Sensitive Detection of Genotoxic Substances in Complex Food Matrices by Multiparametric High-Content Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
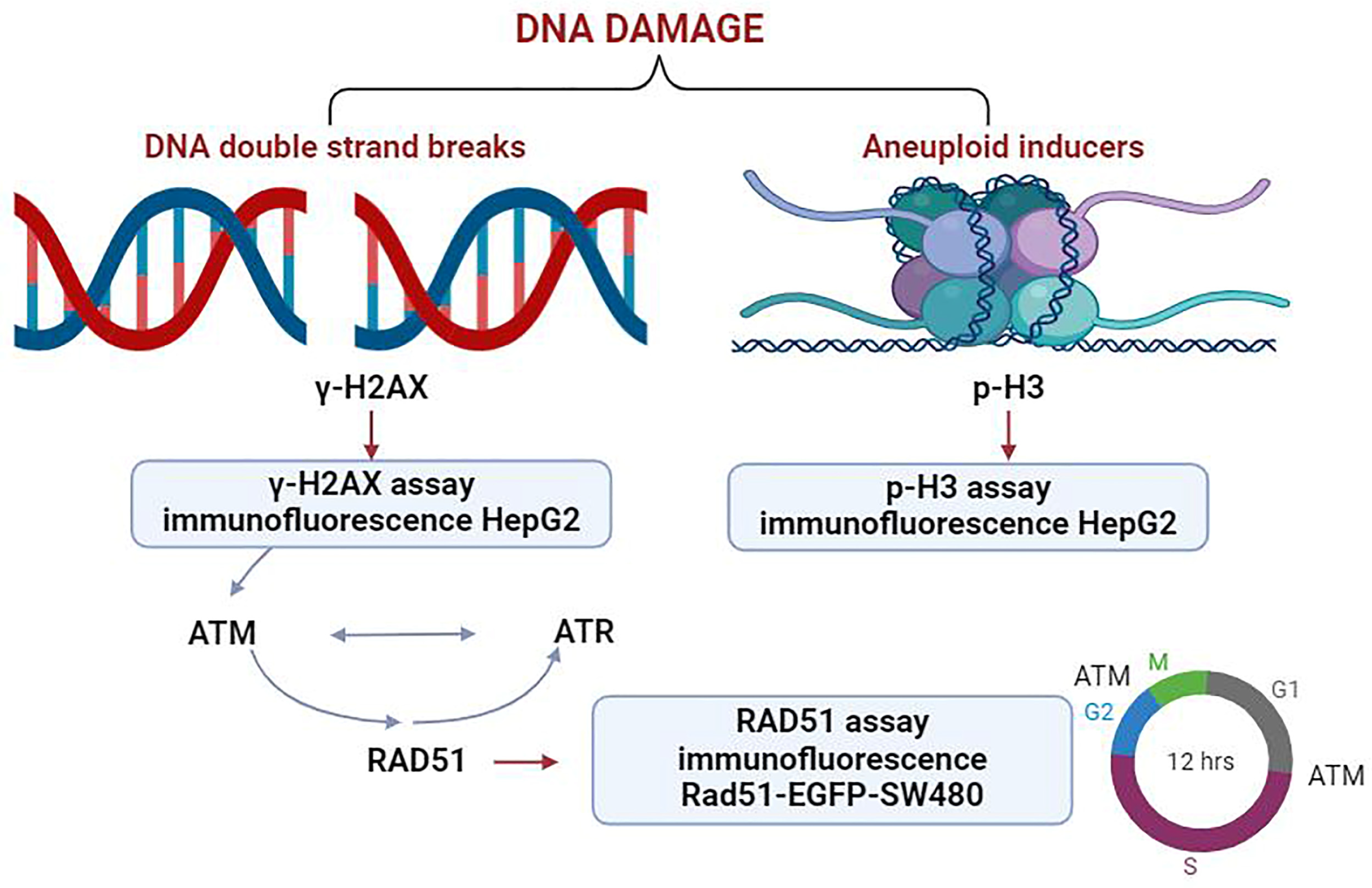
2.1. Establishment of a Multiparametric High-Content Analysis for Genotoxic Substances Detection
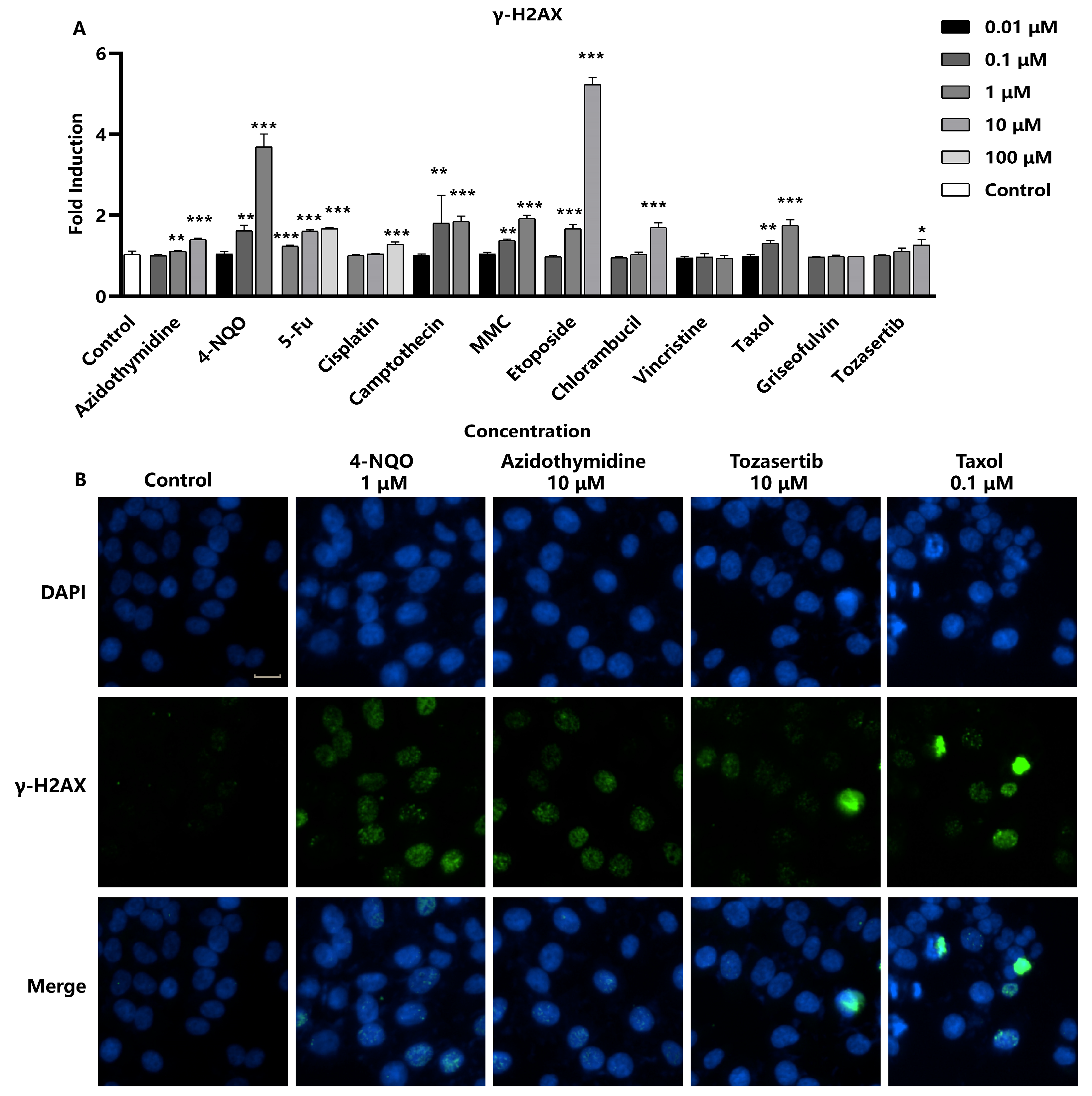
2.2. In Vitro Assessment of γ-H2AX as a DNA Damage Marker
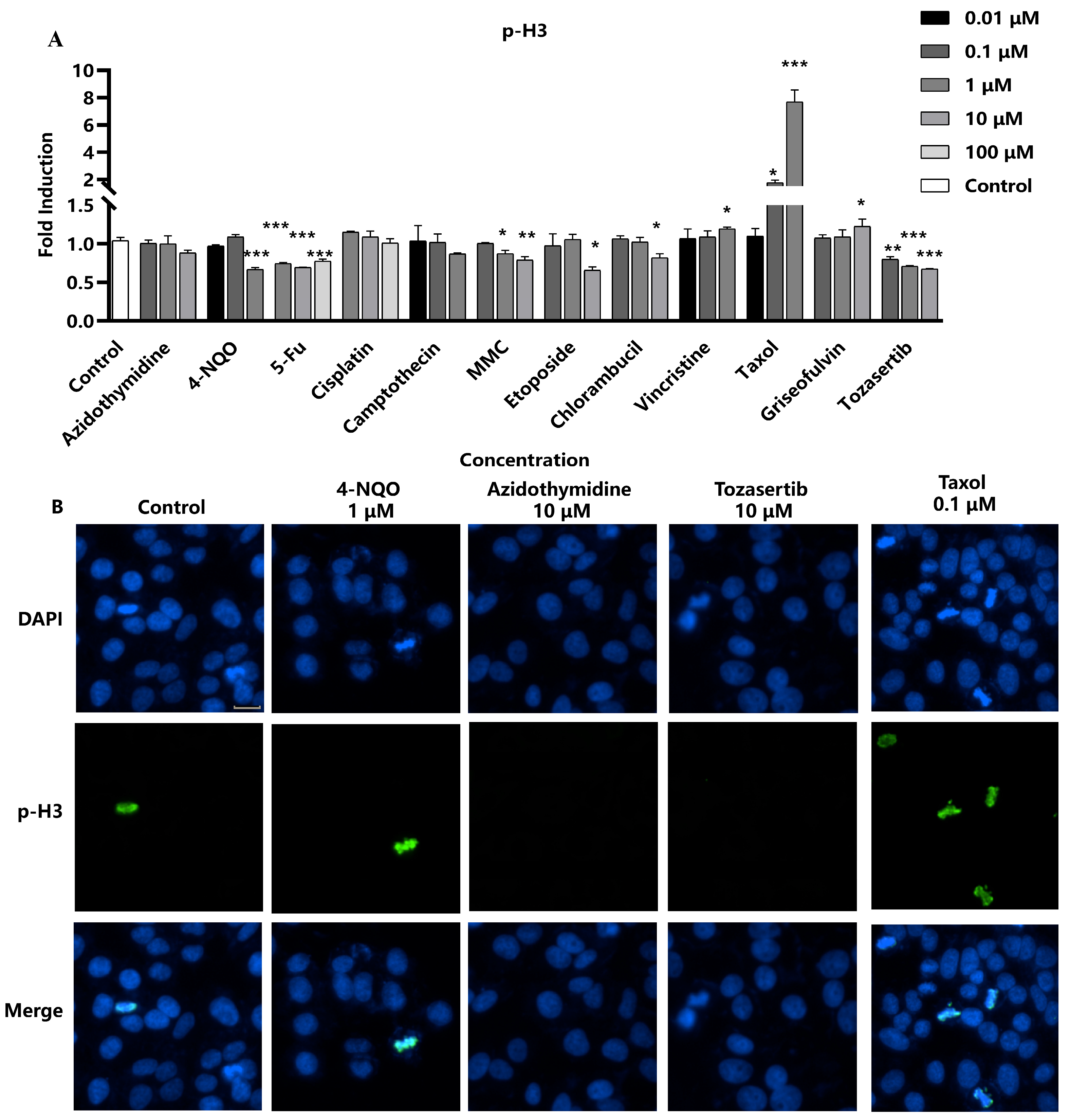
2.3. Assessment of p-H3 as a Marker for DNA Damage Induced by Aneuploid Genotoxic Compounds
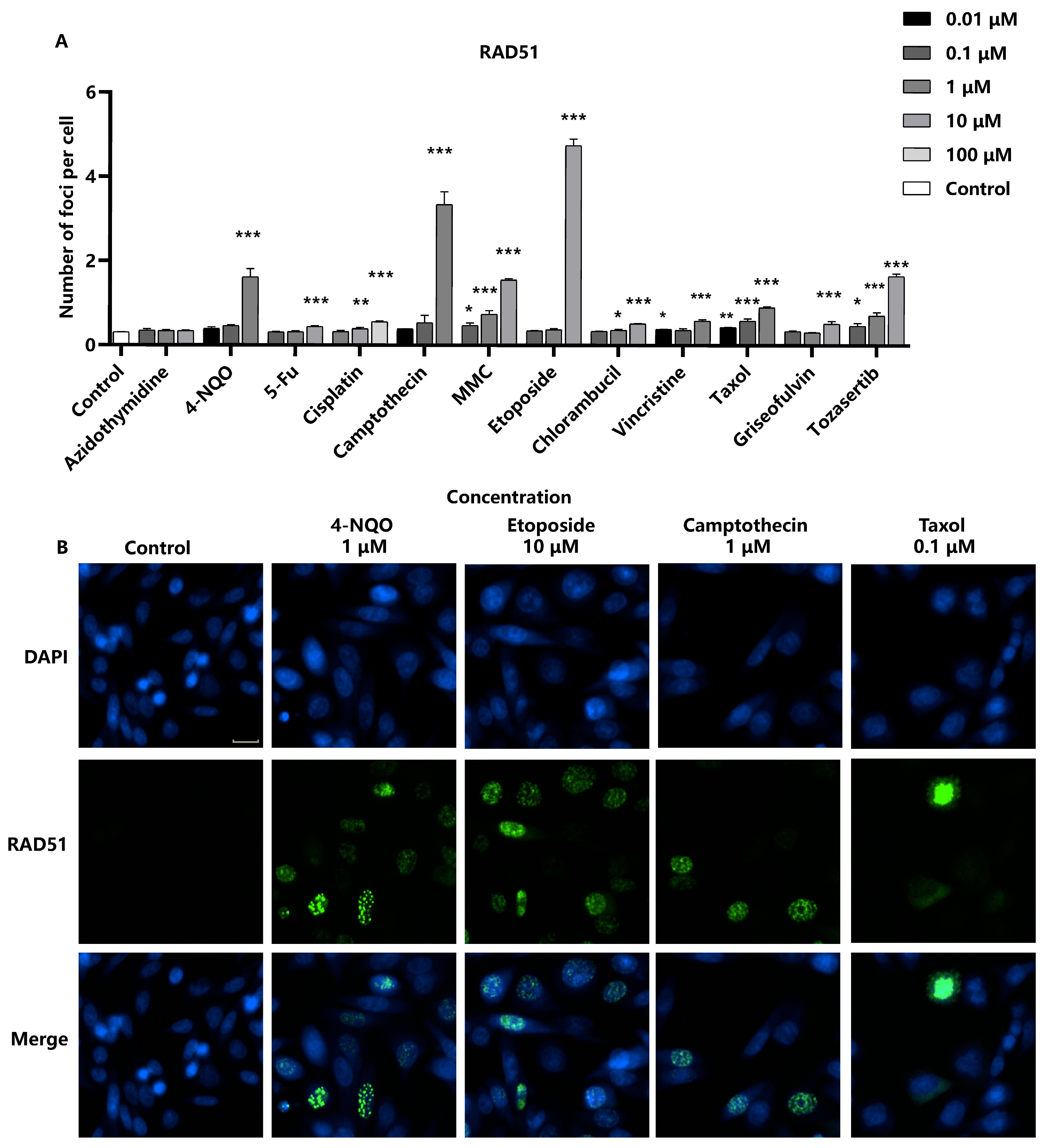
2.4. Detection of RAD51 as a Marker for DNA Repair in Response to Genotoxic Stress
2.5. Distinguishing Genotoxic Compounds with Different Modes of Action through Multiple Biomarkers
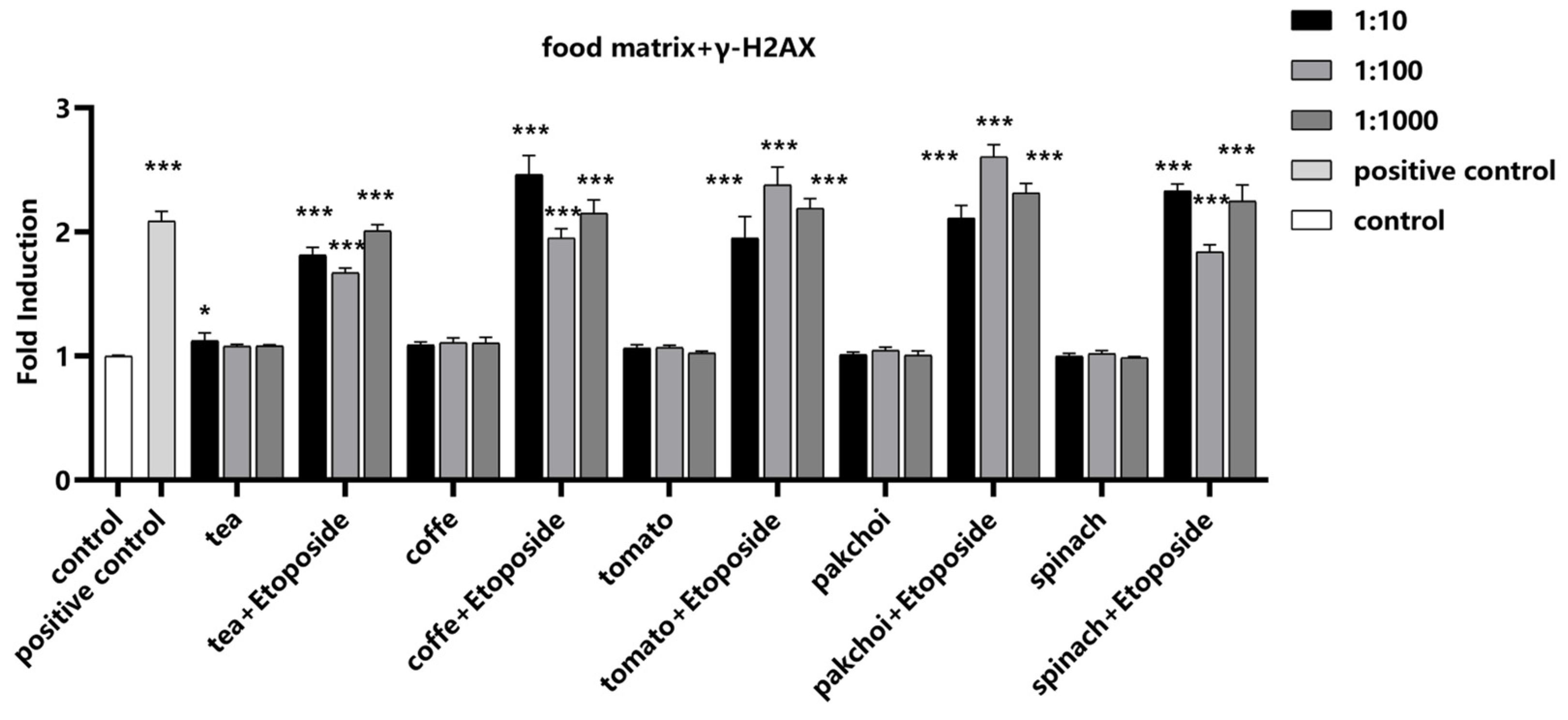
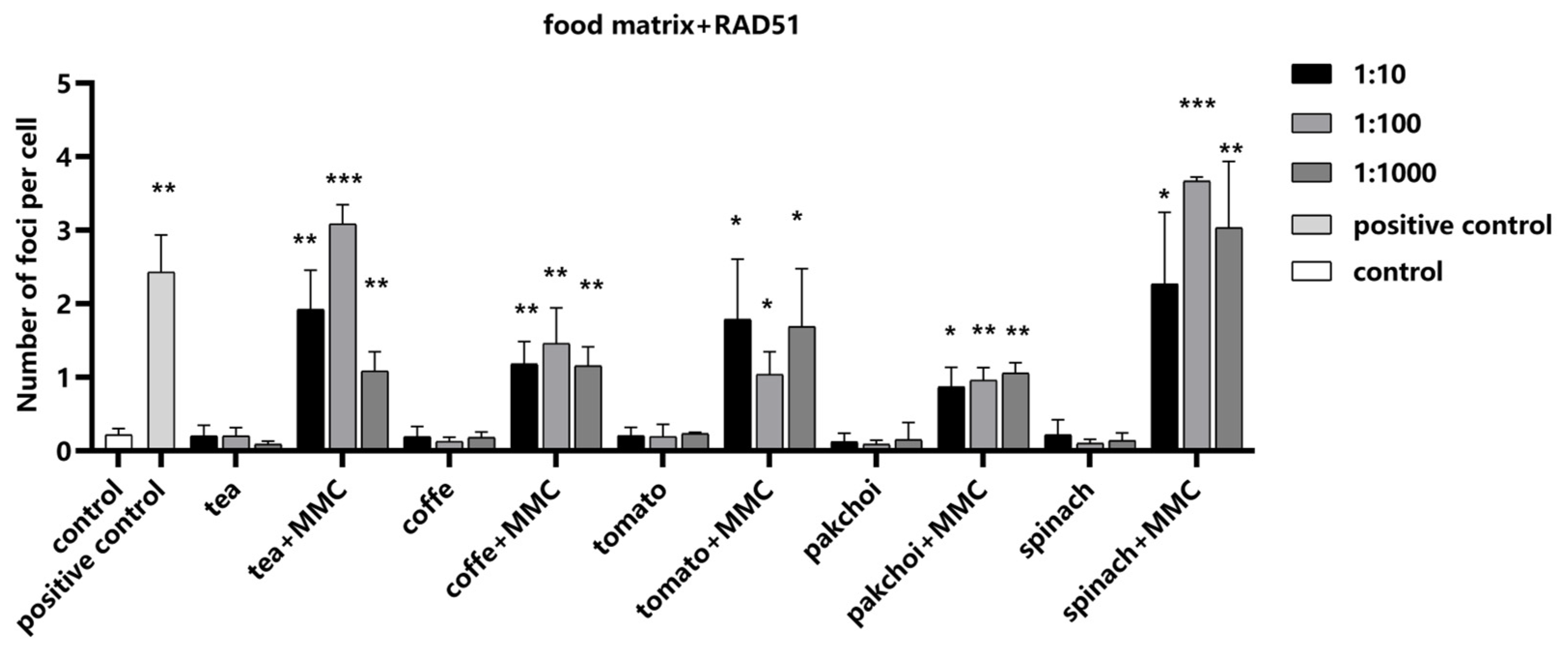
2.6. Impact of Food Matrices on the Detection System
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Treatment with Genotoxic Substances
3.4. Treatment of the Food Matrices
3.5. Immunofluorescence Assay
3.6. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopp, B.; Dario, M.; Zalko, D.; Audebert, M. Assessment of a panel of cellular biomarkers and the kinetics of their induction in comparing genotoxic modes of action in HepG2 cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2018, 59, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, L.; Zalko, D.; Audebert, M. Complementarity of phosphorylated histones H2AX and H3 quantification in different cell lines for genotoxicity screening. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, L.; Zalko, D.; Audebert, M. Validation of high-throughput genotoxicity assay screening using γH2AX in-cell western assay on HepG2 cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2013, 54, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, L.; Zalko, D.; Audebert, M. Evaluation of four human cell lines with distinct biotransformation properties for genotoxic screening. Mutagenesis 2016, 31, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmanian, N.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Eskandani, M. Recent advances in γH2AX biomarker-based genotoxicity assays, A marker of DNA damage and repair. DNA Repair 2021, 108, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plappert-Helbig, U.; Libertini, S.; Frieauff, W. Gamma-H2AX immunofluorescence for the detection of tissue-specific genotoxicity in vivo. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2019, 60, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.F.; Dawood, M.; Mahmoud, N.; Elbadawi, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Klauck, S.M.; Mohamed, N.; Efferth, T. 2α-Hydroxyalantolactone from Pulicaria undulata, activity against multidrug-resistant tumor cells and modes of action. Phytomedicine 2021, 81, 153409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, R.; Wang, L. The Emerging Roles of Rad51 in Cancer and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 935593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.J.; Yang, L.X. Gamma-H2AX—A novel biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks. In Vivo 2008, 22, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, D.; Ahmedi, K.; Harvey, J.; Lynch, A. Genotoxicity screening via the γH2AX by flow assay. Mutat. Res. 2011, 715, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Harada, A.; Takeiti, A.; Tanaka, K.; Mishima, M. Whole cellELISA to measure the γH2AX response of six aneu-gens and eight DNA-damaging chemicals. Mutat. Res. 2010, 700, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H. DNA doublestranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, B.; Khoury, L.; Audebert, M. Validation of the γH2AX biomarker for genotoxicity assessment, a review. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, L.; Xie, J. Distinct Orchestration and Dynamic Processes on γ-H2AX and p-H3 for Two Major Types of Genotoxic Chemicals Revealed by Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Pathways and assays for DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, B.; Hengel, S.R.; Grundy, M.K.; Bernstein, K.A. RAD51 Gene Family Structure and Function. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xia, M. Review of high-content screening applications in toxicology. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Canton, C.; Anadon, A. Assessment of the in vitro γH2AX assay by High Content Screening as a novel genotoxicity test. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2013, 757, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamou, M.; Jennen, D.G.; Claessen, S.M.; Yano, M.; Harada, A.; Katoh, C.; Tanaka, K.; Mishima, M. Performance of in vitro γH2AX assay in HepG2 cells to predict in vivo genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeiri, A.; Matsuzaki, K.; Motoyama, S. High-content imaging analyses of γH2AX-foci and micronuclei in TK6 cells elucidated genotoxicity of chemicals and their clastogenic/aneugenic mode of action. Genes. Environ. 2019, 41, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.M. Compound Genotoxicity and Its Mechanism of Action Revealed by Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Histone Phosphorylation Modification. Ph.D. Thesis, Academy of Military Science, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Iwase, Y.; Ishiura, S. Usefulness of monitoring γ-H2AX and cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells for estimating genotoxicity using a high-content analysis system. J. Biomol. Screen. 2014, 19, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothkamm, K.; Barnard, S.; Moquet, J.; Ellender, M.; Rana, Z.; Burdak-Rothkamm, S. DNA damage foci, Meaning and significance. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, C.A.; Boulton, S.J. Metabolism of postsynaptic recombination intermediates. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backer, L.C.; Allen, J.W.; Harrington-Brock, K.; Campbell, J.A.; DeMarini, D.M.; Doerr, C.L.; Howard, D.R.; Kligerman, A.D. Moore MM. Genotoxicity of inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases I (camptothecin) and II (m-AMSA) in vivo and in vitro. Mutagenesis 1990, 5, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesudas, R.; Nichols, K.E. Recent advances in the treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and macrophage activation syndrome. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 22, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povirk, L.F.; Shuker, D.E. DNA damage and mutagenesis induced by nitrogen mustards. Mutat. Res. 1994, 318, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, B.; Alassaf, A.; Abu-Humdan, A.; Dardas, Z.; Almousa, H.; Alsalem, M.; Khabour, O.; Hammad, H.; Saleh, T.; Awidi, A. Genotoxicity of cisplatin and carboplatin in cultured human lymphocytes, a comparative study. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2019, 12, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.M.; Fedorov, Y.; Brown, D.D.; Suh, M.; Proctor, D.M.; Kuriakose, L.; Haws, L.C.; Harris, M.A. Assessment of Cr(VI)-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity using high content analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, M.A.; Abd-Alla, H.I.; Hassan, E.E.; Hassan, Z.M.; Sweelam, H.M. Genotoxicity and sperm defects induced by 5-FU in male mice and the possible protective role of Pentas lanceolata-iridoids. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 850–851, 503145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, K.; Tamta, A.; Ali, I.Y.; Gupta, J.; Gaikwad, A.B. Tannic acid prevents azidothymidine (AZT) induced hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity along with change in expression of PARG and histone H3 acetylation. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound Name | Minimum Effective Concentration (μmol/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-H2AX | p-H3 | Rad51 | |
| AZT | 1 | 10 | 10 |
| 4-NQO | 0.1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5-Fu | 1 | 1 | 10 |
| Cisplatin | 100 | 100 | 10 |
| Camptothecin | 0.1 | 1 | 1 |
| MMC | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Etoposide | 1 | 10 | 10 |
| Chlorambucil | 10 | 10 | 1 |
| Vincristine | 1 | 1 | 0.01 |
| Taxol | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Griseofulvin | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Tozasertib | 10 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Compound Name | CAS No. | Mode of Toxic Action | Ames | In Vitro Assays | DNA Strand Break | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camptothecin | 7689-03-4 | Topoisomerase I inhibitor | Pos | Pos | Pos | [25] |
| Etoposide | 33419-42-0 | Topoisomerase II inhibitor | Pos | Pos | Pos | [26] |
| Chlorambucil | 305-03-3 | DNA alkylation | Pos | Pos | Pos | [27] |
| Cisplatin | 15663-27-1 | cross-linking agent | Pos | Pos | Pos | [28] |
| Mitomycin C | 1189805-46-6 | cross-linking agent | Pos | Pos | Pos | [29] |
| 5-Fu | 51-21-8 | Nucleoside analogue agents | Neg | Pos | Pos | [30] |
| Taxol | 33069-62-4 | Spindle poison | Neg | Pos | Neg | [3] |
| Vincristine | 143-6709 | Spindle poison | Pos | Pos | Neg | [3] |
| Griseofulvin | 126-07-8 | Spindle poison | Pos | Pos | Neg | [15] |
