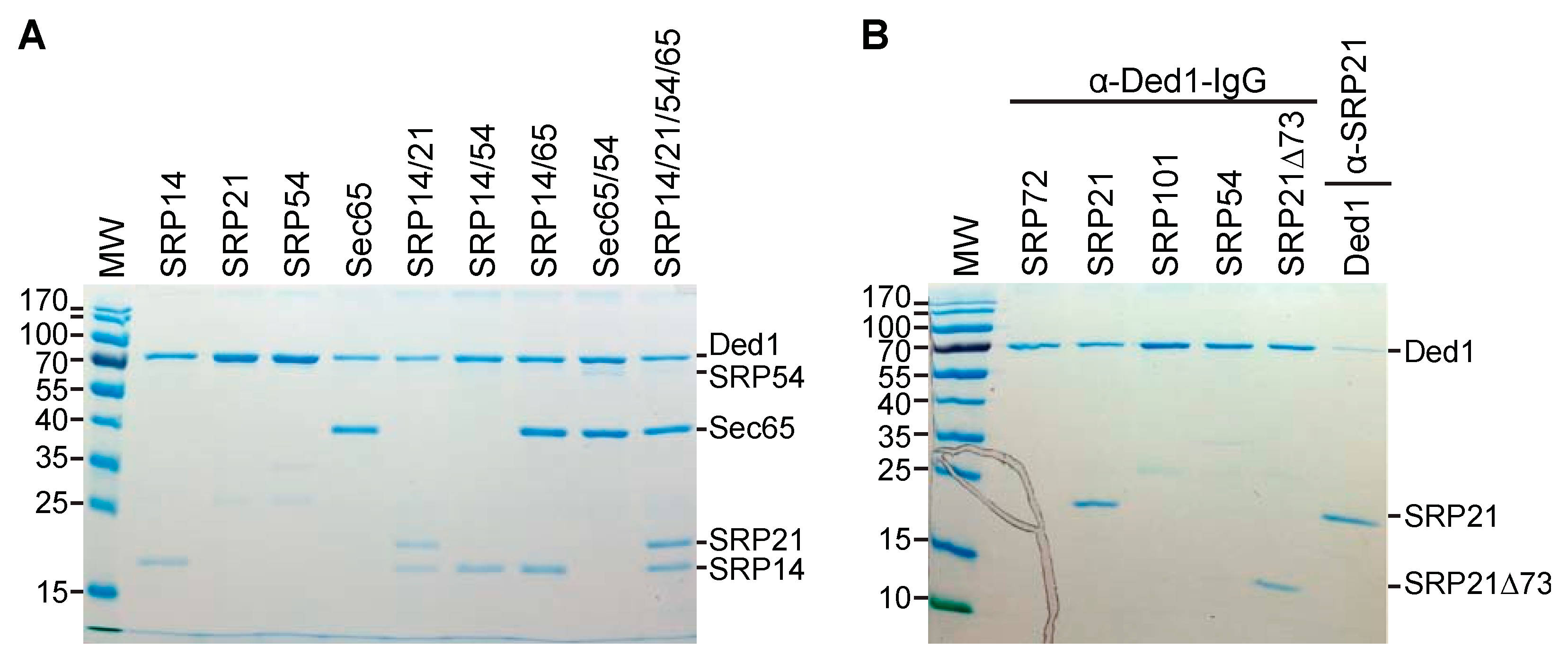
2.4. Ded1 Physically Interacted with SRP Factors
2.5. The Enzymatic Activity of Ded1 Is Affected by the SRP Proteins
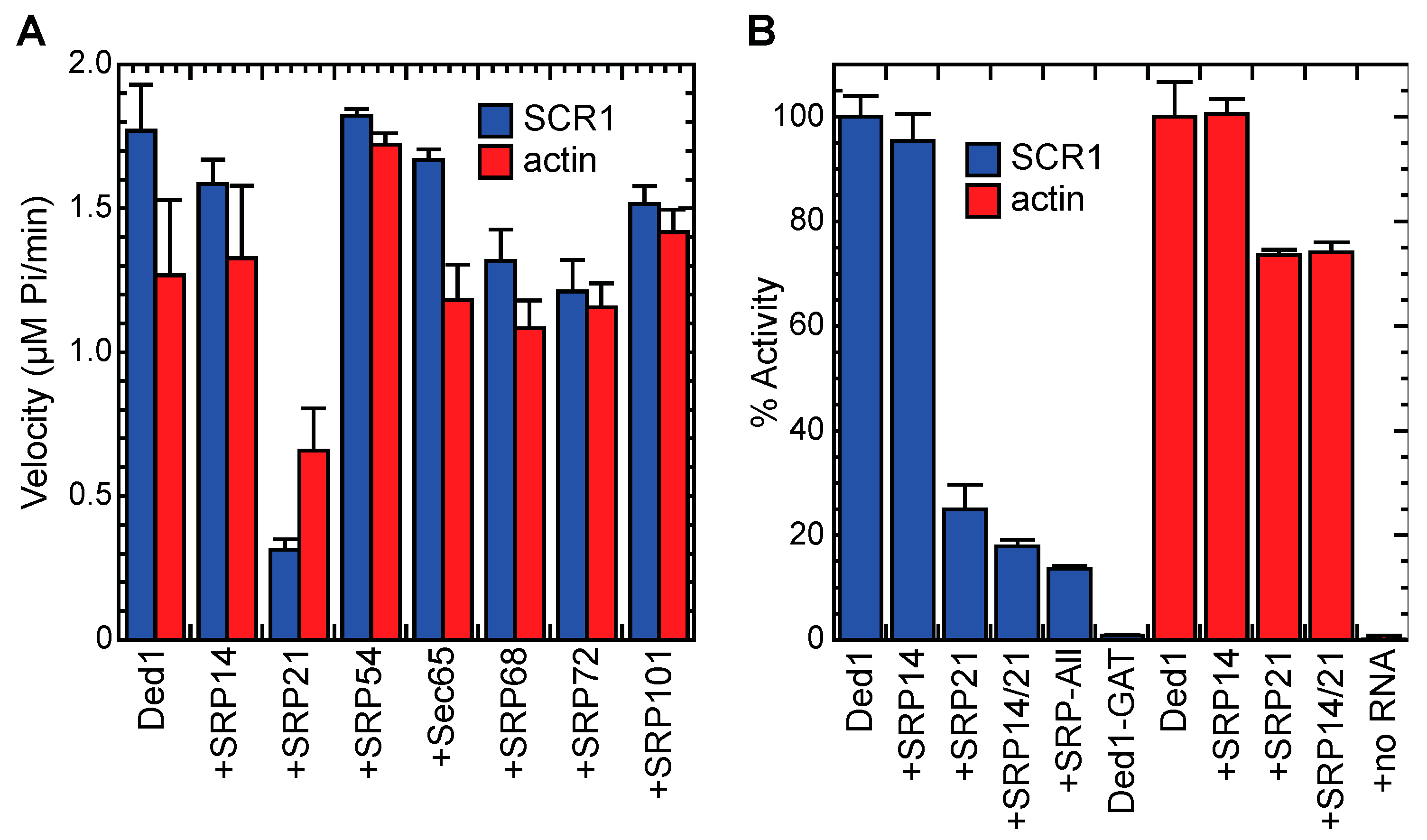
2.5.1. The SRP Proteins Inhibited the ATPase Activity of Ded1
2.5.2. SRP21 Inhibited the SCR1-Dependent ATPase Activity of Ded1
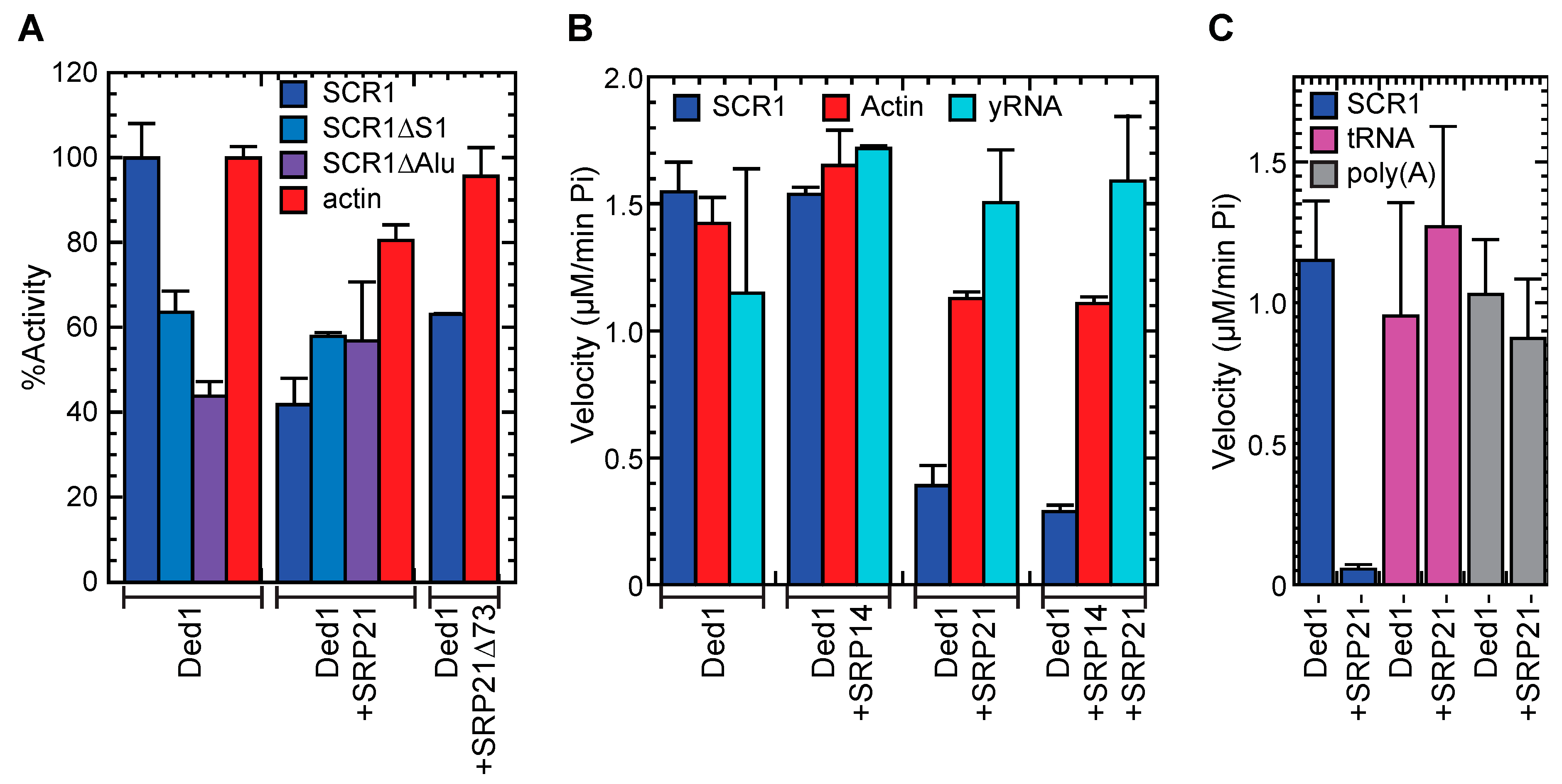
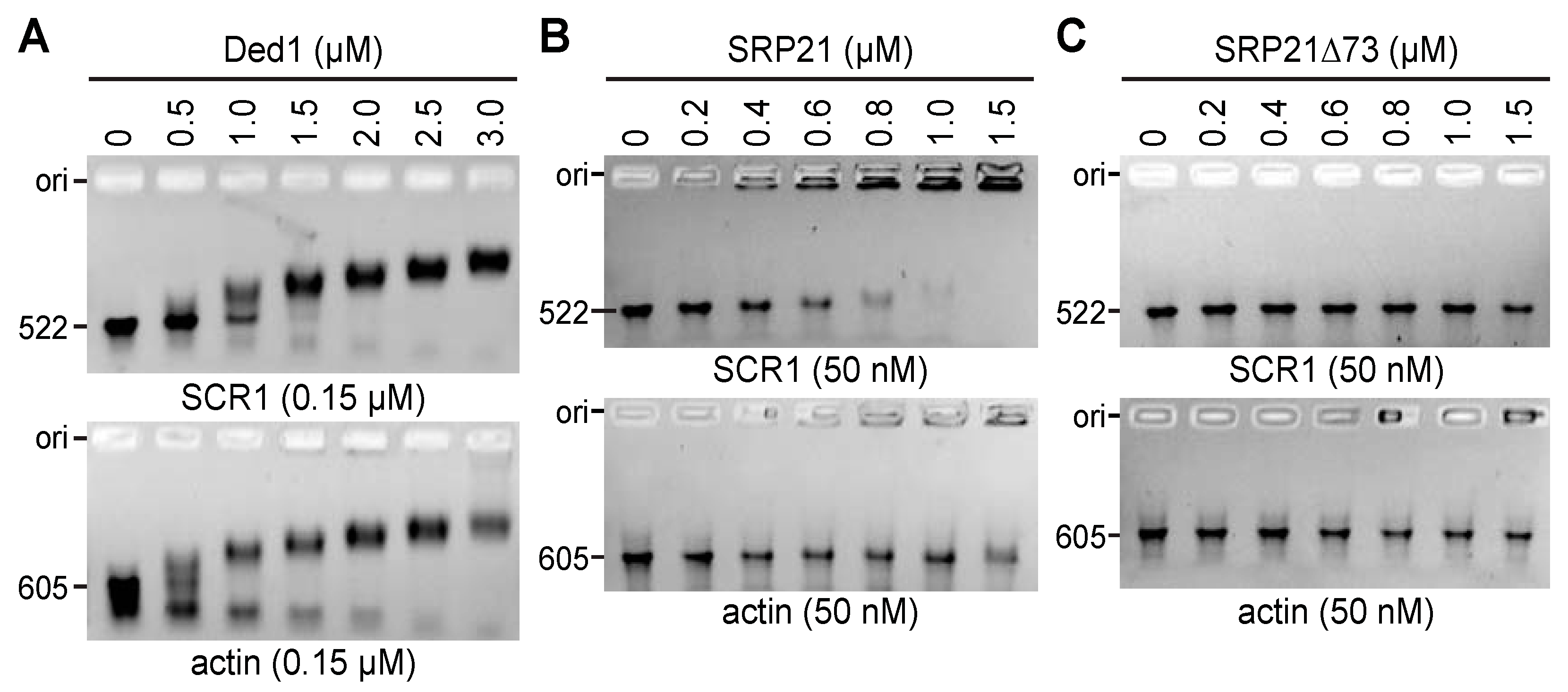
2.6. The RNA Binding Properties of Ded1 and SRP21
2.6.1. Ded1 Bound Actin and SCR1 RNAs with High Affinity, but SRP21 Preferred SCR1
2.6.2. Ded1 and SRP21 Bound SCR1 and Actin RNAs Separately
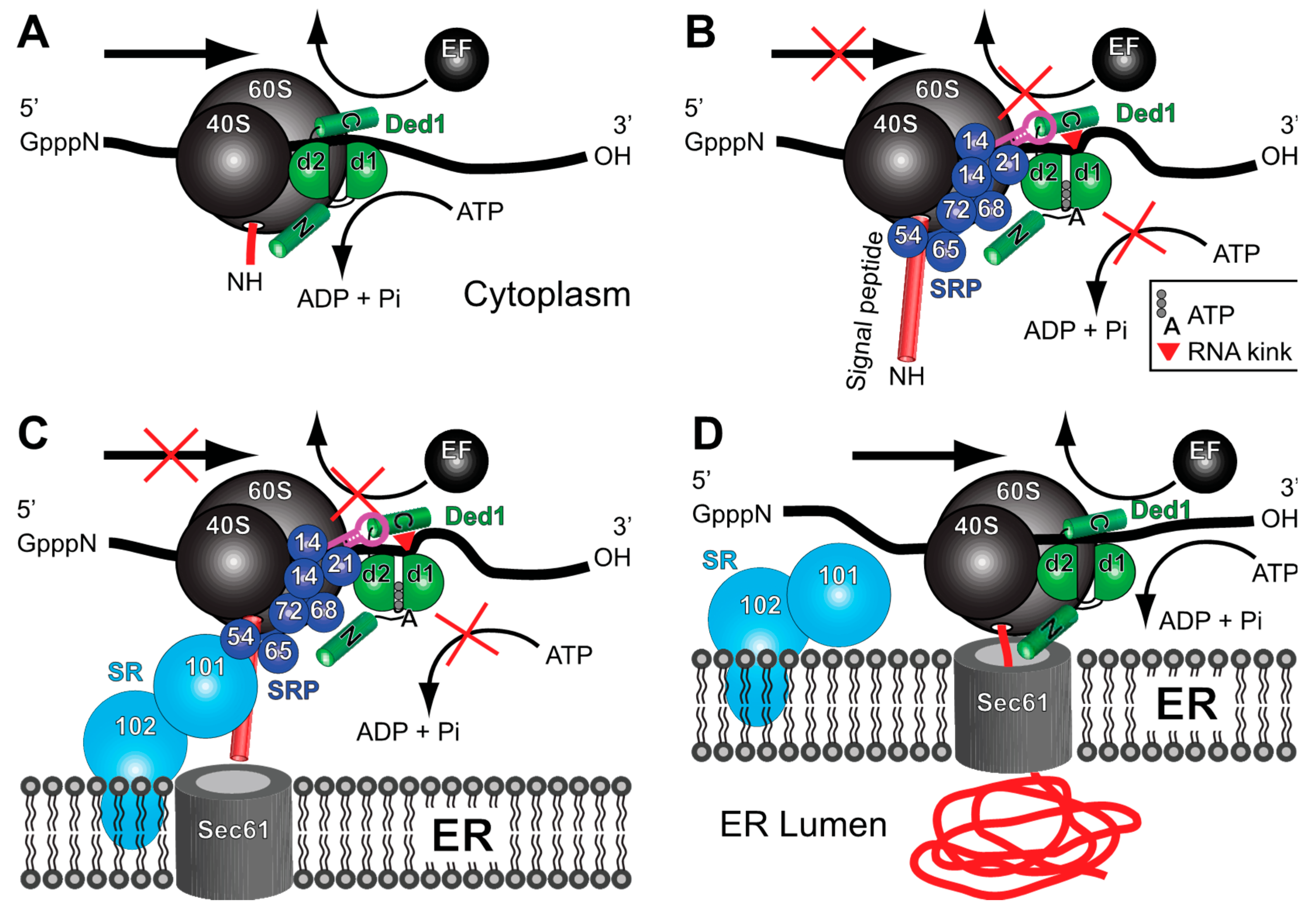
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Constructs
4.1.1. Yeast Protein-Expression Constructs
4.1.2. E. coli Expression and Yeast Fluorescence Protein Constructs
4.1.3. SCR1 and Actin Constructs
4.2. Yeast Strains and Manipulations
4.3. Northern Blot Probes
4.4. In Situ Localization
4.5. RNA Transcripts
4.6. Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
4.7. Immunoglobulin G-Protein A-Sepharose-Bead Pull-Down Experiments
4.8. Other Pull-Down Experiments
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Reverse-Transcriptase PCR
4.11. In Vitro RNA-Dependent ATPase Activities
4.12. Electrophoretic Mobility-Shift Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cordin, O.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K.; Linder, P. The DEAD-box protein family of RNA helicases. Gene 2006, 367, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, P.; Jankowsky, E. From unwinding to clamping—The DEAD box RNA helicase family. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, A.A.; Jankowsky, E. DEAD-box helicases as integrators of RNA, nucleotide and protein binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.K.; Raney, K.D. Superfamily 2 helicases. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2012, 17, 2070–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairman-Williams, M.E.; Guenther, U.P.; Jankowsky, E. SF1 and SF2 helicases: Family matters. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, S.; Bagchi, D.; Orero, J.V.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K.; Croquette, V. Mechanistic characterization of the DEAD-box RNA helicase Ded1 from yeast as revealed by a novel technique using single-molecule magnetic tweezers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3699–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgur, S.; Buchwald, G.; Falk, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Prabu, J.R.; Conti, E. The conformational plasticity of eukaryotic RNA-dependent ATPases. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Putnam, A.A.; Jankowsky, E. DEAD-box helicases form nucleotide-dependent, long-lived complexes with RNA. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Jankowsky, E. The Ded1/DDX3 subfamily of DEAD-box RNA helicases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Liu, W.S. The molecular evolution of PL10 homologs. