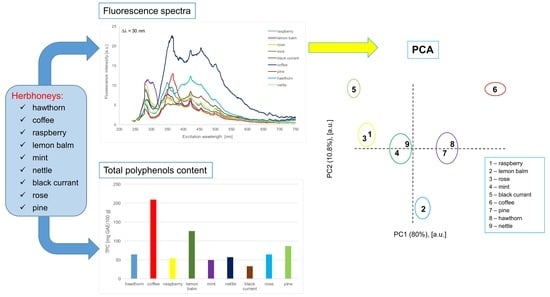
Combined Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis in Characterisation of Selected Herbhoneys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
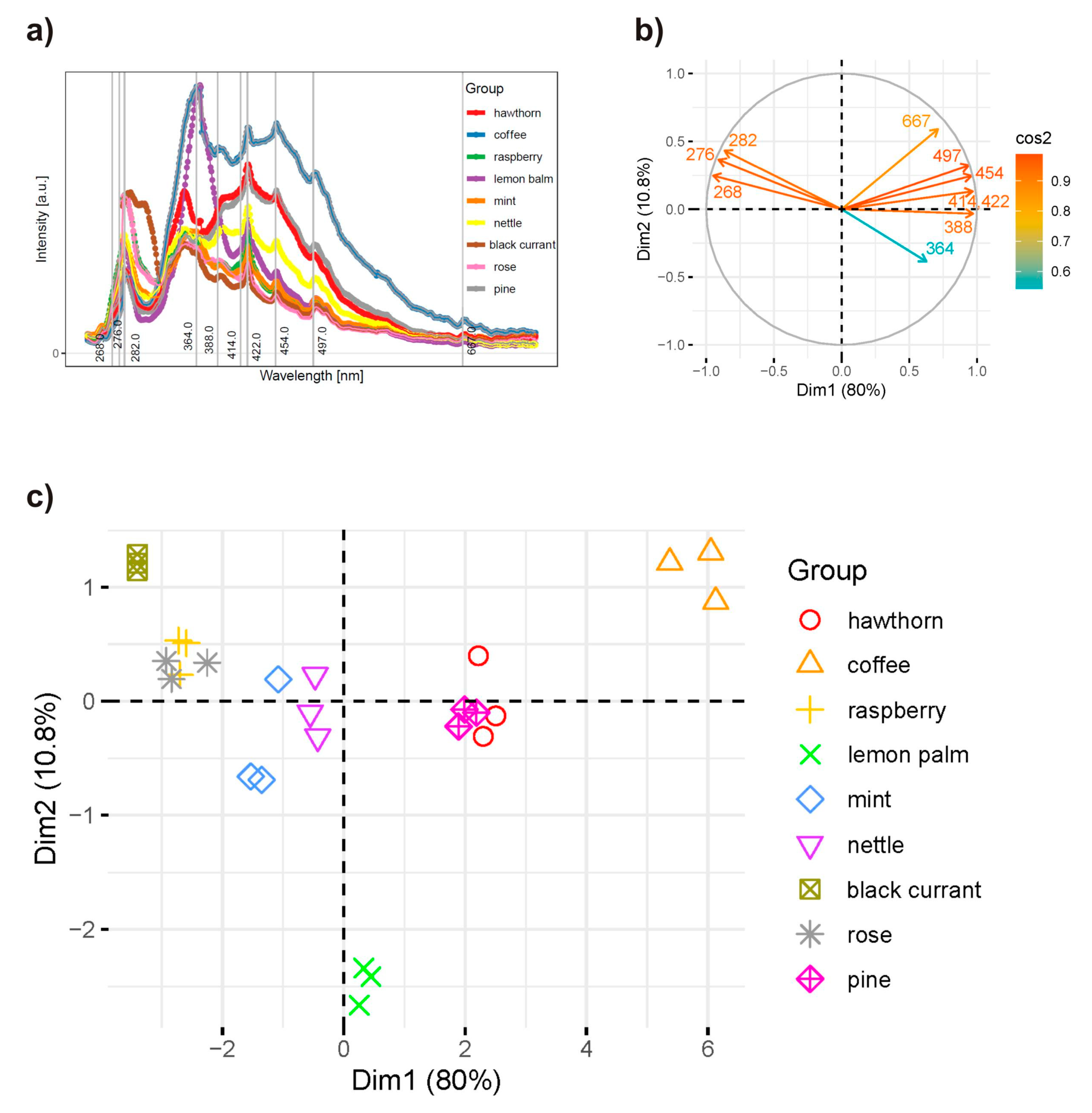
2.1. Emission Spectra in the Wavelength Range of 280–480 nm
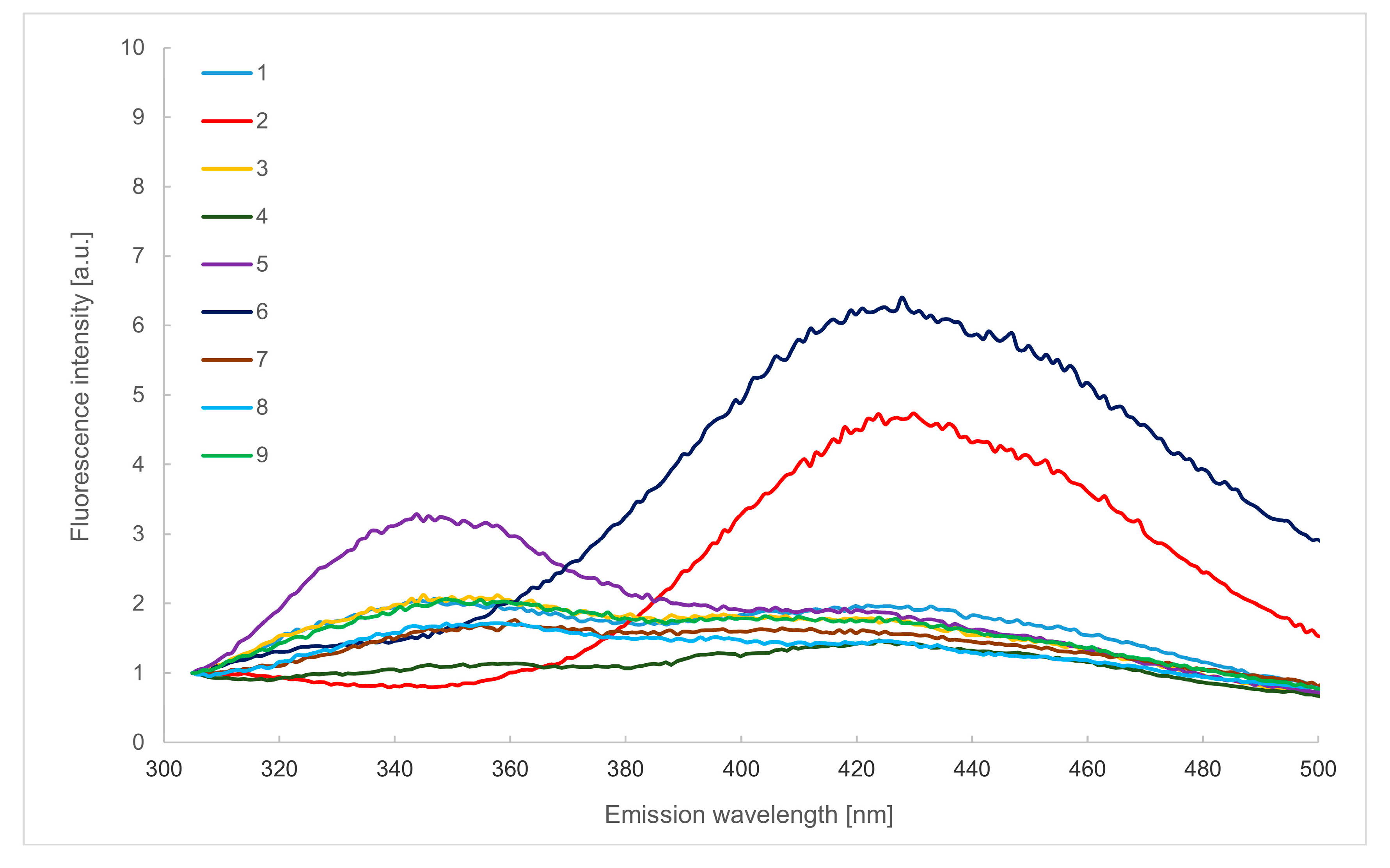
2.2. Emission Spectra in the Wavelength Range of 305–500 nm
2.3. Emission Spectra in the Wavelength of 390–600 nm
2.4. Principal Component Analysis of the Synchronous Spectra
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piszcz, P.; Głód, B.K. Antioxidative properties of selected Polish honeys. J. Apicult. Sci. 2019, 63, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, G.; Rosicka-Kaczmarek, J.; Olejnik, T.P.; Dędek, K. The influence of selected process factors on the physicochemical and biological properties of honeys: A review. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 83, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Czaplicki, J. Garść informacji o ziołomiodach. Pasieka 2003, 3, 48–50. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Juszczak, L.; Socha, R.; Rożnowski, J.; Fortuna, T.; Nalepka, K. Physicochemical properties and quality parameters of herbhoneys. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidorov, V.A.; Bagan, R.; Bakier, S.; Swiecicka, I. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Polish herbhoneys. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Miniaturized NIR spectroscopy in food analysis and quality control: Promises, challenges, and perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xagoraris, M.; Revelou, P.K.; Alissandrakis, E.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Pappas, C.S. The use of right angle fluorescence spectroscopy to distinguish the botanical origin of greek common honey varieties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, N.M.; Elghani, G.E.A.; Farag, M.A. The super-food Manuka honey, a comprehensive review of its analysis and authenticity approaches. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Loomes, K.M.; Prijic, G.; Schlothauer, R.; Stephens, J.M. Lepteridine as a unique fluorescent marker for the authentication of manuka honey. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.M.; Loomes, K.M.; Braggins, T.J.; Bong, J.; Lin, B.; Prijic, G. Fluorescence: A novel method for determining manuka honey floral purity. In Honey Analysis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelec, I.; Brodar, L.; Flanjak, I.; Kenjerić, F.Č.; Kovač, T.; Kenjerić, D.