Anisotropic Microparticles with a Controllable Structure via Soap-Free Seeded Emulsion Polymerization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
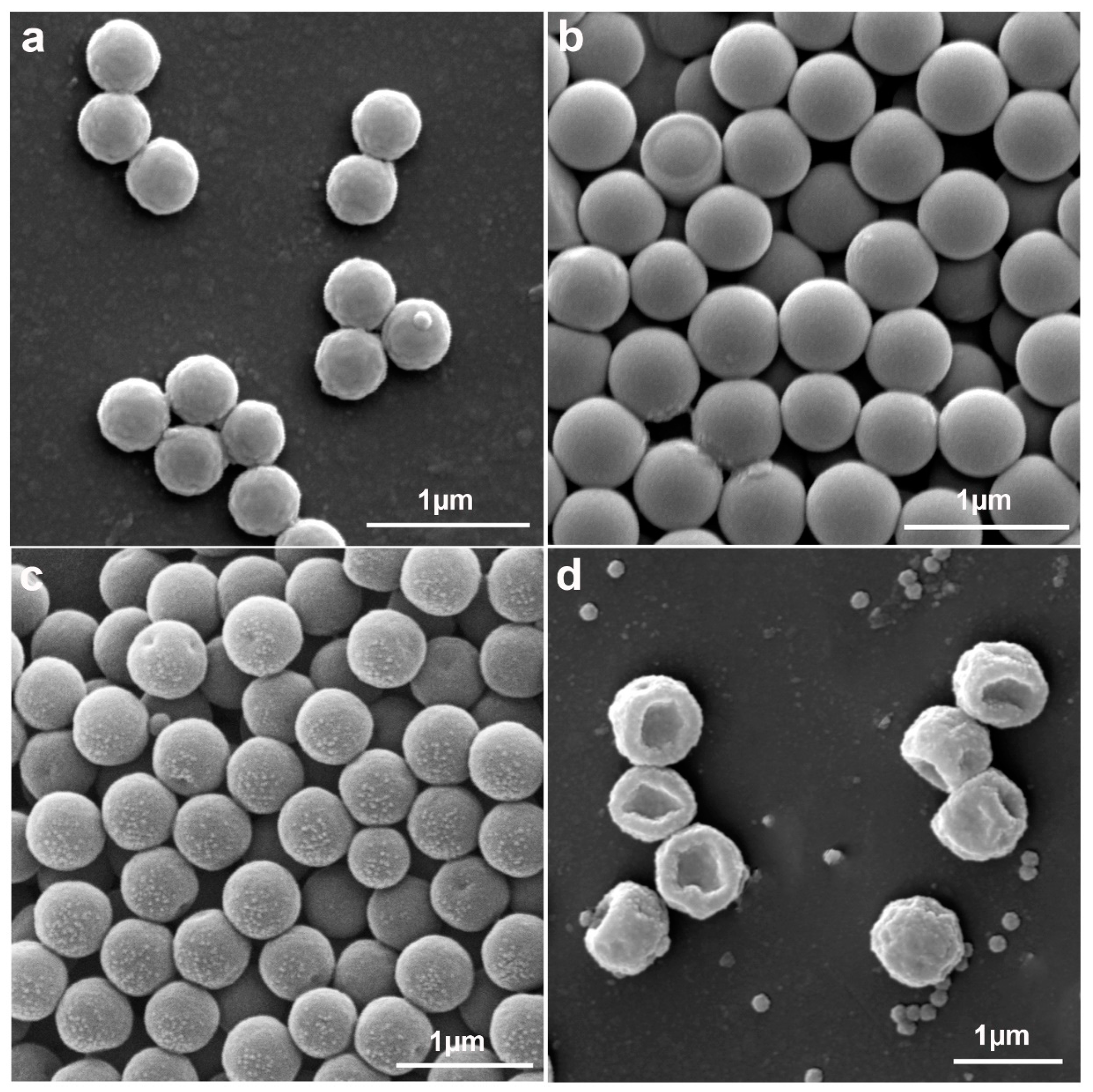
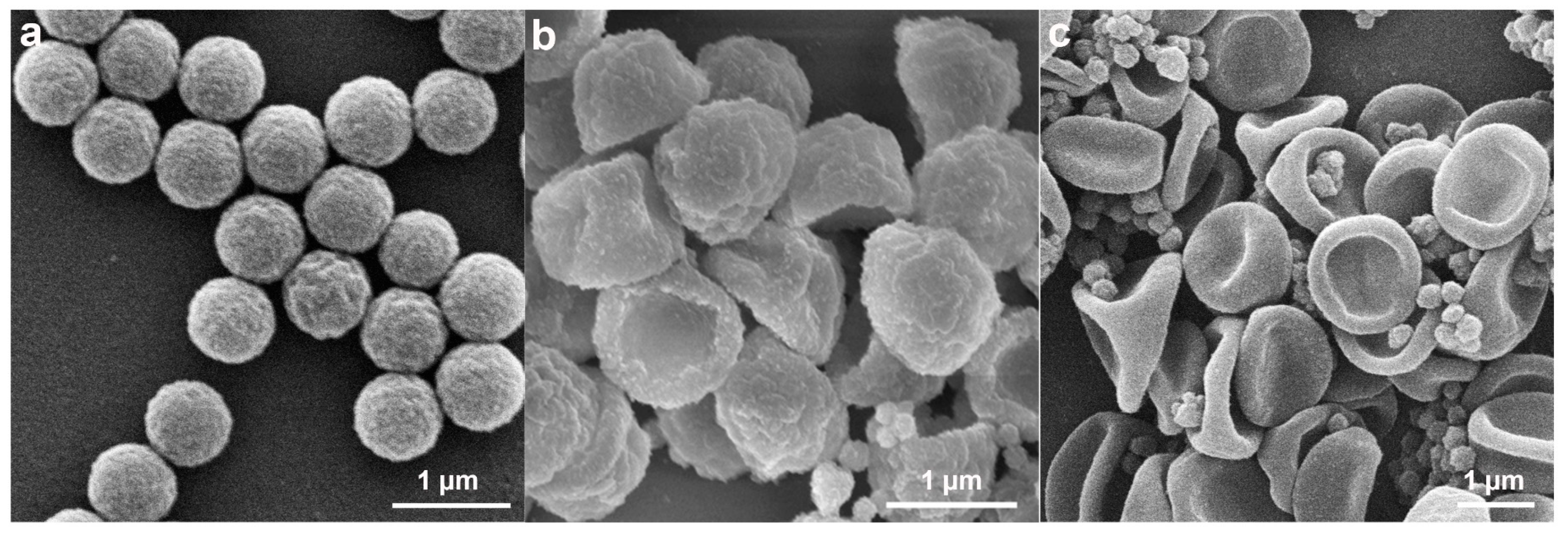
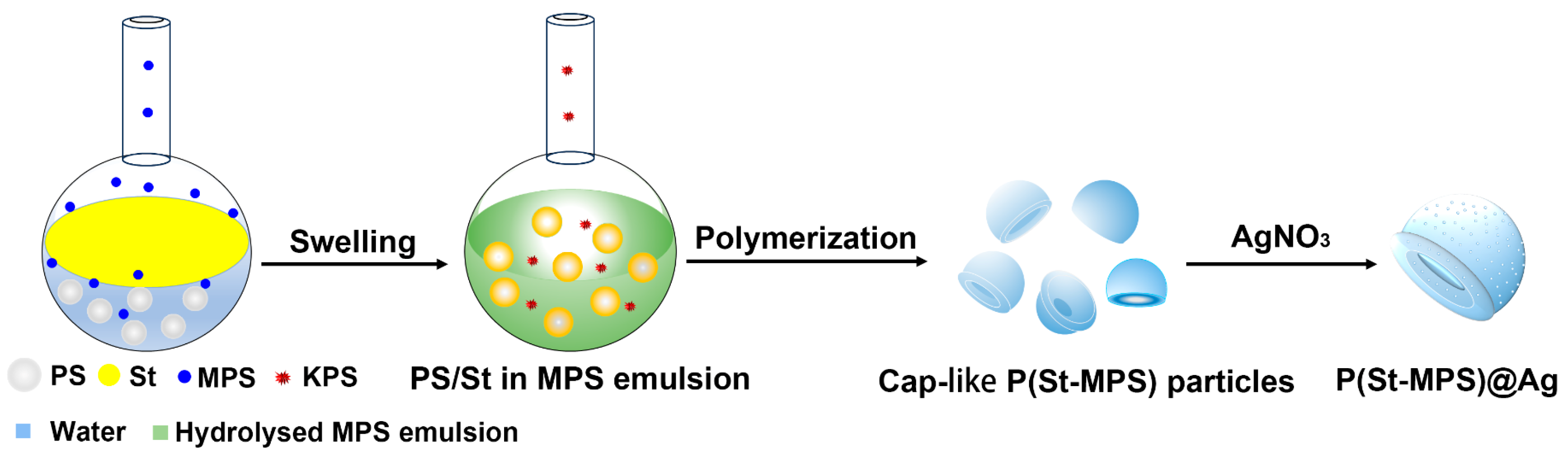
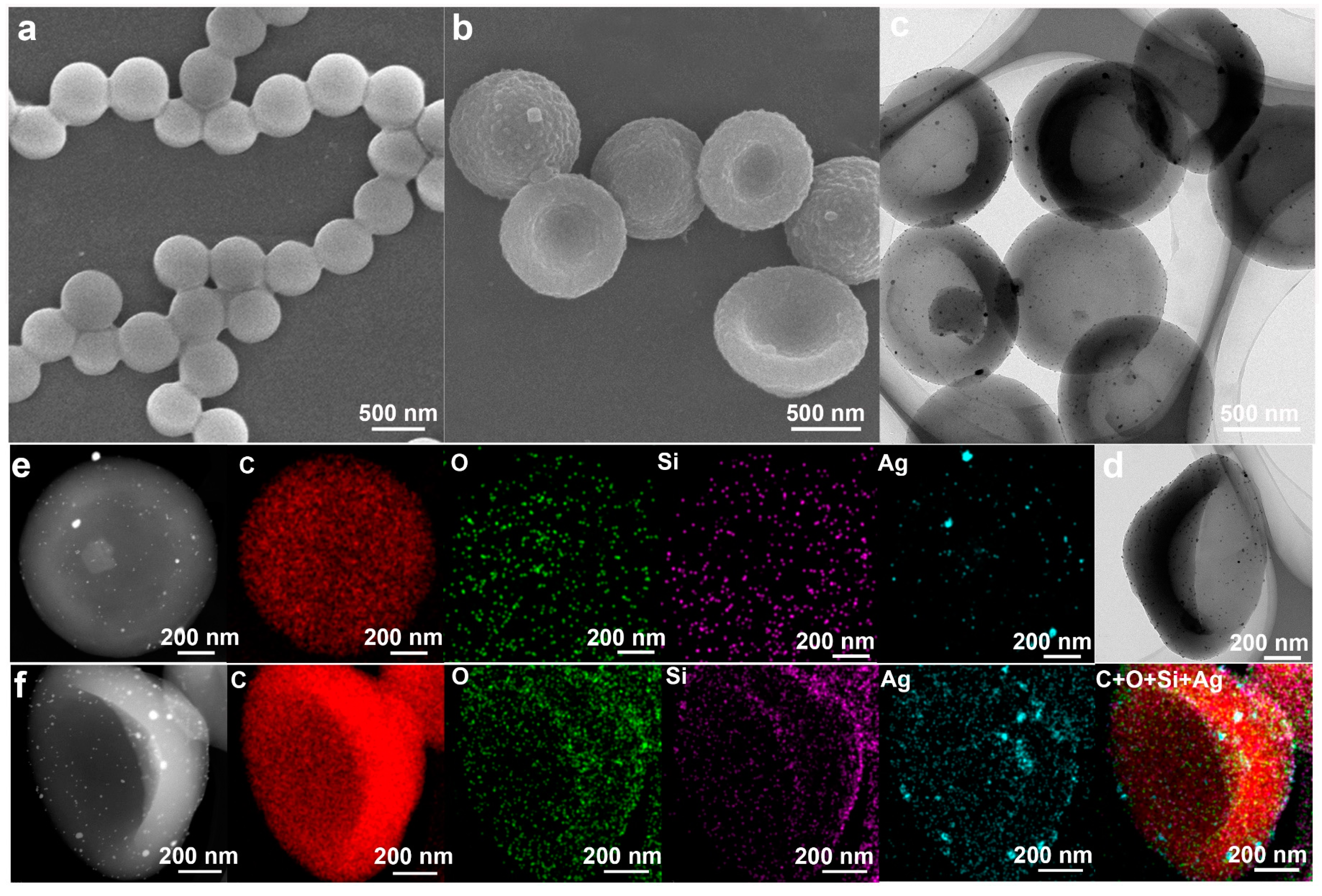
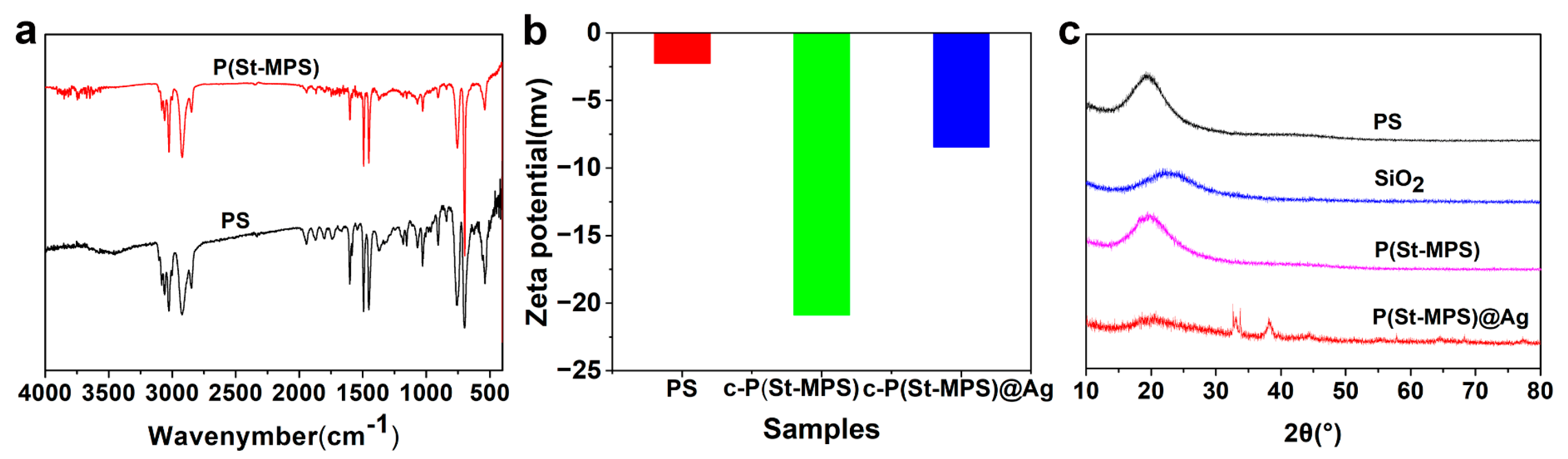
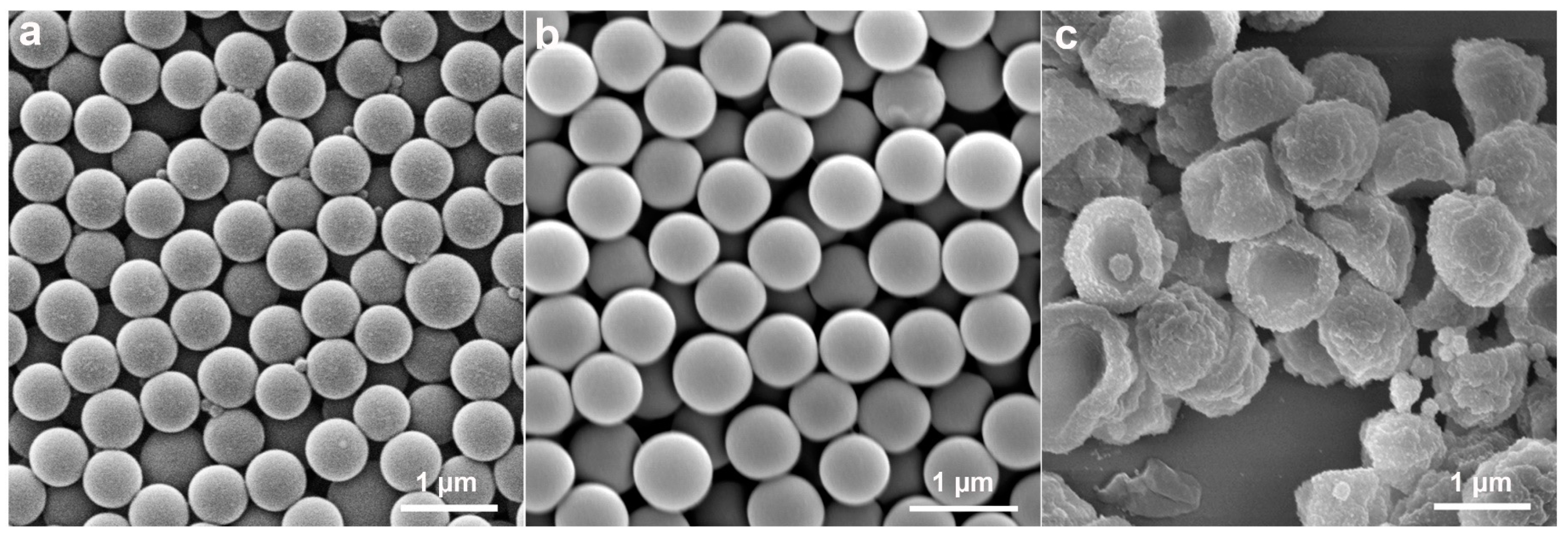
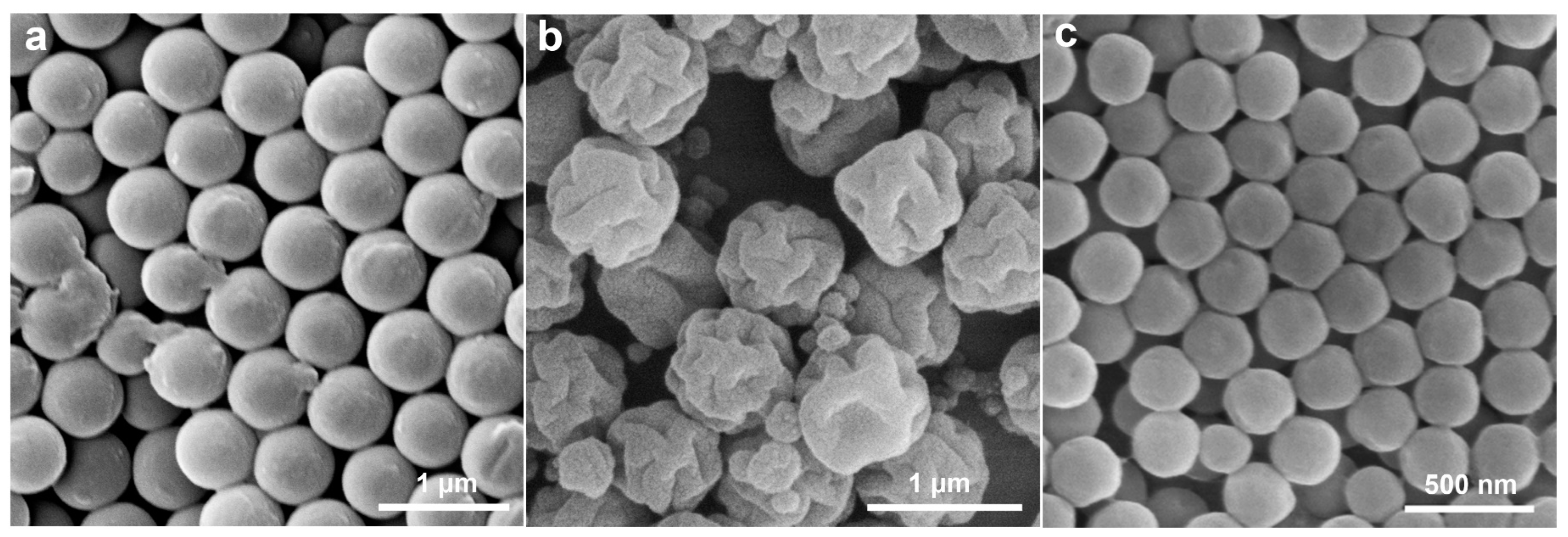
2.1. Preparation and Characterizations of the Anisotropic Microparticles
2.2. The Formation Mechanism of Anisotropic P(St-MPS) Particles
2.2.1. Effects of Components in the Reaction System on Particle Morphology
2.2.2. Effect of St to PS Seeds Mass Ratio on Particle Morphology
2.2.3. Effects of MPS Concentration on Particle Morphology
2.3. Applications of P(St-co-MPS) Microparticles with Surface Functionalities
2.4. Applications of P(St-co-MPS)@Ag Particles and Kinetics of Catalytic 4-NP Reduction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of PS Seed Particles
3.3. Synthesis of Anisotropic Hybrid Particles
3.3.1. Synthesis of Cap-like P(St-MPS) Particles
3.3.2. Synthesis of Spherical P(St-MPS) Particles
