Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Phosphatase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Groups of Mice
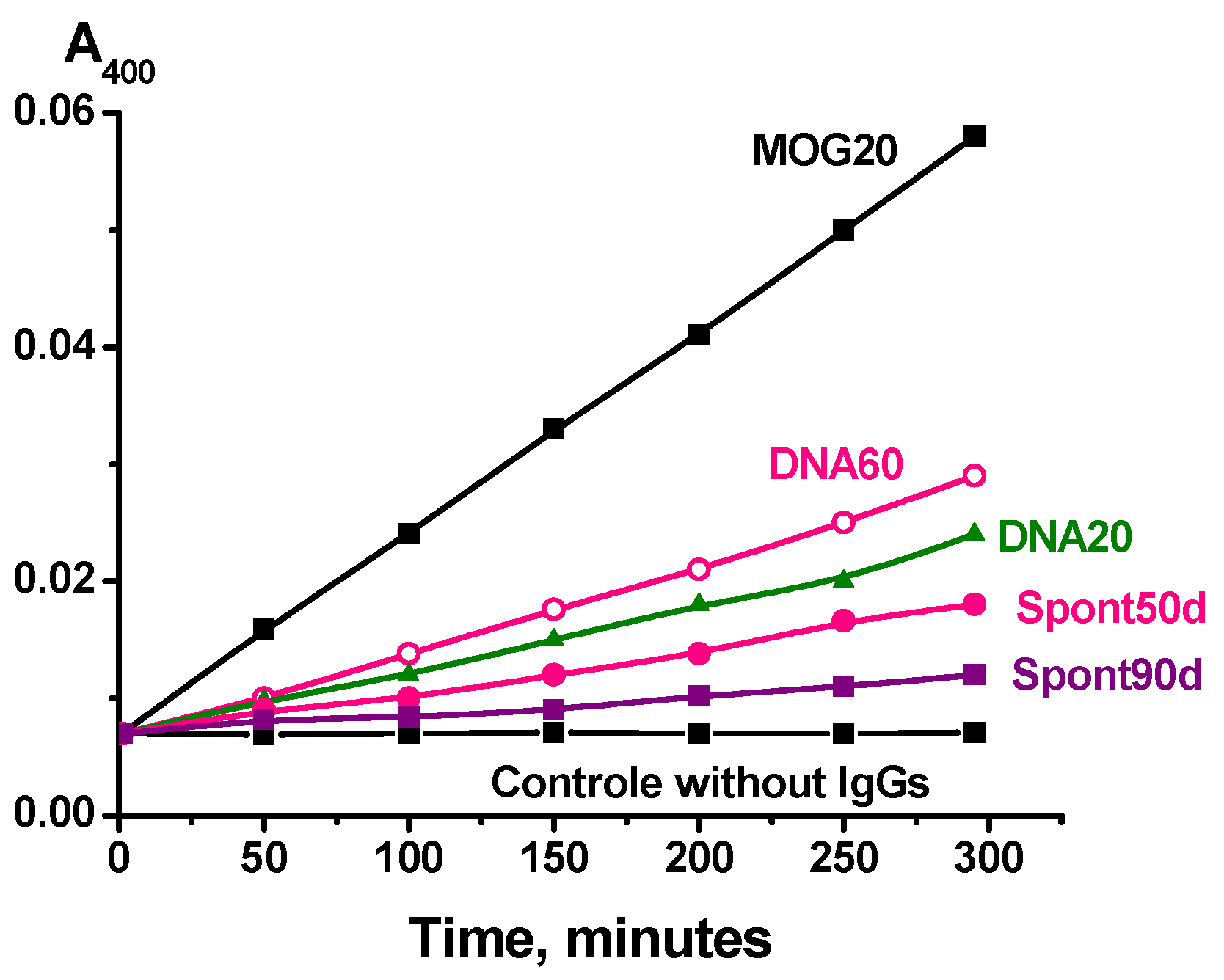
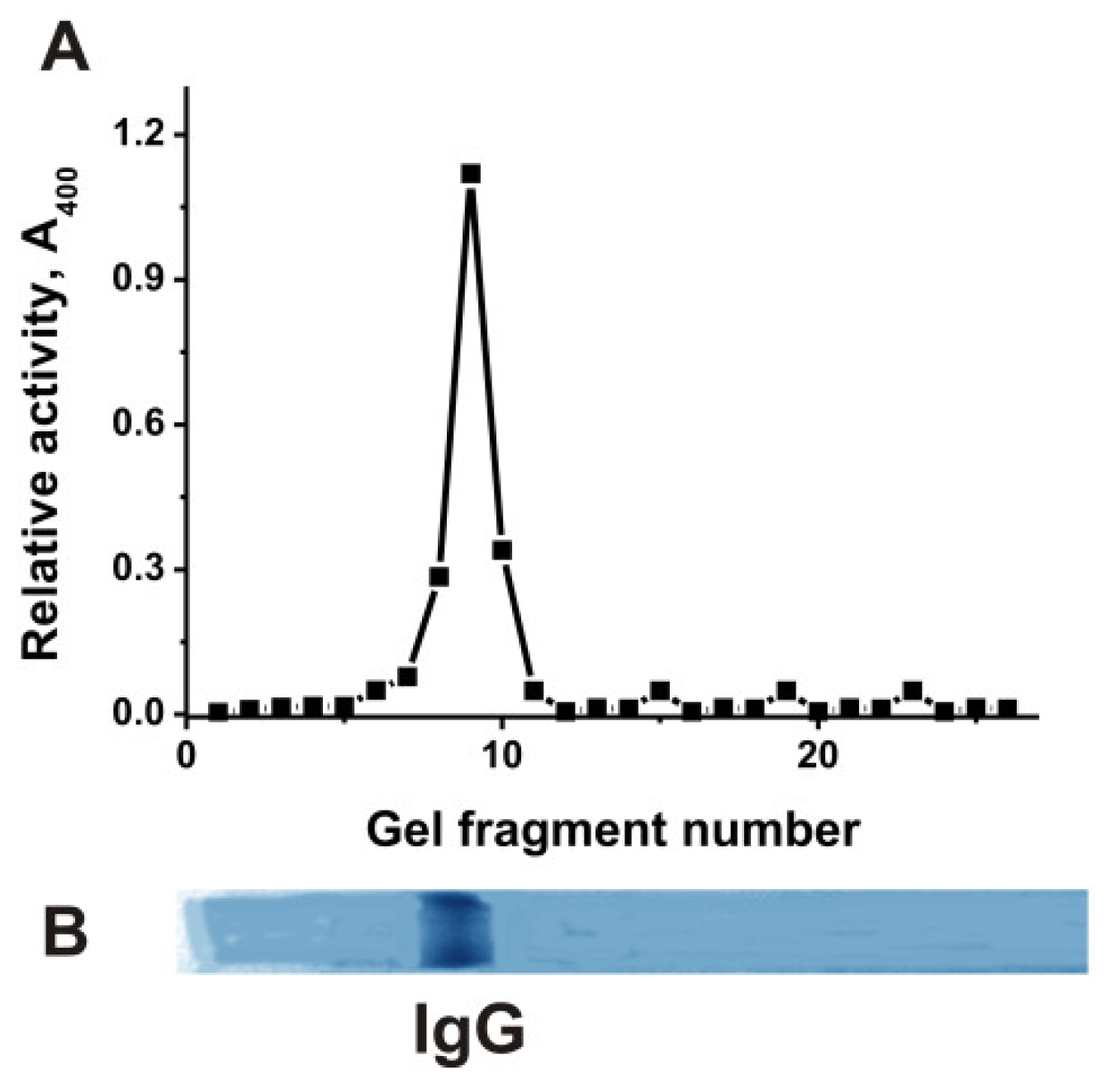
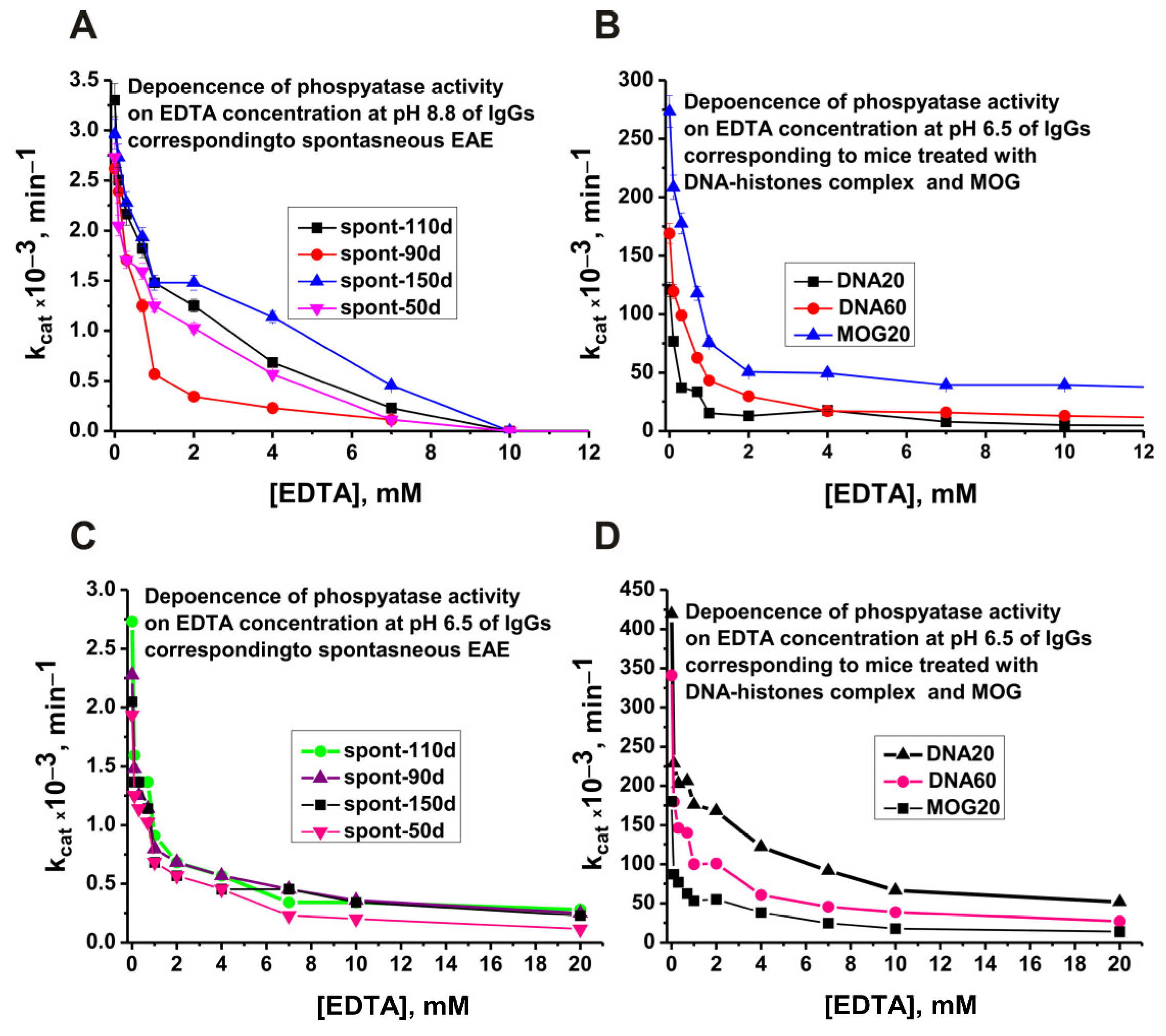
2.2. Phosphatase Activity Assay
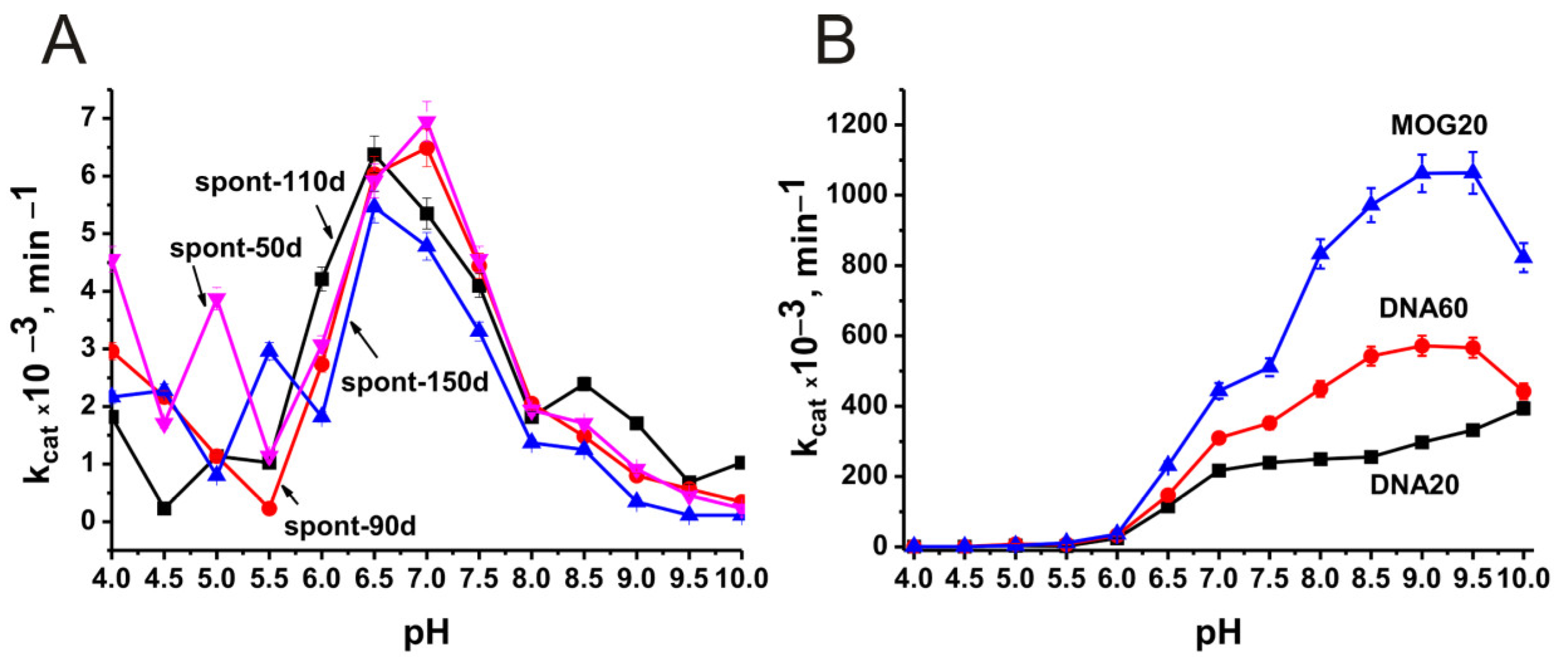
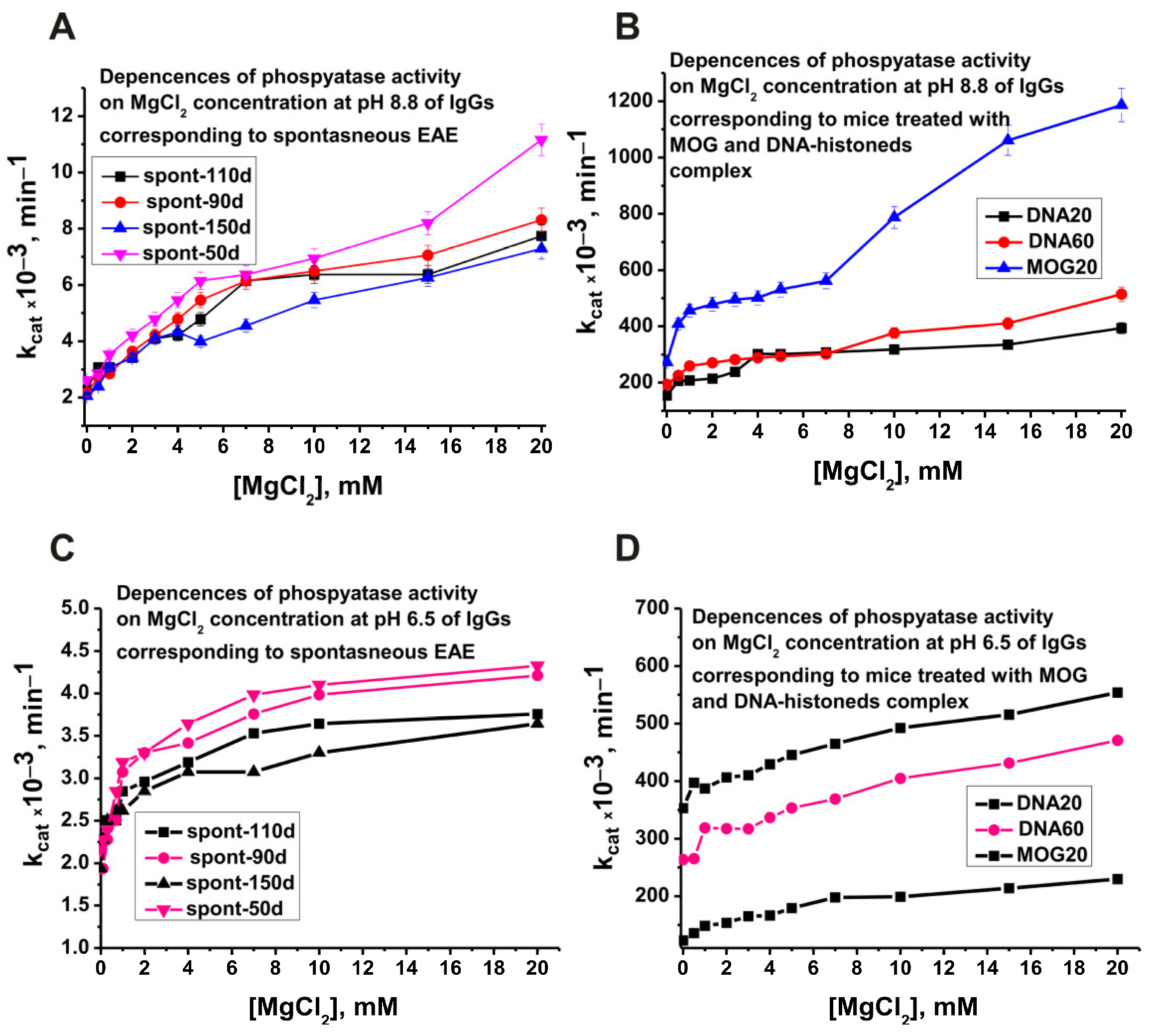
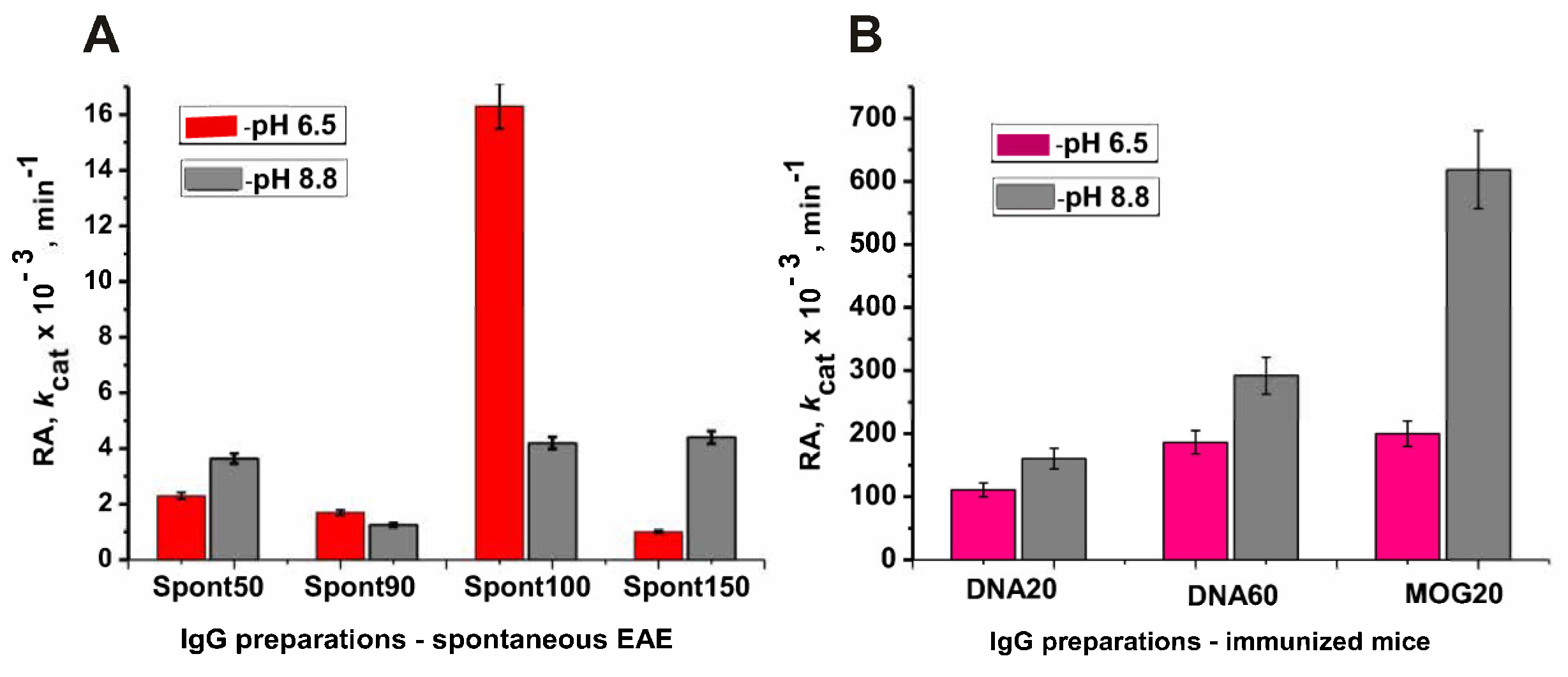
2.3. Optimal pH of Substrate Hydrolysis
2.4. Changes in the Phosphatase Activity over Time during the Development of EAE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Immunization of Mice
4.4. IgG Purification
4.5. Phosphatase Activity Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lerner, R.A.; Tramontano, A. Antibodies as enzymes. Trends Bioch. Sci. 1987, 12, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.D.; Benkovic, S.J. Recent developments in catalytic antibodies. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.B.; Schultz, P.G. Opportunities at the interface of chemistry and biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, A.; Gololobov, G.; Paul, S. Proteolytic antibodies: Origins, selection and induction. Chem. Immunol. 2000, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S. Catalytic Antibodies: Design, Expression, and Their Applications in Medicine. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 1514–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keinan, E.E. (Ed.) Catalytic Antibodies; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ostler, E.L.; Resmini, M.; Brocklehurst, K.; Gallacher, G.J. Polyclonal catalytic antibodies. Immunol. Methods 2002, 269, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padiolleau-Lefèvre, S.; Ben Naya, R.; Shahsavarian, M.A.; Friboulet, A.; Avalle, B. Catalytic antibodies and their applications in biotechnology: State of the art. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.V.; Nishiyama, Y.; Paul, S. Catalytic antibodies and their applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S. Natural catalytic antibodies. Mol. Biotechnol. 1996, 5, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, J.D.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S. Noncanonical functions of antibodies. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootla, B.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Warrington, A.E.; Bieber, A.J.; Kaveri, S.V.; Rodriguez, M. Autoantibodies with enzymatic properties in human autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 37, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalanathan, A.S.; Goulvestre, C.; Weill, B.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A. Proteolysis activity of IgM antibodies from Rheumatoid arthritis patients’ sera: Evidence of atypical catalytic site. J. Mol. Recogn. 2010, 23, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabibov, A.G.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Tretyak, E.B.; Paltsev, M.A.; Suchkov, S.V. Catalytic autoantibodies in clinical autoimmunity and modern medicine. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyr, A.V.; Gabibov, A.G. DNA-hydrolyzing Ab: Is catalytic activity a clue for physiological significance? Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, N.A.; Vorobiev, I.I.; Alexandrova, E.S.; Reshetnyak, A.V.; Telegin, G.B.; Khaidukov, S.V.; Avalle, B.; Karavanov, A.; Morse, H.C., 3rd; Thomas, D.; et al. Induction of a protein-targeted catalytic response in autoimmune prone mice: Antibody-mediated cleavage of HIV-1 glycoprotein GP120. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belogurov, A., Jr.; Kozyr, A.; Ponomarenko, N.; Gabibov, A. Catalytic antibodies: Balancing between Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. Bioessays 2009, 31, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Autoimmune processes in multiple sclerosis: Production of harmful catalytic antibodies associated with significant changes in the hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and proliferation. In Multiple Sclerosis; Conzalez-Quevedo, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 100–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A. The extreme diversity of autoantibodies and abzymes against different antigens in patients with various autoimmune diseases. In Advances in Medicine and Biology; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 184, pp. 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, K.C.; Bar-Or, A.; Hafler, D.A. The neuroimmunology of multiple sclerosis: Possible roles of T and B lymphocytes in immunopathogenesis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 21, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjaly, Z.M.; Harrison, N.A.; Critchley, H.D.; Do, C.T.; Stefanics, G.; Wenderoth, N.; Lutterotti, A.; Müller, A.; Stephan, K.E. Pathophysiological and cognitive mechanisms of fatigue in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, H.N.; Warrington, A.E.; Rodriguez, M. Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms of Disease and Strategies for Myelin and Axonal Repair. Neurol. Clin. 2018, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, B.; Archelos, J.J.; Hartung, H.P. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Murúa, S.; Farez, M.F.; Quintana, F.J. The Immune Response in Multiple Sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, F.; Vigne, S.; Pot, C. Resolution of inflammation during multiple sclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, A.L.; Kurschus, F.C.; Waisman, A. Mouse models for multiple sclerosis: Historical facts and future implications. Bochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; Karpus, W.J. Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in the Mouse. In Current Protocols in Immunology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Chapter 15; pp. 15.1.1–15.1.18. [Google Scholar]
- Mouse EAE Models. Overview and Model Selection Hooke Laboratories, Inc.; 2011–2013. Available online: https://blog.crownbio.com/models-multiple-sclerosis (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Pucino, V.; Formisano, L.; Matarese, G. Animal models of Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 759, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Amor, S. Mouse models of multiple sclerosis: Lost in translation? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.; McKee, C.; Halassy, S.; Kojan, S.; Feinstein, D.L.; Chaudhry, G.R. Neural stem cells derived from primitive mesenchymal stem cells reversed disease symptoms and promoted neurogenesis in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheikl, T.; Pignolet, B.; Mars, L.T.; Liblau, R.S. Transgenic mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 4011–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehara, S.; Kawamura, M.; Takao, F. Organ-specific and systemic autoimmune diseases originate from defects in hematopoietic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8341–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, J.P.; Risitano, A. Hematopoietic stem cells in aplastic anemia. Arch. Med. Res. 2003, 34, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.A.; Rossi, D.J. Stem cells and aging in the hematopoietic system. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, Z.W.; Ju, Z.; Wang, Z.Q. DNA Damage Response in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Ageing. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andryushkova, A.S.; Kuznetsova, I.