Sustainable Nanomedicine: Enhancement of Asplatin’s Cytotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo Using Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Formed via Microwave-Assisted and Gambogic Acid-Mediated Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
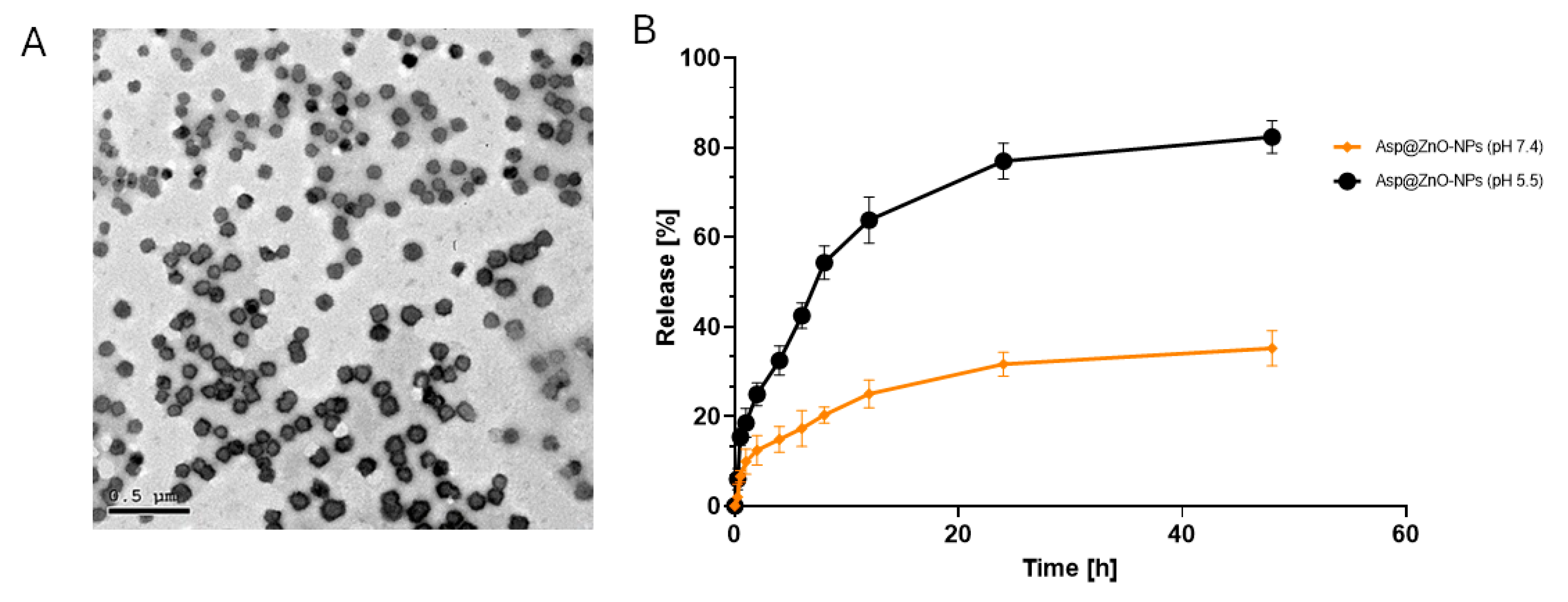
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Prepared Nanoparticles
2.2. The Release Profile In Vitro
2.3. In Vitro Assessment
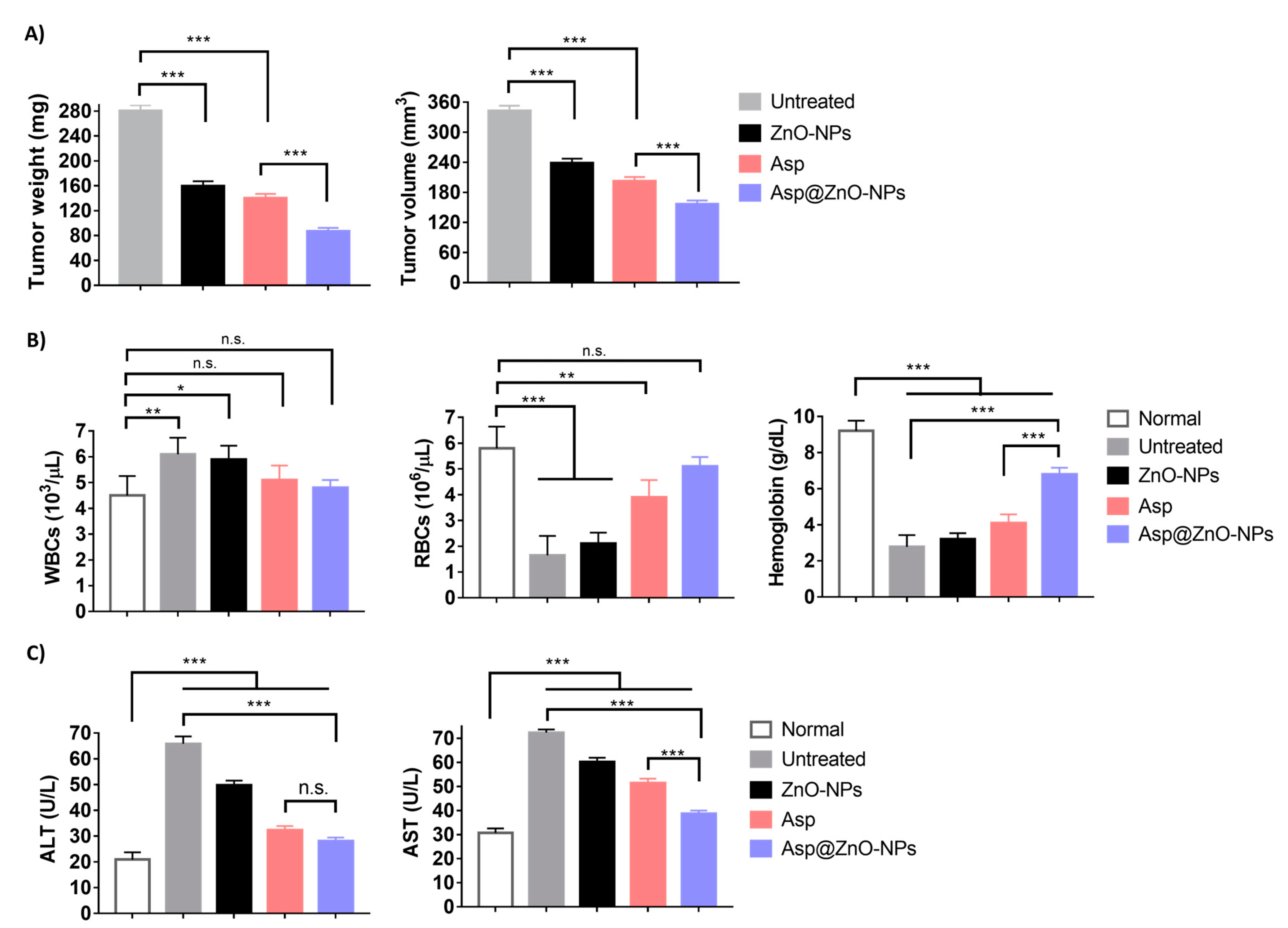
2.4. In Vivo Assessments
2.4.1. Antitumor Activity
2.4.2. Assessment of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Microwave-Assisted Green Synthesis of ZnO-NPs
3.3. Preparation of Asp@ZnO-NPs
3.4. Physicochemical Characterization of the Prepared Nanoparticles
3.4.1. Zeta Potential (ZP) Analysis
3.4.2. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy (UV-Vis)
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
3.6. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
3.7. Entrapment Efficiency (EE%)
3.8. In Vitro Release
3.9. In Vitro Studies
3.9.1. Cells and Culture Media
3.9.2. Cell Viability Studies
3.9.3. Determination of Cell Apoptosis
3.10. In Vivo Studies
3.10.1. Animals
3.10.2. Assessment of Antitumor Activity
3.10.3. Hematological and Biochemical Analyses of Blood Samples
3.11. Histopathological Analysis
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kannampuzha, S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Cancer chemoresistance and its mechanisms: Associated molecular factors and its regulatory role. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritacco, I.; Al Assy, M.; El-Rahman, M.K.A.; Fahmy, S.A.; Russo, N.; Shoeib, T.; Sicilia, E. Hydrolysis in Acidic Environment and Degradation of Satraplatin: A Joint Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6013–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, S.; Disler, C.; Perego, P. The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, S.A.; Ponte, F.; Grande, G.; Fawzy, I.M.; Mandour, A.A.; Sicilia, E.; Azzazy, H.M.E.-S. Synthesis, Characterization and Host-Guest Complexation of Asplatin: Improved In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility as Compared to Cisplatin. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood, P.; Morgan, G.; Watkins, J.; Protty, M.; Mason, M.; Adams, R.; Dolwani, S.; Pickering, J.; Delon, C.; Longley, M. Aspirin and cancer treatment: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of evidence: For and against. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovizio, M.; Tacconelli, S.; Sostres, C.; Ricciotti, E.; Patrignani, P. Mechanistic and Pharmacological Issues of Aspirin as an Anticancer Agent. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1346–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. Current Studies of Aspirin as an Anticancer Agent and Strategies to Strengthen its Therapeutic Application in Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2209–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood, P.; Protty, M.; Morgan, G.; Pickering, J.; Delon, C.; Watkins, J. Aspirin and cancer: Biological mechanisms and clinical outcomes. Open Biol. 2022, 12, 220124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Nishihara, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Masugi, Y.; Hamada, T.; Kosumi, K.; Liu, L.; da Silva, A.; et al. Aspirin exerts high anti-cancer activity in PIK3CA-mutant colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87379–87389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Asplatin enhances drug efficacy by altering the cellular response†. Metallomics 2016, 8, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Min, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. The ligation of aspirin to cisplatin demonstrates significant synergistic effects on tumor cells. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7427–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, H.A.F.M.; Haider, M.; Fahmy, S.A. From antigen uptake to immune modulation: The multifaceted potential of peptide nanofibers as vaccine nanocarriers. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 4112–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelić, K.; Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Bulog, A.; Agaj, A.; Rojnić, B.; Čolić, M.; Trivanović, D. Nanoparticles in Medicine: Current Status in Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, M.; Ali, S.; Shahid, N.; Rehman, K.; Amin, U.; Raza, M. Formulation considerations and factors affecting transdermal drug delivery system—A review. Int. J. Pharm. Integr. Life Sci. 2014, 2, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Szwed, M.; Marczak, A. Application of Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia for Cancer Treatment—The Current State of Knowledge. Cancers 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, J.B.; Rajapaksha, W.; Albrecht, H. Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Kostevsek, N.; Monaco, I.; Ruiz, A.; Markelc, B.; Cheung, C.C.L.; Hudoklin, S.; Kreft, M.E.; Hassan, H.; Barker, M.; et al. PD1 blockade potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of photothermally-activated and MRI-guided low temperature-sensitive magnetoliposomes. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2021, 332, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Provenza, A.C.; Reverchon, G.; Baldino, L.; Reverchon, E. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers: Bridging Diagnosis and Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzazy, H.M.E.-S.; Abdelnaser, A.; Al Mulla, H.; Sawy, A.M.; Shamma, S.N.; Elhusseiny, M.; Alwahibi, S.; Mahdy, N.K.; Fahmy, S.A. Essential Oils Extracted from Boswellia sacra Oleo Gum Resin Loaded into PLGA–PCL Nanoparticles: Enhanced Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effects against Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedky, N.K.; Braoudaki, M.; Mahdy, N.K.; Amin, K.; Fawzy, I.M.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Youness, R.A.; Fahmy, S.A. Box–Behnken design of thermo-responsive nano-liposomes loaded with a platinum(iv) anticancer complex: Evaluation of cytotoxicity and apoptotic pathways in triple negative breast cancer cells. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 5399–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, M.; Lopes, A.R.; Escudeiro, M.; Esteves, B.; Monteiro, A.R.; Trindade, T.; Cruz-Lopes, L. Application of Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment: A Concise Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, S.A.; Sedky, N.K.; Hassan, H.A.F.M.; Abdel-Kader, N.M.; Mahdy, N.K.; Amin, M.U.; Preis, E.; Bakowsky, U. Synergistic Enhancement of Carboplatin Efficacy through pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles Formulated Using Naturally Derived Boswellia Extract for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.; Hashim, M.; Malik, S.A.; Khan, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C. Recent Advances in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for Cancer Diagnosis, Target Drug Delivery, and Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmann, N.; Tremel, W.; Brieger, J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for therapeutic purposes in cancer medicine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 4973–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, K.; Choudhary, C.; Mishra, P.K.; Vaidya, B. Development and characterization of metal oxide nanoparticles for the delivery of anticancer drug. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Jin, S.; Xue, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, T.; Guo, W.; Liang, X.-J. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Adjuvant To Facilitate Doxorubicin Intracellular Accumulation and Visualize pH-Responsive Release for Overcoming Drug Resistance. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, D.B.; Bharati, A.V. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using a hydrothermal method and a study its optical activity. Luminescence 2017, 32, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Shih, Y.-L.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Li, Z.-Y.; Tsai, C.-J. Generation of ZnO nanoparticles by chemical vapor synthesis using quenching air. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2021, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripal, R.; Gupta, A.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Mishra, S.K. Photoconductivity and photoluminescence of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.; Wang, X.; Guo, M.; Hu, Z.; Hu, W.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, S.; Wu, K.; Du, S.; et al. Gambogic acid and IR780 self-assembled nanoparticles for combined chemo-phototherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarip, N.A.; Aminudin, N.I.; Danial, W.H. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using Garcinia extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminuzzaman, M.; Ying, L.P.; Goh, W.-S.; Watanabe, A. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Garcinia mangostana fruit pericarp and their photocatalytic activity. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 41, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.-Y.; Shin, S.