3.3.3. Synthesis of Microphase-Separated PS@PMPS Core–Shell Particles
3.3.4. Synthetic Hydrophilic Spherical Crosslinked Polystyrene (CPS) Particles
3.3.5. Synthesis of Cap-like P(St-MPS-AA) Particles
3.3.6. Synthesis of PS@P(MMA-MPS) and PS@P(AA-MPS) Core–Shell Particles
3.3.7. Synthesis of PS@P(St-DVB)
3.4. Preparation of P(St-MPS)@Ag Composites Particles
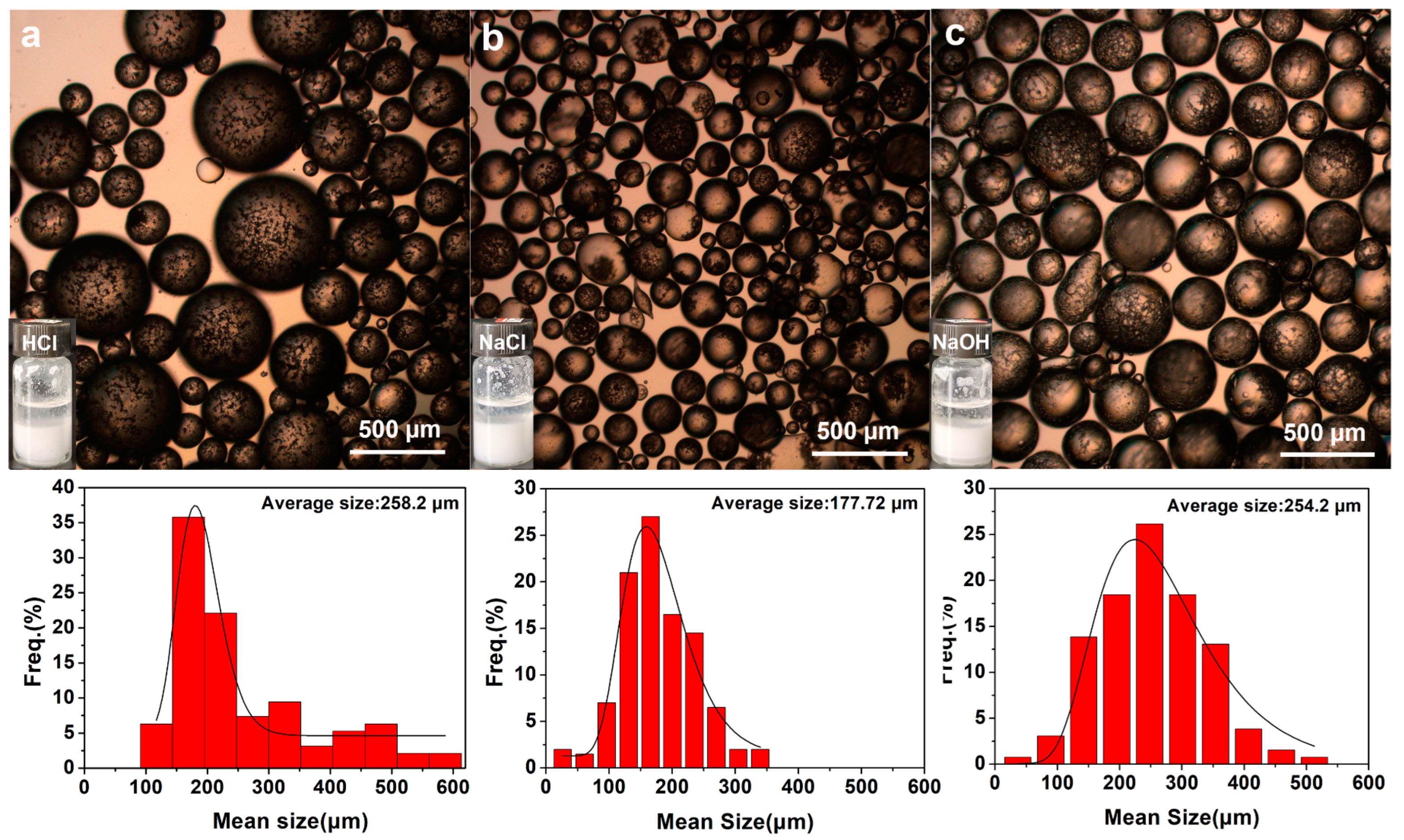
3.5. Study of Emulsion Stability
- H1: Emulsion layer height.
- H: Total height of the hybrid system.
3.6. Study of Catalytic Performance
3.7. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Liang, C.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Magnetically responsive Janus nanoparticles synthesized using cellulosic materials for enhanced phase separation in oily wastewaters and water-in-crude oil emulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Bao, M.; Wang, Z. Amphiphilic Janus particles for efficient dispersion of oil contaminants in seawater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Reactive amphiphilic hollow SiO2 Janus nanoparticles for durable superhydrophobic coating. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16443–16450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Bai, S.; Yu, L.; Sun, Y. Magnetically Driven Muco-Inert Janus Nanovehicles for Enhanced Mucus Penetration and Cellular Uptake. Molecules 2022, 27, 7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.; Shu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Liang, F. Catalytic Janus Nanoparticle-Based Recyclable Emulsifiers for Collaborative Treatment of Water-Soluble and Water-Insoluble Organic Pollutants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 14820–14828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Sun, D.; Yang, Z. Janus Composite Particles and Interfacial Catalysis Thereby. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2300280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Muller, A.H. Janus particles: Synthesis, self-assembly, physical properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5194–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Lang, F.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z. Responsive Single-Chain/Colloid Composite Janus Nanoparticle. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Agrawal, R. Janus Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Their Interfacial and Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1738–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, M.; Hao, H. Research Advances in the Synthesis, Application, Assembly and Calculation of Janus Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1071–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.T.; Such, C.H.; Hawkett, B.S. Synthesis of polymeric Janus nanoparticles and their application in surfactant-free emulsion polymerizations. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfika, V.; Tsitsilianis, C. pH Responsive Heteroarm Starlike Micelles from Double Hydrophilic ABC Terpolymer with Ampholitic A and C Blocks. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9551–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Larsen, R.J.; Weitzd, A. Uniform Nonspherical Colloidal Particles with Tunable Shapes. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Larsen, R.J.; Weitzd, A. Synthesis of nonspherical colloidal particles with anisotropic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14374–14377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, E.B.; Bruyn, H.D.; Hawkett, B.S.; Gilbert, R.G.; Zukoski, C.F. Synthesis of Anisotropic Nanoparticles by Seeded Emulsion Polymerization. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4037–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, M.; Song, S.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, J.; Liu, G. Intriguing Morphology Evolution from Noncrosslinked Poly(tert-butyl acrylate) Seeds with Polar Functional Groups in Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization of Styrene. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7829–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wan, X.; Wang, S. Heterostructured Microparticles: From Emulsion Interfacial Polymerization to Separation Applications. Acc. Mater. Res. 2023, 4, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y. Syntheses and applications of concave and convex colloids with precisely controlled shapes. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.-B.; Zhai, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, S. Hydrophilic/Oleophilic Magnetic Janus Particles for the Rapid and Efficient Oil-Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, T.; Gao, Y.; Du, F. Topology-Regulated Pesticide Retention on Plant Leaves through Concave Janus Carriers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13148–13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-B.; Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lu, Z.; Wang, S. Janus Particles Synthesis by Emulsion Interfacial Polymerization: Polystyrene as Seed or Beyond? Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Song, Y.; Gao, Z.; Fan, J.-B.; Wang, S. Precise Synthesis of Polymer Particles Spanning from Anisotropic Janus Particles to Heterogeneous Nanoporous Particles. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3237–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lin, S.; Ng, F.T.T.; Mitra, S.K.; Pan, Q. Synthesis of Shape-Controllable Anisotropic Microparticles and “Walnut-like” Microparticles via Emulsion Interfacial Polymerization. Langmuir 2021, 37, 6007–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Liu, T.; He, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Tang, J.; Liang, K.; Jiang, L.; et al. Kinetics-Regulated Interfacial Selective Superassembly of Asymmetric Smart Nanovehicles with Tailored Topological Hollow Architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, D.; Choi, W.