Antibacterial Activity of Plant Polyphenols Belonging to the Tannins against Streptococcus mutans—Potential against Dental Caries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antibacterial Activity against S. mutans—MIC and MBC Studies
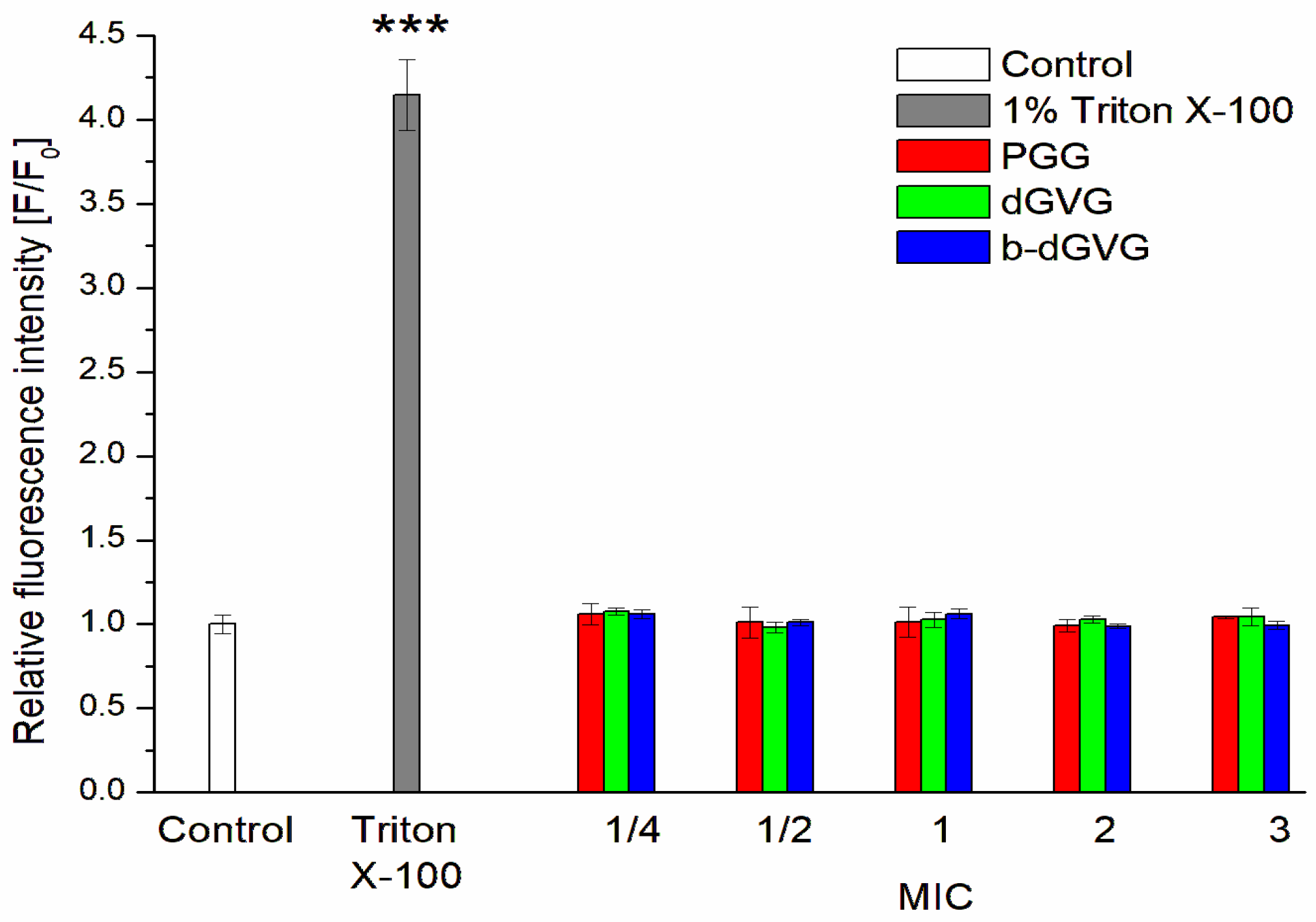
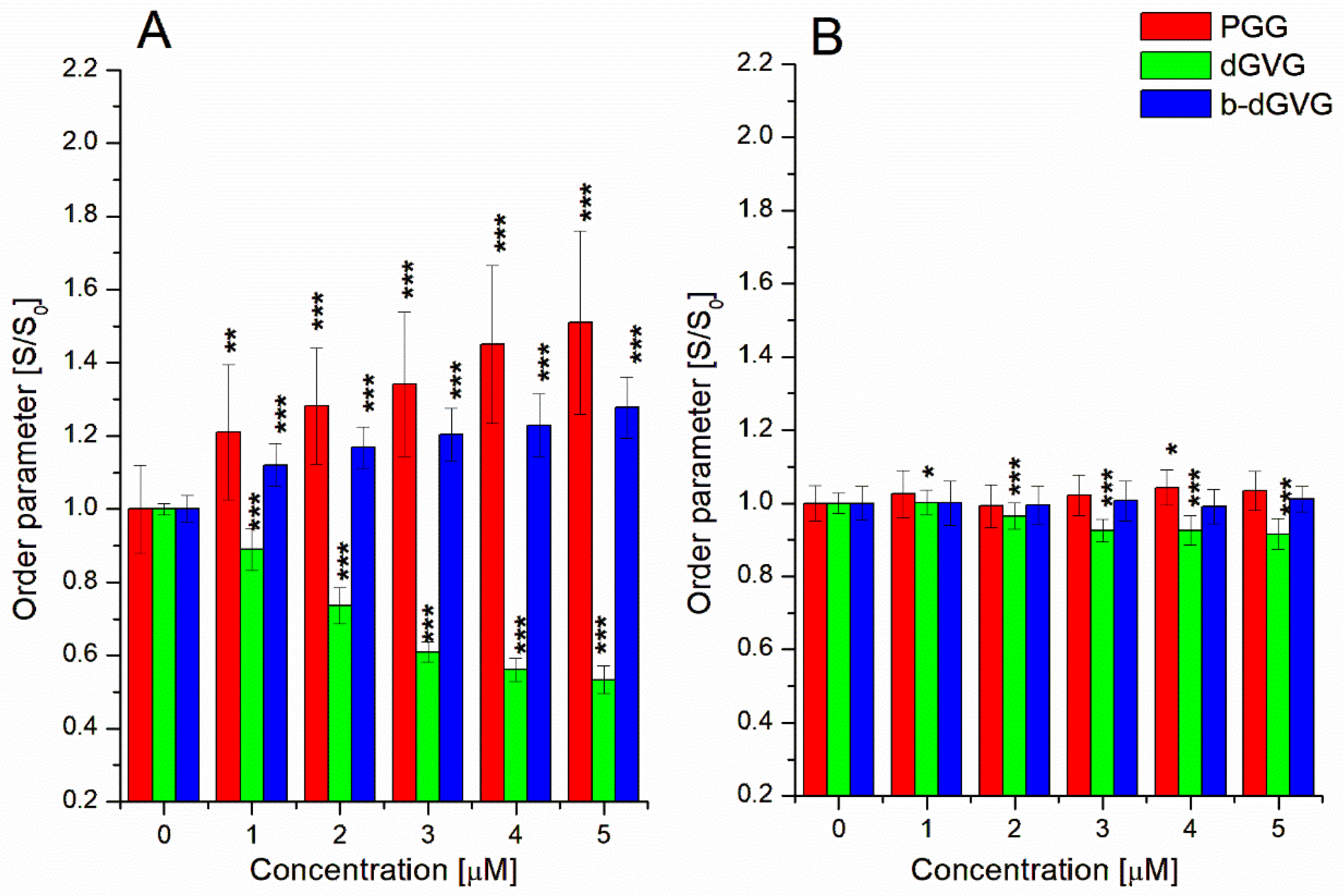
2.2. Evaluation of Tannins Interaction with S. mutans Membranes
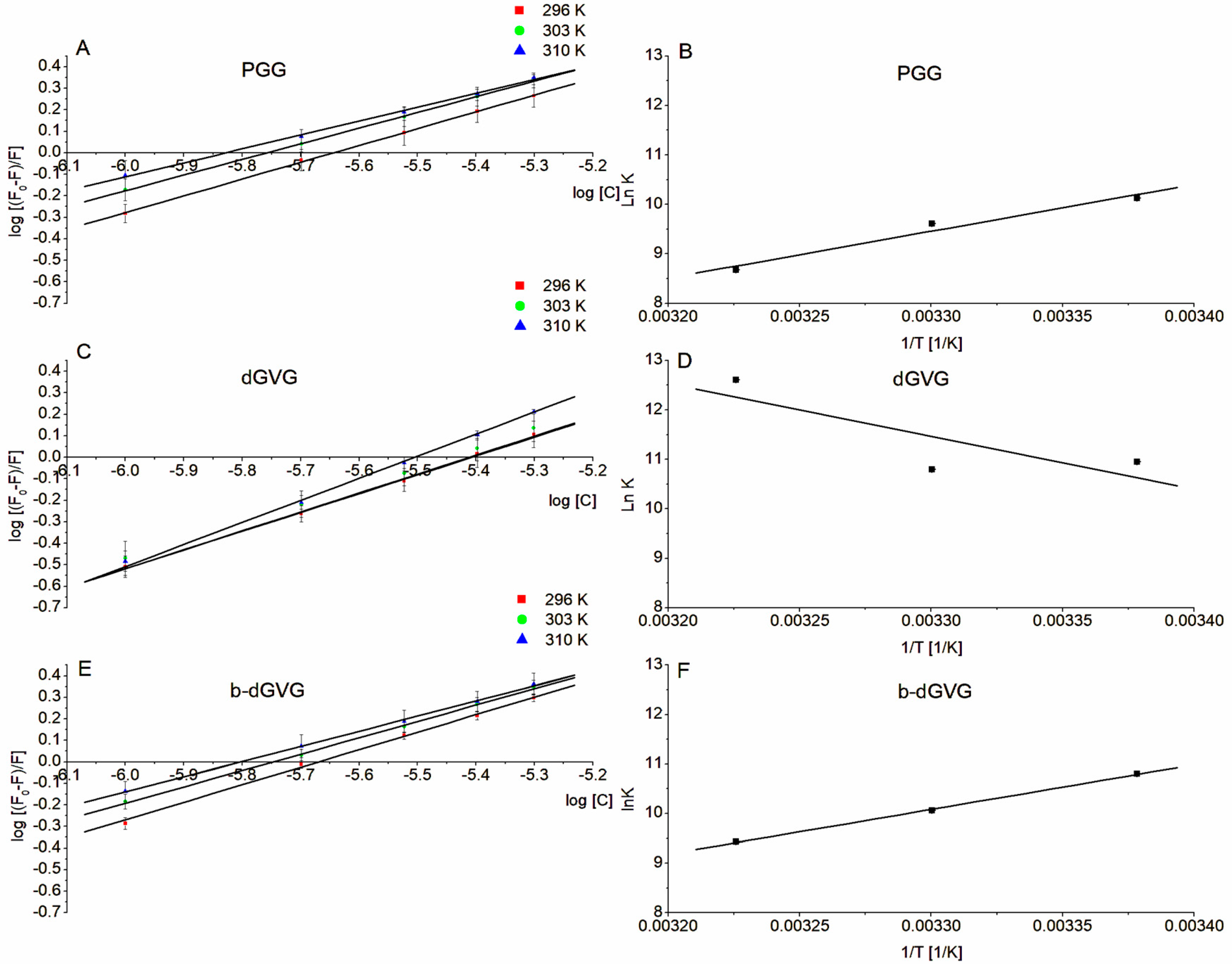
2.3. Evaluation of Tannin Interaction with S. mutans Membrane Proteins through Tryptophan Fluorescence
2.4. Analyses of S. mutans’ Zeta Potential Changes in the Presence of PGG, d-GVG, and b-dGVG
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity—Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
3.4. Studies of S. mutans Membrane Permeability—Sytox Staining
3.5. Measurements of S. mutans Membrane Fluidity
3.6. Fluorescence Analysis of Tannins’ Interactions with S. mutans Membrane Proteins
3.7. Analysis of ϛ-Potential
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kováč, J.; Slobodníková, L.; Trajčíková, E.; Rendeková, K.; Mučaji, P.; Sychrová, A.; Bittner Fialová, S. Therapeutic Potential of Flavonoids and Tannins in Manaent of Oral Infectious Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, F.; Sun, X.; Dong, Y.; Lin, P.T.; Yu, H.H. Antibacterial activity of a modified unfilled resin containing a novel polymerizable quaternary ammonium salt MgemAE-HB. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.D. Grape Products and Oral Health. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1818S–1823S. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, S.M.; Aboulwafa, M.M.; Hashem, A.M.; Saleh, S.E. Biofilm Formation by Streptococcus mutans and Its Inhibition by Green Tea Extracts. AMB Expr. 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto-Nakano, M. Role of Streptococcus mutans Surface Proteins for Biofilm Formation. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2018, 54, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Srivastava, V.K.; Parray, Z.A.; Jyoti, A.; Islam, A.; Kaushik, S. Identification of potential inhibitors of sortase A: Binding studies, in-silico docking and protein-protein interaction studies of sortase A from Enterococcus faecalis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Fiehn, N.E. Dental biofilm infections—An update. APMIS 2017, 125, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Banerjee, R.; Mukherjee, D.; Garai, S.; Sarkar, T.; Ankita, D.; Hassan, L.S.; Sushil, K.P.; Hisham, A.E.; et al. Amylases: Biofilm inducer or biofilm inhibitor? Front. Cell. Infect. 