Č.; Primorac, L. Characterization of Croatian honeys by right-angle fluorescence spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Anal. Meth. 2018, 11, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, A.; Mohammed, S.E.A.; Ansari, M.J.; Adgaba, N. Comparison of physicochemical properties and effects of heating regimes on stored Apis mellifera and Apis florea honey. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, E.; Khmelinskii, I.V.; Sikorski, M.; Caponio, F.; Bilancia, M.T.; Pasqualone, A.; Gomes, T. Fluorescence spectroscopy in monitoring of extra virgin olive oil during storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Dufour, E.; Bosset, J.O.; De Baerdemaeker, J. The use of front face fluorescence spectroscopy to classify the botanical origin of honey samples produced in Switzerland. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehretie, S.; Al Riza, D.F.; Yoshito, S.; Kondo, N. Classification of raw Ethiopian honeys using front face fluorescence spectra with multivariate analysis. Food Control 2018, 84, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY., USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Stober, F.; Lichtenthaler, H.K. Fluorescence emission spectra of plant leaves and plant constituents. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1991, 30, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, S.; Ullah, R.; Khan, B. Fluorescence fingerprints of Sidr honey in comparison with uni/polyfloral honey samples. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Honey as a source of dietary antioxidants: Structures, bioavailability and evidence of protective effects against human chronic diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socha, R.; Juszczak, L.; Pietrzyk, S.; Fortuna, T. Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of herbhoneys. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Sowa, P.; Kwaśniewska, M.; Wesołowska, M.; Czernicka, M. Physicochemical Parameters and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Honey Enriched With Herbs. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2017, 72, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamróz, M.K.; Paradowska, K.; Zawada, K.; Makarova, K.; Kaźmierski, S.; Wawer, I. 1H and 13C NMR-based sugar profiling with chemometric analysis and antioxidant activity of herbhoneys and honeys. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniawska, E.; Baj, T.; Los, R.