Novel 1-(1-Arylimiazolin-2-Yl)-3-Arylalkilurea Derivatives with Modulatory Activity on Opioid MOP Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
Structure–Activity Relationship
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. General Procedure
3.3. Preparation of Solutions of Test and Reference Compounds
3.4. Functional Assays
3.4.1. cAMP Ultra LANCE Assay
3.4.2. β-Arrestin Tango Method
3.4.3. Reagents and Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sneddon, L.U. Comparative Physiology of Nociception and Pain. Physiology 2018, 33, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laycock, H.; Bantel, C. Opioid mechanisms and opioid drugs. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 20, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machelska, H.; Celik, M.O. Advances in Achieving Opioid Analgesia without Side Effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineyro, G.; Nagi, K. Signaling diversity of mu- and delta- opioid receptor ligands: Re-evaluating the benefits of β-arrestin/G protein signaling bias. Cell. Signal. 2021, 80, 109906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listos, J.; Łupina, M.; Talarek, S.; Mazur, A.; Orzelska-Górka, J.; Kotlińska, J. The Mechanisms involved in Morphine Addiction: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Martin, B.; Brenneman, R.; Luttrell, L.M.; Maudsley, S. Allosteric modulators of G protein-coupled receptor: Future therapeutics for complex physiological disorders. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burford, N.T.; Clark, M.J.; Wehrman, T.S.; Gerritz, S.W.; Banks, M.; O’Connell, J.; Traynor, J.R.; Alt, A. Discovery of positive allosteric modulators and silent allosteric modulators of the -opioid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10830–10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohbuchi, K.; Miyagi, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Mizuhara, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Omiya, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Warabi, E.; Sudo, Y.; Yokoyama, A.; et al. Ignavine: A novel allosteric modulator of the opioid receptor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, N.T.; Traynor, J.R.; Alt, A. Positive allosteric modulators of the -opioid receptor: A novel approach for future pain medications. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaysse, P.J.; Gardner, E.L.; Zukin, R.S. Modulation of rat brain opioid receptors by cannabinoids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 241, 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, S.A.; Arnatt, C.K.; He, H.; Selly, D.E.; Mosier, P.D.; Kellogg, G.E.; Zhang, Y. Binding mode characterization of 6α- and 6β-N-heterocyclic substituted naltrexamine derivatives via docking in opioid receptor crystal structures and site-directed mutagenesis studies: Application of the ‘message-address’ concept in development of mu opioid receptor selective antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6405–6413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obeng, S.; Wang, H.; Jali, A.; Stevens, D.L.; Akbarali, H.I.; Dewey, W.L.; Selley, D.E.; Zhang, Y. Structure-activity relationship studies of 6α- and 6β-indolylacetamidonaltrexamine derivatives as bitopic mu opioid receptor modulators and elaboration of the “message-address concept” to comprehend their functional conversion. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.T.; Pitis, P.; Liu, G.; Yuan, C.; Gotchev, D.; Cowan, C.L.; Rominger, D.H.; Koblish, M.; DeWire, S.M.; Crombie, A.L.; et al. Structure-activity relationships and discovery of a G protein biased μ opioid receptor ligand, [(3-methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]({2-[(9R)-9-(pyridin-2-yl)-6-oxaspiro-[4.5]decan-9-yl]ethyl})amine (TRV130), for the treatment of acute severe pain. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8019–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWire, S.M.; Yamashita, D.S.; Rominger, D.H.; Liu, G.; Cowan, C.L.; Graczyk, T.M.; Chen, X.T.; Pitis, P.M.; Gotchev, D.; Yuan, C.; et al. A G protein-biased ligand at the μ-opioid receptor is potently analgesic with reduced gastrointestinal and respiratory dysfunction compared with morphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves New Opioid for Intravenous Use in Hospitals, Other Controlled Clinical Settings; U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020.
