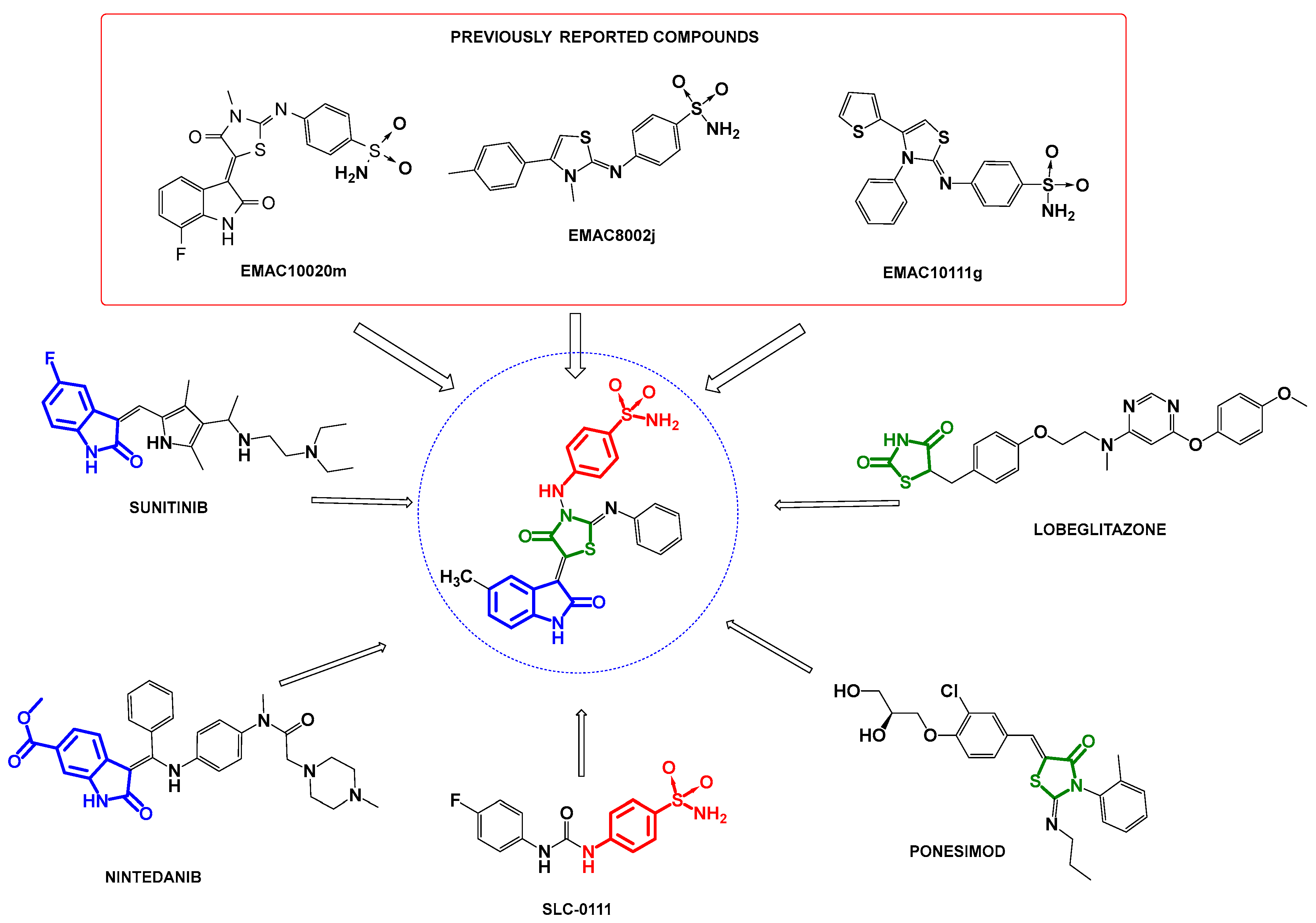
Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
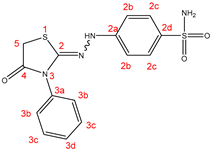
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Carbonic Anhydrases Assay and Data Inhibition
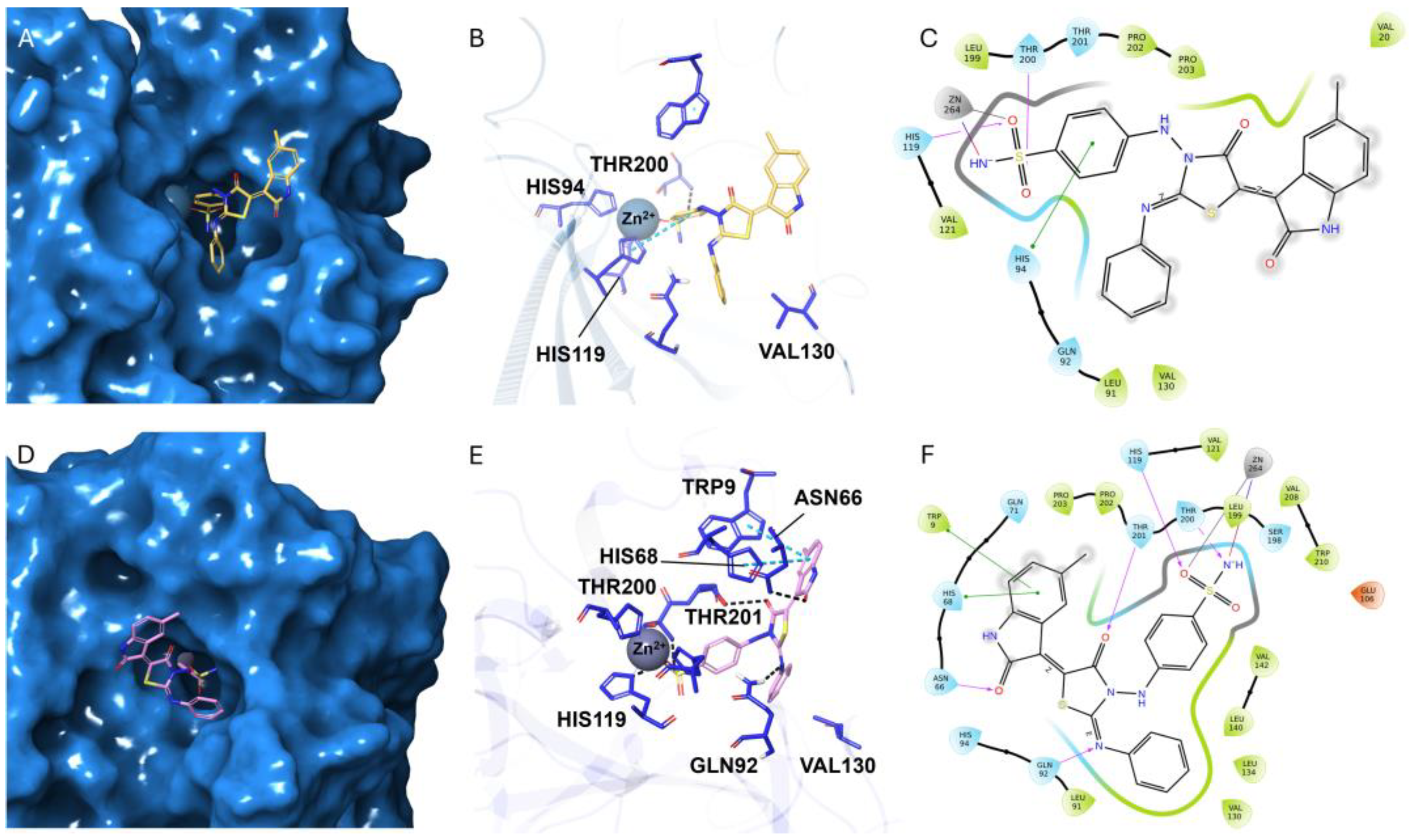
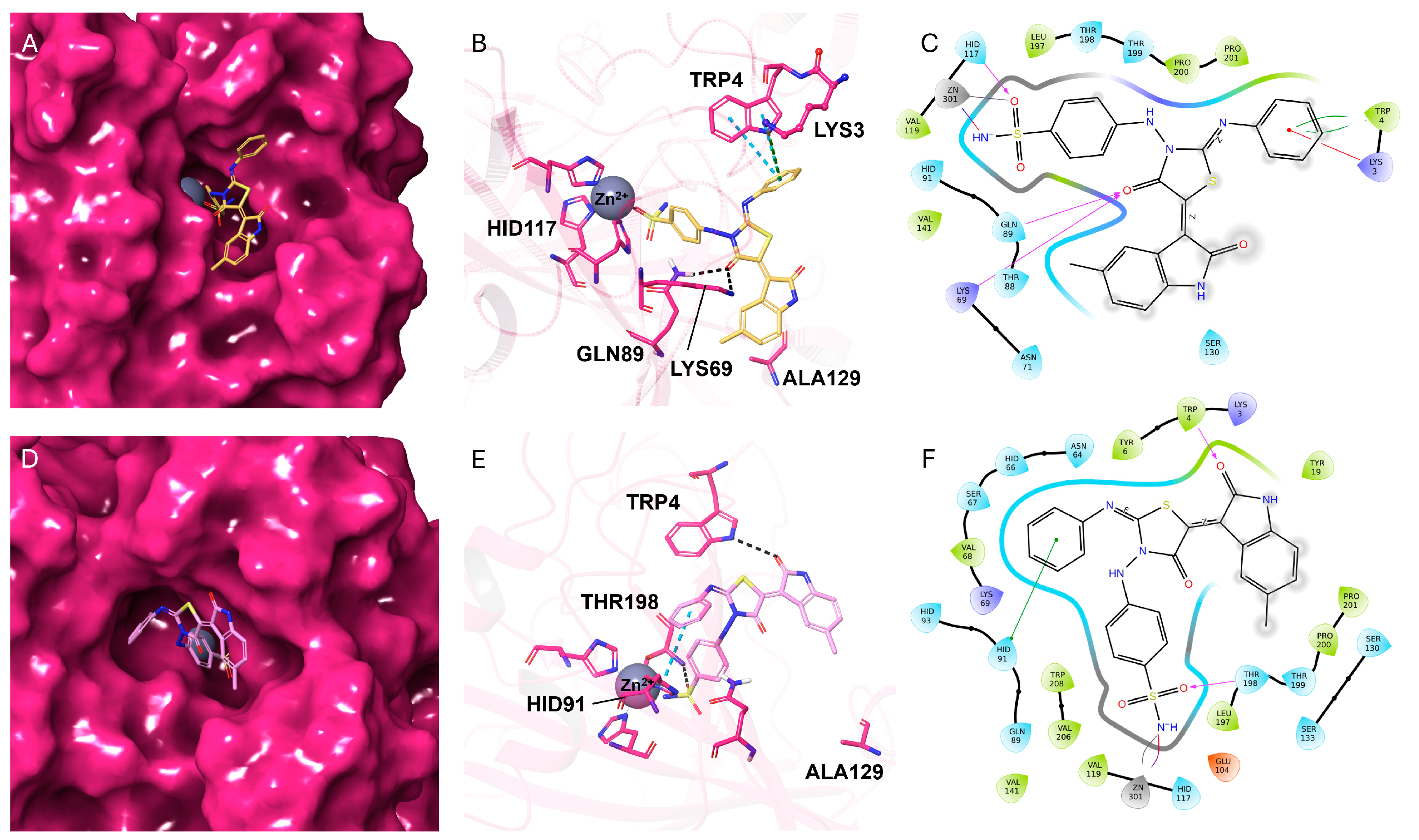
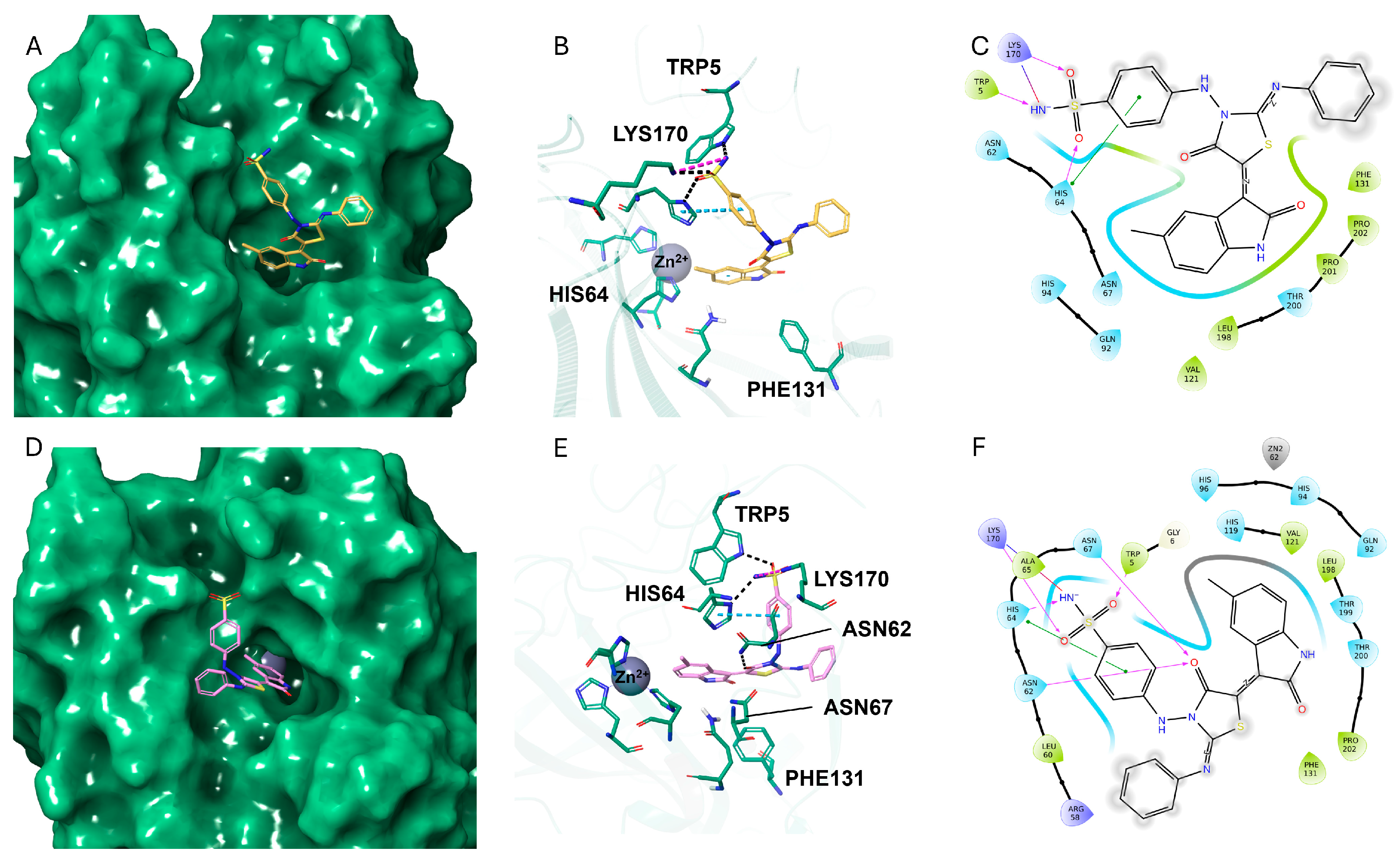
2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthetic Procedures
- Synthesis of 4-hydrazineylbenzenesulfonamide (1)
- Synthesis of N-phenyl-2-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide (2)
- Synthesis of 4-((4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (3) and 4-(2-(4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-2-ylidene)hydrazineyl)benzenesulfonamide (4)
General Procedures for the Synthesis of 5a–i Series
- Synthesis of 4-((5-((Z)-5-chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5a)
- 4-((5-((Z)-5-fluoro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5c)
- 4-((5-((Z)-5-bromo-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5d)
- 4-((5-((Z)-5-methoxy-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5e)
- 4-((5-((Z)-5-methyl-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5f)
- 4-((4-oxo-5-((Z)-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5g)
- 4-((5-((Z)-7-fluoro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5h)
- 4-((5-((Z)-7-bromo-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-3-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide (5i)v
3.2. Biochemical Evaluation of hCA Inhibition
3.3. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salamat, M.S. Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8th Edition. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, L.A.; Wedren, S.; Tamimi, R.M.; Trichopoulos, D.; Adami, H.O. The role of gene-environment interaction in the aetiology of human cancer: Examples from cancers of the large bowel, lung and breast. J. Intern Med. 2001, 249, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Oosterwijk, E.; Tu, C.; Shiverick, K.T.; Silverman, D.N.; Frost, S.C. Expression and activity of carbonic anhydrase