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, W.Y.; Chang, T.H. The current understanding of Ded1p/DDX3 homologs from yeast to human. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosner, A.; Rinkevich, B. The DDX3 subfamily of the DEAD box helicases: Divergent roles as unveiled by studying different organisms and in vitro assays. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senissar, M.; Le Saux, A.; Belgareh-Touze, N.; Adam, C.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K. The DEAD-box helicase Ded1 from yeast is an mRNP cap-associated protein that shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10005–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Lorsch, J.R.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Yeast Ded1 promotes 48S translation pre-initiation complex assembly in an mRNA-specific and eIF4F-dependent manner. eLife 2018, 7, e38892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dever, T.E.; Kinzy, T.G.; Pavitt, G.D. Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2016, 203, 65–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulay, S.; Gupta, N.; Lorsch, J.R.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Distinct interactions of eIF4A and eIF4E with RNA helicase Ded1 stimulate translation in vivo. eLife 2020, 9, e58243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanpur, P.P.; Regan, C.A.; Collins, J.M.; Mittelmeier, T.M.; Renner, D.M.; Vergara, A.M.; Brown, N.P.; Bolger, T.A. Gle1 Regulates RNA Binding of the DEAD-Box Helicase Ded1 in Its Complex Role in Translation Initiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00139-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, G.; Bowman, G.D. Formation of a Trimeric Xpo1-Ran[GTP]-Ded1 Exportin Complex Modulates ATPase and Helicase Activities of Ded1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, P.; Kedersha, N.; Anderson, P. Stress Granules and Processing Bodies in Translational Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.Y.; Dyakov, B.J.A.; Zhang, J.; Knight, J.D.R.; Vernon, R.M.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; Gingras, A.C. Properties of Stress Granule and P-Body Proteomes. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzikowski, A.R.; Chen, Y.S.; Zid, B.M. Stress-induced mRNP granules: Form and function of processing bodies and stress granules. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2019, 10, e1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondele, M.; Sachdev, R.; Heinrich, S.; Wang, J.; Vallotton, P.; Fontoura, B.M.A.; Weis, K. DEAD-box ATPases are global regulators of phase-separated organelles. Nature 2019, 573, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rifo, R.; Ohlmann, T. The role of the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX3 in mRNA metabolism. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2013, 4, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeter-Alat, H.; Belgareh-Touzé, N.; Huvelle, E.