Titanium Tetrachloride-Assisted Direct Esterification of Carboxylic Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
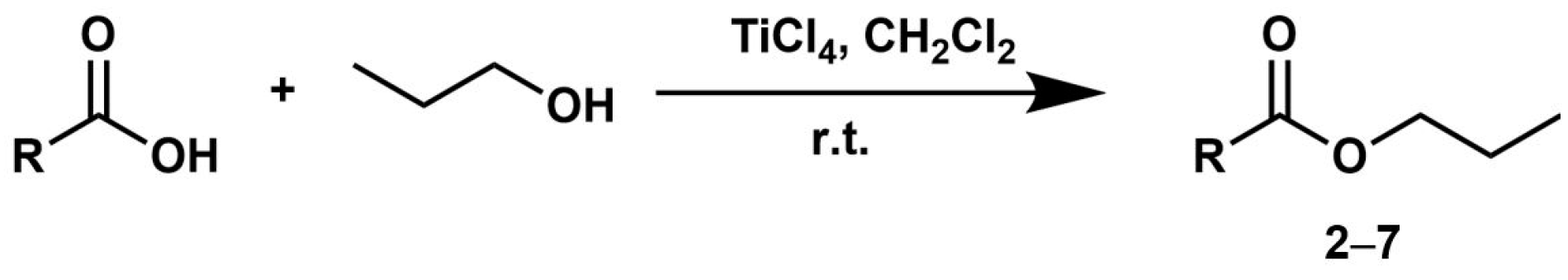
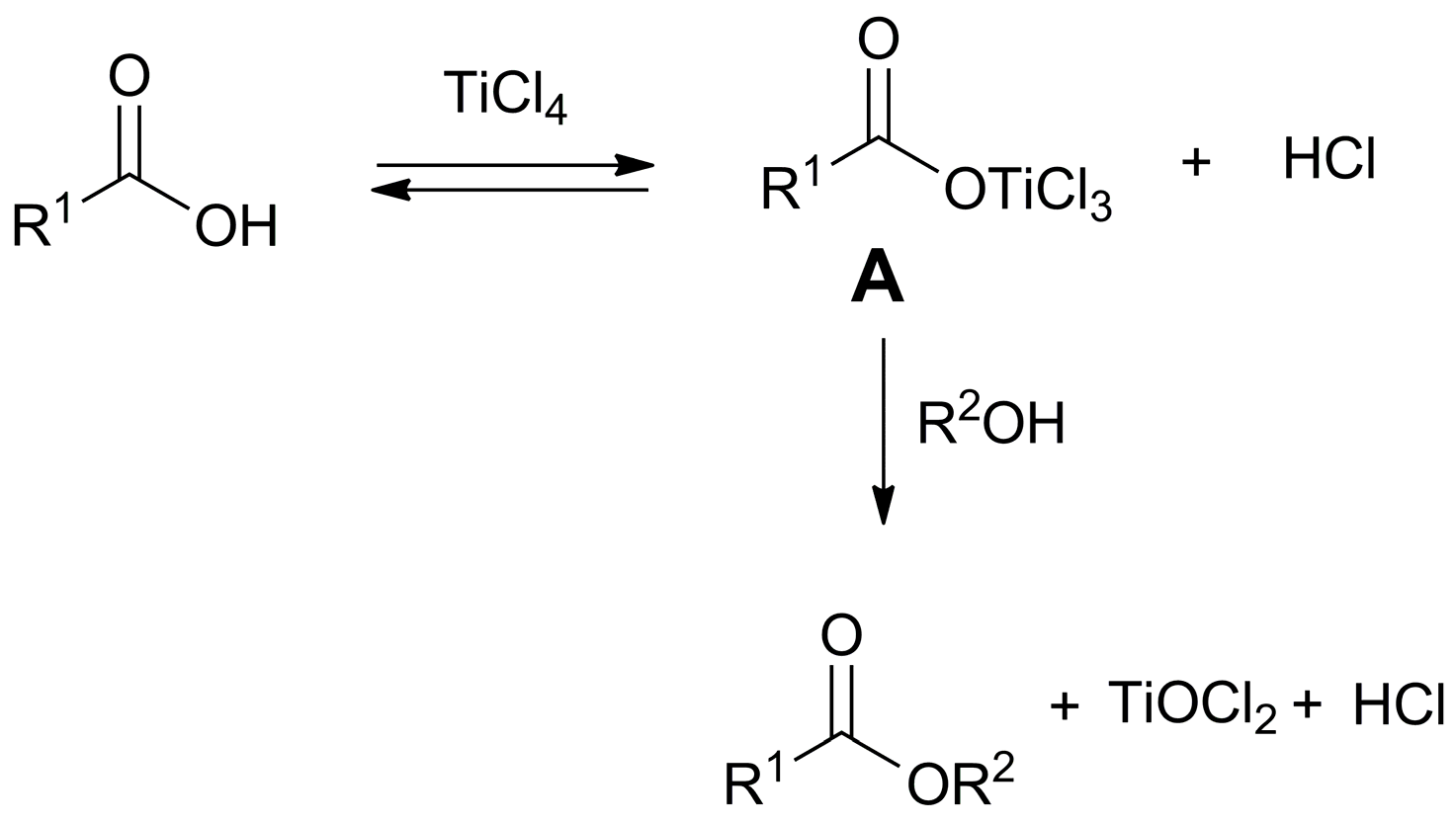
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General One-Pot Synthesis Procedure for Esters 1–10
- Propyl phenylacetate (1): Oil, 89%, rf = 0.89; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.40–7.23 (m, 5H, ArH), 4.07 (t, 2H, J = 6.7 Hz, COOCH2), 3.65 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO), 1.72–1.61 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 0.93 (t, 3H, J = 7.4 Hz, CH2CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.68, 134.24, 129.25, 128.53, 127.02, 66.45, 41.48, 21.96, 10.31; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 178 [M+] (17.5), 136 (23), 119 (7), 92 (31), 91 (100), 65 (24).
- Propyl 4-methoxyphenylacetate (2): Oil, 82%, rf = 0.71; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.21 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz, ArH), 6.87 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz, ArH), 4.05 (t, 2H, J = 6.7 Hz, COOCH2), 3.80 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.57 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO), 1.71–1.59 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 0.92 (t, 3H, J = 7.4 Hz, CH2CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.98, 159.69, 130.25, 126.31, 113.9, 66.36, 55.22, 40.53, 21.96, 10.32; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 208 [M+] (21), 121 (100), 78 (8).