- Azzam, A.A.; McDonald, J.; Lambert, D.G. Hot topics in opioid pharmacology: Mixed and biased opioids. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, e136–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Lin, H.; Aryal, D.K.; McCorvy, J.D.; Dengler, D.; Corder, G.; Levit, A.; Kling, R.C.; Bernat, V.; Hubner, H.; et al. Structure-based discovery of opioid analgesics with redused side effects. Nature 2016, 537, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matosiuk, D.; Fidecka, S.; Antkiewicz-Michaluk, L.; Dybała, I.; Kozioł, A.E. Synthesis and pharmacological activity of new carbonyl derivatives of 1-aryl-2-iminoimidazolidine: Part 1. Synthesis and pharmacological activity of chain derivatives of 1-aryl-2-iminoimidazolidine containing urea moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 36, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straszak, D.; Siwek, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Mordyl, B.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Pietrzak, A.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Drop, B.; Matosiuk, D. Modulation of the MOP receptor (μ opioid receptor) by imidazo [1,2-a]imidazole-5,6-diones: In search of the elucidation of the mechanism of action. Molecules 2022, 27, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartuzi, D.; Kedzierska, E.; Kaczor, A.A.; Schmidhammer, H.; Matosiuk, D. Novel positive allosteric modulators of opioid receptor—Insight from in silico and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Faust, G. Verfahren zur herstellug von derivaten des n-phenylaethyldiamins. German Democratic Republic patent DD155614A1, 23 June 1982. Available online: https://patent.google.com/patent/DD155614A1/en/en17 (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Strecker, A. Ueber die kunstliche Bildung der Milchsaure und einen neuen, dem Glycocoll homologen Korper. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1850, 75, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A. Synthesis of ring-substituted N-phenylglycines, their nitriles and amides. J. Org. Chem. 1957, 22, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, H.; Nguyen, T.; Nicoletti, G.; Jackson, N.; Hugel, H. Comparisons of halogenated β-nitrostyrenes as antimicrobial agents. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X. Enantioselective hydrogenation of α, β-disubstituted nitroalkenes. ChemComm 2014, 50, 8878–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumilova, L.A.; Korsakov, M.K.; Dorogov, M.V.; Shalygina, E.E. Synthesis of sulfonate derivatives of hetaryl-isoxazoles. Russ. Chem. Bull. Int. Ed. 2014, 63, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gładkowski, W.; Skrobiszewski, A.; Mazur, M.; Siepka, M.; Pawlak, A.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B.; Białońska, A.; Poradowski, D.; Drynda, A.; Urbaniak, M. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel halolactones with β-aryl substituents from simple aromatic aldehydes. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 10414–10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xie, R.; Zhang, T.; Mei, X.; Yang, J.; Ning, J. Design, synthesis and bioactivities of novel oxime ether derivatives. J. Pestic. Sci. 2013, 38, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, T.C.; Wakchaure, V.N.; Ghosh, A.K.; Mohanty, R.R. Evaluation of titanium(IV) alkoxides and Raney nickel for asymmetric reductive amination of prochiral aliphatic ketones. Org. Lett. 2005, 22, 4967–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

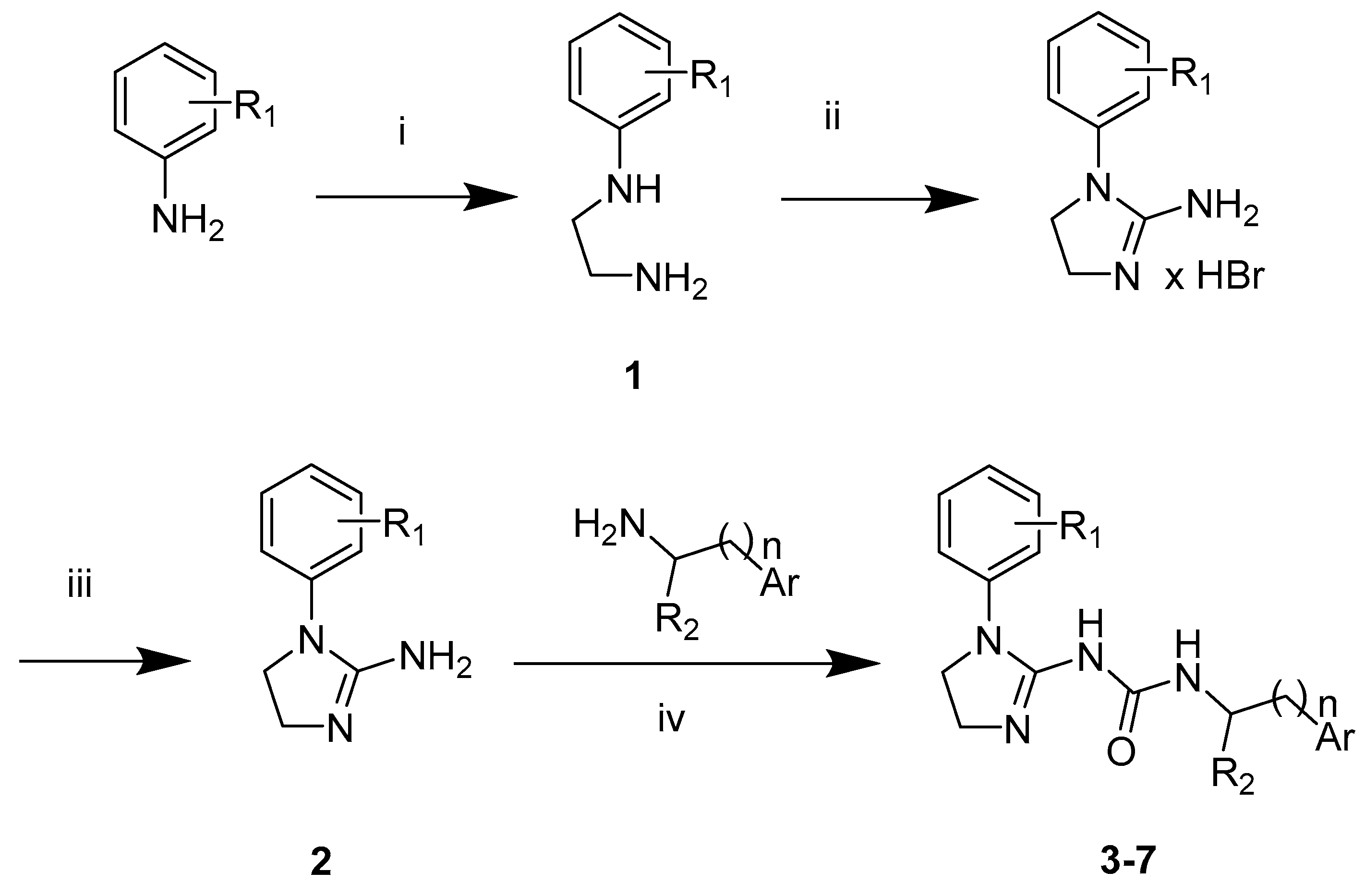
