Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
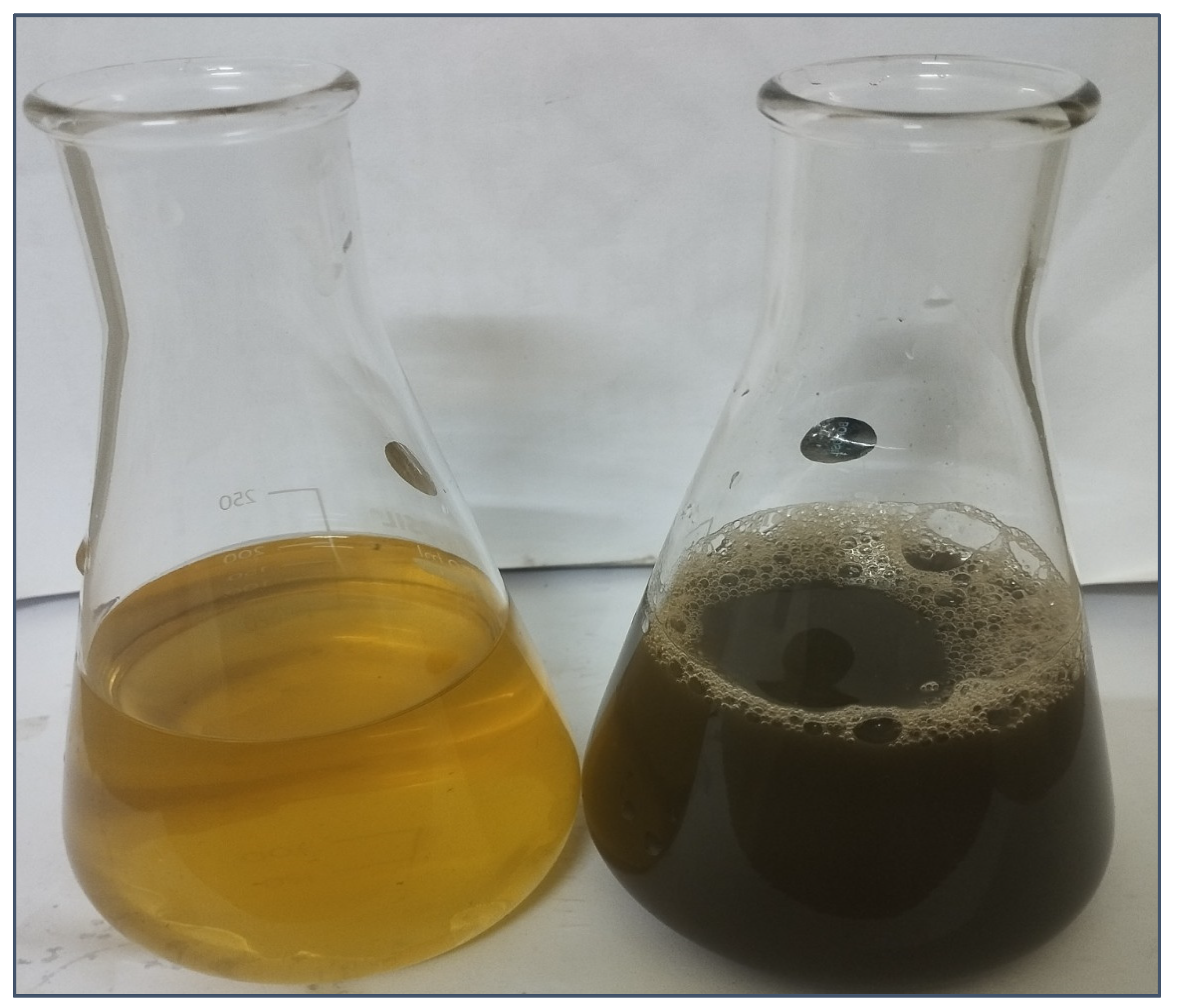
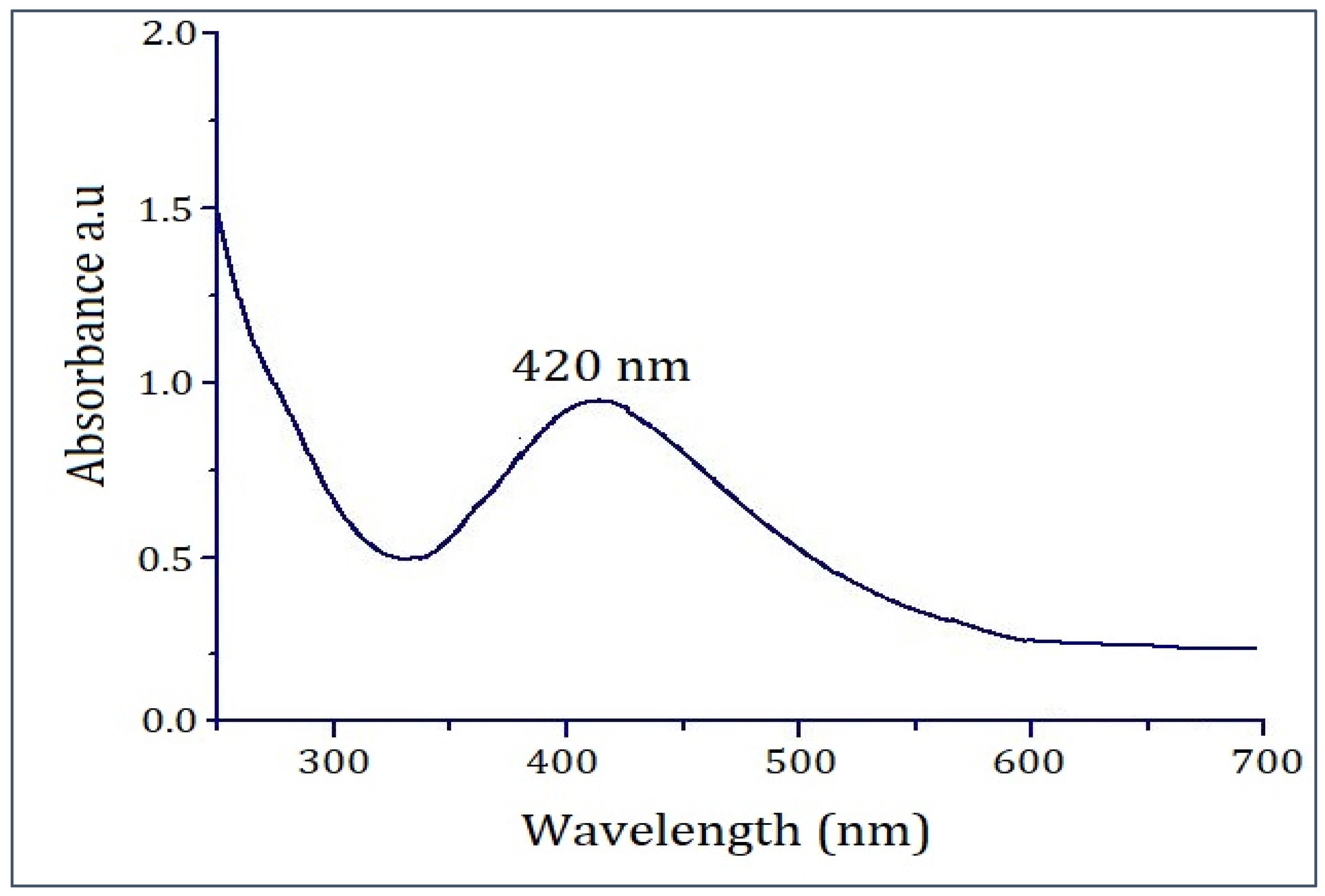
2.1. UV–Visible Spectroscopic Study of PFRAE-AgNPs
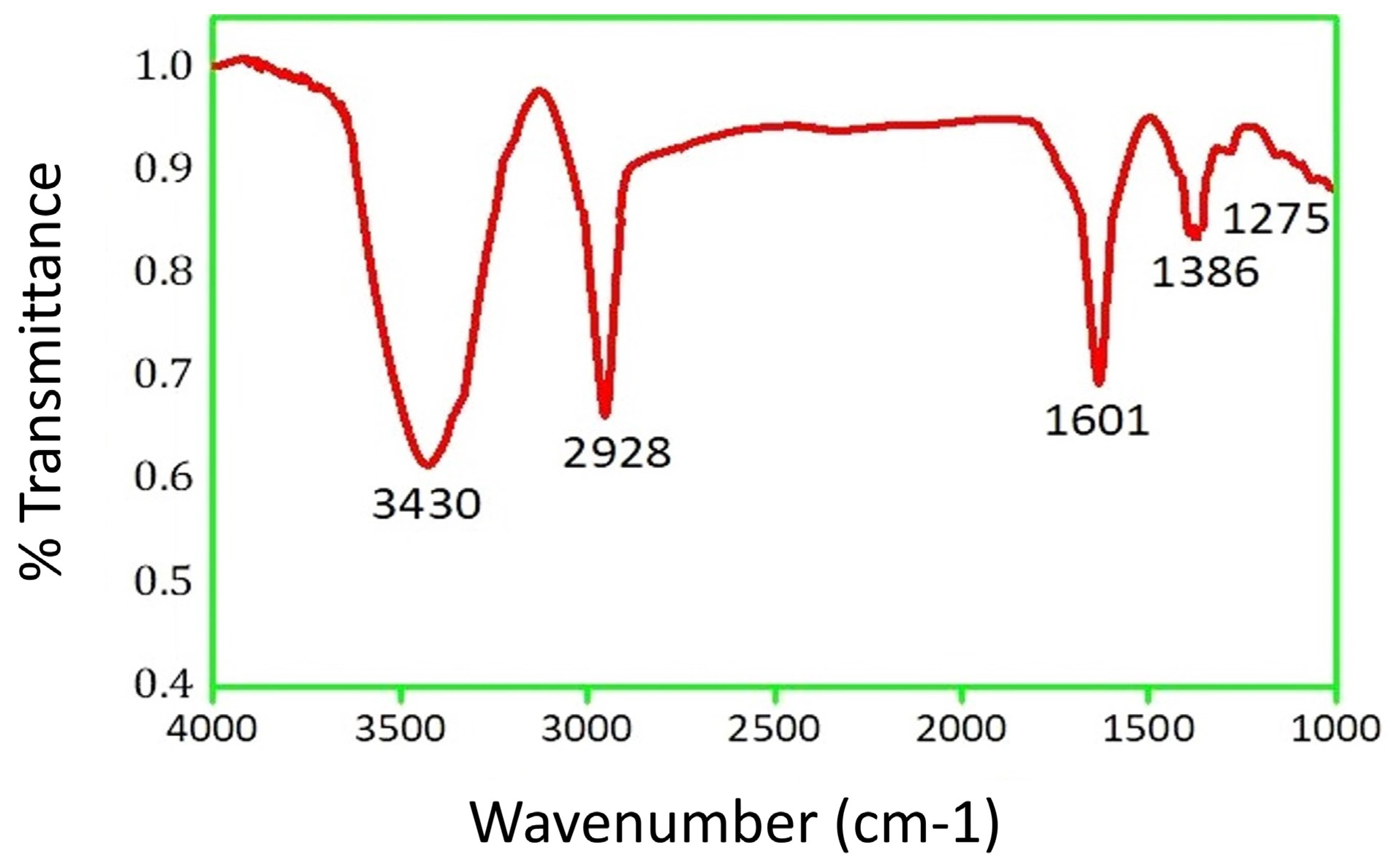
2.2. Functional Group Study of PFRAE-AgNPs Using FTIR Spectroscopy
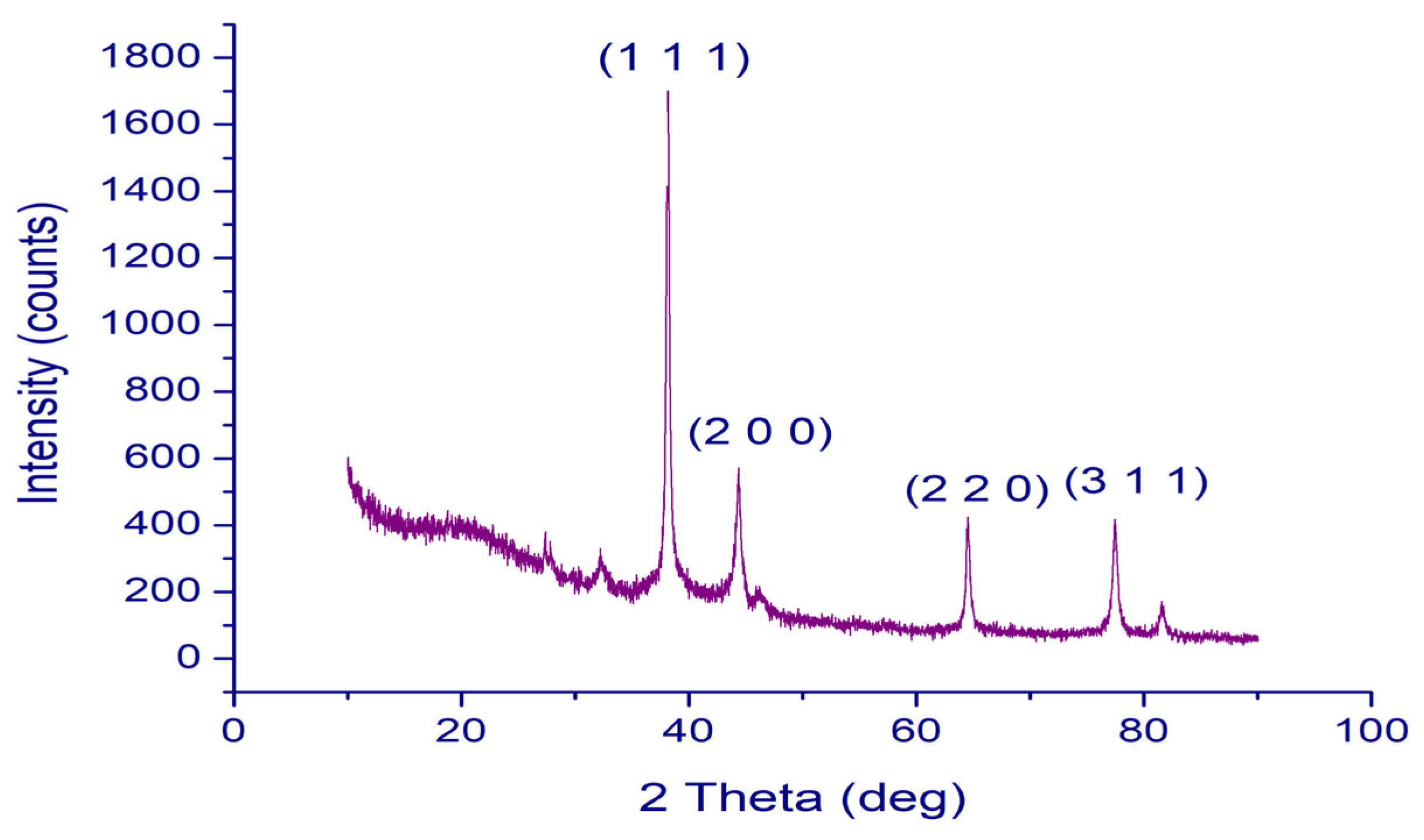
2.3. XRD Analysis of PFRAE-AgNPs for Crystalline Structure Elucidation
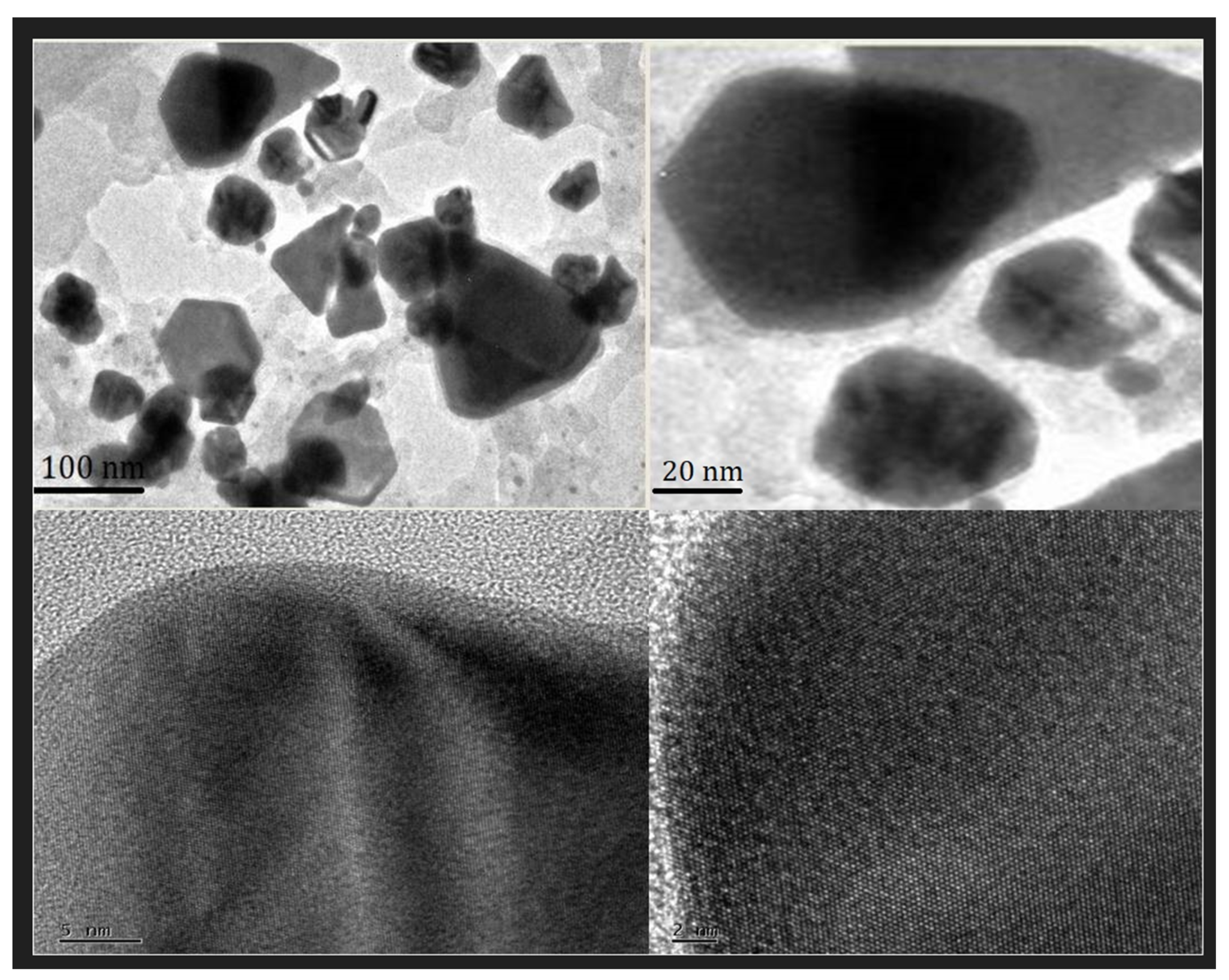
2.4. TEM Analysis of PFRAE-AgNPs for Size and Morphology
2.5. DLS Analysis of PFRAE-AgNPs to Reveal Particle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Measurement
2.6. Antibacterial Activity of PFRAE-AgNPs
2.7. Antioxidant Activity of PFRAE-AgNPs Using DPPH and ABTS Assays
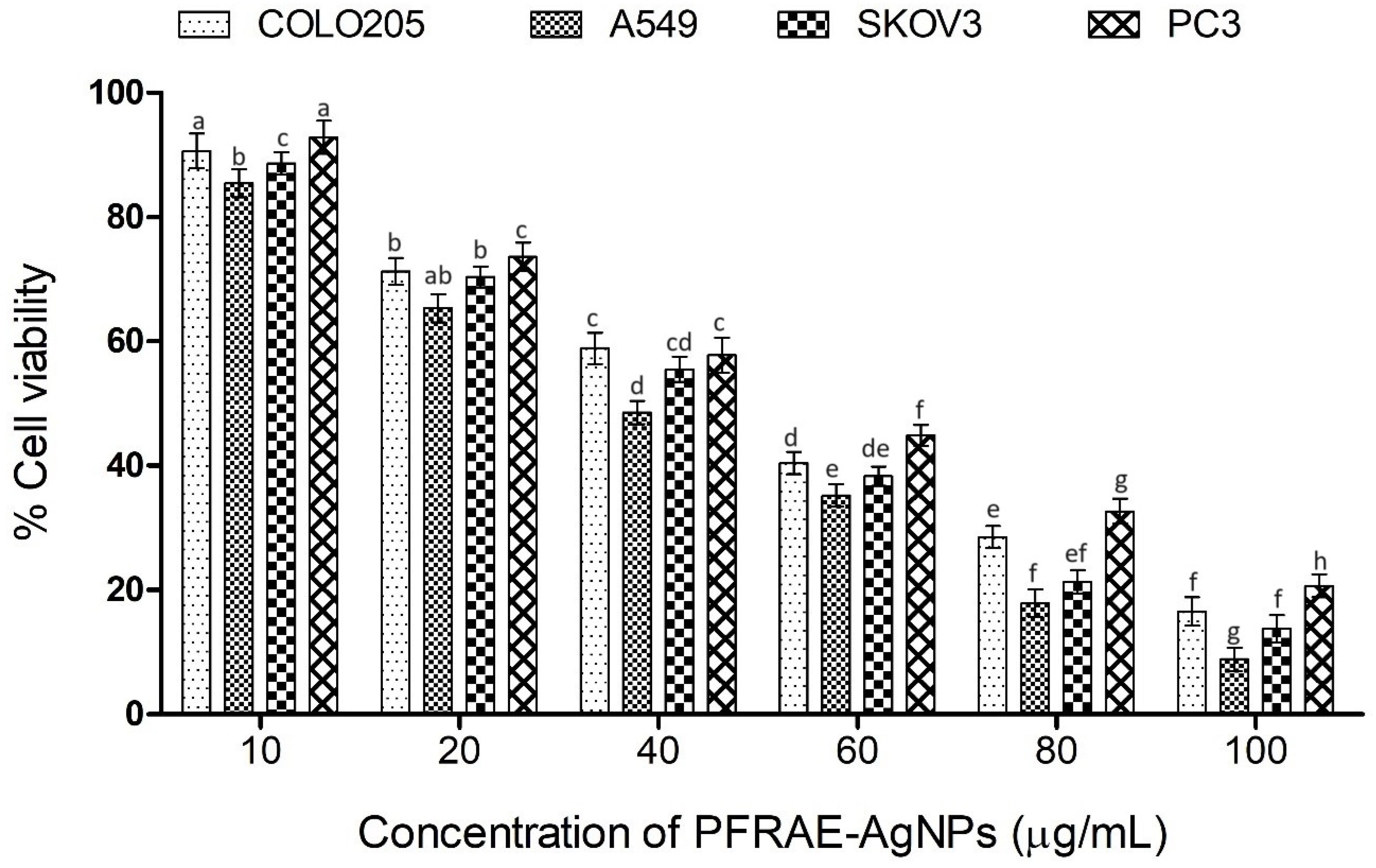
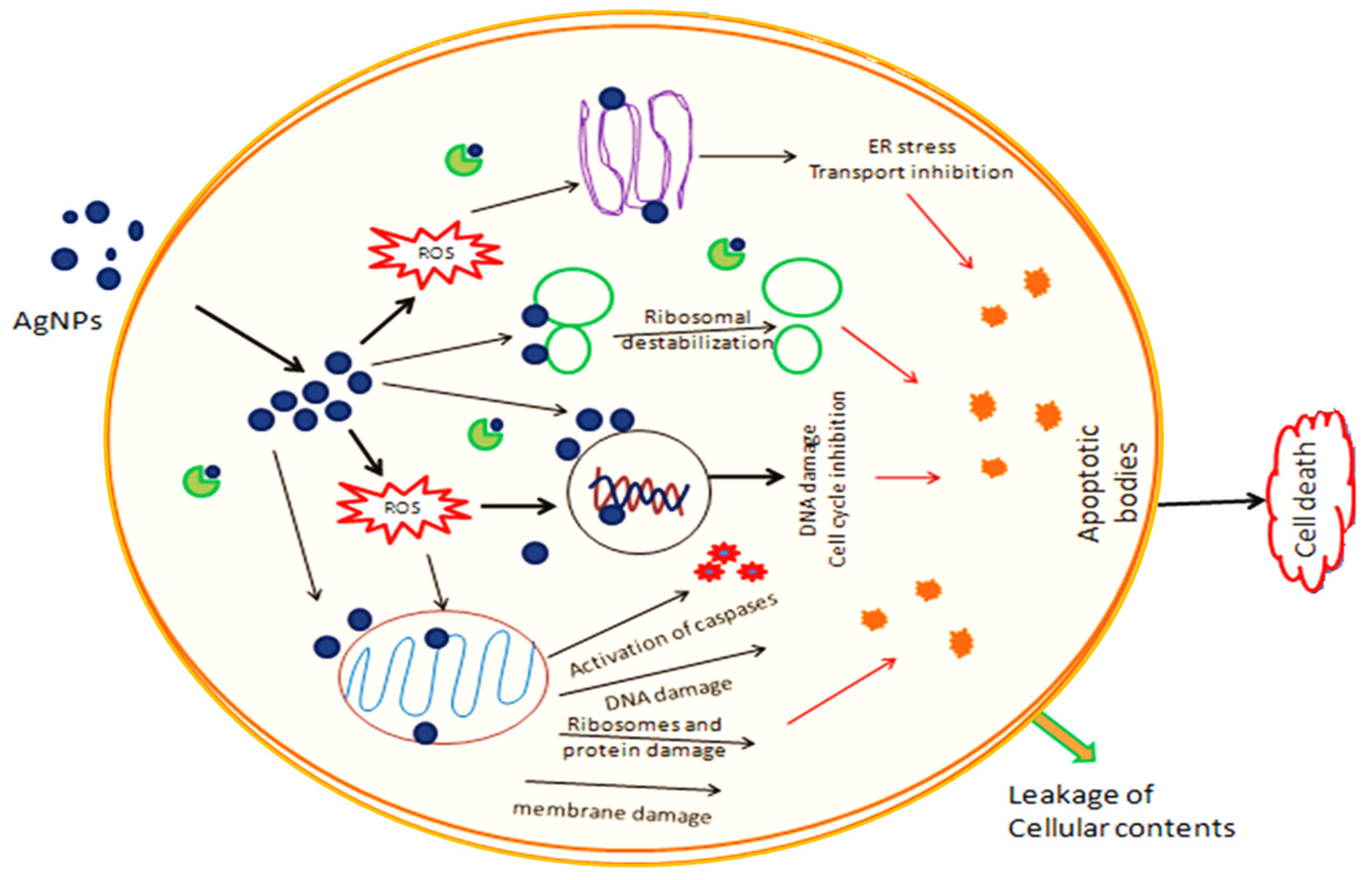
2.8. Cytotoxicity of PFRAE-AgNPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of PFRAE and Biomimetic Synthesis of PFRAE-AgNPs
3.2. Spectral Characterization of PFRAE-AgNPs
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of PFRAE-AgNPs
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of PFRAE-AgNPs
3.4.1. DPPH Scavenging Assay
3.4.2. ABTS Scavenging Assay
3.5. Cytotoxicity of PFRAE-AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Loessl, M.; Baeumner, A.J. Signaling strategies of silver nanoparticles in optical and electrochemical biosensors: Considering their potential for the point-of-care. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Li, F.; Hu, C.; Yin, L.; Li, D.; Ji, C.; Zhuge, X.; Zhang, K.; Luo, K. Highly dispersed silver nanoparticles for performance-enhanced lithium oxygen batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 73, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.A.; Chen, L.T.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hu, C.C.; Tsai, D.H. Silver nanoparticles-decorating manganese oxide hybrid nanostructures for supercapacitor applications. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14203–14212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, N.; Mayani, S.V.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Environmental implications of nanoceramic applications. Results Chem. 2022, 5, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Morsy, M.S. Facile synthesis of novel nanocomposite as antibacterial and flame retardant material for textile fabrics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese Alex, K.; Tamil Pavai, P.; Rugmini, R.; Shiva Prasad, M.; Kamakshi, K.; Sekhar, K.C. Green synthesized Ag nanoparticles for bio-sensing and photocatalytic applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13123–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M.; Mudila, H.; Gupta, G.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, D.; Bakshi, H.A.; Negi, P.; Kapoor, D.N.; Chellappan, D.K.; et al. Emerging trends in clinical implications of bio-conjugated silver nanoparticles in drug delivery. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 35, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker Ardakani, L.; Surendar, A.; Thangavelu, L.; Mandal, T. Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) as catalyst in chemical reactions. Synth. Commun. 2021, 51, 1516–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, B.; Krajewska, U.; Nowak, A.; Dziedzic, A.; Barylyak, A.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Noncytotoxic silver nanoparticles as a new antimicrobial strategy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Pohl, P. Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles (Agcl-NPs) using a pulicaria vulgaris gaertn. aerial part extract and their application as antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant agents. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takáč, P.; Michalková, R.; Čižmáriková, M.