Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Adlay Bran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
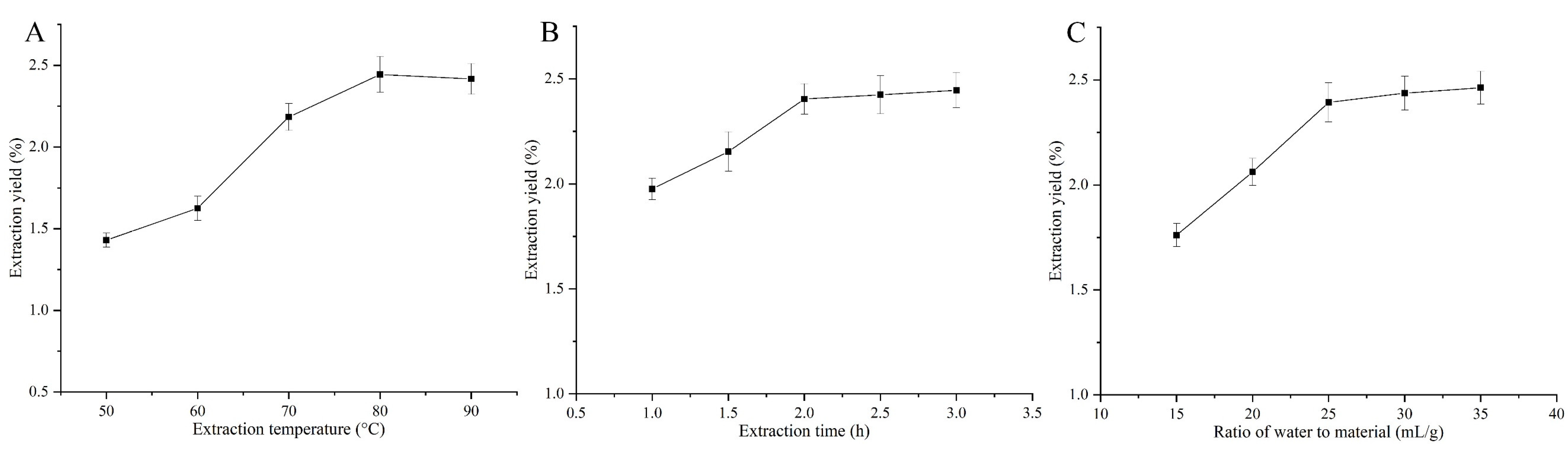
2.1. Effect of Single Factors on the Yield of ABPs
2.2. Optimization of Extraction Conditions for ABPs Using BBD
2.3. Structural Characteristics of ABPs
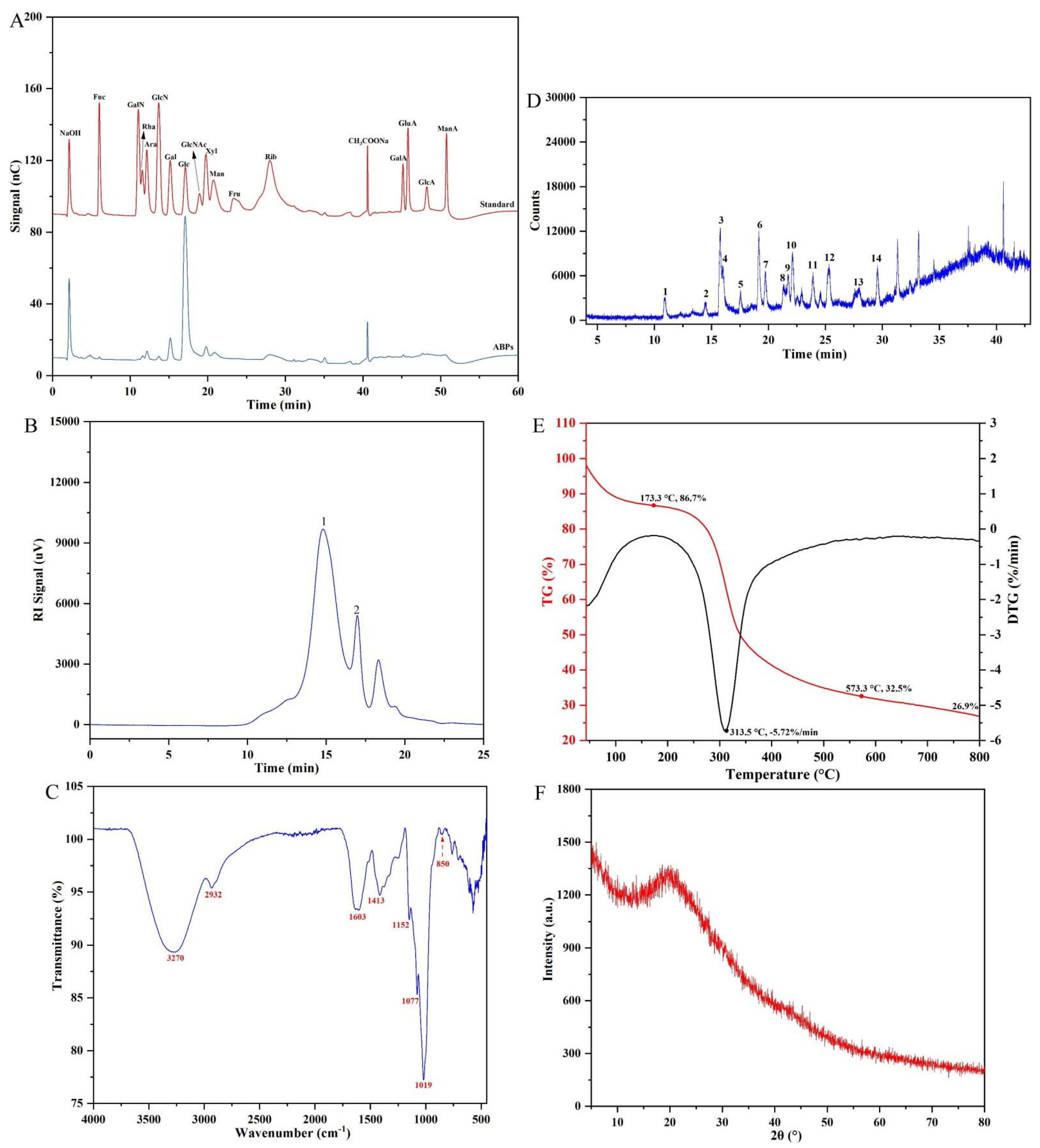
2.3.1. Chemical and Monosaccharide Composition and Analysis
2.3.2. Molecular Weight
2.3.3. FT-IR Spectrum
2.3.4. Methylation and GC–MS Analysis
2.3.5. Thermal Stability and Crystal Structure Analysis
2.3.6. SEM Analysis
2.3.7. AFM Analysis
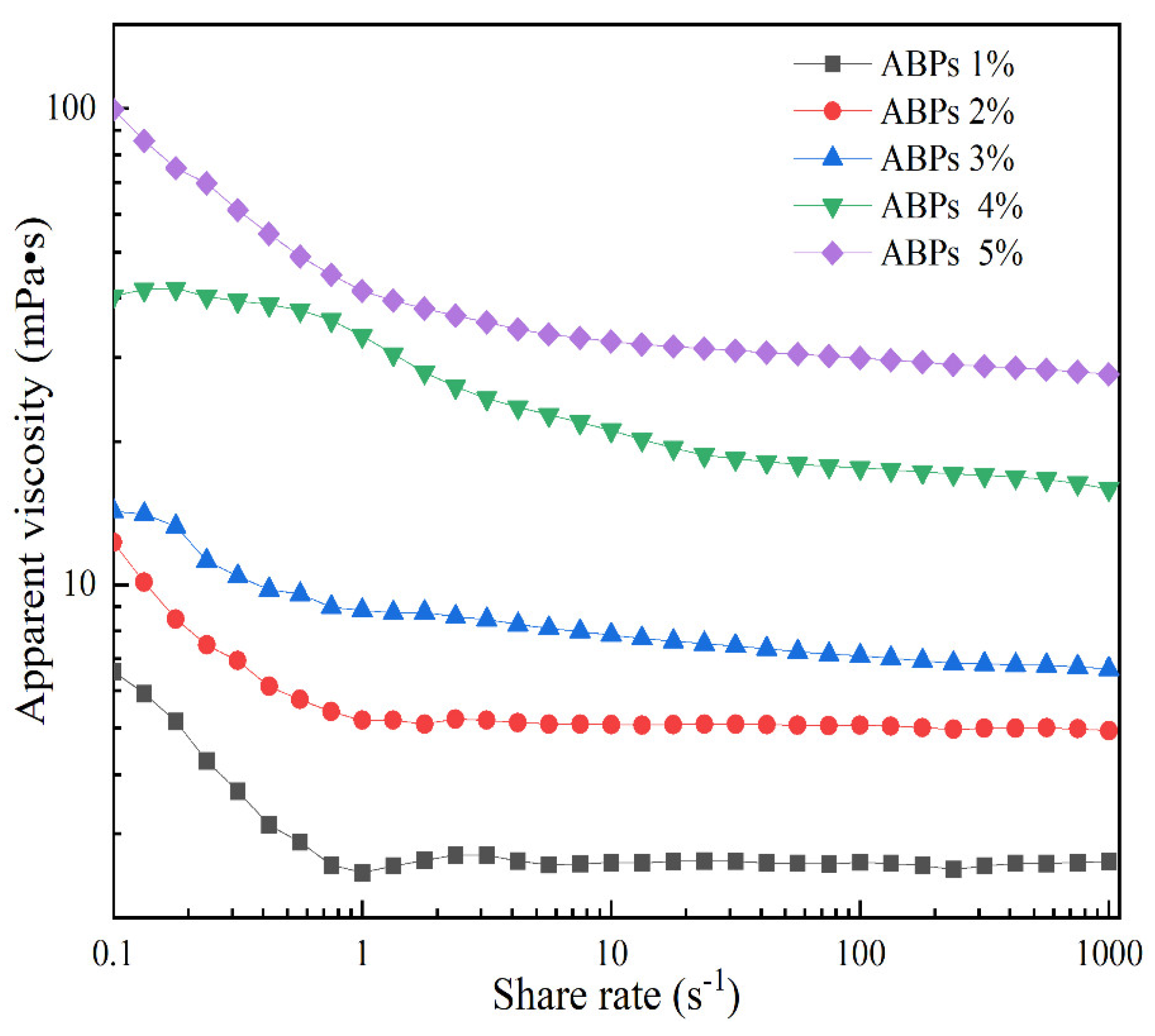
2.4. Rheological Properties
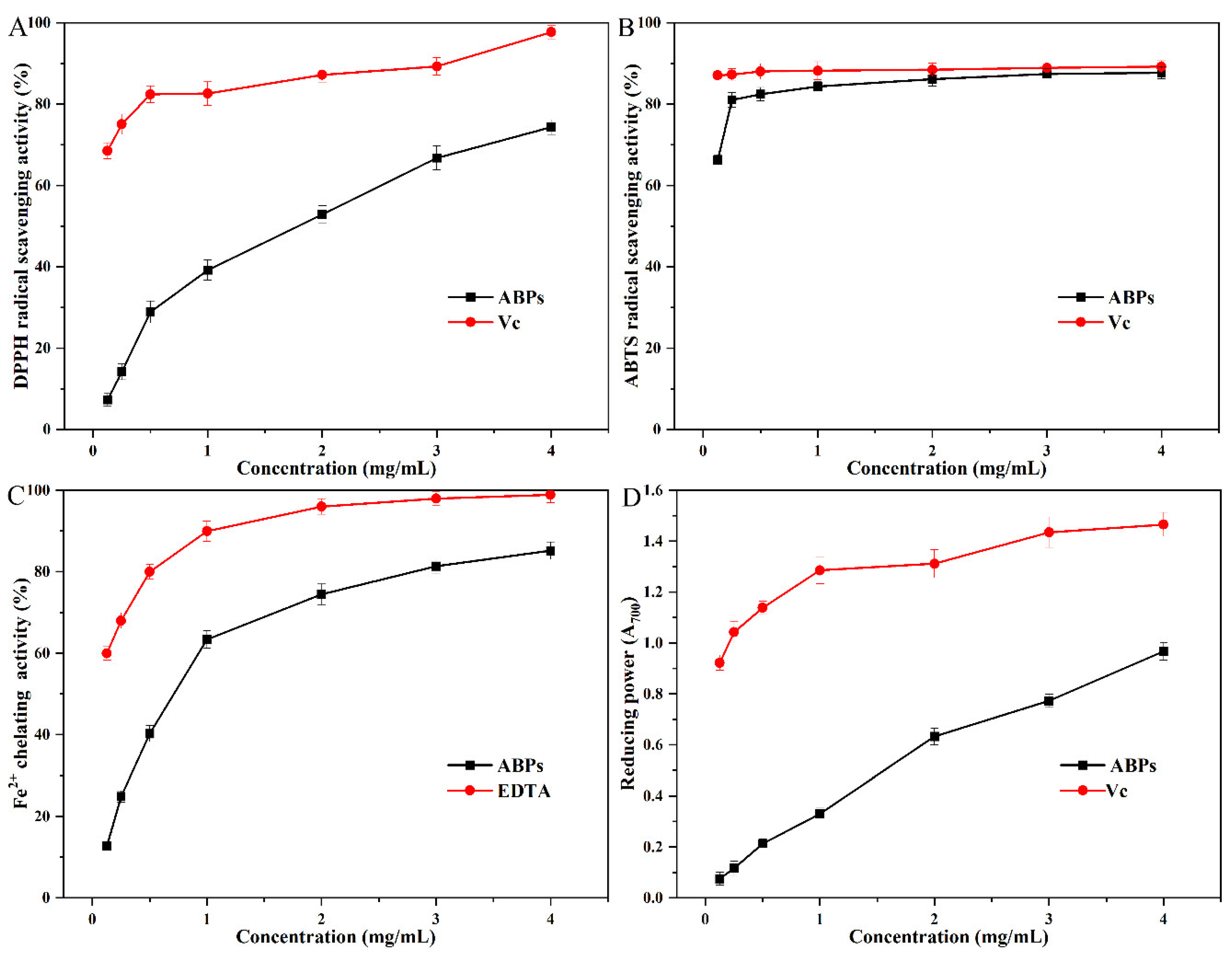
2.5. Antioxidant Activity of ABPs
2.6. α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitory Capacities of ABPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Hot Water Extraction Process of ABPs
3.3. Optimization via the Response Surface Methodology Test
3.4. Structural Characterization of ABPs
3.4.1. Chemical Composition and Molecular Weight Analysis
3.4.2. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
3.4.3. Methylation Analysis
3.4.4. FT-IR Analysis
3.4.5. Thermal Analysis
3.4.6. XRD Analysis
3.4.7. SEM Analysis
3.4.8. AFM Analysis
3.5. Rheological Measurement
3.6. Assay of Antioxidant Activity In Vitro of ABPs
3.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.3. Fe2+ Chelating Ability
3.6.4. Reducing Power
3.7. Assay of Hypoglycemic Activity In Vitro of ABPs
3.7.1. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
3.7.2. α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G. Comparative study on the impact of different extraction technologies on structural characteristics, physicochemical properties, and biological activities of polysaccharides from seedless chestnut rose (Rosa sterilis) fruit. Foods 2024, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Fan, H.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Xia, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, B. Chemical structure and immunomodulatory activity of a polysaccharide from Saposhnikoviae Radix. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; He, Z.; Yang, J.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, B.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Effect of structural features on the antitumor activity of plant and microbial polysaccharides: A review. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Dou, Z.M.; Duan, Q.F.; Chen, C.; Liu, R.H.; Jiang, Y.M.; Yang, B.; Fu, X. A comparison study on structure-function relationship of polysaccharides obtained from sea buckthorn berries using different methods: Antioxidant and bile acid-binding capacity. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.C.; Wu, L.B.; Li, L.Q.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, L.; Yan, J.K. Physicochemical, structural, and rheological characteristics of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.) peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, X.H.; Yang, K.; Sun, P.L.; Liao, X.J.; Cai, M. Rheological behaviors of ethanol-fractional polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale in aqueous solution: Effects of concentration, temperature, pH, and metal ions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Guo, J.; Cao, T.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y. Review on mechanisms and structure-activity relationship of hypoglycemic effects of polysaccharides from natural resources. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ren, W.; Li, G.; Yang, P.; Chen, R.; He, H. The effect of structure and preparation method on the bioactivity of polysaccharides from plants and fungi. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12541–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ni, C.; Yu, G.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, H. Understanding the mechanism of change in morphological structures, visualization features, and physicochemical characteristics of adlay seeds (Coix lacryma jobi L.): The role of heat soaking. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 91, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, R.D.; Jeepipalli, S.P.K.; Xu, B. Phytochemistry and health promoting effects of Job’s tears (Coix lacryma-jobi)—A critical review. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, C.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. The Differences of nutrient components in edible and feeding coix seed at different developmental stages based on a combined analysis of metabolomics. Molecules 2023, 28, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-J.; Shih, C.-K.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chiang, W. Mast cell-dependent allergic responses are inhibited by ethanolic extract of adlay (Coix lachrymal jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Testa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2596–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Hou, C.