- Propyl 4-chlorophenylacetate (3): Oil, 80%, rf = 0.81; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.32–7.27 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.26–7.19 (m, 2H, ArH), 4.05 (t, 2H, J = 6.7 Hz, COOCH2), 3.60 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO), 1.71–1.58 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 0.91 (t, 3H, J = 7.3 Hz, CH2CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.19, 133.01, 132.64, 130.62, −128.66, 66.59, 40.72, 21.93, 10.30; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 212 [M+] (25), 170 (18), 153 (5), 125 (100), 89 (25).
- Propyl myristate (4): Oil, 99%, rf = 0.84; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 4.02 (t, 2H, J = 6.7 Hz, COOCH2), 2.29 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, CH2CH2CO), 1.71–1.55 (m, 4H, COOCH2CH2CH3, CH2CH2CH2CO), 1.35–1.20 (m, 20H, CH3(CH2)10CH2), 0.98–0.84 (m, 6H, OCH2CH2CH3, CH3(CH2)12CO); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 173.92, 65.76, 34.37, 31.90, 29.65, 29.62, 29.57, 29.44, 29.33, 29.24, 29.14, 25.01, 22.66, 22.00, 14.05, 10.34; MS (EI) m/z (% rel): 270 [M+] (20), 229 (70), 211 (63), 185 (17), 171 (20), 129 (21), 115 (40), 102 (48), 71 (46), 61 (100).
- Propyl palmitate (5): Oil, 97%, rf = 0.78; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 4.02 (t, 2H, J = 6.7 Hz, COOCH2), 2.29 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, CH2CH2CO), 1.72–1.55 (m, 4H, COOCH2CH2CH3, CH2CH2CH2CO), 1.35–1.19 (m, 24H, CH3(CH2)12CH2), 0.98–0.83 (m, 6H, OCH2CH2CH3, CH3(CH2)14CO); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 173.90, 65.76, 34.37, 31.90, 29.66, 29.63, 29.57, 29.44, 29.33, 29.24, 29.14, 25.01, 22.65, 22.00, 14.04, 10.33; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 298 [M+] (29), 257 (56), 239 (54), 213 (16), 171 (20), 129 (18), 115 (42), 102 (50), 85 (26), 73 (46), 61 (100).
