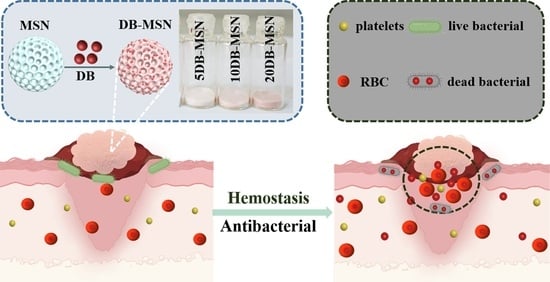
Dragon’s Blood-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Rapid Hemostasis and Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
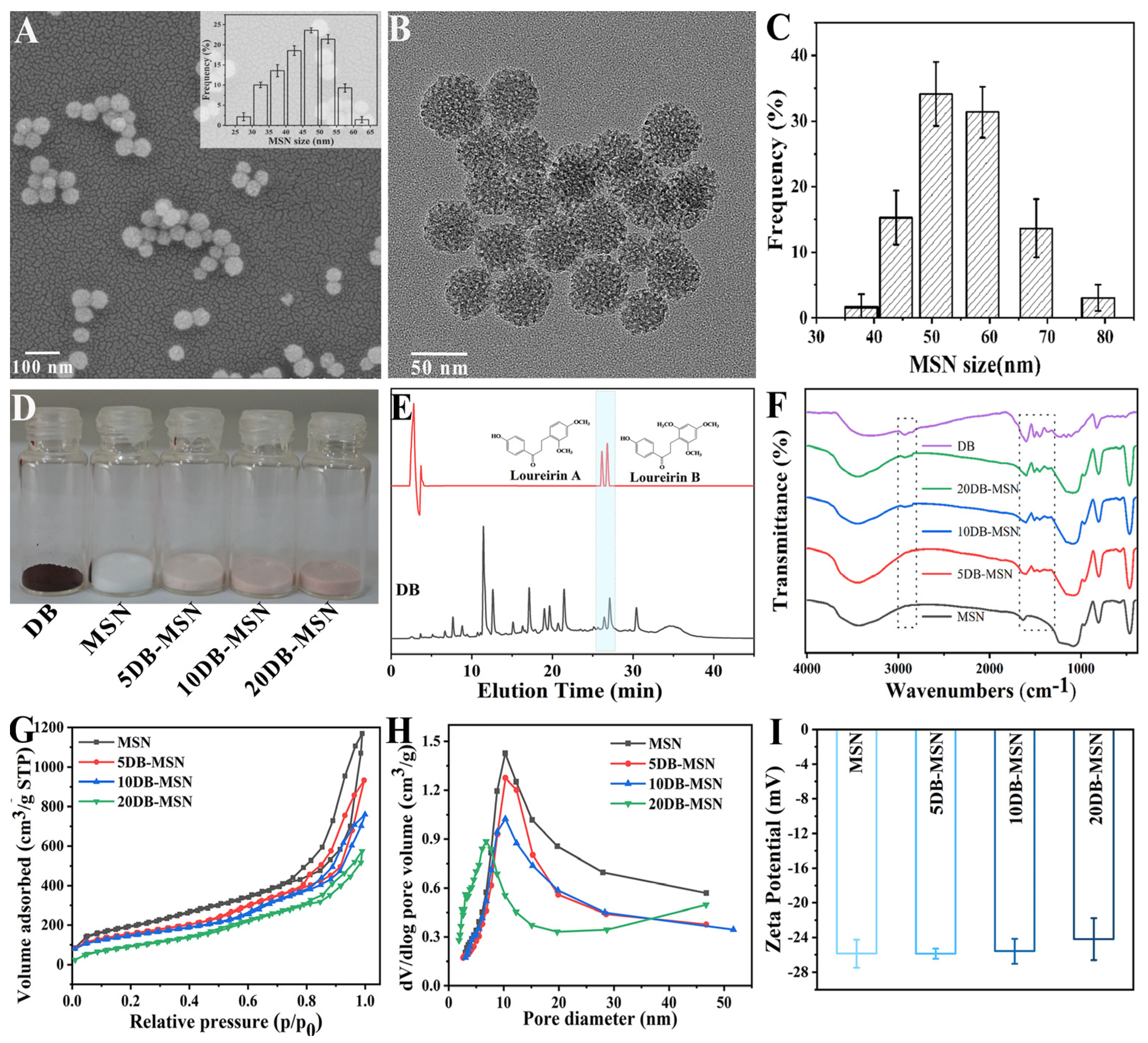
2.1. The Characterization of MSN, 5DB-MSN, 10DB-MSN, and 20DB-MSN
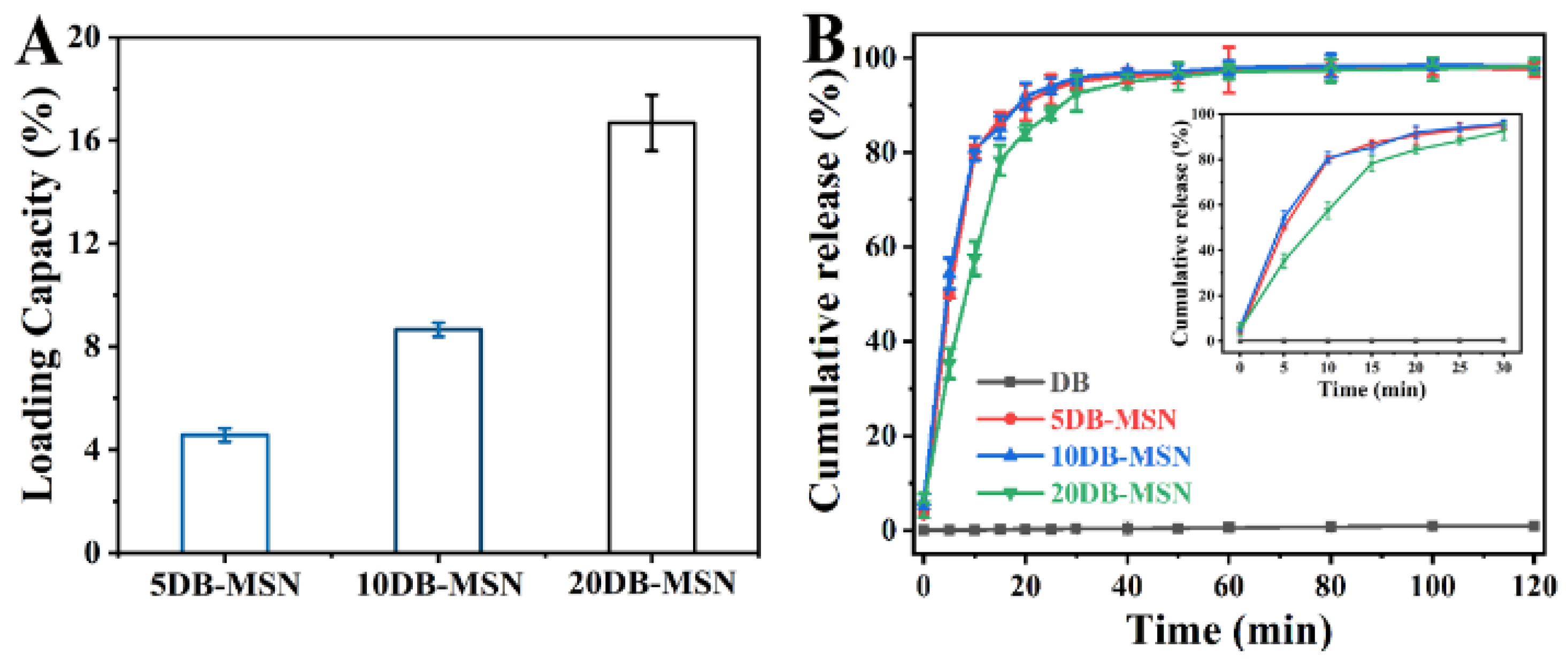
2.2. The Loading Capability of DB-MSN and DB Release from DB-MSN In Vitro
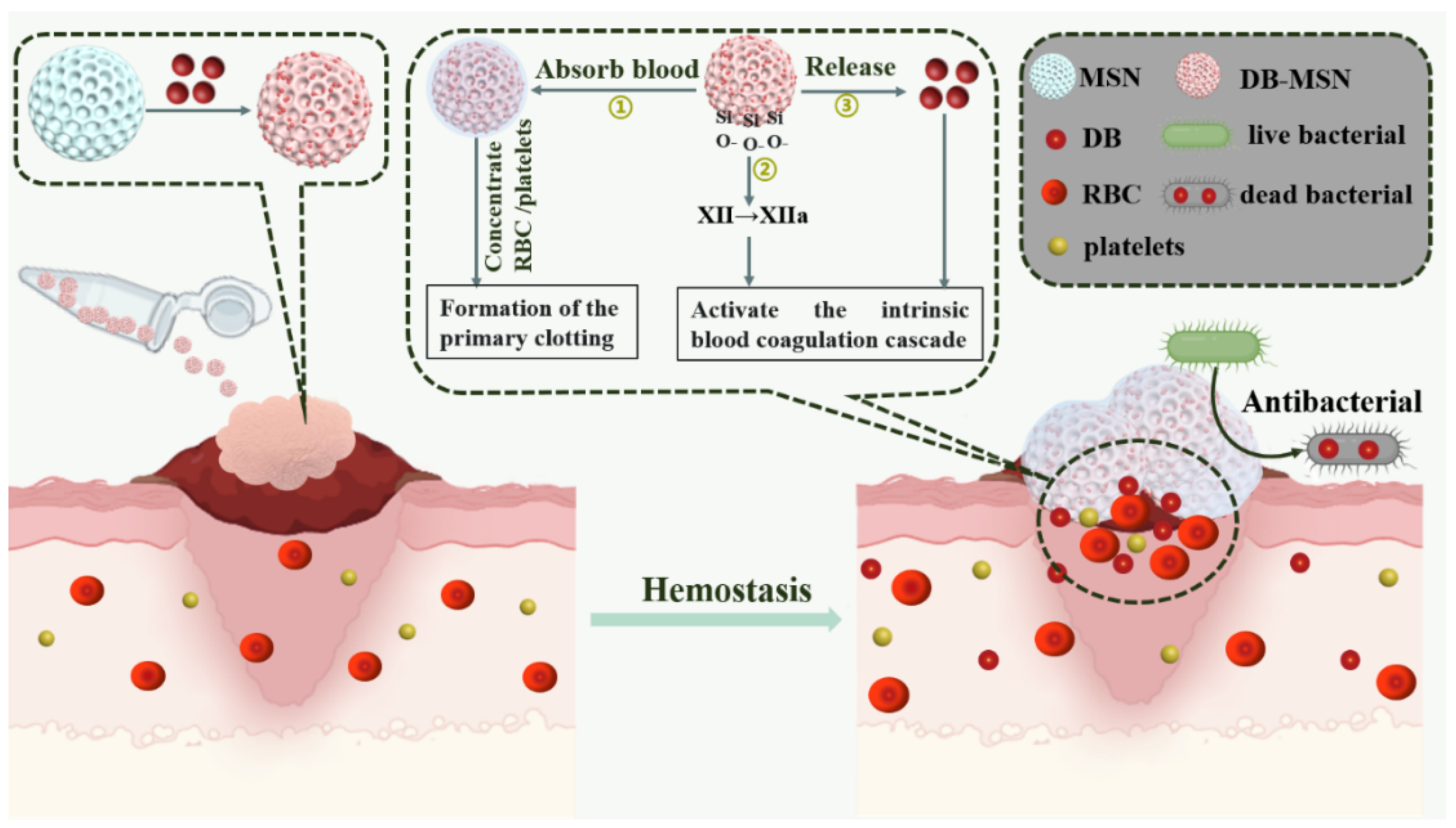
2.3. Hemostatic Efficiency Evaluation In Vitro
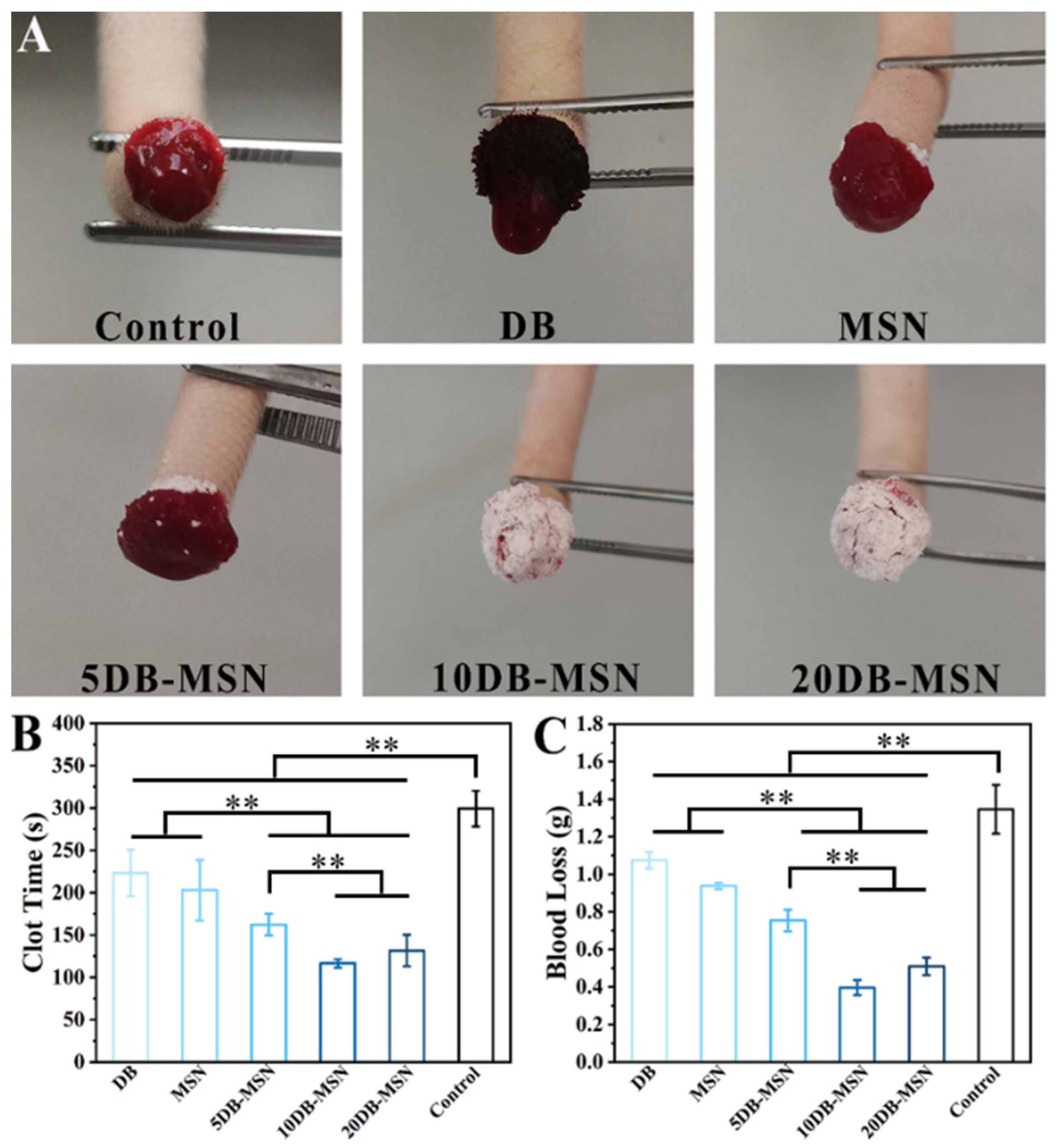
2.4. Hemostatic Efficiency Evaluation in Animal Models
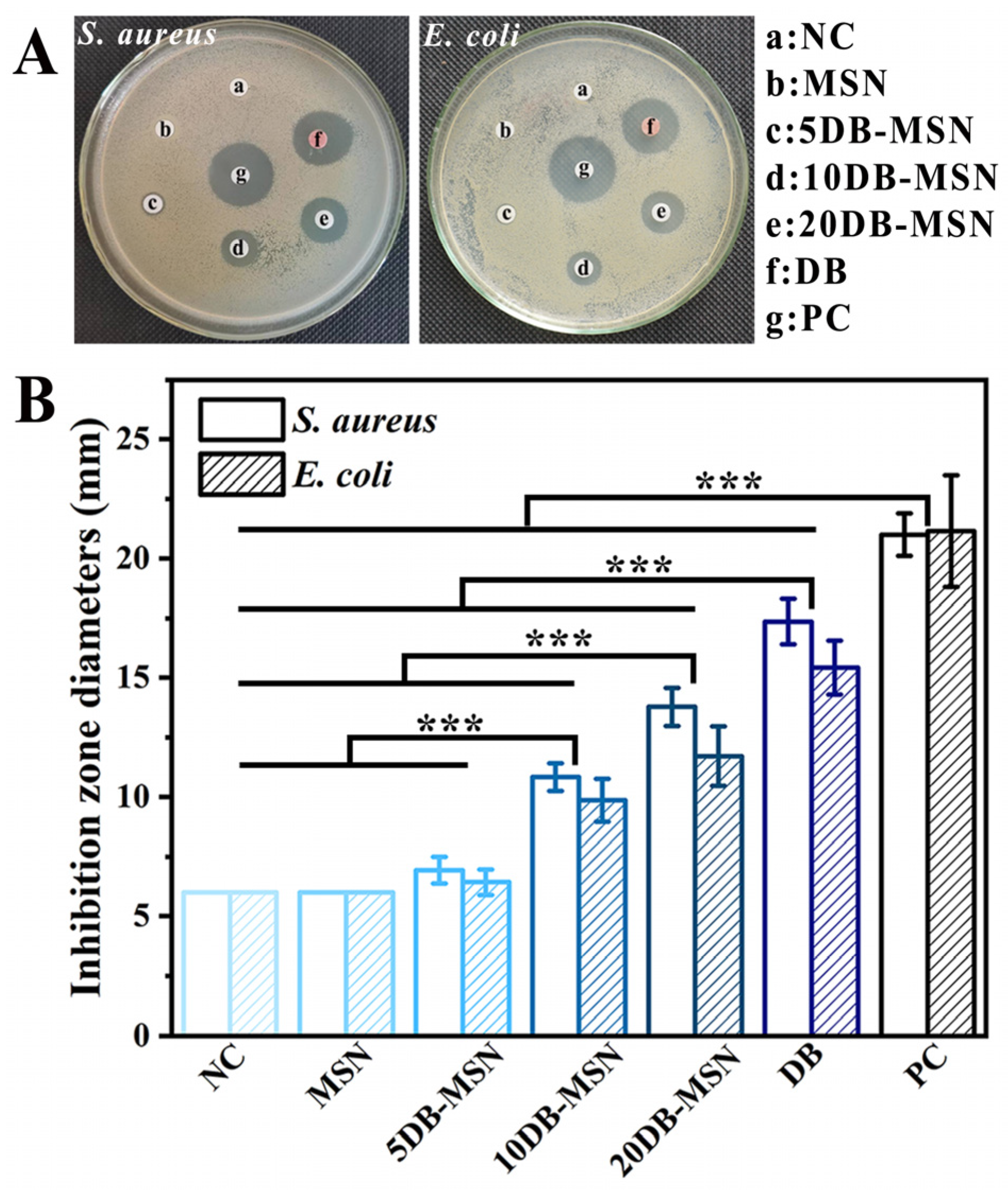
2.5. Antibacterial Performance
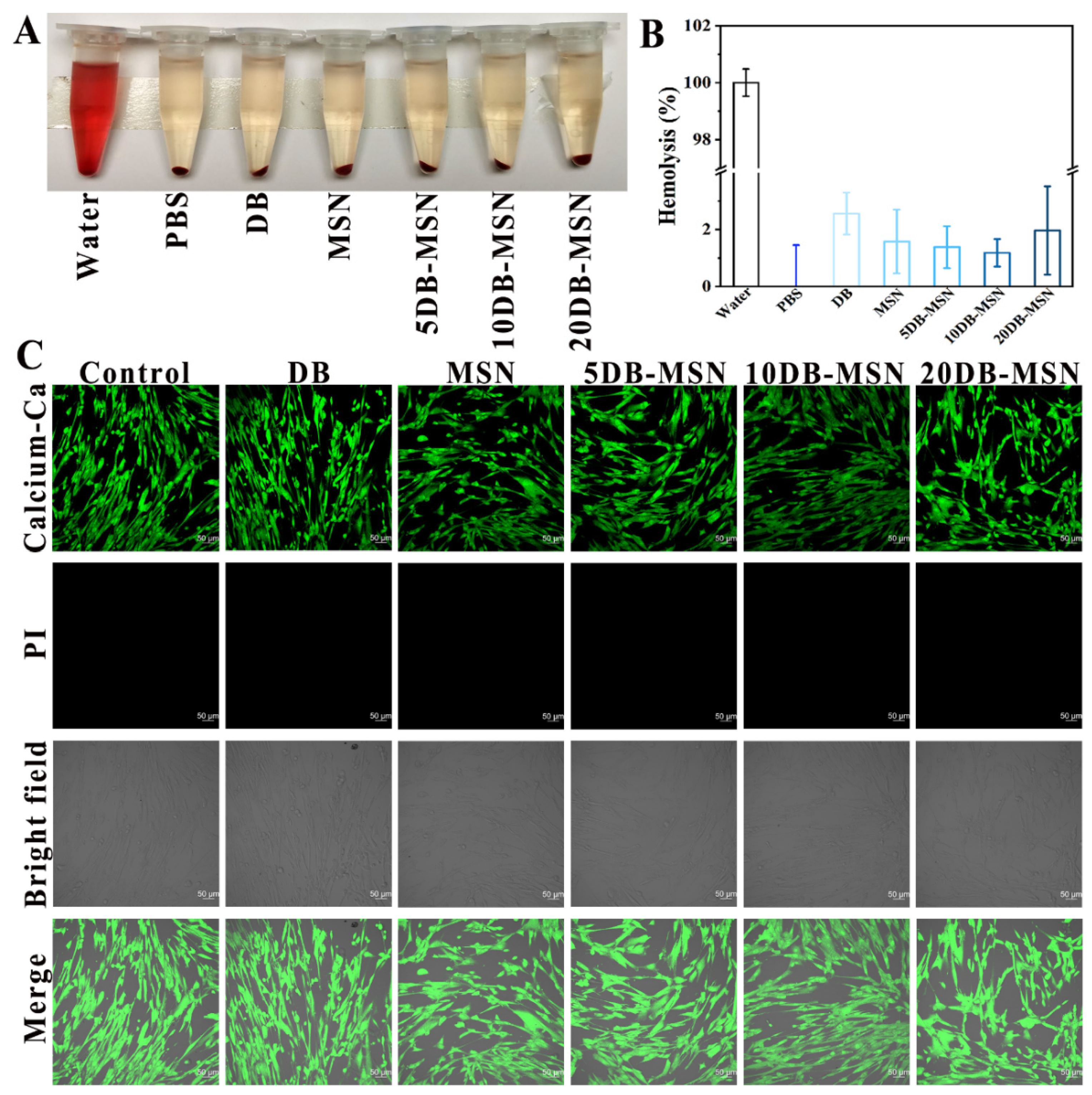
2.6. Biocompatibility Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of MSNs and DB-MSN
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Loading Efficiency and DB-Release Behavior Study
3.5. Hemostatic Efficiency Evaluation In Vitro
3.6. Hemostatic Efficiency Evaluation In Vivo
3.7. Antibacterial Assay In Vitro
3.8. Biocompatibility Test
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spahn, D.R.; Bouillon, B.; Cerny, V.; Duranteau, J.; Filipescu, D.; Hunt, B.J.; Komadina, R.; Maegele, M.; Nardi, G.; Riddez, L.; et al. The European guideline on management of major bleeding and coagulopathy following trauma. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastridge, B.J.; Holcomb, J.B.; Shackelford, S. Outcomes of traumatic hemorrhagic shock and the epidemiology of preventable death from injury. Transfusion 2019, 59, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Bieler, D.; Friemert, B.; Schwab, R.; Kollig, E.; Gusgen, C. The first aid and hospital treatment of gunshot and blast injuries. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.X.; Lei, X.X.; Lv, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.N. Recent advances of chitosan as a hemostatic material: Hemostatic mechanism, material design and prospective application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 327, 121673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Huang, Z.Z.; McCarthy, A.; Huang, Y.Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Chen, S.X.; Wan, W.B. Super-Elastic Carbonized Mushroom Aerogel for Management of Uncontrolled Hemorrhage. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.W.; Zheng, Y.K.; Ming, J.F.; Bai, S.M. Natural polymer-based bioadhesives as hemostatic platforms for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 256, 128275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, K.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Liu, G.; Ran, F.; Zhou, L.L.; Wu, Y.T.; Peng, L.Q.; Shao, M.H.; Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.P. A review of hemostatic chemical components and their mechanisms in traditional Chinese medicine and ethnic medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 307, 116200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkura, N.; Yokouchi, H.; Mimura, M.; Nakamura, R.; Atsumi, G. Screening for hemostatic activities of popular Chinese medicinal herbs in vitro. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.C.; Shen, L.D.; Xie, H.B.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Hemostatic Effects Using Traditional Chinese Medicine as a Biomass Carbon Source. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.R.; Yuen, S.C.; Fan, G.Y.; Cong, W.H.; Leung, S.W.; Lee, S.M. Identification of certain Panax species to be potential substitutes for Panax notoginseng in hemostatic treatments. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Bi, T.; Zhou, Y.N.; Wang, C.M.; Ma, Y.N.; Xu, H.P.; Shen, H.P.; Ren, W.; Yang, S.J. Carbonized platycladus orientalis derived carbon dots accelerate hemostasis through activation of platelets and coagulation pathways. Small 2023, 19, 2303498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, C.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.F.