Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules
Abstract
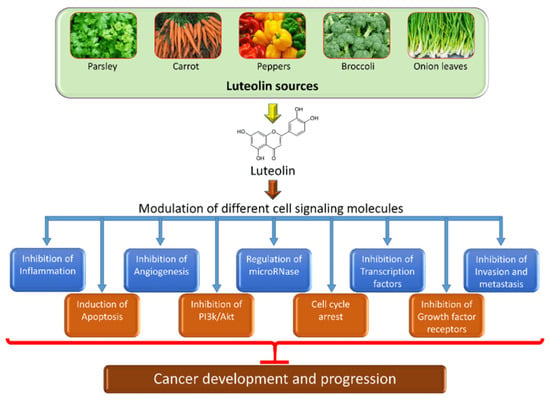
:1. Introduction
2. Chemical Structure and Sources of Luteolin
3. The Role of Luteolin in Cancer Prevention through Modulation of Cell Signaling Pathways
3.1. Inflammation
3.2. Angiogenesis
3.3. Apoptosis
3.4. Autophagy
3.5. Cell Cycle
3.6. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)
3.7. PI3K/Akt Pathway
3.8. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
3.9. Telomerase
3.10. Activator Protein 1 (AP-1)
3.11. Cell and Growth Factors Receptors
- i.
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
- ii.
- Androgen Receptor
- iii.
- Insulin-Like Growth Factors (IGFs)

3.12. Notch Signaling Cascade
3.13. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway
3.14. Invasion and Metastasis
| Signaling Pathways | Cancer Types | Study Types | Mechanism | The Outcome of the Study | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | Colon cancer | In vitro and in vivo | IL-6, interferon-β, TNF-α, and IL-1 β ↓ |
| [23] |
| Angiogenesis | Prostate cancer | Angiogenesis (VEGF) and metalloproteinase (MMP 2,9) ↓ |
| [33] | |
| Apoptosis | Cervix cancer | In vitro | Apaf1, Bax, Bad & Caspases ↑ & Bcl 2 ↓ |
| [42] |
| Colon cancer | In vitro | Bax ↑ and Bcl2 ↓ |
| [43] | |
| Brain cancer | In vitro | Apoptosis induction |
| [44] | |
| Autophagy | Ovarian | In vitro | Suppression of autophagy ↓ |
| [53] |
| Lung cancer | In vitro | LC3 puncta and autophagy flux ↑ |
| [55] | |
| Cell cycle | Colon cancer | In vitro | % of cells in G1 ↓ and G2/M phase ↑ |
| [61] |
| Breast cancer | In vitro | Cell-cycle arrest in S-phase |
| [62] | |
| STAT3 | Gastric cancer | In vitro and in vivo | STAT3 ↓ |
| [68] |
| Skin cancer | In vitro and in vivo | STAT3 ↓ |
| [69] | |
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR | Breast cancer | In vitro | PI3K/AKT/mTOR ↓ |
| [76] |
| Gastric cancer | In vitro | PI3K/AKT ↓ |
| [78] | |
| Skin cancer | In vitro and in vivo | PI3K/AKT ↓ |
| [79] | |
| Wnt signaling | Prostate cancer | In vitro | Wnt ↓ |
| [85] |
| Telomerase | Breast cancer | In vitro | Telomerase ↓ |
| [62] |
| Transcription factors AP-1 | Synovial sarcoma | AP-1 ↓ |
| [93] | |
| Epidermal growth factor receptor | Breast cancer | In vivo and in vitro | EGFR ↓ |
| [97] |
| In vitro | EGFR ↓ |
| [98] | ||
| Notch signaling | Breast cancer | In vitro | Notch ↓ |
| [112] |
| Gastric cancer | In vitro | Notch ↓ |
| [113] | |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) | Gastric cancer | In vitro | MAPK ↓ |
| [78] |
| Colorectal cancer | In vitro | MAPK ↓ |
| [117] |
4. Luteolin Shows the Ability to Target microRNAs (miRs) in Cancer
5. The Anti-Cancer Activity of Luteolin in Comparison with Other Flavonoids/Similar Compounds
6. The Potential Role of Luteolin in Cancer Using Molecular Modeling Techniques
7. Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Nano-Delivery System of Luteolin in Cancer Treatment
8. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Huang, T.; Wu, B.L.; He, W.X.; Liu, D. Stem cells in cancer therapy: Opportunities and challenges. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, T. Herbs Are Often More Toxic Than Magical; Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1984.
