Metabolomic Diversity in Polygonatum kingianum Across Varieties and Growth Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phenotypic Differences Among Different Germplasms of P. kingianum
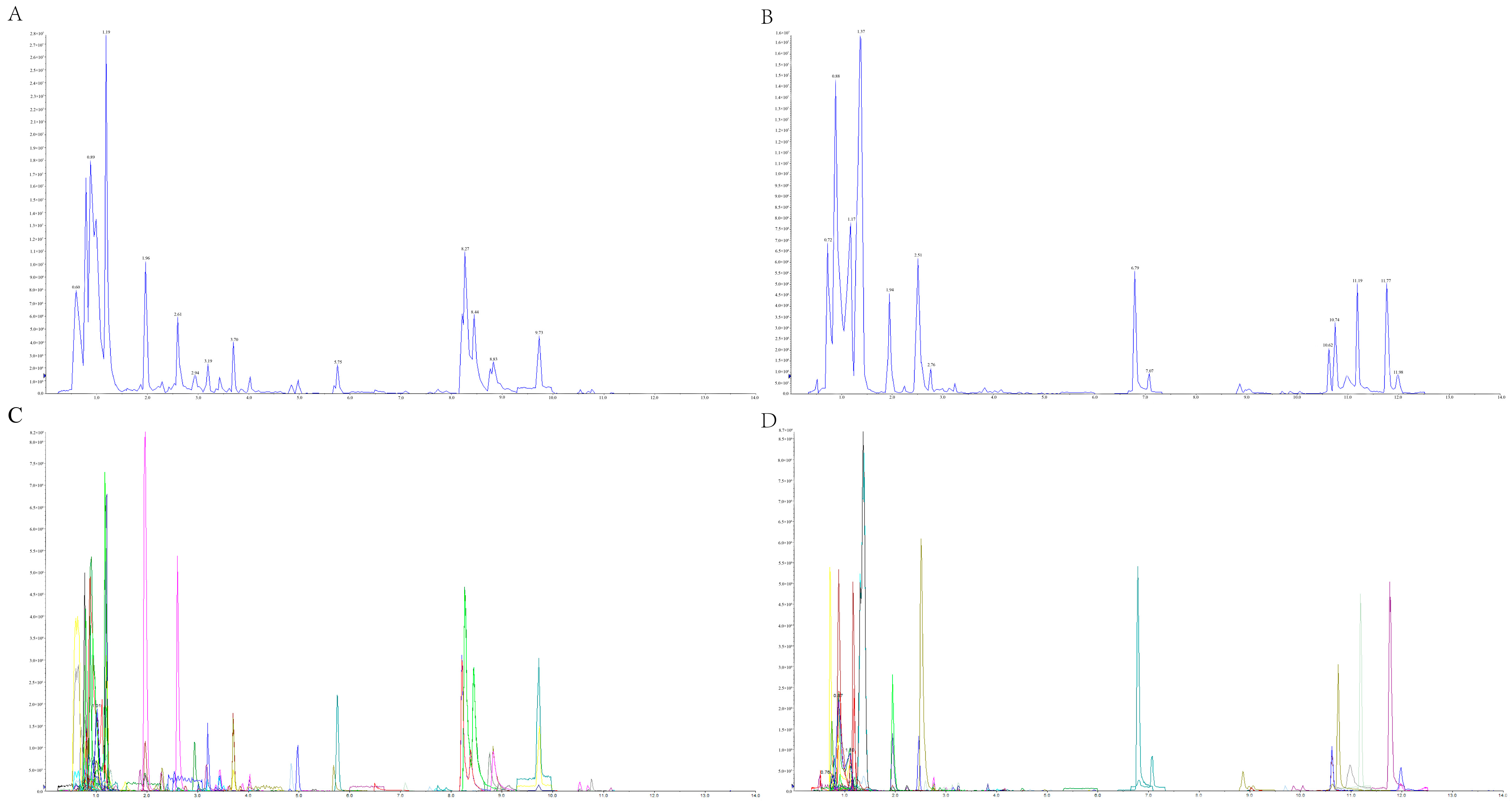
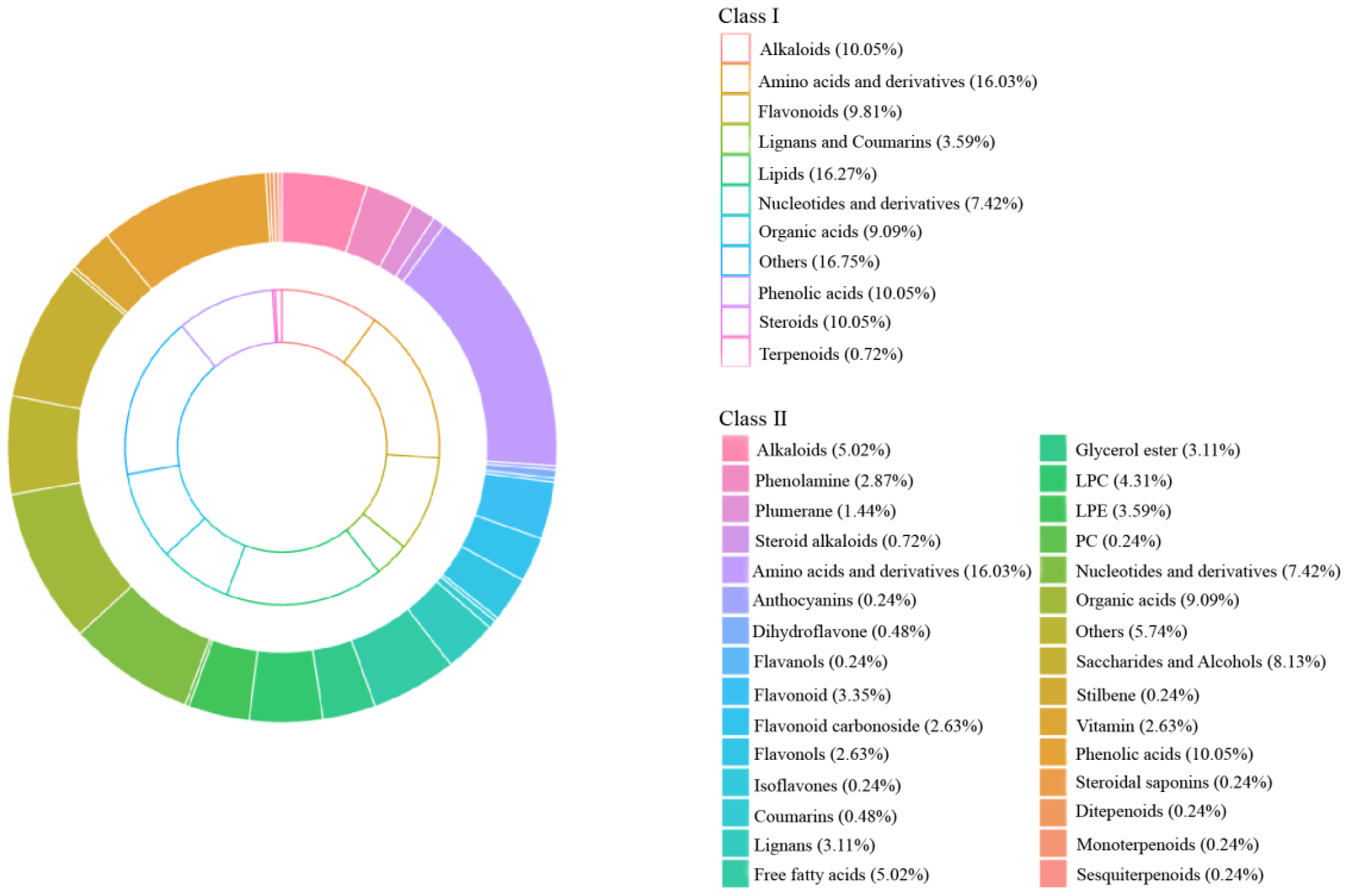
2.2. Analysis of the Overall Composition of Metabolites