-W.; Kim, K.; Park, Y. Facile Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles by Upcycling Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) Pericarp Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Prospective Biotechnological Applications: An Overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, S.F.; Assal, M.E.; Khan, M.; Al-Warthan, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and prospects toward green chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 9709–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.K.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Applications and Limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjunaswamy, C.; Ranganatha, V.L.; Ramu, R.; Udayabhanu; Nagaraju, G. Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Application to photodegradation, antibacterial and antioxidant. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 1004–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzazy, H.M.E.-S.; Sawy, A.M.; Abdelnaser, A.; Meselhy, M.R.; Shoeib, T.; Fahmy, S.A. Peganum harmala Alkaloids and Tannic Acid Encapsulated in PAMAM Dendrimers: Improved Anticancer Activities as Compared to Doxorubicin. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 7228–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Ali, A.I.; ElDesawy, E.M.; ElShafeey, A.H. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Gemifloxacin Chitosan Nanoparticles As an Antibacterial Ocular Dosage Form. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, J.; Chakraborty, N.; Chatterjee, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Dasgupta, D.; Acharya, K. Green Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Defence and Antioxidant Enzymes in Lens culinaris. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzinjy, A.A.; Azeez, H.H. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus Labill. leaf extract and zinc nitrate hexahydrate salt. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, R.S.; Adjei, A.A. Review of the comparative pharmacology and clinical activity of cisplatin and carboplatin. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Belely, E.F.; Farag, M.M.S.; Said, H.A.; Amin, A.S.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Arthrospira platensis (Class: Cyanophyceae) and Evaluation of their Biomedical Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yuan, C.; Chai, H.-B.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.-C.; Ferreira, D.; Kinghorn, A.D. Absolute Configuration of (−)-Gambogic Acid, an Antitumor Agent. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, B.; Tesfaye, J.L.; Anatol, D.; Shanmugam, R.; Dwarampudi, L.P.; Nagaprasad, N.; Bhargavi, V.L.N.; Krishnaraj, R. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Methods and Spectroscopic Investigation of Ultraviolet Radiation Protective Properties. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 8617290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, R.; Suhana, H.; Paradesi, D. Characterization Study of Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles Loaded with Anti-Cancer Doxorubicin Drug. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 4533–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Miyamoto, C.; Maehata, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Maeda, T.; Baba, Y. Acidic extracellular microenvironment and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedtkjer, E.; Pedersen, S.F. The Acidic Tumor Microenvironment as a Driver of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghari-Tabari, M.; Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Mohammadi, M.; Hashemzadeh, M.S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Cancer Chemotherapy: Helpful Tools for Enhancing Chemo-sensitivity and Reducing Side Effects? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 1878–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frajacomo, F.T.T.; de Souza Padilha, C.; Marinello, P.C.; Guarnier, F.A.; Cecchini, R.; Duarte, J.A.R.; Deminice, R. Solid Ehrlich carcinoma reproduces functional and biological characteristics of cancer cachexia. Life Sci. 2016, 162, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.H.; El-Missiry, M.A.; Othman, A.I.; Ali, D.A.; Gouida, M.S.; Ismail, A.H. Ameliorative effects of melatonin against solid Ehrlich carcinoma progression in female mice. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 67, e12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Mathai, M.L.; Zulli, A. Cisplatin for cancer therapy and overcoming chemoresistance. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberger, L.M. Using aspirin to prevent and treat cancer. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Sengupta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Adhikary, A.; Das, T. Aspirin enhances cisplatin sensitivity of resistant non-small cell lung carcinoma stem-like cells by targeting mTOR-Akt axis to repress migration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilreath, J.A.; Rodgers, G.M. How I treat cancer-associated anemia. Blood 2020, 136, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, D.U.; Lebrecht, A.; Schmidt, M.; Siggelkow, W.; Lindner, C.; Litz, A.; Ulbrich, E.; Koelbl, H. Prognostic impact of haemoglobin levels in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R.S.Y. Role of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in Cancer Prevention and Cancer Promotion. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 2019, 3418975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Zhao, W.; Yue, Y.; Guo, M.; Nan, K.; Liao, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhou, D.; Miao, C. High preoperative white blood cell count determines poor prognosis and is associated with an immunosuppressive microenvironment in colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 943423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Xue, N.; Wu, M.-T.; Chen, H.; He, X.; Li, J.-P.; Liu, W.-L.; Dai, S.-Q. Influence of Preoperative Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) Level on the Prognosis of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; He, L.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Elevated AST/ALT ratio is associated with all-cause mortality and cancer incident. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Hao, M.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Dang, S. Hepatoprotective effects of aspirin on diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by reducing inflammation levels and PD-L1 expression. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedky, N.K.; Abdel-Kader, N.M.; Issa, M.Y.; Abdelhady, M.M.M.; Shamma, S.N.; Bakowsky, U.; Fahmy, S.A. Co-Delivery of Ylang Ylang Oil of Cananga odorata and Oxaliplatin Using Intelligent pH-Sensitive Lipid-Based Nanovesicles for the Effective Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
