Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Substituted Aniline Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Dual Mer/c-Met Inhibitors
Abstract
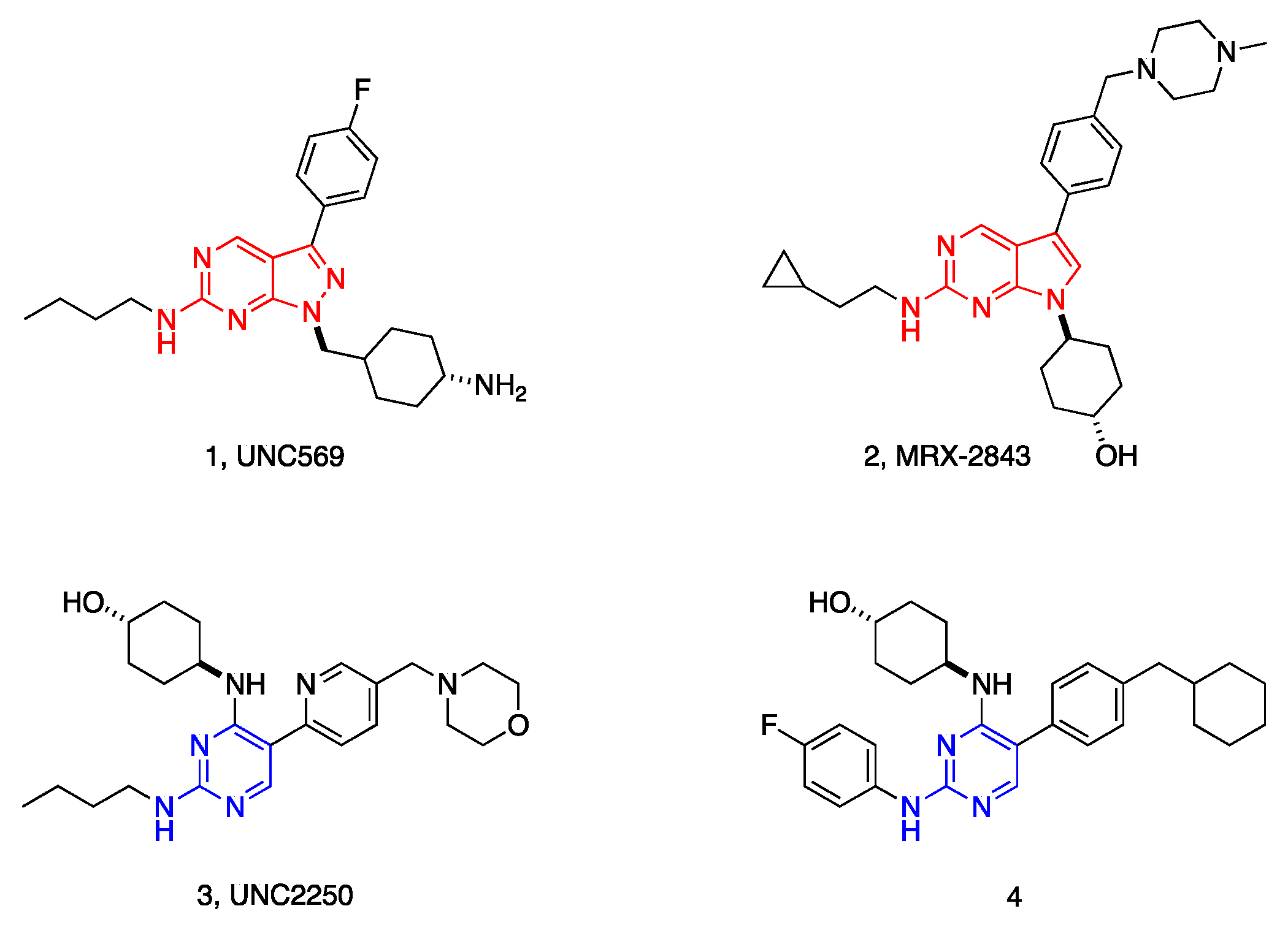
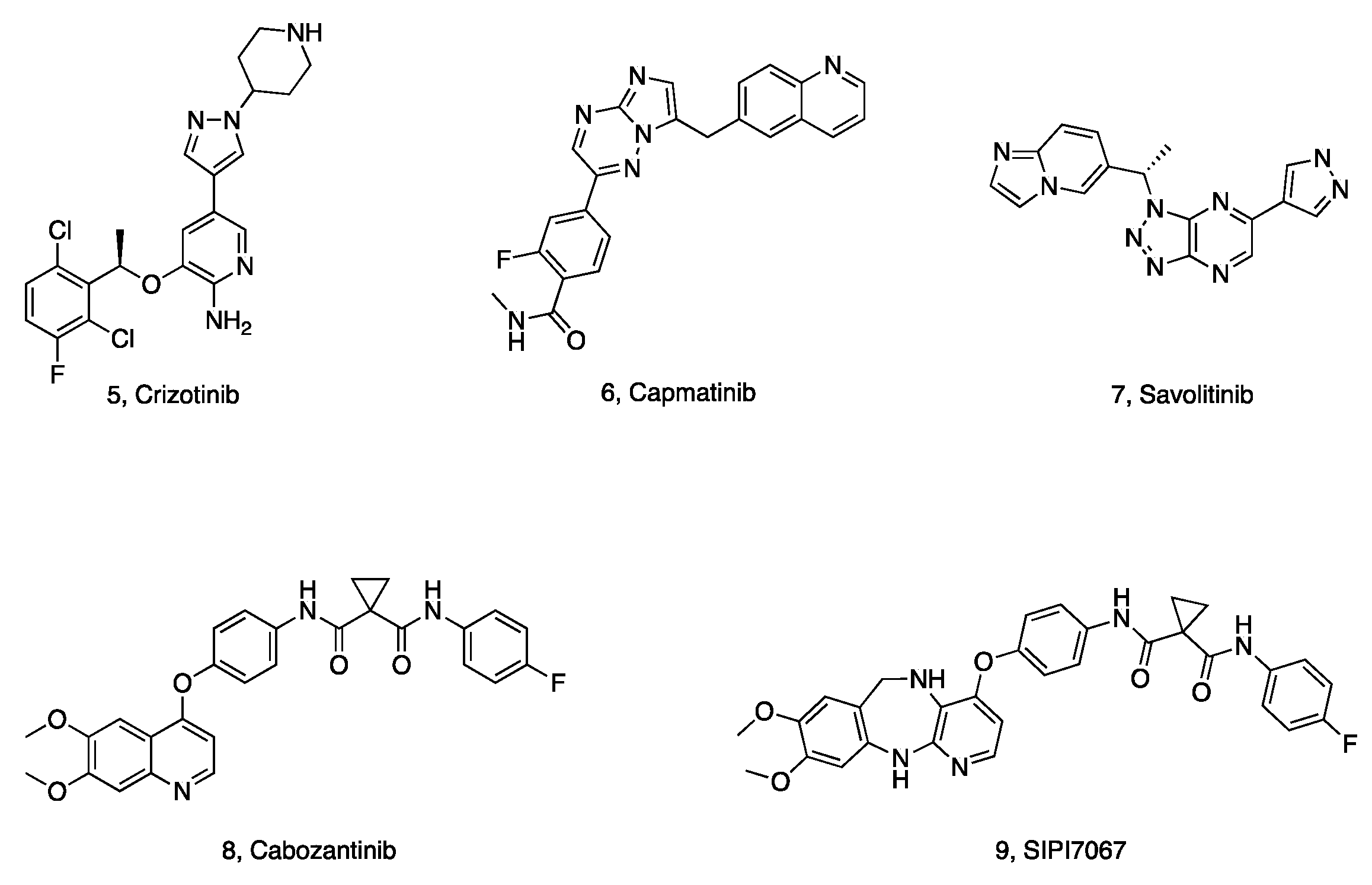
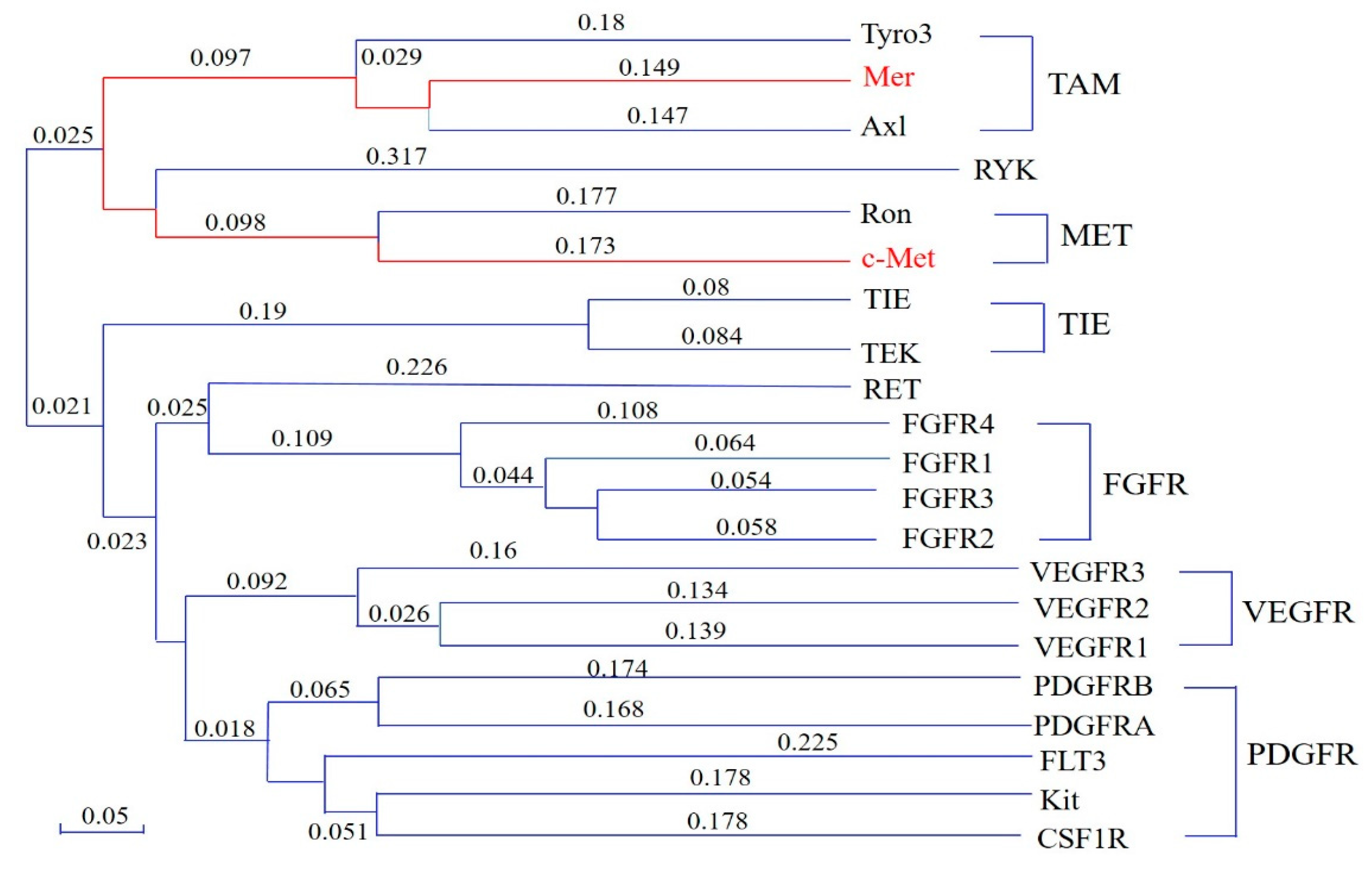
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
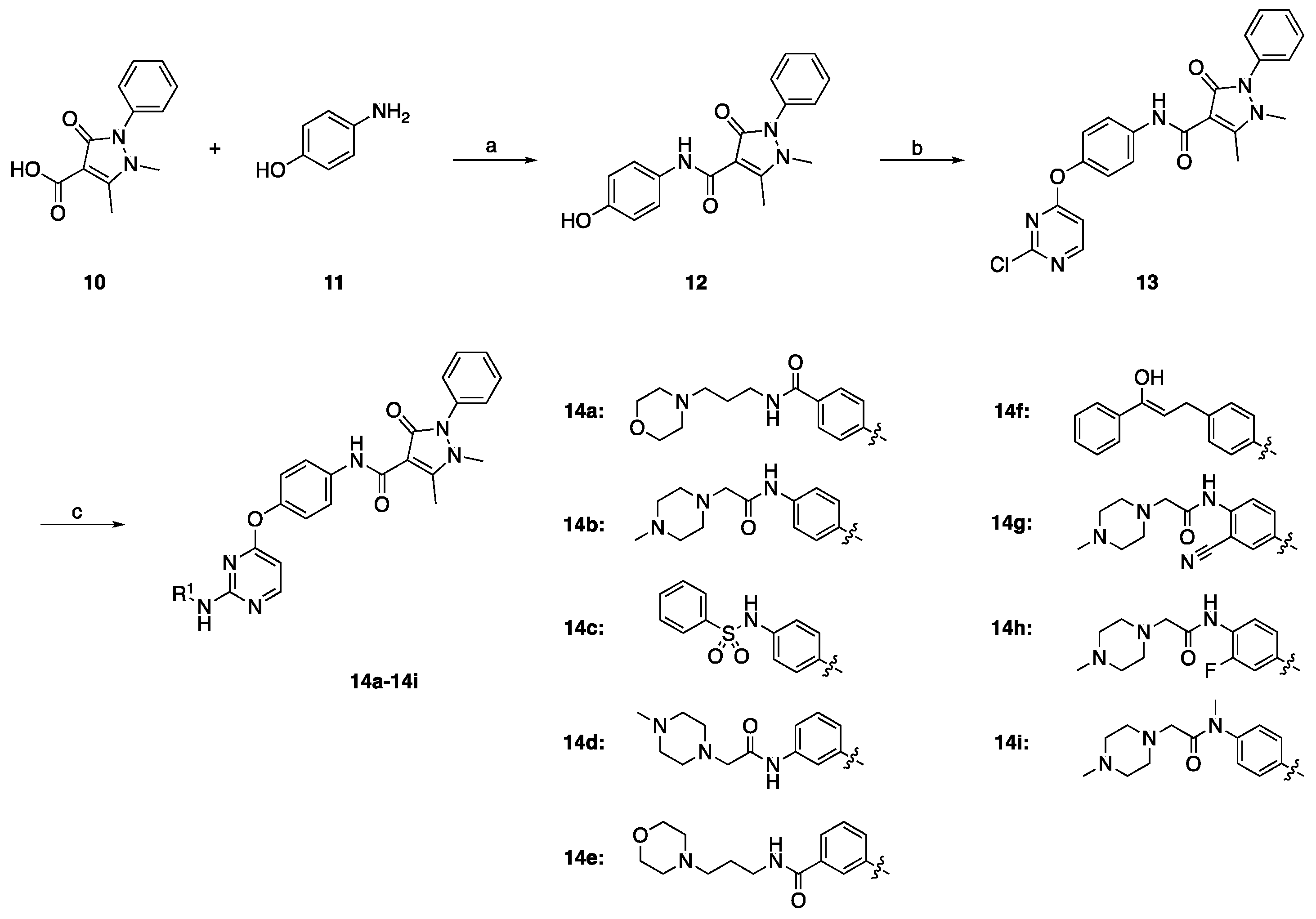
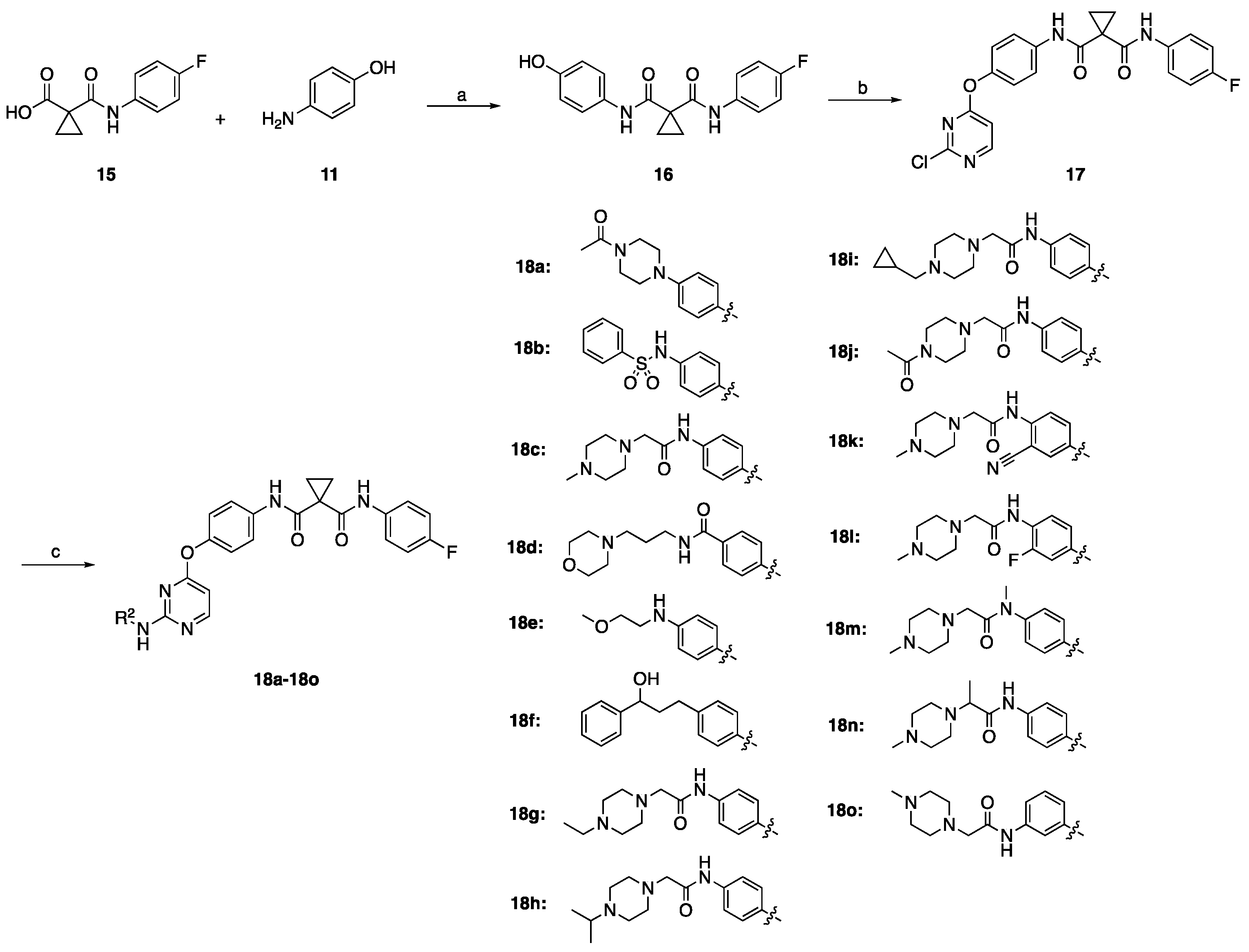
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Kinase Inhibitory Activities
2.3. In Vitro Liver Microsomal Stability
2.4. Antiproliferation Assay In Vitro
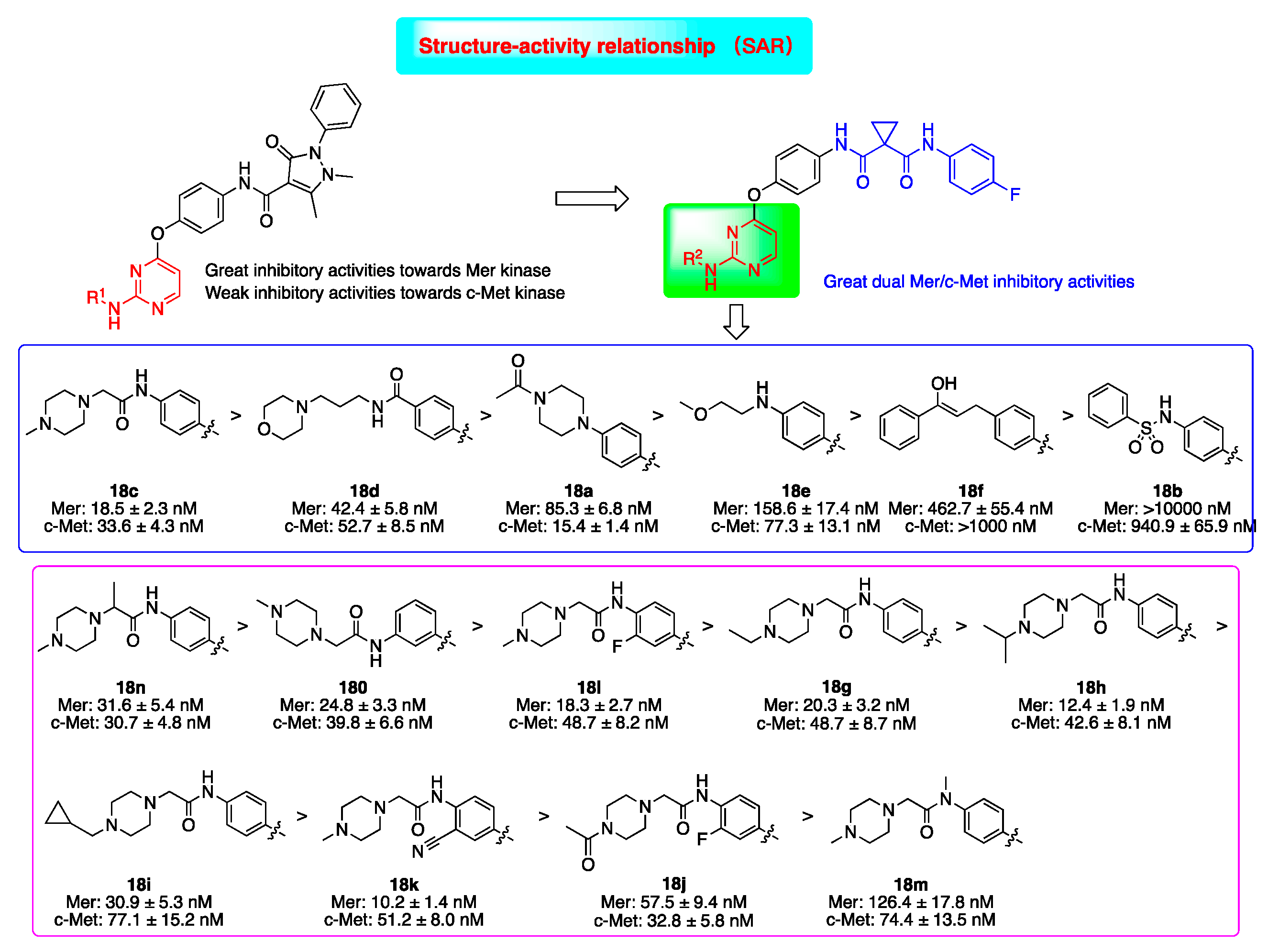
2.5. Preliminary SAR Analysis
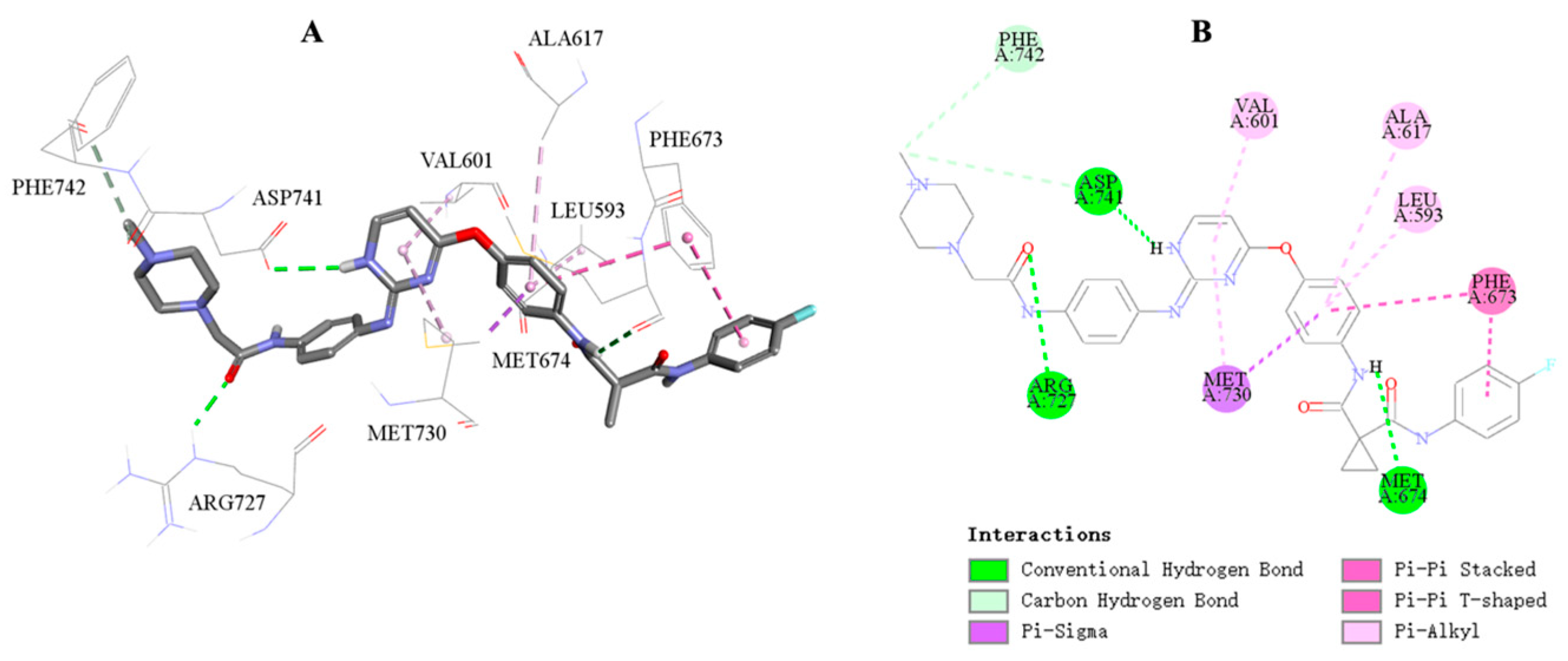
2.6. Molecular Docking Study of Compound 18c
2.7. The hERG Tests
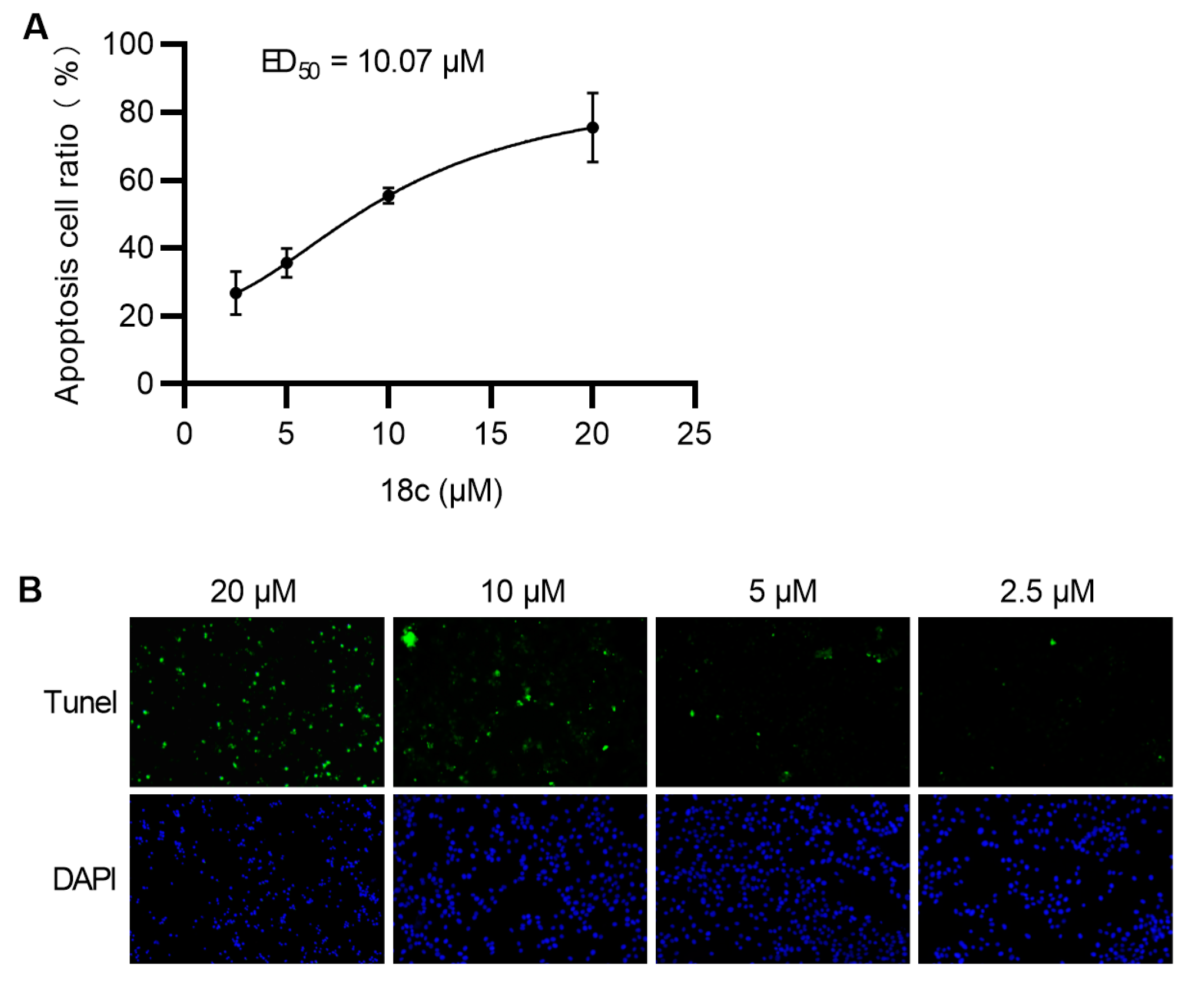
2.8. Apoptosis Assay
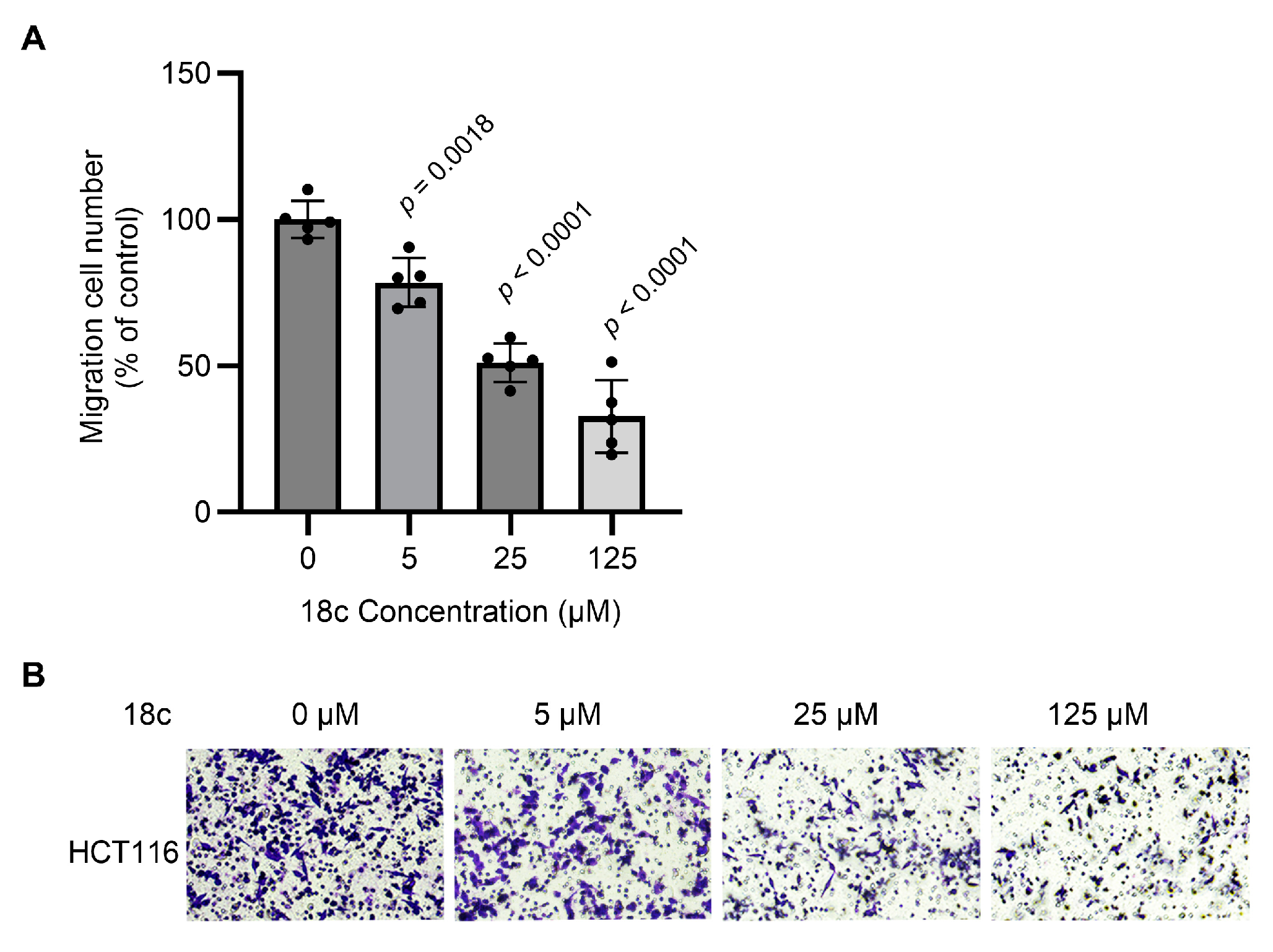
2.9. Transwell Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Part
3.1.1. Preparation of N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (Intermediate 12)
3.1.2. Preparation of N-(4-((2-Chloropyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (Intermediate 13)
3.1.3. General Procedure for Preparation of Compound 14a–14i
3.1.4. Preparation of N-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide (Intermediate 16)
3.1.5. Preparation of N-(4-((2-Chloropyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide (Intermediate 17)
3.1.6. General Procedure for Preparation of the Title Compounds 18a–18o
3.2. Mer and c-Met Inhibitory Activity Assay
3.3. Antiproliferation Assay
3.4. hERG Potassium Currents Assay
3.5. Liver Microsome Stability Assay
3.6. Apoptosis Study
