Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones by Simple Alkane-Diyl-Based Ir(P,N,O) Catalysts: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
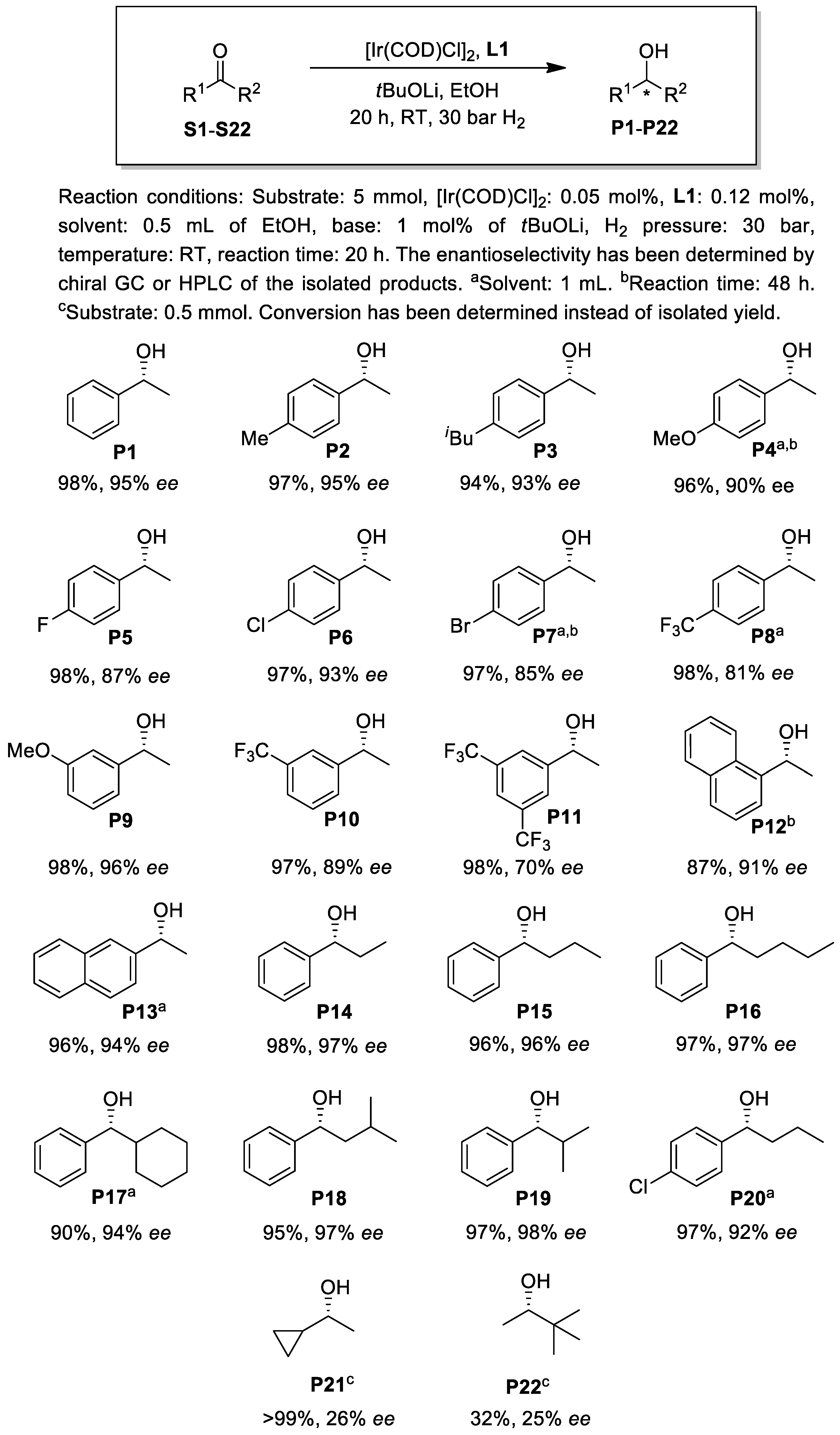
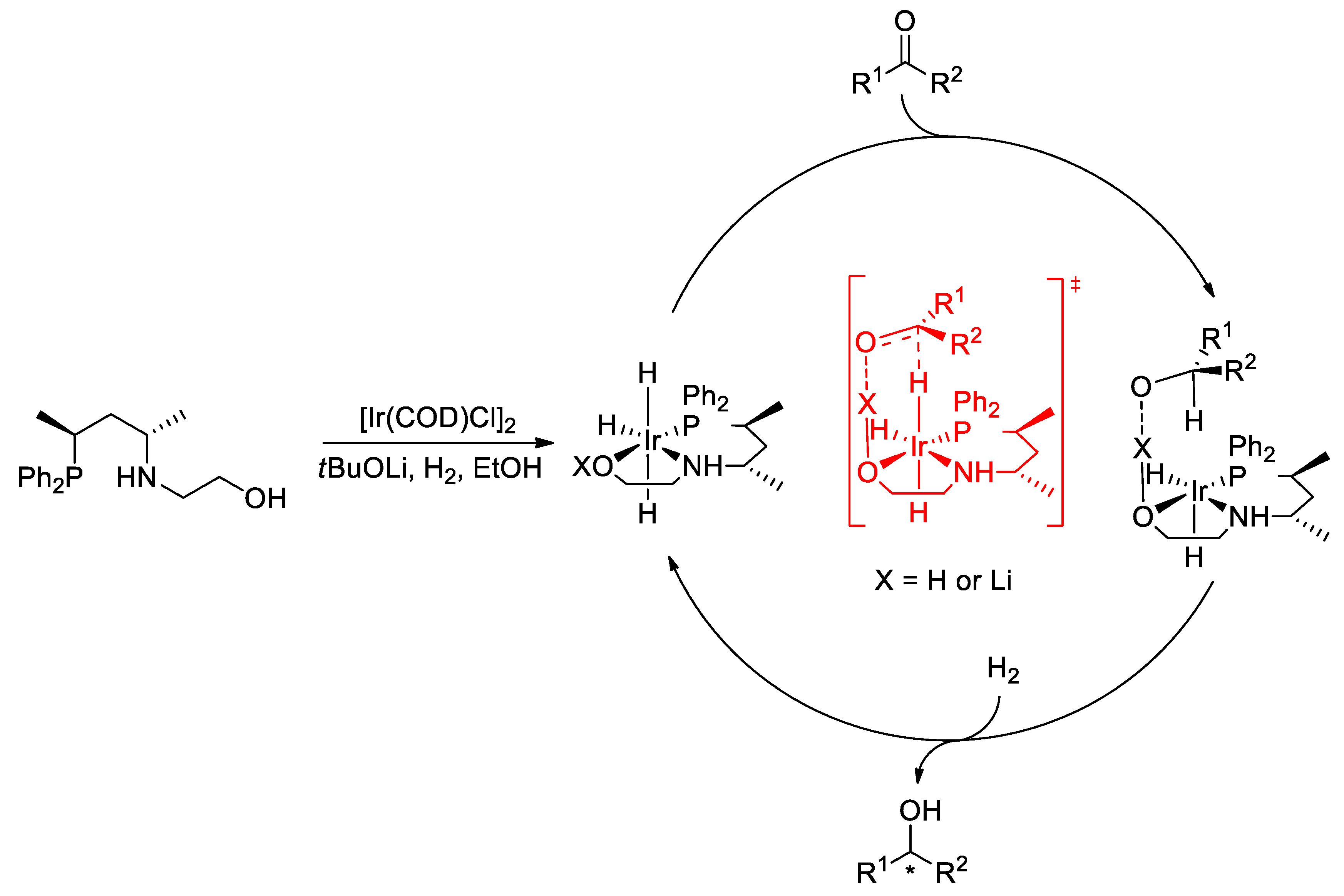
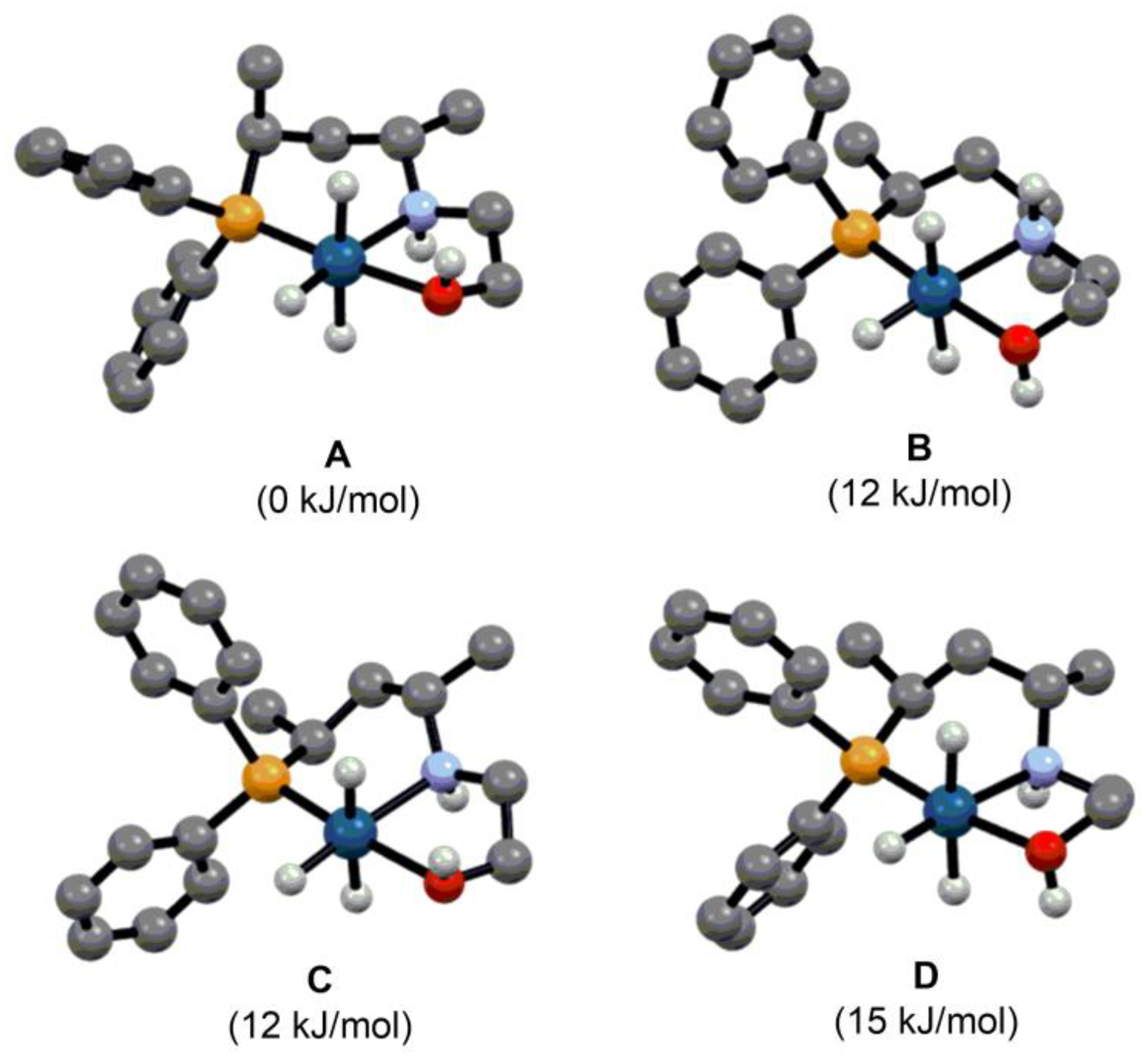
2. Results and Discussion
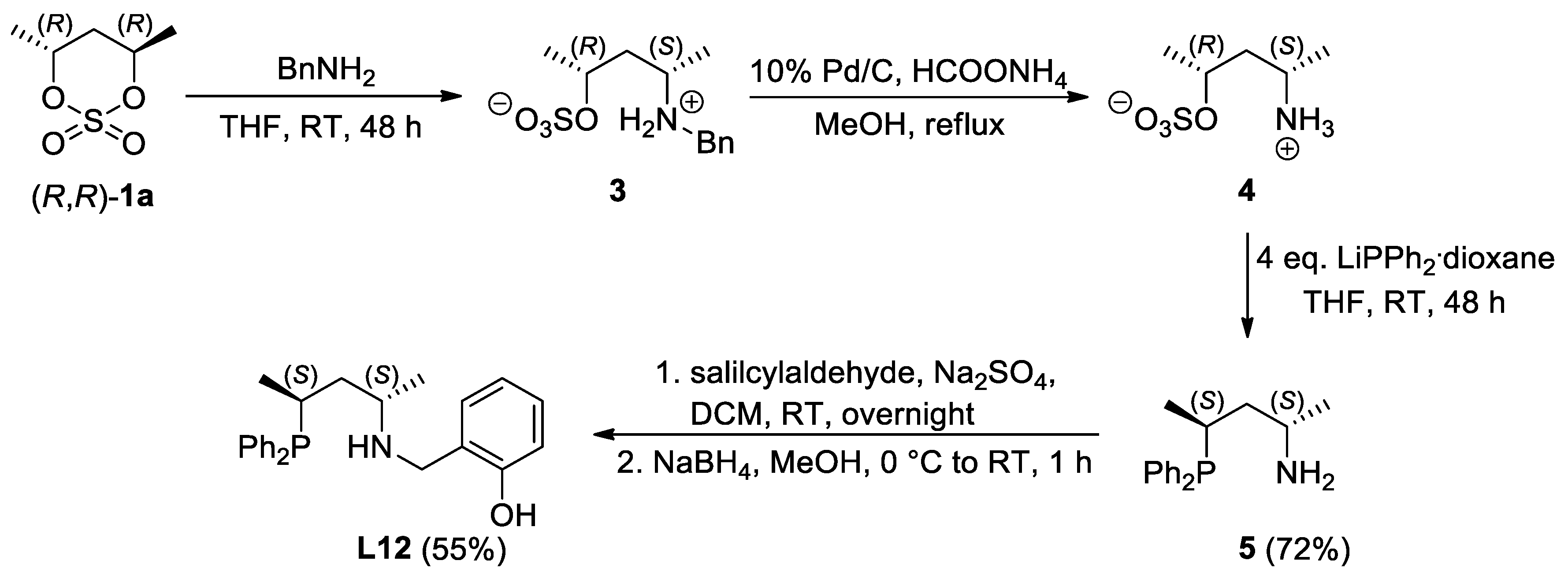
2.1. Synthesis of the Novel Ligands
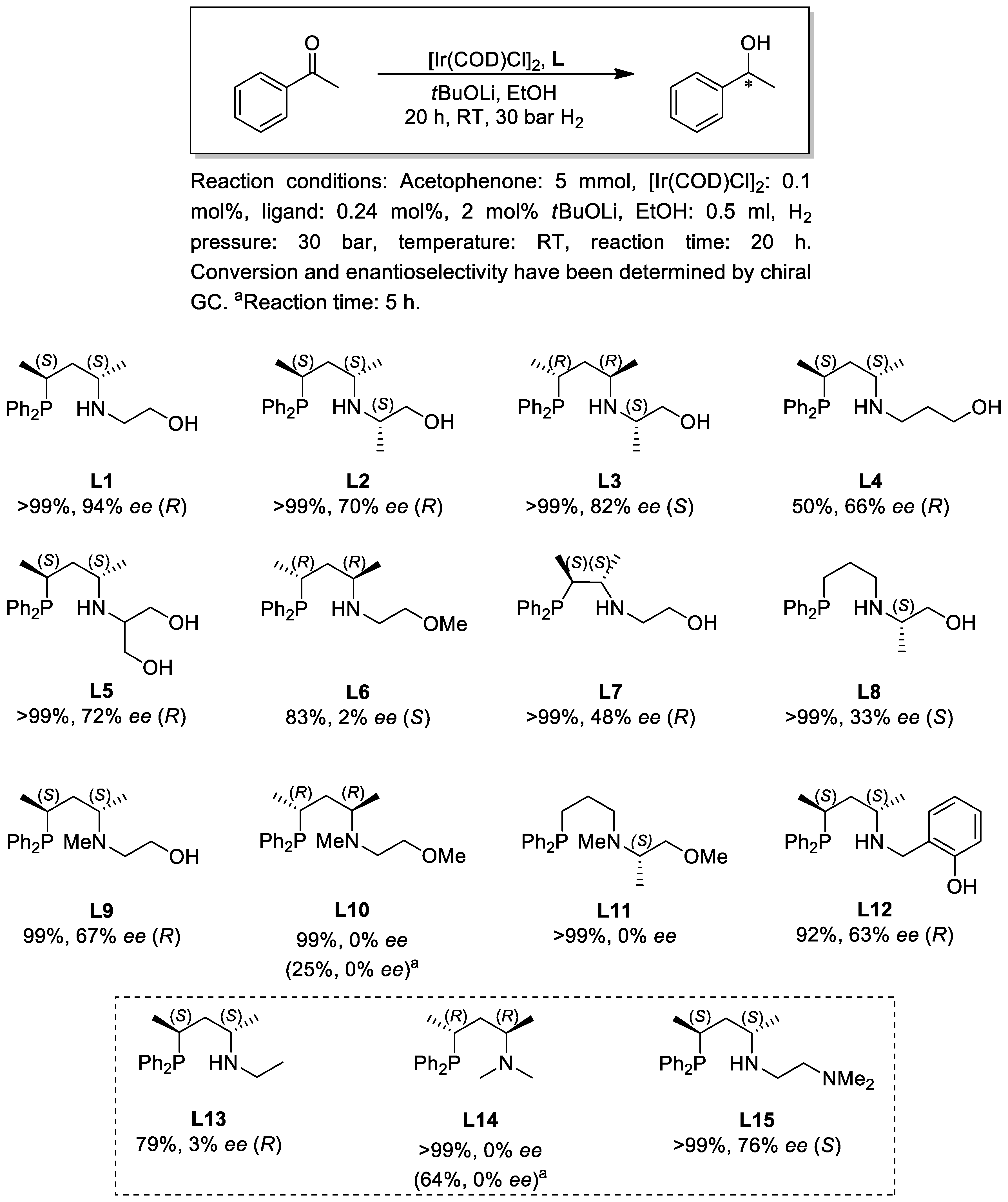
2.2. Asymmetric Hydrogenation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the New Compounds
3.1.1. Synthesis of 3-(((2S,4S)-4-(diphenylphosphino)pentan-2-yl)amino)propan-1-ol (L4)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 2-(((2S,4S)-4-(diphenylphosphino)pentan-2-yl)amino)propane-1,3-diol (L5)
3.1.3. Synthesis of 2-(((2S,3S)-3-(diphenylphosphino)butan-2-yl)amino)ethanol (L7)
3.1.4. Synthesis of (S)-2-((3-(diphenylphosphino)propyl)amino)propan-1-ol (L8)
3.1.5. Synthesis of 2-(((2S,4S)-4-(diphenylphosphino)pentan-2-yl)(methyl)amino)ethanol (L9)
3.1.6. Synthesis of (2R,4R)-4-(diphenylphosphino)-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-N-methylpentan-2-amine (L10)
3.1.7. Synthesis of (2S,4S)-4-(diphenylphosphino)pentan-2-amine (5)
3.1.8. Synthesis of 2-((((2S,4S)-4-(diphenylphosphino)pentan-2-yl)amino)methyl)phenol (L12)
3.2. Asymmetric Hydrogenation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noyori, R.; Ohkuma, T. Enantioselective ketone and β-Keto Ester hydrogenations (including mechanisms). In The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 1105–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, N.; Ohkuma, T. Reduction of Carbonyl Groups: Hydrogenation. In Science of Synthesis: Stereoselective Synthesis 2, Stereoselective Reactions of Carbonyl and Imino Groups; Molander, G.A., Ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010; pp. 9–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Arai, N. Reduction—Hydrogenation: C=O; Chemoselective. In Comprehensive Chirality; Carreira, E.M., Yamamoto, H., Maruoka, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 270–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.U.; Federsel, H.-J. Asymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale: Challenges, Approaches and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.