Abstract
Tozadenant (4-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamide) is a highly selective adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) antagonist and a promising lead structure for the development of A2AR-selective positron emission tomography (PET) probes. Although several 18F-labelled tozadenant derivatives showed favorable in vitro properties, recent in vivo PET studies observed poor brain penetration and lower specific binding than anticipated from the in vitro data. While these findings might be attributable to the structural modification associated with 18F-labelling, they could also reflect inherent properties of the parent compound. However, PET studies with radioisotopologues of tozadenant to evaluate its cerebral pharmacokinetics and brain distribution are still lacking. In the present work, we applied N-Boc-O-desmethyltozadenant as a suitable precursor for the preparation of [O-methyl-11C]tozadenant ([11C]tozadenant) by O-methylation with [11C]methyl iodide followed by acidic deprotection. This approach afforded [11C]tozadenant in radiochemical yields of 18 ± 2%, with molar activities of 50–60 GBq/µmol (1300–1600 mCi/µmol) and radiochemical purities of 95 ± 3%. In addition, in vitro autoradiography in pig and rat brain slices demonstrated the expected striatal accumulation pattern and confirmed the A2AR specificity of the radioligand, making it a promising tool for in vivo PET studies on the cerebral pharmacokinetics and brain distribution of tozadenant.
1. Introduction
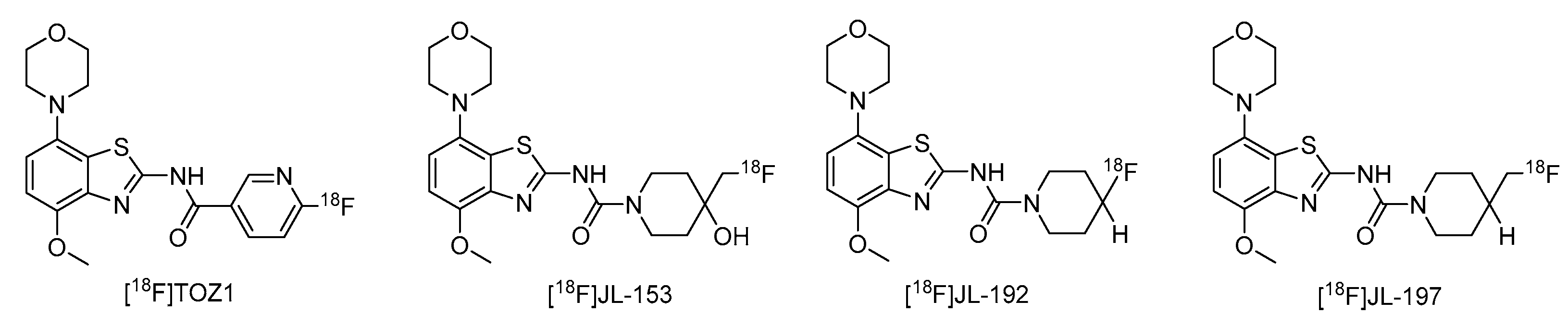
The nucleoside adenosine is a pleiotropic signaling molecule that mediates its cellular effects by activation of four different adenosine receptor (AR) subtypes (A1R, A2AR, A2BR and A3R) [1]. The predominant AR subtypes in the central nervous system are A1R and A2AR, which participate in the regulation of many physiological processes like wakefulness, cognition and motor function [2,3,4]. While A1Rs are widely expressed throughout the whole brain, A2ARs show a more restricted expression pattern, with high levels in the striatum and much lower levels in extra-striatal brain regions [1,5,6,7,8]. In addition, many neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions have been shown to be associated with changes in the distribution and/or function of A2ARs, making them attractive therapeutic targets for a wide spectrum of neurological diseases [8,9,10]. For example, inhibition of the striatopallidal motor pathway with selective A2AR antagonists like tozadenant (4-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-1,3-benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamide) has been pursued as a non-dopaminergic treatment option for Parkinson’s disease (PD) [11,12]. Although tozadenant effectively improved PD symptomatology with virtually no off-target effects, reports of hematological toxicity during long-term treatment necessitated early termination of phase 3 clinical trials [13]. Nevertheless, its high affinity (Ki = 3.9–4.9 nM for human A2AR) [8,14], unique target selectivity [15] and high in vivo stability [16,17] position tozadenant as a promising lead structure for the development of positron emission tomography (PET) probes, which could be used to visualize and quantify cerebral A2ARs in patients with PD or other neurological diseases [9,18]. Thus, taking into account reported densities of A2ARs in the human striatum (Bmax = 259–870 fmol/mg protein [8,19,20]), the estimated (in vitro) binding potential (Bmax/Ki) for tozadenant (>5) indicates that radiolabeled analogs with comparable or superior affinity could be suitable for quantitative comparisons with PET imaging [21]. Accordingly, a number of 18F-labeled tozadenant derivates have been developed (Figure 1) and evaluated by in vitro autoradiography, which generally demonstrated an excellent A2AR specificity of these radioligands [14,22]. On the other hand, preclinical in vivo evaluation of 18F-labeled tozadenant derivates performed so far revealed a rather low brain penetration and considerably lower specific binding than anticipated from in vitro studies [22,23].
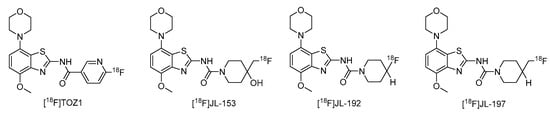
Figure 1.
Tozadenant-derived 18F-labeled A2AR antagonists for PET imaging [14,22].
Given that the cerebral pharmacokinetics and brain distribution of tozadenant itself have never been examined, these findings could reflect undesirable in vivo properties of the benzothiazole scaffold and/or negative effects of the structural modifications associated with 18F-labeling. For example, while the quotient of receptor density and affinity (i.e., Bmax/Ki) provides an upper limit for striatal accumulation, slow blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration, active export across the BBB or other pharmacokinetic features of the benzothiazole scaffold itself (e.g., unsuitable lipophilicity) could significantly reduce the in vivo availability of tozadenant or derived radioligands in the brain [8]. Thus, although existing evidence indicates that the extent of brain entry during continued treatment with tozadenant was sufficient for clinical efficiency, neither the kinetics of brain penetration nor the lipophilicity or interaction with drug excretion pumps like P-gp have been studied to date and multiple probabilistic scores indicative of BBB penetration were indeed rather low [24]. Alternatively, 18F-labeling might have reduced BBB penetration or resulted in other pharmacokinetic changes that negatively influence in vivo performance, in which case derivatives with suitable imaging properties could potentially be obtained through the use of alternative radiolabeling strategies. However, so far, isotopologues of tozadenant labeled with carbon-11 which could be used to distinguish between these two possibilities have not been disclosed. In the present article, we describe a protocol for automated production of the 11C-labeled tozadenant isotopologue [O-methyl-11C]tozadenant ([11C]tozadenant) and a preliminary in vitro evaluation of this novel radioligand.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 11C-Methylation of Unprotected Desmethyl Precursors
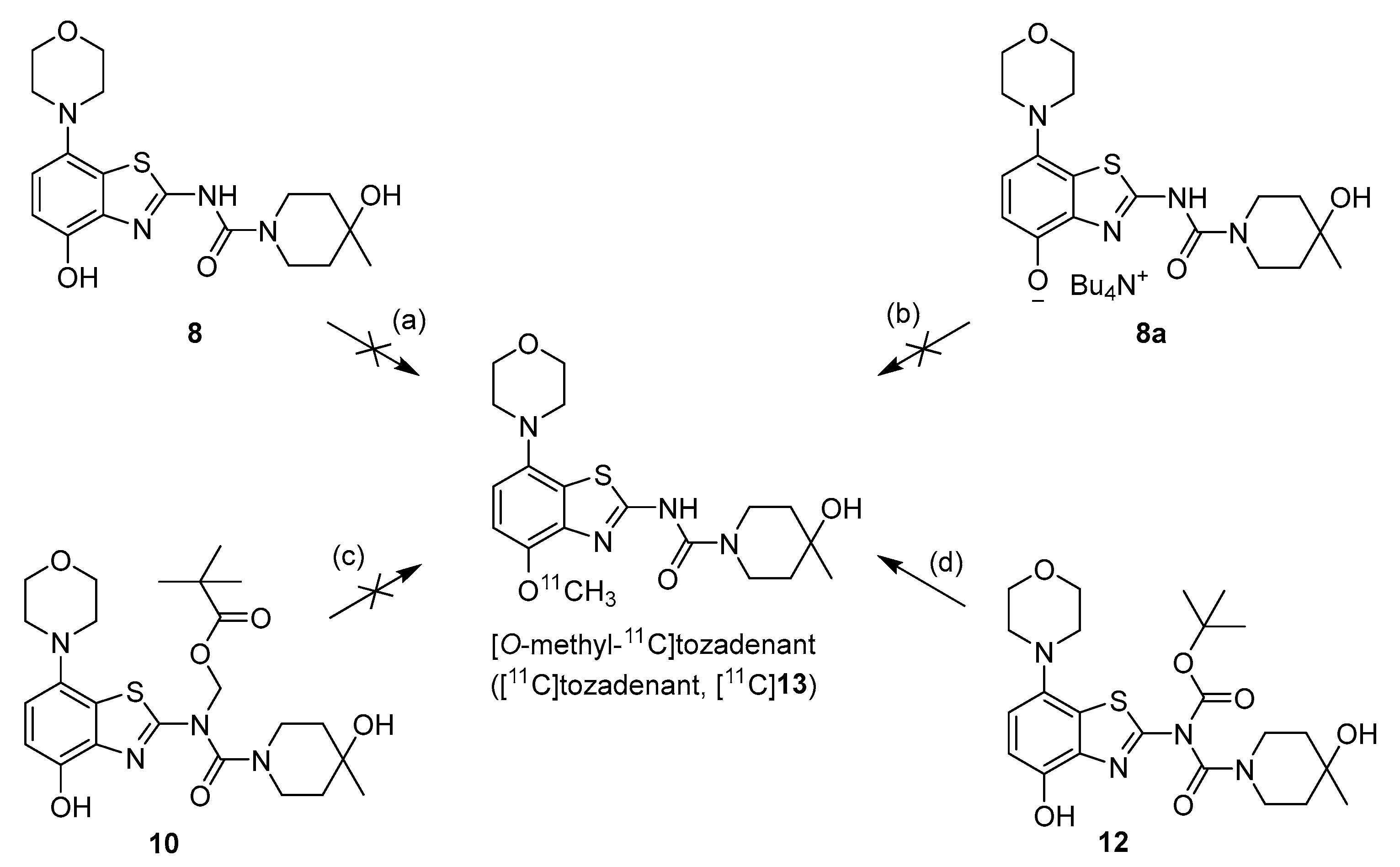
We initially selected O-methylation of O-desmethyltozadenant (8) with [11C]MeI (Figure 2, route a) as a straightforward route for the preparation of [11C]tozadenant ([11C]13).
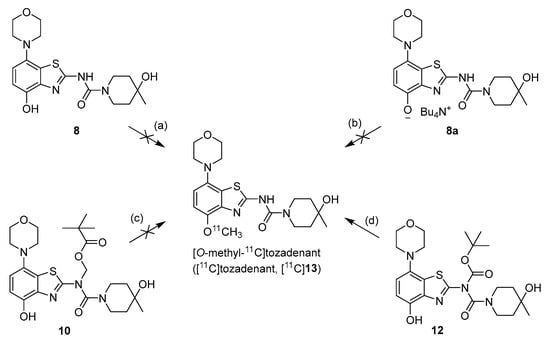
Figure 2.
Investigated radiolabeling protocols for the preparation of [11C]tozadenant ([11C]13). Conditions: (a) [11C]MeI, base, solvent, t; (b) [11C]MeOTf, acetone or MeCN, rt; (c) [11C]MeI, 1 m NaOHaq (2 equiv), DMF, 60 °C; (d) [11C]MeI, 1 m NaOHaq (2 equiv), solvent, 60 °C.