| Compound Yield | R1 | R2 | n | Ar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3a 51% | H | H | 0 | 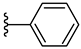 |
| 3b 31% | 2-CH3 | H | 0 | 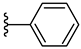 |
| 3c 41% | 3-CH3 | H | 0 | 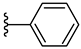 |
| 3d 48% | 4-CH3 | H | 0 | 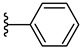 |
| 3e 32% | 2-Cl | H | 0 | 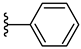 |
| 3f 44% | 3-Cl | H | 0 | 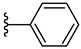 |
| 3g 56% | 4-Cl | H | 0 | 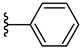 |
| 4a 58% | H | CH3 | 0 | 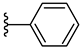 |
| 4b 34% | 2-CH3 | CH3 | 0 |  |
| 4c 46% | 3-CH3 | CH3 | 0 | 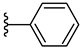 |
| 4d 39% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 0 |  |
| 4e 46% | 2-Cl | CH3 | 0 | 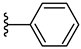 |
| 4f 42% | 3-Cl | CH3 | 0 | 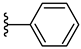 |
| 4g 51% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 0 |  |
| 5a 49% | H | H | 1 | 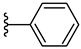 |
| 5b 49% | 2-CH3 | H | 1 | 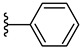 |
| 5c 45% | 3-CH3 | H | 1 | 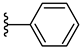 |
| 5d 51% | 4-CH3 | H | 1 |  |
| 5e 32% | 2-Cl | H | 1 | 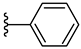 |
| 5f 41% | 3-Cl | H | 1 | 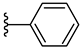 |
| 5g 48% | 4-Cl | H | 1 | 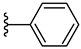 |
| 6a 41% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6b 38% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 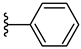 |
| 6c 46% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 | 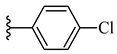 |
| 6d 46% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 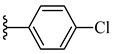 |
| 6e 54% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 | 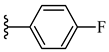 |
