A Study of the Micellar Formation of N-Alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides Based on the Physicochemical Properties of Their Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Density and Speed of Sound Measurements
2.2. Surface Properties
2.3. Apparent Molar Properties
2.4. Viscosity
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Dimethyl Alkyl Amines (Step 1—See Scheme 2)

- N,N-dimethylhexan-1-amine.
- N,N-dimethyloctan-1-amine.
- N,N-dimethyldecan-1-amine.
- N,N-dimethyldodecan-1-amine.
3.2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides (Step 2—See Scheme 2)
- N-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-N,N-dimethylhexan-1-aminium chloride (C6BetC2Cl).
- N-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-N,N-dimethyloctan-1-aminium chloride (C8BetC2Cl).
- N-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-N,N-dimethyldecan-1-aminium chloride (C10BetC2Cl).
- N-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-N,N-dimethyldodecan-1-aminium chloride (C12BetC2Cl).
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Density and Speed of Sound
3.5. Surface Tension
3.6. Viscosity
3.7. Dynamic Light Scattering
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernely, G.W. Zwitterionic surfactants: Structure and performance. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1978, 55, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rakshit, A.; Acharjee, A.; Saha, B. Biodegradability and biocompatibility: Advancements in synthetic surfactants. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleppan, V.T.; King, J.P.; Butler, C.S.G.; Williams, A.P.; Tuck, K.L.; Tabor, R.F. Heads or tails? The synthesis, self-assembly, properties and uses of betaine and betaine-like surfactants. Adv. Coll. Int. Sci. 2021, 297, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordes, R.; Holmberg, K. Amino acid-based surfactants—Do they deserve more attention? Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marignan, J.; Gauthier-Fournier, F.; Appell, J.; Akoum, F. Size and shape of micelles in the ternary system n-dodecylbetaine/water/1-pentanol. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weers, J.G. Solubilization in mixed micelles. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1990, 67, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorro, M.; Kamenka, N.; Faucompre, B.; Partyka, S.; Lindheimer, M.; Zana, R. Micellization and adsorption of a zwitterionic surfactant: N-dodecyl betaine effect of salt. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 110, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristori, S.; Maggiulli, C.; Appell, J.; Marchionni, G.; Martini, G. Magnetic resonance characterization of betaine micelles betaine−perfluoropolyether mixed vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 4155–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, C.R.; Malamud, D.; Schnaare, R.L. Antimicrobial evaluation of N-Alkyl betaines and N-Alkyl-N,N-Dimethylamine oxides with variations in chain length. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2514–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and physicochemical investigation of long alkyl chain betaine zwitterionic surfactant. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2008, 11, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleppan, V.T.; Moore, J.E.; McCoy, T.M.; Sokolova, A.V.; de Campo, L.; Wilkinson, B.L.; Tabor, R.F. Self-assembly of long-chain betaine surfactants: Effect of tailgroup structure on wormlike micelle formation. Langmuir 2018, 34, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, T.M.; King, J.P.; Moore, J.E.; Kelleppan, V.T.; Sokolova, A.V.; de Campo, L.; Manohar, M.; Darwish, T.A.; Tabor, R.F. The effects of small molecule organic additives on the self-assembly and rheology of betaine wormlike micellar fluids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, C.L.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety assessment of alkyl betaines as used in cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37 (Suppl. S1), 28S–46S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, A.H.; Idris, A.K.; Mohshim, D.F.; Yekeen, N.; Buriro, M.A. Influence of lauryl betaine on aqueous solution stability, foamability and foam stability. J. Petrol. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2019, 9, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.-J.; Zhang, T.-C.; Pan, Y.-P.; Zhang, X. The effect of betaine surfactants on the association behavior of associating polymer. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucka, M.; Oświęcimska, M.; Witek, S. New biocides for cooling water treatment part, I.I.I. Quaternary ammonium salts derivatives of glycine esters. Environ. Prot. Eng. 1983, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Różycka-Roszak, B.; Przestalski, S.; Witek, S. Calorimetric studies of the micellization of some amphiphilic betaine ester derivatives. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 125, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różycka-Roszak, B.; Walkowiak, U.; Witek, S.; Przestalski, S. Micelle hydration by1H-NMR. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1989, 267, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstedt, M.; Allenmark, S.; Thompson, R.A.; Edebo, L. Antimicrobial activity of betaine esters, quaternary ammonium amphiphiles which spontaneously hydrolyze into nontoxic components. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, A.; Mezzetta, A.; Nowicki, J.; Łuczak, J.; Guazzelli, L. Betaine and L-carnitine ester bromides: Synthesis and comparative study of their thermal behaviour and surface activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, D.; Stjerndahl, M.; Holmberg, K. Ester-based surfactants: Are they stable enough? J. Surfact. Deterg. 2023, 26, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medoš, Ž.; Plechkova, N.V.; Friesen, S.; Buchner, R.; Bester-Rogač, M. Insight into the hydration of cationic surfactants: A thermodynamic and dielectric study of functionalized quaternary ammonium chlorides. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3759–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. A taste of the future. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, H.; Singla, M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clendennen, S.K.; Boaz, N.W. Betaine Amphoteric Surfactants—Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. In Biobased Surfactants, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oremusová, J.; Vitková, Z.; Vitko, A.; Tárník, M.; Miklovičová, E.; Ivánková, O.; Murgaš, J.; Krchňák, D. Effect of molecular composition of head group and temperature on micellar properties of ionic surfactants with C12 alkyl chain. Molecules 2019, 24, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvirova, I.M.; Kruchenok, T.B.; Épshtein, A.E.; Gleiberman, S.E.; Gorin, S.V.; Tsetlin, V.M. Comparative Bactericidal Activity of Quaternary Ammonium Salts. Pharm. Chem. J. 1984, 18, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, K.; Dey, R.; Acharya, Y.; Aswal, V.K.; Haldar, J. Cleavable, Amphiphilic Biocides with Ester-Bearing Moieties: Aggregation Properties and Antibacterial Activity. Langmuir 2024, 40, 3414–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Rub, M.A.; Azum, N.; Asiri, A.M. Mixed Micellization Study of Ibuprofen (Sodium Salt) and Cationic Surfactant (Conventional as Well as Gemini). J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2018, 31, e3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 84, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Effect of hard river water on the surface properties of surfactants. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1996, 41, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Chauhan, S. Effect of biologically active amino acids on the surface activity and micellar properties of industrially important ionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2014, 453, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, A.H.; Woodward, R.J. Surface-active betaines: N-Alkyl-N,N-Dimethylglycines and their critical micelle concentrations. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1963, 15, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenaizi, R.; Radiman, S.; Abdul Rahman, I.; Mohamed, F. Zwitterionic betaine transition from micelles to vesicles induced by cholesterol. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.D. The preparation of surface chemically pure sodium n-dodecyl sulfate by foam fractionation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 180, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, P.; Rhodes, C.T.; Swarbrick, J. Thermodynamics of micellization of N-alkyl betaines. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1965, 61, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevens, H.B. Structure and aggregation in dilute solution of surface active agents. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1953, 30, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-S.; Kida, T.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Hirao, T.; Ikeda, I. Surface-active properties of novel cationic surfactants with two alkyl chains and two ammonio groups. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Micelle shape and size. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. The molal volumes of electrolytes. Chem. Rev. 1971, 71, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucker, F.T. The apparent molal heat capacity, volume, and compressibility of electrolytes. Chem. Rev. 1933, 13, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.B.; Grigg, R.B.; Hepler, L.G. Thermodynamic properties of aqueous solutions of surfactants: Molar heat capacities and volumes. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1986, 18, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musbally, G.M.; Perron, G.; Desnoyers, J.E. Apparent molal volumes and heat capacities of ionic surfactants in water at 25 °C. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 48, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.B. On the characterization of micelle formation by means of experimental thermodynamic quantities. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1981, 259, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lisi, R.; Milioto, S.; Verrall, R.E. Partial molar volumes and compressibilities of alkyltrimethylammonium bromides. J. Solut. Chem. 1990, 19, 665–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Hazra, D.K. Micellization behaviour of lithium dodecyl sulphate in aqueous solutions using conductivity, density and adiabatic compressibility measurements. Indian J. Chem. 2005, 44, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, R.H.; Mills, R. Viscosities of Electrolytes and Related Properties; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, T.S.; Ahluwalia, J.C. Experimental studies on the structures of aqueous solutions of hydrophobic solutes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1973, 2, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisáirčik, M.; Devínsky, F.; Švajdlenka, E. Spherical dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide micelles in the limit region of transition to rod-like micelles. A light scattering study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 1996, 119, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, M.; Andreu, R.; González, D.; Calvente, J.J.; López-Pérez, G. An isotropic model for micellar systems: Application to sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions. Langmuir 2001, 17, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, A.; Patel, R.; Saraswat, J.; Khatoon, B.S.; Parray, M.U.D.; Wani, F.A.; Khan, M.R.; Busquets, R. Interfacial and antibacterial properties of imidazolium based ionic liquids having different counterions with ciprofloxacin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 629, 127474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishat, R.; Chabba, S.; Aswal, V.K.; Mahajan, R.K. Probing molecular interactions of tetracaine with surface active ionic liquid and subsequent formation of vesicle in aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, V.P.; Harikrishna, A.S.; Venkitasamy, K.; Gardas, R.L. Synergistic interaction and antibacterial properties of surface-active mono and di-cationic ionic liquids with ciprofloxacin. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, F.M.; Peresypkin, A.V. A combinatorially-derived structural phase diagram for 42 zwitterionic geminis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5614–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Synthesis, surface activity and thermodynamic properties of cationic gemini surfactants with diester and rigid spacers. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, J.-F.; Yin, B.; Zeng, F. Investigation of NNN pincer ruthenium(ii) complexes with a pendant hydroxyl group for n-monomethylation of amines and nitroarenes by methanol. ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-L.; Hnatyk, C.; Heaton, A.R.; Wood, B.; Goyette, C.M.; Gibson, J.M.; Tischler, J.L. A simplified, green synthesis of tertiary amines using the Leuckart-Wallach reaction in subcritical water. Tetrahedron Lett. 2022, 106, 154079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Lateef, H.M.; Soliman, K.A.; Tantawy, A.H. Novel synthesized Schiff Base-based cationic gemini surfactants: Electrochemical investigation, theoretical modeling and applicability as biodegradable inhibitors for mild steel against acidic corrosion. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 232, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5725-2; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 2: Basic Method for the Determination of Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Standard Measurement Method (ISO 5725-2:1994 Including Technical Corrigendum 1:2002). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Wandschneider, A.; Lehmann, J.K.; Heintz, A. Surface tension and density of pure ionic liquids and some binary mixtures with 1-propanol and 1-butanol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder-Kubis, J.; Geppert-Rybczyńska, M.; Musiał, M.; Talik, E.; Guzik, A. Exploring the surface activity of a homologues series of functionalized ionic liquids with a natural chiral substituent: (-)-menthol in a cation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soszka, N.; Hachuła, B.; Tarnacka, M.; Ozimina-Kamińska, E.; Grelska, J.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Geppert-Rybczyńska, M.; Wrzalik, R.; Grzybowska, K.A.; Pawlus, S.; et al. The impact of the length of alkyl chain on the behavior of benzyl alcohol homologous. The interplay between dispersive and hydrogen bond interaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 23796–23807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
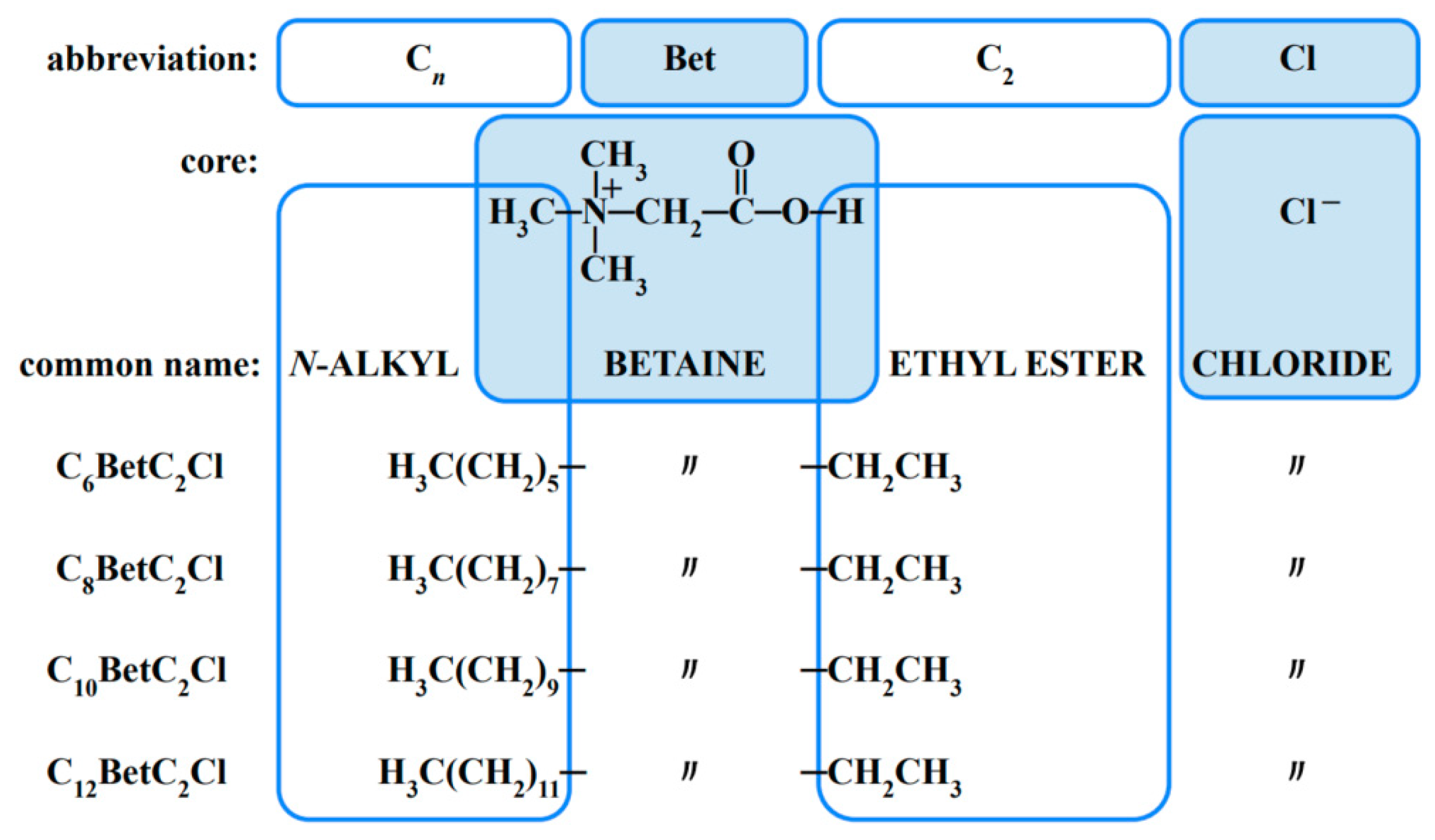
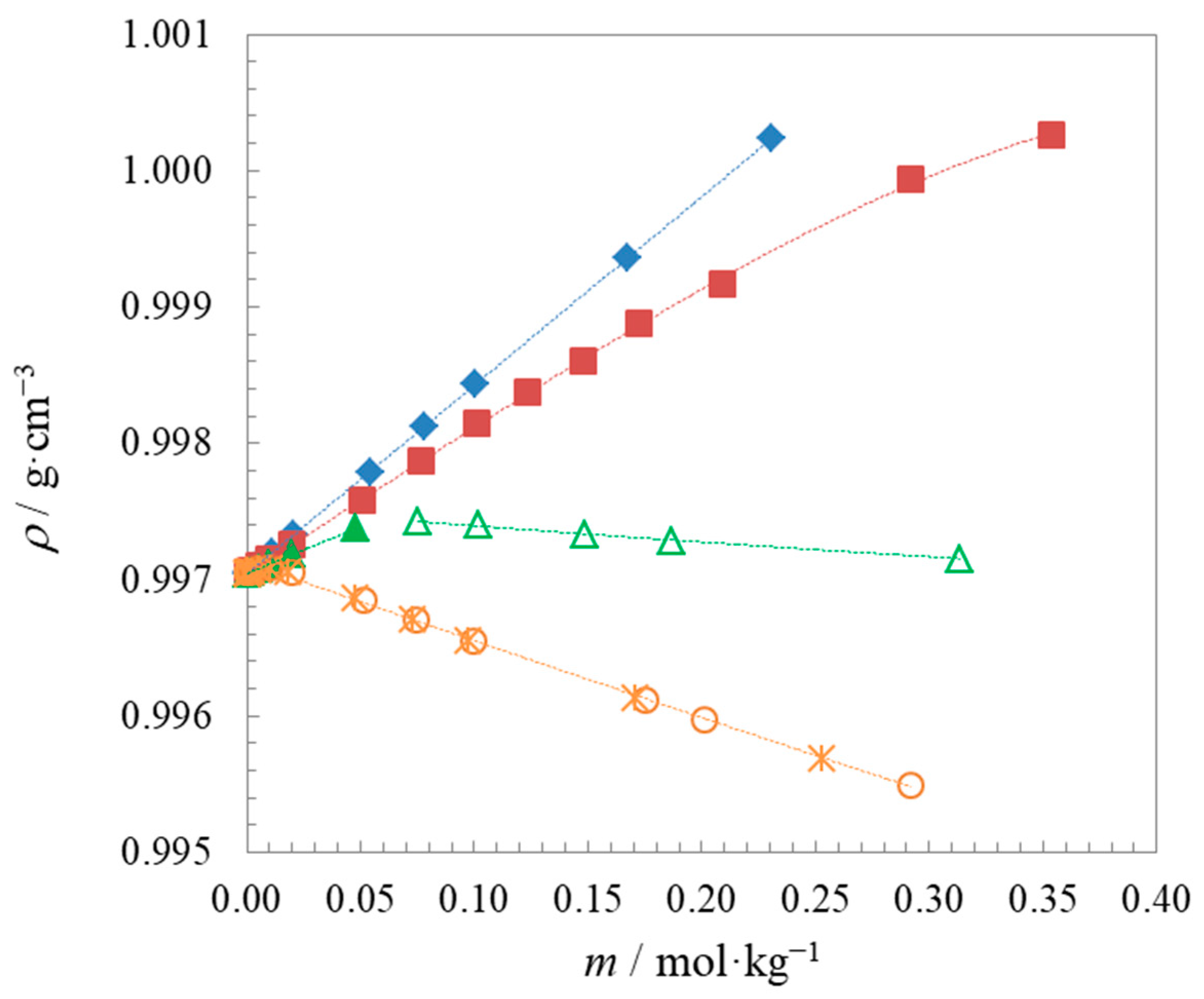
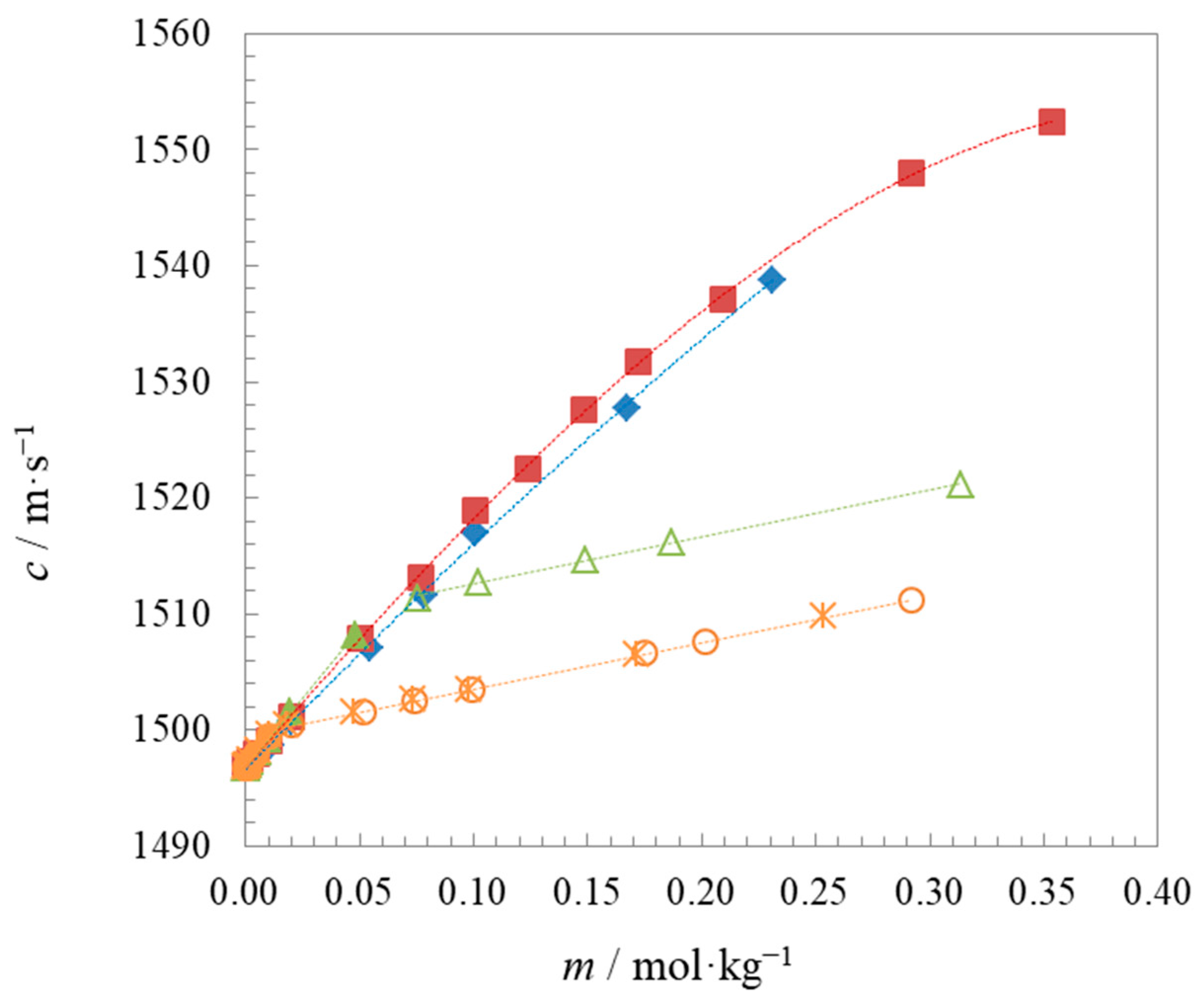
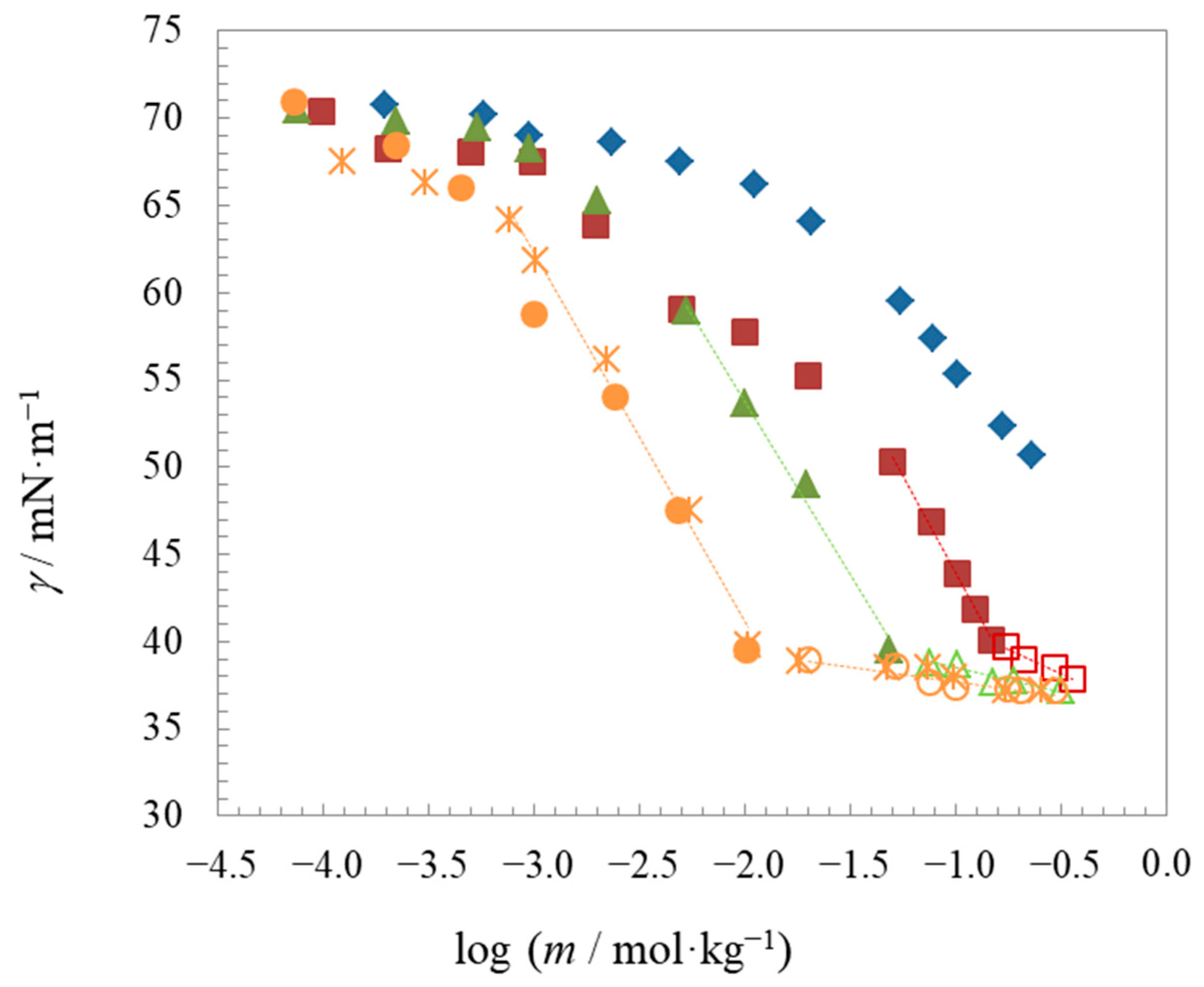
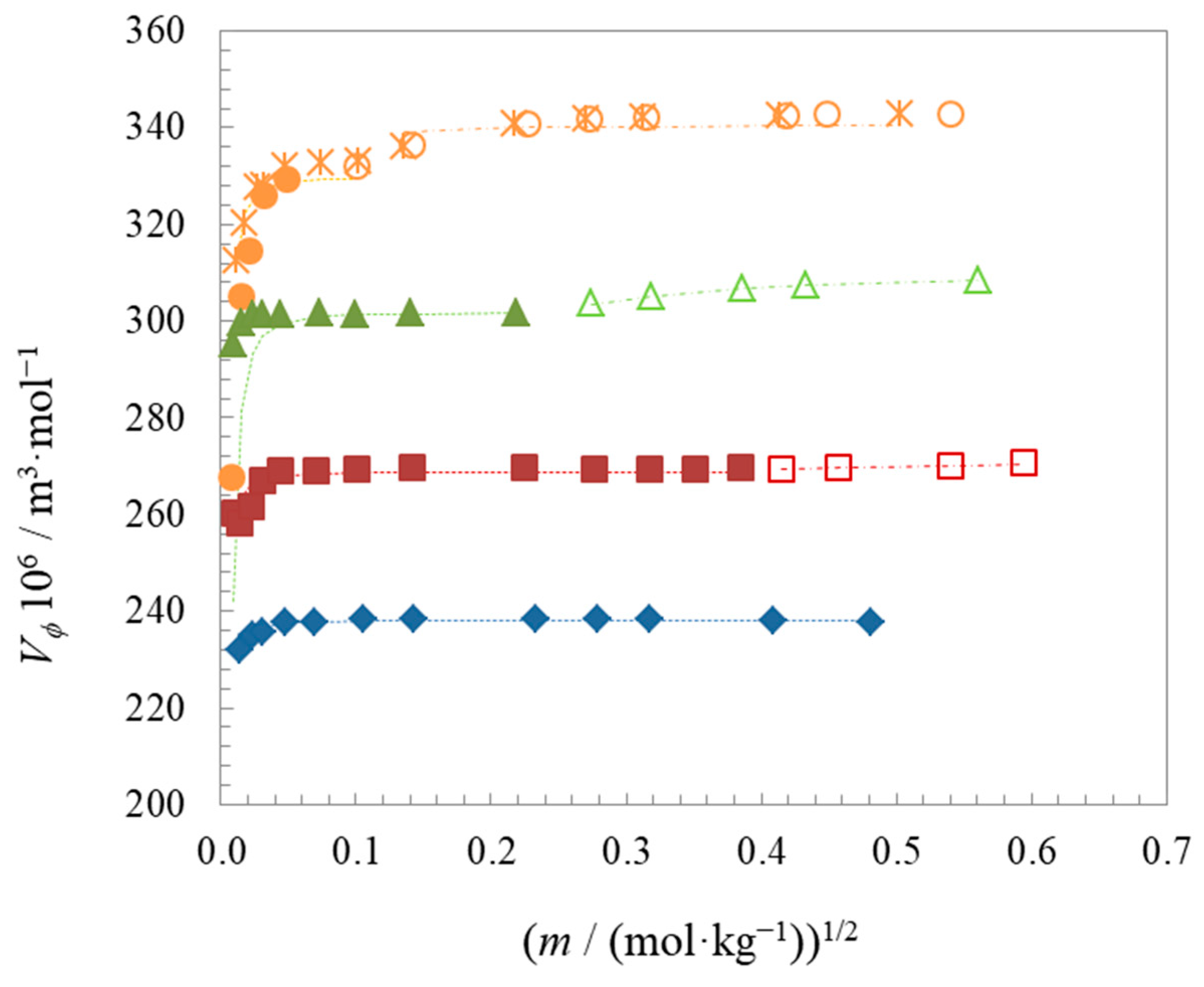
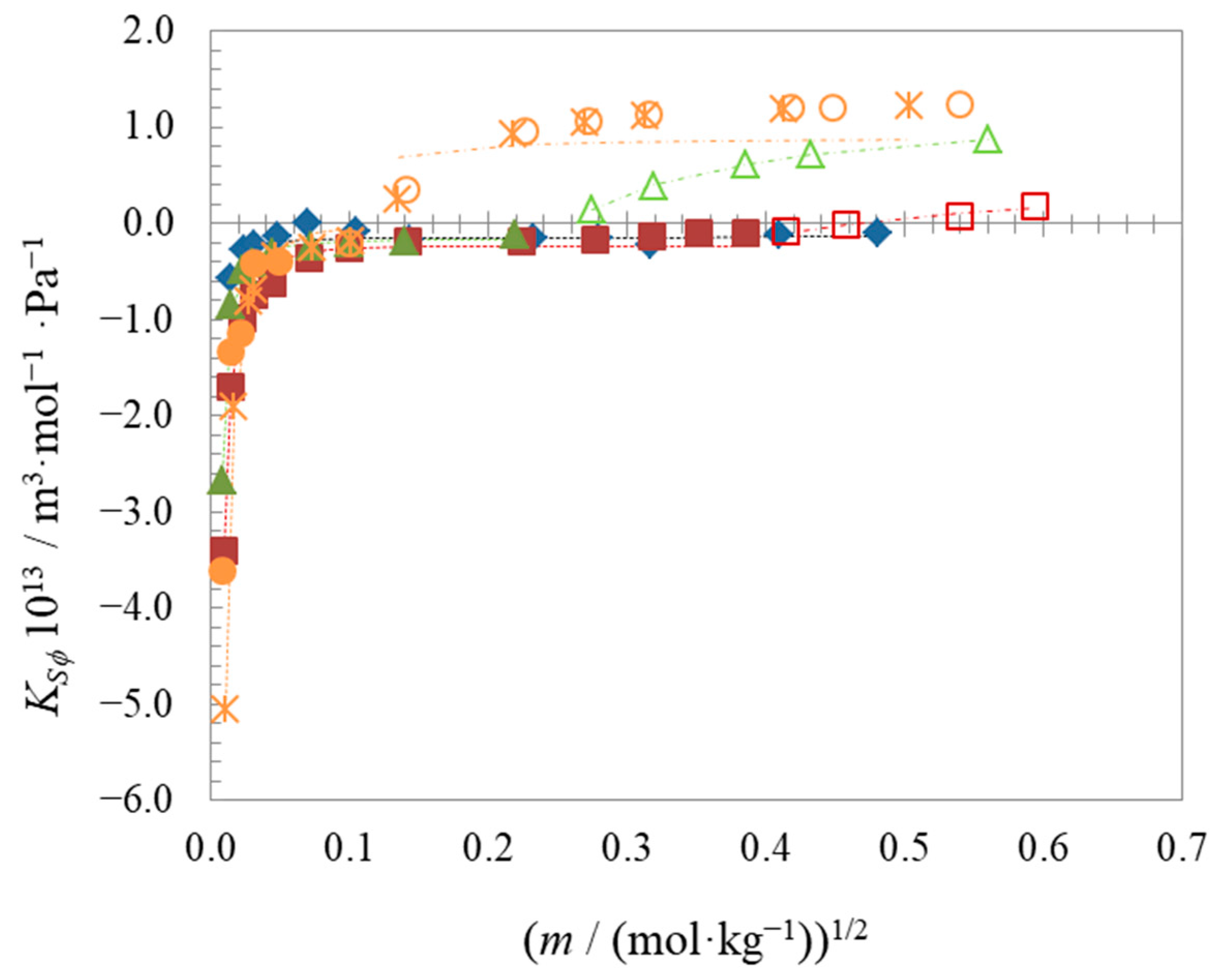
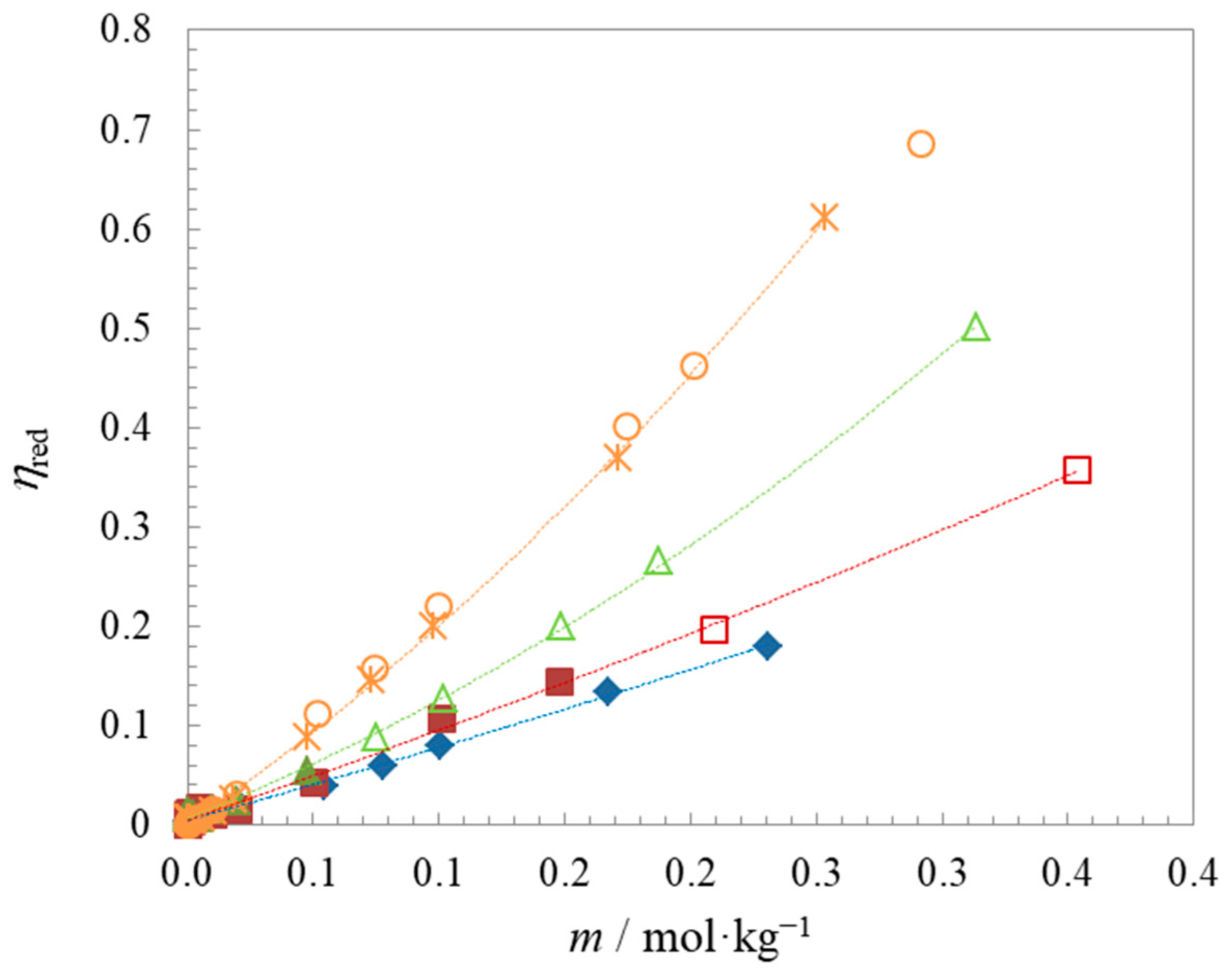