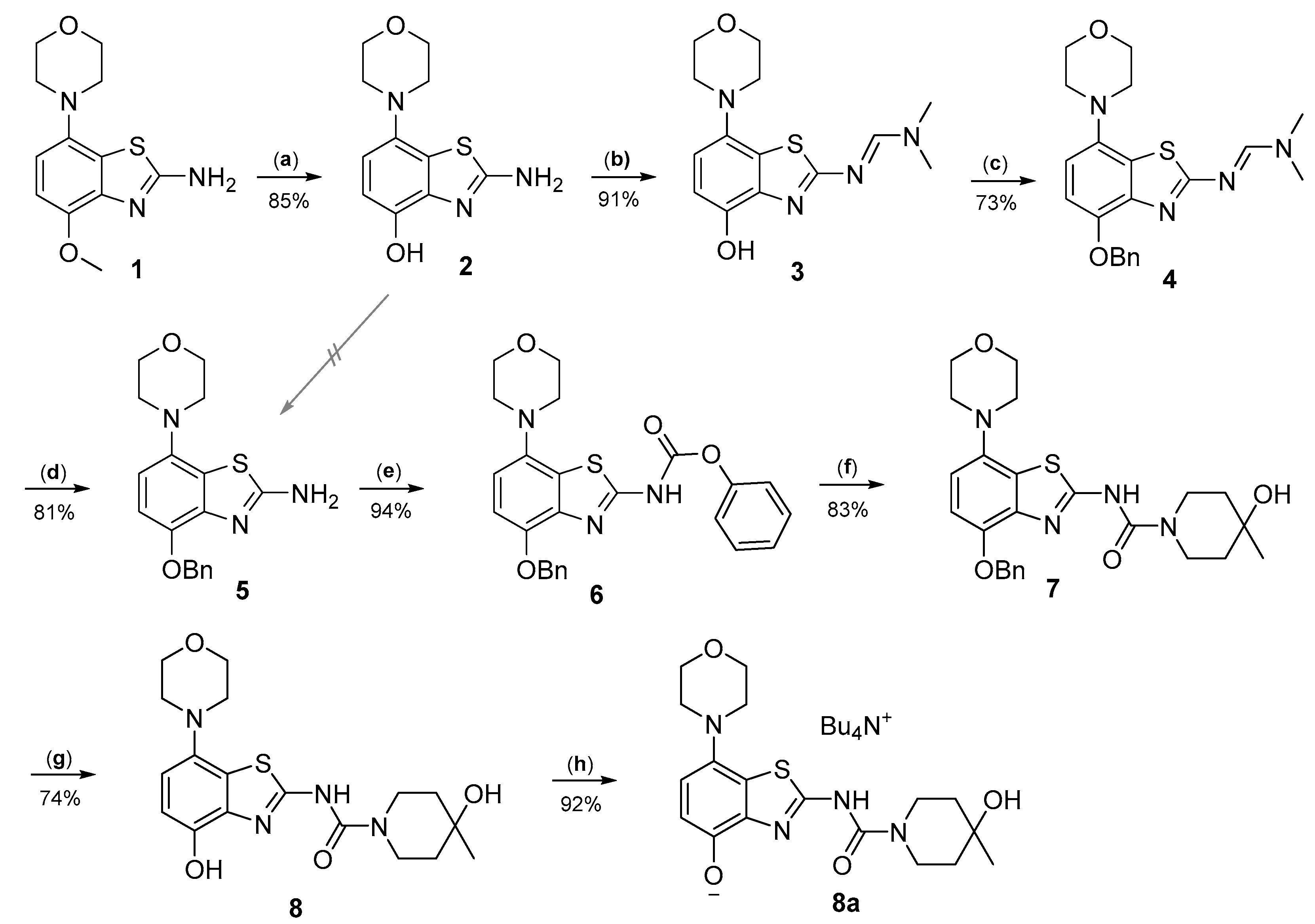
Radiomethylation precursor 8 was prepared in seven steps, starting from known 4-methoxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-amine (1) [14] (Figure 3). To this end, 1 was first demethylated with boiling aqueous 48% hydrobromic acid, which afforded 2-amino-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-4-ol (2) in excellent yield. Although subsequent Cs2CO3-supported O-alkylation of 2 with benzyl bromide directly furnished benzyl ether 5, the desired product was obtained in low yields and always contaminated with a lipophilic impurity that proved difficult to remove by chromatography. In addition, sufficient chemoselectivity for benzylation of the phenolic OH over the amino group in 2 could be achieved neither at low temperatures nor by the use of stoichiometric reagent amounts, which necessitated chromatographic purification and resulted in low yields of the desired benzyl ether. As such, we instead opted to perform O-benzylation after appropriate protection of the amino group. Condensation of 2 with benzaldehyde to form the imine of the primary exocyclic amine while preserving the phenolic OH was unsuccessful. As an alternative, the amino group was protected by reaction of 2 with N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (DMF-DMA), which furnished the corresponding N,N-dimethylformamidine 3 in an over 90% yield. Subsequent Cs2CO3-supported O-benzylation of 3 at ambient temperature followed by N-deprotection of the resulting intermediate 4 with potassium hydroxide afforded benzyl ether 5 in a 77% yield over two steps. Compound 5 was then condensed with phenyl chloroformate using pyridine as a base to prepare phenyl carbamate 6 as a stable solid in almost quantitative yield. Next, the asymmetric N,N′-disubstituted urea 7 was synthesized by aminolysis of 6 under neutral conditions with DMSO as reaction solvent [25]. To this end, 6 was treated with a slight excess of 4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine at 50 °C, which rapidly generated 7 in an 83% yield. Finally, 7 was O-debenzylated by catalytic transfer hydrogenation (CTH) with Pd/C and a sixfold excess of ammonium formate as hydrogen donor [26] for ten min, which afforded precursor 8 in 74% yield.
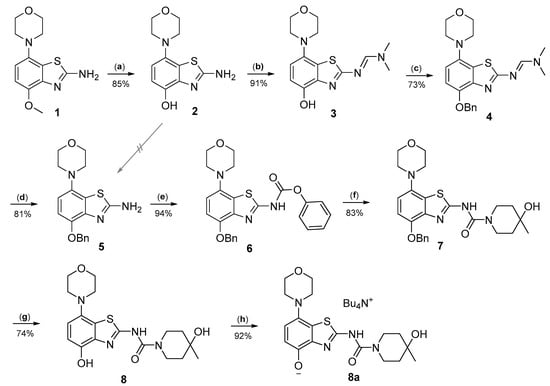
Figure 3.
Preparation of radiolabeling precursors 8 and 8a. Conditions: (a) HBraq, reflux; (b) DMF-DMA, DMF; (c) BnBr, Cs2CO3, DMF; (d) KOH, MeOH, reflux; (e) phenyl chloroformate, THF; (f) 4-methyl-4-piperidinol, DMSO, 50 °C; (g) Pd/C, ammonium formate, DMF, 50 °C; (h) Bu4NOH, MeOH.
Unexpectedly, radiomethylation of 8 with [11C]MeI using various reaction solvents, bases and reaction conditions failed and only unidentified products could be detected. In an attempt to enhance the nucleophilicity of the phenolic oxygen and the chemoselectivity of the methylation reaction [27], we also prepared the tetrabutylammonium (TBA) salt of precursor 8. To this end, a suspension of 8 (1.2 equivalents) in MeOH was reacted with TBA hydroxide (1 equivalent) in MeOH followed by separation of unreacted precursor 8 by centrifugation, which afforded 8a in 90% yield.
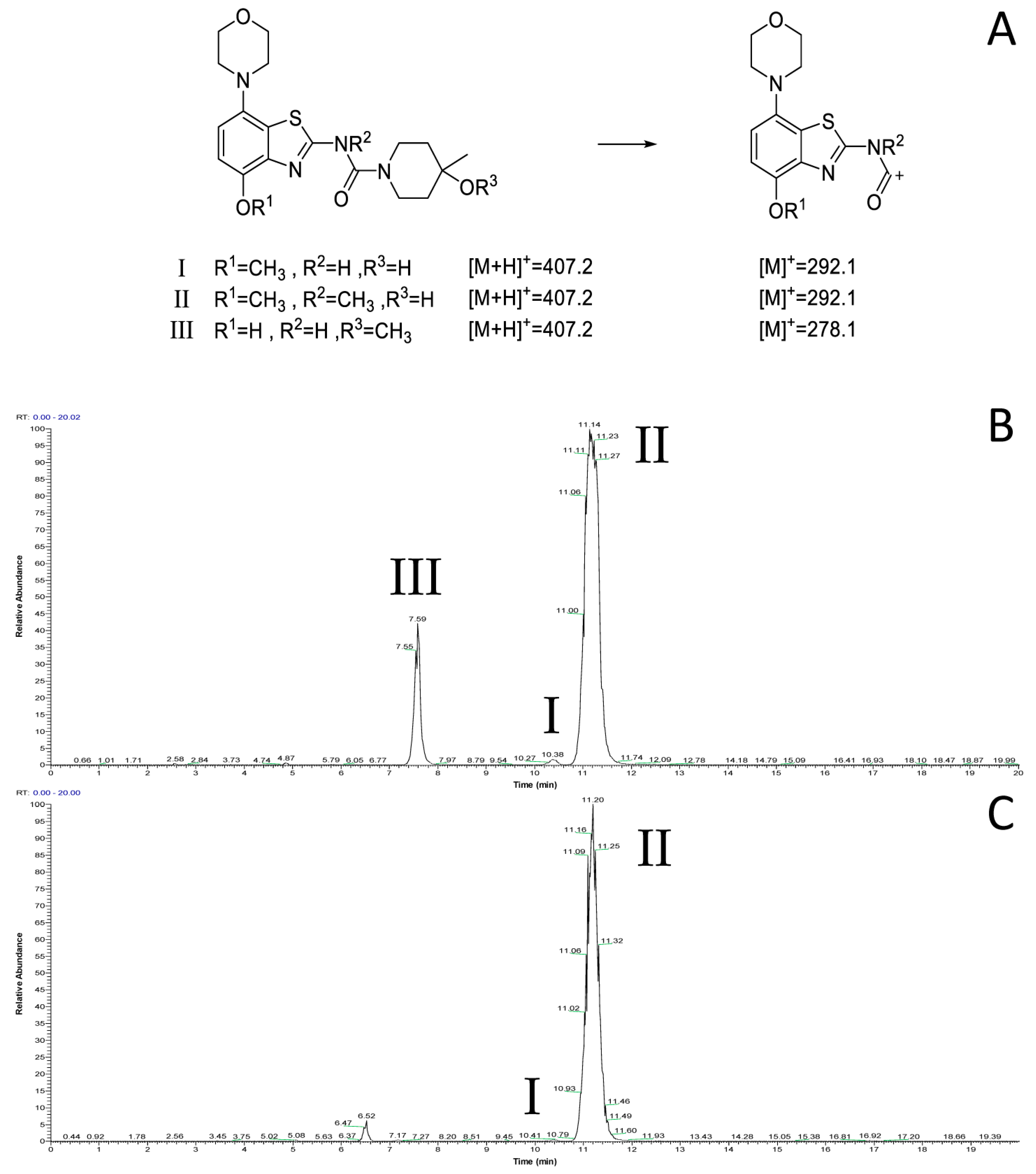
However, radiomethylation of 8a with [11C]methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate ([11C]methyl triflate) [28] in acetone or acetonitrile (Figure 2, route b) did not yield the desired product. To identify possible causes, we performed methylation experiments with sub-stoichiometric amounts of non-radioactive methyl triflate in acetone and analyzed the reaction mixture by ESI(+) HPLC-MS. Besides small amounts of several unidentified polar side products, these experiments revealed the formation of three main products with the m/z of tozadenant (Figure 4). Comparison of their retention times with that of the reference compound demonstrated that tozadenant was the least abundant product (I in Figure 4) and obtained in less than one percent yield (determined by comparison of the integrated UV absorption signals of the three compounds). ESI in-source fragmentation of the less polar main product (II in Figure 4), which constituted approximately 90%, resulted in formation of a fragment characteristic for the methylated aminobenzothiazol moiety (m/z 293) [17], suggesting that it corresponded to the N-methylated regioisomer of tozadenant. The slightly more polar third product (III in Figure 4) could not be fragmented and most likely resulted from methylation of the tertiary hydroxy group as the only remaining nucleophile that would not give rise to a highly polar onium product. Interestingly, this product constituted approximately 10% and was thus formed in more than 10-fold higher amounts than tozadenant, indicating a surprisingly low nucleophilicity of the phenolic hydroxy group. These results, although unexpected, were in line with the competing O- and N-benzylation reactions observed during precursor preparation.
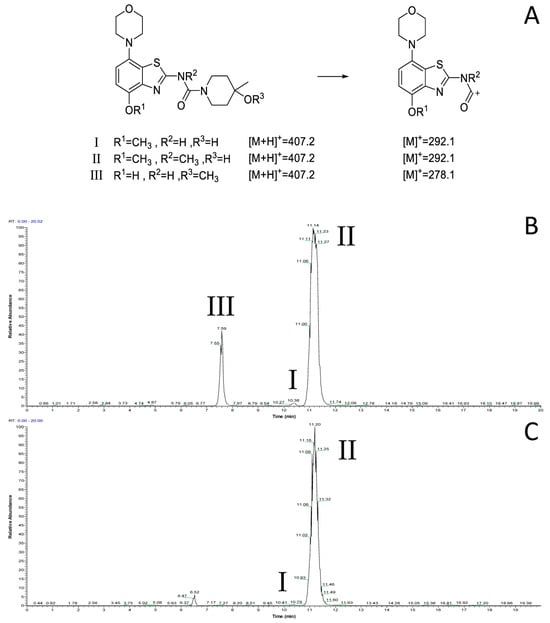
Figure 4.