2021, 11, 660048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, Q.; Suo, H. New Strategies and Mechanisms for Targeting Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Formation to Prevent Dental Caries. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 278, 127526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.; Lores, M.; de Miguel, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Natural Polyphenolic Extracts on Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.; Walsh, L.J. Cranberry Polyphenols: Natural Weapons against Dental Caries. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Sękowski, S.; Kwiatek, A.; Płaczkiewicz, J.; Abdulladjanova, N.; Shlyonsky, V.; Swiecicka, I.; Zamaraeva, M. The Structural Changes in the Membranes of Staphylococcus aureus Caused by Hydrolysable Tannins Witness Their Antibacterial Activity. Membranes 2022, 12, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Sekowski, S.; Mies, F.; Bitiucki, M.; Swiecicka, I.; Abdulladjanova, N.; Shlyonsky, V.; Zamaraeva, M. Electrophysiological and Spectroscopic Investigation of Hydrolysable Tannins Interaction with α-Hemolysin of S. aureus. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 150, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrich, A.B. Flavonoid-membrane interactions: Possible consequences for biological effects of some polyphenolic compounds. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Sekowski, S.; Bitiucki, M.; Dobrzynska, I.; Shlyonsky, V.; Ionov, M.; Burzynski, P.; Roszkowska, A.; Swiecicka, I.; Abdulladjanova, N.; et al. Inhibition of interaction between Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin and erythrocytes membrane by hydrolysable tannins: Structure-related activity study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekowski, S.; Ionov, M.; Kaszuba, M.; Mavlyanov, S.; Bryszewska, M.; Zamaraeva, M. Biophysical studies of interaction between hydrolysable tannins isolated from Oenothera gigas and Geranium sanguineum with human serum albumin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekowski, S.