| Compound | t | Surface Tension | Density | Speed of Sound | Γmax∙106 | Amin∙1018 | pC20 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | CMC/mol∙kg−1 | mN∙m−1 | mol∙m−2 | m2 | kJ∙mol−1 | kJ∙mol−1 | ||||
| C8BetC2Cl | 25 | 0.154 | - | - | 37.8 | 1.91 | 0.87 | 1.5 | −14.6 | −32.4 |
| C10BetC2Cl | 25 | 0.053 | 0.058 | 0.059 | 37.2 | 1.74 | 0.95 | 2.0 | −17.2 | −37.1 |
| C12BetC2Cl (1) | 25 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 37.2 | 1.85 | 0.90 | 2.6 | −20.9 | −39.6 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 15 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 38.1 | 1.60 | 1.04 | 2.6 | −20.2 | −42.2 |
| C12BetC2Cl (2) | 25 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 38.1 | 1.72 | 0.99 | 2.6 | −20.7 | −40.9 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 35 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 36.6 | 1.53 | 1.09 | 2.7 | −21.4 | −43.6 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 45 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 36.1 | 1.44 | 1.15 | 2.6 | −22.1 | −44.9 |
| Compound | t | ∙106 | ∙106 | ∙106 | ∙1013 | ∙1013 | ∙1013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | (m3∙mol−1) | (m3∙mol−1) | (m3∙mol−1) | (m3·mol−1∙Pa−1) | (m3·mol−1∙Pa−1) | (m3·mol−1∙Pa−1) | |
| C6BetC2Cl | 25 | 238.11 ± 0.17 | - a | - a | −0.140 ± 0.019 | - a | - a |
| C8BetC2Cl | 25 | 268.77 ± 0.74 | 271.36 ± 0.54 | 2.6 | −0.229 ± 0.039 | 0.400 ± 0.059 | 0.63 |
| C10BetC2Cl | 25 | 301.767 ± 0.071 | 309.953 ± 0.033 | 8.2 | −0.161 ± 0.028 | 1.1073 ± 0.0058 | 1.3 |
| C12BetC2Cl (1) | 25 | 329.7 ± 1.3 | 340.5 ± 1.3 | 11 | −0.008 ± 0.083 | 0.89 ± 0.19 | 0.9 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 15 | 325.3 ± 2.0 | 340.331 ± 0.054 | 15 | −0.82 ± 0.17 | 1.2004 ± 0.0095 | 2.0 |
| C12BetC2Cl (2) | 25 | 330.0 ± 1.6 | 343.425 ± 0.050 | 13 | −0.272 ± 0.076 | 1.3143 ± 0.0066 | 1.6 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 35 | 337.14 ± 0.38 | 346.416 ± 0.049 | 9.3 | 0.090 ± 0.045 | 1.4271 ± 0.0045 | 1.3 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 45 | 343.2 ± 4.3 | 349.369 ± 0.050 | 6.2 | 0.450 ± 0.076 | 1.5400 ± 0.0035 | 1.1 |
| Compound | t/°C | A/kg1/2∙mol−1/2 | B/kg∙mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C6BetC2Cl | 25 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.72 ± 0.05 |
| C8BetC2Cl | 25 | −0.01 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.06 |
| C10BetC2Cl | 25 | −0.16 ± 0.04 | 1.84 ± 0.10 |
| C12BetC2Cl (1) | 25 | −0.20 ± 0.04 | 2.76 ± 0.10 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 15 | −0.18 ± 0.03 | 2.77 ± 0.07 |