ESI(+) HPLC-MS analysis of the crude product solution obtained by reaction of precursor 8 with methyl triflate. (A) Calculated m/z values for the different main products and the derived benzothiazol fragments. (B) Total ion current (TIC) chromatogram filtered to m/z 407, which corresponds to tozadenant (tR = 10.4 min) and its regioisomers (tR = 7.6 and 11.2 min). (C) TIC filtered to m/z 292, which corresponds to the methylated benzothiazol fragment expected for tozadenant and its N-methylated regioisomer. The peak at 6.5 min (m/z = 421) corresponds to a product formed by double methylation and is therefore not relevant for no-carrier-added 11C-methylation reactions. HPLC conditions: Column: Phenomenex Kinetex® F5, 5 µm, 250 × 4.6 mm; eluent: 25% MeCN in H2O + 0.2% HCOOH, flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
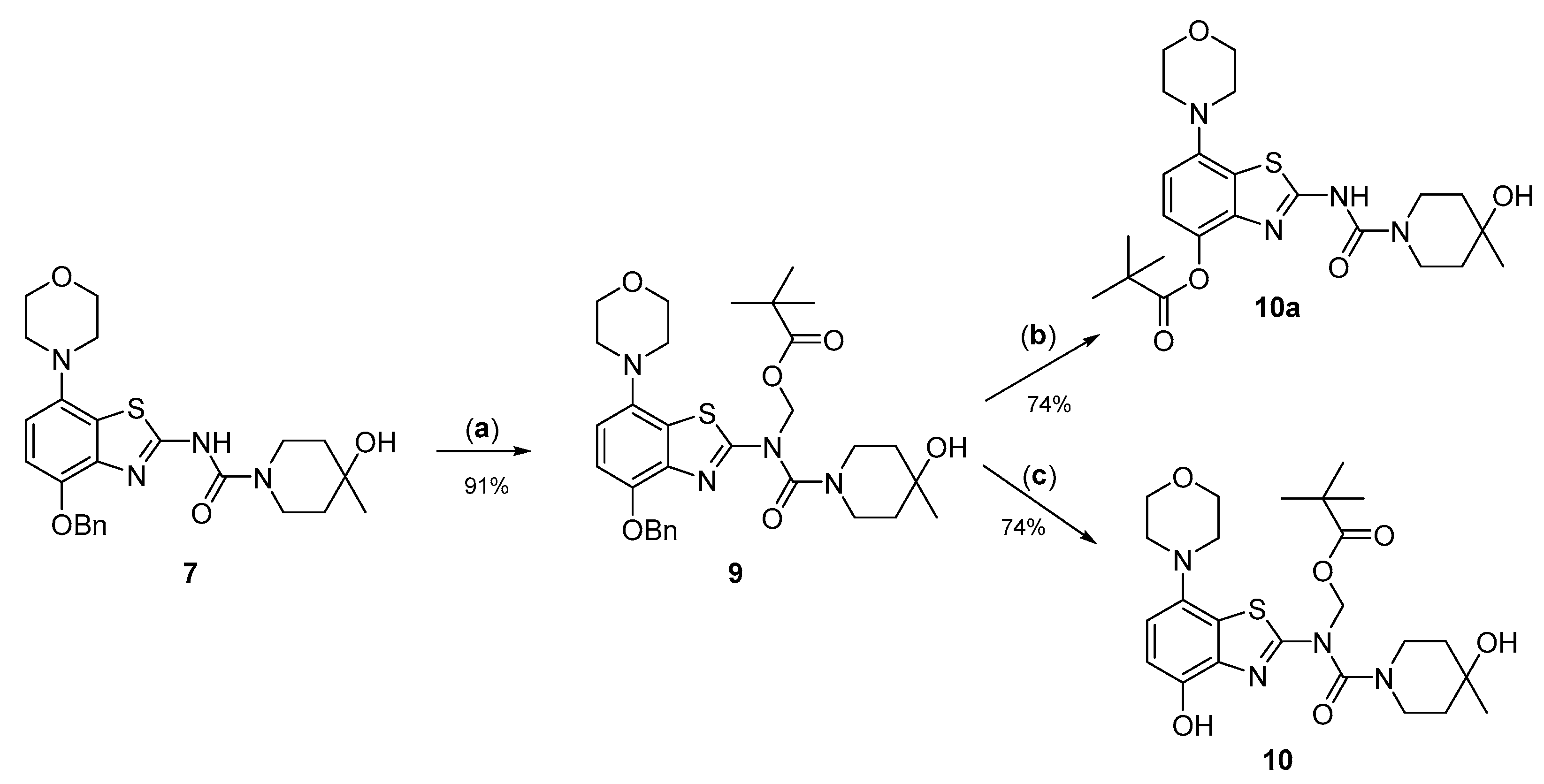
2.2. 11C-Methylation of a Base-Labile Protected Desmethyl Precursor
Due to its relatively high nucleophilicity, we next assessed whether radiomethylation could be achieved after protection of the amidic nitrogen in precursor 8 with a pivaloyloxymethyl (Pom) protecting group (Figure 2, route c). Accordingly, O-benzyl urea 7 was reacted with chloromethyl pivalate and potassium carbonate in DMF to produce N-protected intermediate 9 in a >90% yield (Figure 5). Subsequent O-debenzylation of 9 by CTH under the same conditions as described above for 7 resulted in formation of pivaloyl ester 10a instead of the expected Pom-protected radiolabeling precursor 10. This result can most likely be explained by rapid base-induced migration of the Pom protecting group with the concomitant release of formaldehyde, as previously observed during Pom-protection of the nucleobase adenine [29]. Thus, catalytic decomposition of ammonium formate is well known to release ammonia [30], which could result in sufficient alkalinity to induce the observed acyl migration. In line with this assumption, O-debenzylation of 9 by CTH in a mixture of MeOH and acetic acid instead of DMF furnished the desired radiolabeling precursor 10 in a 74% yield as a bench-stable powder.
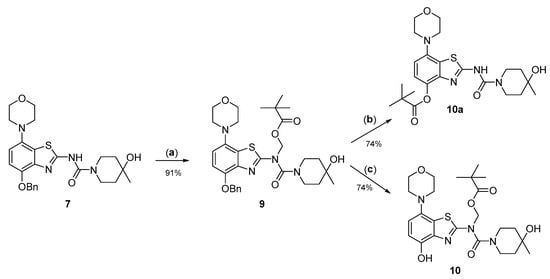
Figure 5.
Preparation of N-Pom-protected precursor 10. Depending on reaction conditions, O-debenzylation of 9 by catalytic transfer hydrogenation furnished either 10 or (due to base-induced rearrangement) 10a. Conditions: (a) Pom-Cl, K2CO3, DMF, 60 °C; (b) Pd/C, ammonium formate, DMF, 55 °C; (c) Pd/C, ammonium formate, MeOH-AcOH, 55 °C.
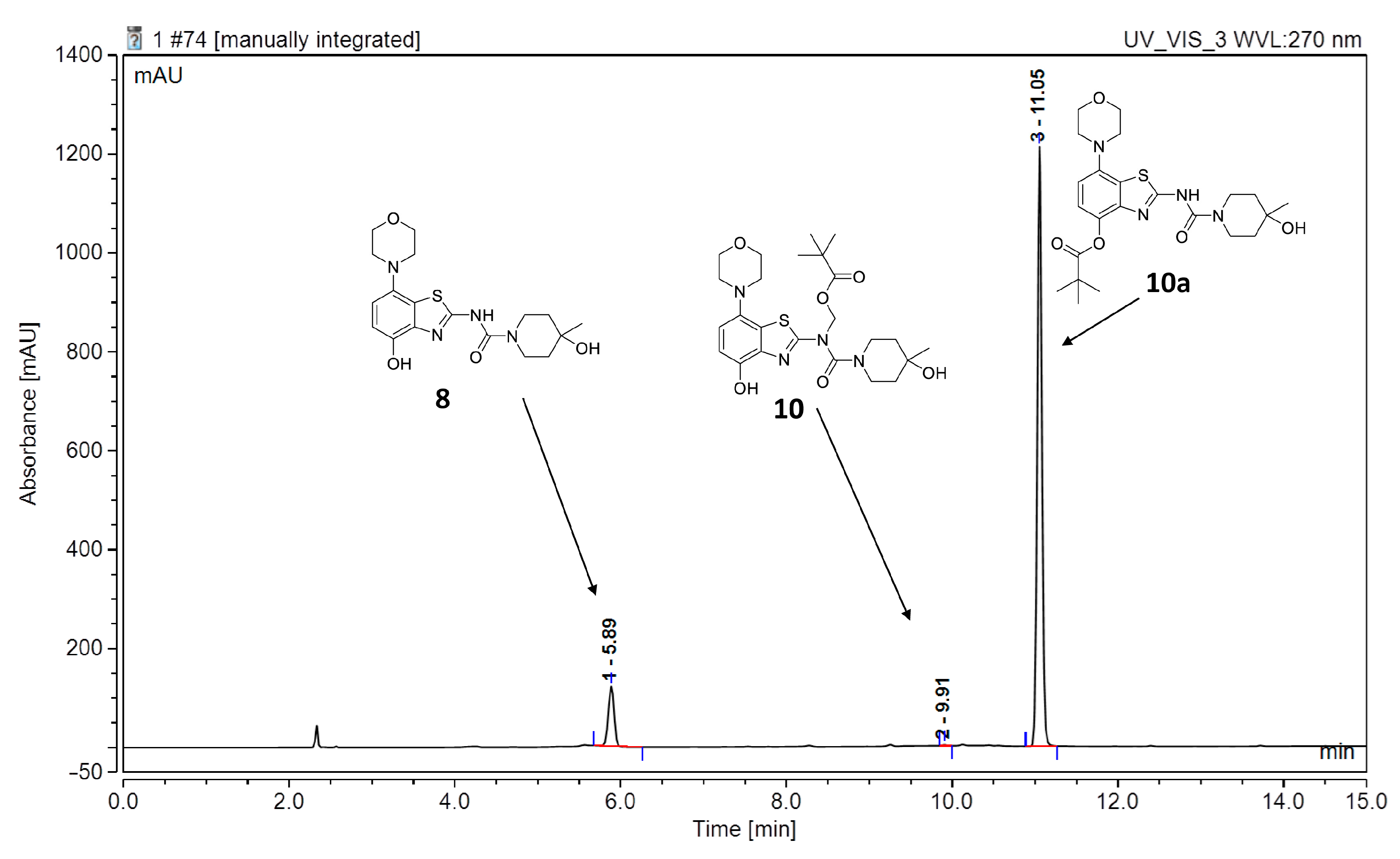
However, first screening experiments by methylation of 10 with non-radioactive MeI (0.1 equivalents) using different solvents (DMF, DMSO or acetonitrile), bases (Cs2CO3, K2CO3, NaOH, (n-Bu)4NOH or NaH) and reaction temperatures (20–120 °C) followed by deprotection also did not furnish the desired product tozadenant. Suspecting insufficient base stability of the precursor, a solution of 10 in DMF was treated with 1 N aqueous NaOH (two equivalents) and heated to 60 °C to simulate the slightly basic radiolabeling conditions. ESI HPLC-MS analysis revealed almost complete disappearance of 10 (m/z 507) within minutes and formation of two new compounds (m/z 477 and m/z 393) in a ratio of 9:1 (Figure 6). Based on the mass difference of 30 units compared to 10, the main product (m/z 477) was formed by elimination of formaldehyde, indicating that it corresponded to compound 10a produced by base-induced acyl migration. The mass of the second product (m/z 393) was consistent with that of the Pom-deprotected product, indicating that it corresponded to compound 8. Thus, precursor 10 proved to be unsuitable for preparation of [11C]tozadenant, since even the slightly basic conditions required for radiomethylation resulted in rapid base-induced acyl migration with formation of pivaloyl ester 10a and (to a lesser extent) hydrolysis into the non-protected precursor 8.
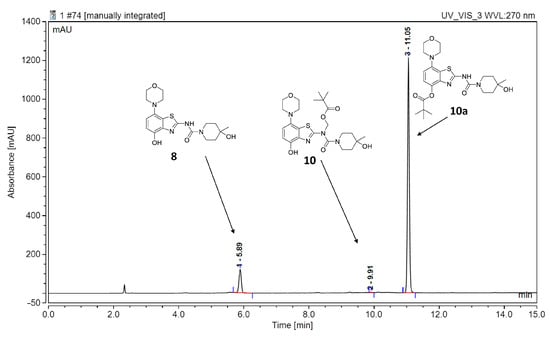
Figure 6.