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Takáčová, G. The Role of Silver Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer: Are There Any Perspectives for the Future? Life 2023, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallineni, S.K.; Sakhamuri, S.; Kotha, S.L.; AlAsmari, A.R.G.M.; AlJefri, G.H.; Almotawah, F.N.; Mallineni, S.; Sajja, R. Silver Nanoparticles in Dental Applications: A Descriptive Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narciso, A.M.; da Rosa, C.G.; Nunes, M.R.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Hansen, C.M.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; Paes, J.V.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Barreto, P.L.M.; Masiero, A.V. Antimicrobial green silver nanoparticles in bone grafts functionalization for biomedical applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 35, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, A.; Sundaresan, R.; Rajwade, J.M.; Srivastava, P.; Naik, A. A concise review on implications of silver nanoparticles in bone tissue engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 141, 213099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istiqola, A.; Syafiuddin, A. A review of silver nanoparticles in food packaging technologies: Regulation, methods, properties, migration, and future challenges. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asafa, T.B.; Odediji, R.A.; Salaudeen, T.O.; Lateef, A.; Durowoju, M.O.; Azeez, M.A.; Yekeen, T.A.; Oladipo, I.C.; Irshad, H.M.; Abbas, S.H. Physico-mechanical properties of emulsion paint embedded with silver nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Song, C.G.; Kang, P.M. Targeting oxidative stress using nanoparticles as a theranostic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Hsiao, I.L.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, C.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Chuang, C.Y. Silver nanoparticles affect on gene expression of inflammatory and neurodegenerative responses in mouse brain neural cells. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Korzeniowska, B.; Gorshkov, V.; Tahir, M.; Schrøder, H.; Skytte, L.; Rasmussen, K.L.; Khandige, S.; Møller-Jensen, J.; Kjeldsen, F. Silver nanoparticle-induced expression of proteins related to oxidative stress and neurodegeneration in an in vitro human blood-brain barrier model. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Thomas, R.K.; Vidya, L.; Aparna, V.M.; Neelima, S.; Sudarsanakumar, C. Exploring the cytotoxicity on human lung cancer cells and DNA binding stratagem of camptothecin functionalised silver nanoparticles through multi-spectroscopic, and calorimetric approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Saini, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Saini, R.V. Apoptosis induction in lung and prostate cancer cells through silver nanoparticles synthesized from Pinus roxburghii bioactive fraction. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 25, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Kotcherlakota, R. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: A step forward for cancer theranostics? Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H.A.; Abdullah, M.A. Novel drug delivery systems based on silver nanoparticles, hyaluronic acid, lipid nanoparticles and liposomes for cancer treatment. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 3071–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakono, N.; Shimizu, M.; Sakono, M. Immobilization Method for Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized via Evaporation/Condensation onto a Glass Plate. Chem. Lett. 2022, 51, 1074–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Oprea, O.; Nicoara, A.I.; Vasile, B.S.; Boanta, L.; Marin, A.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.M. Comparative antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles obtained by wet chemical reduction and solvothermal methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Quiroz, C.; Acevedo, N.; Zapata-Giraldo, J.; Botero, L.E.; Quintero, J.; Zárate-Triviño, D.; Saldarriaga, J.; Pérez, V.Z. Optimization of silver nanoparticle synthesis by chemical reduction and evaluation of its antimicrobial and toxic activity. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.S.N.; Ali, R.R.; Shameli, K.; Hamzah, M.Y.; Kasmani, R.M.; Nasef, M.M. Interaction insight of pullulan-mediated gamma-irradiated silver nanoparticle synthesis and its antibacterial activity. Polymers 2021, 13, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Wei, J. Formation and characterization of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution via ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Zhang, B. Facile size-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles in UV-irradiated tungstosilicate acid solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 5300–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeram, K.J.; Nidhin, M.; Nair, B.U. Microwave assisted template synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, M.; Esposito, M.; Todisco, F.; Simeone, D.; Tarantini, I.; De Marco, L.; De Giorgi, M.; Nicotra, G.; Carbone, L.; Sanvitto, D.; et al. Nanoscale study of the tarnishing process in electron beam lithography-fabricated silver nanoparticles for plasmonic applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 24314–24323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaydarov, R.A.; Khaydarov, R.R.; Gapurova, O.; Estrin, Y.; Scheper, T. Electrochemical method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuDalo, M.A.; Al-Mheidat, I.R.; Al-Shurafat, A.W.; Grinham, C.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a modified Tollens’ method in conjunction with phytochemicals and assessment of their antimicrobial activity. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Raj, S.; Anuradha, P.R.; Sawant, S.N.; Doble, M. Biocompatibility studies on polyaniline and polyaniline–silver nanoparticle coated polyurethane composite. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Mir, N.; Mousavi-Kamazani, M.; Bagheri, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles prepared from two novel natural precursors by facile thermal decomposition methods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, T.; O’Connell, G.; Lunney, J.G. Metal nanoparticle film deposition by femtosecond laser ablation at atmospheric pressure. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswal, T.; Gupta, J. A review on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles on human health. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 81, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Singh, S.; Ravichandiran, V. Toxicity, preparation methods and applications of silver nanoparticles: An update. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Gaur, A.; Jain, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rani, V. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: An approach to overcome toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, R.R.; Kulkarni, A.S.; Gilda, S.S.; Aloorkar, N.H.; Osmani, R.A.; Harkare, B.R. Innovative eco-friendly approaches for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 7, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameem Ahamed, S.; Chola, R.; Venkatachalam, R. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant and Biological Organisms and Their Biomedical Applications. In Modern Nanotechnology: Volume 2: Green Synthesis, Sustainable Energy and Impacts; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 91–121. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, R.; Bhattu, M.; Verma, M.; Acevedo, R.; Duc, N.D.; Singh, J. Biogenic silver based nanostructures: Synthesis, mechanistic approach and biological applications. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, S.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, S.; Josephs, J.; Onani, M.O.; Meyer, M.; Madiehe, A.M. Biomedical applications of plant extract-synthesized silver nanoparticles. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, R.; Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Doughty, S.; Tayebi, L. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, W.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Owens, G.; Islam, R.U. A review of the phytochemical mediated synthesis of AgNP (silver nanoparticle): The wonder particle of the past decade. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 2625–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, M.S.; Tahir, M.B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, N.S.; Alsubhi, N.S.; Felimban, A.I. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using medicinal plants: Characterization and application. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2022, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, R.; Negi, B. Conventional and green methods of synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Oriola, A.O.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Oyedeji, A.O. Plant extracts mediated metal-based nanoparticles: Synthesis and biological applications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseingholian, A.; Gohari, S.D.; Feirahi, F.; Moammeri, F.; Mesbahian, G.; Moghaddam, Z.S.; Ren, Q. Recent advances in green synthesized nanoparticles: From production to application. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24, 100500. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.K.; Vishwakarma, J.; Rai, S.; Alomar, T.S.; AlMasoud, N.; Bhattarai, A. Green route synthesis and characterization techniques of silver nanoparticles and their biological adeptness. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27004–27020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, H.T.; Haes, A.J. What does nanoparticle stability mean? J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 16495–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, R.; Zia, M.; Naz, S.; Aisida, S.O.; Ain, N.U.; Ao, Q. Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: Recent trends and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Huang, Y.; Parsons, J.G.; Zhao, L.; Lopez-Moreno, L.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Plant-based green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Scientific curiosity or a realistic alternative to chemical synthesis? Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2016, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.K.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Applications and limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb Rahuman, H.B.; Dhandapani, R.; Narayanan, S.; Palanivel, V.; Paramasivam, R.; Subbarayalu, R.; Thangavelu, S.; Muthupandian, S. Medicinal plants mediated the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Adamecz, D.I.; Szerencsés, B.; Molnar, C.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Green silver and gold nanoparticles: Biological synthesis approaches and potentials for biomedical applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.; Sherkar, R.; Shirsathe, C.; Sonwane, R.; Varpe, N.; Shelke, S.; More, M.P.; Pardeshi, S.R.; Dhaneshwar, G.; Junnuthula, V.; et al. Biofabrication of nanoparticles: Sources, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1159193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, N.; Singh, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Bhankar, V.; Kumar, K. Plant-Mediated Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Applications: A Review. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 163, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Bhatt, K.C. Diversity distribution and collection of genetic resources of cultivated and weedy type in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton var. frutescens and their uses in Indian Himalaya. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Perilla frutescens: A rich source of pharmacological active compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.V.; Li, H.; Hou, T.; Bethu, M.S.