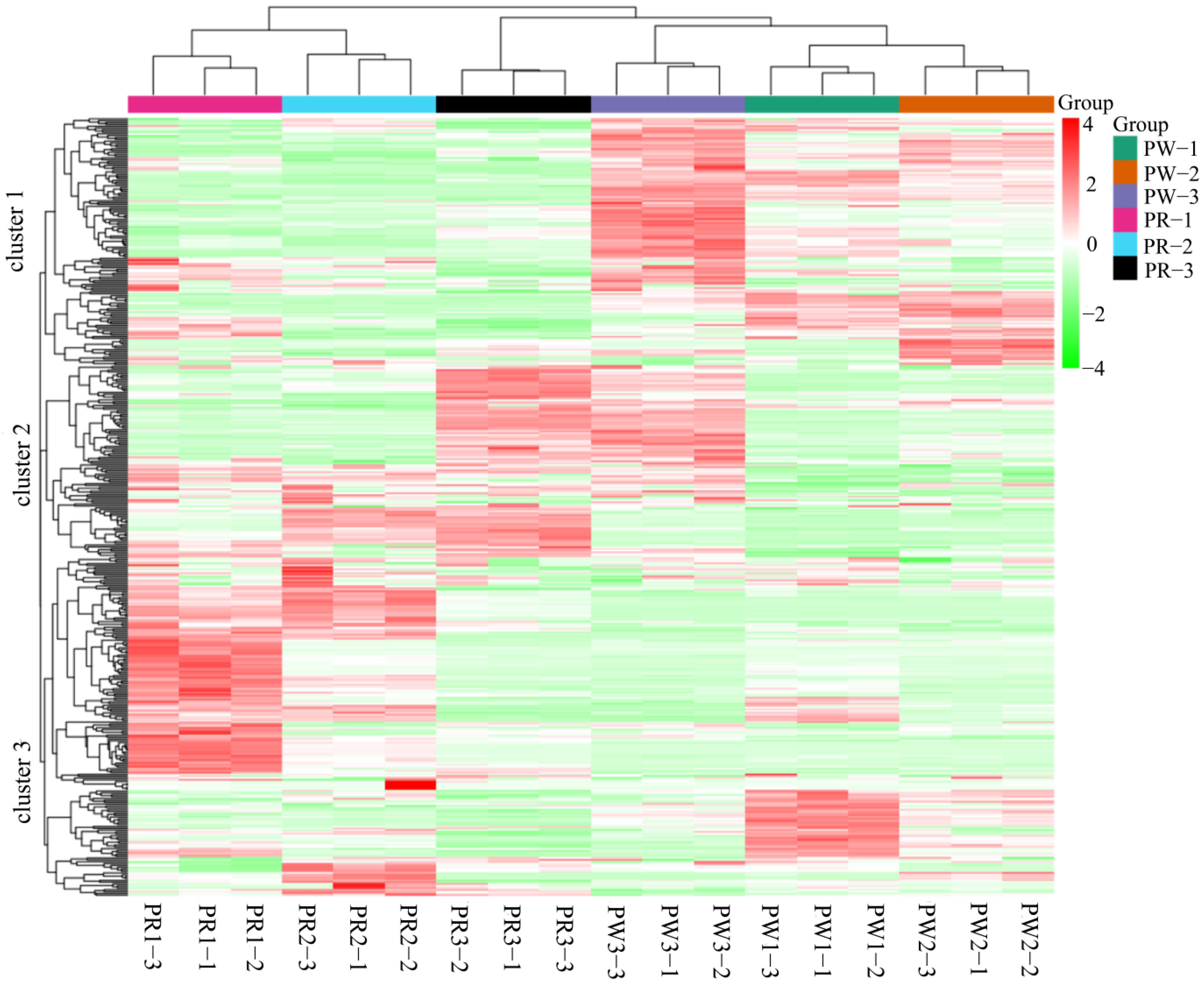
2.3. Multivariate Analysis Revealed the Differences Between the Metabolic Profiles
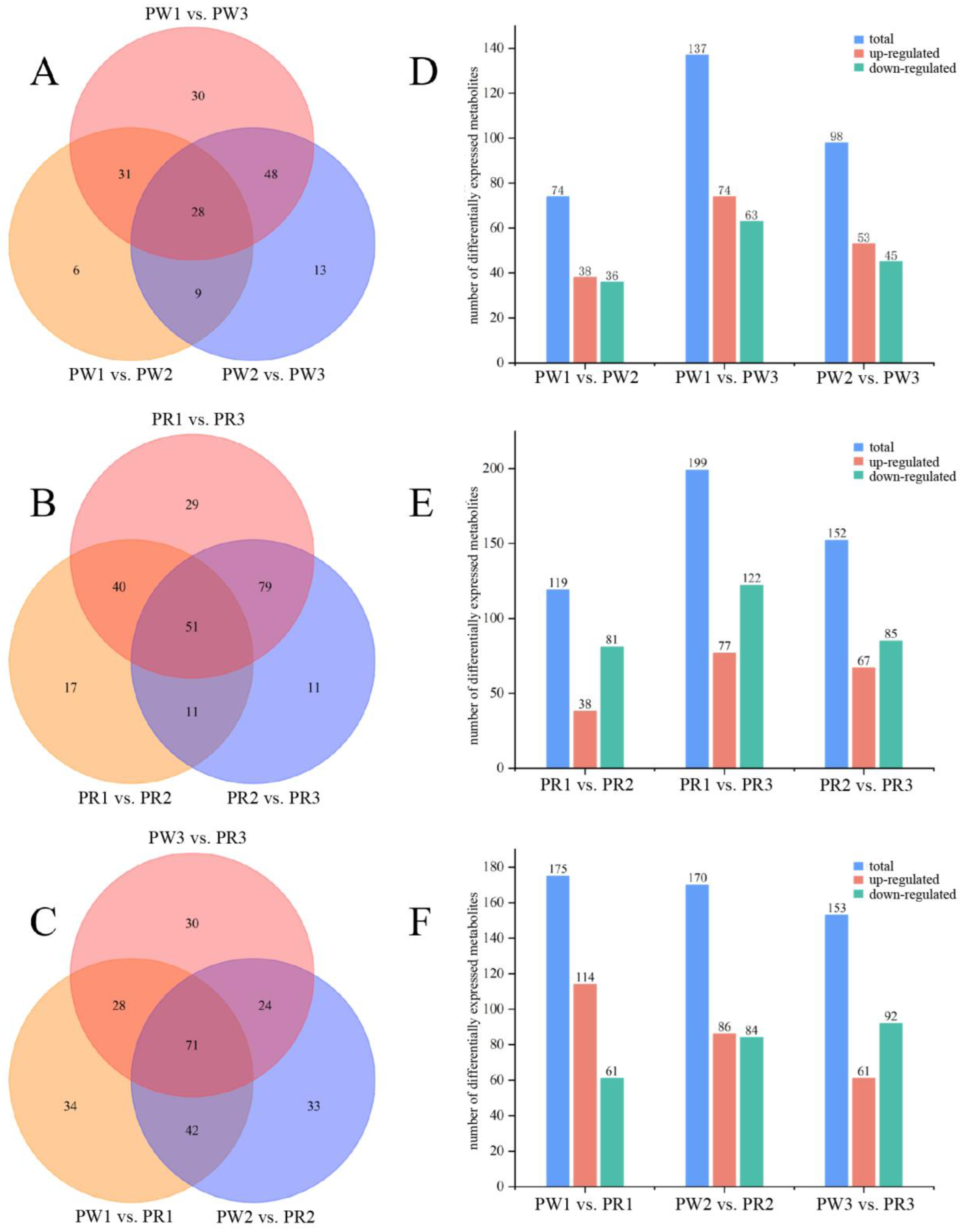
2.4. Screening and Analysis of Differential Metabolites in Different Germplasms of P. kingianum from Different Growth Years