- Saxe, T.G. Toxicity of medicinal herbal preparations. Am. Fam. Physician 1987, 35, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecumberri, E.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Miralbell, R.; Pichard, C. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) as adjuvant in cancer therapy. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K.; Goradel, N.H.; Khanlarkhani, N.; Salehi, E.; Nashtaei, M.S.; Najafi, M.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent: Implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5728–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki Dana, P.; Sadoughi, F.; Asemi, Z.; Yousefi, B. The role of polyphenols in overcoming cancer drug resistance: A comprehensive review. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Bi, A.; Dong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Rui, B.; Liu, J.; Yin, Z.; Luo, L. Luteolin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by blocking the activity of heat shock protein 90 in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Megrin, W.A.; Alkhuriji, A.F.; Yousef, A.O.S.; Metwally, D.M.; Habotta, O.A.; Kassab, R.B.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; El-Khadragy, M.F. Antagonistic Efficacy of Luteolin against Lead Acetate Exposure-Associated with Hepatotoxicity is Mediated via Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Activities. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lazaro, M. Distribution and Biological Activities of the Flavonoid Luteolin. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhouser, M.L. Dietary flavonoids and cancer risk: Evidence from human population studies. Nutr. Cancer 2004, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miean, K.H.; Mohamed, S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Xu, Z.; Wu, C.T.; Janes, M.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; No, H.K. Antioxidant activities of different colored sweet bell peppers (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S98–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; Scesa, C.; Aquino, R. Triterpene, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Compounds from Melissa officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Inflammation and oncogenesis: A vicious connection. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2010, 20, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perwez Hussain, S.; Harris, C.C. Inflammation and cancer: An ancient link with novel potentials. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, H.W.; Yang, D.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Tseng, J.K.; Chang, T.J.; Chang, Y.Y. Luteolin inhibits viral-induced inflammatory response in RAW264. 7 cells via suppression of STAT1/3 dependent NF-κB and activation of HO-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelinger, G.; Merfort, I.; Schempp, C.M. Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of luteolin. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. Modulatory effect of luteolin on redox homeostasis and inflammatory cytokines in a mouse model of liver cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4767–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Luo, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Li, W. Luteolin suppressed growth of colon tumor via inflammation, oxidative stress, and NLRP3/IL-1β signal axis. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2022, 18, 494. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, T.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Yan, S. Luteolin relieved DSS-induced colitis in mice via HMGB1-TLR-NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation 2021, 44, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Kim, D.K.; Kang, O.H.; Choi, Y.A.; Park, H.J.; Choi, S.C.; Kim, T.H.; Yun, K.J.; Nah, Y.H.; Lee, Y.M. Inhibitory effect of luteolin on TNF-α-induced IL-8 production in human colon epithelial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2005, 5, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Kareem Azab, A. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElShamy, W.M.; Sinha, A.; Said, N. Aggressiveness niche: Can it be the foster ground for cancer metastasis precursors? Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4829106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A.; Tosetti, F.; Li, V.W.; Noonan, D.M.; Li, W.W. Cancer prevention by targeting angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagli, E.; Stefaniotou, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Ziche, M.; Psillas, K.; Murphy, C.; Fotsis, T. Luteolin inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis; inhibition of endothelial cell survival and proliferation by targeting phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase activity. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7936–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Liao, H.F. Effect of luteolin on apoptosis and vascular endothelial growth factor in human choroidal melanoma cells. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Son, Y.O.; Budhraja, A.; Wang, X.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Hitron, A.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, D.; Divya, S.P.; et al. Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, Y.; Steller, H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 2011, 147, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plati, J.; Bucur, O.; Khosravi-Far, R. Dysregulation of apoptotic signaling in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 1124–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. Tumor resistance to apoptosis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocakavuk, E.; Anderson, K.J.; Varn, F.S.; Johnson, K.C.; Amin, S.B.; Sulman, E.P.; Lolkema, M.P.; Barthel, F.P.; Verhaak, R.G. Radiotherapy is associated with a deletion signature that contributes to poor outcomes in patients with cancer. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, K.S.; Yau, T.H.; Sideris, M. Chemoradiotherapy in cancer treatment: Rationale and clinical applications. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo-and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. MedComm 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, M.M. Cancer prevention–the potential for diet to modulate molecular signalling. Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, O.M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Anticancer potential of plants and natural products. Am. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 1, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, R.; Pramodh, S.; Rais, N.; Haque, S.; Shafarin, J.; Bajbouj, K.; Hamad, M.; Hussain, A. Luteolin inhibits proliferation, triggers apoptosis and modulates Akt/mTOR and MAP kinase pathways in HeLa cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Hyun, Y.J.; Zhen, A.X.; Cho, S.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Hyun, J.W. Luteolin promotes apoptotic cell death via upregulation of Nrf2 expression by DNA demethylase and the interaction of Nrf2 with p53 in human colon cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Wang, R.; Shao, N.; Zhi, F.; Yang, Y. Luteolin suppresses tumor proliferation through inducing apoptosis and autophagy via MAPK activation in glioma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N. Autophagy: Process and function. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N. The pleiotropic role of autophagy: From protein metabolism to bactericide. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. Deconvoluting the context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.; Kimmelman, A.C.; White, E. Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Pietrocola, F.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Cecconi, F.; Codogno, P.; Debnath, J.; Gewirtz, D.A.; Karantza, V.; et al. Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 856–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim, U.M.; Park, S.Y. Luteolin sensitizes human liver cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via autophagy and JNK-mediated death receptor 5 upregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, X.F.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, S.; Fang, F. Effects of luteolin on proliferation and programmed cell death of human multiple myeloma cell RPMI-8226. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2018, 26, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Fang, W.; Chai, D.; Wen, Y.; Chen, H.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Y. Luteolin promotes cell apoptosis by inducing autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 43, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, D.; Hao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y. Luteolin promotes the sensitivity of cisplatin in ovarian cancer by decreasing PRPA1-medicated autophagy. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Xia, H. The flavonoid luteolin enhances doxorubicin-induced autophagy in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 15190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Chi, G.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Hyun, J.W.; Kim, W.J.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and non-canonical autophagy by luteolin in NCI-H460 lung carcinoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozengurt, E. Autocrine loops, signal transduction, and cell cycle abnormalities in the molecular biology of lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 1999, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, H. Marine polysaccharides as a versatile biomass for the construction of nano drug delivery systems. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, T.; Emanuele, M.J. Dissenting degradation: Deubiquitinases in cell cycle and cancer. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 67, pp. 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, H. Alginate/chitosan-based hydrogel loaded with gene vectors to deliver polydeoxyribonucleotide for effective wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5533–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massagué, J. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature 2004, 432, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.Y.; Jeong, Y.; Tyner, A.L.; Park, J.H. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells by the dietary compound luteolin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G66–G75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jin, K.; Lan, H. Luteolin inhibits cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells through downregulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3842–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Ham, S.; Kwon, T.