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Perilla frutescens leaf extract: Characterization and evaluation of antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Qiu, J.F.; Ma, L.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Li, P.; Wan, J.B. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L. (Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological investigations of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Molecules 2018, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Ren, Z.; Reddy, N.V.; Hou, T.; Zhang, Z.J. In silico evaluation of antimicrobial, antihyaluronidase and bioavailability parameters of rosmarinic acid in Perilla frutescens leaf extracts. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Osakabe, N.; Sanbongi, C.; Yanagisawa, R.; Inoue, K.I.; Yasuda, A.; Natsume, M.; Baba, S.; Ichiishi, E.I.; Yoshikawa, T. Extract of Perilla frutescens enriched for rosmarinic acid, a polyphenolic phytochemical, inhibits seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis in humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Luo, W.; Bao, B.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, F.; Yu, S.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Shan, M. A Comprehensive Review of Rosmarinic Acid: From Phytochemistry to Pharmacology and Its New Insight. Molecules 2022, 27, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ohto, Y.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H. Superoxide scavenging activity of rosmarinic acid from Perilla frutescens Britton var. acuta f. viridis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4545–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Hong, C.O.; Lee, G.P.; Kim, C.T.; Lee, K.W. The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Hwang, B.R.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, E.J. Perilla frutescens var. japonica and rosmarinic acid improve amyloid-β25-35 induced impairment of cognition and memory function. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Tsuji, M.; Matsumiya, T.; Kubo, M. Identification of rosmarinic acid as a novel antidepressive substance in the leaves of Perilla frutescens Britton var. acuta Kudo (Perillae Herba). Jpn. J. Psychopharmacol. 2002, 22, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, W.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, W.; Lou, W.J.; Gong, Y.Z.; Yuan, C.; Shao, Q.; Wang, N.; Guo, C.; Liu, F. Cardioprotective effect of rosmarinic acid against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of the NF-κB inflammatory signalling pathway and ROS production in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakabe, N.; Yasuda, A.; Natsume, M.; Yoshikawa, T. Rosmarinic acid inhibits epidermal inflammatory responses: Anticarcinogenic effect of Perilla frutescens extract in the murine two-stage skin model. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi’Ah, H.I.; Seedeh, F.; Supriyanto, G.; Zaidan, A.H. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and the development in analysis method. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 217, p. 012005. [Google Scholar]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Surface plasmon resonance optical sensor and antibacterial activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 121, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance: Nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Duan, R.; Yuan, J.; Quan, Y.; Yang, H.; Xi, M. A reusable localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for quantitative detection of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen in cervical cancer patients based on silver nanoparticles array. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobley, C.M.; Skrabalak, S.E.; Campbell, D.J.