-H.; Bao, D.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Recent Advances in the Development of Chiral Metal Catalysts for the Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones. Synthesis 2015, 47, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Phansavath, P. Asymmetric Hydrogenation and Transfer Hydrogenation; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ooka, H.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Practical Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Aromatic Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2675–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, H.; Ohkuma, T.; Murata, K.; Yokozawa, T.; Kozawa, M.; Katayama, E.; England, A.F.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. trans-[RuCl2(phosphane)2(1,2-diamine)] and Chiral trans-[RuCl2(diphosphane)(1,2-diamine)]: Shelf-Stable Precatalysts for the Rapid, Productive, and Stereoselective Hydrogenation of Ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kitamura, M. Recent topics in catalytic asymmetric hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3635–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, J.; Zhang, X. Chiral Tridentate Ligands in Transition Metal-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 7530–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-H.; Liu, X.-Y.; Xie, J.-B.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhou, Q.-L. An Additional Coordination Group Leads to Extremely Efficient Chiral Iridium Catalysts for Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7329–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-B.; Xie, J.-H.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhou, Q.-L. Chiral Iridium Spiro Aminophosphine Complexes: Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones, Structure, and Plausible Mechanism. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, E.; Crabtree, R.H. Key factors in pincer ligand design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.-H.; Hou, C.-J.; Li, Q.; Qin, H.; Li, L.; Hu, X.