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, S.J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.J.; Xu, W.L. Biocompatible and degradable Bletilla striata polysaccharide hemostasis sponges constructed from natural medicinal herb Bletilla striata. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pona, A.; Cline, A.; Kolli, S.S.; Taylor, S.L.; Feldman, S.R. Review of future insights of Dragon’s Blood in dermatology. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; Yi, T.; Sze-To, C.M.; Zhu, L.; Peng, W.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Chen, H.B. A systematic review of the botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of Dracaena cochinchinensis, a plant source of the ethnomedicine “dragon’s blood”. Molecules 2014, 19, 10650–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Gupta, R.K. Bioprotective properties of Dragon’s blood resin: In vitro evaluation of antioxidant activity and antimicrobial activity. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoyan, F.; Kiashi, F.; Moosavi, Z.B.; Saffari, F.; Makhmalzadeh, B.S. Efficacy of Dragon’s blood cream on wound healing: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 6, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Yao, W.H.; Tian, M.; Wei, J.N.; Song, Q.L.; Qiao, W.H. Mussel-inspired degradable antibacterial polydopamine/silica nanoparticle for rapid hemostasis. Biomaterials 2018, 179, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudela, D.; Smith, S.A.; May-Masnou, A.; Braun, G.B.; Pallaoro, A.; Nguyen, C.K.; Chuong, T.T.; Nownes, S.; Allen, R.; Parker, N.R.; et al. Clotting activity of polyphosphate-functionalized silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4018–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Niu, H.Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Hong, H.; Liu, C.S. Tannic acid-loaded mesoporous silica for rapid hemostasis and antibacterial activity. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 3318–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Han, L.; Liu, C.J.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Du, G.; Shan, C.; Yang, K.; Wang, C.L.; Li, M.G.; et al. A rapid hemostatic sponge based on large, mesoporous silica nanoparticles and N-alkylated chitosan. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20234–20245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.B.; Cao, K.; Hu, P.; Liu, Y. Orthogonal experimental preparation of Sanguis Draconis-Polyvinylpyrrolidone microfibers by electrospinning. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.C.; Bai, X.Y.; Jiang, T.