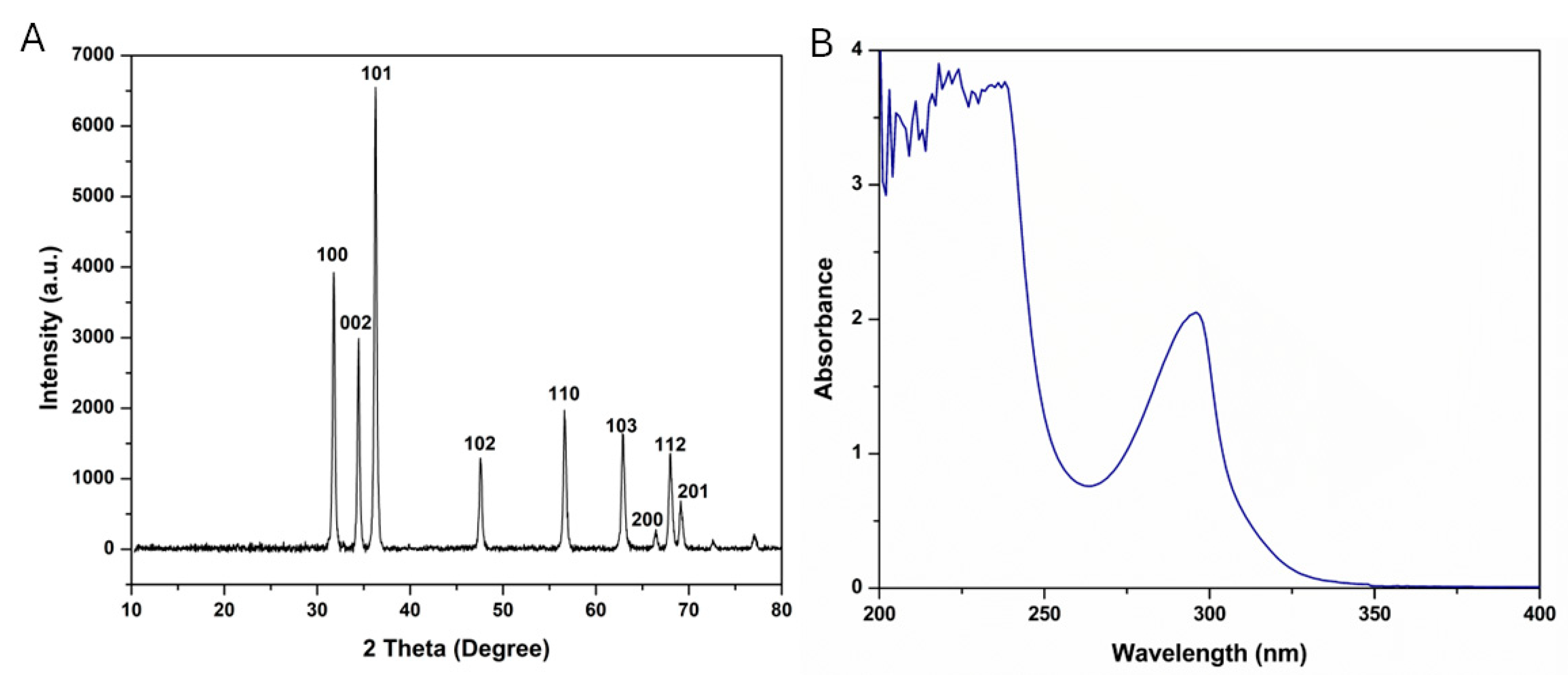



| Peak # | 2 θ (Degree) | 2 θ (Radians) | Cos (θ) | FWHM (Degree) | FWHM (Radians) | ZnO-NPs’ Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31.79 | 0.55 | 0.96 | 0.32 | 0.0055 | 26.16 |
| 2 | 34.45 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 0.31 | 0.0054 | 26.87 |
| 3 | 36.28 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 0.33 | 0.0057 | 25.49 |
| 4 | 47.59 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.35 | 0.0062 | 24.53 |
| 5 | 56.65 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.38 | 0.0066 | 23.76 |
| 6 | 62.93 | 1.10 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.0072 | 22.44 |
| 7 | 66.45 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.0063 | 26.40 |
| 8 | 68.03 | 1.19 | 0.83 | 0.43 | 0.0076 | 22.04 |
| 9 | 69.17 | 1.21 | 0.82 | 0.42 | 0.0074 | 22.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, H.A.F.M.; Sedky, N.K.; Nafie, M.S.; Mahdy, N.K.; Fawzy, I.M.; Fayed, T.W.; Preis, E.; Bakowsky, U.; Fahmy, S.A. Sustainable Nanomedicine: Enhancement of Asplatin’s Cytotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo Using Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Formed via Microwave-Assisted and Gambogic Acid-Mediated Processes. Molecules 2024, 29, 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225327
Hassan HAFM, Sedky NK, Nafie MS, Mahdy NK, Fawzy IM, Fayed TW, Preis E, Bakowsky U, Fahmy SA. Sustainable Nanomedicine: Enhancement of Asplatin’s Cytotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo Using Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Formed via Microwave-Assisted and Gambogic Acid-Mediated Processes. Molecules. 2024; 29(22):5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Hatem A. F. M., Nada K. Sedky, Mohamed S. Nafie, Noha Khalil Mahdy, Iten M. Fawzy, Toka Waleed Fayed, Eduard Preis, Udo Bakowsky, and Sherif Ashraf Fahmy. 2024. "Sustainable Nanomedicine: Enhancement of Asplatin’s Cytotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo Using Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Formed via Microwave-Assisted and Gambogic Acid-Mediated Processes" Molecules 29, no. 22: 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225327
APA StyleHassan, H. A. F. M., Sedky, N. K., Nafie, M. S., Mahdy, N. K., Fawzy, I. M., Fayed, T. W., Preis, E., Bakowsky, U., & Fahmy, S. A. (2024). Sustainable Nanomedicine: Enhancement of Asplatin’s Cytotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo Using Green-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Formed via Microwave-Assisted and Gambogic Acid-Mediated Processes. Molecules, 29(22), 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225327