3.7. Transwell Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, L.; He, C.; Yang, A.; Zhou, H.; Lu, Q.; Birge, R.B.; Wu, Y. Receptor tyrosine kinases Tyro3, Axl, and Mertk differentially contribute to antibody-induced arthritis. Cell. Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, C.K.V.; de Groot, A.E.; Mendez, S.A.; Mallin, M.M.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting MerTK decreases efferocytosis and increases anti-tumor immune infiltrate in prostate cancer. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Migdall-Wilson, J.; Middleton, D.H.; Lu, X.; Barón, A.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Merrick, D.T.; et al. Mer or Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes apoptosis, blocks growth and enhances chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.X.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.Y.; Yang, X.S.; He, J.X.; Tang, X.X. Elevated expression of macrophage MERTK exhibits profibrotic effects and results in defective regulation of efferocytosis function in pulmonary fibrosis. Resp. Res. 2023, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, J.; Sambade, M.J.; Sather, S.; Moschos, S.J.; Tan, A.C.; Winges, A.; DeRyckere, D.; Carson, C.C.; Trembath, D.G.; Tentler, J.J.; et al. MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase is a therapeutic target in melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayama, A.; Okado, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Samata, N.; Imaoka, M.; Kai, K.; Mori, K. The impact of the timing of dosing on the severity of UNC569-induced ultrastructural changes in the mouse retina. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 48, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, Y.; Itoh, M.; Tohda, S. Effects of MERTK inhibitors UNC569 and UNC1062 on the growth of acute myeloid Leukaemia cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeRyckere, D.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Hill, A.A.; Tyner, J.W.; Jacobsen, K.M.; Page, L.S.; Kirkpatrick, G.G.; Eryildiz, F.; Montgomery, S.A.; et al. UNC2025, a MERTK small-molecule inhibitor, is therapeutically effective alone and in combination with methotrexate in leukemia models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Huelse, J.M.; Kireev, D.; Tan, Z.; Chen, L.; Goyal, S.; Wang, X.; Frye, S.V.; Behera, M.; Schneider, F.; et al. MERTK activation drives osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e150517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; DeRyckere, D.; Hunter, D.; Liu, J.; Stashko, M.A.; Minson, K.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Lee, M.; Glaros, T.G.; Newton, D.L.; et al. UNC2025, a potent and orally bioavailable MER/FLT3 dual inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7031–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchford, B.R.; Stalker, T.J.; Law, L.; Acevedo, G.; Sather, S.; Brzezinski, C.; Wilson, K.M.; Minson, K.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Davizon-Castillo, P.; et al. The small-molecule MERTK inhibitor UNC2025 decreases platelet activation and prevents thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Jacobsen, K.M.; Henry, C.J.; Huey, M.G.; Parker, R.E.; Page, L.S.; Hill, A.A.; Wang, X.; Frye, S.V.; Earp, H.S.; et al. MERTK inhibition alters the PD-1 axis and promotes anti-leukemia immunity. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e97941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Stashko, M.A.; DeRyckere, D.; Hunter, D.; Kireev, D.; Miley, M.J.; Cummings, C.; Lee, M.; Norris-Drouin, J.; et al. Pseudo-cyclization through intramolecular hydrogen bond enables discovery of pyridine substituted pyrimidines as new Mer kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9683–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ding, N.; Ping, L.Y.; Shi, Y.; Mi, L.; Lai, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J. The proto-oncogene Mer tyrosine kinase is a novel therapeutic target in mantle cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, E.; Birchmeier, W.; Birchmeier, C.; Woude, G.V. Targeting MET in cancer: Rationale and progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiella, A.; Riccardi, F.; Cartenì, G.; Chiurazzi, M.; Onofrio, L. The emerging role of c-Met in carcinogenesis and clinical implications as a possible therapeutic target. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 5179182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Jain, P.; Wang, F.; Ma, P.C.; Borczuk, A.; Halmos, B. MET alterations and their impact on the future of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) targeted therapies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2021, 25, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouattour, M.; Raymond, E.; Qin, S.; Cheng, A.L.; Stammberger, U.; Locatelli, G.; Faivre, S. Recent developments of c-Met as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1132–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Efficacy and safety of iruplinalkib (WX-0593) in ALK-positive crizotinib-resistant advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients: A single-arm, multicenter phase II study (INTELLECT). BMC Med. 2023, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Cabozantinib: A review of its use in patients with medullary thyroid cancer. Drugs 2014, 74, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Si, X.; Zhang, L. Savolitinib versus crizotinib for treating MET positive non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Capmatinib: First approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.W.; Li, J.Q. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 6, 11-dihydro-5H-benzo [e] pyrimido-[5, 4-b][1, 4] diazepine derivatives as potential c-Met inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, N.; Wu, Y.J. Preparation of Bicyclic Pyrazolone Compounds for Inhibiting or Modulating the Activity of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. US20150299219A1, 22 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Naresh, G.K.; Guruprasad, L. Enhanced metastable state models of TAM kinase binding to cabozantinib explains the dynamic nature of receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 1213–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Yim, H.; Won, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Yoon, Y. Effective Amidation of Carboxylic Acids Using (4, 5-Dichloro-6-oxo-6H-pyridazin-1-yl)-phosphoric Acid Diethyl Ester. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, 29, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.R.; Li, M.Y.; Lv, Y.C.; Cao, S.F.; Tong, L.J.; Wei, L.X.; Ding, J.; Xie, H.; Duan, W.H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of biphenylurea derivatives as VEGFR-2 kinase inhibitors (II). Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jung, H.Y.; Mah, S.; Hong, S. Systematic computational design and identification of low Picomolar inhibitors of Aurora kinase A. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Fan, H.; Zheng, K.; Qin, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, C.; Hu, L. Synthesis and anti-tumor activity of [1, 4] dioxino [2, 3-f] quinazoline derivatives as dual inhibitors of c-Met and VEGFR-2. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; Ling, H. HNRNPU promotes the progression of triple-negative breast cancer via RNA transcription and alternative splicing mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yang, J.X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.Q. Structure-guided design and development of novel N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine derivatives as potential c-Met inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compd. | R 1 | IC50 (nM) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mer | c-Met | ||
| 14a | 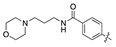 | 7.9 ± 1.3 | 151.2 ± 22.6 |
| 14b | 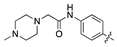 | 9.4 ± 1.5 | 179.3 ± 25.2 |
| 14c | 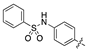 | 165.8 ± 21.6 | >1000 |
| 14d | 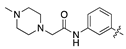 | 24.2 ± 2.6 | 143.6 ± 17.3 |
| 14e |  | 40.3 ± 3.6 | 321.2 ± 25.6 |
| 14f | 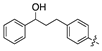 | 461.7 ± 41.6 | >1000 |
| 14g |  | 7.1 ± 0.9 | 89.4 ± 12.6 |