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles for plasmonic and sensing applications. Plasmonics 2009, 4, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustina, T.E.; Handayani, W.; Imawan, C. The UV-VIS spectrum analysis from silver nanoparticles synthesized using Diospyros maritima blume. Leaves extract. In Proceedings of the 3rd KOBI Congress, International and National Conferences (KOBICINC 2020), Bengkulu, Indonesia, 24–25 November 2020; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ider, M.; Abderrafi, K.; Eddahbi, A.; Ouaskit, S.; Kassiba, A. Silver metallic nanoparticles with surface plasmon resonance: Synthesis and characterizations. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Nath, S.S.; Chakdar, D.; Gope, G.; Bhattacharjee, R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their optical properties. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2010, 5, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface plasmon resonance: A versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azharuddin, M.; Zhu, G.H.; Das, D.; Ozgur, E.; Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.; Patra, H.K. A repertoire of biomedical applications of noble metal nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6964–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, M.; Hosny, S.; Alshangiti, D.M.; Nady, N.; Alkhursani, S.A.; Alkhaldi, H.; Al-Gahtany, S.A.; Ghobashy, M.M.; Gaber, G.A. Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 731–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Al Minshid, A.; Grassian, V.H. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy as a tool to probe surface adsorption on nanoparticles at the liquid–solid interface in environmentally and biologically relevant media. Analyst 2014, 139, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wypij, M.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Ostrowski, M.; Trzcińska, J.; Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Assessment of Their Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Study of Capping Proteins. Molecules 2020, 25, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Buchman, J.T.; Rodriguez, R.S.; Ring, H.L.; He, J.; Bantz, K.C.; Haynes, C.L. Stabilization of silver and gold nanoparticles: Preservation and improvement of plasmonic functionalities. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 664–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Senthamil Selvi, S.; Govindaraju, M.J.A.N. Seaweed-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Gracilaria corticata for its antifungal activity against Candida spp. Appl. Nanosci. 2013, 3, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J.; Beedu, S.R.; Jayaraman, A. Size-controlled green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its biological activity. Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, C.F.; Schaak, R.E. Tutorial on powder X-ray diffraction for characterizing nanoscale materials. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7359–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Kalyane, D.; Youngren-Ortiz, S.R.; Chougule, M.B.; Tekade, R.K. Importance of physicochemical characterization of nanoparticles in pharmaceutical product development. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 369–400. [Google Scholar]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londoño-Restrepo, S.M.; Jeronimo-Cruz, R.; Millán-Malo, B.M.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Rodriguez-García, M.E. Effect of the nano crystal size on the X-ray diffraction patterns of biogenic hydroxyapatite from human, bovine, and porcine bones. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.; Chang, R.K.; Hussain, M.A. Pharmaceutical development and regulatory considerations for nanoparticles and nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 3867–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lee, J.L. Electron microscopy techniques for imaging and analysis of nanoparticles. In Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 531–584. [Google Scholar]