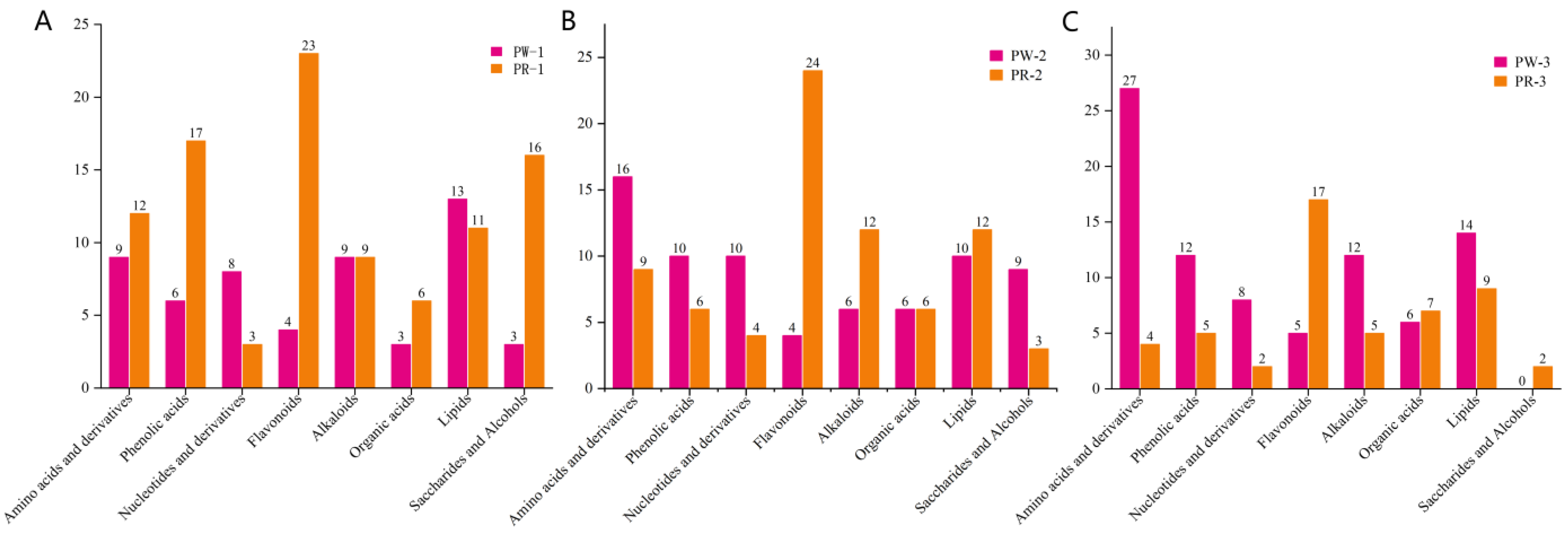
2.5. Analysis of the Contents of Differential Metabolites
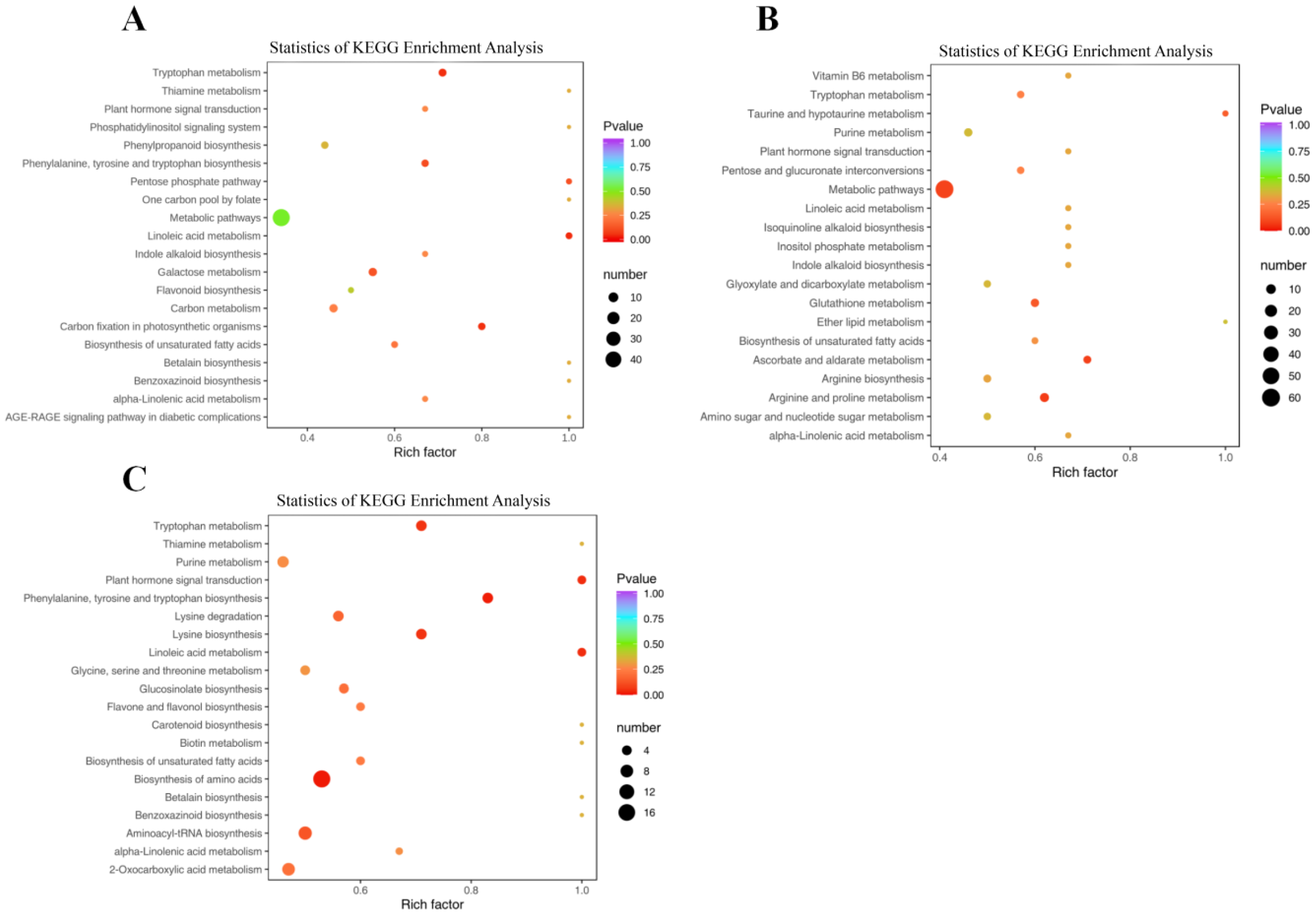
2.6. KEGG Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
2.7. Expression Analysis of Differential Metabolites
2.8. Analysis of the Ideal Harvest Time of Different Germplasms of P. kingianum
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Treatment
3.2. Widely Targeted Metabolomic Method Based on UPLC-MS/MS
3.3. Metabolite Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, J.; Lao, J.; Zhou, R.; He, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhong, C.; Xie, J.; Liu, H.; Wan, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Simultaneous identification and dynamic analysis of saccharides during steam processing of rhizomes of Polygonatum cyrtonema by HPLC–QTOF–MS/MS. Molecules 2018, 23, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: Part 1; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 319.