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kang, J.W.; Oh, S.R.; Yoon, D.Y. Luteolin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2014, 33, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S.; Satelli, A.; Moridani, M.; Jenkins, M.; Rao, U.S. Luteolin induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant cancer cells without affecting the drug transporter function: Involvement of cell line-specific apoptotic mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkson, J.; Jove, R. STAT proteins: Novel molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6613–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.E.; Inghirami, G. STAT3, a multifaceted oncogene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10151–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.I.; Grandis, J.R. STAT signaling in head and neck cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Su, Z.; Xu, H.; Niu, M.; Chen, X.; Min, H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, G.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Correction: Luteolin selectively kills STAT3 highly activated gastric cancer cells through enhancing the binding of STAT3 to SHP-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, P.; Niu, X.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Luteolin binds Src, promotes STAT3 protein ubiquitination and exerts anti-melanoma effects in cell and mouse models. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 200, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Dai, S.; Dai, J.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Luteolin decreases invasiveness, deactivates STAT3 signaling, and reverses interleukin-6 induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and matrix metalloproteinase secretion of pancreatic cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Luteolin induces carcinoma cell apoptosis through binding Hsp90 to suppress constitutive activation of STAT3. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Smith, D.L.; Ram, P.T.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Ni, J.; Hao, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Li, Y. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heavey, S.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Gately, K. Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D.; Hess, J.; Freier, K.; Hoffmann, J.; Freudlsperger, C. Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.T.; Liu, Y.E.; Hsu, K.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Chan, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.R. MLL3 induced by luteolin causes apoptosis in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells through H3K4 monomethylation and suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1221–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, T.H.; Wu, L.C.; Wu, C.C. Luteolin attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells by interfering in the PI3K/Akt–NF-κB–Snail pathway. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Aisa, H.A. Luteolin induces apoptosis in vitro through suppressing the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Jiang, W.; Yu, D.; Yan, Z. Luteolin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, H. Luteolin reduces migration of human glioblastoma cell lines via inhibition of the p-IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Weng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ni, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, P.; et al. The lncRNA NEAT1 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression via interacting with DDX5. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Q.; You, A.B.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhang, K.W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.K.; Li, X.L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashokkumar, P.; Sudhandiran, G. Luteolin inhibits cell proliferation during Azoxymethane-induced experimental colon carcinogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Investig. New Drugs 2011, 29, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Lang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Beuerman, R.W.; Zhou, L.; Min, D. Luteolin attenuates Wnt signaling via upregulation of FZD6 to suppress prostate cancer stemness revealed by comparative proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canela, A.; Vera, E.; Klatt, P.; Blasco, M.A. High-throughput telomere length quantification by FISH and its application to human population studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5300–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, W.E.; Tesmer, V.M.; Huffman, K.E.; Levene, S.D.; Shay, J.W. Normal human chromosomes have long G-rich telomeric overhangs at one end. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, W.; de Lange, T. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W.; Bacchetti, S. A survey of telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulian, E.; Karin, M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E131–E136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1, a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.M.; Lee, Y.S. Luteolin suppresses IL-1β-induced cytokines and MMPs production via p38 MAPK, JNK, NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation in human synovial sarcoma cell line, SW982. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2607–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kang, J.W.; Song, H.H.; Oh, S.R.; Yoon, D.Y. Luteolin 8-C-β-fucopyranoside inhibits invasion and suppresses TPA-induced MMP-9 and IL-8 via ERK/AP-1 and ERK/NF-κB signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, J. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a008912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtiegman, K.; Kochupurakkal, B.S.; Zwang, Y.; Pines, G.; Starr, A.; Vexler, A.; Citri, A.; Katz, M.; Lavi, S.; Ben-Basat, Y.; et al. Defective ubiquitinylation of EGFR mutants of lung cancer confers prolonged signaling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6968–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Sung, M.K. Luteolin exerts anti-tumor activity through the suppression of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated pathway in MDA-MB-231 ER-negative breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.Q.; Xie, K.P.; Xie, M.J. Inhibitory effect of luteolin on the proliferation of human breast cancer cell lines induced by epidermal growth factor. Sheng Li Xue Bao/Acta Physiol. Sin. 2016, 68, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.H.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.L. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemn, E.G.; Coleman, I.M.; Lucas, J.M.; Coleman, R.T.; Hernandez-Lopez, S.; Tharakan, R.; Bianchi-Frias, D.; Dumpit, R.F.; Kaipainen, A.; Corella, A.N.; et al. Androgen Receptor Pathway-Independent Prostate Cancer Is Sustained through FGF Signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, K.H.; Chung, L.C.; Feng, T.H.; Chang, P.L.; Juang, H.H. Upregulation of prostate-derived Ets factor by luteolin causes inhibition of cell proliferation and cell invasion in prostate carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2812–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.E.; Chen, H.F.; Hsu, K.W.; Lin, S.H.; Peng, K.Y.; Lin, K.J.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chen, D.R. Luteolin suppresses androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by epigenetic regulation of MMP9 expression via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 81, 153437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, F.L.; Lin, J.K. Downregulation of androgen receptor expression by luteolin causes inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells and xenografts. Prostate 2008, 68, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baserga, R.; Hongo, A.; Rubini, M.; Prisco, M.; Valentinis, B. The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1332, F105–F126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, J.; Nho, C.W.; Lee, K.W.; Park, J.H. Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.M.; Xie, K.P.; Huo, H.N.; Shang, F.; Zou, W.; Xie, M.J. Luteolin inhibits proliferation induced by IGF-1 pathway dependent ERα in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, X.L.; Jiang, B.H. Luteolin inhibits insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Weaver, K.L.; Capobianco, A.J. Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything but not all the time. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wu, H.; Han, N.; Xu, H.; Chu, Q.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K. Notch signaling and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer: Biological significance and therapeutic application. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedijk, M.; Odorcic, S.; Chang, L.; Zhang, H.; Miller, N.; McCready, D.R.; Lockwood, G.; Egan, S.E. High-level coexpression of JAG1 and NOTCH1 is observed in human breast cancer and is associated with poor overall survival. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8530–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Okuda, H.; Watabe, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Pai, S.K.; Liu, W.; Pandey, P.R.; Fukuda, K.; Hirota, S.; Sugai, T.; et al. Hypoxia-induced Jagged2 promotes breast cancer metastasis and self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4075–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.W.; Zhang, H.D.; Mao, L.; Mao, C.F.; Chen, W.; Cui, M.; Ma, R.; Cao, H.X.; Jing, C.W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Luteolin inhibits breast cancer development and progression in vitro and in vivo by suppressing notch signaling and regulating MiRNAs. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1693–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, M.D.; Hu, L.; Fan, Z.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Zhu, Z.L.; Cao, S.