-l.; Rao, X.-h.; Zhang, A.-q.; Xiao, G.-m.; Wang, L.-y.; Jin, K.-n.; Sun, P.-l.; Chen, L.-C. In vitro fermentation characteristics of polysaccharides from coix seed and its effects on the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-C.; Hu, Y.-T.; Huang, Q.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Ting, Y. Development of a topical applied functional food formulation: Adlay bran oil nanoemulgel. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-W.; Wu, C.-H.; Shih, C.-K.; Liu, C.-Y.; Shih, P.-H.; Shieh, T.-M.; Lin, C.-I.; Chiang, W.; Hsia, S.-M. Application of the solvent extraction technique to investigation of the anti-inflammatory activity of adlay bran. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Kan, J.; Chen, G.; Du, M. Physicochemical, structure properties and in vitro hypoglycemic activity of soluble dietary fiber from adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) bran treated by steam explosion. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1124012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Tang, X.; Hegyi, F.; Nagy, A.; Takacs, K.; Zalan, Z.; Chen, G.; Du, M. In vitro digestion and fermentation characteristics of soluble dietary fiber from adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) bran modified by steam explosion. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, M. Identification of the free phenolic profile of Adlay bran by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and inhibitory mechanisms of phenolic acids against xanthine oxidase. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Chang, L.; Sun, P.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Total polysaccharides of adlay bran (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) improve TNF-α induced epithelial barrier dysfunction in Caco-2 cells via inhibition of the inflammatory response. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Dai, Q.; Hu, P.; Chen, G. Effects of Different drying methods on the structural characteristics and multiple bioactivities of Rosa roxburghii tratt fruit polysaccharides. Foods 2024, 13, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Chen, K.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Chen, X.L.; Hu, P.; Kan, J.Q. Polysaccharides from bamboo shoots processing by-products: New insight into extraction and characterization. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, C.N.; Ge, M.H.; Qian, Y.Y.; Ma, B.J. Physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from the peel of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. extracted by four different methods. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yan, C.; Jia, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhan, X.; Ma, C. Structural characterization of chia seed polysaccharides and evaluation of its immunomodulatory and antioxidant activities. Food Chem.-X 2023, 20, 101011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Li, Q. Structural diversity and physicochemical properties of polysaccharides isolated from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) by different methods. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, H.; Tian, L.; Sun, H.; Li, D.; Wu, W. Comparison in structural, physicochemical and functional properties of sweet potato stems and leaves polysaccharide conjugates from different technologies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.E.; Andrade, R.G.C.; Accardo, C.M.; Maia, L.F.; Oliveira, L.F.C.; Nader, H.B.; Aguiar, J.A.K.; Medeiros, V.P. Influence of sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva lactuca L. upon Xa and IIa coagulation factors and on venous blood clot formation. Algal Res. -Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2020, 45, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pu, Q.; Qiu, H.; Di, D. Polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. by integrated tandem hybrid membrane technology exert antioxidant activities in mitochondria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Qin, T.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Zeng, Q.; Shen, J. Removal of copper ions from water using polysaccharide-constructed hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cheung, P.C.-K.; You, L.; Liao, L.; Pedisic, S.; Kulikouskaya, V. Structural characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of UV/H2O2-treated algal sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, W. A glucomannogalactan from Pleurotus geesteranus: Structural characterization, chain conformation and immunological effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 287, 119346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-Y.; Liao, A.-M.; Huang, J.-H.; Zhang, J.-G.