Hypolipidemic and Antithrombotic Effect of 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum Based on Zebrafish Model, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hypolipidemic Effect of CA
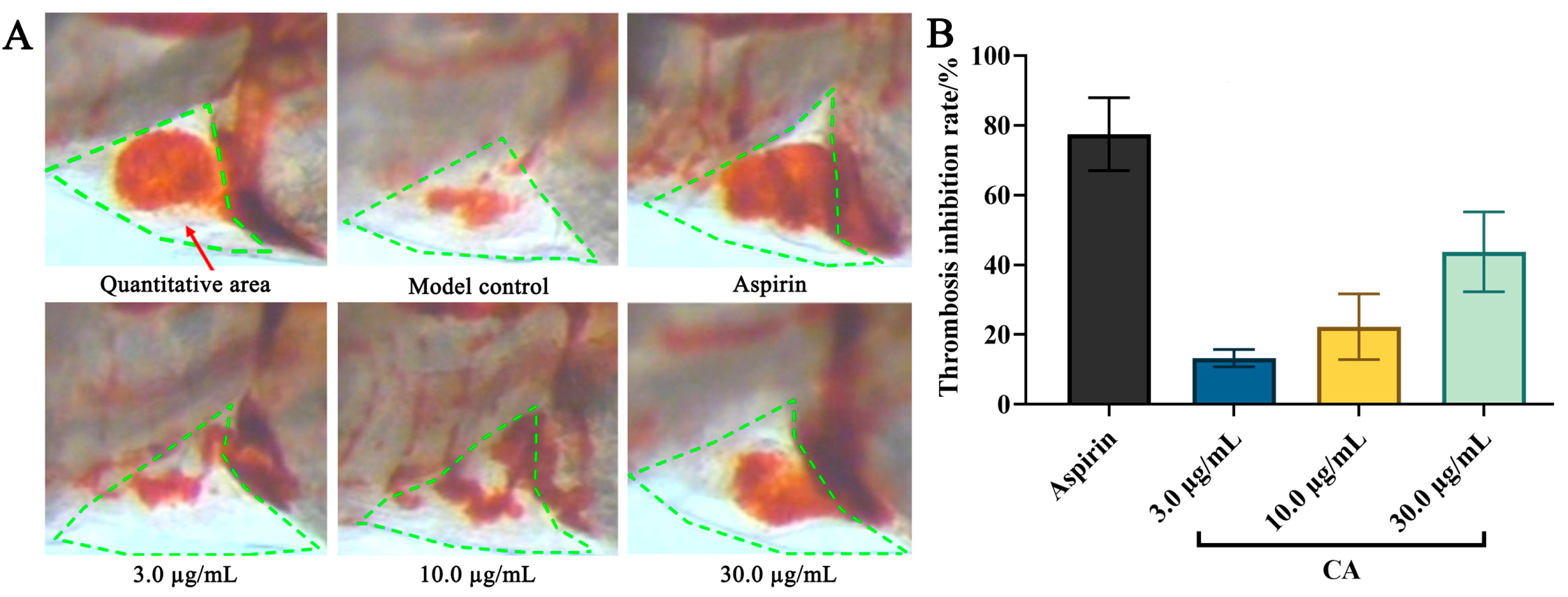
2.2. Antithrombotic Effect of CA
2.3. Intersection Targets of CA, Hyperlipidemia, and Thrombosis
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
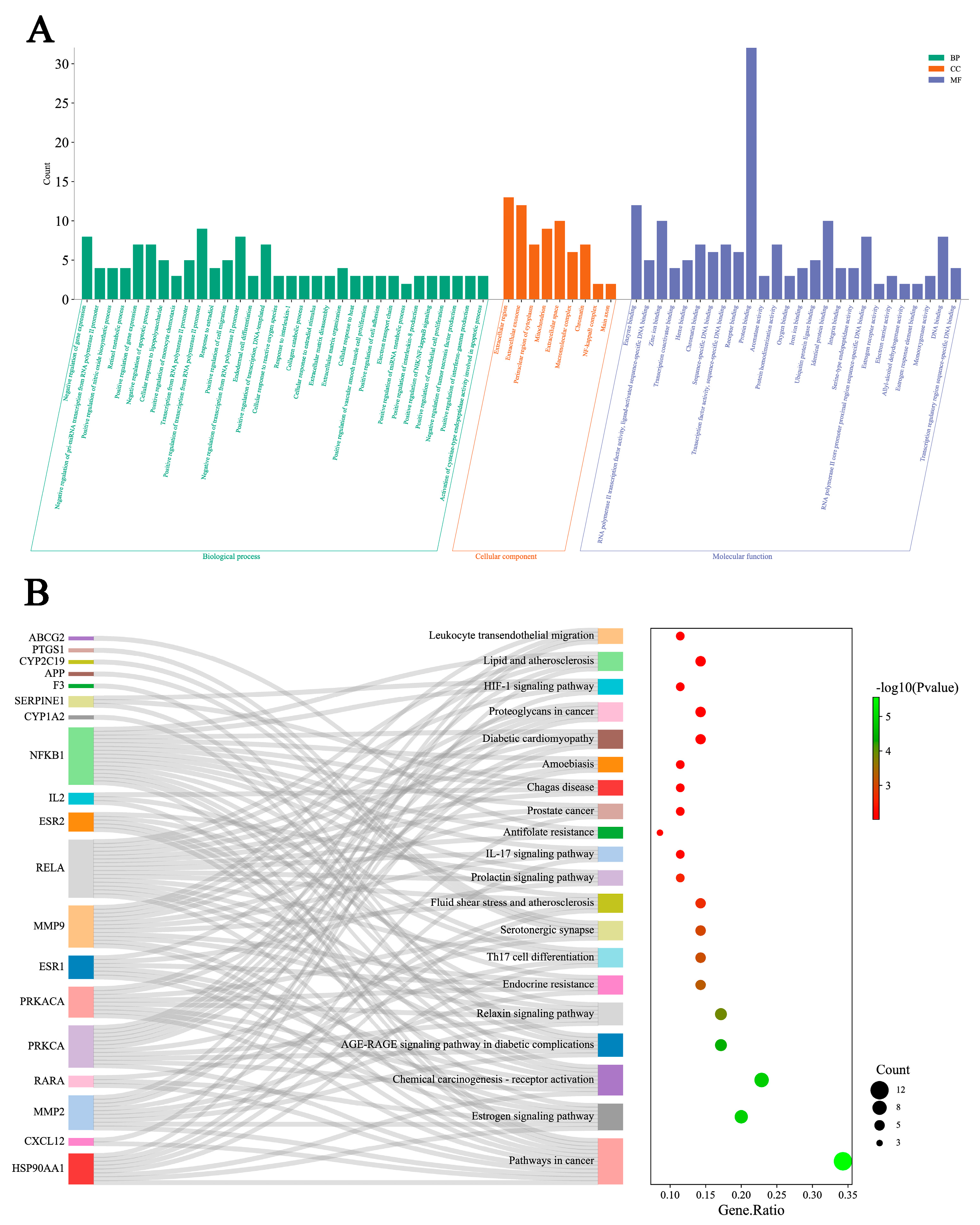
2.5. GO Functional and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
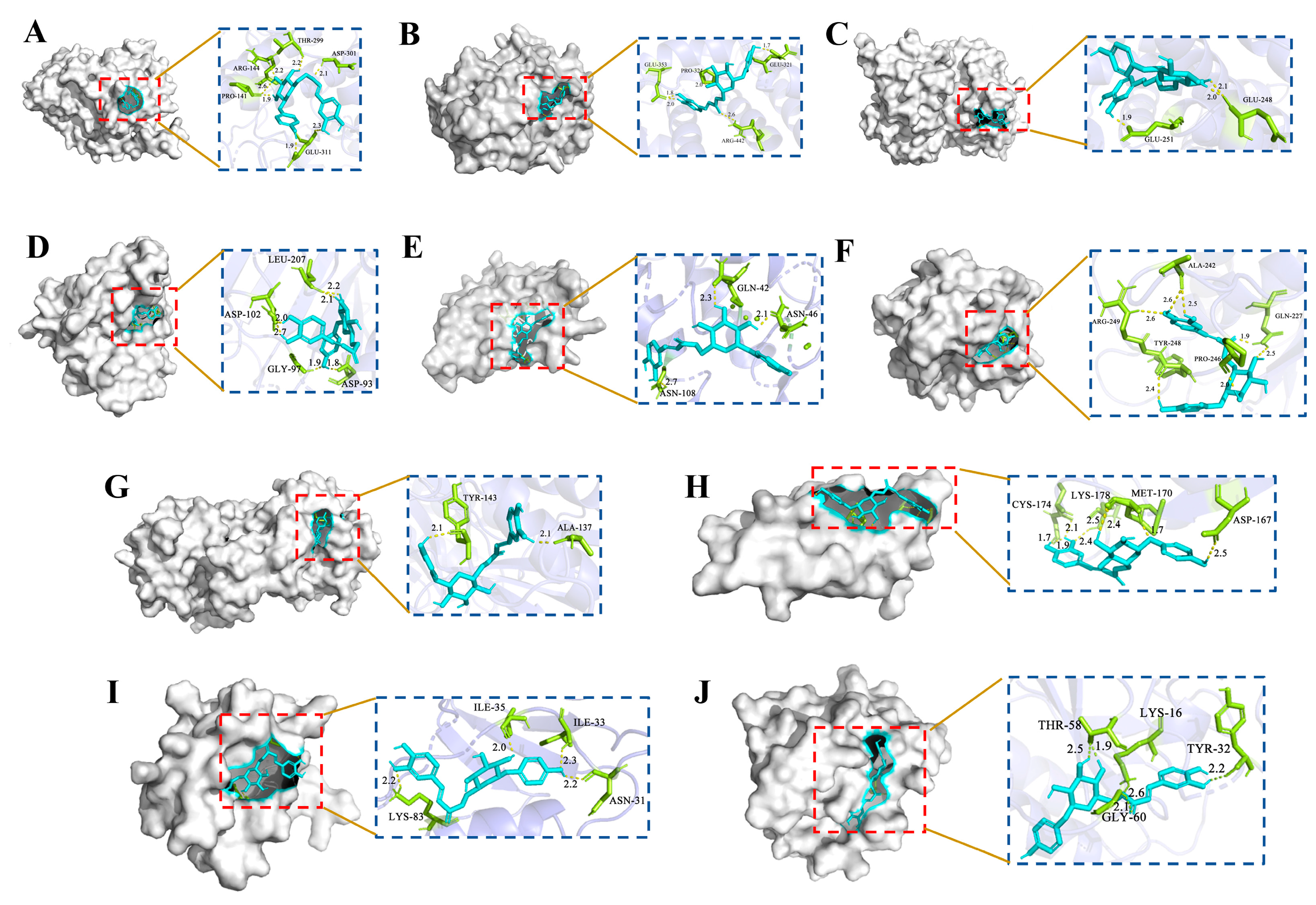
2.6. Molecular Docking and Analysis
2.7. Calculation of ADMET-Related Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of CA and Medicine
4.2. Zebrafish
4.3. The Effect of CA on Hyperlipidemia and Thrombosis
4.4. CA Target Prediction and Disease Target Identification
4.5. PPI Network Construction and Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Prediction of ADMET in Silico
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bu, J.H.; Wu, Y.; Cai, X.X.; Jiang, N.; Jeyalatha, M.V.; Yu, J.W.; He, X.; He, H.; Guo, Y.L.; Zhang, M.J.; et al. Hyperlipidemia induces meibomian gland dysfunction. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, J.F.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, M.H. Effects of phytochemicals from plant-based functional foods on hyperlipidemia and their underpinning mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.M.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.H.; Baek, J.; Heo, J.E.; Joo, H.J.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, H.C. Dyslipidemia fact sheets in Korea 2020: An analysis of nationwide population-based data. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2021, 10, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitzman, D.T.; Westrick, R.J.; Xu, Z.; Tyson, J.; Ginsburg, D. Hyperlipidemia promotes thrombosis after injury to atherosclerotic vessels in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Geffen, J.P.; Swieringa, F.; van Kuijk, K.; Tullemans, B.M.E.; Solari, F.A.; Peng, B.; Clemetson, K.J.; Farndale, R.W.; Dubois, L.J.; Sickmann, A.; et al. Mild hyperlipidemia in mice aggravates platelet responsiveness in thrombus formation and exploration of platelet proteome and lipidome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lerner, R.G.; Frishman, W.H. Statins and venous thromboembolic disease prophylaxis. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 21, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosmann, B.; Behl, C. Selenoprotein synthesis and side-effects of statins. Lancet 2004, 363, 892–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tanaka, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, C.R.; Kouno, I. Caffeoylarbutin and related compounds from the buds of Vaccinium dunalianum. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Li, N.; Xu, M.; Zhu, H.T.; He, P.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.J. HPLC simultaneous determination of arbutin, chlorogenic acid and 6′-O-caffeoylarbutin in different parts of Vaccinium dunalianum Wight. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1963–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lao, Q.C.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhu, H.T.; Luo, X.L.; Yang, C.R.; He, J.H.; Li, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.J. 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin inhibits melanogenesis in zebrafish. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wang, Y.D.; Liu, Y.P.; Cao, J.X.; Yang, M.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Khan, A.; Zhao, T.R.; Cheng, G.G. 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Que Zui tea ameliorates acetaminophen-induced liver injury via enhancing antioxidant ability and regulating the PI3K signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5299–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, Ş.; Eyupoglu, V.; Sarfraz, I.; Rasul, A.; Zahoor, A.F.; Ali, M.; Abdalla, M.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Elfiky, A.A. Caffeic acid derivatives (CAFDs) as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2: CAFDs-based functional foods as a potential alternative approach to combat COVID-19. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Qi, C.; Feng, F.; Wang, Y.; Di, T.T.; Meng, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, P.; et al. Combining network pharmacology, RNA-seq, and metabolomics strategies to reveal the mechanism of Cimicifugae Rhizoma-Smilax glabra Roxb herb pair for the treatment of psoriasis. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Gupta, H.; Min, B.H.; Ganesan, R.; Sharma, S.P.; Won, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Lee, S.B.; Cha, M.G.; Kwon, G.H.; et al. Elucidation of prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, and target from gut microbiota to alleviate obesity via network pharmacology study. Cells 2022, 11, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, N.B. Network target for screening synergistic drug combinations with application to traditional Chinese medicine. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zon, L.I.; Peterson, R.T. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug discov. 2005, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, G.; Mhalhel, K.; Briglia, M.; Levanti, M.; Abbate, F.; Guerrera, M.C.; D’Alessandro, E.; Laurà, R.; Germanà, A. Zebrafish and flavonoids: Adjuvants against obesity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickolas, T.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Appel, G.B. Hyperlipidemia and thrombotic complications in patients with membranous nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W. Hyperlipidemia in children. Thromb. Res. 2006, 118, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors for treatment of hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.S.; Ma, Y.F.; Pan, F.B.; Li, M.S.; Zheng, Y.G.