| Tozasertib | 639089-54-6 | Aurora A inhibitor | N/A | N/A | Neg | [3] |
| Azidothymidine | 92586-35-1 | Nucleoside analogue agents | Neg | Pos | Pos | [31] |
| 4-NQO | 56-57-5 | DNA adduct agents | Pos | Pos | Pos | [1] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Li, Z.; Gong, M.; Ma, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, J. Sensitive Detection of Genotoxic Substances in Complex Food Matrices by Multiparametric High-Content Analysis. Molecules 2024, 29, 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143257
Gao P, Li Z, Gong M, Ma B, Xu H, Wang L, Xie J. Sensitive Detection of Genotoxic Substances in Complex Food Matrices by Multiparametric High-Content Analysis. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143257
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Pengxia, Zhi Li, Mengqiang Gong, Bo Ma, Hua Xu, Lili Wang, and Jianwei Xie. 2024. "Sensitive Detection of Genotoxic Substances in Complex Food Matrices by Multiparametric High-Content Analysis" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143257
APA StyleGao, P., Li, Z., Gong, M., Ma, B., Xu, H., Wang, L., & Xie, J. (2024). Sensitive Detection of Genotoxic Substances in Complex Food Matrices by Multiparametric High-Content Analysis. Molecules, 29(14), 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143257







