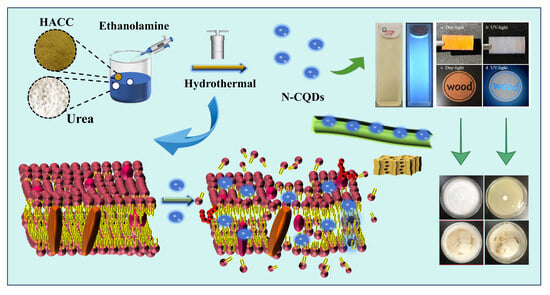
Construction Strategy and Mechanism of a Novel Wood Preservative with Excellent Antifungal Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of Modification Methods
2.2. N-CQD Process Optimization Results (Single-Factor and Orthogonal Tests)
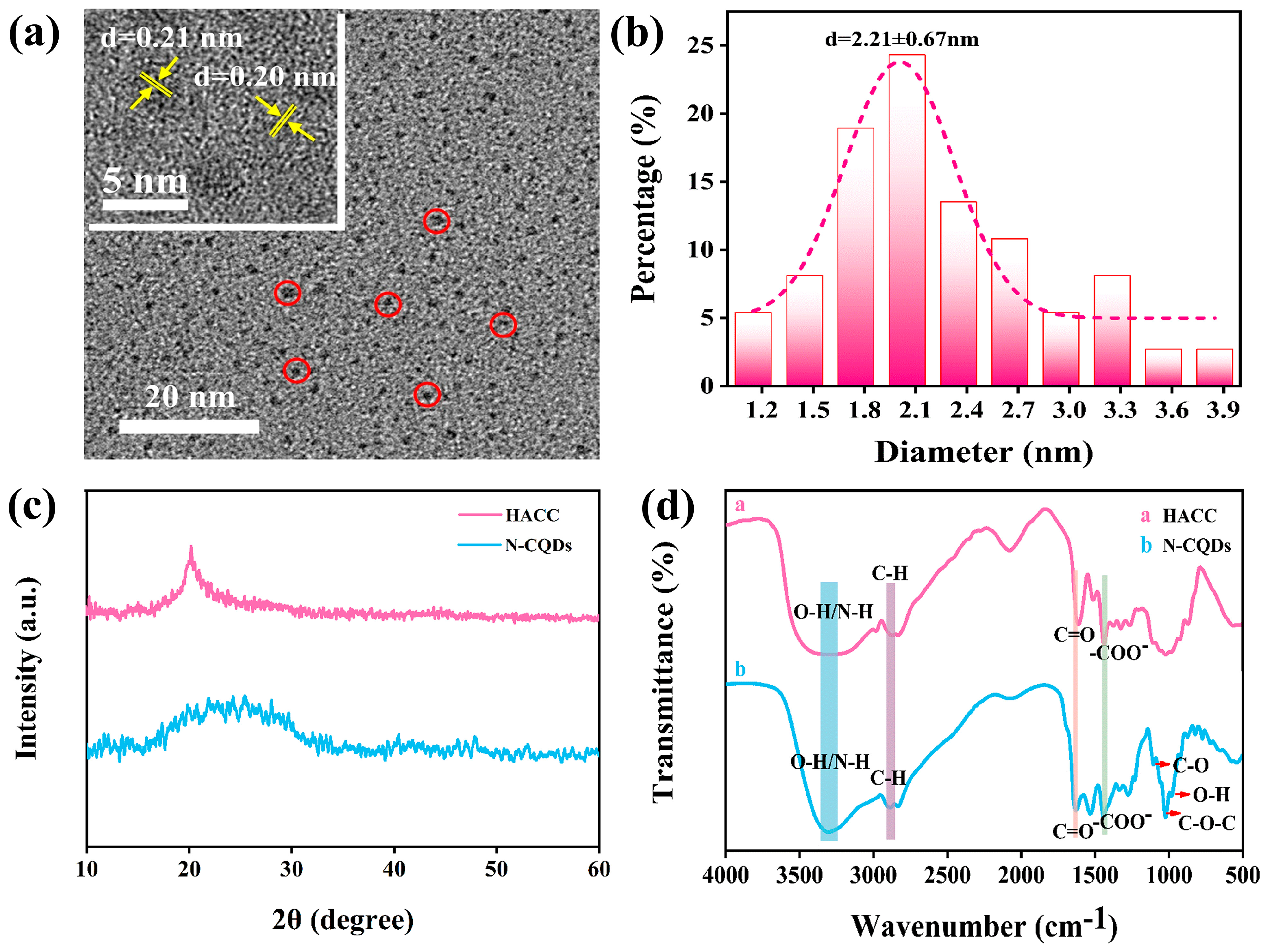
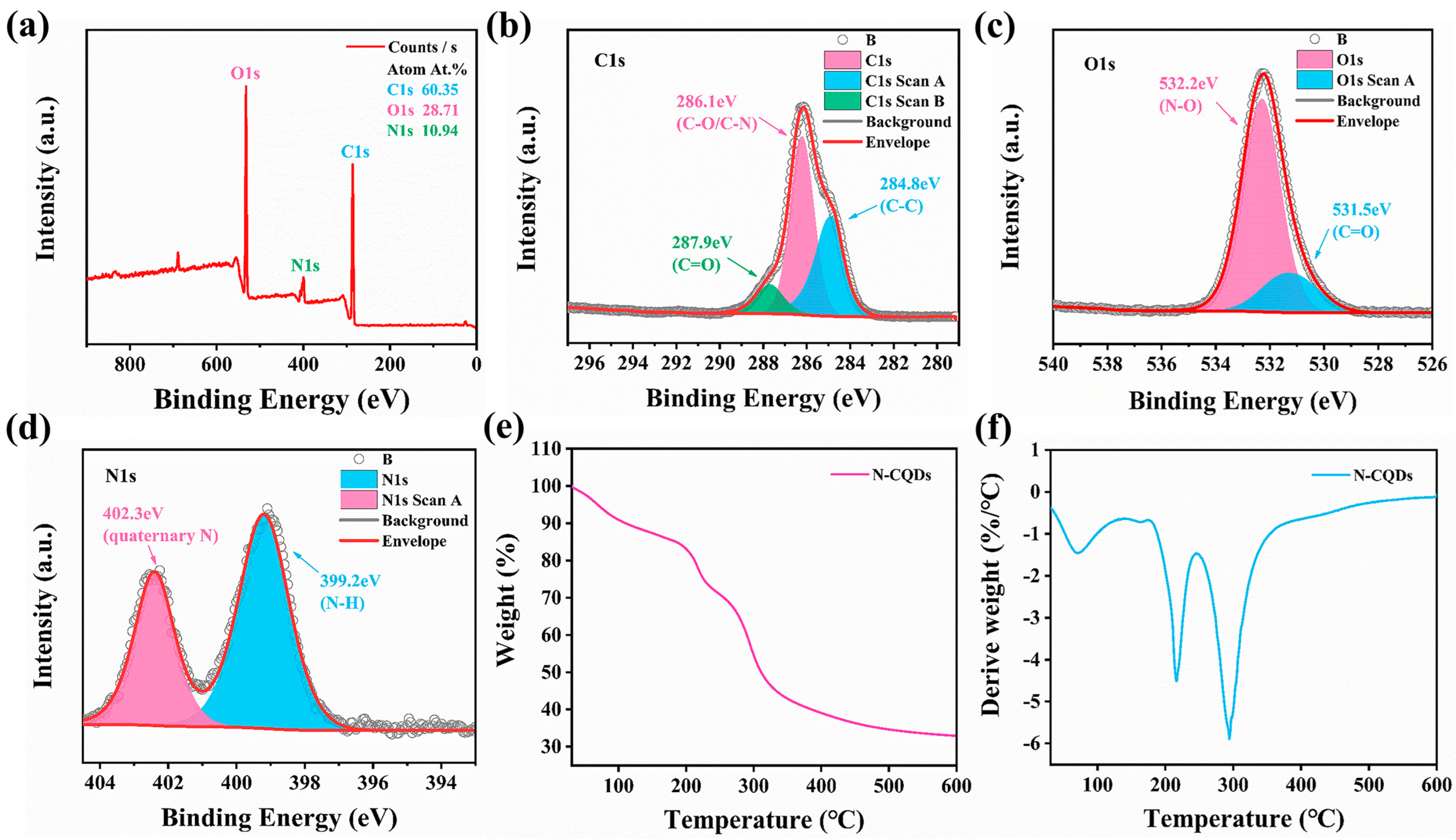
2.3. Characterization of N-CQDs
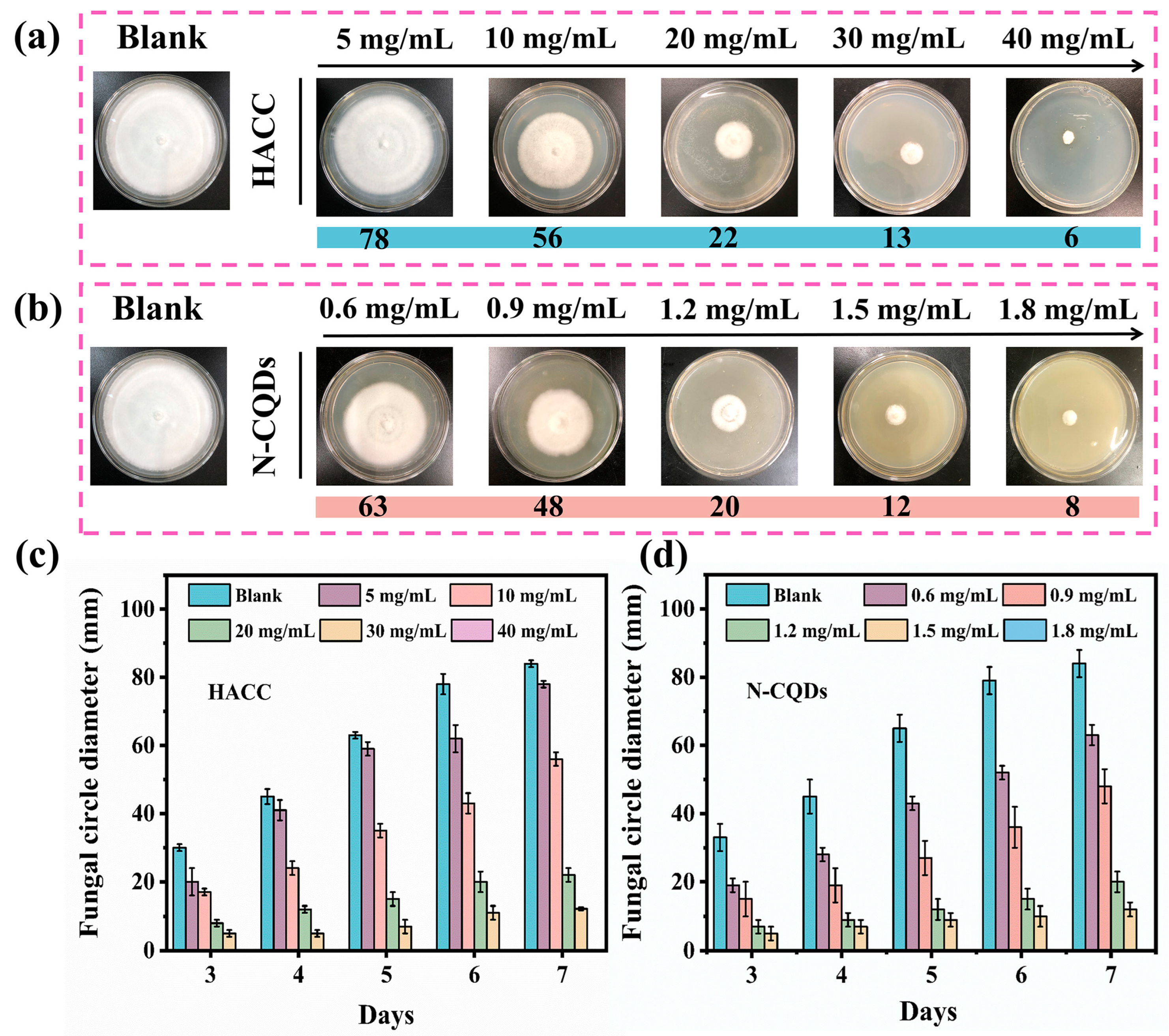
2.4. Antifungal Effects of HACC and N-CQDs
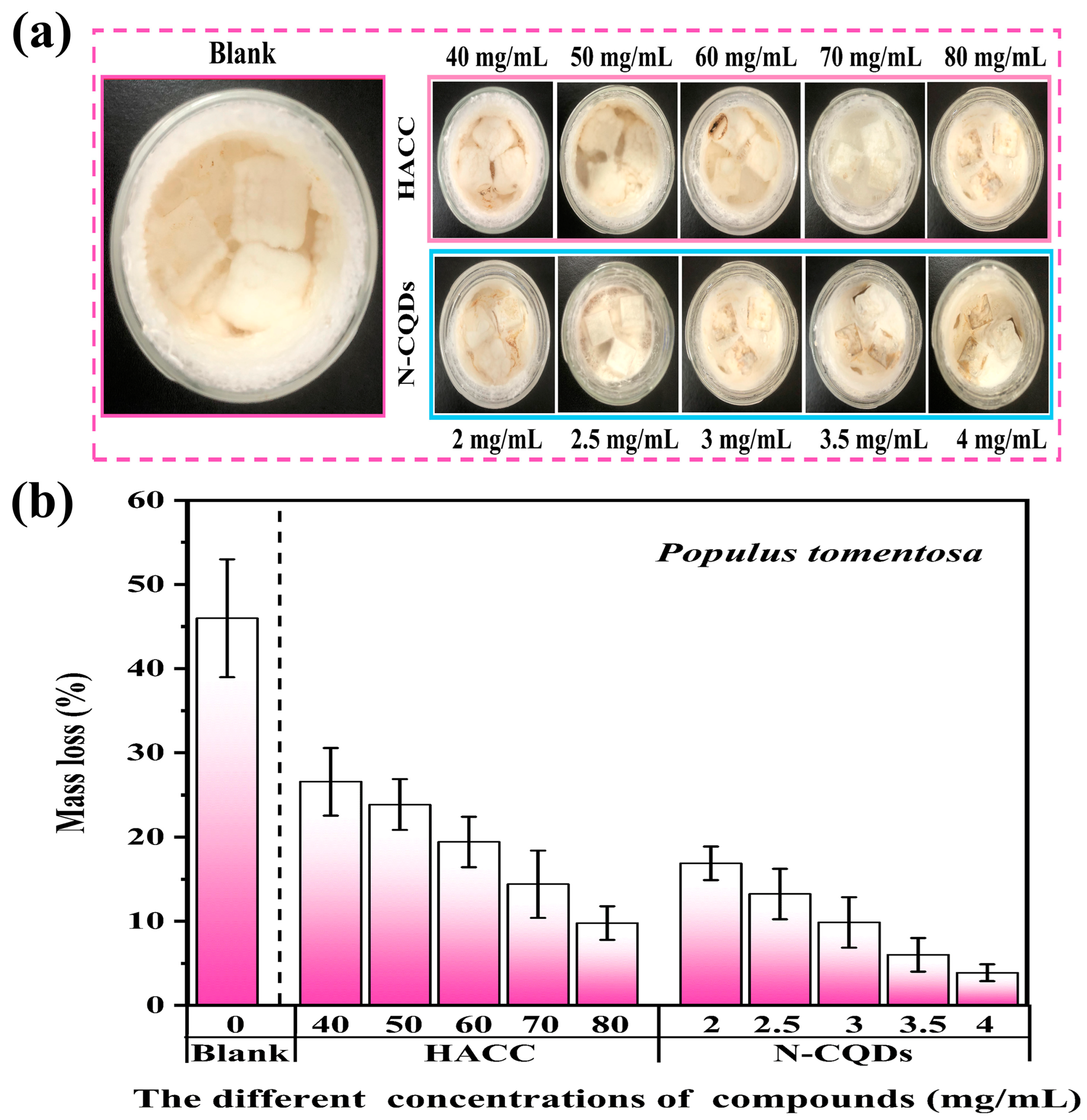
2.5. Decay Resistance of Wood
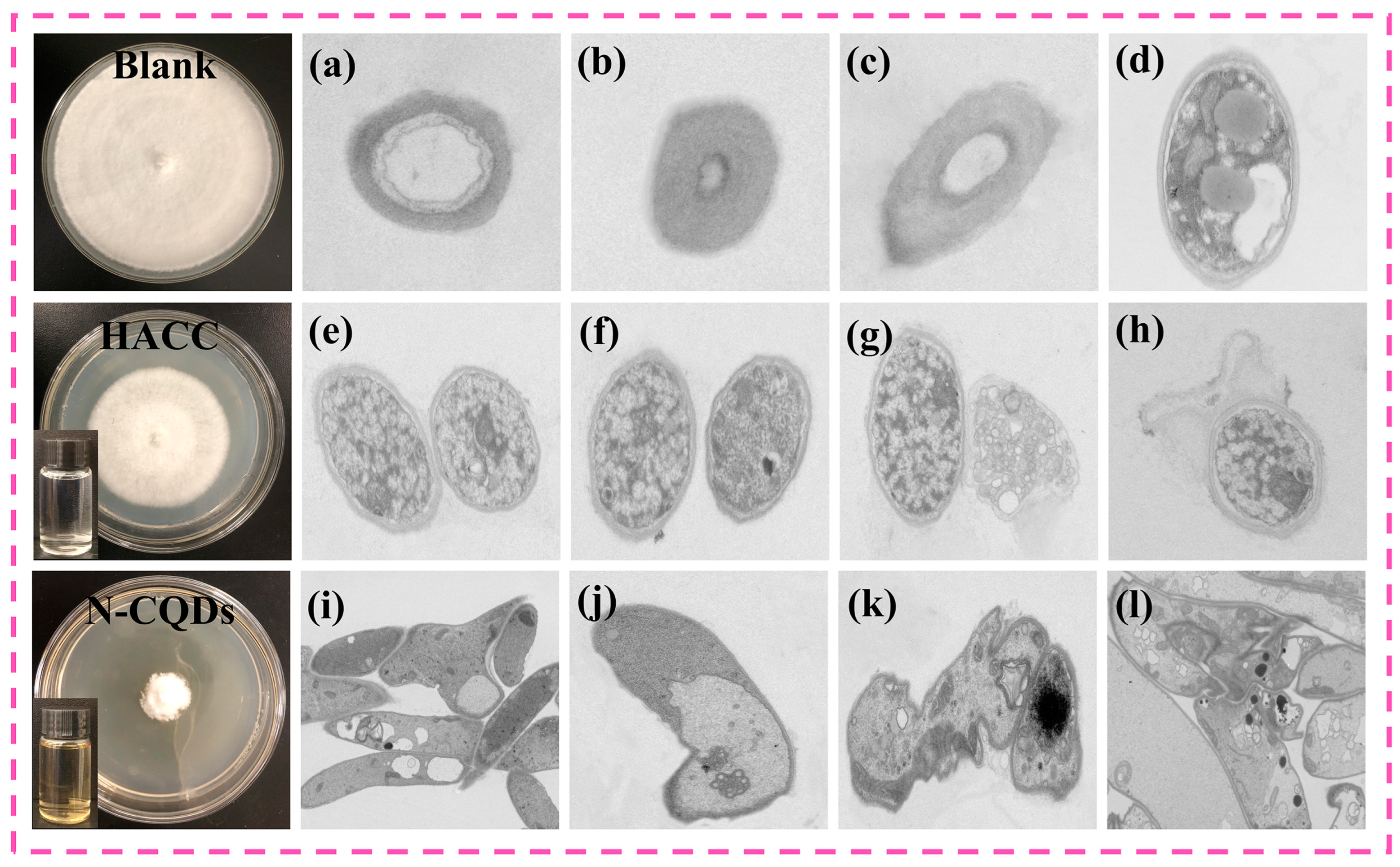
2.6. Inhibitory Mechanism of N-CQDs against C. versicolor
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumental Analysis
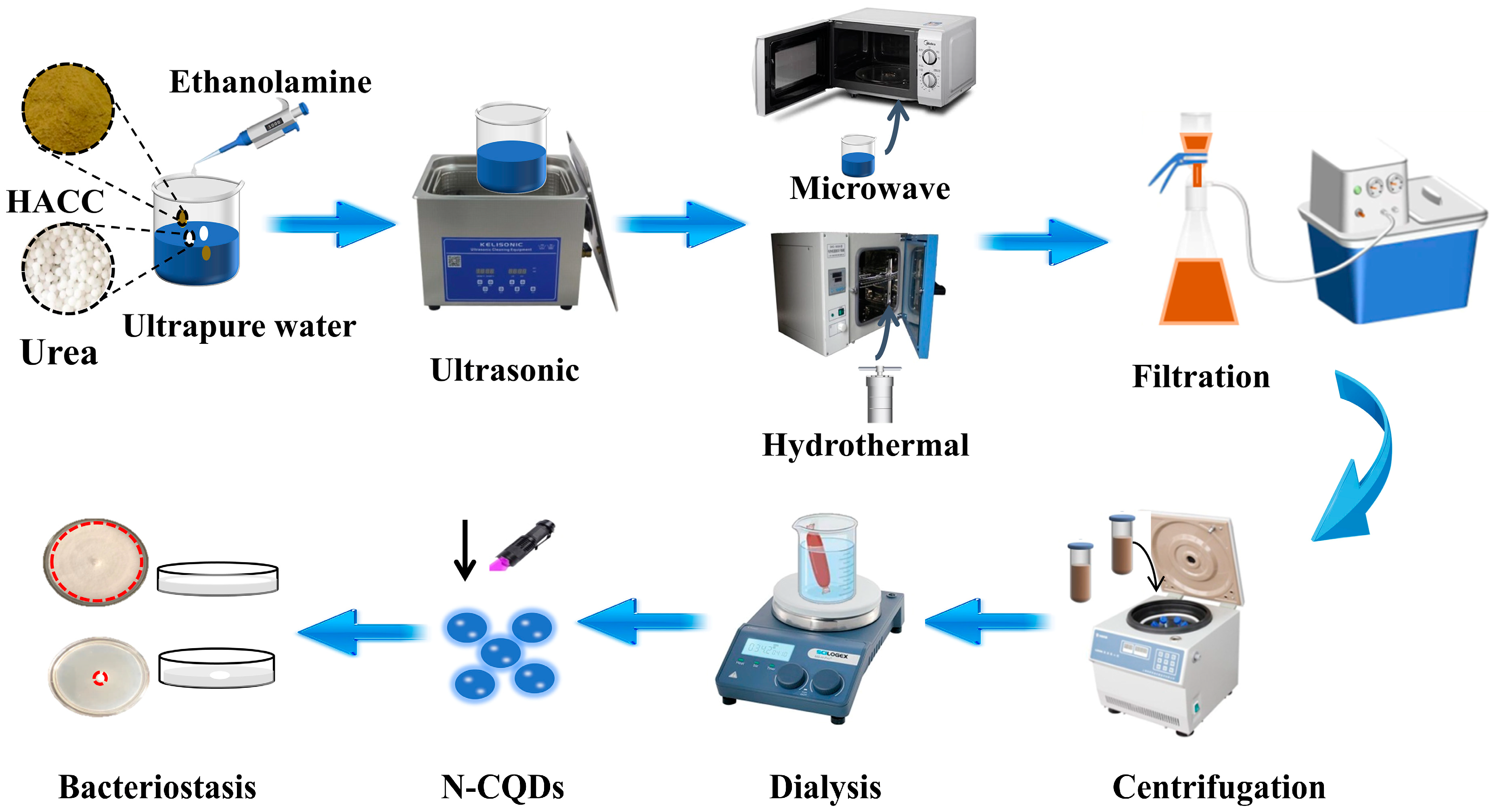
3.3. Preparation of N-CQDs and Screening of the Modification Methods
3.4. Optimization of N-CQD Synthesis
3.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Test
3.6. In Vivo Test for Determining the Degradation Resistance of Wood
3.7. Pretreatment of C. versicolor Specimens
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, E.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hu, L. Engineered Wood: Sustainable Technologies and Applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2023, 53, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.; Jung, E.-M.; Lindner, J.; Hardiman, I.; Poetschner, J.; Madhavan, S.; Matthäus, C.; Kai, M.; Menezes, R.C.; Popp, J.; et al. Response of the wood-decay fungus Schizophyllum commune to co-occurring microorganisms. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnková, K.; Reinprecht, L.; Nábělková, J.; Hýsek, Š.; Kindl, J.; Borůvka, V.; Lišková, T.; Šobotník, J.; Pánek, M. Caffeine—Perspective natural biocide for wood protection against decaying fungi and termites. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 127110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera, J.; Fink, S.; Bas, M.d.C.