Corrosion Inhibition of Expired Cefazolin Drug on Copper Metal in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. WL Measurements
2.1.1. The Impact of Drug Concentration
2.1.2. Impact of Temperature on Inhibition Efficiency
2.2. Adsorption Type and Chemical Thermodynamics Approach
2.3. PP Measurements
2.4. EIS Study
2.5. EFM Study
2.6. SEM and EDX Studies
2.7. Quantum Chemical Calculations
2.7.1. DFTB Results
2.7.2. Monte Carlo Simulation (MC)
2.8. Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibition
2.9. A Comparison between the Expired Cefazolin Drug and Other Drugs Previously Mentioned
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cu Coupons
3.2. Chemicals and Solutions
3.3. WL Method
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.5. Surface Examination
3.6. Computational Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J.E.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G.S.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L.G. Fundamentals and Advances in Magnesium Alloy Corrosion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 92–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López–Ortega, A.; Bayón, R.; Arana, J.L. Evaluation of Protective Coatings for Offshore Applications. Corrosion and Tribocorrosion Behavior in Synthetic Seawater. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, F.O.; Kolawole, S.K.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Bello, S.A.; Hassan, S.B. Mitigation of Corrosion Problems in API 5L Steel Pipeline—A Review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 2397–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Asghar, B.H.; Zaafarany, I.; Fouda, A.S. The Inhibition of Carbon Steel Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Solution Using some Phenolic Compounds. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 282–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ebenso, E.E.; Qurashi, M.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in HCl Solution by some Plant Extracts. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012, 897430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, I.L. Corrosion Inhibitors; McGraw–Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, N.; Tavakkoli, N.; Ghasemi, M. Corrosion Inhibition of Low Carbon Steel by C Nux–Vomica Extract as Green Corrosion Inhibitor in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 8827–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, A.S.; Khadom, A.A.; Ibraheem, H.F. Peach Juice as an Anti–Corrosion Inhibitor of Mild Steel. Anti–Corros. Methods Mater. 2011, 5, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, A.S.; Khadom, A.A.; Wael, R.K. Apricot Juice as Green Corrosion Inhibitor of Mild Steel in Phosphoric Acid. Alexandria Eng. J. 2013, 52, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, A.S.; Khadom, A.A.; Wael, R.K. Garlic Powder as a Safe Environment Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Acidic Media; Adsorption and Quantum Chemical Studies. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2014, 61, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.G.; Green, N.D. Corrosion Engineering; McGraw–Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, M.M.; Rashwan, S.M.; Mahmoud, M.A.; El–Mekawy, S.A.; Awad, M.K.; Ibrahim, H.E. Resorcinol Derivative as an Environmentally Friendly Low Carbon Steel Inhibitor in HCl Medium. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17609–17619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Rashwan, S.M.; Meleek, S.; Kamel, M.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Mitigation Action of Innovative Schiff Base on Steel Disintegration in Sulfuric Acid Solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al–Najjar, S.S.; Al–Baitai, A.Y. Synthesized of Novel Imidazole–derived Schiff Base as a Corrosion Inhibitor of Carbon Steel in Acidic Medium Supported by Electrochemical and DFT Studies. Phys. Chem. Res. 2022, 10, 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Antonijevic, M.M.; Milić, S.M.; Petrović, M.B. Films Formed on Copper Surface in Chloride Media in the Presence of Azoles. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, E.S.M.; Erasmus, R.; Comins, J. Inhibition of Copper Corrosion in Acidic Chloride Pickling Solutions by 5–(3–Aminophenyl)−Tetrazole as a Corrosion Inhibitor. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Polo, J.; La Iglesia, A.; Bastidas, J. A Study on the Adsorption of Benzotriazole on Copper in Hydrochloric Acid Using the Inflection Point of the Isotherm. Adsorption 2004, 10, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Ghaffari, S.; Hajizadeh, A. Film Former Corrosion Inhibitors for Oil and Gas Pipelines—A Technical Review. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 58, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Mishra, P. Drugs as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Review. Inter. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 669–671. [Google Scholar]
