One-Pot Synthesis and Surfactant Removal from MCM-41 Using Microwave Irradiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
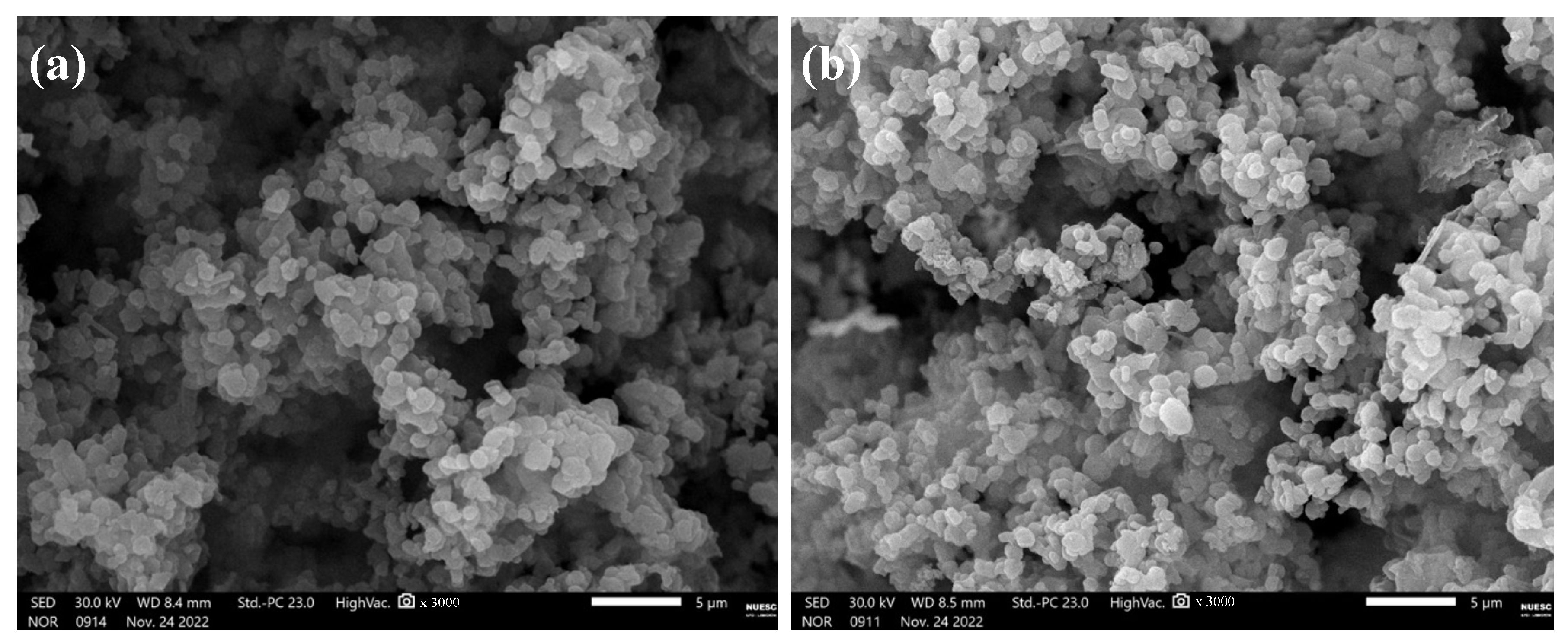
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. One-Pot Synthesis and Removal of CTAB Surfactant from Ordered Mesoporous Silica MCM-41 Assisted by Microwave Irradiation
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; Mccullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Uriostegui, L.; Melendez-Ortiz, H.I.; Mata-Padilla, J.M.; Toriz, G. Fast fabrication of mesostructured MCM-41-type nanoparticles by microwave-induced synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 28693–28701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric surfactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.L.; Shu, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, W.N.; Wang, C.B. Rapid removal of organic template from SBA-15 with microwave assisted extraction. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, J.H.; Kaw, S.; Goh, A.H. Organic template removal from hexagonal mesoporous silica by means of methanol-enhanced CO2 extraction: Effect of temperature, pressure and flow rate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 77, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirez, C.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. An energy-efficient route to the rapid synthesis of organically-modified SBA-15 via ultrasonic template removal. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deekamwong, K.; Wittayakun, J. Template removal by ion-exchange extraction from siliceous MCM-41 synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2017, 239, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Conto, J.F.; Oliveira, M.R.; Oliveira, R.J.; Campos, K.V.; De Menezes, E.W.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Franceschi, E.; Santana, C.C.; Egues, S.M. Synthesis of silica modified with 1-methylimidazolium chloride by sol-gel method: A comparison between microwave radiation-assisted and conventional methods. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 471, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Deon, M.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Barros, V.A.; Melo, D.C.; Franceschi, E.; Egues, S.M.; De Conto, J.F. Effect of microwave irradiation on the structural, chemical, and hydrophilicity characteristics of ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 94, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabariyan, S.; Zanjanchi, A. A simple and fast sonication procedure to remove surfactant templates from mesoporous MCM-41. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Qi, G.S. Microwave synthesis of MCM-41 and its application in CO2 absorption by nanofluids. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 6187656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Cecília, J.A.; De Conto, J.F.; Egues, S.M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Rapid synthesis of MCM-41 and SBA-15 by microwave irradiation: Promising adsorbents for CO2 adsorption. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 105, 370–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazula, B.B.; Oliveira, L.G.; Machado, B.; Alves, H.J. Optimization of experimental conditions for the synthesis of Si-MCM-41 molecular sieves using different methods and silica sources. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Timmiati, S.N. Microwave-assisted synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle. Malaysian J. Anal. Sci. 2016, 20, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaignon, J.; Bouizi, Y.; Davin, L.; Calin, N.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L. Minute-made and low carbon fingerprint microwave synthesis of high quality templated mesoporous silica. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3130–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priecel, P.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A. Advantages and limitations of microwave reactors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, P.M.; Goldani, B.S.; Alves, D.; Sathicq, A.G.; Eimer, G.A.; Romanelli, G.P.; Luque, R. Stability and activity of Zn/MCM-41 materials in toluene alkylation: Microwave irradiation vs continuous flow. Catalysts 2019, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachemaoui, M.; Molina, C.B.