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.-J. The rheological properties of differentially extracted polysaccharides from potatoes peels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.; Roy, S.; Devra, A.; Dhiman, A.; Prabhakar, P.K. Ultrasonication of mayonnaise formulated with xanthan and guar gums: Rheological modeling, effects on optical properties and emulsion stability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Fu, X. Physicochemical, functional, and biological properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Hao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Cai, X.; Tang, J.; Liao, X.; Tan, J. Research progress on the hypoglycemic activity and mechanisms of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zheng, L.; Su, G.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Electrostatic interactions with anionic polysaccharides reduced the degradation of pepsin soluble undenatured type II collagen during gastric digestion under pH 2.0. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevag, M.G.; Lackman, D.B.; Smolens, J. The isolation of the components of streptococcal nucleoproteins in serologically active form. J. Biol. Chem. 1938, 124, 0425–0436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, S.; Steinhart, H.; Paschke, A. Comparison of different extraction solutions for the analysis of allergens in hen’s egg. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkr, N.; Asboehan, G. New method for quantitative-determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S.I. Rapid permethylation of glycolipid polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Pan, S. Effect of pulp cell wall polysaccharides on citrus fruit with different mastication traits. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.W.; Fan, L.P.; Gu, Z.H.; Shi, G.Y.; Ding, Z.Y. Rheological properties and thickening effect of high molecular weight exopolysaccharide and intracellular polysaccharide from Schizophyllum commune. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Fang, C.C.; Ran, C.X.; Tan, Y.; Yu, Q.Q.; Kan, J.Q. Comparison of different extraction methods for polysaccharides from bamboo shoots (Chimonobambusa quadrangularis) processing by-products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, M.; Liu, M.; Bi, J. Physicochemical, rheological properties and in vitro hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharide fractions from peach gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Std. Order | X1 (Extraction Temperature, °C) | X2 (Extraction Time, h) | X3 (Ratio of Water to Raw Material, mL/g) | Extraction Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 (70) | −1 (2) | 0 (30) | 1.61 |