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, D.S. An insight into antihyperlipidemic effects of polysaccharides from natural resources. Molecules 2022, 27, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, I.; Mancusi, A. Weight loss supplements. Molecules 2023, 28, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.K.; Zhou, X.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Yang, M.L.; Liu, Y.P.; Cao, J.X.; Cheng, G.G. Que Zui tea ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in high fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Bai, T.C.; Shi, L.L.; Hou, B.; Tang, R.; Zhang, R.P.; Chen, X.L. Antihyperlipidemic effect of Vaccinium dunalianum buds based on biological activity screening and LC-MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjali, S.; Blesso, C.N.; Banach, M.; Pirro, M.; Majeed, M.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of curcumin on HDL functionality. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S. Atheroprotective effects and molecular targets of tanshinones derived from herbal medicine danshen. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.Y.; Liao, W.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.K.; Sun, G.J. The effect of resveratrol on blood lipid profile: A dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstein, L.M. Clinical usage of hypolipidemic and antidiabetic drugs in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koene, R.J.; Prizment, A.E.; Blaes, A.; Konety, S.H. Shared risk factors in cardiovascular disease and cancer. Circulation 2016, 133, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Biological role of estrogen and estrogen receptors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E. Estrogen signaling and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, A.; Lubahn, D.; Shelby, L.; Lloyd, K.; Barthold, S. Susceptibility to early atherosclerosis in male mice is mediated by estrogen receptor alpha. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Du, L.J.; Hong, J.N.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, H.J.; Li, S.S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, S.K. Molecular mechanism underlying the hypolipidemic effect of Shanmei Capsule based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Technol. Health Care 2021, 29, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moggs, J.G.; Orphanides, G. Estrogen receptors: Orchestrators of pleiotropic cellular responses. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, H.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, M.; Liao, P.; Cao, L.; Guo, P.; Sun, G.B.; Sun, X. Gypenoside XVII prevents atherosclerosis by attenuating endothelial apoptosis and oxidative stress: Insight into the ERα-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, D.M. Role of estrogen receptor-alpha in pharmacogenetics of estrogen action. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casazza, K.; Page, G.P.; Fernandez, J.R. The association between the rs2234693 and rs9340799 estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: A review. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2010, 12, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinoff, E.M.S.; del Pozo, C.H.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Emerging targets for therapeutic development in diabetes and its complications: The RAGE signaling pathway. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 98, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Z.; Pan, J.X.; Yu, J.J.; Kang, J.; Hou, S.Y.; Cheng, M.J.; Xu, L.; Gong, L.H.; Li, Y. DiDang decoction improves mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism via the HIF-1 signaling pathway to treat atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 308, 116289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadipooya, K.; Lankarani, K.B.; Raj, R.; Kalantarhormozi, M. RAGE is a potential cause of onset and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 2151302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.H.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.X. Exploring the molecular mechanism of action of Yinchen Wuling powder for the treatment of hyperlipidemia, using network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Bio. Med. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9965906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Griendling, K.K.; Harrison, D.G. The vascular NAD(P)H oxidases as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.; Nakamura, K.; Matsui, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Jinnouchi, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Narama, I.; Motomiya, Y.; et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits advanced glycation end product-induced retinal vascular hyperpermeability by blocking reactive oxygen species-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20213–20220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamioka, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Uekita, H.; Nagai, R.; Sakamoto, N.; Ando, K.; Ohkawara, H.; Teramoto, T.; Maruyama, Y.; et al. Blockade of renin-angiotensin system attenuates advanced glycation end products-mediated signaling pathways. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gut, P.; Reischauer, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Arnaout, R. Little fish, big data: Zebrafish as a model for cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 889–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.J.; Shi, Y.L.; Yang, G.Z.; Shi, J.; Ji, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lv, H. Hypolipidaemic and antioxidant effects of various Chinese dark tea extracts obtained from the same raw material and their main chemical components. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.N.; Long, F.W.; Yang, D.M.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhong, K.; Bu, Q.; Gao, H.; et al. Insight into structural characteristics of theabrownin from Pingwu Fuzhuan brick tea and its hypolipidemic activity based on the in vivo zebrafish and in vitro lipid digestion and absorption models. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Cheng, J.; Liang, X.G.; Tan, C.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, Y.Z.; Lu, Y.M.; Fukunaga, K.; Han, F.; Li, X.A. H2O2-responsive theranostic probe for endothelial injury imaging and protection. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3803–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Lan, C.H.; Zhao, D.; Wang, N.; Du, D.; Luo, H.B.; Peng, Z.F.; Wang, Y.M.; Qiao, Z.W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Wuliangye Baijiu but not ethanol reduces cardiovascular disease risks in a zebrafish thrombosis model. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.T.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, M.J.; Roth, B.L.; Armbruster, B.N.; Ernsberger, P.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.J.; Dong, J.; Che, Y.J.; Zhu, M.F.; Wen, M.; Wang, N.N.; Wang, S.; Lu, A.P.; Cao, D.S. TargetNet: A web service for predicting potential drug-target interaction profiling via multi-target SAR models. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.H.; Huang, H.Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y.X.; McGarvey, P.B.; Wu, C.H.; Arighi, C.N.; UniProt Consortium. A crowdsourcing open platform for literature curation in UniProt. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshir, R.; Fishilevich, S.; Iny-Stein, T.; Zelig, O.; Mazor, Y.; Guan-Golan, Y.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. GeneCaRNA: A comprehensive gene-centric database of human non-coding RNAs in the GeneCards suite. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamosh, A.; Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.; Scott, A.F.; Rasmussen, S.A. Online Mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM®): Victor McKusick’s magnum opus. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Chen, X.M.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhou, T.; Du, M.H.; Xu, R.; Chen, Y.C.; Tang, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. BIRC5 inhibition is associated with pyroptotic cell death via caspase3-GSDME pathway in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.L.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, M.A.; Danielson, M.L. Computer-aided drug design platform using PyMOL. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Yi, J.C.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.J.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.Z.; Zeng, X.X.; Wu, C.K.; Lu, A.P.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Groups | Concentration (µg/mL) | IOD (Mean ± SE) | Effect on Lipid Lowering (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | - | 3276 ± 51 | - |
| Lovastatin | 22.5 | 2259 ± 83 *** | 31 ± 3 |
| CA | 3.0 | 2129 ± 233 *** | 35 ± 7 |
| 10.0 | 2310 ± 214 *** | 29 ± 7 | |
| 30.0 | 2535 ± 273 *** | 23 ± 8 |
| Groups | Concentration (µg/mL) | IES (Mean ± SE) | Thrombosis Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | - | 987 ± 94 | - |