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, K.S.; Lee, J.Y. Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elham, D.; Mehdi, S.-K.; Hossein, R.-M. Fabricating cauliflower-like and dumbbell-like Janus particles: Loading and simultaneous release of DOX and ibuprofen. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, E.C.; Ribbe, A.E.; Bradley, L.C.; Emrick, T. Alkyne-rich patchy polymer colloids prepared by surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, W.; Huang, H.; Qi, D. Controllable synthesis of monodisperse nonspherical colloidal particles with cavity structures. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 57, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, D.; Hashimoto, M.; Hayasaka, K.; Konno, M. Synthesis of Anisotropic Polymer Particles with Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization in the Presence of a Reactive Silane Coupling Agent. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.S.J.; Wong, S.L.Y.; Chen, Z. Preparation of Janus Titanium Dioxide Particles via Ultraviolet Irradiation of Pickering Emulsions. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Nan, X.; Sun, Z.; Lei, X.; Wang, W.; Hao, H.; Li, J. Anisotropic Microparticles with a Controllable Structure via Soap-Free Seeded Emulsion Polymerization. Molecules 2025, 30, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010166
Duan Y, Zhao X, Nan X, Sun Z, Lei X, Wang W, Hao H, Li J. Anisotropic Microparticles with a Controllable Structure via Soap-Free Seeded Emulsion Polymerization. Molecules. 2025; 30(1):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010166
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yanping, Xia Zhao, Xiang Nan, Zhifeng Sun, Xiaoyun Lei, Wei Wang, Hong Hao, and Jianfang Li. 2025. "Anisotropic Microparticles with a Controllable Structure via Soap-Free Seeded Emulsion Polymerization" Molecules 30, no. 1: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010166
APA StyleDuan, Y., Zhao, X., Nan, X., Sun, Z., Lei, X., Wang, W., Hao, H., & Li, J. (2025). Anisotropic Microparticles with a Controllable Structure via Soap-Free Seeded Emulsion Polymerization. Molecules, 30(1), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010166