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Mokhtar, A.; Hamacha, R.; Boukoussa, B. Metal-loaded mesoporous MCM-41 for the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation (CWPO) of acetaminophen. Catalysts 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-López, S.L.; Montes-Morán, M.A.; Arenillas, A. Carbon/silica hybrid aerogels with controlled porosity by a quick one-pot synthesis. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 569, 120992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, W.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Shan, W.; Xiong, Y. Microwave-assisted one-pot rapid synthesis of mesoporous silica-chitosan composites for efficient recovery of rhenium (VII). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukoussa, B.; Kibou, Z.; Abid, Z.; Ouargli, R.; Choukchou-Braham, N.; Villemin, D.; Bengueddach, A.; Hamacha, R. Key factor affecting the basicity of mesoporous silicas MCM-41: Effect of surfactant extraction time and Si/Al ratio. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bein, T. Microwave synthesis of molecular sieve MCM-41. Chem. Commun. 1996, 8, 925–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.S.B.; Barros, T.R.B.; Barbosa, T.L.A.; Rodrigues, M.G.F. Green synthesis for MCM-41 and SBA-15 silica using the waste mother liquor. Silicon 2022, 14, 6233–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yin, H. Effect of Ni-doping on the pore structure of pure silica MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve under microwave irradiation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 315, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y. Pot economy and one-pot synthesis. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
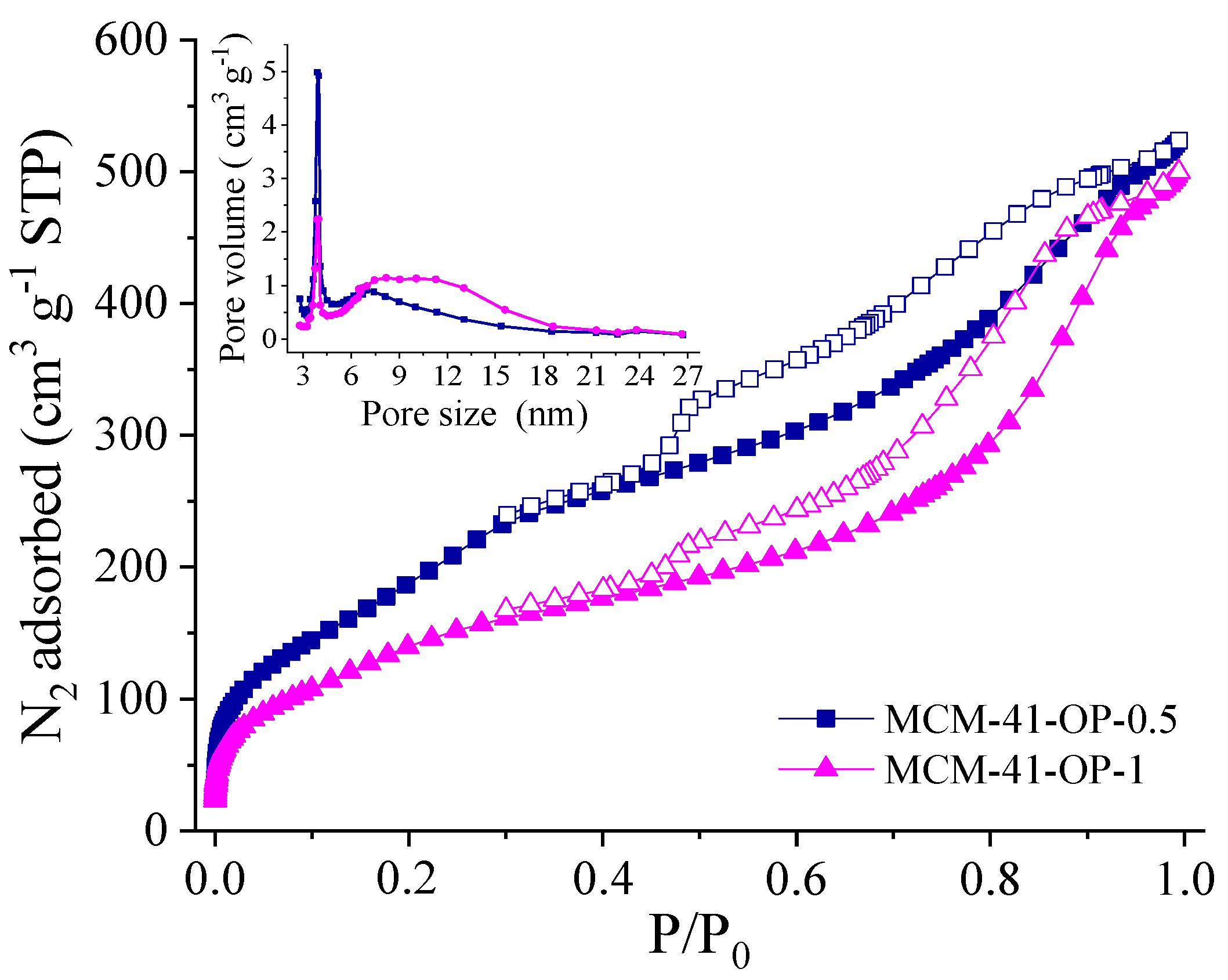
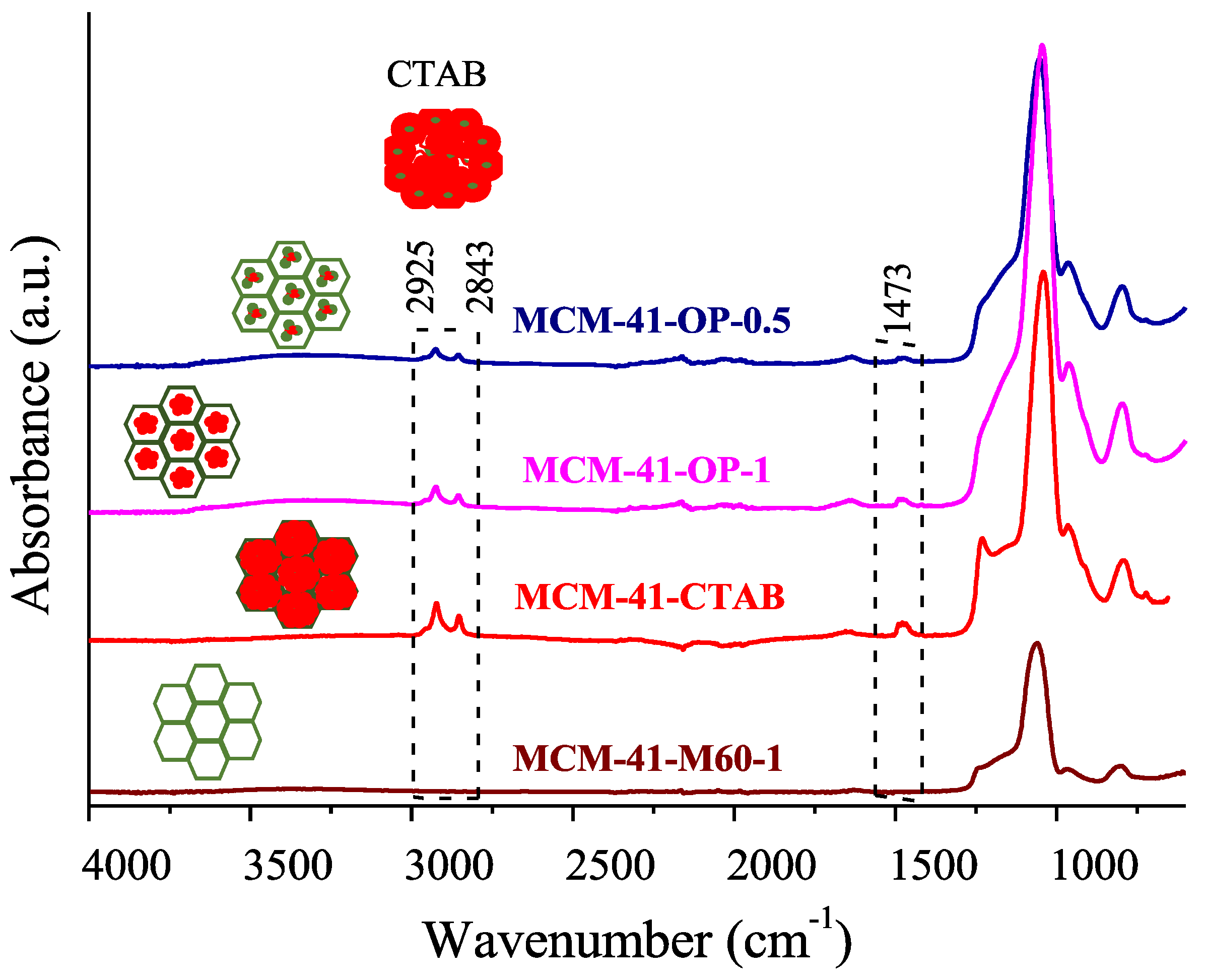
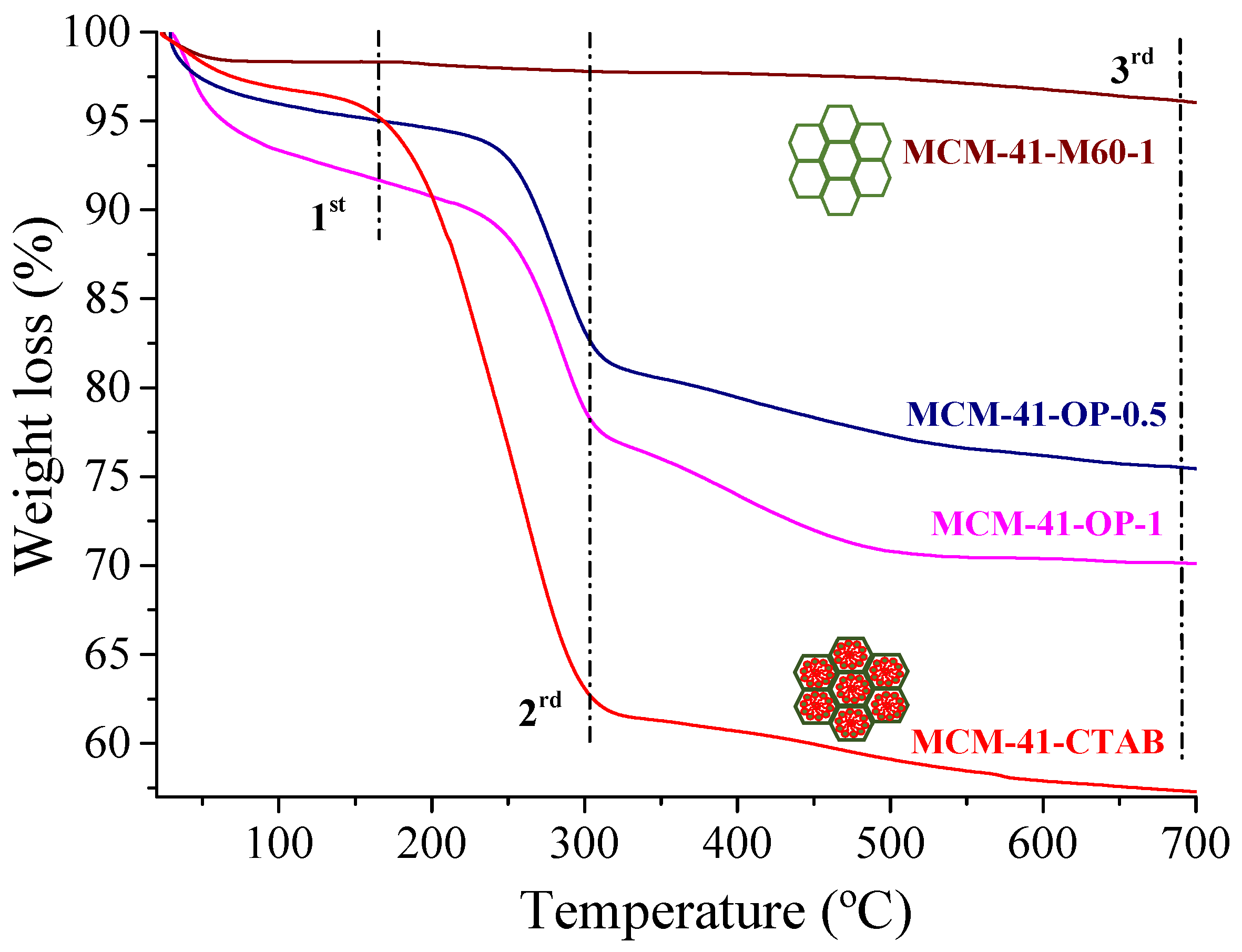

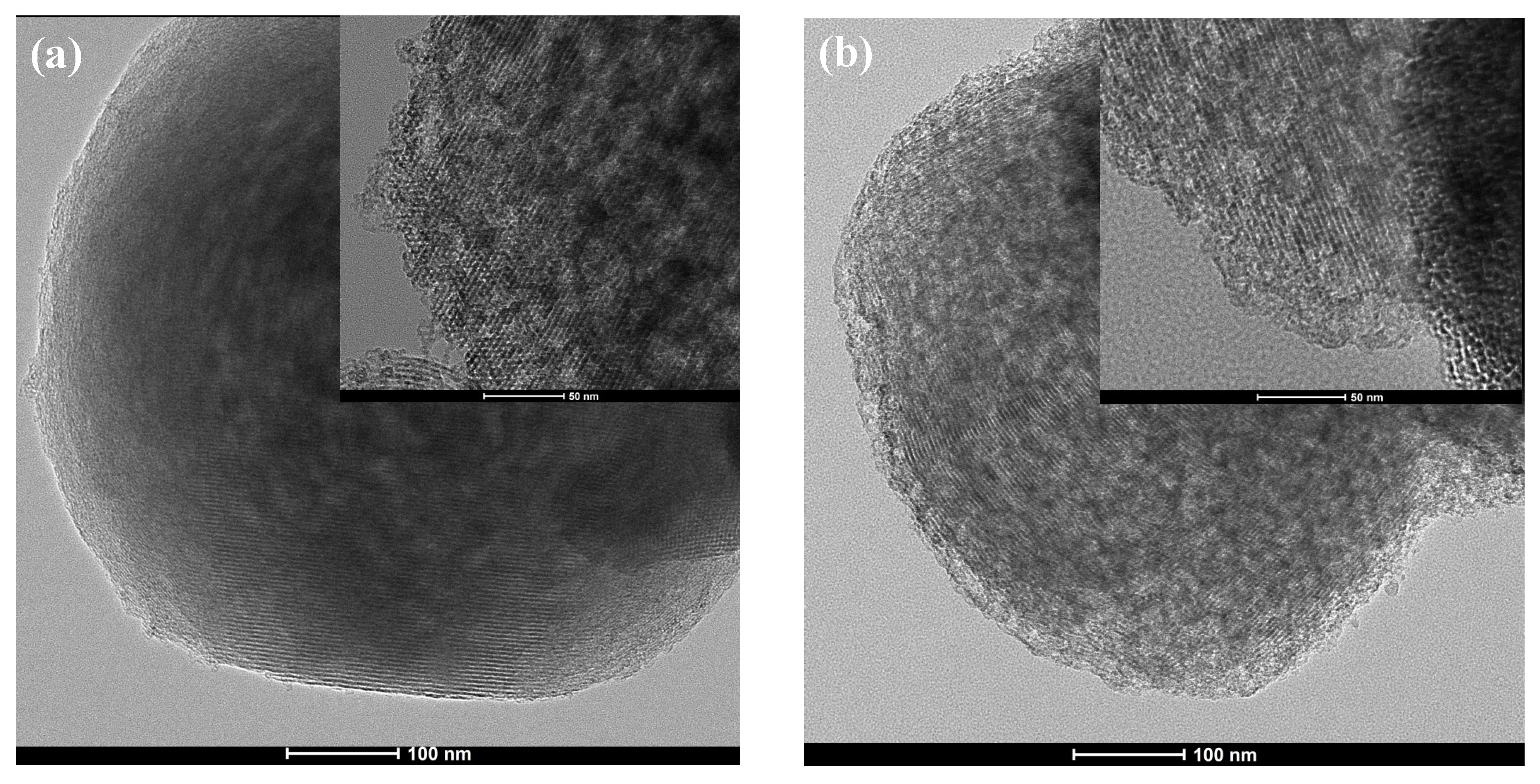


| Samples | N2 Adsorption/Desorption | CHN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET | Vp | Vmp t-plot | Dp | a0 | C | H | N | |
| (m2 g−1) | (cm3 g−1) | (cm3 g−1) | (nm) | (nm) | % | % | % | |
| MCM-41-OP-0.5 | 760 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 4.04 | 4.54 | 14.1 | 3.2 | 0.7 |
| MCM-41-OP-1 | 537 | 0.72 | 0.05 | 5.40 | 4.73 | 15.2 | 3.4 | 0.8 |
| ABET (m2 g−1) | Vp (cm3 g−1) | Hydrothermal Treatment | CTAB Removal | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1182 | 1.11 | Domestic MW: 10 min—80 °C | Muffle furnace: 550 °C—4 h | [2] |
| 1138 | - | MW MARs 6: 90 min—100 °C | Muffle furnace: 550 °C—6 h | [7] |
| 740 | 0.26 | Conventional: 120 min—25 °C | Stirred in ethanol: 25 °C—15 min | [10] |
| 1210 | - | MW CEM: 15 min—100 °C | Muffle furnace: 500 °C—5 h | [11] |
| 999 | 0.89 | MW CEM: 60 min—60 °C | Muffle furnace: 550 °C—6 h | [13] |
| 744 | 0.84 | MW CEM: 60 min—80 °C | Muffle furnace: 550 °C—6 h | |
| 575 | 0.76 | Conventional: 12,100 min—30 °C | Muffle furnace: 520 °C—6 h | [14] |