- Li, R.; Tao, A.; Yang, R.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Shang, F.; Xia, C.; Duan, B. Structural characterization, hypoglycemic effects and antidiabetic mechanism of a novel polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum coll. et hemsl. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Dong, J.; Bi, Q.; Yang, X.; Che, Y.; He, S.; Yu, J. Polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum improve glucose and lipid metabolism in rats fed a high fat diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelithao, K.; Surayot, U.; Lee, J.H.; You, S. RAW264. 7 cell activating glucomannans extracted from rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, J.F.; Ma, Y.G.; Jiang, J.G. Effect of fermentation modification on the physicochemical characteristics and anti-aging related activities of Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Zuo, X.D.; Duan, J.H.; Qiu, B.; Li, X.F.; Li, J.P.; Yu, J. Effect and mechanisms of Polygonatum kingianum (polygonati rhizome) on wound healing in diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115612. [Google Scholar]
- Huyen, D.T.T.; Phuong, N.T.; Hien, N.T.T.; Nga, N.T.; Hung, L.N.; Thao, D.T.; Ha, L.M. Polygonatum kingianum rhizome extract alleviates collagen antibody-induced arthritis by modulating proinflammatory cytokine production in mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 10, 490–495. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Qian, L. Research progress in diversity of origin plants of Chinese medicinal Polygonati rhizoma and its utilization. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2022, 41, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. The development status and countermeasures of Polygonatum industry under the rural revitalization strategy. New Agric. 2023, 5, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Ruan, P.; Zhang, X. Development status and countermeasures of Polygonatum industry in Bijie city. Agric. Eng. 2023, 13, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, K.; Hou, C.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Dong, L.; Chen, S. Metabolomics analysis revealed the characteristic metabolites of hemp seeds varieties and metabolites responsible for antioxidant properties. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 904163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Hu, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, C. Metabolomics analysis reveals the differences between Bupleurum Chinense DC. And Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 933849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, L.; Song, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Comparative metabolomics provides novel insights into correlation between dominant habitat factors and constituents of Stellaria radix (Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1035712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Yu, M.; Liu, S. Integration of transcriptome and metabolome provides new insights to flavonoids Biosynthesis in Dendrobium huoshanense. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 850090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Kharchenko, V.A.; Moldovan, A.I.; Koshevarov, A.A.; Zamana, S.; Nadezhkin, S.; Soldatenko, A.; Sekara, A.; Tallarita, A.; Caruso, G. Yield, growth, quality, biochemical characteristics and elemental composition of plant parts of celery leafy, stalk and root types grown in the Northern Hemisphere. Plants 2020, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, R. Comparison of flavonoids, amino acids and phenolic acids in different Polygonatum rhizomes. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Yang, M.Q.; Yang, W.Z.; Yang, S.B.; Zhang, J.Y. Identification and evaluation of Polygonatum kingianum with different growth ages based on data fusion strategy. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Dry matter accumulation and polysaccharides distribution in different sections of perennial Polygonatum sibiricum red. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2007, 27, 384–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Meng, F.; Gu, W.; Fu, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Influence of polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum on short-chain fatty acid production and quorum sensing in Lactobacillus faecis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 758870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, F.; Cao, G.; Yu, J. Optimization of the ultrasonic-assisted extraction technology of steroidal saponins from Polygonatum kingianum collett & hemsl and evaluating its quality planted in different areas. Molecules 2022, 27, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segla, K.D.S.; Xu, F.; You, J.