- Bamal, D.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, G.; Kumar, M.; Singh, M.; Rani, N.; Mundlia, P.; Sehrawat, A.R. Silver nanoparticles biosynthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activities, applications, cytotoxicity and safety issues: An updated review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falke, S.; Betzel, C. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Principles, Perspectives, Applications to Biological Samples. In Radiation in Bioanalysis: Spectroscopic Techniques and Theoretical Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 173–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rajwar, A.; Vaswani, P.; Naveena, A.H.; Bhatia, D. Designer 3D-DNA nanodevices: Structures, functions, and cellular applications. In Advances in Protein Molecular and Structural Biology Methods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, R.; Singh, N.; Dhankhar, J.; Kama, G.; Sharma, R. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique, principle, theoretical considerations and applications. Nanotechnol. Biochem. Technol. Assess. Qual. Saf. Milk Milk Prod. 2018, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Vanitha, G.; Rajavel, K.; Boopathy, G.; Veeravazhuthi, V.; Neelamegam, P. Physiochemical charge stabilization of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial applications. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 669, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.N.; Kwon, S.; Cho, D. Formation and stability study of silver nano-particles in aqueous and organic medium. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria—“A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendrachari, S.; Swamy, B.E.K.; Reddy, S.; Chaira, D. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2013, 5, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, T.D.; Antunes, J.C.; Padrão, J.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Zille, A.; Amorim, M.T.P.; Ferreira, F.; Felgueiras, H.P. Activity of specialized biomolecules against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomoni, R.; Léo, P.; Montemor, A.F.; Rinaldi, B.G.; Rodrigues, M.F.A. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 12, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, P.R.; Pandit, S.; Filippis, A.D.; Franci, G.; Mijakovic, I.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles: Bactericidal and mechanistic approach against drug resistant pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of action and probable bio-application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Interactions of gold and silver nanoparticles with bacterial biofilms: Molecular interactions behind inhibition and resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, S.; Subramaniyan, S.; Karunanithi, N.; Vasanthakumar, P.; Kutzner, A.; Kim, P.S.; Heese, K. antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Bauhinia Tomentosa Linn. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, R.S.; Geetha, D.; Ramesh, P.S. Antioxidant activity of chemically synthesized AgNPs and biosynthesized Pongamia pinnata leaf extract mediated AgNPs–A comparative study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sytu, M.R.C.; Camacho, D.H. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from Lenzites betulina and the potential synergistic effect of AgNP and capping biomolecules in enhancing antioxidant activity. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Ram Singh, S.P.; Deenadhayalan, R.; Rajesh, V.V.; Padmanaban, S.; Radhakrishnan, K. Nanoparticles, a double-edged sword with oxidant as well as antioxidant properties—A review. Oxygen 2022, 2, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Huy, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, K.; Taratula, O.; Farsad, K. Applications of nanoparticles in biomedical imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 11, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, O.; Puiu, R.A.