| 2 | 1 (90) | −1 (2) | 0 (30) | 1.82 |
| 3 | −1 (70) | 1 (3) | 0 (30) | 1.75 |
| 4 | 1 (90) | 1 (3) | 0 (30) | 1.72 |
| 5 | −1 (70) | 0 (2.5) | −1 (25) | 1.69 |
| 6 | 1 (90) | 0 (2.5) | −1 (25) | 1.91 |
| 7 | −1 (70) | 0 (2.5) | 1 (35) | 2.05 |
| 8 | 1 (90) | 0 (2.5) | 1 (35) | 1.93 |
| 9 | 0 (80) | −1 (2) | −1 (25) | 2.23 |
| 10 | 0 (80) | 1 (3) | −1 (25) | 1.80 |
| 11 | 0 (80) | −1 (2) | 1 (35) | 1.98 |
| 12 | 0 (80) | 1 (3) | 1 (35) | 2.30 |
| 13 | 0 (80) | 0 (2.5) | 0 (30) | 2.55 |
| 14 | 0 (80) | 0 (2.5) | 0 (30) | 2.56 |
| 15 | 0 (80) | 0 (2.5) | 0 (30) | 2.54 |
| 16 | 0 (80) | 0 (2.5) | 0 (30) | 2.51 |
| 17 | 0 (80) | 0 (2.5) | 0 (30) | 2.55 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1.95 | 9 | 0.2168 | 210.61 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| X1 | 0.0098 | 1 | 0.0098 | 9.52 | 0.0177 | Significant |
| X2 | 0.0006 | 1 | 0.0006 | 0.5951 | 0.4657 | |
| X3 | 0.0496 | 1 | 0.0496 | 48.20 | 0.0002 | Significant |
| X1X2 | 0.0144 | 1 | 0.0144 | 13.99 | 0.0073 | Significant |
| X1X3 | 0.0289 | 1 | 0.0289 | 28.08 | 0.0011 | Significant |
| X2X3 | 0.1406 | 1 | 0.1406 | 136.62 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| X12 | 1.05 | 1 | 1.05 | 1021.66 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| X22 | 0.4238 | 1 | 0.4238 | 411.72 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| X32 | 0.0913 | 1 | 0.0913 | 88.70 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Residual | 0.0072 | 7 | 0.0010 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.0057 | 3 | 0.0019 | 5.16 | 0.0735 | Not significant |
| Pure Error | 0.0015 | 4 | 0.0004 | |||
| Std. Dev. | 0.0321 | |||||
| Mean | 2.09 | |||||
| R2 | 0.9963 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9916 | |||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.9520 | |||||
| C.V. % | 1.54 |
| Chemical Composition (%, g/g) | ABPs |
|---|---|
| Neutral sugar | 84.12 ± 1.55 |
| Protein | 2.32 ± 0.43 |
| Uronic acid | 3.03 ± 0.37 |
| Monosaccharide composition (molar%) | |
| Rha | 2.12 ± 0.04 |
| Ara | 2.40 ± 0.08 |
| GlcN | 0.52 ± 0.01 |
| Gal | 7.94 ± 0.23 |
| Glc | 77.12 ± 1.47 |
| Xyl | 3.51 ± 0.67 |
| Man | 2.55 ± 0.59 |