- Propyl benzoate (6): Oil, 74%, rf = 0.89; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 8.14–8.01 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.65–7.36 (m, 3H, ArH), 4.29 (t, 2H, J = 6.6 Hz, COOCH2), 1.87–1.74 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 1.04 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, t, 3H, J = 7.4 Hz, CH2CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 166.71, 132.80, 130.53, 129.54, 128.32, 66.55, 22.12, 10.53; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): [M+] 164, (3), 135 (2), 123 (52), 105 (100), 77 (47).
- N-Fmoc-Valine propyl ester (7): Oil, 70%, rf = 0.58; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.78 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.62 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.48–7.28 (m, 4H, ArH), 5.34 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H, NH), 4.41 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2Fmoc), 4.33 (dd, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H, CHCH(CH3)2), 4.25 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H, CHFmoc), 4.18–4.06 (m, 2H, COOCH2), 2.20 (m, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.77–1.61 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 1.06–0.87 (m, 9H, CH(CH3)2, CH2CH3). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 172.13, 156.21, 143.83, 141.33, 127.68, 127.05, 125.07, 119.96, 67.03, 66.89, 59.10, 47.26, 31.40, 21.95, 18.91, 17.59, 10.35.
- 3-Phenylpropyl acetate (8): Oil, 97%, rf = 0.74; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.36–7.16 (m, 5H, ArH), 4.11 (t, 2H, J = 6.6 Hz, COOCH2), 2.75–2.68 (m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2Ph), 2.08 (s, 3H, CH3CO), 2.05–1.90 (m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2Ph); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.09, 141.22, 128.44, 128.39, 126.01, 63.83, 32.19, 30.18, 20.94; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 178 [M+] (2), 118 (94), 117 (100), 105 (11), 91 (41), 77 (10).
- 3-PhenylPropyl α-Naphthylacetate (9): Oil, 50%, rf = 0.81; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 8.10–8.01 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.95–7.78 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.61–7.42 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.29–7.13 (m, 3H, ArH), 7.03–6.95 (m, 2H, ArH), 4.13–4.03 (m, 4H, COOCH2, NaphthylCH2CO), 2.55–2.46 (m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2Ph), 1.97–1.81 (m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2Ph); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.54, 141.06, 133.88, 130.73, 128.75, 128.35, 128.06–127.99, 126.35, 125.93–125.78, 125.49, 123.86, 64.11, 39.35, 31.93, 30.14; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 304 [M+] (26), 186 (100), 141 (97), 115 (30), 91 (50).
- 3-Phenylpropyl 2-phenylbutanoate (10): Oil, 40%, rf = 0.88; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.49–7.01 (m, 10H, ArH), 4.08 (t, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz, COOCH2), 3.48 (t, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, CH2CH(Ph)CO), 2.63–2.53 (m, 2H, OCH2CH2CH2Ph), 2.24–2.05 (m, 1H, CH3CH2CHPh), 1.97–1.76 (m, 3H, CH3CH2CHPh, OCH2CH2CH2Ph), 0.93 (t, 3H, J = 7.4 Hz, CH3CH2CHPh); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.01, 141.15, 139.27, 128.55, 128.40, 127.98, 127.16, 125.95, 63.79, 53.63, 32.01, 30.23, 26.52, 12.19; MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 118 (100), 105 (4), 91 (76), 65 (7).
3.3. One-Pot Synthesis Procedure for Ester 11
- Phenyl phenylacetate (11): Oil, 84%; rf = 0.75; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.47–7.02 (m, 10H, ArH), 3.88 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO). MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 212 [M+] (2), 118 (100), 91 (94), 77 (3), 65 (19).
3.4. General One-Pot Synthesis Procedure for Esters 12–14
- Benzyl phenylacetate (12): Oil, 81%, rf = 0.73; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.51–7.24 (m, 10H, ArH), 5.17 (s, 2H, OCH2Ph), 3.71 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.35, 135.93, 133.95, 129.31, 128.58, 128.54, 128.20, 128.11, 127.13, 66.60, 41.38. MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 226 [M+] (10), 108 (4), 91 (100), 77 (4), 65 (16).
- Benzhydryl phenylacetate (13): Oil, 67%, rf = 0.63; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.48–7.24 (m, 15H, Ar-H), 6.87 (s, 1H, OCH(Ph)2) 3.74 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.41, 140.11, 129.36, 128.54, 128.43, 127.85, 127.57, 127.11, 127.01, 126.54, 77.24, 41.65. MS (EI,) m/z (% rel.): 302 [M+] (2), 210 (4), 184 (8), 167 (100), 118 (4), 91 (12), 77 (5).