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K. The DEAD-Box RNA Helicase Ded1 Is Associated with Translating Ribosomes. Genes 2023, 14, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, T.A.; Li, L.; Park, E. Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Protein Translocation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 33, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, K.; Becker, M.M.M.; Kempf, G.; Sinning, I. Structure, dynamics and interactions of large SRP variants. Biol. Chem. 2019, 401, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.A.; Palazzo, A.F. Localization of mRNAs to the endoplasmic reticulum. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopian, D.; Shen, K.; Zhang, X.; Shan, S.O. Signal recognition particle: An essential protein-targeting machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 693–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, M.R. Signal recognition particles in chloroplasts, bacteria, yeast and mammals (review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2005, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblad, M.A.; Larsen, N.; Samuelsson, T.; Zwieb, C. Kinship in the SRP RNA family. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massenet, S. In vivo assembly of eukaryotic signal recognition particle: A still enigmatic process involving the SMN complex. Biochimie 2019, 164, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
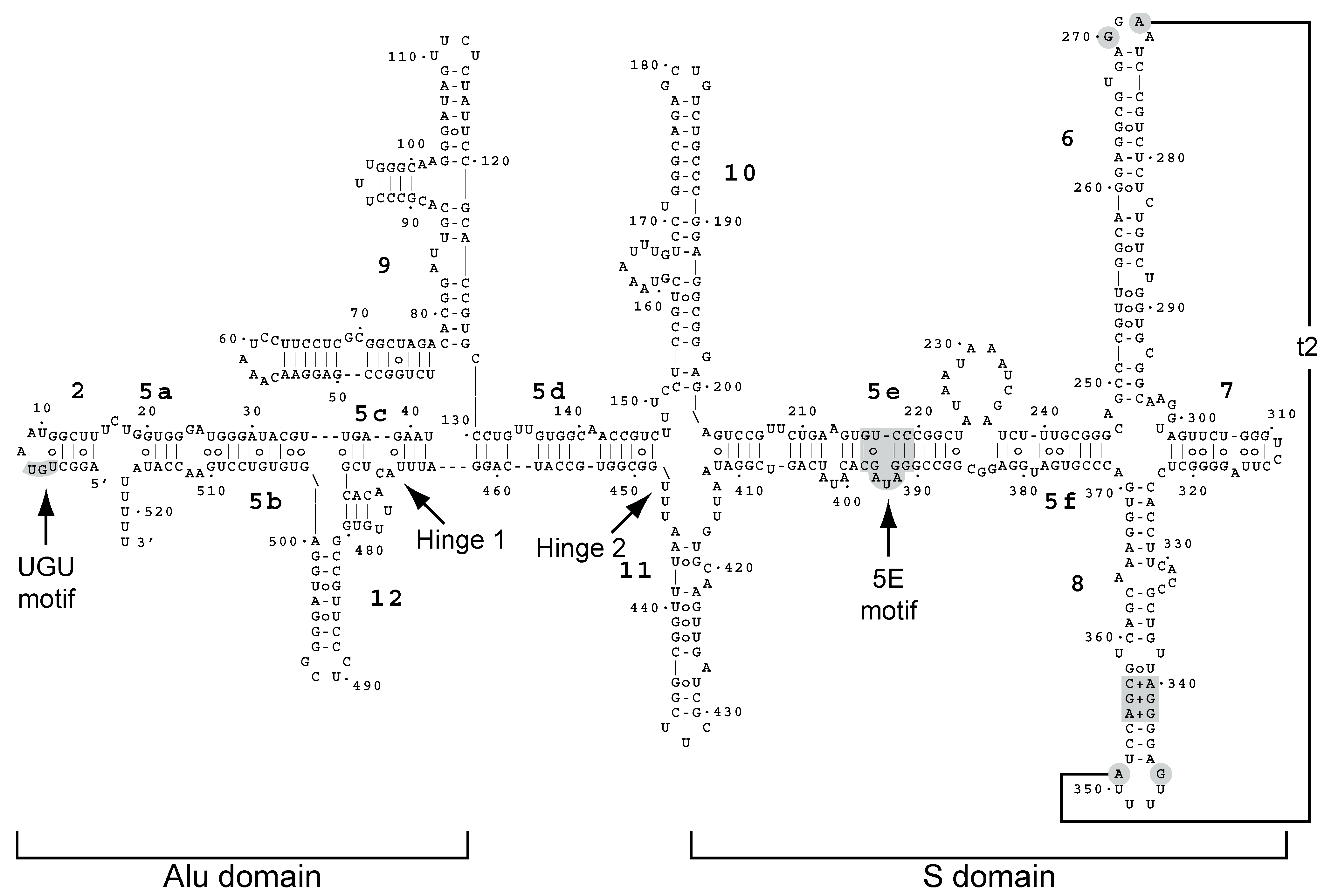
- Zwieb, C.; van Nues, R.W.; Rosenblad, M.A.; Brown, J.D.; Samuelsson, T. A nomenclature for all signal recognition particle RNAs. RNA 2005, 11, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nues, R.W.; Brown, J.D. Saccharomyces SRP RNA secondary structures: A conserved S-domain and extended Alu-domain. RNA 2004, 10, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyathi, Y.; Wilkinson, B.M.; Pool, M.R. Co-translational targeting and translocation of proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strub, K.; Fornallaz, M.; Bui, N. The Alu domain homolog of the yeast signal recognition particle consists of an Srp14p homodimer and a yeast-specific RNA structure. RNA 1999, 5, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, N.; Ciufo, L.F.; Brown, J.D. Elongation arrest is a physiologically important function of signal recognition particle. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4164–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblad, M.A.; Zwieb, C.; Samuelsson, T. Identification and comparative analysis of components from the signal recognition particle in protozoa and fungi. BMC Genom. 2004, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halic, M.; Becker, T.; Pool, M.R.; Spahn, C.M.; Grassucci, R.A.; Frank, J.; Beckmann, R. Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome. Nature 2004, 427, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousset, L.; Mary, C.; Brooks, M.A.; Scherrer, A.; Strub, K.; Cusack, S. Crystal structure of a signal recognition particle Alu domain in the elongation arrest conformation. RNA 2014, 20, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, K.; Juaire, K.D.; Soni, K.; Shanmuganathan, V.; Hendricks, A.; Segnitz, B.; Beckmann, R.; Sinning, I. Reconstitution of the human SRP system and quantitative and systematic analysis of its ribosome interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashe, M.P.; De Long, S.K.; Sachs, A.B. Glucose depletion rapidly inhibits translation initiation in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, J.; Campbell, S.G.; Ashe, M.P. Inhibition of translation initiation following glucose depletion in yeast facilitates a rationalization of mRNA content. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janapala, Y.; Preiss, T.; Shirokikh, N.E. Control of Translation at the Initiation Phase During Glucose Starvation in Yeast. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuman, S. Transcriptional interference at tandem lncRNA and protein-coding genes: An emerging theme in regulation of cellular nutrient homeostasis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8243–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.; Baryshnikova, A.; Brown, G.W. Unification of Protein Abundance Datasets Yields a Quantitative Saccharomyces cerevisiae Proteome. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 192–205.e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, U.P.; Weinberg, D.E.; Zubradt, M.M.; Tedeschi, F.A.; Stawicki, B.N.; Zagore, L.L.; Brar, G.A.; Licatalosi, D.D.; Bartel, D.P.; Weissman, J.S.; et al. The helicase Ded1p controls use of near-cognate translation initiation codons in 5’ UTRs. Nature 2018, 559, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willer, M.; Jermy, A.J.; Steel, G.J.; Garside, H.J.; Carter, S.; Stirling, C.J. An in vitro assay using overexpressed yeast SRP demonstrates that cotranslational translocation is dependent upon the J-domain of Sec63p. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 7171–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordin, O.; Tanner, N.K.; Doere, M.; Linder, P.; Banroques, J. The newly discovered Q motif of DEAD-box RNA helicases regulates RNA-binding and helicase activity. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Hann, B.C.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Niwa, M.; Burlingame, A.L.; Walter, P. Subunits of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae signal recognition particle required for its functional expression. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4390–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, B.C.; Walter, P. The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell 1991, 67, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirling, C.J.; Hewitt, E.W. The S. cerevisiae SEC65 gene encodes a component of yeast signal recognition particle with homology to human SRP19. Nature 1992, 356, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogg, S.C.; Poritz, M.A.; Walter, P. Signal recognition particle receptor is important for cell growth and protein secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 1992, 3, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutka, S.C.; Walter, P. Multifaceted physiological response allows yeast to adapt to the loss of the signal recognition particle-dependent protein-targeting pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.R.; Marton, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; Roberts, C.J.; Stoughton, R.; Armour, C.D.; Bennett, H.A.; Coffey, E.; Dai, H.; He, Y.D.; et al. Functional discovery via a compendium of expression profiles. Cell 2000, 102, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckham, C.; Hilliker, A.; Cziko, A.M.; Noueiry, A.; Ramaswami, M.; Parker, R. The DEAD-box RNA helicase Ded1p affects and accumulates in Saccharomyces cerevisiae P-bodies. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 984–993, Erratum in Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banroques, J.; Cordin, O.; Doère, M.; Linder, P.; Tanner, N.K. Analyses of the functional regions of DEAD-box RNA "helicases" with deletion and chimera constructs tested in vivo and in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 413, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumberg, D.; Muller, R.; Funk, M. Yeast vectors for the controlled expression of heterologous proteins in different genetic backgrounds. Gene 1995, 156, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, R.Y.; Weaver, P.L.; Liu, Z.; Chang, T.H. Requirement of the DEAD-Box protein Ded1p for messenger RNA translation. Science 1997, 275, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserman, C.; Desroches Altamirano, C.; Jegers, C.; Friedrich, U.; Zarin, T.; Fritsch, A.W.; Mittasch, M.; Domingues, A.; Hersemann, L.; Jahnel, M.; et al. Condensation of Ded1p Promotes a Translational Switch from Housekeeping to Stress Protein Production. Cell 2020, 181, 818–831.e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Schekman, R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Schekman, R. SEC62 encodes a putative membrane protein required for protein translocation into the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, S.I.; Fewell, S.W.; Kato, Y.; Brodsky, J.L.; Endo, T. Molecular chaperones in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum maintain the solubility of proteins for retrotranslocation and degradation. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M.; Zurek, N.; Hoenger, A.; Voeltz, G.K. A 3D analysis of yeast ER structure reveals how ER domains are organized by membrane curvature. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.; Vlasblom, J.; Pu, S.; Guo, X.; Graham, C.; Bean, B.D.; Burston, H.E.; Vizeacoumar, F.J.; Snider, J.; Phanse, S.; et al. Interaction landscape of membrane-protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 2012, 489, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, K.; Sinning, I. RNA gymnastics in mammalian signal recognition particle assembly. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.; Brown, J.D. Biogenesis of the signal recognition particle. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciufo, L.F.; Brown, J.D. Nuclear export of yeast signal recognition particle lacking Srp54p by the Xpo1p/Crm1p NES-dependent pathway. Curr. Biol. CB 2000, 10, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, H.; Deinert, K.; Hurt, E.; Simos, G. Biogenesis of the signal recognition particle (SRP) involves import of SRP proteins into the nucleolus, assembly with the SRP-RNA, and Xpo1p-mediated export. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baßler, J.; Hurt, E. Eukaryotic Ribosome Assembly. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedavalli, V.S.; Neuveut, C.; Chi, Y.H.; Kleiman, L.; Jeang, K.T. Requirement of DDX3 DEAD box RNA helicase for HIV-1 Rev-RRE export function. Cell 2004, 119, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Fujiwara, D.; Nishikawa, M.; Horinouchi, S.; Beppu, T. Leptomycin B targets a regulatory cascade of crm1, a fission yeast nuclear protein, involved in control of higher order chromosome structure and gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 6320–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.; Rosbash, M. The NES-Crm1p export pathway is not a major mRNA export route in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3746–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hann, B.C.; Stirling, C.J.; Walter, P. SEC65 gene product is a subunit of the yeast signal recognition particle required for its integrity. Nature 1992, 356, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iost, I.; Dreyfus, M.; Linder, P. Ded1p, a DEAD-box protein required for translation initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is an RNA helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17677–17683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banroques, J.; Cordin, O.; Doère, M.; Linder, P.; Tanner, N.K. A conserved phenylalanine of motif IV in superfamily 2 helicases is required for cooperative, ATP-dependent binding of RNA substrates in DEAD-box proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3359–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin-Vega, Y.A.; Wang, Y.D.; Parker, M.; Patmore, D.M.; Kanagaraj, A.; Moore, J.; Rusch, M.; Finkelstein, D.; Ellison, D.W.; Gilbertson, R.J.; et al. Cancer-associated DDX3X mutations drive stress granule assembly and impair global translation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, T.; Strauss, D.; Petfalski, E.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E. The path from nucleolar 90S to cytoplasmic 40S pre-ribosomes. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C. What Are 3’ UTRs Doing? Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a034728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartron, J.W.; Hunt, K.C.; Frydman, J. Cotranslational signal-independent SRP preloading during membrane targeting. Nature 2016, 536, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, R.M.; Hegde, R.S. Toward a structural understanding of co-translational protein translocation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 41, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, S.L.; Walter, P. Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 2617–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, J.K.; Ataide, S.F. Structural Changes of RNA in Complex with Proteins in the SRP. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorhees, R.M.; Hegde, R.S. Structures of the scanning and engaged states of the mammalian SRP-ribosome complex. eLife 2015, 4, e07975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collart, M.A.; Weiss, B. Ribosome pausing, a dangerous necessity for co-translational events. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dever, T.E.; Dinman, J.D.; Green, R. Translation Elongation and Recoding in Eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a032649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, I., Jr.; Kim, H.K.; Yan, S. Frameshifting dynamics. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.L.; Chuang, R.Y.; Tung, L.; Chang, T.H. Ded1p, a conserved DExD/H-box translation factor, can promote yeast L-A virus negative-strand RNA synthesis in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickner, R.B. Double-stranded RNA viruses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabaugh, P.J. Programmed translational frameshifting. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1996, 30, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itano, M.S.; Arnion, H.; Wolin, S.L.; Simon, S.M. Recruitment of 7SL RNA to assembling HIV-1 virus-like particles. Traffic 2018, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.O.; Brosh, R.M., Jr.; Oliver, D.B. Escherichia coli SecA helicase activity is not required in vivo for efficient protein translocation or autogenous regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37076–37085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Jomaa, A.; Jaskolowski, M.; Yang, C.I.; Ban, N.; Shan, S.O. The molecular mechanism of cotranslational membrane protein recognition and targeting by SecA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knüpffer, L.; Fehrenbach, C.; Denks, K.; Erichsen, V.; Petriman, N.A.; Koch, H.G. Molecular Mimicry of SecA and Signal Recognition Particle Binding to the Bacterial Ribosome. mBio 2019, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, N.K.; Cordin, O.; Banroques, J.; Doere, M.; Linder, P. The Q motif: A newly identified motif in DEAD box helicases may regulate ATP binding and hydrolysis. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Cruz, J.; Iost, I.; Kressler, D.; Linder, P. The p20 and Ded1 proteins have antagonistic roles in eIF4E-dependent translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5201–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janke, C.; Magiera, M.M.; Rathfelder, N.; Taxis, C.; Reber, S.; Maekawa, H.; Moreno-Borchart, A.; Doenges, G.; Schwob, E.; Schiebel, E.; et al. A versatile toolbox for PCR-based tagging of yeast genes: New fluorescent proteins, more markers and promoter substitution cassettes. Yeast 2004, 21, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcova, I.; Farkasovsky, M.; Senohrabkova, L.; Vasicova, P.; Hasek, J. New integrative modules for multicolor-protein labeling and live-cell imaging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res. 2016, 16, fow027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Newman, A.J.; Cheng, S.C.; Abelson, J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 14780–14792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, C.; Fink, G.R. (Eds.) Guide to Yeast Genetics and Molecular Biology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991; Volume 194. [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis, A.J.; Khemici, V.; Aït-Bara, S.; Poljak, L. Co-immunopurification of multiprotein complexes containing RNA-degrading enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 447, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ream, J.A.; Lewis, L.K.; Lewis, K.A. Rapid agarose gel electrophoretic mobility shift assay for quantitating protein: RNA interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 511, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiano, R.; Nagaraj, N.; Frohlich, F.; Walther, T.C. Global proteome turnover analyses of the Yeasts S. cerevisiae and S. pombe. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1959–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeter-Alat, H.; Belgareh-Touzé, N.; Le Saux, A.; Huvelle, E.; Mokdadi, M.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K. The RNA Helicase Ded1 from Yeast Is Associated with the Signal Recognition Particle and Is Regulated by SRP21. Molecules 2024, 29, 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122944
Yeter-Alat H, Belgareh-Touzé N, Le Saux A, Huvelle E, Mokdadi M, Banroques J, Tanner NK. The RNA Helicase Ded1 from Yeast Is Associated with the Signal Recognition Particle and Is Regulated by SRP21. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122944
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeter-Alat, Hilal, Naïma Belgareh-Touzé, Agnès Le Saux, Emmeline Huvelle, Molka Mokdadi, Josette Banroques, and N. Kyle Tanner. 2024. "The RNA Helicase Ded1 from Yeast Is Associated with the Signal Recognition Particle and Is Regulated by SRP21" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122944
APA StyleYeter-Alat, H., Belgareh-Touzé, N., Le Saux, A., Huvelle, E., Mokdadi, M., Banroques, J., & Tanner, N. K. (2024). The RNA Helicase Ded1 from Yeast Is Associated with the Signal Recognition Particle and Is Regulated by SRP21. Molecules, 29(12), 2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122944