ESI HPLC-MS analysis of the products formed upon treatment of precursor 10 in DMF with two equivalents of NaOH and heating to 60 °C to simulate radiolabeling conditions. HPLC conditions: Column: Phenomenex Kinetex® F5 5 µm, 250 × 4.6 mm; eluent (solvent A = 0.2% HCOOH in H2O, solvent B = 0.2% HCOOH in MeCN): linear gradient: 0 min 20% B, 15 min: 80% B; flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
2.3. 11C-Methylation of an Acid-Labile Protected Desmethyl Precursor
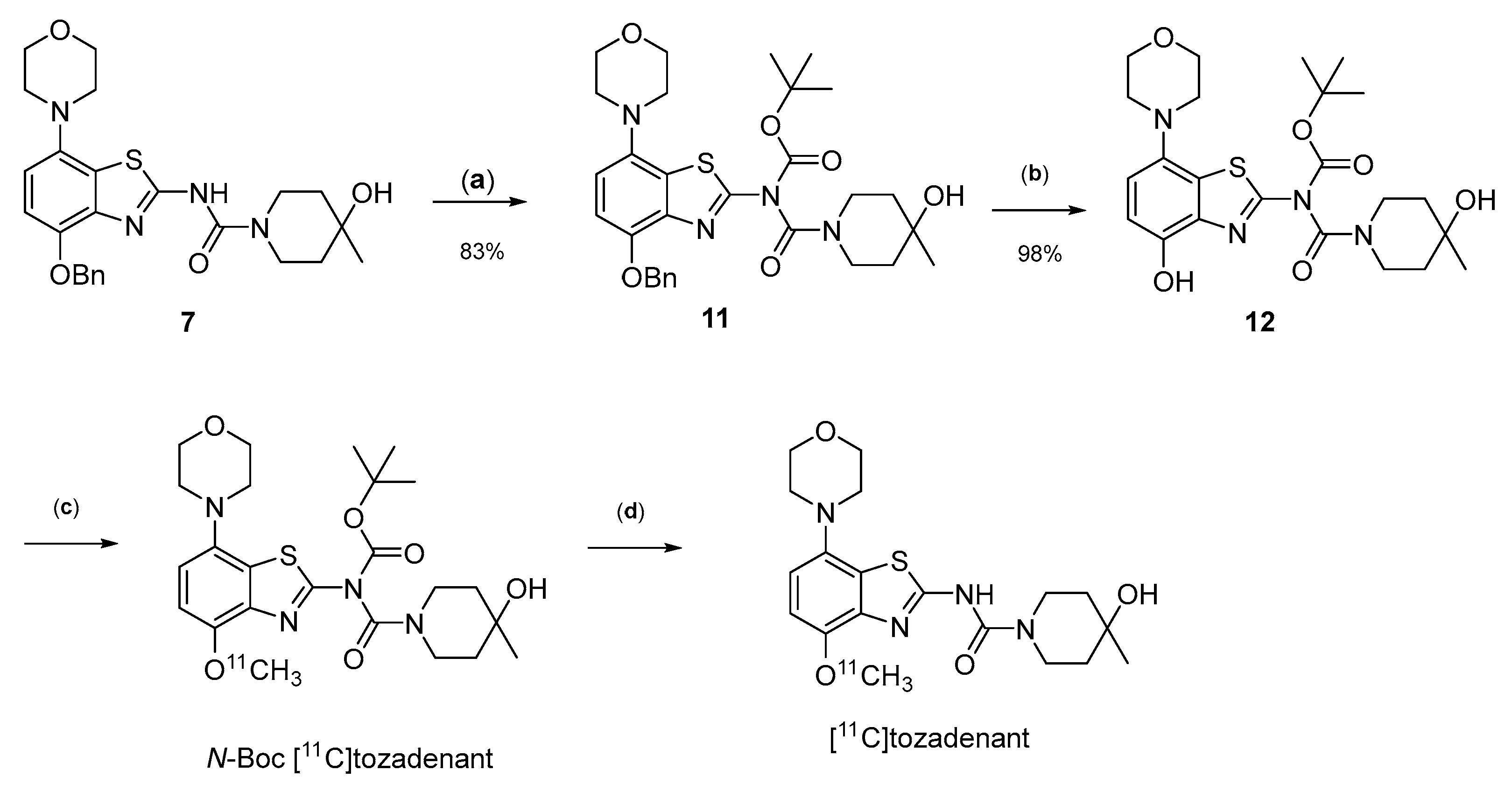
Owing to its low stability, we next replaced the base-labile Pom-protecting group with a base-stable but acid-labile tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) residue. To this end, O-benzyl urea 7 was reacted with di-tert-butyldicarbonate and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP)/triethylamine in THF, which afforded the O-Bn-N-Boc diprotected intermediate 11 in a yield of 89%. Subsequent O-debenzylation of 11 by CTH under the same conditions as described for 7 furnished the desired N-Boc protected radiomethylation precursor 12 as bench-stable crystals in near-quantitative yield (Figure 7).
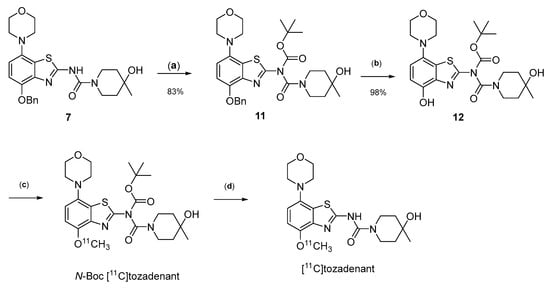
Figure 7.
Preparation of [11C]tozadenant from the N-Boc protected precursor 12. Conditions: (a) (Boc)2O, TEA, DMAP, THF, rt; (b) ammonium formate, Pd/C, DMF, 55 °C; (c) n.c.a. [11C]methyl iodide, NaOH, DMF, 60 °C; (d) conc. HCl, 100 °C.
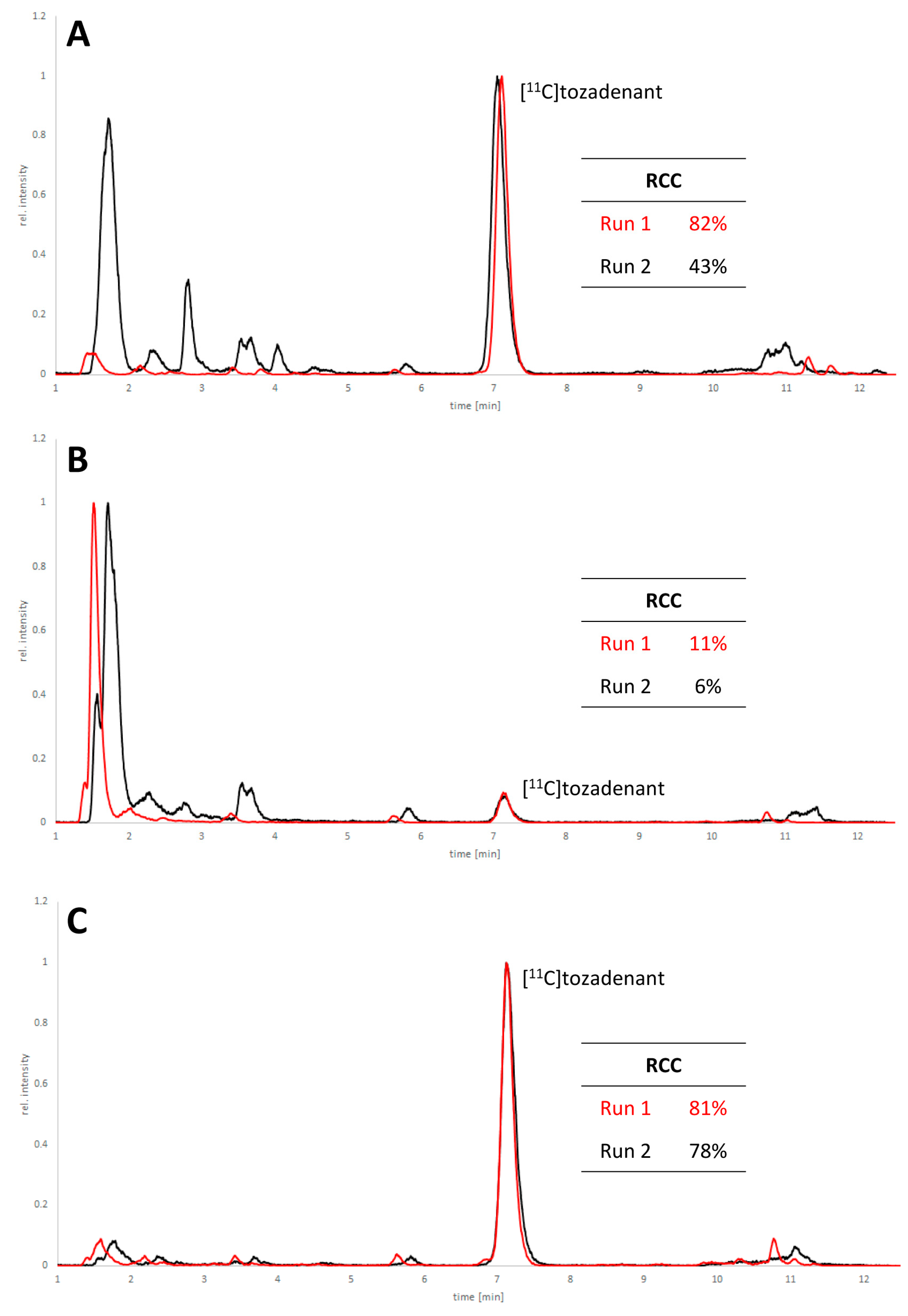
Non-radioactive screening experiments similar to those performed with 10 (i.e., treatment of precursor in DMF with 1 N aqueous NaOH and heating to 60 °C) indicated a sufficient base stability of 12. Accordingly, radiomethylation of 12 was performed with [11C]MeI in DMF and 1 N aqueous NaOH (2 equivalents) for 5 min at 60 °C (Figure 2, Route d). Subsequent Boc-deprotection with concentrated aqueous HCl at 100 °C for 5 min furnished the desired tracer [11C]tozadenant, albeit in highly variable yields. Likewise, small-scale manual radiolabeling experiments performed in close succession produced distinctly different results, with a moderate radiochemical conversion (RCC) of 43% and large quantities of polar side products in one case and an excellent RCC of 82% and few side products in the other (Figure 8A). These discrepancies could potentially be explained by hydroxide-assisted thermal decomposition of DMF with formation of dimethylamine as a competing nucleophile in amounts that depended on the exact timing [31]. With this in mind, additional small-scale experiments were performed with DMSO or DMA as alternative reaction solvents. While the use of DMSO proved to be unsuitable and resulted in RCCs of only 5–10% (Figure 8B), 11C-methylation of 12 in DMA proceeded smoothly and afforded the desired tracer in reproducible RCCs of 78–81% with only a few minor side products (Figure 8C).
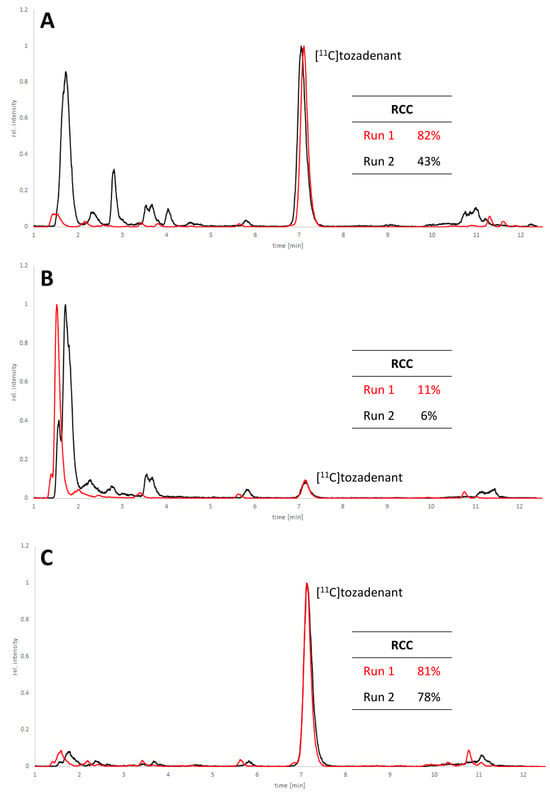
Figure 8.
HPLC chromatograms of crude reaction mixtures obtained by 11C-methylation of precursor 12 with [11C]MeI in DMF (A), DMSO (B) or DMA (C) followed by de-protection of the radiolabeled intermediate. Two reactions were performed in close succession with each solvent (indicated in red and black) and all signals were normalized to the highest peak in the corresponding chromatogram. Reaction conditions: (i) Radiomethylation: precursor (2 µmol), 1 N NaOHaq (4 µL), solvent (300 µL), 5 min, 60 °C; (ii) Deprotection: 37% HCl (150 µL), 5 min, 100 °C. HPLC conditions: Column: MultoKrom® 100-5 C18 250 × 4.6 mm; eluent: 0–10 min: 32.5% MeCNaq + 0.2% HCOOH, 10–15 min: 80% MeCNaq + 0.2% HCOOH; flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Having established suitable reaction parameters, [11C]tozadenant could be reliably produced on a custom-built automated synthesis module. After rapid semipreparative HPLC purification (Figure S1) and formulation, the tracer was obtained in radiochemical yields of 18 ± 2% (850–1250 MBq), radiochemical purities of 95 ± 3%, high chemical purities (Figure S2) and molar activities of 50–60 GBq/µmol (1300–1600 mCi/µmol) in an overall synthesis time of 40 min. All quality control parameters were within the specifications for preclinical in vivo studies (Table 1, n = 3).