-P. Chiral P,N,N-Ligands for Asymmetric Hydrogenation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, S.D.; Fuentes, J.A.; Clarke, M.L. On the NH Effect in Ruthenium-Catalysed Hydrogenation of Ketones: Rational Design of Phosphine-Amino-Alcohol Ligands for Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8002–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.A.; Philips, S.D.; Clarke, M.L. New phosphine-diamine and phosphine-amino-alcohol tridentate ligands for ruthenium catalysed enantioselective hydrogenation of ketones and a concise lactone synthesis enabled by asymmetric reduction of cyano-ketones. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Duan, M.; Wu, W.; Qi, X.; Xue, P.; Lan, Y.; Dong, X.-Q.; Zhang, X. Readily Accessible and Highly Efficient Ferrocene-based Amino-phosphine-alcohol (f-Amphol) Ligands for Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Lu, J.; Yu, O.; Wen, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, X. Enantioselective and Diastereoselective Ir-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of α-Substituted β-Ketoesters via Dynamic Kinetic Resolution. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Dong, X.-Q.; Zhang, X. Iridium/f-Amphol-catalyzed Efficient Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Benzo-fused Cyclic Ketones. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 4319–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.; Liu, L.-X.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Y.-G. Synthesis of Tridentate PNO Ligands with Planar Chirality and Application in Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 7863–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Mo, W.; Yan, X.; Xu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, B. Iridium Catalysts with f-Amphbinol Ligands: Highly Stereoselective Hydrogenation of a Variety of Ketones. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 8845–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Long, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Xue, P.; Chung, L.W.; Dong, X.-Q.; Zhang, X. Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones with Accessible and Modular Ferrocene-Based Amino-phosphine Acid (f-Ampha) Ligands. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, F.; Fang, W.; Yin, C.; Shi, C.; Lang, Q.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhang, X. Discovery and development of ferrocene-based tetradentate ligands for Ir-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation of ketone. Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, W.; He, L.; Lv, H. Iridium-catalyzed chemoselective asymmetric hydrogenation of conjugated enones with ferrocene-based multidentate phosphine ligands. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5841–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Huang, F.; Xu, C.-Q.; Pan, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, G.-Q.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.-T.; Lang, Q.; et al. A 13-million turnover-number anionic Ir-catalyst for a selective industrial route to chiral nicotine. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Császár, Z.; Guóth, M.; Farsang, E.; Bényei, A.C.; Bakos, J.; Farkas, G. Hydrogen bond-directed coordination of phosphine-amino-alcohol (P,N,OH) ligands: Stereochemical considerations and catalytic studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 543, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Császár, Z.; Pőrgye, Z.E.; Tóth-Farsang, E.; Kovács, M.; Bényei, A.C.; Bakos, J.; Farkas, G. Ruthenium-complexes of new chiral phosphine-amine-ether (Ru-PNO) for asymmetric hydrogenation—The role of backbone chirality in pincer ligand design. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschweiler, W. Ersatz von an Stickstoff gebundenen Wasserstoffatomen durch die Methylgruppe mit Hülfe von Formaldehyd. Ber. Dsch. Chem. Ges. 1905, 38, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.T.; Gillespie, H.B.; Weisshaus, S.Z. The Action of Formaldehyde on Amines and Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 4571–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, S.; Farkas, G.; Tóth, I.; Bakos, J. Synthesis of new N-substituted chiral phosphine-phosphoramidite ligands and their application in asymmetric hydrogenations and allylic alkylations. Tetrahedron Asymm. 2015, 26, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.J.; Arthurs, R.A. Catalyst Optimisation for Asymmetric Synthesis by Ligand Chirality Element Addition: A Perspective on Stereochemical Cooperativity. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 11460–11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, G.; Császár, Z.; Stágel, K.; Nemes, E.; Balogh, S.; Tóth, I.; Bényei, A.; Lendvay, G.; Bakos, J. Efficient Stereochemical Communication in Phosphine-Amine Palladium-Complexes: Exploration of N-Substituent Effects in Coordination Chemistry and Catalysis. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 846, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szi-Ferenc, L.; Császár, Z.; Lendvay, G.; Bényei, A.; Balogh, S.; Nánási, B.; Farkas, G.; Bakos, J. Synthesis of zwitterionic phosphapalladacycles: Unusual reactivity pattern of six-membered P,N-chelates. Organometallics 2018, 37, 2203–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, N.; Jaseer, E.A.; Munarriz, J.; Sanz Miguel, P.J.; Polo, V.; Iglesias, M.; Oro, L.A. An Insight into Transfer Hydrogenation Reactions Catalysed by Iridium(III) Bis-N-heterocyclic Carbenes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4388–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Császár, Z.; Szabó, E.Z.; Bényei, A.C.; Bakos, J.; Farkas, G. Chelate ring size effects of Ir(P,N,N) complexes: Chemoselectivity switch in the asymmetric hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated ketones. Catal. Commun. 2020, 146, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramspoth, T.-F.; Kootstra, J.; Harutyunyan, S.R. Unlocking the potential of metal ligand cooperation for enantioselective transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choualeb, A.; Lough, A.J.; Gusev, D.G. Hemilabile Pincer-Type Hydride Complexes of Iridium. Organometallics 2007, 26, 5224–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Kirchhoff, M.M. Origins, Current Status, and Future Challenges of Green Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, M.G.; Caille, S.; Içten, E.; Michalak, S.E.; St-Pierre, G.; Thiel, O.R. Green Chemistry as a Driver for Innovation in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Isr. J. Chem. 2021, 61, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Zhou, H.-F.; Wang, T.-L.; He, Y.-M.; Fan, Q.-H. Highly enantioselective hydrogenation of quinolines under solvent-free or highly concentrated conditions. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, S.E.; Guo, R.; Iuliis, M.Z.; Rasool, N.; Lough, A.; Morris, R.H. Probing the Effect of the Ligand X on the Properties and Catalytic Activity of the Complexes RuHX(diamine)(PPh3)2 (X = OPh, 4-SC6H4OCH3, OPPh2, OP(OEt)2, CCPh, NCCHCN, CH(COOMe)2; diamine = 2,3-Diamino-2,3-dimethylbutane, (R,R)-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane). Organometallics 2006, 25, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of a Bulky and Electron-Rich Derivative of SEGPhos and Its Application in Ru-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydrogenation of β-Ketoesters. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Liu, S.; Duan, M.; Tan, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y.; Lan, Y.; Dong, X.-Q.; Zhang, X. Iridium Catalysts with f-Amphox Ligands: Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2938–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linag, Z.-Q.; Yang, T.-L.; Gu, G.; Dang, L.; Zhang, X. Scope and Mechanism on Iridium f-Amphamide Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewicz, A.; Marcos, R.; Sahoo, S.; Inge, A.K.; Zou, X.; Martín-Matute, B. A Highly Active Bifunctional Iridium Complex with an Alcohol/AlkoxideTethered N-Heterocyclic Carbene for Alkylation of Amines with Alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14510–14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Yang, T.; Yu, O.; Qian, H.; Wang, J.; Wen, J.; Dang, L.; Zhang, X. Enantioselective Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of α-Keto Amides to α-Hydroxy Amides. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5920–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Han, Z.; Ding, K. Lutidine-Based Chiral Pincer Manganese Catalysts for Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4973–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-P.; Yuan, M.-L.; Yang, X.-H.; Li, K.; Xie, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Efficient asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones in ethanol with chiral iridium complexes of spiroPAP ligands as catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6123–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, G.V.; Badgujara, K.C.; Bhanage, B.M. Kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols with Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on a biodegradable ternary blend polymer matrix as a highly efficient and heterogeneous recyclable biocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Császár, Z.; Kovács, R.; Fonyó, M.; Simon, J.; Bényei, A.; Lendvay, G.; Bakos, J.; Farkas, G. Testing the role of the backbone length using bidentate and tridentate ligands in manganese-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation. Mol. Catal. 