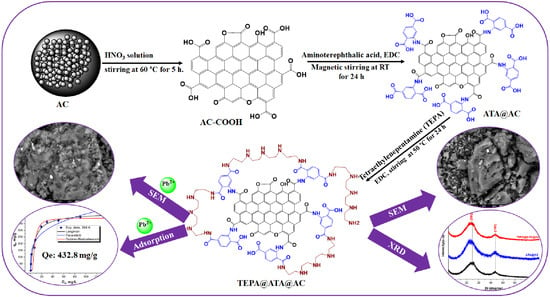
Tetraethylenepentamine-Grafted Amino Terephthalic Acid-Modified Activated Carbon as a Novel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Toxic Pb(II) from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
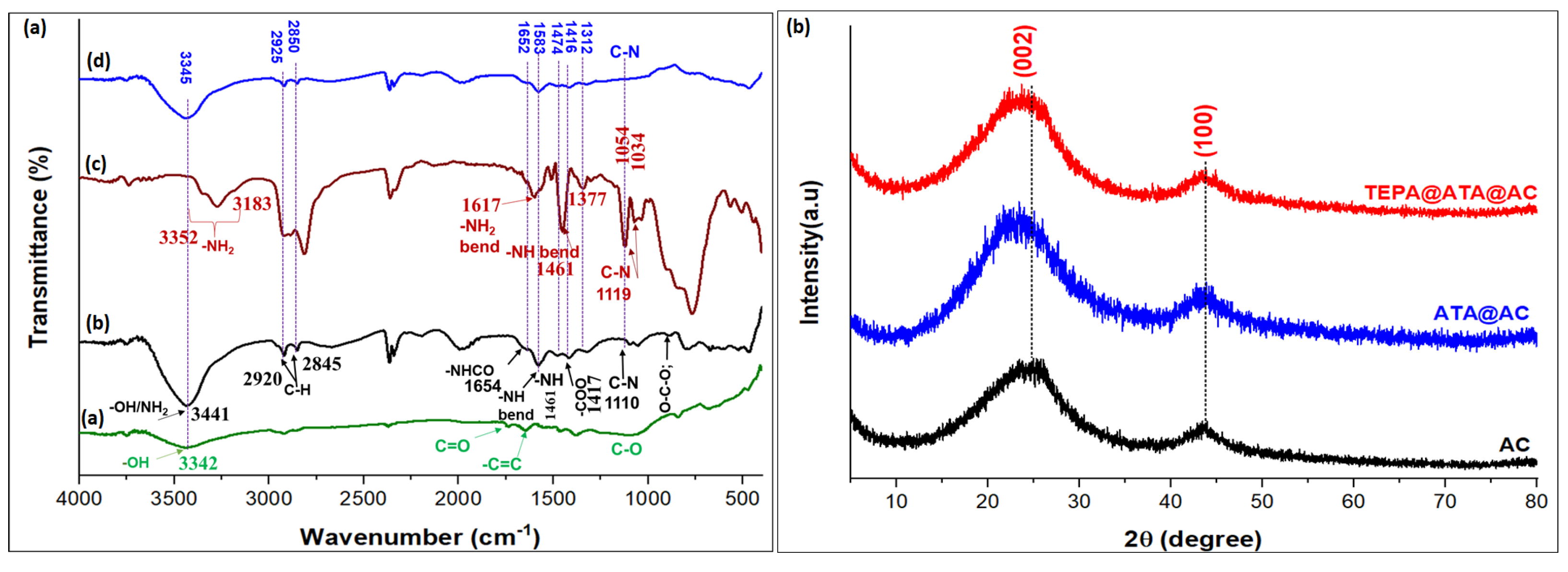
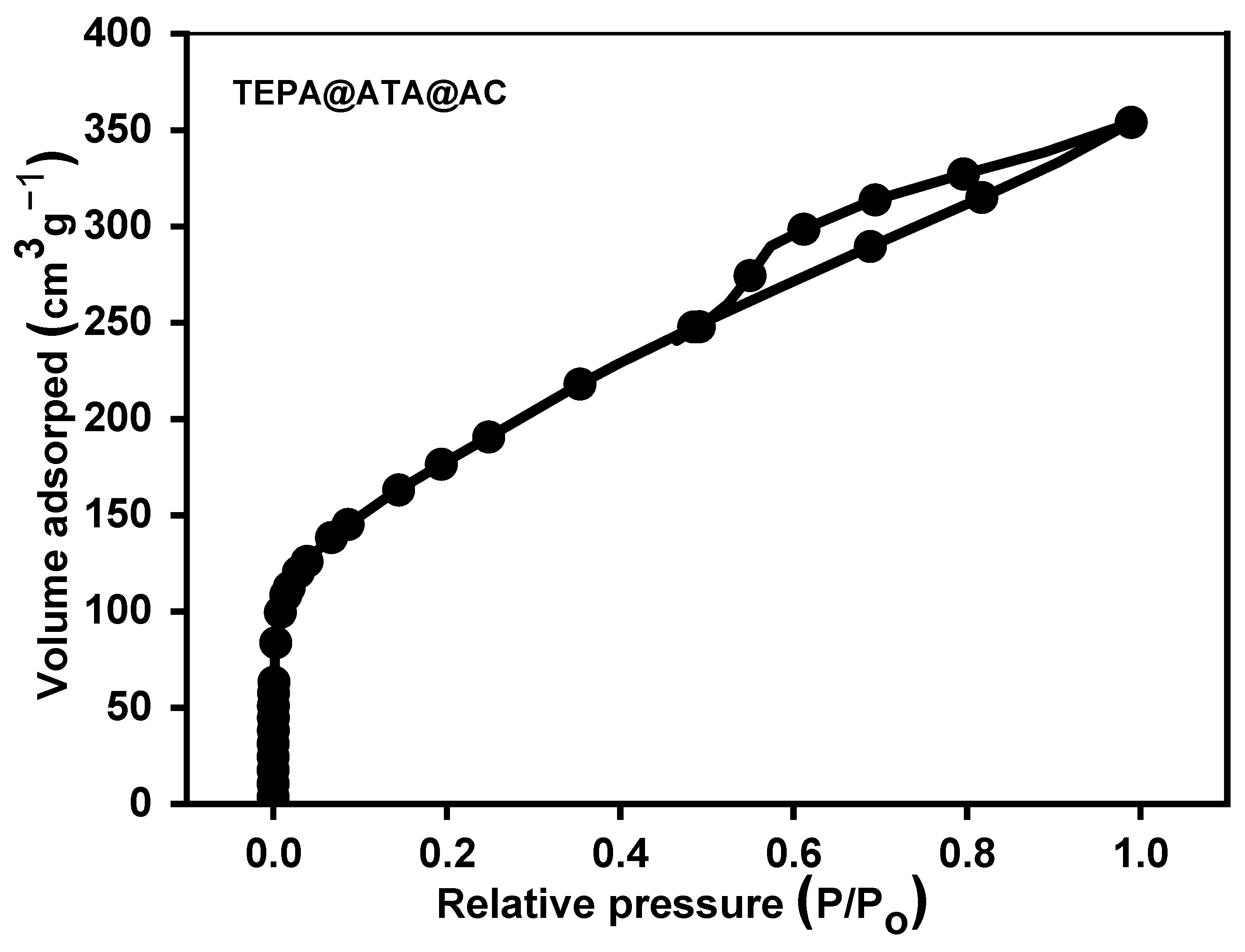
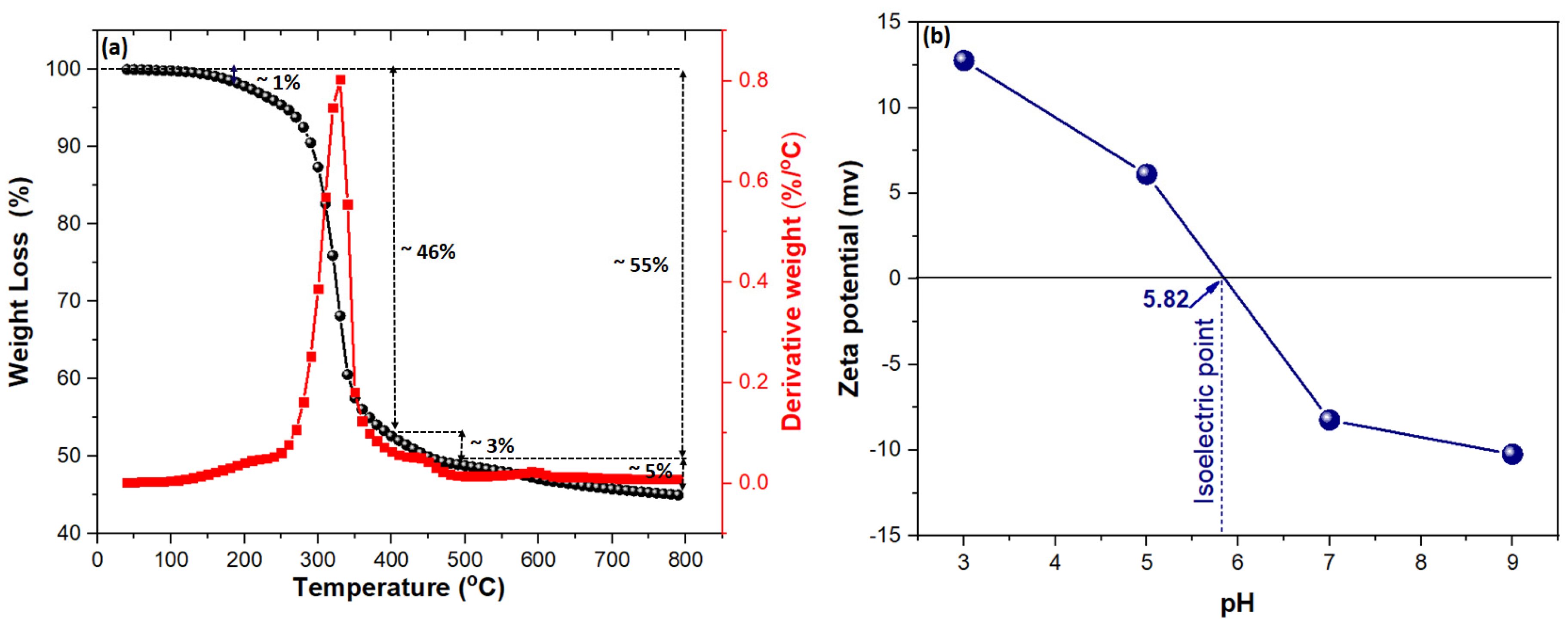
2.1. Characterization of Adsorbent
2.2. Optimization Conditions
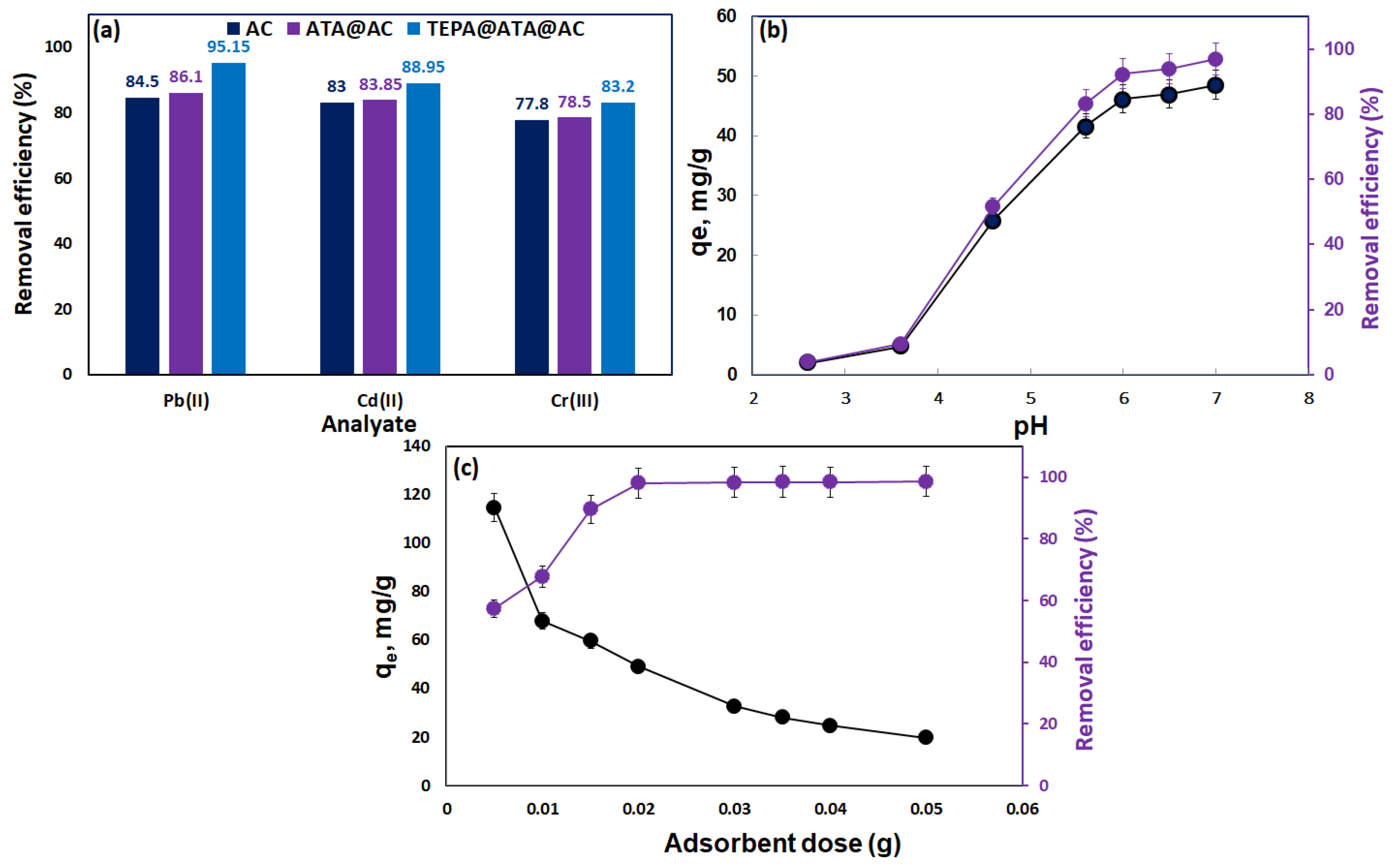
2.2.1. Selectivity Study
2.2.2. Impact of Initial pH
2.2.3. Effect of Composite Dose
2.3. Modeling Adsorption
2.3.1. Isotherms
2.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3.3. Thermodynamic Parameters
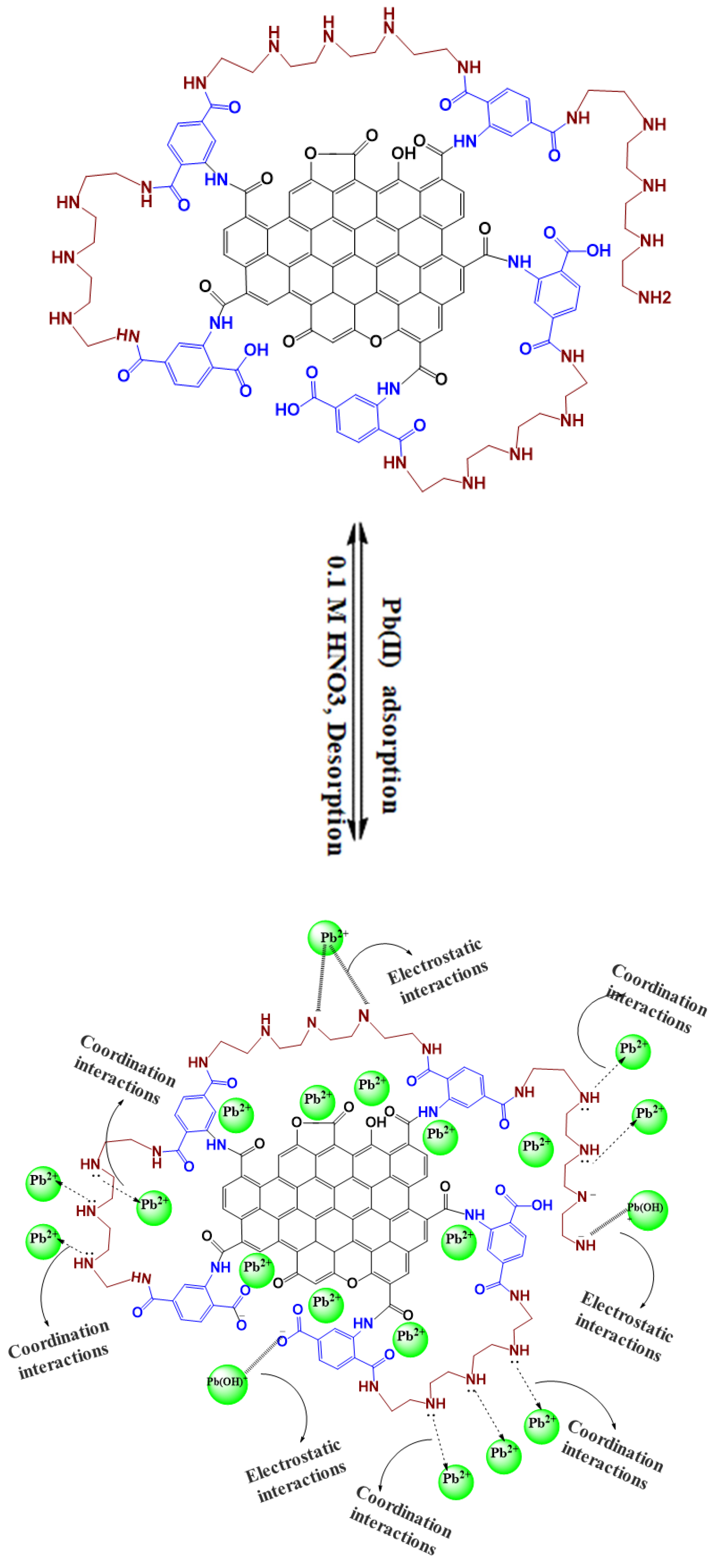
2.4. Removal Mechanism
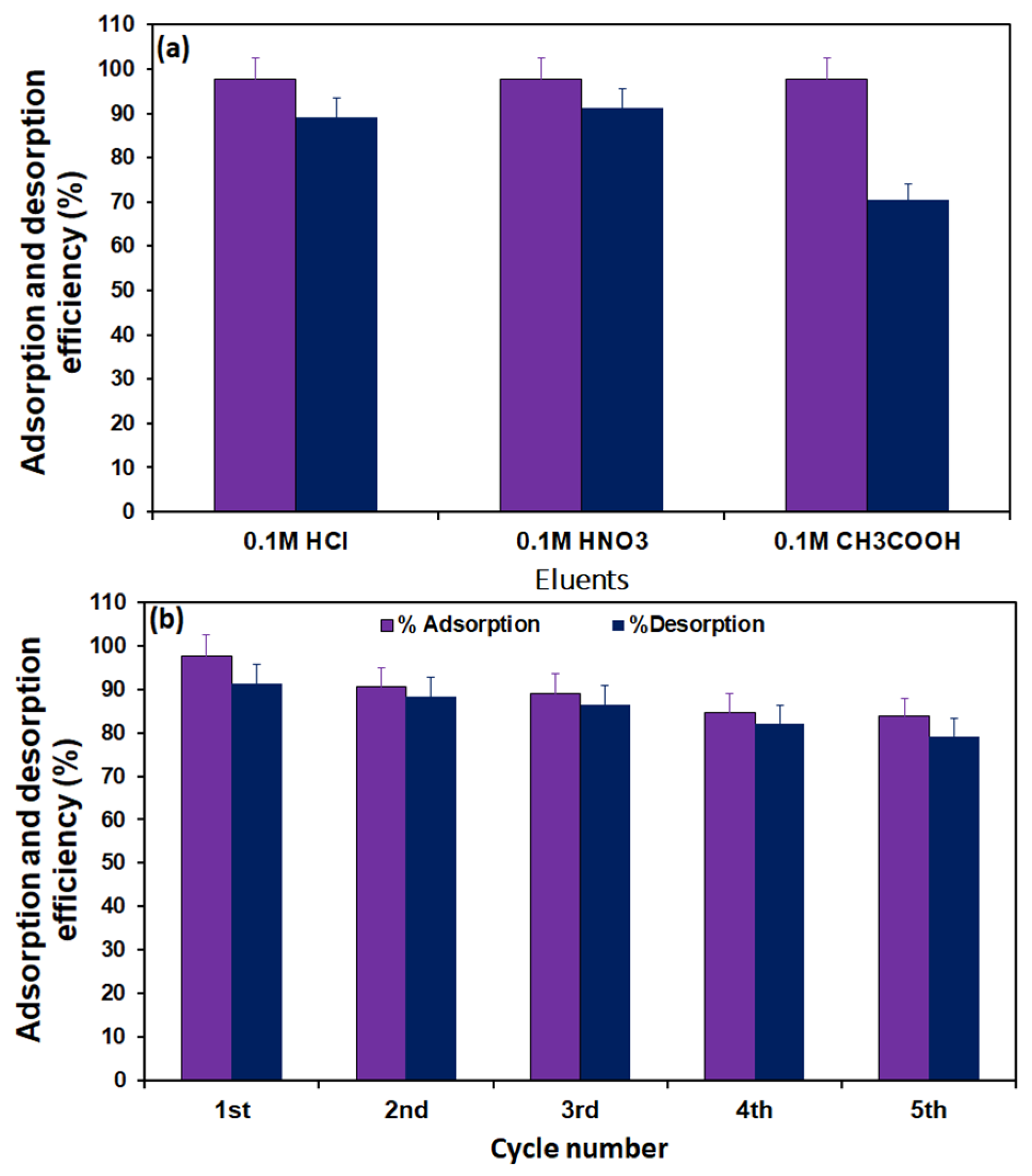
2.5. Regeneration of the Adsorbent
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization
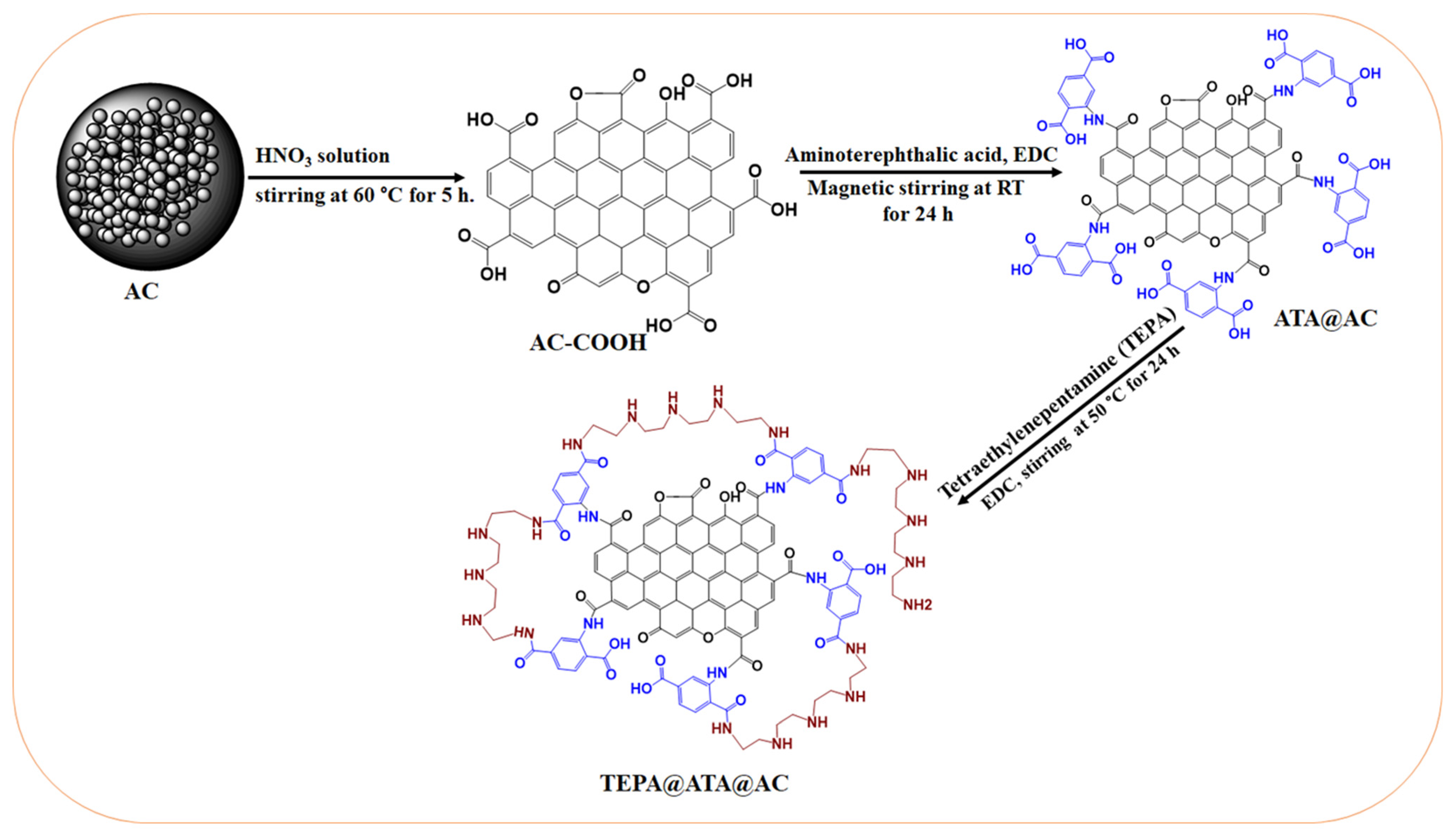
3.3. Preparation of TEPA@ATA@AC Composite
3.4. Adsorption Tests
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Al-Maswari, B.M.; Abdullah Alqadami, A.; Alshehri, S.M. Nickel ferrite bearing nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon as efficient adsorbent for the removal of highly toxic metal ion from aqueous medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Al-Sheetan, K.M. Development of a polymeric nanocomposite as a high performance adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from water medium: Equilibrium, kinetic and antimicrobial activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaimess, M.S. Sulfhydryl functionalized activated carbon for Pb(II) ions removal: Kinetics, isotherms, and mechanism. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Khan, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Ghfar, A.A. Determination of heavy metals in skin-whitening cosmetics using microwave digestion and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. IET Nanobiotechnology 2017, 11, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badvi Loulic, F.; Haji Seyed Mohammad Shirazi, R.; Miralinaghi, M.; Ahmad Panahi, H.; Moniri, E. Highly efficient removal of toxic As(V), Cd (II), and Pb(II) ions from water samples using MnFe2O4@SBA-15-(CH2)3-adenine as a recyclable bio-nanoadsorbent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 356, 112567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, R.; Sun, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y. Cellulose phosphonate/polyethyleneimine nano-porous composite remove toxic Pb(II) and Cu(II) from water in a short time. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar-Mahboub, M.; Khodeir, E.; Bahadori, M.; Mahdizadeh, S.M. Preparation of magnetic MgO/Fe3O4 via the green method for competitive removal of Pb and Cd from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 589, 124419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, G.; Alhseinat, E.; Ponpandian, N.; Khan, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Ahmed, F.; Alsharaeh, E.H. Development of adsorption and electrosorption techniques for removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater using novel magnetite/porous graphene-based nanocomposites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, S.A.; Otero, M.; Alanazi, H.S.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Khan, M.A.; Alothman, Z.A. Upcycling olive oil cake through wet torrefaction to produce hydrochar for water decontamination. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 170, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A. Development of citric anhydride anchored mesoporous MOF through post synthesis modification to sequester potentially toxic lead (II) from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Ghfar, A.A. Novel Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) Based Composite Material for the Sequestration of U(VI) and Th(IV) Metal Ions from Aqueous Environment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36026–36037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Algamdi, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Uslu, H.; Shukla, S.K. Removal of highly toxic Cd(II) metal ions from aqueous medium using magnetic nanocomposite: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Desalin Water Treat. 2020, 181, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, A.M.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alqadami, A.A.; Ali Abdalla, Z.E.; Saleh, E.A.M. Adsorptive performance of aminoterephthalic acid modified oxidized activated carbon for malachite green dye: Mechanism, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotan Alsohaimi, I.; Alhumaimess, M.S.; Abdullah Alqadami, A.; Tharwi Alshammari, G.; Fawzy Al-Olaimi, R.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; El-Sayed, M.Y.; Hassan, H.M. Adsorptive performance of aminonaphthalenesulfonic acid modified magnetic-graphene oxide for methylene blue dye: Mechanism, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 147, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xing, X.; Li, J.; Shi, M.; Lin, A.; Xu, C.; Zheng, J.; Li, R. Preparation of thiol-functionalized activated carbon from sewage sludge with coal blending for heavy metal removal from contaminated water. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, X.; Tu, Z.; Zhang, L. Preconcentration of Cu(II), Fe(III) and Pb(II) with 2-((2-aminoethylamino)methyl)phenol-functionalized activated carbon followed by ICP-OES determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtazaoğlu, Ç.; Teğin, İ.; Saka, C. Facile hydrogen peroxide modification of activated carbon particles produced by potassium hydroxide activation for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Barakat, S.; Van Bramer, S.E.; Nelson, K.A.; Hensley, D.K.; Chen, J. Noncompetitive and Competitive Adsorption of Heavy Metals in Sulfur-Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous Carbon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34132–34142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsohaimi, I.H.; Alhumaimess, M.S.; Hassan, H.M.A.; Reda, M.; Aldawsari, A.M.; Chen, Q.; Kariri, M.A. Chitosan Polymer Functionalized-Activated Carbon/Montmorillonite Composite for the Potential Removal of Lead Ions from Wastewater. Polymers 2023, 15, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirenda, J.; Kalaba, G.; Munyati, O. Synthesis and characterization of an activated carbon-supported silver-silica nanocomposite for adsorption of heavy metal ions from water. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, K.; Gong, Y.; Peng, H.; Qi, W. PEI-modified chitosan/activated carbon composites for Cu(II) removal from simulated pyrophosphate plating rinsing wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Larese-Casanova, P. Application of positively-charged ethylenediamine-functionalized graphene for the sorption of anionic organic contaminants from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Shahrom, M.S.; Nordin, A.R.; Wilfred, C.D. Activated Carbon Supported Amine Functionalized Ionic Liquids for CO2 Sorption. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1123, 12069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Preparation and amino modification of mesoporous carbon from bagasse via microwave activation and ethylenediamine polymerization for Pb (II) adsorption. Desalin Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24004–24018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Yahya, M.D.; Auta, M.; Obayomi, K.S. Facile preparation of amine-functionalized corn husk derived activated carbon for effective removal of selected heavy metals from battery recycling wastewater. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.T.; Huong, N.T.; Dan, L.L.; Tung, N.D.; Trung, V.B.; Minh, T.D. Removal of Heavy Metal Ion Using Polymer-Functionalized Activated Carbon: Aspects of Environmental Economic and Chemistry Education. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8887488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ran, X.; Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Dai, J. Single step synthesis of amine-functionalized mesoporous magnetite nanoparticles and their application for copper ions removal from aqueous solution. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 481, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Dai, K.; Sun, S.; Liu, G.; Yao, J. Novel ternary nanohybrids of tetraethylenepentamine and graphene oxide decorated with MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles for the adsorption of Pb(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsohaimi, I.H.; Alhumaimess, M.S.; Alqadami, A.A.; Hassan, H.M.A.; Chen, Q.; Alamri, M.S.; Alanzi, M.M.J.; Alraddadi, T.S. Chitosan-carboxylic acid grafted multifunctional magnetic nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for effective removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous environment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 280, 119017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Mashhadi, S.; Asif, M.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Microwave-assisted synthesis of tetraethylenepentamine functionalized activated carbon with high adsorption capacity for Malachite green dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Hou, X. AS-synthesized mesoporous silica MSU-1 modified with tetraethylenepentamine for CO2 adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Peng, X.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Meng, X.; Yu, G. Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by ion-imprinted tetraethylenepentamine modified chitosan beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Ou, H. A novel tetraethylenepentamine crosslinked chitosan oligosaccharide hydrogel for total adsorption of Cr(VI). Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Niu, C.-G.; Li, X.-T.; Liang, C.; Guo, H.; Lin, L.-S.; Zheng, C.-W.; Zeng, G.-M. Efficient removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solution with amino- and thiol-functionalized activated carbon: Isotherm and kinetics modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhaleefa, A.; Ali, I.H.; Brima, E.I.; Elhag, A.B.; Karama, B. Efficient Removal of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution by Date Seeds Powder Biosorbent: Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamics. Processes 2020, 8, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnour, A.Y.; Alghyamah, A.A.; Shaikh, H.M.; Poulose, A.M.; Al-Zahrani, S.M.; Anis, A.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar Microstructural Evolution, Physicochemical Characteristics, and Its Influence on Biochar/Polypropylene Composites. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Singh, A.; Jha, J.M.; Srivastava, N.; Hashem, A.; Alakeel, M.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Gupta, V.K. Low-cost biochar adsorbents prepared from date and delonix regia seeds for heavy metal sorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B.; Fang, P. Stabilization of Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Sites Using Sodium Tetraethylenepentamine-Multi Dithiocarbamate. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2016, 228, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Ma, Z. Microwave preparation of triethylenetetramine modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite for adsorption of Cr(VI). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farma, R. Physical properties analysis of activated carbon from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber on methylene blue adsorption. J. Technomaterial Phys. 2019, 1, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; Aly, M.H.; El-Howety, M.A.; El-Fadaly, E.; Al-Said, A. Synthesis of Chitosan@activated Carbon Beads with Abundant Amino Groups for Capture of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from Aqueous Solutions. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3590–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z. Removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions using magnetic chitosan resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, A.; Khan, M.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Alqadami, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Ahmed, A.Y.B.H. Mercerized mesoporous date pit activated carbon—A novel adsorbent to sequester potentially toxic divalent heavy metals from water. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Alsuhybani, M.; Algamdi, M. Excellent adsorptive performance of a new nanocomposite for removal of toxic Pb(II) from aqueous environment: Adsorption mechanism and modeling analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhybani, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Algamdi, M.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alqadami, A.A. Highly efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous systems using a new nanocomposite: Adsorption, isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaimess, M.S.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Alqadami, A.A.; Kamel, M.M.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Alshammari, H. Synthesis of phosphorylated raw sawdust for the removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous medium: Adsorption mechanism for clean approach. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, V.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Habibi, N.; Javanbakht, M. A novel magnetic chitosan/clinoptilolite/magnetite nanocomposite for highly efficient removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Mubeen, I.; Pervaiz, E.; Nasir, H. Enhanced removal of toxic Cr(vi) and Pb(ii) from water using carboxylic terminated Ti3C2Tx nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 23320–23333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, A.; Dollard, M.F. Local and global factors in work stress—The Australian dairy farming examplar. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health Suppl. 2008, 34, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M.; Radushkevich, L.V. Equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Proc. Acad. Sci. USSR Phys. Chem. Sect. 1947, 1, 857. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, M.D.; Obayomi, K.S.; Abdulkadir, M.B.; Iyaka, Y.A.; Olugbenga, A.G. Characterization of cobalt ferrite-supported activated carbon for removal of chromium and lead ions from tannery wastewater via adsorption equilibrium. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Aniagor, C.O.; Nasr, M.F.; Abou-Okeil, A. Efficacy of treated sodium alginate and activated carbon fibre for Pb(II) adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishri, H.M.; Marwani, H.M.; Batterjee, M.G.; Soliman, E.M. Eriochrome Blue Black modified activated carbon as solid phase extractor for removal of Pb(II) ions from water samples. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1955–S1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by magnetic activated carbon and its mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Liu, Y.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Baig, S.A.; Xu, X. Adsorptive removal of Pb(II) by magnetic activated carbon incorporated with amino groups from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 62, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, K.; Lou, Z.; Baig, S.A.; Xu, X. Application of EDTA-functionalized bamboo activated carbon (BAC) for Pb(II) and Cu(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Y.; Liu, H. Rapid and efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using biomass-derived activated carbon with humic acid in-situ modification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, S.M.; El-Wakil, A.M.; El-Maaty, W.M.A.; Awad, F.S. Efficient removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution by amine and thiol modified activated carbon. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.; Nada, A.A. Polyethylenimine −functionalized amorphous carbon fabricated from oil palm leaves as a novel adsorbent for Cr(VI) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xin, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q. Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption of Cr(III) and Pb(II) by graphene oxide/alginate hydrogel membrane: Characterization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Alshehri, S.M. Fabrication of magnetic polymeric resin for the removal of toxic metals from aqueous medium: Kinetics and adsorption mechanisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Response to “Some remarks on a critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the van’t Hoff equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S.; Eris, S.; Wilson, L.D. Re-evaluation of the century-old Langmuir isotherm for modeling adsorption phenomena in solution. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Adsorption-desorption characteristics and mechanisms of Pb(II) on natural vanadium, titanium-bearing magnetite-humic acid magnetic adsorbent. Powder Technol. 2019, 344, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Cagnetta, G.; Wang, W.; Meng, P.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Repo, E.; Yin, D.; Sillanpää, M.E.T. Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by a novel EGTA-modified chitosan material: Kinetics and isotherms. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 409, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Adsorption of Pb(II) on activated carbon prepared from Polygonum orientale Linn.: Kinetics, isotherms, pH, and ionic strength studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.S.; Hadavifar, M.; Ghasemi, S.S.; Arab Chamjangali, M. Synthesis of ZnO nanostructure using activated carbon for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Elemental Content (Wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | Pb(II) | |
| TEPA@ATA@AC | 72.33 | 24.20 | 3.47 | - |
| TEPA@ATA@AC/Pb(II) | 73.42 | 22.78 | 2.92 | 0.88 |
| Adsorbent | T (K) | qe,exp. (mg/g) | Langmuir | Freundlich | Dubinin-R | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm, (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg1−1/n·L1/n g−1) | n | R2 | qs, mg/g | KD-R (mol2 KJ−2) | E (kJ mol−1) | R2 | |||
| TEPA@ATA@AC | 298 | 410.4 | 432.8 | 0.1407 | 0.9728 | 125.4 | 3.79 | 0.9225 | 391.3 | 18.4 | 2.24 | 0.9017 |
| 318 | 354.5 | 395.7 | 0.0843 | 0.9687 | 93.5 | 3.46 | 0.8925 | 353.9 | 49.5 | 2.89 | 0.8874 | |
| 328 | 324.3 | 387.8 | 0.0488 | 0.9543 | 67.3 | 2.99 | 0.8774 | 334.8 | 117.5 | 10 | 0.8810 | |
| Adsorbent | Conditions | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfhydryl functionalized activated carbon | [Pb(II)]0—20–70 mg/L; pH—5.6; T—298 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.02 L; time—120 min | 116.3 | [4] |
| Thiol-functionalized activated carbon | [Pb(II)]0—5–300 mg/L; pH—5; T—298 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.02 L; time—1440 min | 232.02 | [36] |
| Cobalt ferrite-supported activated carbon | [Pb(II)]0—0.849 mg/L; pH—5; T—333 K; dose—800 mg; volume—0.1 L; time—80 min | 6.27 | [54] |
| Sodium alginate (TSA) and activated carbon fiber | [Pb(II)]0—400 mg/L; pH—5; T—303 K; dose—30 mg; volume—0.1 L; time—30 min | 221.3 | [55] |
| Eriochrome Blue Black-modified activated carbon | [Pb(II)]0—150 mg/L; pH—7; T—298 K; dose—25 mg; volume—0.025 L; time—60 min | 127.9 | [56] |
| Magnetized activated carbons (MAC) | [Pb(II)]0—40–700 mg/L; pH—5; T—298 K; dose—0.25 mg/L: time—720 min | 253.2 | [57] |