Table 1.
Quality control parameters of the final [11C]tozadenant tracer formulation.
2.4. Preliminary In Vitro Evaluation of [11C]tozadenant
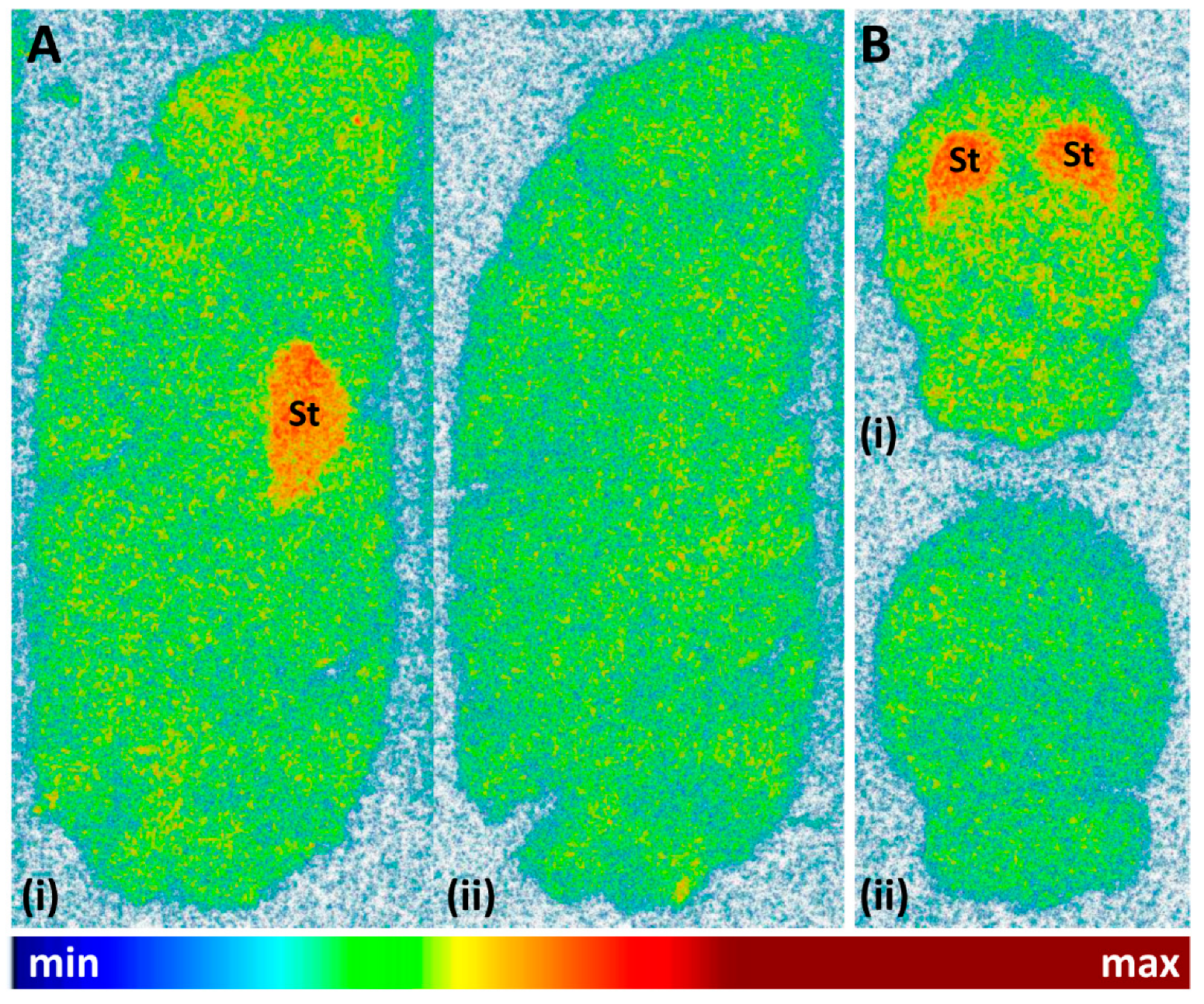
Finally, the cerebral binding pattern of [11C]tozadenant was determined using in vitro autoradiography with brain slices from rat and pig as two common preclinical species. As illustrated in Figure 9, the regional distribution of radioactivity observed in these experiments was consistent with the established expression patterns of A2ARs in both species [5,6,32], with pronounced accumulation in the striatum and much lower levels in extra-striatal brain regions. Specific binding of the radioligand, determined from the difference between total binding and binding in the presence of the A2AR-selective antagonist ZM241385 (1 µm), amounted to approximately 68%.
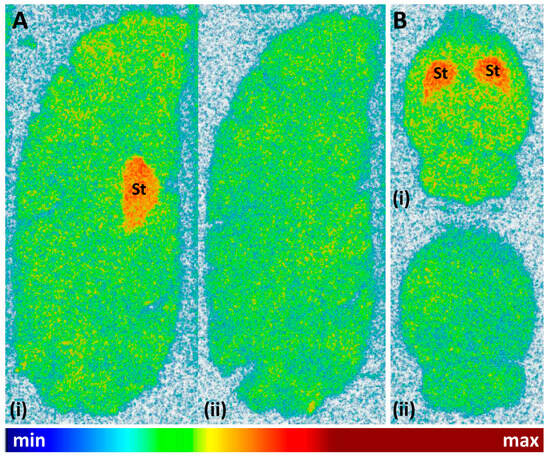
Figure 9.
Representative autoradiographic images obtained after incubation of (A) sagittal pig brain slices or (B) horizontal rat brain slices with 12 kBq/mL (0.24 nM) [11C]tozadenant in the absence (i = total binding) or presence (ii = non-specific binding) of 1 µM ZM241385. Abbreviations: St = striatum.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
Unless noted otherwise, all reactions were carried out under argon at ambient temperature (22 ± 2°C) in oven-dried glassware. Standard inert atmosphere techniques were used in handling all air and moisture-sensitive reagents. Melting points were measured on a FP62—Melting Point Meter (Mettler Toledo, Gießen, Germany) and are uncorrected.
3.1.1. Solvents and Reagents
Solvents were either purchased in sufficient purity (MerckKGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) or purified and dried using standard methods [33]. Chemicals were purchased from Merck (Taufkirchen, Germany), Activate Scientific (Prien, Germany) and ABCR (Karlsruhe, Germany) or prepared as described in the text. 2-Amino-4-methoxy-7-morpholinobenzothiazole (1), 2-amino-4-hydroxy-7-morpholinobenzothiazole (2) and the reference compound tozadenant (13) were prepared as described previously [14].
3.1.2. Spectroscopy
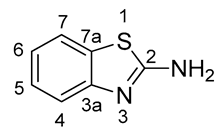
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded in a 5% solution at 298 K (1H: 400.13 MHz; 13C: 100.61 MHz; 19F: 376.49 MHz) using a Bruker Avance Neo 400 (Bruker Bio Spin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany). The measured chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm) relative to the residual solvent signals (for CDCl3, δH = 7.26, δC = 77.16; for DMSO-d6, δH = 2.50, δC = 50.32). The 1H-NMR spectra are reported as follows: δ, multiplicity, coupling constant J (in Hz) where appropriate, number of protons, assignment. The following abbreviations and their combinations are used when reporting NMR data: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet, sbr = broad singlet, mobsc = obscured multiplet and v = very. NMR signals were assigned based on information from additional two-dimensional experiments (COSY, gHSQC, gHMBC, NOESY). Coupling constants for protons are given in the form of nJ(1H, X), and those for carbons as nJ(13C, 19F). All 13C- and 19F-NMR spectra were recorded under 1H-broadband decoupling (CPD). Compound names were generated by ChemBioDraw™ (CambridgeSoft) following IUPAC nomenclature. The numbering of the benzo[d]thiazol-2-amine (2-aminobenzothiazole) scaffold was performed as shown below.
Low-resolution mass spectra were obtained in electrospray ionization (ESI-positive) mode with a Thermo Fischer Scientific MSQ Plus mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific GmbH, Dreieich, Germany). The analytes were dissolved in MeOH (about 1 mg/mL) and injected directly through a valve on the ionisation interface. The flow rate of the eluent (MeOH/water/AcOH, 50/50/0.2, v/v/v) was 200 μL/min. Reported are the m/z-values of the pseudo-ion [M + H]+.
High-resolution mass spectra were determined in the Central Division of Analytical Chemistry at the Forschungszentrum Jülich. Elemental analyses were performed using HEKAtech GmbH (Wegberg, Germany). Analyses indicated by the symbols of the elements are within ±0.4% of the theoretical values.
3.1.3. Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) on silica-coated aluminium sheets with a fluorescent indicator (ALUGRAM SIL G/UV254 Macherey-Nagel GmbH, Düren, Germany) was performed to monitor the progress of all reactions and to confirm the purity of the resulting products. The respective eluent was selected so that the Rf values of the individual compounds ranged from 0.2 to 0.8. Compounds were visualized under UV light and/or by iodine staining.
Flash chromatography was performed with a Büchi Pure C-815 flash chromatography system (BÜCHI Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland) equipped with multisignal (UV/ELSD) detection and FlashPure silica cartridges (particle size 40 µm) as a stationary phase. Solvent proportions are indicated in a volume/volume ratio.
3.2. Chemical Syntheses
3.2.1. Preparation of 2-Amino-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-4-ol (2)
A solution of 2-amino-4-methoxy-7-morpholinobenzothiazole 1 (1.3 g, 5 mmol) in 48% HBr (8.9 m, 50 mL, 445 mmol, good quality: colorless to slightly yellowish) was stirred at 130 °C for 24 h. The resulting suspension was cooled to ambient temperature and left to stand overnight at 5 °C. The grey–brown solid was then collected by filtration and taken up into water (50–60 mL). Under efficient stirring, the mixture was titrated with 10 N aqueous sodium hydroxide until a precipitate started to form, followed by saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate until the pH reached 8–9. The resulting suspension was diluted with water (50 mL), stirred for 10 min at ambient temperature and left to stand at 5 °C for one hour. The product was collected by filtration, washed with water and dried in an oven at 100 °C to afford the title compound (1.15 g, 85%) as a tan solid (TLC: ethyl acetate/MeOH/AcOH, 98/2/0.2, Rf 0.69; ethyl acetate/hexane/AcOH, 80/20/0.2, Rf 0.57), mp 267 °C (dec.). The product was soluble in 0.5 N NaOH.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.90 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.72 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 6.55 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H6), 6.61 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H5), 7.23 (sbr, 2H, NH2), 8.89 (s, 1H, OH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 51.8 (CNC), 67.1 (COC), 111.3 (C5), 112.1 (C6), 126.2 (C7a), 138.8 (C3a), 142.3 (C7), 144.5 (C4), 165.1 (C2). Anal. calcd for C11H13N3O2S: C, 52.57; H, 5.21; N, 16.72; found: C, 52.55; H, 5.17; N, 16.74. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 252.0801; found: 252.0796.
3.2.2. Preparation of (E)-N′-(4-Hydroxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylformamidine (3)
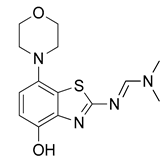
N,N-Dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (160 µL, 1.2 mmol) was added to a solution of 2 (251 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (7 mL) and the mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 30 min (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane/AcOH, 80/20/0.2, Rfsm 0.56, Rfp 0.25–0.39 extended spot). The reaction mixture was cooled to ambient temperature, poured into ice/half-saturated brine (50:50, 100 mL) and stirred for 10 min. Crystallization was induced by scratching with a glass rod and the mixture was left to stand at 5 °C overnight. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 100 °C to afford the title compound (280 mg, 91%) as off-white crystals, mp 244 °C (dec.).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.94 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.02 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 3.16 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 3.73 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 6.56 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H6), 6.69 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H5), 8.38 (s, 1H, N-CH), 9.27 (s, 1H, OH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 35.1 (N-CH3), 40.8 (N-CH3), 51.8 (CNC), 67.1 (COC), 111.7 (C5), 112.9 (C6), 127.6 (C7a), 138.8 (C3a), 141.8 (C7), 146.0 (C4), 158.1 (N-CH), 170.7 (C2). Anal. calcd for C14H18N4O2S: C, 54.88; H, 5.92; N, 18.29; found: C, 54.86; H, 5.89; N, 18.31. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 307.1223; found: 307.1220.