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Toporkova, L.B.; Sakhno, L.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Chernykh, E.R.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Formation of different abzymes in autoimmune-prone MRL-lpr/lpr mice is associated with changes in colony formation of haematopoetic progenitors. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronin, V.B.; Parkhomenko, T.A.; Korablev, A.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaja, A.A.; Sennikov, S.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Changes in different parameters, lymphocyte proliferation and hematopoietic progenitor colony formation in EAE mice treated with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulova, K.S.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaya, A.A.; Sedykh, S.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Changes in cell differentiation and proliferation lead to production of abzymes in EAE mice treated with DNA-Histone complexes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5816–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusov, A.E.; Tolmacheva, A.S.; Aulova, K.S.; Nevinsky, G.A. Autoantibody-Abzymes with Catalase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyr, A.V.; Kolesnikov, A.V.; Aleksandrova, E.S.; Sashchenko, L.P.; Gnuchev, N.V.; Favorov, P.V.; Kotelnikov, M.A.; Iakhnina, E.I.; Astsaturov, I.A.; Prokaeva, T.B.; et al. Novel functional activities of anti-DNA autoantibodies from sera of patients with lymphoproliferative and autoimmune diseases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1998, 75, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.L. Alkaline Phosphatases: Structure, substrate specificity and functional relatedness to other members of a large superfamily of enzymes. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, L.; Huttová, J.; Mistrk, I.; Kogan, G. Effect of carboxymethyl chitin-glucan on the activity of some hydrolytic enzymes in maize plants. Chem. Pap. 2002, 56, 326–329. [Google Scholar]