2022, 529, 112531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Hou, C.-J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.-J.; Huang, D.-Z.; Hu, X.-P. Ir-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of simple ketones with chiral ferrocenyl P,N,N-ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contente, M.L.; Molinari, F.; Zambelli, P.; De Vitis, V.; Gandolfi, R.; Pinto, A.; Romano, D. Biotransformation of aromatic ketones and ketoesters with the non-conventional yeast Pichia glucozyma. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 7051–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collados, J.F.; Ortiz, P.; Pérez, J.M.; Xia, Y.; Koenis MA, J.; Buma, W.J.; Nicu, V.P.; Harutyunyan, S.R. Enantiospecific Brook Rearrangement of Tertiary Benzylic α-Hydroxysilanes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 3900–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagawa, H.; Maejima, Y.; Nagano, T. Sodium Bromide-Catalyzed Oxidation of Secondary Benzylic Alcohols Using Aqueous Hydrogen Peroxide as Terminal Oxidant. Synlett 2016, 27, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- Yanai, T.; Tew, D.; Handy, N. A new hybrid exchange–correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrae, D.; Häußermann, U.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuß, H. Energy-adjustedab initio pseudopotentials for the second and third row transition elements. Theor. Chim. Acta 1990, 77, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-Consistent Molecular Orbital Methods. XII. Further Extensions of Gaussian-Type Basis Sets for Use in Molecular Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francl, M.M.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J.; Binkley, J.S.; Gordon, M.S.; DeFrees, D.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XXIII. A polarization-type basis set for second-row elements. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Binkley, J.S.; Pople, J.A.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J. Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods. 22. Small split-valence basis sets for second-row elements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 2797–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