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Malm, A.; Glowniak, K. Phenolic acids content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Ligusticum mutellina L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Ma, G.; Fang, Y.; Yang, W.; Ma, N.; Fang, D.; Hu, Q.; Pei, F. The antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of different phenolic acids grafted onto chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, T.; Starowicz, M.; Kłębukowska, L.; Hanus, P. The profile of polyphenolic compounds, contents of total phenolics and flavonoids, and antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of bee products. Molecules 2022, 27, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Lamas, L.B.; Flórez, S.M.; Toyos, P.A.; et al. Phenolic compounds in honey and their associated health benefits: A review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Antioxidant activity, total phenolic content, individual phenolics and physicochemical parameters suitability for Romanian honey authentication. Foods 2020, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, E.; Santinami, G.; Domenici, V. Front-face fluorescence of honey of different botanic origin: A case study from Tuscany (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Stryjecka, M.; Teter, A.; Skałecki, P.; Domaradzki, P.; Florek, M. Relationships between the content of phenolic compounds and the antioxidant activity of polish honey varieties as a tool for botanical discrimination. Molecules 2021, 26, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiszewska, K.; Aniołowska, M.; Howis, M.; Nowakowski, P. Free amino acids composition as a marker for the origin of honey (Kompozycja wolnych aminokwasów jako marker źródła pochodzenia miodów). Przem. Chem. 2011, 90, 806. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar, A.; Nausheen, R.; Muzaffar, H.; Naeem, M.A.; Farooq, M.; Khurshid, M.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Allemailem, K.S.; Anwar, H. Potential therapeutic benefits of honey in neurological disorders: The role of polyphenols. Molecules 2022, 27, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Chen, Y.T.; Ruan, J.C.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, J.G.; Zhang, Q.F. Structure-activity relationship of dietary flavonoids on pancreatic lipase. Cur. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rijke, E.; Joshi, H.C.; Sanderse, H.R.; Ariese, F.; Brinkman, U.A.T.; Gooijer, C. Natively fluorescent isoflavones exhibiting anomalous Stokes’ shifts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 468, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Dimitriou, E.; Kontakos, S.; Kontominas, M.G. Phenolic profile, colour intensity, and radical scavenging activity of Greek unifloral honeys. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, D.; Gabriele, M.; Summa, M.; Colosimo, R.; Leonardi, D.; Domenici, V.; Pucci, L. Antioxidant, nutraceutical properties, and fluorescence spectral profiles of bee pollen samples from different botanical origins. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunat-Budzyńska, M.; Rysiak, A.; Wiater, A.; Grąz, M.; Andrejko, M.; Budzyński, M.; Bryś, M.S.; Sudziński, M.; Tomczyk, M.; Gancarz, M.; et al. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of new honey varietals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sádecká, J.; Uríčková, V.; Májek, P.; Jakubíková, M. Comparison of different fluorescence techniques in brandy classification by region of production. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 216, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Gu, C.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, P.; Tan, L. Effects of hydroxylation at C3′ on the B ring and diglycosylation at C3 on the C ring on flavonols inhibition of α-glucosidase activity. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Le, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Soft. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F.; Factoextra: Extract and Visualise the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. R Package Version 1.0.999. 2020. Available online: http://www.sthda.com/english/rpkgs/factoextra (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | Sample | TPC (mg GAE/100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | raspberry | 54.49 ± 1.10 a,A |
| 2 | lemon balm | 126.55 ± 1.21 b,B |
| 3 | rose | 64.77 ± 0.32 c,C |
| 4 | mint | 49.52 ± 0.96 a,A,C |
| 5 | black currant | 32.86 ± 1.78 d,D |
| 6 | coffee | 209.38 ± 4.04 e,E |
| 7 | pine | 86.62 ± 0.93 f,F |
| 8 | hawthorn | 64.21 ± 5.11 c,C |
| 9 | nettle | 57.11 ± 1.42 a,A,C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banaś, J.; Banaś, M. Combined Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis in Characterisation of Selected Herbhoneys. Molecules 2024, 29, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040749
Banaś J, Banaś M. Combined Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis in Characterisation of Selected Herbhoneys. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040749
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanaś, Joanna, and Marian Banaś. 2024. "Combined Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis in Characterisation of Selected Herbhoneys" Molecules 29, no. 4: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040749
APA StyleBanaś, J., & Banaś, M. (2024). Combined Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis in Characterisation of Selected Herbhoneys. Molecules, 29(4), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040749