- Alkaline Phosphatase Level Test (ALP). Healthline. Available online: https://www.testing.com/tests/alkaline-phosphatase-alp/ (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Badve, S.V.; Zhang, L.; Coombes, J.S.; Pascoe, E.M.; Cass, A.; Clarke, P.; Ferrari, P.; McDonald, S.P.; Morrish, A.T.; Pedagogos, E.; et al. Association between serum alkaline phosphatase and primary resistance to erythropoiesis stimulating agents in chronic kidney disease: A secondary analysis of the HERO trial. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2015, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, M.; Mizumori, M.; Watanabe, C.; Wang, J.H.; Inoue, T.; Nakano, T.; Guth, P.H.; Engel, E.; Kaunitz, J.D.; Akiba, Y. Endogenous luminal surface adenosine signaling regulates duodenal bicarbonate secretion in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, F.; Perfetto, L.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G. The human phosphatase interactome: An intricate family portrait. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaline Phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1)|Protein Target—PubChem. Available online: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov›protein/EC:3.1.3.1 (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Savel’ev, A.N.; Eneyskaya, E.V.; Shabalin, K.A.; Filatov, M.V.; Neustroev, K.N. Antibodies with amylolytic activity. Protein Pept. Lett. 1999, 6, 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Volle, D.J.; Beach, C.M.; Johnson, D.R.; Powell, M.J.; Massey, R.J. Catalytic hydrolysis of vasoactive intestinal peptide by human autoantibody. Science 1989, 244, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Paul, S.; Tyutyulkova, S.