Cold Pressed Oil from Japanese Quince Seeds (Chaenomeles japonica): Characterization Using DSC, Spectroscopic, and Monolayer Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Measurements
Deconvolution of DSC Transitions
2.2. ATR-FTIR Spectra
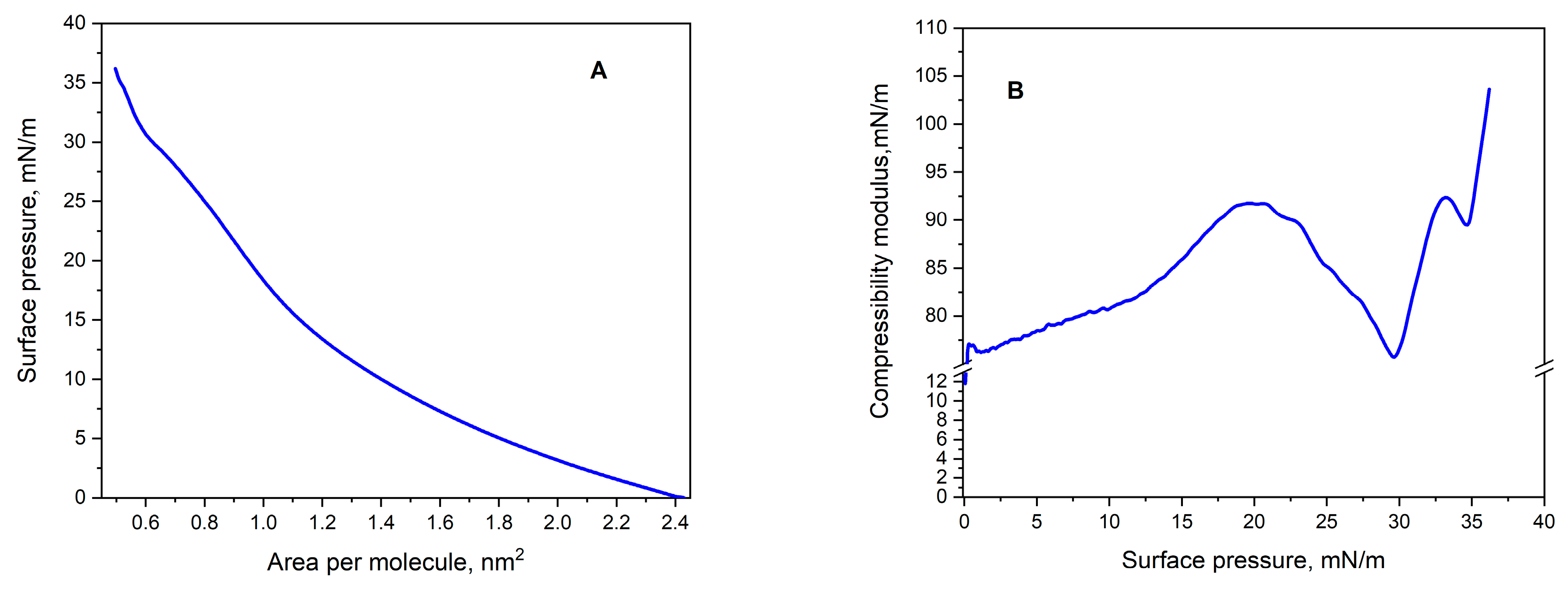
2.3. Monolayer Studies
2.3.1. Monolayer Compression
2.3.2. The Compressibility Modulus (Cs−1)
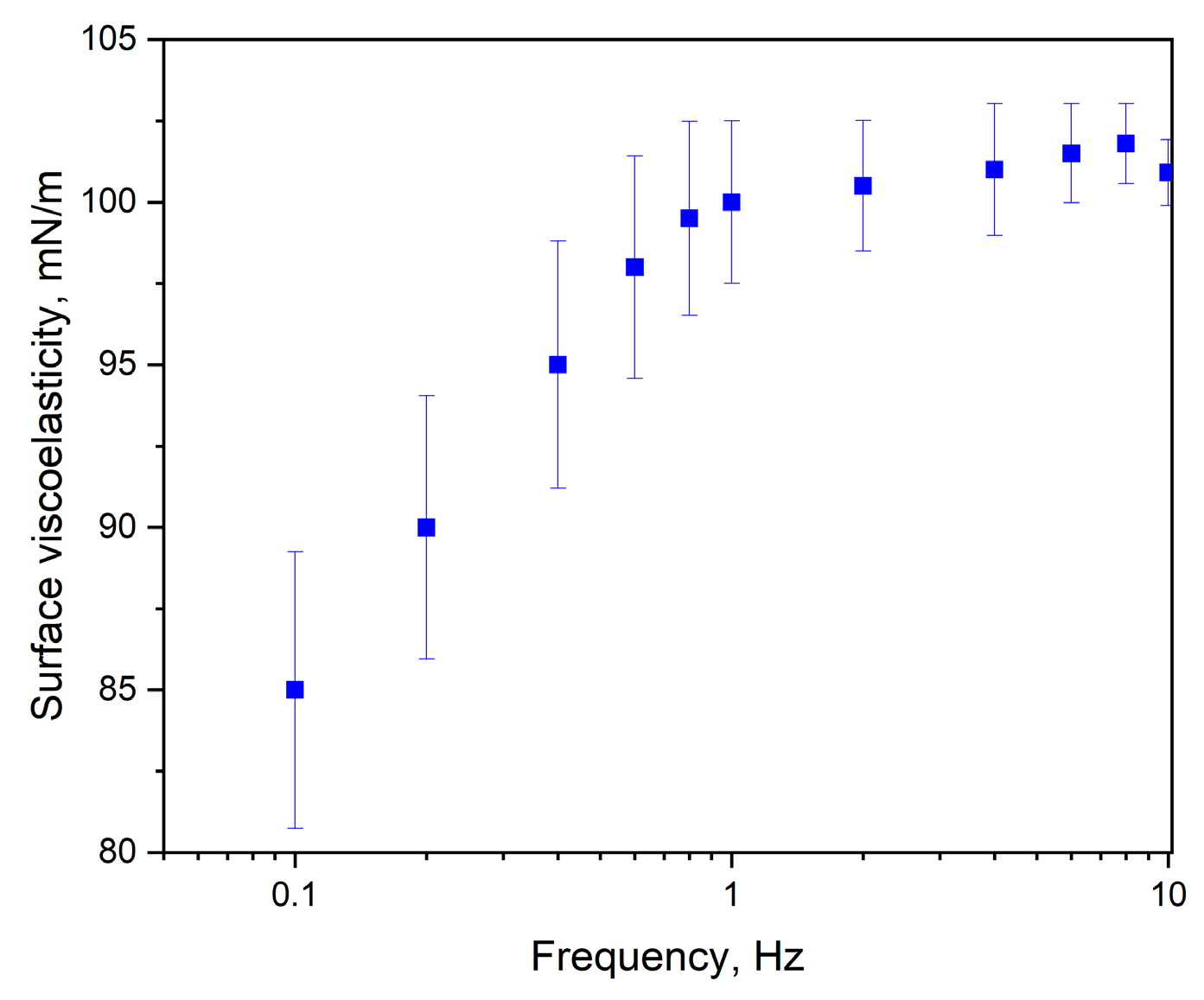
2.3.3. Surface Viscoelasticity Modulus (ε)
2.4. Absorption and Fluorescence Spectra
2.4.1. Absorption Spectra
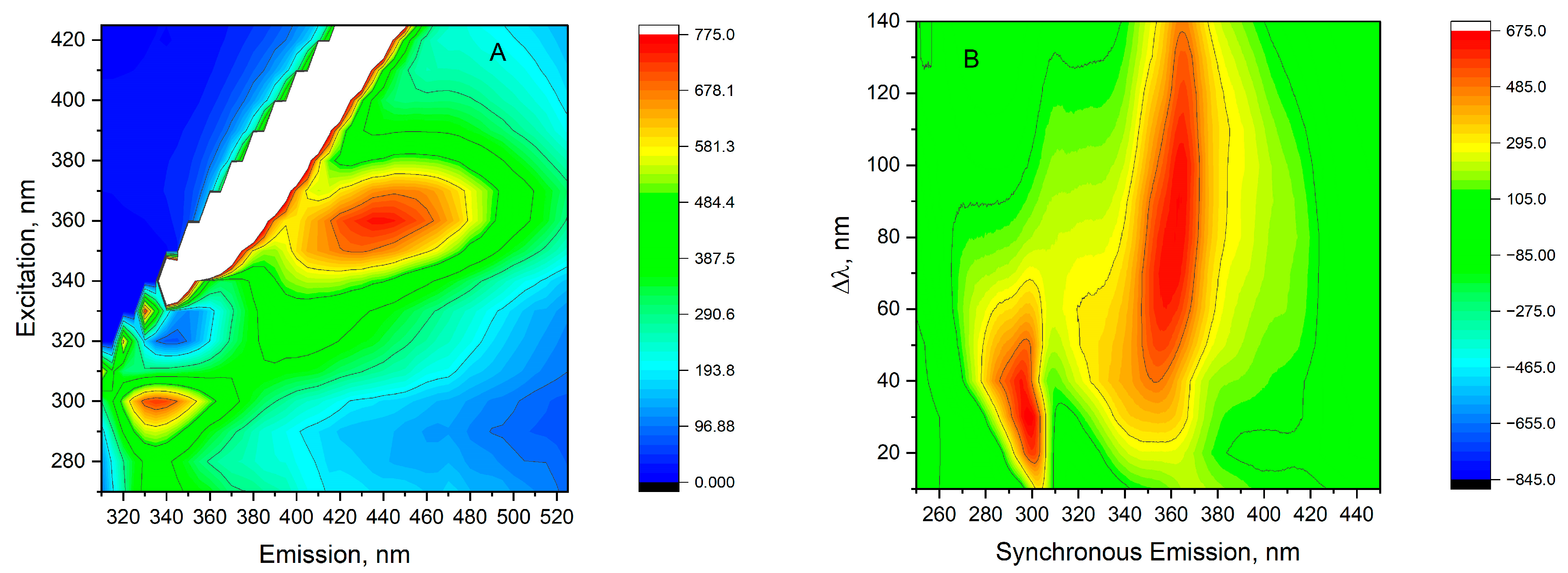
2.4.2. Fluorescence Spectra
Total Luminescence Spectra
Total Fluorescence Synchronous Spectra
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Crystallization and Melting Phase Transition Determination by DSC
3.2.2. Absorption and Fluorescence Spectra
3.2.3. ATR-FTIR Measurements
3.2.4. Monolayer Studies
Langmuir Monolayer Method
Oscillatory Dilatational Rheology
3.2.5. Statistical and Graphical Programs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Othman, S.; Bleive, U.; Kaldmäe, H.; Aluvee, A.; Rätsep, R.; Karp, K.; Maciel, L.S.; Herodes, K.; Rinken, T. Phytochemical characterization of oil and protein fractions isolated from Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) wine by-product. LWT 2023, 178, 114632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Rudzińska, M.; Grygier, A.; Marszałkiewicz, S.; Ying, Q.; Sobieszczańska, N.; Segliņa, D. Impact of the Extraction Technique and Genotype on the Oil Yield and Composition of Lipophilic Compounds in the Oil Recovered from Japanese Quince (Chaenomeles japonica) Seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Segliņa, D. Physicochemical characteristics of the cold-pressed Japanese quince seed oil: New promising unconventional bio-oil from by-products for the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 48, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, M.; Vila, R.; Laencina, J.; Rumpunen, K.; Ros, J. Characteristics and composition of chaenomeles seed oil. In Japanese Quince—Potential Fruit Crop for Northern Europe; Rumpunen, K., Ed.; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Alnarp, Sweden, 2003; pp. 141–147. ISBN 91-631-3765-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mierina, I.; Serzane, R.; Strele, M.; Moskaluka, J.; Seglina, D.; Jure, M. Extracts of Japanese quince seeds—Potential source of antioxidants. In Proceedings of the 6th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology: Innovations for Food Science and Production, FOODBALT-2011, Jelgava, Latvia, 5–6 May 2011; Straumite, E., Ed.; Latvia University of Agriculture: Jelgava, Latvia, 2011; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Juhņeviča, K.; Lacis, G.; Šne, E.; Segliņa, D. Cold-pressed Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. ex Spach) seed oil as a rich source of α-tocopherol, carotenoids and phenolics: A comparison of the composition and antioxidant activity with nine other plant oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A. Cold pressed Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. ex Spach) seed oil. In Cold Pressed Oils: Green Technology, Bioactive Compounds, Functionality, and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanavičiūte, I.; Liaudanskas, M.; Bobinas, Č.; Šarkinas, A.; Rezgiene, A.; Viskelis, P. Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) as a potential source of phenols: Optimization of the extraction parameters and assessment of antiradical and antimicrobial activities. Foods 2020, 9, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanavičiūtė, I.; Viškelis, P.; Urbanavičiūtė, I.; Viškelis, P. Biochemical Composition of Japanese Quince (Chaenomeles japonica) and Its Promising Value for Food, Cosmetic, and Pharmaceutical Industries. In Fruit Industry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wua, J.; Li, H.; Zhong, P.X.