- Gikonyo, D.; Gikonyo, A.; Luvayo, D.; Ponoth, P. Drug Expiry Debate: The Myth and the Reality. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2737–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaszilcsin, N.; Kellenberger, A.; Dan, M.L.; Duca, D.A.; Ordodi, V.L. Efficiency of Expired Drugs Used as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamry, A.A.; Khan, A.; Aslam, J.; Haussien, M.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution by the Expired Ampicillin Drug. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, R.G.; Vengatesh, G.; Sundaravadivelu, M. Surface Morphological and Quantum Chemical Studies of some Expired Drug Molecules as Potential Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Chloride Medium. J. Surf. Interface 2021, 22, 100841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, K.; Abbas, M.A.; Bedair, M.A. Herbal Expired Drug Bearing Glycosides and Polysaccharides Moieties as Green and Cost–effective Oilfield Corrosion Inhibitor: Electrochemical and Computational Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 352, 118689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfakeer, M.; Abdallah, M.; Fawzy, A. Corrosion Inhibition Effect of Expired Ampicillin and Flucloxacillin Drugs for Mild Steel in Aqueous Acidic Medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3283–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Fawzy, A.; Al Bahir, A. The Effect of Expired Acyclovir and Omeprazole Drugs on the Inhibition of Sabic Iron Corrosion in HCl Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 4739–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, N.V.; Hublikar, L.V.; Ganiger, P.J.; Bhinge, A.S. Expired Ceftin as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 5% HCl Solution. Int. J. Green Herbal Chem. 2019, 8, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Njoku, C.N.; Enendu, B.N.; Okechukwu, S.J.; Igboko, N.; Anyikwa, S.O.; Ikeuba, A.I.; Onyeachu, I.B.; Etim, I.N.; Demian, I.; Njoku, D.I. Review on Anti–Corrosion Properties of Expired Antihypertensive Drugs as Benign Corrosion Inhibitors for Metallic Materials in Various Environments. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.; Soliman, K.A.; Alfakeer, M.; Hawsawi, H.; Mohsen Al–bonayan, A.; Al–Juaid, S.S.; Salah Abd El Wanees, S.A.; Motawea, M.S. Expired Antifungal Drugs as Effective Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in 1 M HCl Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches. ASC Omega 2023, 8, 34516–34533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Moussa, N.A.M.; Mahmoud, A.H.M.; Sayed, S.R.M.; Sidhom, P.A.; Abd El–Rahman, M.K.; Shoeib, T.; Mohamed, L.A. Density Functional Theory Study of The Corrosion Inhibition Performance of 6–Mercaptopurine and 6–thioguanine Expired Drugs toward the Aluminum (111) Surface. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 29023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.A.; El–Mahdy, M.S.; Elsayed, E.E.; Mahmoud, E.E.E.; Fouda, A.S. Recycling of Expired Ciprofloxacin in Synthetic Acid Rain (SAR) Solution as A Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper: A Theoretical and Experimental Evaluation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2024, 54, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, S.; Rongkai Pan, Y.Z.; Du, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y. Expired Glucosamine Drugs as Green Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in H2SO4 Solution and Synergistic Effect of Glucosamine Molecules with Iodide Ions: Combined Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. Crystals 2023, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, L. Expired Flunarizine Hydrochloride as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Medium: Experimental and Computational Investigation. Surf. Interface Anal. 2023, 55, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim Sheit, H.M.; Musthafa Kani, S.; Anwar Sathiq, M.; Syed Abuthahir, S.S.; Subhapriya, P.; Nivedhitha, K.S.; Umarfarooq, M.A.; Badruddin, I.B.; Kamangar, S.; Shaik, A.S. Experimental Studies on the Effect of Expired Amiodarone Drug (EAD) as a Corrosion Inhibitor on Mild Steel in 1 M HCl. Materials 2024, 17, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, R.A.; Samawi, K.A.; Salman, T.A. Inhibition Studies of Aluminium Alloy (2024) Corrosion in Acid Hydrochloride Solution Using an Expired Phenylphrine Drug. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Attar, T.; Benchadli, A. Studying the Effectiveness of an Expired Betamethasone Drug in Sulfuric Acid Solutions to Examine the Corrosive Behavior of Copper Using Weight Loss and Experimental Design. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2024, 11, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A. Expired Podocip Drug as Potential Corrosion Inhibitor for Carbon Steel in Acid Chloride Solution. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2018, 7, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasulu, A.; Kasthuri, P.K. Study of Inhibition and Adsorption Properties of Mild Steel Corrosion by Expired Pharmaceutical Gentamicin Drug in Hydrochloric Acid Media. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hameed, R.S.; Essa, A.; Nassar, A.; Magd Badr, M.; Huwaimel, B.; Al–Mhyawi, S.R.; Alshammary, F.; Abu Seni, A.; Abdallah, M. Chemical and Electrochemical Studies on Expired Lioresal Drugs as Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in Sulfuric Acid. J. New Mat. Electrochem. Syst. 2022, 25, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, A.; Duca, D.A.; Dan, M.L.; Medeleanu, M. Recycling Unused Midazolam Drug as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitor for Copper in Nitric Acid Solution. Materials 2022, 15, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, N.; Hublikar, L.V.; Bhinge, A.S.; Ganiger, P.J. Corrosion Inhibition Property of Expired Fluoxymesterone Drug on the Aluminum (Al) Surface in 3 % NaCl Solution. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2019, 11, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka Singh, P.; Chauhan, D.S.; Srivastava, K.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A. Expired Atorvastatin Drug as Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2017, 8, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhead, H.A.; Briggs, G.B.; Saunders, L.Z. Toxicology of Cefazolin in Animals. J. Infec. Dis. 1973, 128 (Suppl. 2), S379–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A. Novel Cationic Surfactant Based on Triazole as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Carbon Steel in Phosphoric Acid Produced by Dihydrate Wet Process. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 208, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobina, M.; Kellenberger, A.; Millet, J.P.; Muntean, C.; Vaszilcsin, N. Corrosion Resistance of Carbon Steel in Weak Acid Solutions in the Presence of l–Histidine as Corrosion Inhibitor. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, E.M. Corrosion Behavior of Copper in 0.50 M Hydrochloric Acid Pickling Solutions and its Inhibition by 3–amino–1, 2, 4–triazole and 3–amino–5–mercapto–1, 2, 4–triazole. Int. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Gao, L.X.; Zhou, G.D. Inhibition of Copper Corrosion by bis–(1–Benzotriazolymethylene)−(2,5–Thiadiazoly)−disulfide in Chloride Media. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 225, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Warraky, A.A.; El Shayeb, H.A.E.; Sherif, E.M. Pitting Corrosion of Copper in Chloride Solutions. Anti–Corros. Methods Mater. 2004, 51, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, B.I.; Offiong, O.E. The Study of the Inhibitory Properties of Benzoin, Benzil, Benzoin–(4–phenylthiosemicarbazone) and Benzyl–(4–phenylthiosemi carbazone) on the Corrosion of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 70, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, K.F. New Synthesized Guanidine Derivative as a Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Acidic Solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.S.; El–desoky, A.M.; Nabih, A. Inhibitive, Adsorption, Synergistic Studies on Copper Corrosion in Nitric Acid Solutions by some Organic Derivatives. Adv. Mater. Corros. 2013, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Najem, A.; Campos, O.S.; Girst, G.; Raji, M.; Hunyadi, A.; García–Antón, J.; Bellaouchou, A.; Amin, H.M.A.; Boudalia, M. Experimental and DFT Atomistic Insights into the Mechanism of Corrosion Protection of Low–Carbon Steel in an Acidic Medium by Polymethoxyflavones from Citrus Peel Waste. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 093512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.M.; Mohsen, Q.; Anwer, Z.M.; Sherif, M.A. An Expired Ceftazidime Antibiotic as an Inhibitor for Disintegration of Copper Metal in Pickling HCl Media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, S.; Qiang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, S.; He, J. Papaya Leaves Extract as a Novel Eco–friendly Corrosion Inhibitor for Cu in H2SO4 Medium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Li, W. Insight into Anti–corrosion Nature of Betel Leaves Water Extracts as the Novel and Eco–friendly Inhibitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Quraishi, M.A. Effect of Cefazolin on the Corrosion of Mild Steel in HCl Solution. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, S.; Zou, X.; Chen, S. Three Indazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors of Copper in a Neutral Chloride Solution. Corros. Sci. 2017, 126, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrini, M.; Lagrenee, M.; Vezin, H.; Gengembre, L.; Bentiss, F. Electrochemical and Quantum Chemical Studies of New Thiadiazole Derivatives Adsorption on Mild Steel in Normal Hydrochloric Acid Medium. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, R.; Ayappan, S. Study of Corrosion Inhibition Properties of Novel Semicarbazones on Mild Steel in Acidic Solutions. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2015, 60, 2786–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddahhaoui, F.Z.; Najem, A.; Elhawary, M.; Boudalia, M.; Campos, O.S.; Tabyaoui, M.; Garcia, A.J.; Bellaouchou, A.; Amin, H.M.A. Experimental and Computational Aspects of Green Corrosion Inhibition for Low Carbon Steel in HCl Environment Using Extract of Chamaerops Humilis Fruit Waste. J. Alloys Compds. 2024, 977, 173307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, I.; Sabongi, M.; Hagiuda, H.; Oshibe, T.; Yuasa, M.; Imahama, T.; Shibata, Y.; Wake, T. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel by Cationic and Anionic Polymers in Cooling Water System. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Atlam, F.M. Three Novel Bola Amphiphiles as Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in Hydrochloric Acid: Experimental and Computational Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrini, M.; Lagrenee, M.; Traisnel, M.; Gengembre, L.; Vezin, H.; Bentiss, F. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of Mild Steel in Normal Sulfuric Acid Medium by 2,5–bis(n–thienyl)−1,3,4–thiadiazoles: Electrochemical, X–ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Theoretical Studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 9267–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Qiang, Y.; Guo, L.; Feng, L.; Liao, C. A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study of the Inhibition Effect of Three Disulfide–based Flavouring Agents for Copper Corrosion in 0.5 M Sulfuric Acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennane, J.; Ebn Touhami, M.; Zehra, S.; Baymou, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, I.M.; Lgaz, H. Influence of Sodium Gluconate and Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide on the Corrosion Behavior of Duplex (α–β) Brass in Sulfuric Acid Solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, A.; EL Basiony, N.M.; Migahed, M.A.; Abd–El–Bary, H.M.; Mohamed, T.A. Experimental and Theoretical Insights into Synthesized Gemini Corrosion Inhibitor for X65–Steel in 1M HCl. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 845–867. [Google Scholar]
- Pais, M.; Rao, P. Electrochemical, Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies for Acid Corrosion of Zinc Using Glycogen. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Gazi, K.; Ghosh, D.C. Computation of the Atomic Radii through the Conjoint Action of the Effective Nuclear Charge and the Ionization Energy. Mol. Phys. 2010, 108, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Kumar, A.; Liu, W.; Songsong, C.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical, Surface and Quantum Chemical Studies of Novel Imidazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for J55 Steel in Sweet Corrosive Environment. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N. Quantum Chemical Approach of Corrosion Inhibition. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Basiony, N.; Elgendy, A.; El–Tabey, A.E.; Al Sabagh, A.; Abd El–Hafez, G.M.; Abd El–raouf, M.; Migahed, M. Synthesis, Characterization, Experimental and Theoretical Calculations (DFT, and MC) of Ethoxylated Aminothiazole as Inhibitor for X65 Steel Corrosion in Highly Aggressive Acidic Media. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, S.; Gong, Y. Monte Carlo Simulations of Corrosion Inhibition of Copper by Two Schiff Bases. In International Conference on Materials, Environmental and Biological Engineering (MEBE 2015); Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, W. Corrosion Inhibition of Copper in Sulfuric Acid by Leonurus Japonicas Houtt, Extract as a Green Corrosion Inhibitor: Combination of Experimental and Theoretical Research. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 139, 104532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.S.; El–Azaly, A.M. Expired Concor Drug as Potential Non–toxic Corrosion Inhibitor for 304 Stainless Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Zastita Materijala 2018, 59, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, A.; Abdel Hameed, R.S.; Ali, F.A.; Aboul Magd, A.S.; Salah, M. Effect of Expired Drugs as Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in 1M HCl Solution. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 27, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, L.P.; Patel, S.N. Corrosion Inhibition Study of Expired Acetazolamide on Mild Steel in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution. J. Bio. Tribo. Corros. 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, I.; Saleemi, A.R.; Naveed, S. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in HCl Solution by Tinidazole. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2011, 13, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hameed, R.S. Ranitidine Drugs as Non–toxic Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Medium. Port. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 29, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, I.; Varvara, S.; Gaina, L.; Muresan, L.M. Antibacterial Drugs as Corrosion Inhibitors for Bronze Surfaces in Acidic Solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El–Haddad, M.N.; Fouda, A.S.; Hassan, A.F. Data from Chemical, Electrochemical and Quantum Chemical Studies for Interaction Between Cephapirin Drug as an Eco–friendly Corrosion Inhibitor and Carbon Steel Surface in Acidic Medium. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 22, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Tiwari, P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Prakash, R.; Ji, G. Electrochemical Investigation of Irbesartan Drug Molecules as an Inhibitor of Mild Steel Corrosion in 1M HCl and 0.5 M H2SO4 Solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Designation: G 1–03; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 19428–22959.