| 6f 44% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6g 39% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 | 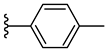 |
| 6h 36% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 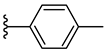 |
| 6i 32% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6j 44% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6k 45% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 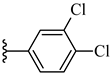 |
| 6l 37% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6m 42% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 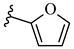 |
| 6n 33% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 6o 39% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 | 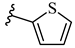 |
| 6p 29% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 1 | 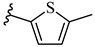 |
| 6r 31% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 1 |  |
| 7a 34% | 4-OCH3 | CH3 | 2 | 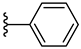 |
| 7b 42% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 2 | 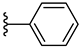 |
| 7c 38% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 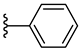 |
| 7d 32% | 4-OCH3 | CH3 | 2 | 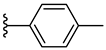 |
| 7e 30% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 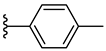 |
| 7f 39% | 4-OCH3 | CH3 | 2 | 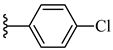 |
| 7g 45% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 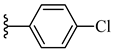 |
| 7h 42% | 4-OCH3 | CH3 | 2 | 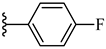 |
| 7i 41% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 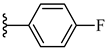 |
| 7j 37% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 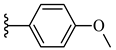 |
| 7k 37% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 |  |
| 7l 39% | 4Cl | CH3 | 2 | 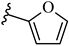 |
| 7m 31% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 | 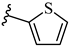 |
| 7n 42% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 2 | 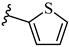 |
| 7o 33% | 4-CH3 | CH3 | 2 |  |
| 7p 29% | 4-Cl | CH3 | 2 |  |
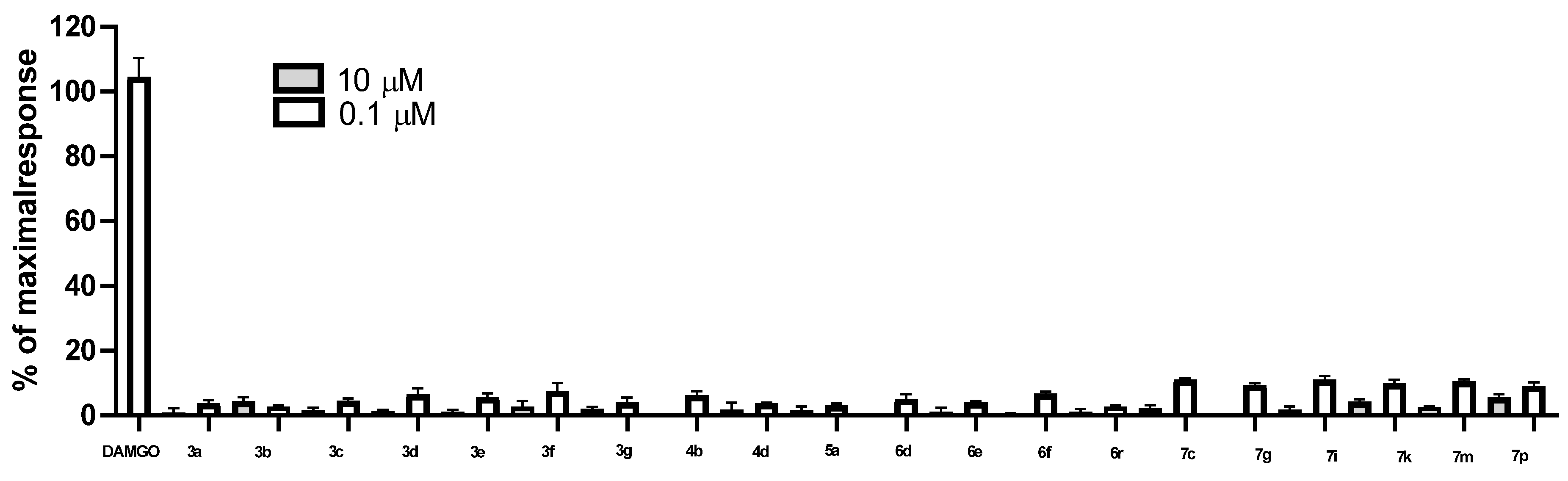
| Compound | Percentage of Maximal Response at Tested Concentrations (% ± SEM) | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 μM | 0.1 μM | |
| DAMGO | n.d. | 104.5 ± 5.9 |
| 3a | 0.8 ± 1.5 | 3.8 ± 0.9 |
| 3b | 4.4 ± 1.2 | 2.8 ± 0.5 |
| 3c | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 4.6 ± 0.7 |
| 3d | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 6.6 ± 1.8 |
| 3e | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 5.6 ± 1.3 |
| 3f | 2.8 ± 1.6 | 7.5 ± 2.6 |
| 3g | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 1.5 |
| 4b | 0.0 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 1.2 |
| 4d | 1.8 ± 2.2 | 3.7 ± 0.2 |
| 5a | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 3.1 ± 0.7 |
| 6d | 0.0 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 1.6 |
| 6e | 1.1 ± 1.3 | 4.0 ± 0.4 |
| 6f | 0.1 ± 0.7 | 6.8 ± 0.5 |
| 6r | 1.1 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 0.4 |
| 7c | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 11.0 ± 0.5 |
| 7g | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 9.4 ± 0.5 |
| 7i | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 11.1 ± 1.2 |
| 7k | 4.2 ± 0.8 | 9.9 ± 1.2 |
| 7m | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 10.5 ± 0.7 |