3.2.3. Preparation of (E)-N′-(4-Benzyloxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylformamidine (4)
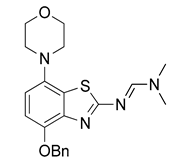
Cs2CO3 (489 mg, 1.5 mmol) was added, followed by benzyl bromide (155 µL, 1.3 mmol), under argon to a stirred solution of 3 (306 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (5 mL). The dark solution was stirred for 2 h at ambient temperature (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane/AcOH, 80/20/0.2, Rfsm 0.25–0.39, Rfp 0.54), poured into ice/half-saturated brine (50:50, 100 mL), stirred for 10 min and cooled to 5 °C for 1 h. The resulting gelatinous precipitate was collected by filtration (40 mm diam. filter funnel!) and dried at 100 °C to afford the title compound (290 mg, 73%) as a dark solid. Recrystallization from 2-propanol (25 mL/g, some dark insoluble material remained) furnished the product as chocolate-colored brown crystals, mp 272 °C (dec.).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.98 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.03 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 3.17 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 3.74 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 5.22 (s, 2H, C6H5-CH2), 6.74 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H6), 6.91 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H5), 7.30–7.36 (m, 1H, C6H5-H4), 7.43–7.37 (m, 2H, C6H5-H3), 7.46–7.51 (m, 2H, C6H5-H2), 8.40 (s, 1H, N-CH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 35.1 (N-CH3), 40.8 (N-CH3), 51.6 (CNC), 67.0 (COC), 70.9 (C6H5-CH2), 110.8 (C5), 112.2 (C6), 127.9 (C7a), 128.2 (C6H5-C2,4,6), 128.8 (C6H5-C3,5), 138.0 (C6H5-C1), 140.6 (C3a), 143.1 (C7), 147.0 (C4), 157.9 (N-CH), 171.8 (C2). Anal. calcd for C21H24N4O2S: C, 63.61; H, 6.10; N, 14.13; found: C, 63.60; H, 6.06; N, 14.11. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 397.1693; found: 397.1689.
3.2.4. Preparation of 4-Benzyloxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-amine (5)
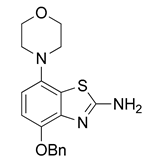
2 N aqueous KOH (2 mL, 4 mmol) was added to a well-stirred suspension of 4 (396 mg, 1 mmol) in MeOH (8 mL) and the suspension was stirred at 80 °C for 1 h (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane/AcOH, 80/20/0.2, Rfsm 0.54, Rfp 0.85), after which water (8 mL) was added and the mixture cooled to ambient temperature. The precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 100 °C to afford the title compound (277 mg, 81%) as fawn solid, mp 208 °C (dec.).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 3.04 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.88 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 5.15 (s, 2H, C6H5-CH2), 6.66 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H6), 6.79 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz, H5), 7.29–7.35 (m, 1H, C6H5-H4), 7.36–7.42 (m, 2H, C6H5-H3), 7.43–7.49 (m, 2H, C6H5-H2). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 51.7 (CNC), 67.0 (COC), 70.9 (C6H5-CH2), 109.0 (C5), 111.0 (C6), 126.2 (C7a), 128.1 (C6H5-C2,4,6), 128.8 (C6H5-C3,5), 138.1 (C6H5-C1), 140.6 (C3a), 142.7 (C7), 146.3 (C4), 166.1 (C2). Anal. calcd for C18H19N3O2S: C, 63.32; H, 5.61; N, 12.31; found: C, 63.34; H, 5.62; N, 12.28. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 342.1271; found: 342.1268.
3.2.5. Preparation of Phenyl(4-benzyloxy)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)carbamate (6)
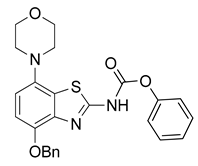
Pyridine (243 µL, 3 mmol) was added to a well-stirred and pre-cooled (0–5 °C, ice bath) suspension of 5 (341 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous THF (7.5 mL). After stirring for 5 min, phenyl chloroformate (144 µL, 1.15 mmol) was slowly added and the mixture was stirred for another 5 min. The ice bath was removed, the reaction mixture was stirred at ambient temperature for 0.5 h (TLC: sample in acetone not MeOH, ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.70, Rfp 0.90) and then diluted with dichloromethane (50 mL) and water (15 mL). The organic layer was separated, washed with aqueous HCl (0.5 N, 50 mL) and brine (50 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. Extraction of the residue with hot ethanol followed by cooling to ambient temperature, filtration and drying at 60 °C afforded the title compound (433 mg, 0.94 mmol, 94%) as porcelain-colored crystals, mp 229 °C (dec.).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 3.00 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.75 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 5.24 (s, 2H, Bn-CH2), 6.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H6), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H5), 7.26–7.54 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 12.70 (sbr, 1H, NH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 158.3 (C2), 51.9 (CNC), 67.0 (COC), 70.7 (Bn-CH2), 110.3 (C5), 113.4 (C6), 127.4 (C7a), 126.6 (Bn-C2,3,4 + Ph-C2,3,4), 136.8 (Bn-C1), 137.6 (Bn-C1), 140.6 (C3a), 145.7 (C7), 147.6 (C4), 153.1 (C=O). Anal. calcd for C25H23N3O4S: C, 65.06; H, 5.02; N, 9.10; found: C, 65.08; H, 5.00; N, 9.08. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 462.1482; found: 462.1480.
3.2.6. Preparation of N-(4-(Benzyloxy)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamide (7) [25]
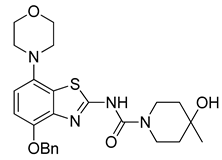
4-Hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine (126 mg, 1.08 mmol) was added to a stirred solution (prepared under argon) of 6 (461 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous DMSO (10 mL) and the clear brown mixture was stirred at 50 °C for 1 h (TLC: sample in acetone not MeOH, do not dry with a heat gun, ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, RfCarbamate 0.90, RfUrea 0.35, RfPhenol 0.98). After cooling to ambient temperature, 50% brine (40 mL) was added and the resulting precipitate was extracted into ethyl acetate (2 × 50 mL). The organic phase was washed with 10% citric acid (50 mL), saturated aqueous Na2CO3 (50 mL), water and brine and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Concentration under reduced pressure produced a solid that was treated with boiling ethanol (ca. 7 mL) and cooled overnight. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 60 °C to afford the title compound (400 mg, 83%) as beige crystals, mp 210 °C.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.14 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.35–1.53 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 3.00 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.19–3.32 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2), 3.76 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.79–3.90 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pipc6H2), 4.42 (sbr, 1H, OH), 5.17 (s, 2H, Bn-CH2), 6.78 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H6), 6.96 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H5), 7.30–7.55 (m, 5H, C6H5), 12.21 (sbr, 1H, NH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 30.3 (CH3), 38.7 (Pip-C3,5), 40.8 (Pip-C2,6), 51.9 (CNC), 66.5 (Pip-C4), 67.1 (COC), 70.7 (Bn-CH2), 109.7 (C5), 112.4 (C6), 127.4 (C7a), 128.9, 128.7, 128.4, (Bn-C2,3,4), 137.6 (Bn-C1), 140.4 (C3a), 147.3 (C7), 150.7 (C4), 153.7 (C=O), 160.4 (C2). Anal. calcd for C25H30N4O4S: C, 62.22; H, 6.27; N, 11.61; found: C, 62.20; H, 6.23; N, 11.56. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 483.2061; found: 483.2055.
3.2.7. Preparation of 4-Hydroxy-N-(4-hydroxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamide (8) [34]
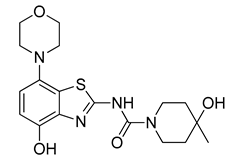
Ammonium formate (380 mg, 6 mmol) followed by 10% Pd/C (300 mg, 0.3 mmol) were added to a stirred solution of 7 (482 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (5 mL). The flask was sealed with a bubble counter and immersed in a pre-heated (55 °C) oil bath. The reaction mixture was stirred at 55 °C for ten min (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.42, Rfp 0.08–0.2, extended spot), cooled to ambient temperature and filtered through a layer of Quartz/Celite (prewetted with DMF). The filter cake was washed with DMF, the combined filtrate and washings were poured into ice/half-saturated brine (50:50, 50 mL) and the resulting mixture was stirred for 10 min. Crystallization was induced by scratching with a glass rod and the mixture was cooled to 5 °C overnight. The solid was collected by filtration, washed with MeOH and dried at 50 °C to afford the title compound (290 mg, 74%) as a light grey solid. For further purification, the solid was dissolved in a minimum amount of hot DMF and the same volume of water was added. The nearly colorless precipitate formed upon cooling was collected by filtration and treated with boiling MeOH. After cooling to ambient temperature, the solid was collected by filtration, washed with MeOH and dried at 50 °C, mp 265 °C (dec.).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.15 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.57–1.33 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 2.96 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.19–3.32 (mobsc, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2), 3.76 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.80–3.96 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pipc6H2), 4.39 (sbr, 1H, OH), 6.66–6.76 (m, 2H, H5, H6), 9.37 (sbr, 1H, OH), 11.16 (sbr, 1H, NH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 30.2 (CH3). 38.6 (Pip-C3,5), 40.8 (Pip-C2,6), 51.8 (CNC), 66.5 (Pip-C4), 67.0 (COC), 109.5 (C5), 112.2 (C6), 127.1 (C7a), 140.3 (C3a), 140.5 (C7), 147.1 (C4), 153.6 (C=O), 160.7 (C2). Anal. calcd for C18H24N4O4S: C, 55.08; H, 6.16; N, 14.28; found: C, 54.99; H, 6.11; N, 14.31. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 393.1591; found: 393.1588.
3.2.8. Preparation of Tetrabutylammonium 2-(4-Hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamido)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-4-olate (8a) (According to a Modification of the Procedure in [27])
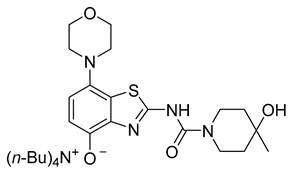
Tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (1 m solution in MeOH, 100 µL, 100 µmol, 1 equiv) was added dropwise to a vortexed suspension of 8 (47 mg, 120 µmol, 1.2 equiv) in MeOH (2.4 mL, 20 µL/µmol 8, c = 0.05 m). The mixture was vortexed for 1 min and then centrifuged at 20,000 rpm for 1 min to remove unreacted 8. The clear yellow supernatant was recovered with a pipette and MeOH evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was dried using careful heating (<40 °C) under reduced pressure to afford the title compound (58 mg, 92% yield based on TBAOH) as a greenish semi-solid.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 0.90 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 12H, TBAC4H3), 1.21–1.30 (m, 11H, TBAC3H2 + CH3), 1.34–1.42 (m, 8H, TBAC2H2), 1.57 (t, J = 5.5 Hz, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 3.08 (sbr, 4H, CH2NCH2), 2.87–2.91 (m, 8H, TBAC1H2), 3.46–3.50 (m, 3H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2 + OH), 3.82 (t, 4H, J = 4.3 Hz, CH2OCH2), 4.05 (sbr, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pipc6H2), 6.38 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H, H6), 6.88 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H, H5). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.7 (TBAC4), 19.5 (TBAC3), 23.8 (TBAC2),29.6 (CH3), 39.1 (Pip-C3,5), 40.1 (Pip-C2,6), 51.5 (CNC), 58.3 (TBAC1), 67.6 (COC), 68.7 (Pip-C4), 109.6 (C6), 111.9 (C5), 124.7 (C7a), 137.8 (C3a), 139.5 (C7), 142.2 (C4), 162.3 (C=O), 170.8 (C2). C34H59N5O4S, 633.92 g/mol. MS not possible due to decomposition.