| GlcA | 3.82 ± 0.44 |
| Molecular weight | |
| Peak 1 (kDa) | 12.88 ± 1.55 |
| Peak 2 (kDa) | 2.31 ± 0.17 |
| RT (min) | Methylated Alditol Acetate | Major Mass Fragments (m/z) | Molar Ratio (%) | Type of Linkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.506 | 2-Me1-Rha | 43, 87, 99, 113, 117, 129, 141, 159, 173 | 3.52 | →3,4)-Rhap-(1→ |
| 15.761 | 2,3,6-Me3-Glc | 43, 87, 99, 101, 113, 117, 129, 131, 161, 173, 233 | 25.64 | →4)-Glcp-(1→ |
| 15.99 | 2,3,4,6-Me4-Glc | 43, 71, 87, 101, 117, 129, 145, 161, 205 | 9.70 | Glcp-(1→ |
| 19.163 | 2,6-Me2-Glc | 43, 87, 97, 117, 159, 185 | 19.11 | →3,4)-Glcp-(1→ |
| 19.755 | 2,3-Me2-Xyl | 43, 71, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 189 | 7.05 | →4)-Xylp-(1→ |
| 22.114 | 2,4,6-Me3-Glc | 43, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 173, 233 | 13.23 | →3)-Glcp-(1→ |
| 23.911 | 2,6-Me2-Gal | 43, 87, 99, 117, 129, 143, 159 | 9.26 | →3,4)-Galp-(1→ |
| 25.341 | 2,3-Me2-Glc | 59, 102, 118, 142, 201, 231, 261 | 12.49 | →4,6)-Gclp-(1→ |
| ABPs (mg/mL) | Cross Model Fitting Parameters | Carreau Model Fitting Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (s) | d | η0 (Pa·s) | η∞ (Pa·s) | R2 | c (s) | p | η0 (Pa·s) | η∞ (Pa·s) | R2 | |
| 10 | 4.1190 | 0.7669 | 0.0074 | 0.0026 | 0.9875 | 34.1964 | 0.0469 | 0.0127 | 0.0025 | 0.9811 |
| 20 | 4.7690 | 0.5646 | 3.8333 | 0.0047 | 0.9833 | 31.6451 | 0.1338 | 0.0143 | 0.0046 | 0.9804 |
| 30 | 5.0450 | 0.5276 | 9.2999 | 0.0069 | 0.9885 | 18.3896 | 0.4247 | 0.0273 | 0.0068 | 0.9821 |
| 40 | 6.0632 | 0.4810 | 9.6951 | 0.0138 | 0.9987 | 1.2686 | 0.7399 | 0.0156 | 0.0122 | 0.9931 |
| 50 | 16.6411 | 0.2868 | 21.2648 | 0.0294 | 0.9986 | 0.0001 | 0.7861 | 0.1580 | 0.0216 | 0.9950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, P.; Chen, G. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Adlay Bran. Molecules 2024, 29, 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194707
Hu P, Chen G. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Adlay Bran. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194707
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Peng, and Guangjing Chen. 2024. "Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Adlay Bran" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194707
APA StyleHu, P., & Chen, G. (2024). Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Adlay Bran. Molecules, 29(19), 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194707