- Bosch, R.W.; Hubrecht, J.; Bogaerts, W.F.; Syrett, B.C. Electrochemical Frequency Modulation: A New Electrochemical Technique for Online Corrosion Monitoring. Corrosion 2001, 57, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, D.; Smit, B. Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fihey, A.; Hettich, C.; Touzeau, J.; Maurel, F.; Perrier, A.; Köhler, C.; Aradi, B.; Frauenheim, T. Complexes of Gold and Imidazole Formed in Helium Nanodroplets. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Witek, H.A.; Bobadova–Parvanova, P.; Irle, S.; Musaev, D.G.; Prabhakar, R.; Morokuma, K.; Lundberg, M.; Elstner, M.; Köhler, C.; et al. Modeling Dynamical Phenomena in Fe(II) Dyes and Dye–semiconductor Assemblies. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 1349–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
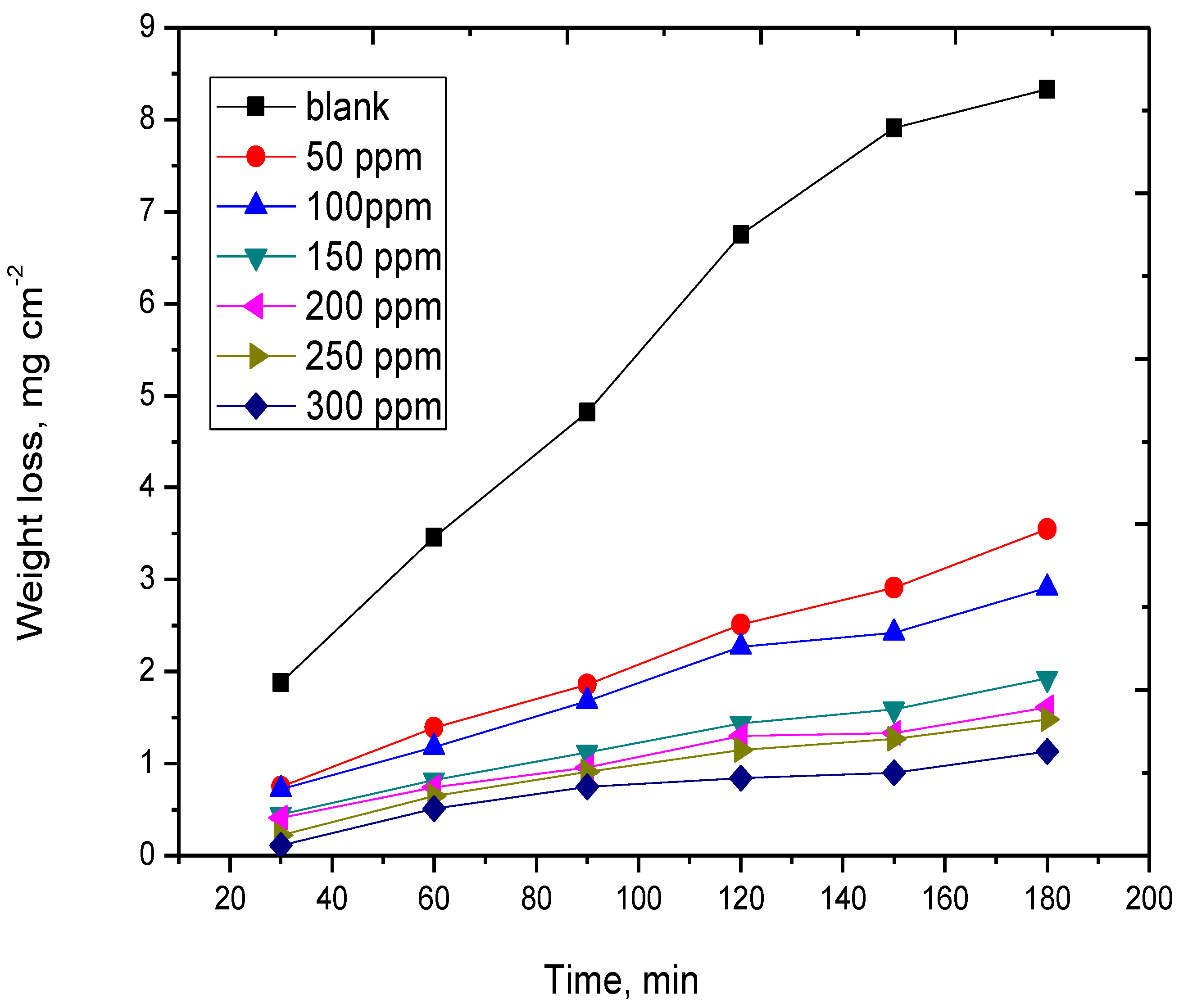














| Temperature (K) | Dose of Drug (ppm) | Weight Loss (mg cm−2) | k × 10−3 (mg cm−2 min−1) | Surface Coverage θ | IEw (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 0.00 | 8.50 | 11.8 | – | – |
| 50 | 3.5 | 4.86 | 0.59 | 59 ± 0.2 | |
| 100 | 3 | 4.16 | 0.65 | 65 ± 0.1 | |
| 150 | 2.7 | 3.75 | 0.68 | 68 ± 0.3 | |
| 200 | 1.9 | 2.64 | 0.78 | 78 ± 0.2 | |
| 250 | 1.5 | 2.08 | 0.82 | 82 ± 0.3 | |
| 300 | 1.1 | 1.50 | 0.87 | 87 ± 0.2 | |
| 303 | 0.00 | 9.1 | 12.6 | – | – |
| 50 | 3.7 | 5.13 | 0.53 | 53 ± 0.3 | |
| 100 | 3.3 | 4.58 | 0.64 | 64 ± 0.5 | |
| 150 | 3.1 | 4.30 | 0.66 | 66 ± 0.4 | |
| 200 | 2.2 | 3.05 | 0.76 | 76 ± 0.2 | |
| 250 | 1.65 | 2.28 | 0.82 | 82 ± 0.1 | |
| 300 | 1.3 | 1.81 | 0.86 | 86 ± 0.2 | |
| 308 | 0.00 | 11 | 15.2 | – | – |
| 50 | 5.3 | 7.36 | 0.52 | 52 ± 0.5 | |
| 100 | 4.2 | 5.83 | 0.62 | 62 ± 0.6 | |
| 150 | 3.9 | 5.41 | 0.65 | 65 ± 0.1 | |
| 200 | 2.9 | 4.03 | 0.74 | 74 ± 0.3 | |
| 250 | 2.3 | 3.19 | 0.79 | 79 ± 0.3 | |
| 300 | 1.9 | 2.63 | 0.83 | 83 ± 0.2 | |
| 318 | 0.00 | 16.5 | 22.9 | – | – |
| 50 | 8.43 | 11.7 | 0.49 | 49 ± 0.3 | |
| 100 | 7.34 | 10.2 | 0.56 | 56 ± 0.1 | |