| Aspirin | 22.5 | 1729 ± 99 *** | 78 ± 10 |
| CA | 3.0 | 1102 ± 25 | 13 ± 3 |
| 10.0 | 1191 ± 94 * | 22 ± 10 | |
| 30.0 | 1398 ± 113 *** | 44 ± 12 |
| Ligand | Core Proteins Target | PDB ID | LiDockScore (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA | IL2 | 7M2G | −4.61 |
| PRKCA | 2GZV | −6.11 | |
| HSP90AA1 | 6TN5 | −5.98 | |
| RELA | 8ONV | −6.53 | |
| APP | 2FMA | −5.23 | |
| PRKACA | 5M6Y | −4.29 | |
| MMP2 | 7XJO | −6.25 | |
| MMP9 | 6ESM | −7.32 | |
| ESR1 | 7NFB | −4.53 | |
| HNF4A | 8O1L | −3.12 |
| Property | Predicted Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical property | CA | lovastatin |
| TPSA | 166.140 | 72.830 |
| LogS (solubility) | −2.421 | −4.665 |
| LogD (distribution coefficient D) | 1.581 | 4.067 |
| LogP (distribution coefficient P) | 1.013 | 3.414 |
| Medicinal chemistry | ||
| QED | 0.211 | 0.672 |
| SA score | 3.710 | 4.690 |
| Absorption | ||
| Papp (Caco-2 permeability) | −6.257 | −4.824 |
| Pgp-inhibitor | 0.001 | 0.998 |
| Pgp-substrate | 0.227 | 0.005 |
| HIA (human intestinal absorption) | 0.765 | 0.161 |
| Distribution | ||
| Plasma protein binding (PPB) | 97.47% | 94.28% |
| Volume distribution (VD) | 0.420 L/kg | 1.005 L/kg |
| Blood–brain barrier (BBB) | 0.293 | 0.746 |
| Elimination | ||
| T 1/2 (half life time) | 0.839 | 0.232 |
| CL (clearance rate) | 7.014 | 18.012 |
| Toxicity | ||
| hERG (hERG blockers) | 0.020 | 0.388 |
| H-HT (human hepatotoxicity) | 0.042 | 0.966 |
| DILI (drug-induced liver injury) | 0.037 | 0.033 |
| SkinSen (skin sensitization) | 0.932 | 0.957 |
| FDAMDD (FDA maximum daily dose) | 0.021 | 0.970 |
| Respiratory toxicity | 0.034 | 0.678 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Li, C.; Kan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P. Hypolipidemic and Antithrombotic Effect of 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum Based on Zebrafish Model, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking. Molecules 2024, 29, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040780
Wu B, Li C, Kan H, Zhang Y, Rao X, Liu Y, Zhao P. Hypolipidemic and Antithrombotic Effect of 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum Based on Zebrafish Model, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040780
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Boxiao, Churan Li, Huan Kan, Yingjun Zhang, Xiaoping Rao, Yun Liu, and Ping Zhao. 2024. "Hypolipidemic and Antithrombotic Effect of 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum Based on Zebrafish Model, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking" Molecules 29, no. 4: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040780
APA StyleWu, B., Li, C., Kan, H., Zhang, Y., Rao, X., Liu, Y., & Zhao, P. (2024). Hypolipidemic and Antithrombotic Effect of 6′-O-Caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum Based on Zebrafish Model, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking. Molecules, 29(4), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040780