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Widely targeted metabolome profiling of different colored sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds provides new insight into their antioxidant activities. Food Res Int. 2022, 151, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, G.; Su, S.; Yan, P.; Shang, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Xu, H. Integrative analyses of widely targeted metabolomic profiling and derivatization-based LC-MS/MS reveals metabolic changes of Zingiberis Rhizoma and its processed products. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; An, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.; He, J.; Wan, R. Widely-Targeted metabolic profiling in Lyciumbarbarum fruits under salt-alkaline stress uncovers mechanism of salinity tolerance. Molecules 2022, 27, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, M.; Jin, B.; Yin, B.; Chen, T.; Guo, J.; Tang, J.; Cui, G.; Huang, L. Integrating metabolomics and transcriptomics to unveil atisine Biosynthesis in Aconitum gymnandrum maxim. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.S.; El-Banna, A.A.; Ghareeb, D.A.; El-Hosseny, M.F.; Seadawy, M.G.; Dawood, H.M. Chemical profiling and unraveling of anti-COVID-19 biomarkers of red sage (Lantana camara L.) cultivars using UPLC-MS/MS coupled to chemometric analysis, in vitro study and molecular docking. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, H.; He, J. Quantitative comparison and chemical profile analysis of different medicinal parts of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. from different varieties and harvest periods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8838–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, X.; Wu, T. A new Polygonatum kingianum cultivar ‘linyun 1’. Acta Acta Hortic. Sinic. 2022, 49, 707–708. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Xiao, L.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Su, B.; Liu, Z. Genetic relationship of Polygonatum kingianum with three different flower colors. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Men, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Han, Y. Total protein content, amino acid composition and eating-quality vealuation of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv). Foods 2022, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.N.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ru, J.N.; Lu, J.H.; Ding, B.; Wu, J. amino acid metabolism in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; An, L. Research status of determination and analysis technology of amino acid content in Chinese medicinal materials. Rural. Econ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, X. Syringaresinol-di-O-β-D-glucoside, a phenolic compound from Polygonatum sibiricum, exhibits an antidiabetic and antioxidative effect on a streptozotocin-induced mouse model of diabetes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5511–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z. Research progress on lipid metabonomics. Feed Rev. 2016, 9, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, L. Analysis of current status and trends of patent application of glycerophosphoryl choline in medical area. China Invent. Pat. 2018, 15, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Calis, Z.; Mogulkoc, R.; Baltaci, A.K. The roles of flavonoles/flavonoids in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wen, D.; Fu, Z.; Qian, H. The secretion of organic acids is also regulated by factors other than aluminum. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 186, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Nie, S.; Xie, M.; Hu, J. Antioxidant and antibacterial capabilities of phenolic compounds and organic acids from Camellia oleifera cake. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; He, S.; Kong, L.; Cheng, G. The protective effect of 6’-O-caffeoylarbutin on type l diabetes. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 22, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Alasmary, F.A.; Awaad, A.S.; Alqahtani, S.M.; El-Meligy, R.M.; Abdullah, D.A.; Alqasoumi, S.I. Evaluation of the chemical constituents and potential biological activities of Cunninghamella blakesleeana. Saudi Pharm. 2020, 28, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Murphy, C.D. 3-hydroxytyrosol regulates biofilm growth in Cunninghamella elegans. Fungal Biol. 2021, 125, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, C.; Khan, M.F.; Murphy, C.D. Endogenous production of 2-phenylethanol by Cunninghamella echinulata inhibits biofilm growth of the fungus. Fungal Biol. 2023, 127, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, M.; Mittal, A.; Mehta, P.K. Microbial metabolites in nutrition, healthcare and agriculture. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, F.A., Jr.; Egan, R.W. Prostaglandins, arachidonic acid, and inflammation. Science 1980, 210, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Hu, T.; Xue, X.; Dong, X. Metabolism of phenylalanine in host andintestinal microorganism: Research progress. Chin. J. Microecol. 2023, 35, 857–859. [Google Scholar]