IX is associated with metabolic dysfunction in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opavsky, R.; Pastorekova, S.; Zelnik, V.; Gibadulinova, A.; Stanbridge, E.J.; Zavada, J.; Kettmann, R.; Pastorek, J. Human MN/CA9 gene, a novel member of the carbonic anhydrase family: Structure and exon to protein domain relationships. Genomics 1996, 33, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabianova, A.; Barathova, M.; Csaderova, L.; Simko, V.; Zatovicova, M.; Labudova, M.; Pastorek, J. Hypoxic marker CA IX and adhesion mediator beta-catenin are downregulated by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus persistent infection. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12879–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, B.W.; Supuran, C.T. A perspective on quantitative structure-activity relationships and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsic, J.F.; Avvaru, B.S.; Kim, C.U.; Gruner, S.M.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Silverman, D.N.; McKenna, R. Entrapment of carbon dioxide in the active site of carbonic anhydrase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30766–30771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, C.B.; Tiwari, M.; Supuran, C.T. Progress in the development of human carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and their pharmacological applications: Where are we today? Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2485–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, V.; Vitale, R.M.; Monti, S.M.; Pedone, C.; Scozzafava, A.; Cecchi, A.; De Simone, G.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: X-ray and molecular modeling study for the interaction of a fluorescent antitumor sulfonamide with isozyme II and IX. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8329–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, C.; Meleddu, R.; Angeli, A.; Distinto, S.; Bianco, G.; Capasso, C.; Cottiglia, F.; Angius, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Maccioni, E. Isatin: A privileged scaffold for the design of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorekova, S.; Parkkila, S.; Parkkila, A.K.; Opavsky, R.; Zelnik, V.; Saarnio, J.; Pastorek, J. Carbonic anhydrase IX, MN/CA IX: Analysis of stomach complementary DNA sequence and expression in human and rat alimentary tracts. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.J.P.; Watson, P.H.; Turner, K.J.; Pastorek, J.; Sibtain, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.L.; Maxwell, P.H.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible Expression of Tumor-associated Carbonic Anhydrases1. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, S.; Liao, S.Y.; Ivanova, A.; Danilkovitch-Miagkova, A.; Tarasova, N.; Weirich, G.; Merrill, M.J.; Proescholdt, M.A.; Oldfield, E.H.; Lee, J.; et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible cell-surface transmembrane carbonic anhydrases in human cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.; Watson, P.H.; Campo, L.; Chia, S.K.; English, R.; Pastorek, J.; Sly, W.S.; Ratcliffe, P.; Harris, A.L. Expression of the hypoxia-inducible and tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorekova, S.; Parkkila, S.; Zavada, J. Tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases and their clinical significance. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2006, 42, 167–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ronca, R.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase IX: An atypical target for innovative therapies in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX as a novel anticancer mechanism. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 3, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.F.; Idrees, D.; Hassan, M.I.; Ahmad, K.; Avecilla, F.; Azam, A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyridine-thiazolidinone derivatives as anticancer agents: Targeting human carbonic anhydrase IX. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Advances in structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massière, F.; Wiedemann, N.; Borrego, I.; Hoehne, A.; Osterkamp, F.; Paschke, M.; Zboralski, D.; Schumann, A.; Bredenbeck, A.; Brichory, F.