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Wieckowska, W.; Veiko, A.; Oldak, L.; Gorodkiewicz, E.; Karamov, E.; Abdulladjanova, N.; Mavlyanov, S.; Lapshina, E.; et al. Spectroscopic, Zeta-potential and Surface Plasmon Resonance analysis of interaction between potential anti-HIV tannins with different flexibility and human serum albumin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekowski, S.; Buczkowski, A.; Palecz, B.; Abdulladjanova, N. Inhibitory effect of Euphorbia tannins on α-synuclein aggregation in aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 299, 112112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Mateus, N.; De Freitas, V. Interaction of different polyphenols with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human salivary α-amylase (HSA) by fluorescence quenching. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6726–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, A.K.; Yang, Q.Q.; Kim, G.; Li, H.B.; Zhu, F.; Liu, H.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H. Tannins as an alternative to antibiotics. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; D’Amato, A.; Lauria, G.; Saturnino, C.; Andreu, I.; Sinicropi, M.S. Diarylureas: New Promising Small Molecules against Streptococcus mutans for the Treatment of Dental Caries. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendamangalam, V.; Choi, O.K.; Seo, Y.; Kim, D.-S. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Polyphenols against Streptococcus mutans. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2011, 1, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloz, J.J.; Alvear, M.; Salazar, L.A. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity against Streptococcus mutans of Individual and Mixtures of the Main Polyphenolic Compounds Found in Chilean Propolis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7602343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Yi, J.; Bao, Y.; Ma, H.; et al. Anti-biofilm activities from Bergenia crassifolia leaves against Streptococcus mutans. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekowski, S.; Veiko, A.