- Ottosson, F.; Ericson, U.; Almgren, P.; Nilsson, J.; Magnusson, M.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O. Postprandial levels of branch chained and aromatic amino acids associate with fasting glycaemia. J. Amino Acids. 2016, 2016, 8576730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.; Zadeh, K.; Vekariya, R.; Ge, Y.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Tryptophan metabolism and gut-brain homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, C.; Pechlaner, R.; Willeit, P.; Langley, S.R.; Mangino, M.; Mayr, U.; Menni, C.; Moayyeri, A.; Santer, P.; Rungger, G.; et al. lipidomics profiling and risk of cardiovascular disease in the prospective population-based Bruneck study. Circulation 2014, 129, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Koike, T.; Izumi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Yoshida, M.; Shiomi, M.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. lipidomic analysis of plasma lipoprotein fractions in myocardial infarction-prone rabbits. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, X. A metabolomics analysis of the effect of water deficit on the freezing tolerance of Medicago sativa. Acta Prat. Sinic. 2020, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Feng, E.; Nie, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, L.; Li, H.; Rao, G. Experiments of agronomic traits and yield of Polygonatum kingianum with different growth years. Yunnan Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 15, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Xiong, X.; Su, Y.; Su, Z. Effects of different planting patterns and years on yield and quality of Polygonatum kingianum. J. West. China For. Sci. 2022, 51, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Ye, H.; Wang, W.; Ye, Y.; Hai, M. The appropriate collection period of Polygonatum cyrtonema in Yunnan. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2017, 33, 88–91. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | One Year Old | Two Years Old | Three Years Old | Four Years Old | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW | PR | PW | PR | PW | PR | PW | PR | |
| Average plant height (m) | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.69 | 0.79 | 1.78 | 2.21 | 1.92 | 2.63 |
| Increase (%) | −0.03 | −0.13 | −0.19 | −0.27 | ||||
| Average ground diameter (cm) | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.71 |
| Increase (%) | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.14 | ||||
| Plant number (plant/clump) | 1.5 | 1.3 | 3 | 2.6 | 15.8 | 10.02 | 18.8 | 14.02 |
| Increase (%) | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 0.34 | ||||
| Parameter | Four Years Old | |
|---|---|---|
| PW | PR | |
| Average individual yield (kg) | 0.88 | 0.51 |
| Increase (%) | 72.55 | |
| Average yield per mu (kg) | 6918.7 | 3616.5 |
| Increase (%) | 91.31 | |
| Category | PW-1 vs. PR-1 | PW-2 vs. PR-2 | PW-3 vs. PR-3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNM 1 | TNDM 2 | NUR 3 | NDR 4 | TNM | TNDM | NUR | NDR | TNM | TNDM | NUR | NDR | |
| Lipids | 68 | 24 | 11 | 13 | 68 | 22 | 12 | 10 | 68 | 23 | 9 | 14 |
| Amino acids and derivatives | 67 | 21 | 12 | 9 | 67 | 25 | 9 | 16 | 67 | 31 | 4 | 27 |
| Alkaloids | 42 | 18 | 9 | 9 | 42 | 18 | 12 | 6 | 39 | 17 | 5 | 12 |
| Phenolic acids | 42 | 23 | 17 | 6 | 42 | 16 | 6 | 10 | 42 | 17 | 5 | 12 |
| Flavones | 41 | 27 | 23 | 4 | 41 | 28 | 24 | 4 | 41 | 22 | 17 | 5 |
| Organic acids | 38 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 38 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 38 | 13 | 7 | 6 |
| Nucleotides and derivatives | 31 | 11 | 3 | 8 | 31 | 14 | 4 | 10 | 31 | 10 | 2 | 8 |
| Lignans and Coumarins | 15 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| Terpenoids | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Steroids | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Others | 70 | 30 | 26 | 4 | 70 | 24 | 8 | 16 | 69 | 12 | 8 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, T.; Xie, Q.; Wen, R.; Wang, L.; Su, B.; Zhang, H. Metabolomic Diversity in Polygonatum kingianum Across Varieties and Growth Years. Molecules 2024, 29, 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215180
Xiao L, Xu H, Wu T, Xie Q, Wen R, Wang L, Su B, Zhang H. Metabolomic Diversity in Polygonatum kingianum Across Varieties and Growth Years. Molecules. 2024; 29(21):5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215180
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Liangjun, Huimei Xu, Tao Wu, Qiufeng Xie, Rouyuan Wen, Le Wang, Baoshun Su, and Haizhu Zhang. 2024. "Metabolomic Diversity in Polygonatum kingianum Across Varieties and Growth Years" Molecules 29, no. 21: 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215180
APA StyleXiao, L., Xu, H., Wu, T., Xie, Q., Wen, R., Wang, L., Su, B., & Zhang, H. (2024). Metabolomic Diversity in Polygonatum kingianum Across Varieties and Growth Years. Molecules, 29(21), 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215180