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of DPI-4452: A 68Ga77Lu Theranostic Ligand for Carbonic Anhydrase IX. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as antitumor/antimetastatic agents: A patent review (2008–2018). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhakeem, M.M.; Morcoss, M.M.; Hanna, D.A.; Lamie, P.F. Design, synthesis and in silico insights of novel 1,2,3-triazole benzenesulfonamide derivatives as potential carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors with promising anticancer activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 144, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, H.; Renzi, G.; Angeli, A.; D’Agostino, I.; Ronca, R.; Massardi, M.L.; Tavani, C.; Carradori, S.; Ferraroni, M.; Governa, P.; et al. Benzenesulfonamide decorated dihydropyrimidin(thi)ones: Carbonic anhydrase profiling and antiproliferative activity. RSC Med. Chem. 2024, 15, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, E.S.; Marzouk, A.A.; Abd-Allah, W.H.; Giovannuzzi, S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Supuran, C.T.; El Hamd, M.A.; El-Behairy, M.F. Tailored Tetrasubstituted Imidazole Carrying the Benzenesulfonamide Fragments as Selective Human Carbonic Anhydrase IX/XII Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, D.; Distinto, S.; Onali, A.; Sanna, E.; Lupia, A.; Demuru, L.; Atzeni, G.; Cottiglia, F.; Meleddu, R.; Angeli, A.; et al. New Structural Features of Isatin Dihydrothiazole Hybrids for Selective Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Siwach, K.; Supuran, C.T.; Sharma, P.K. A decade of tail-approach based design of selective as well as potent tumor associated carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 126, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distinto, S.; Meleddu, R.; Ortuso, F.; Cottiglia, F.; Deplano, S.; Sequeira, L.; Melis, C.; Fois, B.; Angeli, A.; Capasso, C.; et al. Exploring new structural features of the 4-[(3-methyl-4-aryl-2,3-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-ylidene)amino]benzenesulphonamide scaffold for the inhibition of human carbonic anhydrases. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Meleddu, R.; Distinto, S.; Cottiglia, F.; Angius, R.; Gaspari, M.; Taverna, D.; Melis, C.; Angeli, A.; Bianco, G.; Deplano, S.; et al. Tuning the Dual Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase and Cyclooxygenase by Dihydrothiazole Benzensulfonamides. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, N.; Micheletto, L.; Sechi, M.; Aggarwal, M.; Carta, F.; McKenna, R.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition with Benzenesulfonamides and Tetrafluorobenzenesulfonamides Obtained via Click Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminskyy, D.; Khyluk, D.; Vasylenko, O.; Zaprutko, L.; Lesyk, R. A Facile Synthesis and Anticancer Activity Evaluation of Spiro[Thiazolidinone-Isatin] Conjugates. Sci. Pharm. 2011, 79, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, L.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X. Rationally designed multitarget anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 1694–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Gao, H.; Bemis, G.; Salituro, F.; Ledeboer, M.; Harrington, E.; Wilke, S.; Taslimi, P.; Pazhanisamy, S.; Xie, X.; et al. Structure-based design and parallel synthesis of N-benzyl isatin oximes as JNK3 MAP kinase inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2891–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweedar, H.E.; Mahrous, H.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A. Analogue-based design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-substituted-(methylenehydrazono)indolin-2-ones as anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A. Chapter 1—Thiazole, a privileged scaffold in drug discovery. In Privileged Scaffolds in Drug Discovery; Yu, B., Li, N., Fu, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mrowka, P.; Glodkowska-Mrowka, E. PPARγ Agonists in Combination Cancer Therapies. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2020, 20, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhong, H.; Xu, K.; Qi, X. Roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.C.; Chia, S.; Bedard, P.L.; Chu, Q.; Lyle, M.; Tang, L.; Singh, M.; Zhang, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Renouf, D.J.