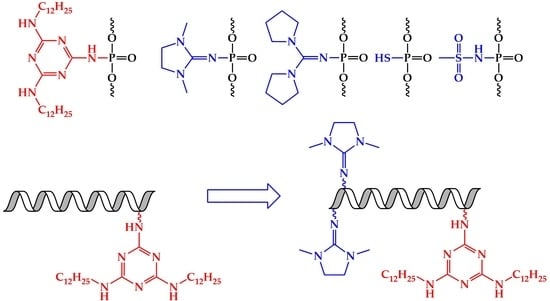
Influence of Combinations of Lipophilic and Phosphate Backbone Modifications on Cellular Uptake of Modified Oligonucleotides
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zharkov, T.D.; Markov, O.V.; Zhukov, S.A.; Khodyreva, S.N.; Kupryushkin, M.S. Influence of Combinations of Lipophilic and Phosphate Backbone Modifications on Cellular Uptake of Modified Oligonucleotides. Molecules 2024, 29, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020452
Zharkov TD, Markov OV, Zhukov SA, Khodyreva SN, Kupryushkin MS. Influence of Combinations of Lipophilic and Phosphate Backbone Modifications on Cellular Uptake of Modified Oligonucleotides. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020452
Chicago/Turabian StyleZharkov, Timofey D., Oleg V. Markov, Sergey A. Zhukov, Svetlana N. Khodyreva, and Maxim S. Kupryushkin. 2024. "Influence of Combinations of Lipophilic and Phosphate Backbone Modifications on Cellular Uptake of Modified Oligonucleotides" Molecules 29, no. 2: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020452
APA StyleZharkov, T. D., Markov, O. V., Zhukov, S. A., Khodyreva, S. N., & Kupryushkin, M. S. (2024). Influence of Combinations of Lipophilic and Phosphate Backbone Modifications on Cellular Uptake of Modified Oligonucleotides. Molecules, 29(2), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020452