3.2.9. Preparation of (N-(4-(Benzyloxy)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamido)methyl Pivalate (9)
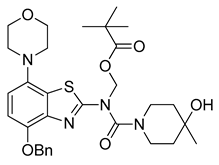
Anhydrous potassium carbonate (207 mg, 1.5 mmol) was added under argon to a stirred solution of 7 (482 mg, 1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (20 mL). The mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 30 min and a solution of chloromethyl pivalate (252 µL, 1.3 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (500 µL) was slowly added. After stirring for another 1 h at 60 °C (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 70/30, RfUrea 0.37, RfPom-urea 0.44), the reaction mixture was cooled to ambient temperature and poured into a combination of ice/water (150 mL). The mixture was stirred for 0.5 h and cooled overnight. The resulting precipitate was collected via filtration and treated with boiling ethyl acetate (± 25 mL). After cooling to ambient temperature, the solid was recovered by filtration and dried at 60 °C to afford the title compound (555 mg, 91%) as colorless crystals, mp >300 °C (ethyl acetate).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.03 (s, 9H, Pom-CH3), 1.13 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.27–1.53 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 2.95 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.12–3.28 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2), 3.76 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.84 + 4.04 (2sbr, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 PipC6H2), 4.36 (sbr, 1H, OH), 5.22 (s, 2H, Bn-CH2), 6.43 (sbr, 2H, Pom-CH2), 6.94 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H6), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H5), 7.30–7.50 (m, 5H, C6H5). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 27.0 (Pom CH3), 30.7 (CH3), 38.7 (Pip-C3,5), 40.9 (Pip-C2,6), 52.0 (CNC), 66.7 (Pip-C4), 67.0 (COC), 70.4 (Bn-CH2), 71.2 (Pom CH2), 112.5 (C5), 114.2 (C6), 122.0 (Bn-C1), 125.6 (C7a), 128.9, 128.5, 127.9, (Bn-C2,3,4), 136.9 (C3a), 141.0 (C7), 142.3 (C4), 160.1 (C=O), 166.2 (C2), 176.9 (Pom C=O). Anal. calcd for C31H40N4O6S: C, 62.39; H, 6.76; N, 9.39; found: C, 62.44; H, 6.69; N, 9.40. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 597.2741; found: 597.2749.
3.2.10. Preparation of (N-(4-(Hydroxy)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamido)methyl Pivalate (10)
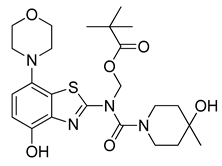
Ammonium formate (315 mg, 5 mmol) was added to a stirred suspension of 9 (291 mg, 0.5 mmol) in MeOH and AcOH (50:50, 5 mL), followed by 10% Pd/C (150 mg). The flask was sealed with a bubble counter and immersed in a pre-heated (55 °C) oil bath. The mixture was stirred at 55 °C for 10 min (evolution of hydrogen gas started after 2 min; TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.51, Rfp 0.41), cooled to ambient temperature and filtered through a layer of Quartz/Celite (prewetted with MeOH). The filter cake was washed with MeOH and the combined filtrate and washings were concentrated under reduced pressure at 40–45 °C to remove most of the MeOH. The remaining solution was poured into a combination of ice/water (50:50, 200 mL) and the resulting mixture was stirred for 10 min and then extracted with dichloromethane (2 × 75 mL). The combined extracts were washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (50 mL) and brine (100 mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Subsequent evaporation of the solvent afforded the analytically pure title compound (187 mg, 74%) as a colorless powder, mp 182 °C.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.11 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 1.14 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.31–1.56 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 2.90 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.17–3.45 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2), 3.74 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.80–4.14 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pipc6H2), 4.35 (sbr, 1H, OH), 6.46 (s, 2H, CH2-Pom), 6.82 (sbr, 2H, H5, H6), 10.18 (sbr, 1H, OH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 27.2 (C(CH3)3), 30.1 (CH3). 38.6 (Pip-C3,5), 40.9 (Pip-C2,6), 52.2 (CNC), 66.7 (Pip-C4), 67.0 (COC), 69.9 (C(CH3)3), 114.4 (C5), 114.7 (C6), 122.2 (C7a), 124.2 (C3a), 139.4 (C7), 141.1 (C4), 160.2 (C=O), 166.2 (C2), 177.2 (Pom C=O). Anal. calcd for C24H34N4O6S: C, 56.90; H, 6.76; N, 11.06; found: C, 56.86; H, 6.72; N, 10.94. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 507.2272; found: 507.2270.
3.2.11. Preparation of 2-(4-Hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carboxamido)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-4-yl Pivalate (10a)
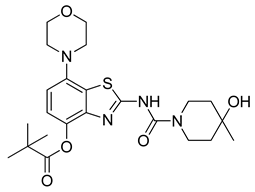
Ammonium formate (315 mg, 5 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of 9 (291 mg, 0.5 mmol) in DMF (5 mL), followed by 10% Pd/C (150 mg). The flask was sealed with a bubble counter and immersed in a pre-heated (55 °C) oil bath. The mixture was stirred at 55 °C for 10 min (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.51, Rfp 0.41), cooled to ambient temperature and filtered through a layer of Quartz/Celite (prewetted with DMF). The filter cake was washed with DMF, and the combined filtrate and washings were poured into a combination of ice/water (50:50, 200 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred for 10 min and then extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 75 mL). The combined extracts were washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (50 mL) and brine (100 mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Subsequent evaporation of the solvent furnished a solid, which was recrystallized from 80% aqueous MeOH to afford the analytically pure title compound (187 mg, 74%) as a light grey solid, mp 246 °C.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.16 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.37 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 1.40–1.58 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 3.08 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.21–3.36 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pipc6H2), 3.79 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.76–3.91 (m, 2H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2), 4.40 (sbr, 1H, OH), 6.83 (d, 2H, H6), 6.99 (d, 2H, H5), 10.93 (s, 1H, NH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 27.4 (C(CH3)3), 30.1 (CH3). 38.5 (Pip-C3,5), 39.0 (C(CH3)3), 40.9 (Pip-C2,6), 51.5 (CNC), 66.3 (Pip-C4), 66.8 (COC), 111.8 (C6), 119.6 (C5), 130.5 (C7a), 141.9 (C3a), 144.3 (C7), 146.3 (C4), 150.9 (C=O), 160.3 (C2), 177.3 (Piv C=O). Anal. calcd for C23H32N4O5S: C, 57.96; H, 6.77; N, 11.76; found: C, 57.93; H, 6.79; N, 11.77. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 477.2166; found: 477.2158.
3.2.12. Preparation of tert-Butyl (4-(benzyloxy)-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)(4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carbonyl)carbamate (11)
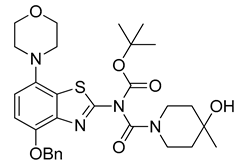
Triethylamine (210 µL, 3 equiv) and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (218 mg, 1 mmol, 2 equiv) were added to a well-stirred suspension of 7 (241 mg, 0.5 mmol, 1 equiv) in anhydrous THF (6 mL). 4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine (61 mg, 0.5 mmol, 0.5 equiv) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 10 min (TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.35, Rfp 0.76), during which the color of the solution changed to orange and then yellow. The reaction was quenched by addition of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (10 mL), and the resulting mixture was extracted with dichloromethane (2 × 40 mL). The combined extracts were washed with 1% aqueous HCl (50 mL), water (50 mL) and brine (50 mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Subsequent evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure afforded the title compound (260 mg, 89%) as off-white crystals, mp 91 °C.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.06 (sbr, 3H, CH3), 1.43–1.63 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 1.52 (s, 9H, Boc-CH3), 3.03 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.25–3.44 (m, 3H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2 + 0.5 Pip-C2/6H2), 3.78 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 3.84 + 4.04 (sbr, 1H, 0.5 Pip- C2/6H2), 4.51 (sbr, 1H, OH), 5.26 (s, 2H, Bn-CH2), 6.94 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H6), 7.03 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H5), 7.28–7.50 (m, 5H, C6H5). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 28.0 (Boc CH3), 30.2 (CH3), 51.9 (CNC), 66.0 (Pip-C4), 67.0 (COC), 71.3 (Bn-CH2), 85.1 (Boc C), 114.1 (C5/6), 122.0 (Bn-C1), 125.6 (C7a), 127.8, 128.2, 128.8, (Bn-C2,3,4), 137.8 (C4a), 140.8 (C7), 147.6 (C4), 149.0 (C2), 150.3 (Boc C=O), 156.3 (Pip C=O)(signals for the piperidine methylene carbons are missing). Anal. calcd for C30H38N4O6S: C, 61.84; H, 6.57; N, 9.61; found: C, 61.79; H, 6.61; N, 9.57. HRMS m/z: [M + H]+ calcd: 583.2585; found: 583.2583.
3.2.13. Preparation of tert-Butyl (4-hydroxy-4-methylpiperidine-1-carbonyl)(4-hydroxy-7-morpholinobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)carbamate (12)
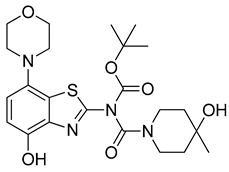
Ammonium formate (126 mg, 2 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of 11 (116 mg, 0.2 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (4 mL), followed by 10% Pd/C (50 mg). The flask was sealed with a bubble counter and immersed in a pre-heated (55 °C) oil bath. The mixture was stirred at 55 °C for 20 min (rapid evolution of hydrogen gas started after 2 min; TLC: ethyl acetate/hexane, 80/20, Rfs.m. 0.76, Rfp 0.51), cooled to ambient temperature and filtered through a layer of Quartz/Celite (prewetted with DMF). The filter cake was washed with DMF, and the combined filtrate and washings were poured into ice/half-saturated brine (50:50, 50 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred for 10 min and then extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 30 mL). The combined extracts were washed with brine and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Evaporation of the solvent afforded a semi-solid residue, which was crystallized by co-evaporation with methyl tert-butyl ether to obtain the crude product as slightly yellow crystals. Further purification by flash chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane, 50/50) afforded the title compound (97 mg, 98%) as colorless crystals, mp 259 °C (dec).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.16 (sbr, 3H, CH3), 1.42–1.69 (m, 4H, Pip-C3H2 + Pip-C5H2), 1.53 (s, 9H, Boc-CH3), 2.97 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2NCH2), 3.25–3.44 (mobsc., 3H, 0.5 Pip-C2H2 + 0.5 Pip-C6H2 + 0.5 Pip-C2/6H2), 3.77 (t, 4H, J = 4.5 Hz, CH2OCH2), 4.01 (sbr, 1H, 0.5 Pip- C2/6H2), 4.55 (sbr, 1H, OH), 6.80 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H6), 6.85 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, H5), 9.55 (s, 1H, OH). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 28.1 (Boc CH3), 30.4 (CH3), 37.9 (Pip-CH2), 38.3 (Pip-CH2), 43.4(Pip-CH2), 52.1 (CNC), 66.2 (Pip-C4), 67.1 (COC), 84.9 (Boc C), 112.3 (C6), 114.6 (C5), 128.2 (C7a), 138.8 (C4a), 138.9 (C7), 146.8 (C4), 149.1 (C2), 150.4 (Boc C=O), 156.4 (Pip C=O).
3.3. Radiochemistry
3.3.1. General Radiochemistry
[11C]CO2 (20–25 GBq) was produced via the 14N(p,α)11C nuclear reaction by irradiating (30–35 µA for 25–40 min) 99.5%mol N2 doped with 0.5%mol O2 in a GE PETtraceTM 800 cyclotron (GE Healthcare GmbH, Munich, Germany). Production of [11C]MeI was performed on a custom-built synthesizer as reported previously [35]. Briefly, [11C]CO2 was reduced to [11C]MeOH using 1 m LiAlH4 in THF (ABX, Radeberg, Germany) and the THF was removed at 100 °C in a stream of helium. After the addition of 4.3 m H3PO4, the [11C]MeOH was distilled off at 150 °C and passed through a pre-heated (170 °C) column with alumina-supported triphenylphosphine diiodide. The resulting [11C]MeI was passed through a second column with phosphorus pentoxide and collected in a reaction vial containing the labelling precursor (8,10 or 12) and the corresponding solvent pre-cooled to −10 °C (DMF, DMA) or 20 °C (DMSO), respectively. [11C]Methyl triflate ([11C]MeOTf) was prepared on a Synthra MeIplus system (Synthra GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) using the process and chemicals specified by the manufacturer. Briefly, [11C]CO2 produced as described above was converted to [11C]methane over nickel at 400 °C, followed by conversion to [11C]MeI by I2 in the gas phase at 700 °C in a continuous flow process where [11C]MeI was trapped on a Porapak Q column. Conversion to [11C]MeOTf was achieved via reaction with silver triflate at 190 °C. [11C]MeOTf was collected in a reaction vial containing precursor 8a and solvent (acetone or acetonitrile) pre-cooled to −10 °C. The syntheses were performed in a helium atmosphere.
3.3.2. Manual Screening Reactions for the Preparation of [11C]tozadenant
Manual methylation reactions with [11C]MeI were performed under air in 2 mL Eppendorf safe lock tubes. The vials were heated in thermoshakers with gentle agitation. The tubes were charged (in this order) with precursor 12 (1 mg, 2 µmol), the corresponding solvent (300 µL), 1 m aqueous NaOH (4 µmol) and a stock solution of [11C]MeI (5–10 MBq) in DMSO. The reaction mixture was heated at 60 °C for 5 min and cooled to 0 °C before the addition of HCl (37%, 150 µL). The mixture was then heated for another 5 min at 100 °C, cooled to 0 °C and diluted with 1 m ammonium formate (1.5 mL). The resulting crude product solution was spiked with the reference compound to identify the desired product and analyzed by analytical radio HPLC.