| AC/Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 | [Pb(II)]0—20–250 mg/L; pH—5.2; T—303 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.025 L; time—1440 min | 104.2 | [58] |
| Bamboo-activated carbon@SiO2-ETDA | [Pb(II)]0—50–100 mg/L; pH—5.3; T—303 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.025 L; time—1440 min. | 45.5 | [59] |
| Humic acid modified activated carbon adsorbent (AC-HA) | [Pb(II)]0—50–100 mg/L; pH—5.5; T—303 K; dose—30 mg; volume—0.05 L; time—720 min | 250 | [60] |
| 2-Aminothiazol-modified activated carbon (AT-AMC) | [Pb(II)]0—10–800 mg/L; pH—5.5; T—298 K; dose—10 mg; volume—0.01 L; time—60 min | 310.9 | [61] |
| Polyethylenimine-modified carbon thin film (ACTF-PEI) | [Pb(II)]0—5–250 mg/L; pH—5; T—298 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.02 L; time—30 min | 143 | [62] |
| Magnetic-activated carbon incorporated with amino groups | [Pb(II)]0—5–250 mg/L; pH—6; T—298.15 K; dose—10 mg; volume—0.02 L; time—180 min | 104.2 | [63] |
| TEPA@ATA@AC | [Pb(II)]0—20–300 mg/L; pH—6.5; T—298 K; dose—20 mg; volume—0.05 L; time—300 min | 432.8 | This study |
| [Pb(II)]0 (mg/L) | qe,exp. (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, cal. (mg/g) | K1 (1/min) | R2 | qe2, cal. (mg/g) | K2 (g/mg-min) | R2 | A (mg/g min) | Β (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| 20 | 48.85 | 48.13 | 0.027 | 0.9933 | 53.47 | 6.61.10–4 | 0.9929 | 4.09 | 0.097 | 0.9536 |
| Adsorbent | Temperature (K) | ΔG (kJ mol−1) | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (J mol−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEPA@ATA@AC | 298 | −23.95 | −42.16 | −60.99 |
| 318 | −23.45 | |||
| 328 | −22.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshammari, M.S. Tetraethylenepentamine-Grafted Amino Terephthalic Acid-Modified Activated Carbon as a Novel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Toxic Pb(II) from Water. Molecules 2024, 29, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071586
Alshammari MS. Tetraethylenepentamine-Grafted Amino Terephthalic Acid-Modified Activated Carbon as a Novel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Toxic Pb(II) from Water. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071586
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshammari, Mutairah S. 2024. "Tetraethylenepentamine-Grafted Amino Terephthalic Acid-Modified Activated Carbon as a Novel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Toxic Pb(II) from Water" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071586
APA StyleAlshammari, M. S. (2024). Tetraethylenepentamine-Grafted Amino Terephthalic Acid-Modified Activated Carbon as a Novel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Toxic Pb(II) from Water. Molecules, 29(7), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071586