- Isopropyl phenylacetate (14): Oil, 70%, rf = 0.83; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.17 (m, 5H, ArH), 5.03 (hept, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, OCH(CH3)2), 3.60 (s, 2H, PhCH2CO), 1.24 (d, 6H, J = 6.3 Hz, OCH(CH3)2). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.15, 134.40, 129.18, 128.49, 126.94, 68.17, 41.74, 21.74. MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 178, 119, 91, 86, 77, 59. MS (EI) m/z (% rel.): 178 [M+] (24), 119 (10), 91 (100), 65 (17).
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larock, R.C. Comprehensive Organic Transformations: A Guide to Functional Group Preparations, 1st ed.; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 966–972. [Google Scholar]
- Otera, J. Esterification: Methods, Reactions and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Larock, R.C.; Rozhkov, R. Inconversion of Nitriles, Carboxylic Acids, and Derivatives. In Comprehensive Organic Transformations: A Guide to Functional Group Preparations, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, A.N.; de Oliveira, D.T.; Angélica, R.S.; de Aguiar Andrade, E.H.; do Rosàrio da Silva, J.K.; da Rocha Filho, G.N.; Coral, N.; de Oliveira Pires, L.H.; Luque, R.; do Nascimento, L.A.S. Efficient esterification of eugenol using a microwave-activated waste kaolin. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2020, 130, 633–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, E.Y.X. Toward infinitely recyclable plastics derived from renewable cyclic esters. Chem 2019, 5, 284–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, V.K.; Rathod, V.K. Enzyme catalyzed synthesis of cosmetic esters and its intensification: A review. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaku, E.; Smith, B.R.; Smith, D.T.; Njardarson, J.T. Top US Pharmaceutical Products of 2013. Available online: https://bpb-us-e2.wpmucdn.com/sites.arizona.edu/dist/9/130/files/2023/11/Top100-US-Pharmaceutical-Products-of-2013.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Carey, J.S.; Laffan, D.; Thomson, C.; Williams, M.T. Analysis of the Reactions Used for the Preparation of Drug Candidate Molecules. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugger, R.W.; Ragan, J.A.; Ripin, D.H.B. Survey of GMP Bulk Reactions Run in a Research Facility between 1985 and 2002. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2005, 9, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakos, M.; Schaffert, E.S.; Clement, L.L.; Villadsen, N.L.; Poulsen, T.B. Ester coupling reactions—An enduring challenge in the chemical synthesis of bioactive natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 605–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Yanagi, R.; Oe, Y. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Esters. In Carboxylic Acid-Key Role in Life Science; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Siengalewicz, P.; Mulzer, J.; Rinner, U. Synthesis of esters and lactones. In Comprehensive Organic Synthesis, 2nd ed.; Knochel, P., Molander, G.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 6, pp. 355–410. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, D. Organic Syntheses Collective; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 5, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Neises, B.; Steglich, W. Simple Method for the Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1978, 17, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.C.; Cruickshank, P.A.; Boshart, G. Notes—A Convenient Synthesis of Water-Soluble Carbodiimides. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 26, 2525–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-A. Recent development of peptide coupling reagents in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2447–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaiyama, T.; Usui, M.; Shimada, E.; Saigo, K. A convenient method for the synthesis of carboxylic esters. Chem. Lett. 1975, 4, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Patel, D.V. BOP as a reagent for mild and efficient preparation of esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 31, 5603–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Li, W. N,N′-Carbonyldiimidazole. In e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kunishima, M.; Kawachi, C.; Morita, J.; Terao, K.; Iwasaki, F.; Tani, S. 4-(4,6-Dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride: An efficient condensing agent leading to the formation of amides and esters. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13159–13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeur, E.; Bradley, M. Amide bond formation: Beyond the myth of coupling reagents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 606–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.C.; Mangroo, D.; Gerber, G.E. A novel method of complete activation by carbonyldiimidazole: Application to ester synthesis. Can. J. Chem. 1988, 66, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzjarrald, V.P.; Pongdee, R. A convenient procedure for the esterification of benzoic acids with phenols: A new application for the Mitsunobu reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, D.; Gazvoda, M.; Kosmrlj, J.; Taniguchi, T. Advances and mechanistic insight on the catalytic Mitsunobu reaction using recyclable azo reagents. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5148–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sha, Y. A Convenient Synthesis of Amino Acid Methyl Esters. Molecules 2008, 13, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaishi, T.; Izumi, M.; Ota, R.; Inoue, C.; Kiyota, H.; Fukase, K. Product Selectivity of Esterification of L-Aspartic Acid and L-Glutamic Acid Using Chlorotrimethylsilane. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, M.A.; Chan, T.H. A simple procedure for the esterification of carboxylic acids. Synthesis 1983, 3, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H. Lewis Acids in Organic Synthesis, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Lewis acids: From conventional homogeneous to green homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4307–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Le Pera, A.; Liguori, A.; Perri, F.; Siciliano, C. Alternative and Chemoselective Deprotection of the α-Amino and Carboxy Functions of N-Fmoc-Amino Acid and N-Fmoc-Dipeptide Methyl Esters by Modulation of the Molar Ratio in the AlCl3/N,N-Dimethylaniline Reagent System. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 21, 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Le Pera, A.; Siciliano, C.; Liguori, A.; Sindona, G. An efficient and highly selective deprotection of N-Fmoc-α-amino acid and lipophilic N-Fmoc-dipeptide methyl esters with aluminium trichloride and N,N-dimethylaniline. J. Pept. Res. 2004, 63, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Guarino, I.F.; Leotta, V.; Romio, E.; Liguori, A. A simple synthesis of anilines by LiAlH4/TiCl4 reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 5341–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, A.; Belsito, E.L.; Gallo, S.; Liguori, A. One-pot conversion of aldehydes to nitriles mediated by TiCl4. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1512–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, A.; Comandè, A.; Belsito, E.L.; Greco, M.; Feudo, L.L.; Liguori, A. Alternative formation of amides and β-enaminones from aroyl chlorides using the TiCl4-trialkylamine reagent system. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5677–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.L.; Dabdoub, M.J.; Hurtado, G.R.; Klein, S.I.; Baroni, A.C.; Cunha, C. Solvent free esterification reactions using Lewis acids in solid phase catalysis. Appl. Catal. 2006, 313, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Leshkov, Y.; Davis, M.E. Activation of carbonyl-containing molecules with solid Lewis acids in aqueous media. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1566–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, G.; Boeglin, J.; Bosco, M.; Locatelli, M.; Massaccesi, M.; Melchiorre, P.; Sambri, L. Highly Efficient Solvent-Free Condensation of Carboxylic Acids with Alcohols Catalysed by Zinc Perchlorate Hexahydrate, Zn(ClO4)2⋅6H2O. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.B.; Lemos Cardoso, A.; da Silva, M.J. Tin-catalyzed esterification and transesterification reactions: A review. ISRN Renew. Energ. 2012, 2012, 142857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Nakayama, M.; Ohara, S.; Yamamoto, H. Direct ester condensation from a 1:1 mixture of carboxylic acids and alcohols catalyzed by hafnium (IV) or zirconium (IV) salts. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 8179–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Sato, A.; Ishihara, K.; Yamamoto, H. Water-Tolerant and Reusable Catalysts for Direct Ester Condensation between Equimolar Amounts of Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Ohara, S.; Yamamoto, H. Direct condensation of carboxylic acids with alcohols catalyzed by Hafnium (IV) salts. Science 2000, 290, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otera, J. In Search of Practical Esterification. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2044–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde Santos, A.M.; Martinez, M.; Mira, J. Comparison study of lewis acid typer catalysts on the esterification of octanoic acid and n-octyl alcohol. Chem. Eng. Technol. 1996, 19, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, M.R.; Meneghetti, S.M.P. Sn(IV)-based organometallics as catalysts for the production of fatty acid alkyl esters. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.S.; Kim, D.T.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, T.J.; Shim, S.C. Catalytic activity of tin (II) chloride in esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, N.N.; Shirodkar, S.G.; Potrekar, R.A.; HKarade, H.N. An Exceedingly Efficient and Chemoselective Esterification with Activated Alcohols Using AlCl3/NaI/CH3CN System. Synth. Commun. Int. J. Rapid Commun. Synth. Org. Chem. 2004, 34, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Xue, W.; Zeng, Z. Mechanism and kinetics of esterification of adipic acid and ethylene glycol by tetrabutyl titanate catalyst. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.K.; Yoon, S.W.; Hwang, Y.T.; Song, B.G. New titanium-based catalysts for the synthesis of poly (ethylene terephthalate). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3445–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wolzak, L.A.; van der Vlugt, J.I.; van den Berg, K.J.; Reek, J.N.; Tromp, M.; Korstanje, T.J. Titanium-catalyzed esterification reactions: Beyond Lewis acidity. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 5229–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, I. An effective method for the synthesis of carboxylic esters and lactones using substituted benzoic anhydrides with Lewis acid catalysts. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, I.; Miyoshi, S.; Miyashita, M.; Mukaiyama, T. A useful method for the preparation of carboxylic esters from free carboxylic acids and alcohols. Chem. Lett. 1994, 23, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Munot, Y.S. Direct atom-efficient esterification between carboxylic acids and alcohols catalyzed by amphoteric, water-tolerant TiO(acac)2. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 8625–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, H.; Brown, D.A.; Alcock, N.W.; Case, H.J.; Wallbridge, M.G.H. Reactions of titanium tetrachloride with carboxylic acids. Crystal and molecular structure of the dinuclear titanium oxo compound [{TiCl2(O2CBut)(ButCO2H)}2O]. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1994, 2, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.V.; Alawaed, A.A.; Hamann, H.J. A Safer Reduction of Carboxylic Acids with Titanium Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 8481–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggio, A.; Bagalà, J.; Belsito, E.L.; Comandè, A.; Greco, M.; Liguori, A. Formation of amides: One-pot condensation of carboxylic acids and amines mediated by TiCl4. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comandè, A.; Greco, M.; Belsito, E.L.; Liguori, A.; Leggio, A. A titanium tetrachloride-based effective methodology for the synthesis of dipeptides. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 22137–22142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.-S.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, H.-J. Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-couplings of potassium malonate monoesters with aryl halides. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuts, P.G.M.; Green, T.W. Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Liguori, A.; Perri, F.; Siciliano, C.; Viscomi, M.C. A preparation of N-Fmoc-N-methyl-α-amino acids and N-nosyl-N-methyl-α-amino acids. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.; Vilaivan, T. Dipeptides bearing nucleobases for the synthesis of novel peptide nucleic acids. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1997, 4, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Product | Carboxylic Acid | Alcohol | Solvent | Reaction Time (h) | Reaction Temperature | Yield (%) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 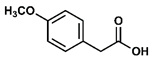 | 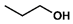 | DCM | 10 | r.t. | 82 |
| 3 | 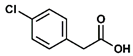 | 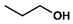 | DCM | 10 | r.t. | 80 |
| 4 |  | 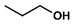 | DCM | 10 | r.t. | 99 |
| 5 | 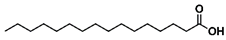 | 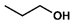 | DCM | 12 | r.t. | 97 |
| 6 | 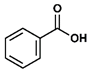 |  | DCM | 8 | r.t. | 74 |
| 7 | 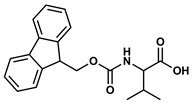 | 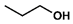 | DCM | 16 | r.t. | 70 |
| Product | R1 | R2 | Solvent | Reaction Time (h) | Reaction Temperature | Yield (%) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | CH3 | 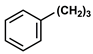 | DCM | 10 | r.t. | 97 |
| 9 | 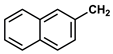 | 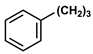 | DCM | 18 | r.t. | 50 |
| 10 | 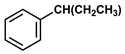 |  | DCM | 20 | r.t. | 40 |
| 11 | 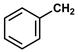 | 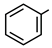 | Toluene | 4 | reflux | 84 |
| 12 | 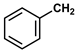 | 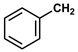 | Hexane | 10 | r.t. | 81 |
| 13 | 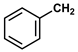 |  | Hexane | 10 | r.t. | 67 |
| 14 | 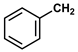 | (CH3)2CH | Hexane | 10 | r.t. | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavallaro, P.A.; De Santo, M.; Greco, M.; Marinaro, R.; Belsito, E.L.; Liguori, A.; Leggio, A. Titanium Tetrachloride-Assisted Direct Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Molecules 2024, 29, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040777
Cavallaro PA, De Santo M, Greco M, Marinaro R, Belsito EL, Liguori A, Leggio A. Titanium Tetrachloride-Assisted Direct Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040777
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavallaro, Palmira Alessia, Marzia De Santo, Marianna Greco, Rocco Marinaro, Emilia Lucia Belsito, Angelo Liguori, and Antonella Leggio. 2024. "Titanium Tetrachloride-Assisted Direct Esterification of Carboxylic Acids" Molecules 29, no. 4: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040777
APA StyleCavallaro, P. A., De Santo, M., Greco, M., Marinaro, R., Belsito, E. L., Liguori, A., & Leggio, A. (2024). Titanium Tetrachloride-Assisted Direct Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Molecules, 29(4), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040777