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for increasing the oral bioavailability and permeation of poorly water soluble drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.D.; Zhang, H.R.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.K.; Li, F.M.; Huang, Q.L. Quaternized chitosan-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers for controlled pesticide release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhi, Z.Z.; Jiang, T.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.L. Spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles for loading and release of the poorly water-soluble drug telmisartan. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Aoyama, M.; Tochigi, S.; Hirai, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nagano, K.; Kamada, H.; Tsunoda, S. Protein corona changes mediated by surface modification of amorphous silica nanoparticles suppress acute toxicity and activation of intrinsic coagulation cascade in mice. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.K.; Chen, L.J.; Zeng, W.L.; Liao, W.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Tian, X.B.; Fang, R.C.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.L. Antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy of chinese dragon’s blood against staphylococcus aureus isolated from infected wounds. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 672943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kim, S.G.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.X.; Ji, Z.X.; Dai, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Ye, F.; Chen, G.; Lv, Z.B. Alginate-based composite microspheres coated by berberine simultaneously improve hemostatic and antibacterial efficacy. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 194, 111168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valgas, C.; Souza, S.M.D.; Smânia, E.F.; Smânia, A., Jr. Screening methods to determine antibacterial activity of natural products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2007, 38, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Feng, S.B.; Han, S.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, Y.D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.B.; Li, X.H.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.X. Facile assembly of cost-effective and locally applicable or injectable nanohemostats for hemorrhage control. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9957–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SBET (m2/g) | Vt (cm3/g) | DBJH (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSNs | 702 | 2.27 | 12.96 |
| 5DB-MSN | 567 | 2.06 | 11.43 |
| 10DB-MSN | 427 | 1.70 | 9.47 |
| 20DB-MSN | 248 | 0.92 | 5.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Deng, Z.; Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Dragon’s Blood-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Rapid Hemostasis and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2024, 29, 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081888
Yin C, Li Y, Yu J, Deng Z, Liu S, Shi X, Tang D, Chen X, Zhang L. Dragon’s Blood-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Rapid Hemostasis and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081888
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Cuiyun, Yihang Li, Jing Yu, Zhaoyou Deng, Shifang Liu, Xuanchao Shi, Deying Tang, Xi Chen, and Lixia Zhang. 2024. "Dragon’s Blood-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Rapid Hemostasis and Antibacterial Activity" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081888
APA StyleYin, C., Li, Y., Yu, J., Deng, Z., Liu, S., Shi, X., Tang, D., Chen, X., & Zhang, L. (2024). Dragon’s Blood-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Rapid Hemostasis and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules, 29(8), 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081888