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Kaveri, S.J. Catalytic activity of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 3328–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaga, R.; Li, L.; O’Dell, J.R.; Paul, S. Unexpected presence of polyreactive catalytic antibodies in IgG from unimmunized donors and decreased levels in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnorutskii, M.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. DNase, RNase, and phosphatase activities of antibodies formed upon immunization by DNA, DNase I, and DNase II. Biochemistry 2011, 76, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnorutskii, M.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Antibodies against pancreatic ribonuclease A hydrolyze RNA and DNA. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusov, A.E.; Aulova, K.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis of Mice: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H4 Histone by IgGs against Histones and Myelin Basic Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusov, A.E.; Aulova, K.S.; Dmitnok, P.S.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. EAE of Mice: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H2B Histone by IgGs against H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 Histones and Myelin Basic Protein. Molecules 2023, 28, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaitov, R.M.; Ignatieva, G.A.; Sidorovich, I.G. Immunology; Medicine: Russia, Moscow, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, R.B.; Bowers, G.N.; Posen, S. Measurement of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity. In Alkaline Phosphatase; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1979; pp. 289–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaya, A.A.; Sennikov, S.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Changes in haematopoietic progenitor colony differentiation and proliferation and the production of different abzymes in EAE mice treated with DNA. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3795–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Increase in Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Peroxidase and Oxidoreductase Activities in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology. Molecules 2021, 26, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovskaya, V.V.; Andryushkova, A.S.; Kuznetsova, I.A.; Toporkova, L.B.; Buneva, V.N.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. DNA-hydrolyzing antibodies from sera of autoimmune-prone MRL/MpJ-lpr mice. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 1081. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urusov, A.E.; Aulova, K.S.; Nevinsky, G.A. Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Phosphatase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Molecules 2024, 29, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061382
Urusov AE, Aulova KS, Nevinsky GA. Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Phosphatase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061382
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrusov, Andrey E., Kseniya S. Aulova, and Georgy A. Nevinsky. 2024. "Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Phosphatase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061382
APA StyleUrusov, A. E., Aulova, K. S., & Nevinsky, G. A. (2024). Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Phosphatase Activity in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Molecules, 29(6), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061382