3.3.3. Analytical HPLC
Samples prepared in manual radiolabeling experiments were analyzed on two different analytical HPLC systems (Knauer, Berlin, Germany) using identical analytical columns (MultoKrom® 100-5 C18 250 × 4.6 mm) and solvents (0–10 min: 32.5% MeCNaq + 0.2% HCOOH, 10–15 min: 80% MeCNaq + 0.2% HCOOH; flow rate: 1.5 mL/min). Each system was equipped with a UV-Detector coupled in series with a LB 500 NaI radioactivity detector (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wilbach, Germany). Since HPLC analysis with post-column injection demonstrated near-quantitative recovery of radioactivity from the column, RCCs were calculated based on the summed integral of all peaks [36]. To account for variable signal strengths and slight differences in the retention time between the systems/columns (ca. 6%), all chromatograms were normalized to the highest peak and the time scale was adjusted with an appropriate correction factor.
3.3.4. Automated Production of [11C]tozadenant ([11C]13)
1 N aqueous NaOH (4 µL, 4 µmol) was added to a solution of precursor 12 (1 mg, 2 µmol) in anhydrous DMA (300 µL) and the resulting slightly yellow solution was transferred into a reactor. The reactor was cooled to -10 °C to trap [11C]MeI and then heated to 60 °C for 5 min. After the addition of concentrated aqueous HCl (12 N, 150 µL, 1.8 mmol), the reactor was heated to 100 °C for 5 min to deprotect the radiolabeled intermediate and then cooled to 30 °C. A total of 2 m aqueous ammonium acetate (700 µL, 1.4 mmol) was added and the crude product solution was purified by semi-preparative HPLC (column: Kromasil 120-5-C18 ace-EPS, 250 × 8 mm; eluent: MeOH/water, 60/40, v/v; flow rate: 4 mL/min; detection: UV at 254 nm, radioactivity). The effluent fraction containing the product was collected, diluted with water for injection (30 mL) and passed through a Strata X 33 C18 cartridge (30 mg, preconditioned with 2 mL ethanol followed by 2 mL sterile water). The cartridge was washed with sterile water (5 mL) and the product was eluted with ethanol (500 µL) and diluted with sterile water (4.5 mL). Filtration through a sterile filter into a sterile vial produced an injectable sterile solution of [11C]tozadenant ([11C]13) containing 10% ethanol in volume, which was used for biological experiments.
3.3.5. Quality Control
QMP compliant quality control of the final tracer formulation was performed based on the following methods and systems. Radio-HPLC: Chromaster HPLC system (Hitachi, Düsseldorf, Germany) coupled in series with an fLumo luminescence detector (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wilbach, Germany), conditions: Kromasil® 100-5-C18 250 × 4.6 mm, 60% MeOH, 1.0 mL/min. Gas chromatography (GC): Intuvo 9000 GC system (Agilent, Ratingen, Germany), conditions: Agilent DB-624 Ultra Inert 30 m × 0.25 mm × 1.4 µm GC column, helium flow: 0–4 min: 2 mL/min, 4–8.5 min: 5 mL/min; temperature: 0–3.5 min: 40 °C, 4.5–8.5 min: 100 °C. Appearance was confirmed visually while pH was determined with pH indicator strips.
3.4. In Vitro Autoradiography
Cryostat sections (20 µm) of rat and pig brains were cut at −18 °C, thaw-mounted onto microscope slides, air-dried, and stored at −80 °C until use. For autoradiography, the cryosections were dried at 37 °C, pre-incubated in 50 mm TRIS (pH 7.4, 1 mm EDTA) for 5 min at ambient temperature, and then incubated with 12 kBq/mL [11C]tozadenant (0.24 nM) in the same buffer supplemented with 100 µm guanosine-5′-[(β,γ)-imido]triphosphate (GppNHp) for 30 min at ambient temperature. Non-specific binding was determined in the presence of 1 µm ZM241385. After the incubation, the sections were dipped twice in ice-cold deionized water, rapidly dried in a stream of cold air and exposed on an imaging plate for 1 h. The imaging plate was analyzed with a phosphor imager (BAS 5000, Fujifilm, Düsseldorf, Germany) and tracer binding was quantified via 2D densitometry (AIDA Image Analysis software V5.1). Specific binding was calculated as the difference between total and non-specific binding (4 slices each).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we synthesized N-Boc protected O-desmethyltozadenant (12) as a suitable precursor for the preparation of [11C]tozadenant by methylation with [11C]MeI, which affords this radioligand in radiochemical yields, molar activities and (radio)chemical purities sufficient for preclinical in vivo studies. In addition, in vitro autoradiography in pig and rat brain slices confirmed A2AR-specific binding of [11C]tozadenant. In vivo biodistribution studies using PET imaging in healthy rats to determine the cerebral pharmacokinetics and in vivo brain distribution of [11C]tozadenant are currently ongoing.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29051089/s1, 1H-, 13C- and 19F-NMR spectra of prepared compounds; HPLC and GC chromatograms of [11C]tozadenant (Figures S1–S3).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., D.S., M.H., D.B. and B.N.; Methodology, S.H., D.S., M.H. and D.B.; Validation, F.N.; Formal Analysis, D.S. and D.B.; Investigation, S.H., D.S., M.L., A.S., M.H. and D.B.; Resources, B.N.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, S.H., D.S., M.H. and D.B.; Writing—Review and Editing, S.H., D.S., F.N., M.H., D.B. and B.N.; Visualization, S.H., D.S., M.H. and D.B.; Supervision, S.H. and B.N.; Project Administration, B.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures involving animals were performed in accordance with established guidelines for the ethical treatment of animals in research, including adherence to the German Animal Welfare Act (TierSchG) and the Directive 2010/63/EU for the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Since the use of tissues from laboratory animals sacrificed for scientific purposes is not an animal experiment according to §7 Abs. 2 Satz 3 TierSchG, no formal ethical review or approval was required for the in vitro autoradiography experiments performed in this study. The respective animal welfare officer at Forschungszentrum Jülich was informed about the sacrifice of the animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article and supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and Classification of Adenosine Receptors—An Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porkka-Heiskanen, T. Adenosine in Sleep and Wakefulness. Ann. Med. 1999, 31, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F. Adenosine Receptor Control of Cognition in Normal and Disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 119, 257–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mori, A. How Do Adenosine A2A Receptors Regulate Motor Function? Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80, S13–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R.; Stehle, J.H.; Rivkees, S.A. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Rat A1-Adenosine Receptor That Is Widely Expressed in Brain and Spinal Cord. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.K.; Gubitz, A.K.; Sirinathsinghji, D.J.S.; Richardson, P.J.; Freeman, T.C. Tissue Distribution of Adenosine Receptor MRNAs in the Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 118, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mir, M.I.; Probst, A.; Palacios, J.M. Adenosine A2 Receptors: Selective Localization in the Human Basal Ganglia and Alterations with Disease. Neuroscience 1991, 42, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Zhou, X.; Khanapur, S.; Tsukada, H.; Ishiwata, K.; Luurtsema, G.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Elsinga, P.H. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Adenosine A2A Receptor Ligands and Opportunities for A2A Receptor Imaging. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 5–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorimaa, A.; Rissanen, E.; Airas, L. In Vivo PET Imaging of Adenosine 2A Receptors in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disease. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2017, 2017, 6975841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, M.R.; Ferrante, A.; Martire, A.; Chiodi, V.; Pepponi, R.; Tebano, M.T.; Popoli, P. Adenosine A2A Receptor as Potential Therapeutic Target in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.; Komoszyński, M.; Wojtczak, A. Adenosine A2A Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease Treatment. Purinergic Signal. 2008, 4, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A.; Olanow, C.W.; Kieburtz, K.D.; Pourcher, E.; Docu-Axelerad, A.; Lew, M.; Kozyolkin, O.; Neale, A.; Resburg, C.; Meya, U.; et al. Tozadenant (SYN115) in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Who Have Motor Fluctuations on Levodopa: A Phase 2b, Double-Blind, Randomised Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Aradi, S.D.; Hauser, R.A.; Rascol, O. The Challenge of Developing Adenosine A2A Antagonists for Parkinson Disease: Istradefylline, Preladenant, and Tozadenant. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80, S54–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renk, D.R.; Skraban, M.; Bier, D.; Schulze, A.; Wabbals, E.; Wedekind, F.; Neumaier, F.; Neumaier, B.; Holschbach, M. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Tozadenant Analogues as Adenosine A2A Receptor Ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 214, 113214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.; Downey, P.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Scheller, D. Unprecedented Therapeutic Potential with a Combination of A2A/NR2B Receptor Antagonists as Observed in the 6-OHDA Lesioned Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancel, V.; Mathy, F.-X.; Boulanger, P.; English, S.; Croft, M.; Kenney, C.; Knott, T.; Stockis, A.; Bani, M. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of [14C]-Tozadenant (SYN-115), a Novel A2a Receptor Antagonist Ligand, in Healthy Volunteers. Xenobiotica 2017, 47, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.I.; Park, M.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; Byeon, J.-J.; Park, Y.; Kim, N.; Choi, J.; Shin, Y.G. Quantitative Analysis of Tozadenant Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometric Method in Rat Plasma and Its Human Pharmacokinetics Prediction Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Molecules 2019, 24, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrinmayeh, H.; Territo, P.R. Purinergic Receptors of the Central Nervous System: Biology, PET Ligands, and Their Applications. Mol. Imaging 2020, 19, 153601212092760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.-D.; Stiles, G.L.; van Galen, P.J.M.; Jacobson, K.A. Characterization of Human Striatal A2-Adenosine Receptors Using Radioligand Binding and Photoaffinity Labeling. J. Recept. Res. 1992, 12, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasanz, J.L.; Rodríguez, A.; Ferrer, I.; Martín, M. Adenosine A2A Receptors Are Up-regulated in Pick’s Disease Frontal Cortex. Brain Pathol. 2006, 16, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Bittner, G.C.; Ricq, E.L.; Hooker, J.M. A Philosophy for CNS Radiotracer Design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.H.; Toussaint, M.; Teodoro, R.; Dukić-Stefanović, S.; Kranz, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Moldovan, R.-P.; Brust, P. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, F.; Lang, M.; Humpert, S.; Schneider, D.; Drechsel, A.; Klein, S.; Mottaghy, F.; Tolba, R.; Neumaier, B.; Drzezga, A.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of 18F-Labeled Tozadenant Analogs as Potential PET Tracers for Cerebral A2A Adenosine Receptors. In Proceedings of the World Molecular Imaging Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 5–9 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Merighi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Travagli, A.; Nigro, M.; Pasquini, S.; Suresh, R.R.; Kim, S.W.; Volkow, N.D.; et al. Pathophysiological Role and Medicinal Chemistry of A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavonekham, B. A Practical Synthesis of Ureas from Phenyl Carbamates. Synthesis 1997, 1997, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Spatola, A.F. An Advantageous Method for the Rapid Removal of Hydrogenolysable Protecting Groups under Ambient Conditions; Synthesis of Leucine-Enkephalin. Synthesis 1980, 1980, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.J.; Breugst, M.; Hampel, N.; Ofial, A.R.; Mayr, H. Ambident Reactivity of Phenolate Anions Revisited: A Quantitative Approach to Phenolate Reactivities. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 8837–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, M.; Schüller, M. An On-Line Method for the Preparation of n.c.a. [11CH3]Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid Methyl Ester. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1993, 44, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.; Leonard, N.J. Synthesis of 3-(2′-Deoxy-D-Erythro-Pentofuranosyl)Adenine. Application of a New Protecting Group, Pivaloyloxymethyl(Pom). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 5439–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolná, Z.; Červený, L. Ammonium Formate Decomposition Using Palladium Catalyst. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2000, 26, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Sorrentino, J.; Diller, E.J.; Chapman, D.; Woydziak, Z.R. General Method for Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution of Aryl Fluorides and Chlorides with Dimethylamine Using Hydroxide-Assisted Decomposition of N,N-Dimethylforamide. Synth. Commun. 2016, 46, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündel, D.; Toussaint, M.; Lai, T.H.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Cumming, P.; Schröder, S.; Teodoro, R.; Moldovan, R.-P.; Pan-Montojo, F.; Sattler, B.; et al. Quantitation of the A2A Adenosine Receptor Density in the Striatum of Mice and Pigs with [18F]FLUDA by Positron Emission Tomography. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 6th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, MA, USA; Elsevier Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780080878249. [Google Scholar]
- Anwer, M.K.; Spatola, A.F. A Rapid Non-Acidolytic Method for Deprotection and Removal of Peptides from Solid Phase Resins—Applications of Ammonium Formate Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 4369–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, M.; Schüller, M. A New and Simple On-Line Method for the Preparation of n.c.a. [11C]Methyl Iodide. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1993, 44, 779–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpert, S.; Hoffmann, C.; Neumaier, F.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Neumaier, B. Validation of Analytical HPLC with Post-Column Injection as a Method for Rapid and Precise Quantification of Radiochemical Yields. J. Chromatogr. B 2023, 1228, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).