| 7p | 5.5 ± 1.0 | 9.2 ± 1.1 |
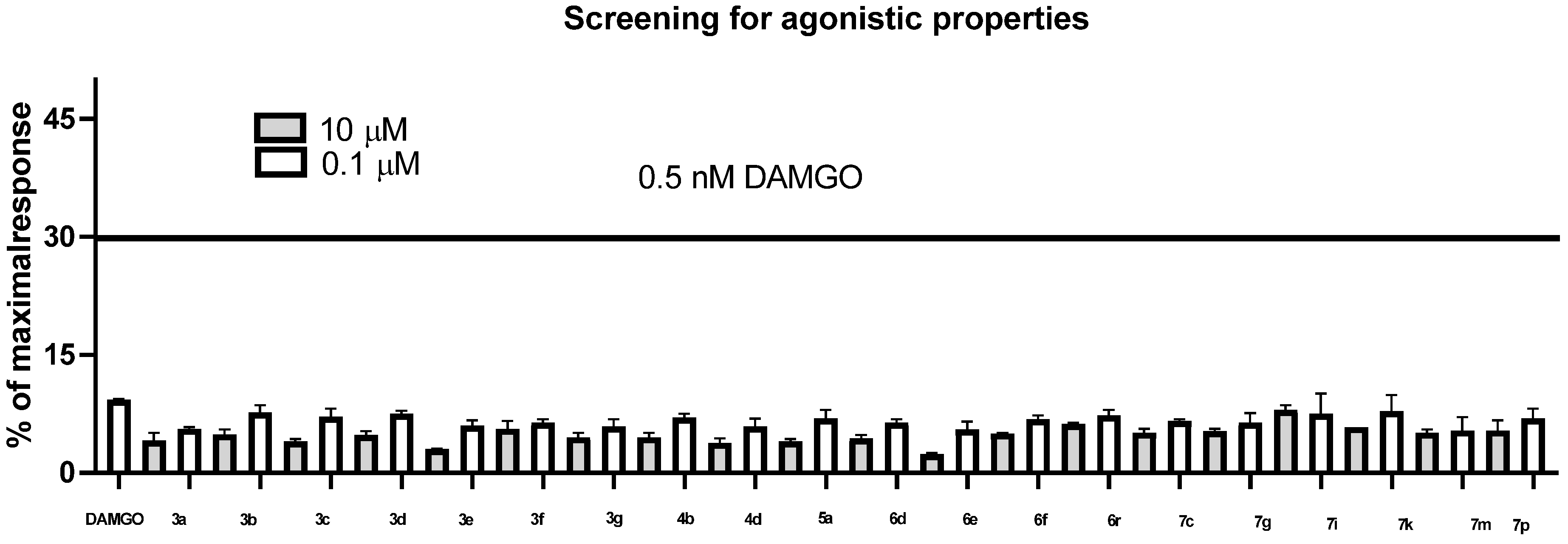
| Compound | Percent of Maximal Response at Tested Concentration (% ± SEM) | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 μM | 0.1 μM | |
| Vehicle | 9.3 ± 0.1 | |
| 3a | 4.1 ± 1.0 | 5.6 ± 0.2 |
| 3b | 4.9 ± 0.6 | 7.7 ± 0.9 |
| 3c | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 7.1 ± 1.1 |
| 3d | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.4 |
| 3e | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 6.0 ± 0.7 |
| 3f | 5.6 ± 1.0 | 6.4 ± 0.4 |
| 3g | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 5.9 ± 0.9 |
| 4b | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 7.0 ± 0.5 |
| 4d | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 5.9 ± 1.0 |
| 5a | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 6.9 ± 1.1 |
| 6d | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 6.4 ± 0.4 |
| 6e | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 5.5 ± 1.0 |
| 6f | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 0.5 |
| 6r | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.7 |
| 7c | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| 7g | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 1.2 |
| 7i | 8.0 ± 0.6 | 7.5 ± 2.6 |
| 7k | 5.8 ± 0.0 | 7.8 ± 2.1 |
| 7m | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 7.4 ± 1.7 |
| 7p | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.3 |
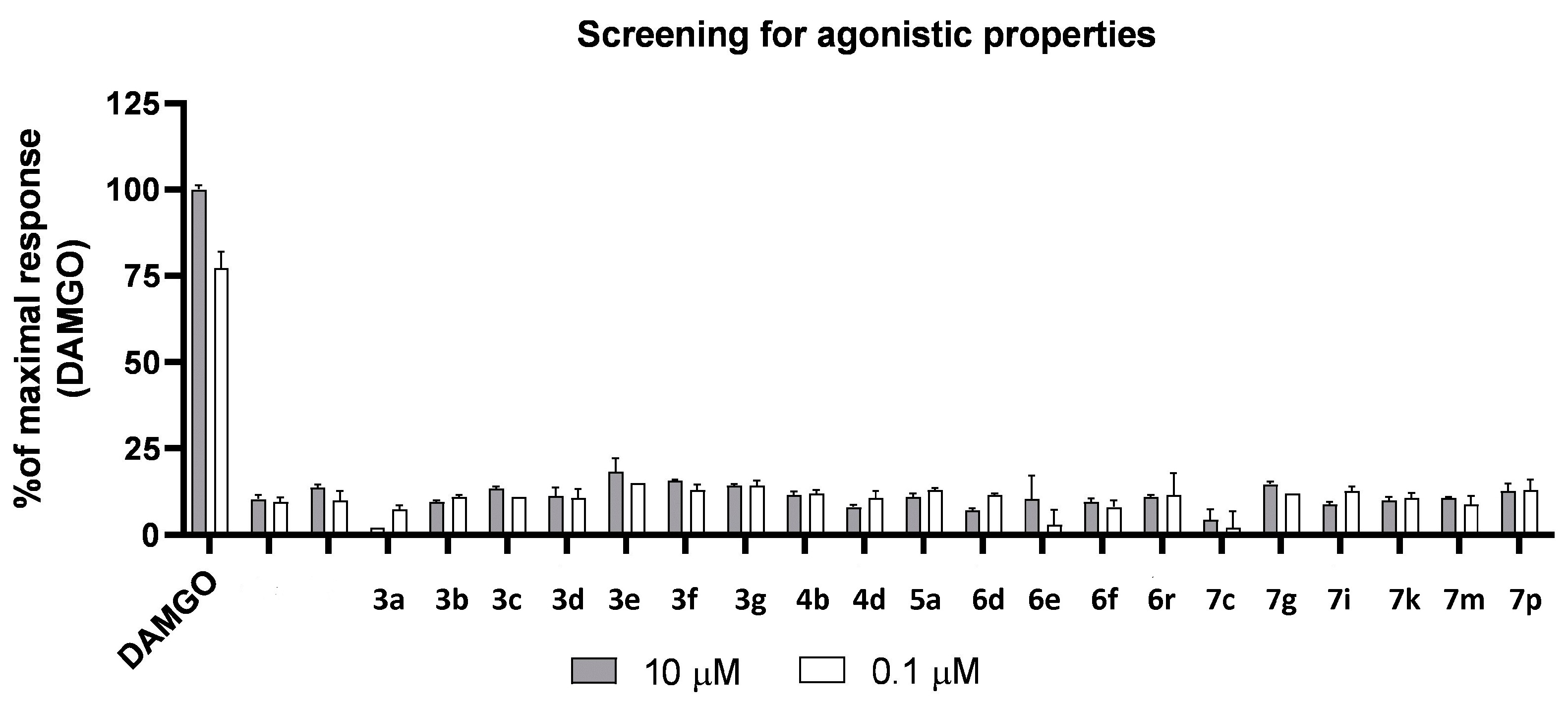
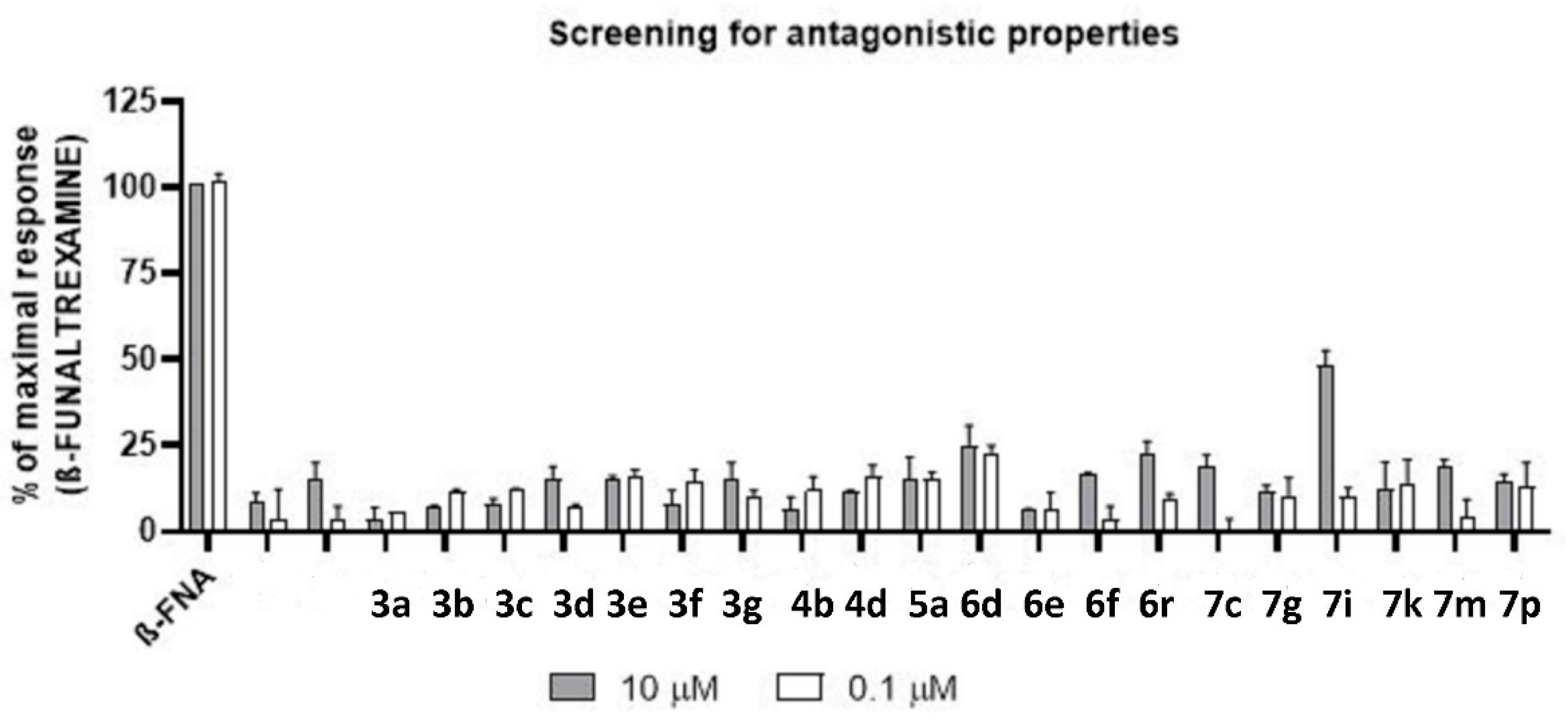
| Compound | Agonist Mode | Antagonist Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emax% (10 µM) | Emax% (0.1 µM) | Emax% (10 µM) | Emax% (0.1 µM) | |
| DAMGO | 100% | 77% | - | - |
| ß-FUNALTREXAMINE | - | - | 100% | 100% |
| 3a | 2% | 7% | 4% | 6% |
| 3b | 10% | 11% | 7% | 12% |
| 3c | 13% | 11% | 8% | 12% |