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, J.F.; Su, L.P.; Li, C.; et al. Luteolin suppresses gastric cancer progression by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of the Notch signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshet, Y.; Seger, R. The MAP kinase signaling cascades: A system of hundreds of components regulates a diverse array of physiological functions. In MAP Kinase Signaling Protocols, 2nd ed.; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sabio, G.; Davis, R.J. TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways. In Seminars in Immunology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 26, pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Plotnikov, A.; Zehorai, E.; Procaccia, S.; Seger, R. The MAPK cascades: Signaling components, nuclear roles and mechanisms of nuclear translocation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.; Xi, G.; Lu, Y.J.; Li, Z. Luteolin impacts deoxyribonucleic acid repair by modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in colorectal cancer. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 10998–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.A.; Lomax-Browne, H.J.; Carter, T.M.; Kinch, C.E.; Hall, D.M. Molecular interactions in cancer cell metastasis. Acta Histochem. 2010, 112, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xie, K.P.; Huo, H.N.; Wang, L.M.; Zou, W.; Xie, M.J. Inhibitory effect of luteolin on the angiogenesis of chick chorioallantoic membrane and invasion of breast cancer cells via downregulation of AEG-1 and MMP-2. Sheng Li Xue Bao/Acta Physiol. Sin. 2013, 65, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, H.; Sun, T.; Fu, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Luteolin suppresses the growth of colon cancer cells by inhibiting the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Rao, C.; Zheng, G.; Wang, S. Luteolin suppresses colorectal cancer cell metastasis via regulation of the miR-384/pleiotrophin axis. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Brkić, J.; Hayder, H.; Peng, C. MicroRNAs in human placental development and pregnancy complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5519–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.P.; Glasner, M.E.; Yekta, S.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science 2003, 299, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, M.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs and cancer—New paradigms in molecular oncology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Fang, X.; Ouyang, G. MicroRNAs: Novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Makabel, B.; Cui, Q.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. The targeting of non–coding RNAs by curcumin: Facts and hopes for cancer therapy. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ma, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Targeting microR- NAs: A new action mechanism of natural compounds. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi, A.A.; Shahabipour, F.; Khatibi, S.; Johnston, T.P.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin as a MicroRNA regulator in cancer: A review. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Luteolin Induces Apoptosis by Up-regulating miR-34a in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 14, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Mao, Z.; Duan, B.; Long, Y.; Xue, F.; Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Gao, Z. Luteolin exerts an anticancer effect on gastric cancer cells through multiple signaling pathways and regulating miRNAs. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, B.Z.; Lin, Y.P.; Wang, H.B. MiR-34a, as a suppressor, enhance the susceptibility of gastric cancer cell to luteolin by directly targeting HK1. Gene 2018, 644, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Li, M.H.; Qin, Y.M.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.H. Luteolin Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Induces Apoptosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Regulation of MicroRNA-34a-5p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Meng, W.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Su, Y.; Lin, S.C.; Gan, Z.H.; Sun, Y.N.; Min, D.L. Luteolin inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through miR-301. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeng, S.; Son, S.W.; Seo, H.A.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, C.K.; Kuh, H.J.; Park, J.K. Luteolin-regulated MicroRNA-301-3p Targets Caspase-8 and Modulates TRAIL Sensitivity in PANC-1 Cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magura, J.; Moodley, R.; Mackraj, I. The effect of hesperidin and luteolin isolated from Eriocephalus africanus on apoptosis, cell cycle and miRNA expression in MCF-7. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Ge, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Luteolin exhibits anti-breast cancer property through up-regulating miR-203. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, M.; Ray, S.K. Anti-tumor activities of luteolin and silibinin in glioblastoma cells: Overexpression of miR-7-1-3p augmented luteolin and silibinin to inhibit autophagy and induce apoptosis in glioblastoma in vivo. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Naiki, T.; Kato, H.; Iida, K.; Etani, T.; Nagayasu, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Inaguma, S.; Onishi, M.; et al. Recruitment of miR-8080 by luteolin inhibits androgen receptor splice variant 7 expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, M.A.; Ozaki, Y.; Okuzaki, D.; Naito, Y.; Sasakura, T.; Okamoto, A.; Tabara, H.; Inoue, T.; Hagiyama, M.; Ito, A.; et al. Gefitinib and Luteolin Cause Growth Arrest of Human Prostate Cancer PC-3 Cells via Inhibition of Cyclin G-Associated Kinase and Induction of miR-630. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.W.; Lu, Z.Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, T.T.; Feng, X.J.; Wang, S.M.; Pan, Y.C.; Zhu, M.H.; Zhang, S.H. MicroRNA-6809-5p mediates luteolin-induced anticancer effects against hepatoma by targeting flotillin 1. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Antiproliferative activity of flavonoids on several cancer cell lines. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, J.M.; Shieh, D.E.; Chiang, W.; Chang, M.Y.; Chiang, L.C. Chemopreventive effects of minor dietary constituents in common foods on human cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, P.P.; Ke, F.C.; Huang, J.H.; Huang, C.J.; Kandaswami, C.; Middleton, E., Jr.; Lee, M.T. Effects of luteolin and quercetin, inhibitors of tyrosine kinase, on cell growth and metastasis-associated properties in A431 cells overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, L.M.; Zigrossi, D.A.; Tauber, R.A.; Hightower, C.; Milner, J.A. Flavonoids suppress androgen-independent human prostate tumor proliferation. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 38, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, M.A.; Tworoger, S.S.; Hecht, J.L.; De Vivo, I.; Rosner, B.; Hankinson, S.E. A prospective study of dietary flavonoid intake and incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Kobori, M.; Shinmoto, H.; Tsushida, T. Structure-activity relationships of flavonoids and the induction of granulocytic- or monocytic-differentiation in HL60 human myeloid leukemia cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Mi, M.T.; Gu, Y.Y.; Yuan, J.L.; Ling, W.H.; Lin, H. Effects of flavonoids with different structures on proliferation of leukemia cell line HL-60. Ai Zheng 2007, 26, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Kilani-Jaziri, S.; Frachet, V.; Bhouri, W.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Ronot, X. Flavones inhibit the proliferation of human tumor cancer cell lines by inducing apoptosis. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2012, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larvol, B.L.; Wilkerson, L.J. In Silico Drug Discovery: Tools for Bridging the NCE Gap. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M. An Anti-Cancer Drug Candidate OSI-027 and Its Analog as Inhibitors of MTOR: Computational Insights into the Inhibitory Mechanisms. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M. Anticancer Compound XL765 as PI3K/MTOR Dual Inhibitor: A Structural Insight into the Inhibitory Mechanism Using Computational Approaches. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Mostafa, M. Virtual Screening of 1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives for Inhibition of a Key Cancer Signaling Protein, AKT1 Kinase. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, S.S.; Lu, J.Y.; Kong, X.Q.; Liang, Z.J.; Luo, C.; Jiang, H. Computational Drug Discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZahrani, W.M.; AlGhamdi, S.A.; Sohrab, S.S.; Rehan, M. Investigating a Library of Flavonoids as Potential Inhibitors of a Cancer Therapeutic Target MEK2 Using in Silico Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhera, S.; Rana, M.; Devlal, K.; Celik, I.; Yadav, R. A comprehensive exploration of pharmacological properties, bioactivities and inhibitory potentiality of luteolin from Tridax procumbens as anticancer drug by in-silico approach. Struct. Chem. 2022, 33, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollur, S.P.; Prasad, S.K.; Pradeep, S.; Veerapur, R.; Patil, S.S.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Lamraoui, G.; Al-Kheraif, A.A.; Elgorban, A.M.; Syed, A.; et al. Luteolin-Fabricated ZnO Nanostructures Showed PLK-1 Mediated Anti-Breast Cancer Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Cui, H.; Liang, J. Advances in the Mechanism of Luteolin against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics and Network Pharmacology. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wu, C.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Tsai, K.J.; Hung, C.M.; Hsu, C.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Hsieh, T.H. Effects of Luteolin on Human Breast Cancer Using Gene Expression Array: Inferring Novel Genes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2107–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, M.; Mo, Y.; Mo, Z. Luteolin potentially treating prostate cancer and COVID-19 analyzed by the bioinformatics approach: Clinical findings and drug targets. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 802447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Yuan, C.; Xing, R.; Ni, J.; Hu, G.; Chen, F.; Wang, X. Luteolin protects mice from severe acute pancreatitis by exerting HO-1-mediated anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, M.T.; Fujita, K.; Hosoya, T.; Imai, S.; Shimoi, K. Absorption and Metabolism of Luteolin and Its Glycosides from the Extract of Chrysanthemum morifolium Flowers in Rats and Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7693–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoi, K.; Okada, H.; Furugori, M.; Goda, T.; Takase, S.; Suzuki, M.; Hara, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Kinae, N. Intestinal Absorption of Luteolin and Luteolin 7-O-β-Glucoside in Rats and Humans. FEBS Lett. 1998, 438, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.; Lu, L.; Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Metabolic Disposition of Luteolin Is Mediated by the Interplay of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases and Catechol-O-methyltransferases in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, N.; Shimizu, N.; Komoda, T.; Mohri, S.; Tsushida, T.; Eitsuka, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Nakagawa, K. Absorption and Metabolism of Luteolin in Rats and Humans in Relation to in Vitro Anti-inflammatory Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11320–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, L.