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Dubis, A.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Zamaraeva, M. Hydrolysable tannins change physicochemical parameters of lipid nano-vesicles and reduce DPPH radical-Experimental studies and quantum chemical analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 183778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahl, H.; Errington, J. Bacterial membranes: Structure, domains, and function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, R. Effects of Sulforaphene on the Cariogenic Properties of Streptococcus Mutans In Vitro and Dental Caries Development In Vivo. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delehanty, J.B.; Johnson, B.J.; Hickey, T.E.; Pons, T.; Ligler, F.S. Binding and neutralization of lipopolysaccharides by plant proanthocyanidins. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jin, C.; Lv, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, F.; Wang, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Applications of Polyphenol-Protein Complexes with Antioxidant Properties: A Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, J.R. Principles and Applications of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shimozu, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Hatano, T. Structures and antibacterial properties of isorugosins H-J, oligomeric ellagitannins from Liquidambar formosana with characteristics bridging groups between sugar moieties. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Dangles, O. Flavonoid–serum albumin complexation: Determination of binding constants and binding sites by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2005, 1721, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Z.; Hu, M.; Wu, A.Z.; Zhu, C.C. Investigation on the differences of four flavonoids with similar structure binding to human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Ramírez, M.; Silva-Jiménez, H.; Banat, I.M.; Díaz De Rienzo, M.A. Surfactants: Physicochemical interactions with biological macromolecules. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, V.D.; Walekar, L.S.; Gore, A.H.; Anbhule, P.V.; Kolekar, G.B. Spectroscopic analysis on the binding interaction of biologically active pyrimidine derivative with bovine serum albumin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, F.Y.; Chan, Y.C. Effect of temperature on hydrophobic interaction between proteins and hydrophobic adsorbents: Studies by isothermal titration calorimetry and the van’t Hoff equation. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9395–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Torres, C.; Hernández, N.; Galeano, A.; Novoa-Aponte, L.; Soto, C.Y. Zeta potential as a measure of the surface charge of mycobacterial cells. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, A.P.F.; Espeche, J.C.; Maturana, P.; Cutro, A.C.; Hollmann, A. Zeta potential beyond materials science: Applications to bacterial systems and to the development of novel antimicrobials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183597. [Google Scholar]
- Kurinčič, M.; Jeršek, B.; Klančnik, A.; Možina, S.S.; Fink, R.; Dražić, G.; Raspor, P.; Bohinc, K. Effects of natural antimicrobials on bacterial cell hydrophobicity, adhesion, and zeta potential. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2016, 67, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Planum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Naveenraj, S.; Anandan, S.; Kathiravan, A.; Renganathan, R.; Ashokkumar, M. The interaction of sonochemically synthesized gold nanoparticles with serum albumins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PGG | dGVG | b-dGVG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical structure |  | 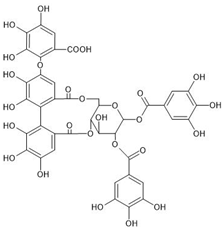 | 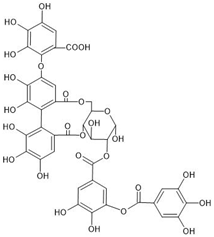 |
| Chemical formula | C41H32O26 | C41H30O27 | C41H30O27 |
| Molecular weight | 940.681 g/mol | 954.664 g/mol | 954.664 g/mol |
| Number of hydroxyl groups (-OH) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Number of gallic acid residues | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Number of glucose moieties | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Origin | Rhus typhina L. | Euphorbia E. turkestanica | Plantago lanceolata L. |
| Tannin | MIC [µM] | MBC [µM] |
|---|---|---|
| PGG | 50 | 200 |
| dGVG | 400 | 800 |
| b-dGVG | 200 | 400 |
| Binding Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tannin | Temperature [K] | Ksv [×106] [M−1] | kq [×1014] [M−1·s−1] | logKb |