| 3d | 11% | 11% | 15% | 8% |
| 3e | 18% | 15% | 15% | 16% |
| 3f | 16% | 13% | 8% | 15% |
| 3g | 14% | 14% | 16% | 10% |
| 4b | 12% | 12% | 7% | 12% |
| 4d | 8% | 11% | 12% | 16% |
| 5a | 11% | 13% | 15% | 15% |
| 6d | 7% | 12% | 25% | 23% |
| 6e | 11% | 3% | 6% | 7% |
| 6f | 10% | 8% | 17% | 4% |
| 6r | 11% | 12% | 22% | 10% |
| 7c | 4% | 2% | 19% | 0% |
| 7g | 15% | 12% | 12% | 10% |
| 7i | 9% | 13% | 48% | 10% |
| 7k | 10% | 11% | 12% | 14% |
| 7m | 11% | 9% | 19% | 5% |
| 7p | 13% | 13% | 14% | 13% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Straszak, D.; Woźniak, S.; Siwek, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Pietrzak, A.; Drop, B.; Matosiuk, D. Novel 1-(1-Arylimiazolin-2-Yl)-3-Arylalkilurea Derivatives with Modulatory Activity on Opioid MOP Receptors. Molecules 2024, 29, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030571
Straszak D, Woźniak S, Siwek A, Głuch-Lutwin M, Kołaczkowski M, Pietrzak A, Drop B, Matosiuk D. Novel 1-(1-Arylimiazolin-2-Yl)-3-Arylalkilurea Derivatives with Modulatory Activity on Opioid MOP Receptors. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030571
Chicago/Turabian StyleStraszak, Dominik, Sylwia Woźniak, Agata Siwek, Monika Głuch-Lutwin, Marcin Kołaczkowski, Aldona Pietrzak, Bartłomiej Drop, and Dariusz Matosiuk. 2024. "Novel 1-(1-Arylimiazolin-2-Yl)-3-Arylalkilurea Derivatives with Modulatory Activity on Opioid MOP Receptors" Molecules 29, no. 3: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030571
APA StyleStraszak, D., Woźniak, S., Siwek, A., Głuch-Lutwin, M., Kołaczkowski, M., Pietrzak, A., Drop, B., & Matosiuk, D. (2024). Novel 1-(1-Arylimiazolin-2-Yl)-3-Arylalkilurea Derivatives with Modulatory Activity on Opioid MOP Receptors. Molecules, 29(3), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030571