| 14h | 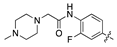 | 12.5 ± 2.0 | 74.9 ± 12.2 |
| 14i | 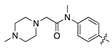 | 97.1 ± 12.7 | 224.2 ± 24.6 |
| Cabozantinib | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Compd. | R 2 | IC50 (nM) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mer | c-Met | ||
| 18a |  | 85.3 ± 6.8 | 15.4 ± 1.4 |
| 18b | 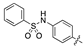 | >10,000 | 940.9 ± 65.9 |
| 18c | 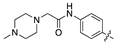 | 18.5 ± 2.3 | 33.6 ± 4.3 |
| 18d | 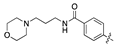 | 42.4 ± 5.8 | 52.7 ± 8.5 |
| 18e | 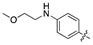 | 158.6 ± 17.4 | 77.3 ± 13.1 |
| 18f | 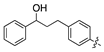 | 462.7 ± 55.4 | >1000 |
| Cabozantinib | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Compd. | R 2 | IC50 (nM) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mer | c-Met | ||
| 18g | 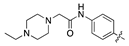 | 20.3 ± 3.2 | 48.7 ± 8.7 |
| 18h |  | 12.4 ± 1.9 | 42.6 ± 8.1 |
| 18i | 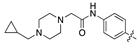 | 30.9 ± 5.3 | 77.1 ± 15.2 |
| 18j |  | 57.5 ± 9.4 | 32.8 ± 5.8 |
| 18k | 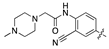 | 10.2 ± 1.4 | 51.2 ± 8.0 |
| 18l | 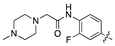 | 18.3 ± 2.7 | 48.7 ± 8.2 |
| 18m | 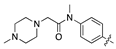 | 126.4 ± 17.8 | 74.4 ± 13.5 |
| 18n |  | 31.6 ± 5.4 | 30.7 ± 4.8 |
| 18o | 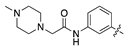 | 24.8 ± 3.3 | 39.8 ± 6.6 |
| Cabozantinib | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Cpd. | Human | |
|---|---|---|
| T1/2 (min) | CL (mL/min/mg) | |
| 18c | 53.1 | 0.06 |
| 18l | 9.6 | 0.36 |
| 18n | 11.9 | 0.29 |
| 18o | 8.6 | 0.40 |
| Testosterone | 32.1 | 0.11 |
| Cpds | IC50(μM) 1 of 3 Cell Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | MDA-MB0231 | HCT116 | |
| 18c | 6.63 | 8.90 | 4.95 |
| Cabozatinib | 1.72 | 28.96 | 7.82 |
| Cpd. | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| 18c | >40 |
| Cisapride | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Chai, T.; Cui, J.; Zhou, X.; Shang, Z. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Substituted Aniline Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Dual Mer/c-Met Inhibitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020475
Huang D, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhao B, Wang S, Chai T, Cui J, Zhou X, Shang Z. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Substituted Aniline Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Dual Mer/c-Met Inhibitors. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020475
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Daowei, Ying Chen, Jixia Yang, Bingyang Zhao, Shouying Wang, Tingting Chai, Jie Cui, Xiaolei Zhou, and Zhenhua Shang. 2024. "Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Substituted Aniline Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Dual Mer/c-Met Inhibitors" Molecules 29, no. 2: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020475
APA StyleHuang, D., Chen, Y., Yang, J., Zhao, B., Wang, S., Chai, T., Cui, J., Zhou, X., & Shang, Z. (2024). Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Substituted Aniline Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Dual Mer/c-Met Inhibitors. Molecules, 29(2), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020475