| PGG | 296 | 0.393 ± 0.045 | 0.786 ± 0.090 | 4.398 ± 0.404 |
| 303 | 0.464 ± 0.042 | 0.927 ± 0.085 | 4.175 ± 0.230 | |
| 310 | 0.484 ± 0.020 | 0.967 ± 0.040 | 3.769 ± 0.491 | |
| dGVG | 296 | 0.261 ± 0.030 | 0.522 ± 0.068 | 4.758 ± 0.216 |
| 303 | 0.281 ± 0.039 | 0.562 ± 0.079 | 4.689 ± 0.186 | |
| 310 | 0.321 ± 0.010 | 0.642 ± 0.020 | 5.474 ± 0.317 | |
| b-dGVG | 296 | 0.417 ± 0.016 | 0.834 ± 0.032 | 4.692 ± 0.240 |
| 303 | 0.468 ± 0.032 | 0.937 ± 0.063 | 4.368 ± 0.416 | |
| 310 | 0.4914 ± 0.059 | 0.983 ± 0.117 | 4.095 ± 0.116 | |
| Tannin | T(K) | ΔH (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS (kJ·mol−1K−1) | ΔG (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGG | 296 | −78.7697 | −0.18131 | −25.1026 |
| 303 | −23.8335 | |||
| 310 | −22.5643 | |||
| dGVG | 296 | 89.11174 | 0.389428 | −26.1589 |
| 303 | −28.8840 | |||
| 310 | −31.6109 | |||
| b-dGVG | 296 | −74.8819 | −0.16328 | −26.5519 |
| 303 | −25.4089 | |||
| 310 | −24.2660 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerkas, K.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Łomanowska, M.; Abdulladjanova, N.; Sękowski, S. Antibacterial Activity of Plant Polyphenols Belonging to the Tannins against Streptococcus mutans—Potential against Dental Caries. Molecules 2024, 29, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040879
Czerkas K, Olchowik-Grabarek E, Łomanowska M, Abdulladjanova N, Sękowski S. Antibacterial Activity of Plant Polyphenols Belonging to the Tannins against Streptococcus mutans—Potential against Dental Caries. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040879
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerkas, Krzysztof, Ewa Olchowik-Grabarek, Magdalena Łomanowska, Nodira Abdulladjanova, and Szymon Sękowski. 2024. "Antibacterial Activity of Plant Polyphenols Belonging to the Tannins against Streptococcus mutans—Potential against Dental Caries" Molecules 29, no. 4: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040879
APA StyleCzerkas, K., Olchowik-Grabarek, E., Łomanowska, M., Abdulladjanova, N., & Sękowski, S. (2024). Antibacterial Activity of Plant Polyphenols Belonging to the Tannins against Streptococcus mutans—Potential against Dental Caries. Molecules, 29(4), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040879