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, A.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z. Luteolin Cocrystals: Characterization, Evaluation of Solubility, Oral Bioavailability and Theoretical Calculation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Q.; He, S.; Xie, J.; Liang, X.; Wu, T.; Li, D. Luteolin-loading of Her-2-poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles and proliferative inhibition of gastric cancer cells via targeted regulation of forkhead box protein O1. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamimi, M.A.; Hussain, A.; AlRajhi, M.; Alshehri, S.; Imam, S.S.; Qamar, W. Luteolin-Loaded Elastic Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery to Control Breast Cancer: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluations. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabzichi, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Ramezani, F.; Sharifi, S.; Tabasinezhad, M.; Pirouzpanah, M.; Ghanbari, P.; Samadi, N. Luteolin-loaded phytosomes sensitize human breast carcinoma MDA-MB 231 cells to doxorubicin by suppressing Nrf2 mediated signalling. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 5311–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Teng, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Application of luteolin nanomicelles anti-glioma effect with improvement in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61146–61162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Vegetables/Fruits | Quantity (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Broccoli | 74.5 |
| Green chili | 33.0 |
| Bird chili | 1035.0 |
| Onion leaves | 391.0 |
| Belimbi fruit | 202.0 |
| Belimbi leaves | 464.5 |
| French bean | 11.0 |
| Carrot | 37.5 |
| White radish | 9.0 |
| Local celery | 80.5 |
| Limau purut leaves | 30.5 |
| Dried asam gelugur | 107.5 |
| Cancer Types | Study Types | Regulation of microRNAs | Outcomes | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric | BGC-823 and SGC-7901 | Upregulation of miR-34a |
| [130] |
| MKN45 or BGC823 | Upregulated miR-107, miR-34a and miR-139 |
| [131] | |
| MKN45 or BGC823 | Upregulated miR-34a and miR-422a |
| [131] | |
| MKN45 or BGC823 | Downregulated miR-21, miR-155 |
| [131] | |
| MKN45 or BGC823 | Downregulated miR-224, miR-340 |
| [131] | |
| AGS, BGC823 and SGC7901 | MiR-34a upregulated |
| [132] | |
| Lung | H460 xenografts mice model | Upregulated 20 miRNAs, including miR-34a-5p and Downregulated miR-3470a, miR-3470b, miR-3472 and miR-3105-5p |
| [133] |
| Prostate | PC3 and LNCaP | Downregulated miR-301 |
| [134] |
| Pancreas | PANC-1 | Down-regulates miRNA-301-3p |
| [135] |
| Breast | MCF-7 | Downregulated the expression of miR-21 and upregulated that of miR-16 |
| [136] |
| MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 | Upregulated miR-139-5p, MiR-181a, miR-224 and miR-246 Downregulated miR-155 |
| [112] | |
| MDA-MB-453 and MCF-7 | Upregulated miR-203 |
| [137] | |
| Brain | U87MG, T98G cells and U87MG and T98G xenografts nude mice | Upregulated miR-7-1-3p, miR-181a and miR-9 |
| [138] |
| U251 | Upregulation miR-124-3p |
| [44] | |
| Prostate | 22Rv1 and VCaP | Upregulation of miR-8080 |
| [139] |
| Colorectal | HT-29 and SW480 | Upregulated miR-384 |
| [121] |
| Prostate | PC-3 | Upregulation of miR-630 and miR-5703 |
| [140] |
| Liver | Huh7 | Upregulated miR-6809-5p |
| [141] |
| Nano-Formulation | Cancer Type | Findings | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luteolin-loaded Her-2-poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) | Gastric |
| [167] |
| Luteolin-loaded elastic liposomes | Breast |
| [168] |
| Luteolin-fabricated ZnO nanostructures | Breast |
| [157] |
| Luteolin-loaded phytosomes | Breast |
| [169] |
| Luteolin-loaded MPEG-PCL (luteolin/MPEG-PCL) micelles | Brain |
| [170] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alharbi, H.O.A.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules. Molecules 2024, 29, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051093
Almatroodi SA, Almatroudi A, Alharbi HOA, Khan AA, Rahmani AH. Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051093
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmatroodi, Saleh A., Ahmad Almatroudi, Hajed Obaid A. Alharbi, Amjad Ali Khan, and Arshad Husain Rahmani. 2024. "Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051093
APA StyleAlmatroodi, S. A., Almatroudi, A., Alharbi, H. O. A., Khan, A. A., & Rahmani, A. H. (2024). Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules. Molecules, 29(5), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051093