| C12BetC2Cl (2) | 25 | −0.10 ± 0.01 | 2.54 ± 0.03 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 35 | −0.12 ± 0.01 | 2.55 ± 0.03 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 45 | −0.14 ± 0.01 | 2.53 ± 0.03 |
| Compound | m/(mol·kg−1) | dh1/nm | dh2/nm | dh3/nm | Peak 1 Area/% | Peak 2 Area/% | Peak 3 Area/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10BetC2Cl | 1.0 a | 1.4 | 863 | 2871 | 75.6 | 23.2 | 1.2 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 0.05 | 1.5 | 173 | 3849 | 37.6 | 59.8 | 2.5 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 0.1 | 1.2 | 194 | 4647 | 53.6 | 43.5 | 2.8 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 0.2 | 1.2 | 178 | 3592 | 77.7 | 19.7 | 2.2 |
| Compound | M/g∙mol−1 | Yield/% | tmelting/°C | tdecomposition/°C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t5%onset | t50%onset | ||||
| C6BetC2Cl | 251.79 | 85 | 95.6–96.4 | 142.25 | 183.58 |
| C8BetC2Cl | 279.85 | 91 | 83.0–84.6 | 144.71 | 179.87 |
| C10BetC2Cl | 307.90 | 93 | 93.8–95.0 | 146.33 | 180.99 |
| C12BetC2Cl | 335.95 | 93 | 87.9–89.8 | 139.41 | 181.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geppert-Rybczyńska, M.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Rawicka, P.; Bartczak, P. A Study of the Micellar Formation of N-Alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides Based on the Physicochemical Properties of Their Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2024, 29, 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081844
Geppert-Rybczyńska M, Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz A, Rawicka P, Bartczak P. A Study of the Micellar Formation of N-Alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides Based on the Physicochemical Properties of Their Aqueous Solutions. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081844
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeppert-Rybczyńska, Monika, Anna Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, Patrycja Rawicka, and Piotr Bartczak. 2024. "A Study of the Micellar Formation of N-Alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides Based on the Physicochemical Properties of Their Aqueous Solutions" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081844
APA StyleGeppert-Rybczyńska, M., Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A., Rawicka, P., & Bartczak, P. (2024). A Study of the Micellar Formation of N-Alkyl Betaine Ethyl Ester Chlorides Based on the Physicochemical Properties of Their Aqueous Solutions. Molecules, 29(8), 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081844