| 774 | 0.55 | Domestic MW: 150 min—100 °C | Muffle furnace: 550 °C—10 h | [25] |
| 536 | 0.72 | MW CEM: 60 min—60 °C | MW CEM: 6 min—120 °C | This work |
| 760 | 0.77 | MW CEM: 30 min—60 °C | MW CEM: 6 min—120 °C | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.R.; Barboza, Y.T.; Silva, T.S.L.; Cecilia, J.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Egues, S.M.; De Conto, J.F. One-Pot Synthesis and Surfactant Removal from MCM-41 Using Microwave Irradiation. Molecules 2024, 29, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020460
Oliveira MR, Barboza YT, Silva TSL, Cecilia JA, Rodríguez-Castellón E, Egues SM, De Conto JF. One-Pot Synthesis and Surfactant Removal from MCM-41 Using Microwave Irradiation. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020460
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Marília R., Yasmin T. Barboza, Thauane S. L. Silva, Juan A. Cecilia, Enrique Rodríguez-Castellón, Silvia M. Egues, and Juliana F. De Conto. 2024. "One-Pot Synthesis and Surfactant Removal from MCM-41 Using Microwave Irradiation" Molecules 29, no. 2: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020460
APA StyleOliveira, M. R., Barboza, Y. T., Silva, T. S. L., Cecilia, J. A., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Egues, S. M., & De Conto, J. F. (2024). One-Pot Synthesis and Surfactant Removal from MCM-41 Using Microwave Irradiation. Molecules, 29(2), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020460