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Burdușel, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. An updated review on silver nanoparticles in biomedicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Baek, K.H. Phyto-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the rind extract of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) under photo-catalyzed condition and investigation of its antibacterial, anticandidal and antioxidant efficacy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Pomi, F.; Papa, V.; Borgia, F.; Vaccaro, M.; Allegra, A.; Cicero, N.; Gangemi, S. Rosmarinus officinalis and Skin: Antioxidant Activity and Possible Therapeutical Role in Cutaneous Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, G.; Ros, G.; Castillo, J. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis, L.): A review. Medicines 2018, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in various cell lines: An in vitro model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grijalva, M.; Vallejo-López, M.J.; Salazar, L.; Camacho, J.; Kumar, B. Cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects of nanomaterials on cancer cell lines: A review. In Unraveling the Safety Profile of Nanoscale Particles and Materials—From Biomedical to Environmental Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 63–85. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/57434 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free. Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Martins, C.S.; Prior, J.A. Silver nanoparticles as carriers of anticancer drugs for efficient target treatment of cancer cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, M.M.; Snyder, C.M.; Sloop, J.; Solst, S.R.; Donati, G.L.; Spitz, D.R.; Furdui, C.M.; Singh, R. The mechanism of cell death induced by silver nanoparticles is distinct from silver cations. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health impact of silver nanoparticles: A review of the biodistribution and toxicity following various routes of exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musicco, C.; Signorile, A.; Pesce, V.; Loguercio Polosa, P.; Cormio, A. Mitochondria Deregulations in Cancer Offer Several Potential Targets of Therapeutic Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.H.; Ngo, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, P.H. Anti-cancer activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Ardisia gigantifolia leaf extract against gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 661, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Merloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Tested Substance | S. aureus ZoI (mm) | B. subtilis ZoI (mm) | P. aeruginosa ZoI (mm) | E. coli ZoI (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomycin | 19.92 ± 1.28 | 19.13 ± 0.86 | 17.20 ± 1.05 | 17.86 ± 0.75 |
| PFRAE | 7.57 ± 0.42 | 8.56 ± 0.53 | 6.83 ± 0.52 | 7.23 ± 0.65 |
| 2 mM AgNO3 | 10.64 ± 0.72 | 9.84 ± 1.23 | 9.97 ± 0.76 | 9.43 ± 0.99 |
| PFRAE-AgNPs | 14.49 ± 1.15 | 15.81 ± 0.68 | 13.06 ± 0.79 | 13.79 ± 0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Netala, V.R.; Hou, T.; Sana, S.S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities. Molecules 2024, 29, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061250
Netala VR, Hou T, Sana SS, Li H, Zhang Z. Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061250
Chicago/Turabian StyleNetala, Vasudeva Reddy, Tianyu Hou, Siva Sankar Sana, Huizhen Li, and Zhijun Zhang. 2024. "Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061250
APA StyleNetala, V. R., Hou, T., Sana, S. S., Li, H., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Perilla frutescens Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach for Multifunctional Biomedical Applications including Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities. Molecules, 29(6), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061250






