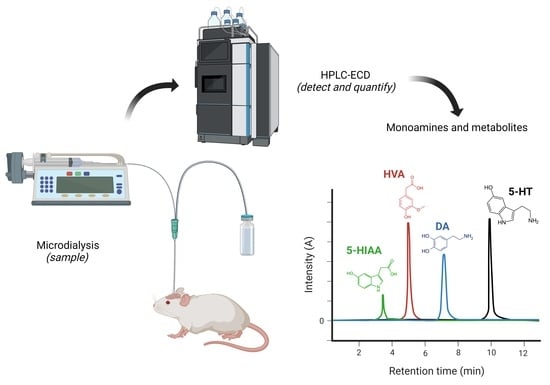
The High-Precision Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection (HPLC-ECD) for Monoamines Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites: A Review
Abstract
Share and Cite
Guiard, B.P.; Gotti, G. The High-Precision Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection (HPLC-ECD) for Monoamines Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020496
Guiard BP, Gotti G. The High-Precision Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection (HPLC-ECD) for Monoamines Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites: A Review. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020496
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuiard, Bruno P., and Guillaume Gotti. 2024. "The High-Precision Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection (HPLC-ECD) for Monoamines Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites: A Review" Molecules 29, no. 2: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020496
APA StyleGuiard, B. P., & Gotti, G. (2024). The High-Precision Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection (HPLC-ECD) for Monoamines Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites: A Review. Molecules, 29(2), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020496