| 150 | 6.33 | 8.79 | 0.62 | 62 ± 0.2 | |
| 200 | 5.28 | 7.33 | 0.68 | 62 ± 0.5 | |
| 250 | 4.67 | 6.48 | 0.61 | 61 ± 0.2 | |
| 300 | 3.55 | 4.93 | 0.78 | 78 ± 0.4 |
| Temperature (K) | Kads (L mol−1) | −ΔGoads (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 298 | 15.14 | 16.68 |
| 303 | 7.59 | 15.22 |
| 308 | 3.55 | 13.53 |
| 313 | 2.82 | 13.15 |
| 318 | 2.29 | 12.81 |
| Concentration (ppm) | −Ecorr × 10−3 (V/SCE) | icorr × 10−6 (A cm−2) | βa × 10−3 (V dec−1) | −βc × 10−3 (V dec−1) | IEp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 420 | 542 | 115 | 136 | _ |
| 50 | 415 | 240 | 122 | 125 | 55.7 ± 0.1 |
| 100 | 403 | 212 | 116 | 133 | 60.9 ± 0.3 |
| 150 | 395 | 165 | 107 | 118 | 69.6 ± 0.3 |
| 200 | 388 | 134 | 114 | 127 | 75.2 ± 0.2 |
| 250 | 380 | 108 | 105 | 134 | 80.1 ± 0.2 |
| 300 | 372 | 78 | 98 | 119 | 85.6 ± 0.1 |
| Concentration (ppm) | Cdl × 10−6 (F cm−2) | Rct (Ω cm2) | θ | IEs (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 343 | 55.4 | _ | – |
| 50 | 163.5 | 130.7 | 0.58 | 58 ± 0.3 |
| 100 | 155.1 | 170.5 | 0.77 | 77 ± 0.3 |
| 150 | 142.4 | 220.3 | 0.75 | 75 ± 0.4 |
| 200 | 104.8 | 270.8 | 0.80 | 80 ± 0.1 |
| 250 | 88.7 | 355.6 | 0.84 | 84 ± 0.2 |
| 300 | 68.9 | 487 | 0.89 | 89 ± 0.2 |
| Concentration (ppm) | icorr × 10−6 (A cm−2) | βa × 10−3 (V dec−1) | −βc × 10−3 (V dec−1) | CF–2 | CF–3 | IEEFM (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 542 | 112 | 124 | 1.95 | 3.09 | – |
| 50 | 230 | 122 | 133 | 2.02 | 3.03 | 57.6 ± 0.2 |
| 100 | 206 | 113 | 215 | 1.98 | 2.98 | 61.2 ± 0.3 |
| 150 | 160 | 126 | 186 | 1.94 | 2.89 | 70.4 ± 0.1 |
| 200 | 128 | 98 | 154 | 2.08 | 3.06 | 76.4 ± 0.2 |
| 250 | 105 | 114 | 164 | 2.01 | 3.04 | 80.6 ± 0.2 |
| 300 | 80 | 99 | 145 | 1.96 | 2.93 | 85.1 ± 0.3 |
| HOMO (au) | LUMO (au) | ∆E (au) | I (au) | A (au) | η (au) | σ (au)−1 | µ (au) | χ (au) | ω (au) | ε (au) | ΔNmax (au) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −6.40 | −2.01 | 4.39 | 6.4 | 2.01 | 2.19 | 0.46 | −4.21 | 4.21 | 4.04 | 0.25 | 1.92 |
