Application of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Metabolomic Data from an ApoA-I Knockout Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
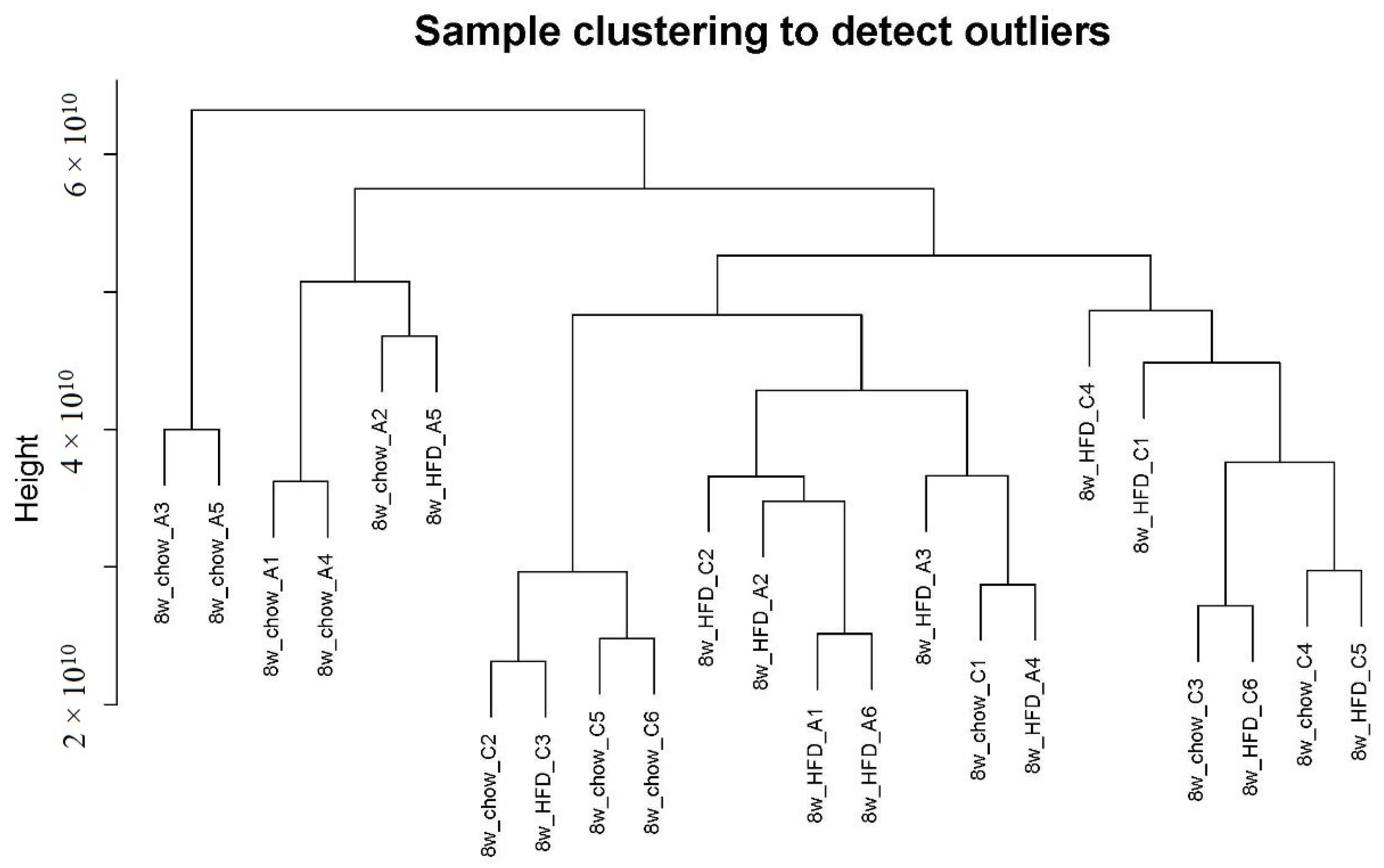
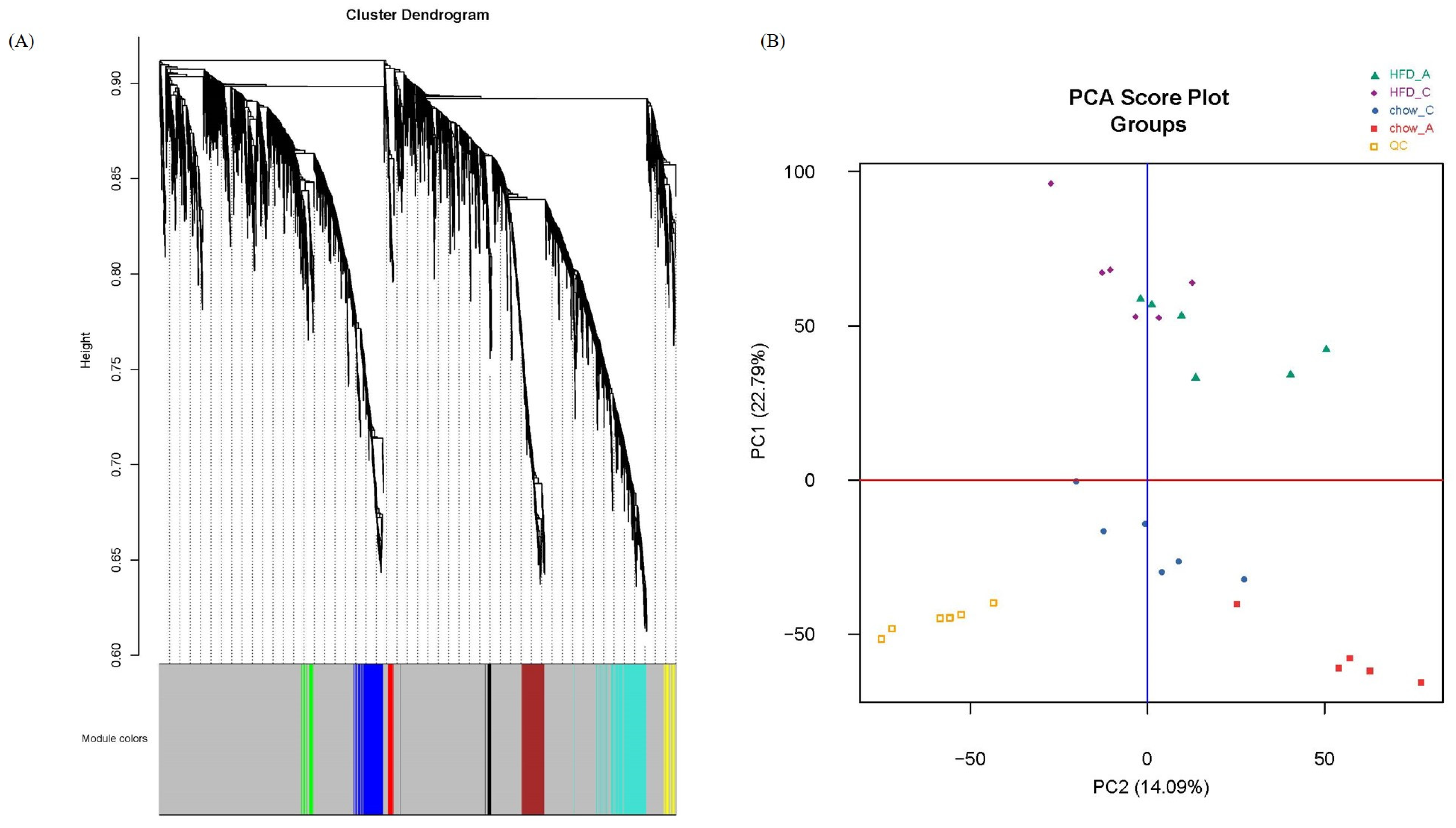
2.1. Non-Targeted LC-MS Metabolomics Data of ApoA-I-Knockout Mice
2.2. Weighted Co-Expression Network Construction
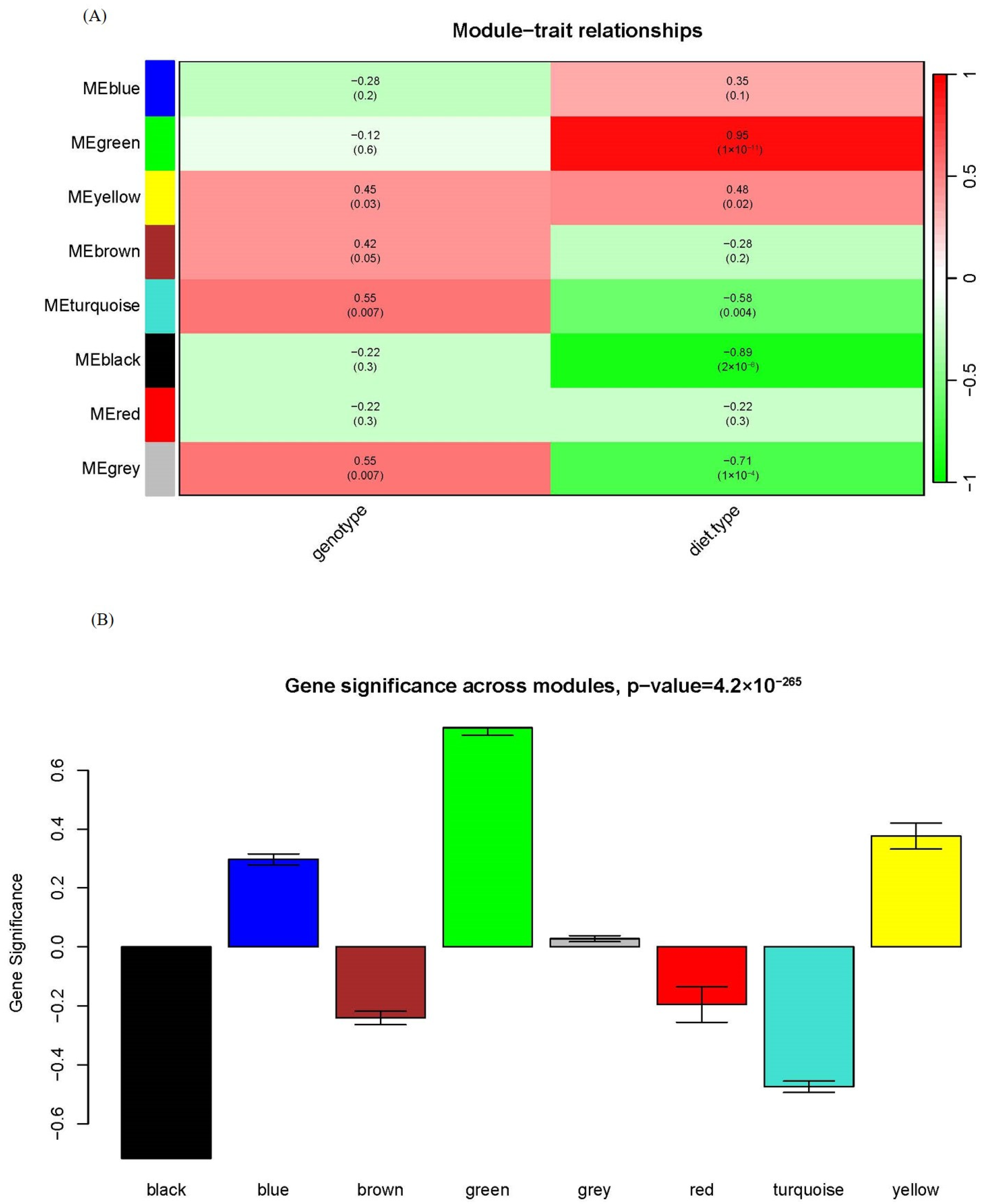
2.3. Association of Modules to Phenotype and Module–Module Relationship
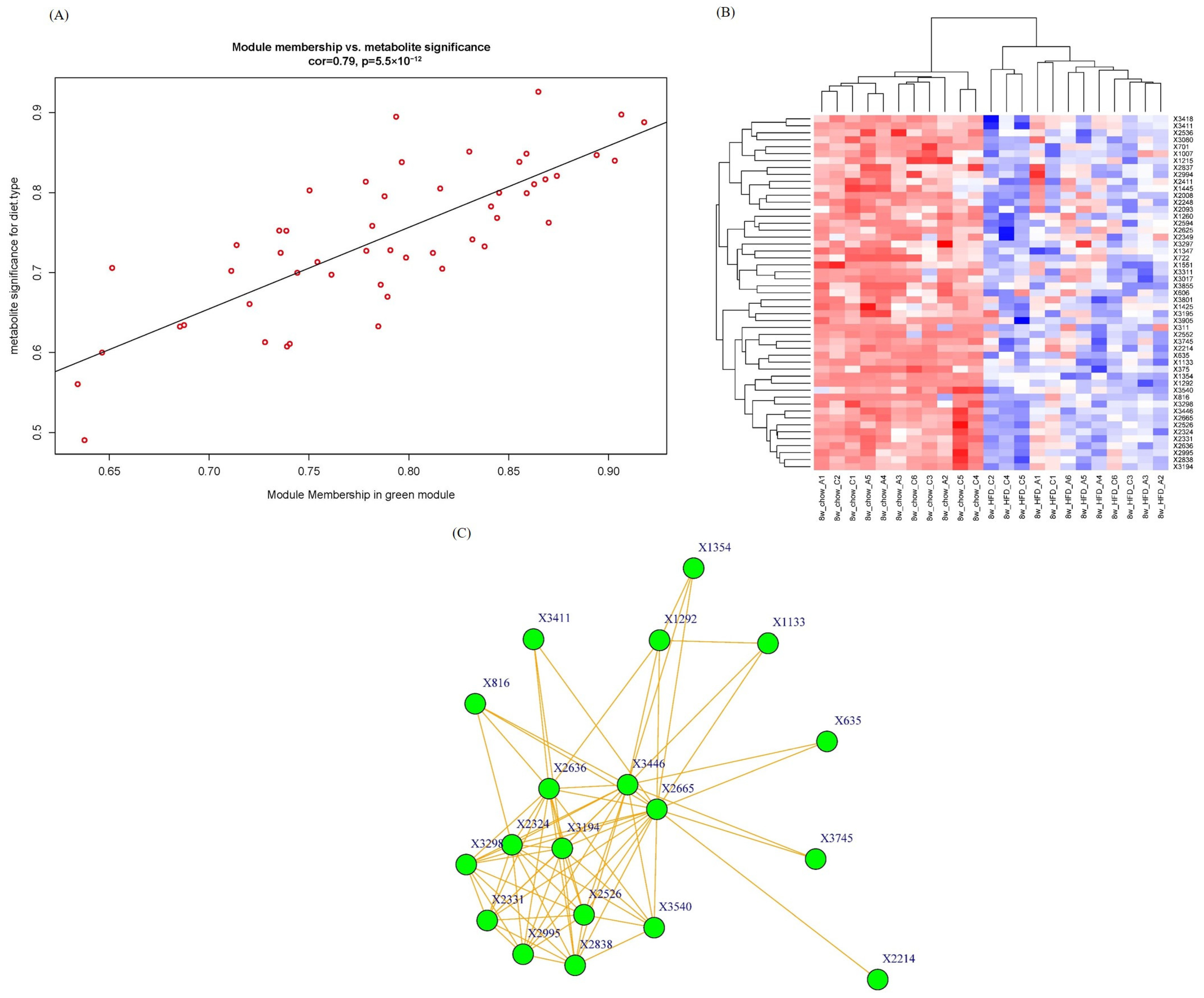
2.4. Intramodular Analysis and Hub Metabolites
3. Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.2.1. WGCNA Network Construction and Module Detection
3.2.2. Association of Modules with Phenotypes and Module–Module Relationships
3.3. Visualization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WGCNA | weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| TOM | Topological Overlap Measure |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| MS | module significant |
| MM | module membership |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
References
- Barnes, S.; Benton, H.P.; Casazza, K.; Cooper, S.J.; Cui, X.; Du, X.; Engler, J.A.; Kabarowski, J.H.; Li, S.; Pathmasiri, W.; et al. Training in metabolomics research. I. Designing the experiment, collecting and extracting samples and generating metabolomics data. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, ii–iii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, X.; Bai, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, G.; Xu, G. LC-MS-based metabonomics analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 866, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guleria, A.; Misra, D.P.; Rawat, A.; Dubey, D.; Khetrapal, C.L.; Bacon, P.; Misra, R.; Kumar, D. NMR-Based Serum Metabolomics Discriminates Takayasu Arteritis from Healthy Individuals: A Proof-of-Principle Study. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3372–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.R.; Nielsen, K.L.; Laursen, M.R.; Nielsen, C.B.; Svendsen, P.; Dimke, H.; Christensen, E.I.; Johannsen, M.; Moestrup, S.K. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of ABCC6-Deficient Mice Discloses an Altered Metabolic Liver Profile. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4591–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, M.E.; Kinross, J.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic phenotyping and systems biology approaches to understanding metabolic syndrome and fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, B.F. Mass spectrometry in systems biology: An overview. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2008, 27, 635–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Xu, G. Current state-of-the-art of nontargeted metabolomics based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with special emphasis in clinical applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1374, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, R.; Salek, R.M.; Moreno, P.; Canueto, D.; Steinbeck, C. Navigating freely-available software tools for metabolomics analysis. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, A.; Tran, V.; Kleensang, A.; Hartung, T. Weighted Gene Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA) Reveals Novel Transcription Factors Associated With Bisphenol A Dose-Response. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. WGCNA Application to Proteomic and Metabolomic Data Analysis. Methods Enzym. 2017, 585, 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Alden, N.; Krishnan, S.; Porokhin, V.; Raju, R.; McElearney, K.; Gilbert, A.; Lee, K. Biologically Consistent Annotation of Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13097–13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, C.; Meret, M.; Schmitt, C.A.; Lisec, J. Compound annotation in liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry based metabolomics: Robust adduct ion determination as a prerequisite to structure prediction in electrospray ionization mass spectra. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiLeo, M.V.; Strahan, G.D.; den Bakker, M.; Hoekenga, O.A. Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) applied to the tomato fruit metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Yin, Y. LC-MS-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics Study of High-Density-Lipoprotein-Modulated Glucose Metabolism with an apoA-I Knockout Mouse Model. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, J.D. Gene Co-expression Network Analysis. In Plant Bioinformatics; Edwards, D., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2443, pp. 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, J.P.; Palejev, D. P-value calibration for multiple testing problems in genomics. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2014, 13, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringner, M. What is principal component analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juigné, C.; Becker, E.; Gondret, F. Small networks of expressed genes in the whole blood and relationships to profiles in circulating metabolites provide insights in inter-individual variability of feed efficiency in growing pigs. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, K.; Ou, J.; Huang, J.; Ou, S. p-Coumaric acid and its conjugates: Dietary sources, pharmacokinetic properties and biological activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.; Yousef, A.I.; Abd El-Twab, S.M.; Abdel Reheim, E.S.; Ashour, M.B. Gallic acid and p-coumaric acid attenuate type 2 diabetes-induced neurodegeneration in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Application of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Metabolomic Data from an ApoA-I Knockout Mouse Model. Molecules 2024, 29, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030694
Zhou Z, Liu J, Liu J. Application of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Metabolomic Data from an ApoA-I Knockout Mouse Model. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030694
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhe, Jiao Liu, and Jia Liu. 2024. "Application of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Metabolomic Data from an ApoA-I Knockout Mouse Model" Molecules 29, no. 3: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030694
APA StyleZhou, Z., Liu, J., & Liu, J. (2024). Application of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis to Metabolomic Data from an ApoA-I Knockout Mouse Model. Molecules, 29(3), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030694