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of SLC-0111, a Novel Inhibitor of Carbonic Anhydrase IX, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Repale, A.; Pal, G. In-Situ Synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Which Content Pyrazole Skeleton. Lett. Org. Chem. 2020, 17, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klika, K.D.; Alsalim, R.; Eftekhari, M.; Makarem, A. Synthesis of a polyaminocarboxylate-based aluminum complex and its structural studies using (1)H(13)C-HMBC NMR and a Karplus-type function. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 12436–12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, F.M.; Aghamiri, B.; Jalalinik, M. A facile one-pot, four-component synthesis of (Z)-isomer of rhodanine-oxindole derivatives under environmentally benevolent conditions. Synth Commun. 2022, 52, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimene, Y.; Eychenne, R.; Rodriguez, F.; Mallet-Ladeira, S.; Saffon-Merceron, N.; Winum, J.-Y.; Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Benoist, E.; Seridi, A. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Inhibitory Activity and Molecular Docking of Coumarins/Sulfonamides Containing Triazolyl Pyridine Moiety as Potent Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX and XII Inhibitors. Crystals 2021, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitans, J.; Kazaks, A.; Balode, A.; Ivanova, J.; Zalubovskis, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Tars, K. Efficient Expression and Crystallization System of Cancer-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase Isoform IX. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9004–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, A.; Zubrienė, A.; Manakova, E.; Gražulis, S.; Matulis, D. Crystal structure correlations with the intrinsic thermodynamics of human carbonic anhydrase inhibitor binding. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifah, R.G. The Carbon Dioxide Hydration Activity of Carbonic Anhydrase: I. Stop-Flow Kinetic Studies On The Native Human Isoenzymes B And C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Angeli, A.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Kiryukhina, A.P.; Milaneschi, A.; De Luca, A.; Bozdag, M.; Carradori, S.; Selleri, S.; Bartolucci, G.; et al. Azidothymidine “Clicked” into 1,2,3-Triazoles: First Report on Carbonic Anhydrase–Telomerase Dual-Hybrid Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7392–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacchiano, F.; Carta, F.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Supuran, C.T. Ureido-Substituted Benzenesulfonamides Potently Inhibit Carbonic Anhydrase IX and Show Antimetastatic Activity in a Model of Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilginer, S.; Gonder, B.; Gul, H.I.; Kaya, R.; Gulcin, I.; Anil, B.; Supuran, C.T. Novel sulphonamides incorporating triazene moieties show powerful carbonic anhydrase I and II inhibitory properties. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger. Maestro, Schrödinger, Editor. 2021: NYC.
- Mohamadi, F.; Richards, N.G.J.; Guida, W.C.; Liskamp, R.; Lipton, M.; Caufield, C.; Chang, G.; Hendrickson, T.; Still, W.C. Macromodel: An integrated software system for modeling organic and bioorganic molecules using molecular mechanics. J. Comput. Chem. 1990, 11, 440–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. II. MMFF94 van der Waals and electrostatic parameters for intermolecular interactions. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 520–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Hah, J.-M.; Cho, A.E. Correlation between Performance of QM/MM Docking and Simple Classification of Binding Sites. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2382–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleddu, R.; Deplano, S.; Maccioni, E.; Ortuso, F.; Cottiglia, F.; Secci, D.; Onali, A.; Sanna, E.; Angeli, A.; Angius, R.; et al. Selective inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX and XII by coumarin and psoralen derivatives. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