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R. Integrated control of wood destroying basidiomycetes combining Cu-based wood preservatives and Trichoderma spp. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, M. Antifungal Agents in Wood Protection—A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Bachtiar, E.V.; Ribera, J.; Heeb, M.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Burgert, I. Non-biocidal preservation of wood against brown-rot fungi with a TiO2/Ce xerogel. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreica, B.-I.; Cheng, X.; Marin, L. Quaternary ammonium salts of chitosan. A critical overview on the synthesis and properties generated by quaternization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xing, Z.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, B.; Ren, B.; Dong, X.; Yi, L. An environmental-friendly oil-based dust suppression microcapsules: Structure with chitosan derivative as capsule wall. Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 165, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xin, M.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Mao, Y. Effect of the structure of chitosan quaternary phosphonium salt and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt on the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Wu, X.; Peng, L.; Yu, N.; Gou, G.; Zuo, W.; Yang, J. pH-responsive bufadienolides nanocrystals decorated by chitosan quaternary ammonium salt for treating colon cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ren, X.; Kong, Q. Preparation and characterization of emulsions of soy protein isolate-chitosan quaternary ammonium salt complexes and peppermint essential oil with extended release effect. Food Hydrocolloid. 2023, 142, 108779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.; Misra, S.K.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Bungau, S.; Najda, A.; Gruszecki, R.; Behl, T. Biomedical Applications of Quaternized Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystyjan, M.; Khachatryan, G.; Grabacka, M.; Krzan, M.; Witczak, M.; Grzyb, J.; Woszczak, L. Physicochemical, Bacteriostatic, and Biological Properties of Starch/Chitosan Polymer Composites Modified by Graphene Oxide, Designed as New Bionanomaterials. Polymers 2021, 13, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candra, A.; Darge, H.F.; Ahmed, Y.W.; Saragi, I.R.; Kitaw, S.L.; Tsai, H.-C. Eco-benign synthesis of nano-gold chitosan-bacterial cellulose in spent ground coffee kombucha consortium: Characterization, microbiome community, and biological performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Pramanik, P. Carbon quantum dots from natural resource: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Yin, Z.; Sun, L. A review on carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, photoluminescence mechanisms and applications. Luminescence 2022, 37, 1612–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Ge, S.; Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lichtfouse, E.; Van Tran, T.; Liew, R.K.; Rezakazemi, M.; et al. Synthesis and applications of carbon quantum dots derived from biomass waste: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 3393–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Wu, C.; Gu, S. State-of-the-Art on the Preparation, Modification, and Application of Biomass-Derived Carbon Quantum Dots. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 22017–22039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yuan, Y.; Labidi, A.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, K.; Lichtfouse, E.; Allam, A.A.; Ajarem, J.S.; Wang, C. Green process of biomass waste derived fluorescent carbon quantum dots for biological imaging in vitro and in vivo. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhu, L. Dispersibility of carbon dots in aqueous and/or organic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5401–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Shui, X.; Fan, J.; Feng, X.; Tao, T. Boosted photocatalytic activity of LaFeO3/Ag3PO4 heterojunction via carbon quantum dots: Higher conductivity, stability, and dispersivity. Colloid Surface. A. 2022, 652, 129895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridova, E.; Barras, A.; Addad, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Di Martino, A.; Deresmes, D.; Nikiforova, K.; Trusova, M.; Szunerits, S.; Guselnikova, O.; et al. Surface modification of carbon dots with tetraalkylammonium moieties for fine tuning their antibacterial activity. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.B.; Sher, I.; Rencus-Lazar, S.; Rotenstreich, Y.; Gazit, E. Functional Carbon Quantum Dots for Ocular Imaging and Therapeutic Applications. Small 2023, 19, 2205754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, H. Controlling the up-conversion photoluminescence property of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) by modifying its surface functional groups for enhanced photocatalytic performance of CQDs/BiVO4 under a broad-spectrum irradiation. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2021, 47, 3469–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, K.M.; Ahn, H.T.; Chung, M.; Le, X.A.; Saini, D.; Bhati, A.; Sonkar, S.K.; Kim, M.I.; Kim, T. N, S, and P-Co-doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Intrinsic Peroxidase Activity in a Wide pH Range and Its Antibacterial Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 5527–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başkaya, S.K.; Tahta, B.; Uruş, S.; Eskalen, H.; Çeşme, M.; Özğan, Ş. Multifunctional B, N, P, and S-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dot synthesis from pigeon manure: Highly effective Hg (II) sensor and fluorescent ink properties. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2024, 14, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Wen, C.; Su, R.; Gong, X.; Liang, W. High luminescent N,S,P co-doped carbon dots for the fluorescence sensing of extreme acidity and folic acid. Dalton T. 2023, 52, 6551–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Qin, D.; Mo, G.; Feng, J.; Zheng, X.; Deng, B. Facile Preparation of Boron and Nitrogen Codoped Green Emission Carbon Quantum Dots for Detection of Permanganate and Captopril. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11455–11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J.; Gao, W.; Rong, X.; Lu, Y.; Gao, C. Novel highly selective fluorescence sensing strategy for Mercury(II) in water based on nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots. Spectrochim. Acta. A. 2023, 286, 122010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Zhou, L.; Chi, Y.; Chen, L.; Pei, S.; Chen, B. Enhanced antibacterial activity with increasing P doping ratio in CQDs. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 27709–27715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, P.; Dev, A. Carbon quantum dots: A promising nanocarrier for bioimaging and drug delivery in cancer. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, N.; Farhadian, N.; Abnous, K.; Matin, M.M.; Khoshnood, A.; Yaghoobi, E. Dual targeting of Mg/N doped-carbon quantum dots with folic and hyaluronic acid for targeted drug delivery and cell imaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, S.; Mehdikhani, M.; Bigham, A.; Poorazizi, E.; Rafienia, M. Poly glycerol sebacate/polycaprolactone/carbon quantum dots fibrous scaffold as a multifunctional platform for cardiac tissue engineering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Tian, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Luan, J. Carbon nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 990362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.-Z.; Li, C.-Q.; Song, L.-B.; He, Y.-F.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.