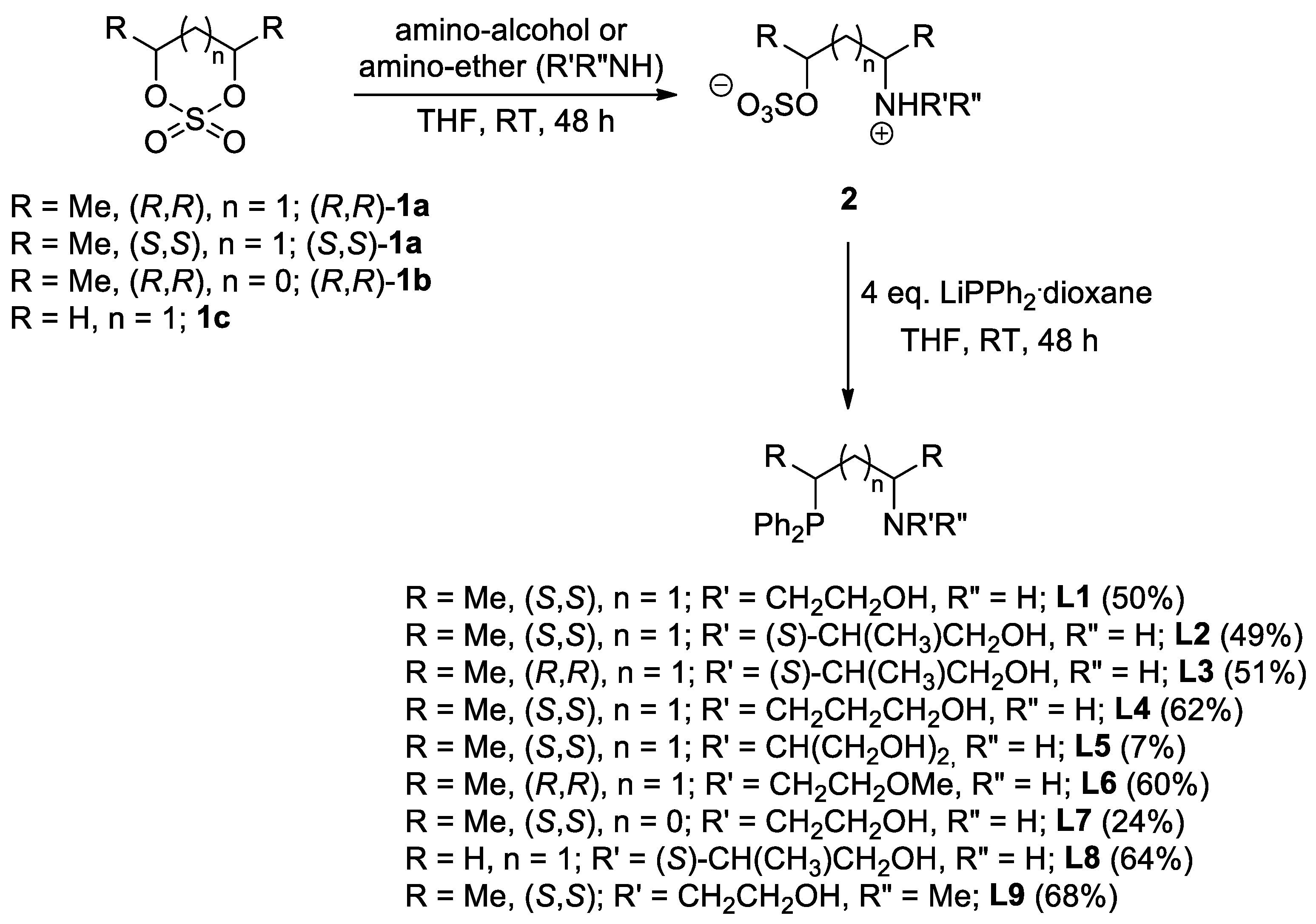
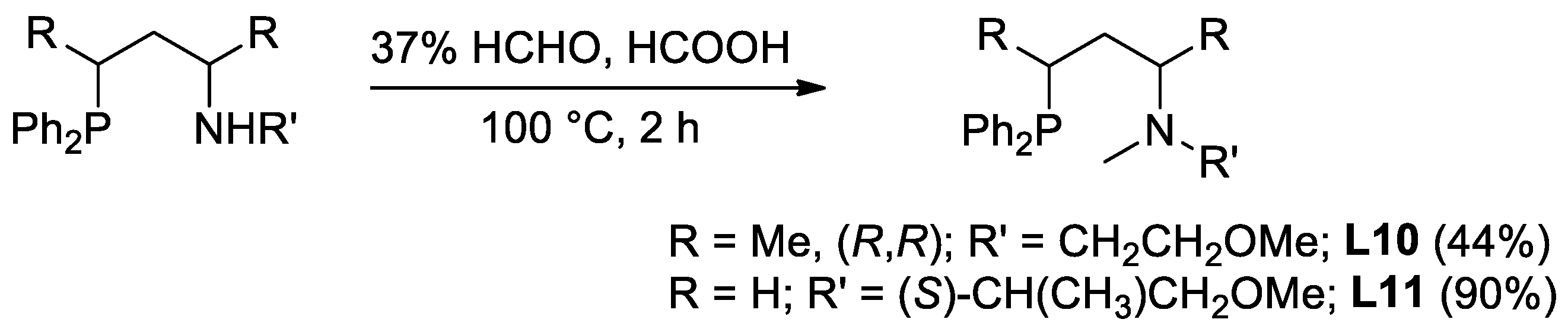
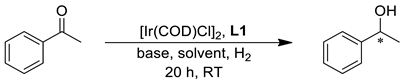 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Base | B/C Molar Ratio | Solvent | Conversion (%) | ee (%) a |
| 1 | tBuOLi | 5 | iPrOH | 76 | 88 |
| 2 | tBuOK | 5 | iPrOH | >99 | 82 |
| 3 | tBuOLi | 10 | iPrOH | >99 | 92 |
| 4 | tBuOLi | 20 | iPrOH | >99 | 92 |
| 5 | KOH | 10 | iPrOH | >99 | 80 |
| 6 | tBuOLi | 10 | MeOH | 98 | 72 |
| 7 | tBuOLi | 10 | EtOH | >99 | 94 |
| 8 | tBuOLi | 10 | nBuOH | >99 | 95 |
| 9 | tBuOLi | 10 | γ-valerolactone | 3 | 60 |
| 10 | tBuOLi | 10 | 2-Me-THF | 9 | 39 |
| 11 | tBuOLi | 10 | 96% EtOH | >99 | 93 |
| 12 b | tBuOLi | 10 | EtOH | >99 | 95 |
| Substrate Concentration (mmol Acetophenone/mL Ethanol) | Conversion (%) | ee (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | >99 | 94 |
| 10 | >99 | 94 |
| 20 | >99 | 93 |
| 50 | >99 | 92 |
| 100 | >99 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Császár, Z.; Guóth, M.; Kovács, M.; Bényei, A.C.; Bakos, J.; Farkas, G. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones by Simple Alkane-Diyl-Based Ir(P,N,O) Catalysts: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163743
Császár Z, Guóth M, Kovács M, Bényei AC, Bakos J, Farkas G. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones by Simple Alkane-Diyl-Based Ir(P,N,O) Catalysts: A Comparative Study. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163743
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsászár, Zsófia, Mária Guóth, Margit Kovács, Attila C. Bényei, József Bakos, and Gergely Farkas. 2024. "Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones by Simple Alkane-Diyl-Based Ir(P,N,O) Catalysts: A Comparative Study" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163743
APA StyleCsászár, Z., Guóth, M., Kovács, M., Bényei, A. C., Bakos, J., & Farkas, G. (2024). Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Ketones by Simple Alkane-Diyl-Based Ir(P,N,O) Catalysts: A Comparative Study. Molecules, 29(16), 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163743