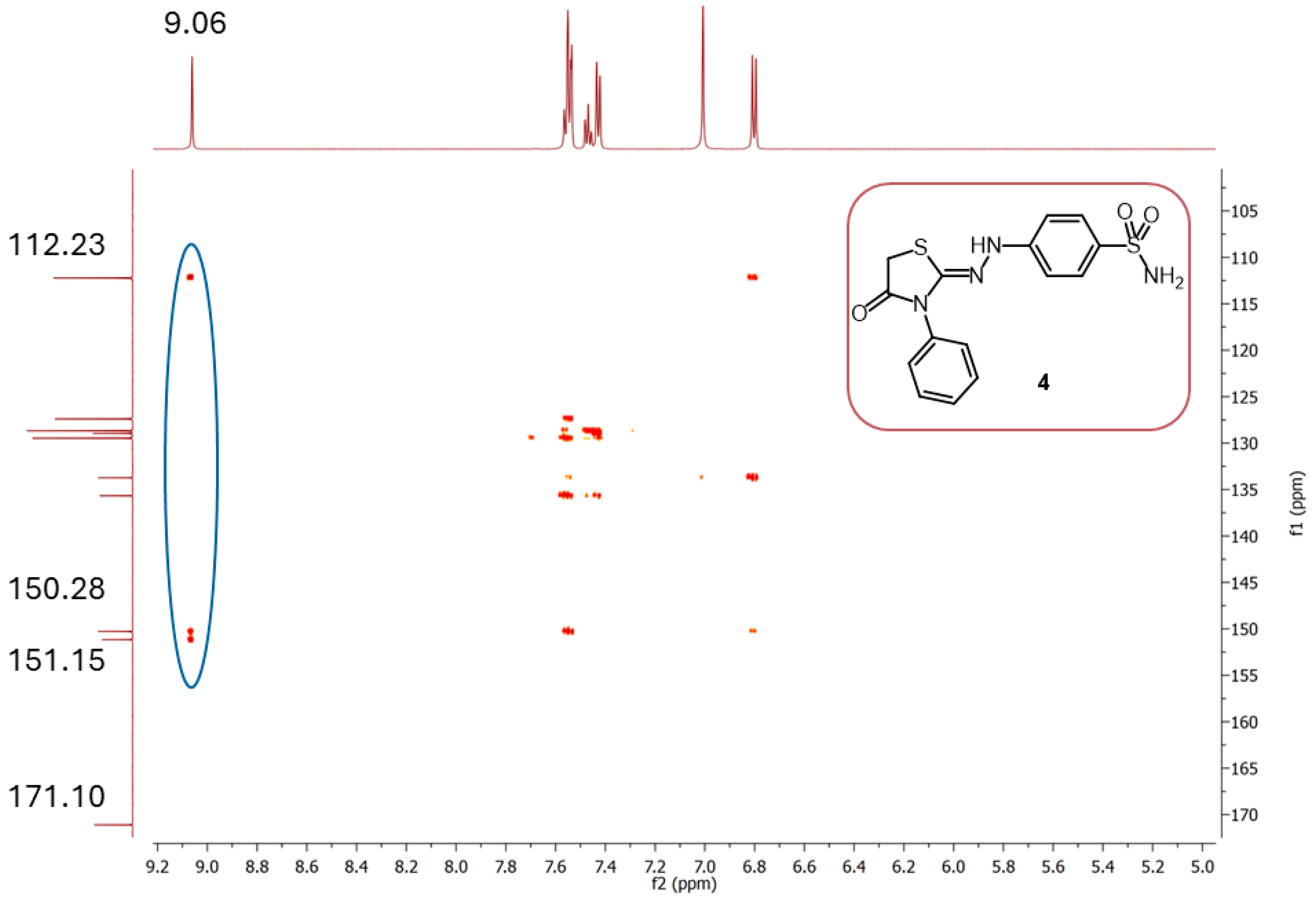
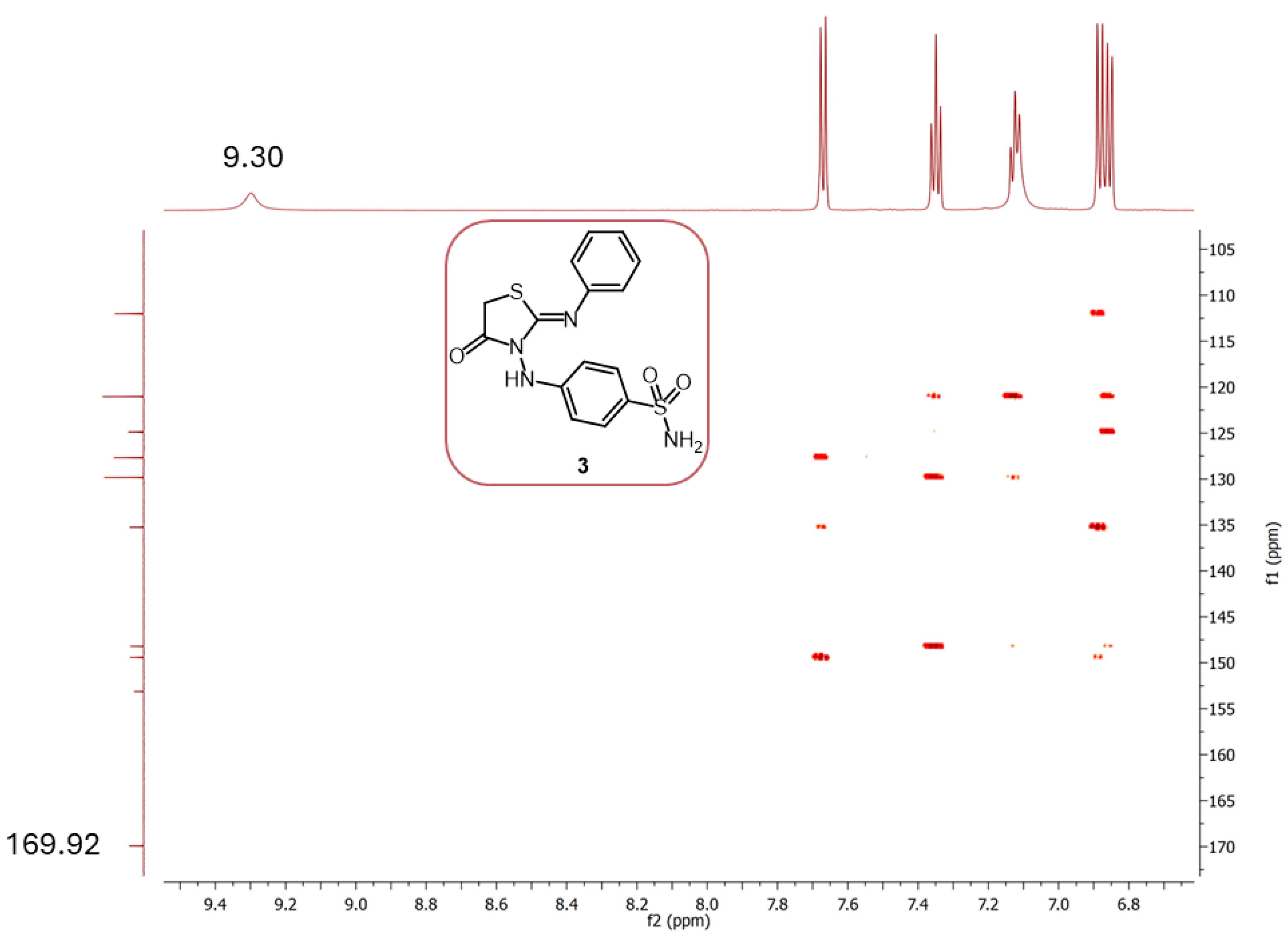
 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 5 | 3b | 2b | 2d | 3c | 2c | 3d | 3a | 2 | 2a | 4 |
| δ | 30.59 | 112.01 | 121.04 | 124.87 | 127.68 | 129.83 | 135.24 | 148.20 | 149.42 | 153.13 | 169.92 |
 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 5 | 2b | 2c | 3b | 3d | 3c | 3a | 2d | 2a | 2 | 4 |
| δ | 33.55 | 112.23 | 127.4 | 128.68 | 128.97 | 129.47 | 133.73 | 135.67 | 150.28 | 151.15 | 171.10 |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki nM | |||||
| Code | R | hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII |
| 5a | 5-Cl | 4591 | 245.8 | 99.4 | 61.1 |
| 5b | 5-NO2 | 6031 | 159.5 | 34.6 | 7.5 |
| 5c | 5-F | 5880 | 6.9 | 23.1 | 21.8 |
| 5d | 5-Br | >10,000 | 104.3 | 87.4 | 193.0 |
| 5e | 5-OCH3 | 9064 | 9.6 | 5.0 | 53.7 |
| 5f | 5-CH3 | >10,000 | 70.8 | 14.9 | 0.6 |
| 5g | -H | 5278 | 9.6 | 2.5 | 16.8 |
| 5h | 7-F | 6625 | 4.1 | 12.7 | 1.3 |
| 5i | 7-Br | 7685 | 17.8 | 50.3 | 94.0 |
| AAZ | 250.0 | 12.0 | 25.0 | 5.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Secci, D.; Sanna, E.; Distinto, S.; Onali, A.; Lupia, A.; Demuru, L.; Atzeni, G.; Meleddu, R.; Cottiglia, F.; Angeli, A.; et al. Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 4444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184444
Secci D, Sanna E, Distinto S, Onali A, Lupia A, Demuru L, Atzeni G, Meleddu R, Cottiglia F, Angeli A, et al. Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184444
Chicago/Turabian StyleSecci, Daniela, Erica Sanna, Simona Distinto, Alessia Onali, Antonio Lupia, Laura Demuru, Giulia Atzeni, Rita Meleddu, Filippo Cottiglia, Andrea Angeli, and et al. 2024. "Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184444
APA StyleSecci, D., Sanna, E., Distinto, S., Onali, A., Lupia, A., Demuru, L., Atzeni, G., Meleddu, R., Cottiglia, F., Angeli, A., Supuran, C. T., & Maccioni, E. (2024). Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Molecules, 29(18), 4444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184444