| Total Energy (kJ mol−1) | Adsorption Energy (kJ mol−1) | Rigid Adsorption Energy (kJ mol−1) | Deformation Energy (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −598.67 | −459.38 | −453.32 | −6.06 |
| Drug Name | Inhibition Efficiency | References |
|---|---|---|
| Expired Concor | 75.1% at 300 ppm | [74] |
| Expired Moxifloxacin | 69.7% at 300 ppm | [75] |
| Expired Acetazolamide | 81.4% at 300 ppm | [76] |
| Expired Phenytoin | 79.0% at 500 ppm | [77] |
| Expired Ranitidine | 89.0% at 400 ppm | [78] |
| Expired Doxycycline | 68.5% at 200 ppm | [79] |
| Expired Cephapirin | 83.0% at 600 ppm | [80] |
| Expired Irbesartan | 83.0% at 300 ppm | [81] |
| Expired Cefazolin | 87.0% at 300 ppm | This work |
| Drug | Chemical Structure | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cefazolin |  | IUPAC name: (6R,7R)–3–{[(5–methyl–1,3,4–thiadiazol–2–yl)thio]methyl}–8–oxo–7–[(1H–tetrazol–1–ylacetyl)amino]–5–thia–1–azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct–2–ene–2–carboxylic acid Molecular Formula: C14H14N8O4S3 Molecular mass: 454.51 g/mol |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaiari, R.A.; Kamel, M.M.; Mohamed, M.M. Corrosion Inhibition of Expired Cefazolin Drug on Copper Metal in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches. Molecules 2024, 29, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051157
Alsaiari RA, Kamel MM, Mohamed MM. Corrosion Inhibition of Expired Cefazolin Drug on Copper Metal in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051157
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaiari, Raiedhah A., Medhat M. Kamel, and Mervate M. Mohamed. 2024. "Corrosion Inhibition of Expired Cefazolin Drug on Copper Metal in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051157
APA StyleAlsaiari, R. A., Kamel, M. M., & Mohamed, M. M. (2024). Corrosion Inhibition of Expired Cefazolin Drug on Copper Metal in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Practical and Theoretical Approaches. Molecules, 29(5), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051157