-D. A simple fluorescent strategy for liver capillary labeling with carbon quantum dot-lectin nanoprobe. Analyst 2022, 147, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, H.O.; Salehnia, F.; Hosseini, M.; Hassan, R.; Faizullah, A.; Ganjali, M.R. Fluorescence immunoassay based on nitrogen doped carbon dots for the detection of human nuclear matrix protein NMP22 as biomarker for early stage diagnosis of bladder cancer. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, Q.; Tan, X.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, A.; He, L.; et al. Photodynamic antibacterial chitosan/nitrogen-doped carbon dots composite packaging film for food preservation applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 314, 120938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, C. Recent Development of Carbon Quantum Dots: Biological Toxicity, Antibacterial Properties and Application in Foods. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 1513–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-B.; Liu, K.-K.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.-K.; Guo, R.; Song, S.-Y.; Shan, C.-X. Antibacterial Carbon Dots: Mechanisms, Design, and Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, R.M.; Amelia, S.R.; Rohmatulloh, Y.; Sanusi; Listiani, P.; Ichikawa, Y.; Honda, M.; Sudiarti, T.; Ivansyah, A.L. The effect of the graphene oxide quantum dot (GOQD) synthesis method on the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of GOQD/ZnO. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 140, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. One-pot synthesis of Forsythia@carbon quantum dots with natural anti-wood rot fungus activity. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanidenko, E.A.; Vedernikova, A.A.; Miruschenko, M.D.; Dadadzhanov, D.R.; Feferman, D.; Zhang, B.; Qu, S.; Ushakova, E.V. Red-Emissive Center Formation within Carbon Dots Based on Citric Acid and Formamide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 11522–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, R.; Long, L.; Ma, E. Preparation and properties of high-performance fast-growing wood modified by exfoliated organo-montmorillonite in waterborne hyperbranched polyacrylate emulsion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Guo, X.; Huang, J.; Shen, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L. Mass production of tunable multicolor graphene quantum dots from an energy resource of coke by a one-step electrochemical exfoliation. Carbon 2018, 140, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Sustainable carbon quantum dots from forestry and agricultural biomass with amplified photoluminescence by simple NH4OH passivation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9760–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, D.; Liu, X.; Han, A. Green Hydrothermal Synthesis of N-doped Carbon Dots from Biomass Highland Barley for the Detection of Hg2+. Sensors 2019, 19, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Ye, Y.; Geng, S.; Ning, D.; Zheng, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Natural biomass-derived carbon dots as potent antimicrobial agents against multidrug-resistant bacteria and their biofilms. Sustain. Mater. Techno. 2023, 36, e00584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Gao, H.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. Self-Targeting Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Diagnosis of Brain Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11455–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Peng, R.; Wei, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Xiao, B. Ethanol-Precipitation-Assisted Highly Efficient Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots from Chitosan. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22574–22580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The preparation and mechanism of garlic-templated fluorescent nanoparticles for degradation of Coriolus versicolor via one-pot. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 186, 115281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 13942.1; Chinese Standard. Method for Laboratory Test of Natural Decay Resistance of Woods. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Hui, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. Antibacterial Property of Graphene Quantum Dots (Both Source Material and Bacterial Shape Matter). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Q.; Liu, Q.; Geng, L.; Fang, Q.; Gong, J.R. Chiral Nanoparticle as a New Efficient Antimicrobial Nanoagent. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendiran, K.; Zhao, Z.; Pei, D.-S.; Fu, A. Antimicrobial Activity and Mechanism of Functionalized Quantum Dots. Polymers 2019, 11, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LY/T 1283; Chinese Standard. Method of Laboratory Test for Toxicity of Wood Preservatives to Decay Fungi. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Hao, R.; Wang, Y. Construction Strategy and Mechanism of a Novel Wood Preservative with Excellent Antifungal Effects. Molecules 2024, 29, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051013
Wang L, Wang T, Hao R, Wang Y. Construction Strategy and Mechanism of a Novel Wood Preservative with Excellent Antifungal Effects. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051013
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Teng Wang, Ruidi Hao, and Yamei Wang. 2024. "Construction Strategy and Mechanism of a Novel Wood Preservative with Excellent Antifungal Effects" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051013
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, T., Hao, R., & Wang, Y. (2024). Construction Strategy and Mechanism of a Novel Wood Preservative with Excellent Antifungal Effects. Molecules, 29(5), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051013