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, C.H.; Ji, K.X.; Wang, L.S. Polyphenols and triterpenes from Chaenomeles fruits: Chemical analysis and antioxidant activities assessment. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, J.M.; Laencina, J.; Hellín, P.; Jordán, M.J.; Vila, R.; Rumpunen, K. Characterization of juice in fruits of different Chaenomeles species. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Rudzińska, M. Seeds recovered from industry by-products of nine fruit species with a high potential utility as a source of unconventional oil for biodiesel and cosmetic and pharmaceutical sectors. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavaro, E.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L. Correlation between thermal properties and chemical composition of Italian virgin olive oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagukguk, Y.V.; Islam, M.; Grygier, A.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J. Thermal and spectroscopic profiles variation of cold-pressed raspberry seed oil studied by DSC, UV/VIS, and FTIR techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 124, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejak, P.; Neunert, G.; Kamińska, W.; Dembska, A.; Polewski, K.; Siger, A.; Grygier, A.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J. A crude, cold-pressed oil from elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) seeds: Comprehensive approach to properties and characterization using HPLC, DSC, and multispectroscopic methods. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiana, M.A.; Alexa, E.; Munteanu, M.F.; Gligor, R.; Moigradean, D.; Mateescu, C. Use of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to detect the changes in extra virgin olive oil by adulteration with soybean oil and high temperature heat treatment. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piosik, E.; Zaryczniak, A.; Mylkie, K.; Ziegler-Borowska, M. Probing of Interactions of Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Native and Aminated Starch with a DPPC Model Membrane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, W.; Cichocki, W.; Maria Baranowska, H.; Walkowiak, K.; Kmiecik, D.; Łukasz Kowalczewski, P. Characteristics of Langmuir monomolecular monolayers formed by the novel oil blends. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20230173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo Rodríguez, J.L.; Dynarowicz-Latka, P.; Miñones Conde, J. Structure of unsaturated fatty acids in 2D system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 158, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.T.; Rideal, E.K. Interfacial Phenomena; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Allen, H.C. DPPC Langmuir monolayer at the air-water interface: Probing the tail and head groups by vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, N.; García-gonzález, D.L.; Aparicio, R. Evaluation of virgin olive oil thermal deterioration by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10505–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Delgado, M.A.; Malovaná, S.; Pérez, J.P.; Borges, T.; García Montelongo, F.J. Separation of phenolic compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography with absorbance and fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 912, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Valencia, R.; Cittadini, A.; Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Elderberry Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Bioactive Compounds: Characterization and Extract Encapsulation. Foods 2023, 12, 4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Szablewski, T.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Świerk, D.; Cegielska-Radziejewska, R.; Krejpcio, Z.; Suchowilska, E.; Tomczyk, Ł.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Sambucus nigra extracts–natural antioxidants and antimicrobial compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulli, K.I.; Mousdis, G.A.; Georgiou, C.A. Rapid synchronous fluorescence method for virgin olive oil adulteration assessment. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, G.L. Thermodynamic relationships for mixed insoluble monolayers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1966, 21, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luviano, A.S.; Campos-Terán, J.; Langevin, D.; Castillo, R.; Espinosa, G. Mechanical Properties of DPPC-POPE Mixed Langmuir Monolayers. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16734–16744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noskov, B.A.; Bykov, A.G. Dilational rheology of monolayers of nano- and micropaticles at the liquid-fluid interfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
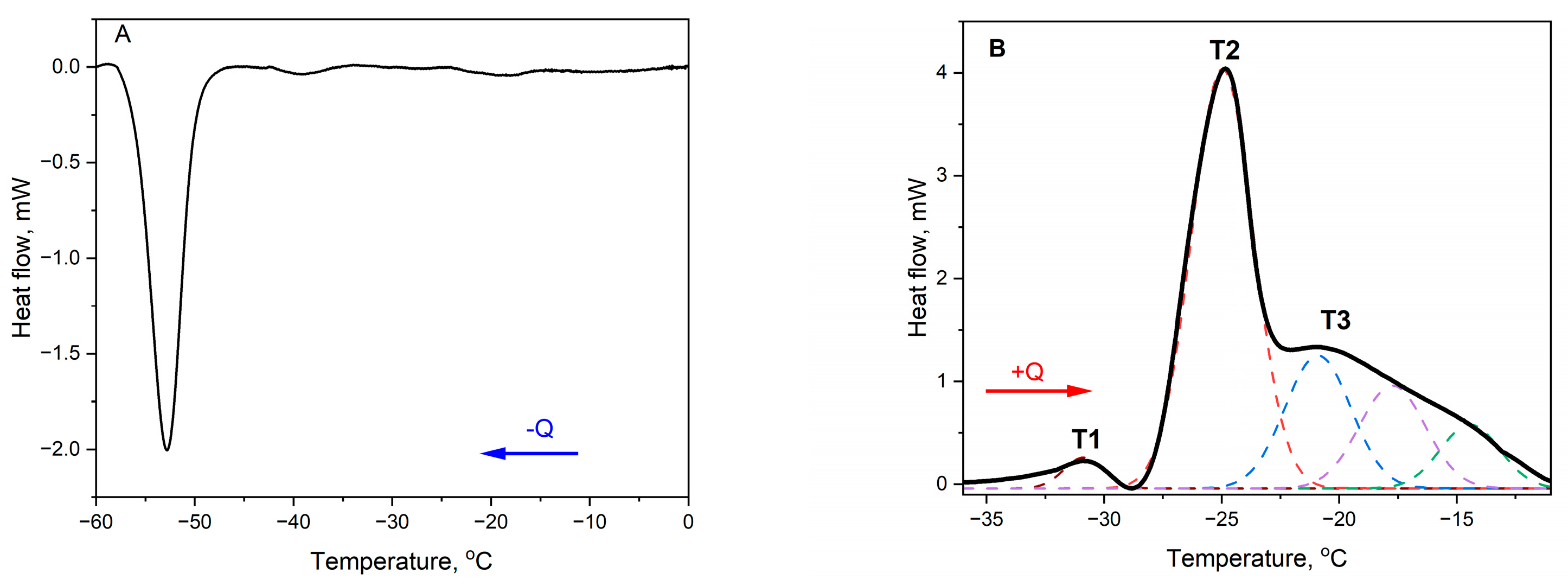


| Onset Temperature (°C) | Peak Temperature (°C) | Total Enthalpy (J/g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystallization | Ton | T | ΔH | ||||
| −50.1 ± 0.04 | −52.9 ± 0.06 | −35.3 ± 0.77 | |||||
| Melting | Peak Temperature (°C) | Total enthalpy (J/g) | Partial enthalpy (J/g) | ||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | ΔH | ΔH1 | ΔH2 | ΔH3 | |
| −30.9 ± 0.04 | −24.9 ± 0.05 | −20.8 ± 0.01 | 55.9 ± 0.01 | 4.8 ± 0.06 | 28.0 ± 0.05 | 23.1 ± 0.00 | |
| Parameter | AEXP [nm2] | AC [nm2] | πC [mN/m] | CS−1MAX [mN/m] | εMAX [mN/m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JQSO | 1.49 ± 0.08 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 36.2 ± 1.1 | 103.6 ± 1.9 | 100.9 ± 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamińska, W.; Neunert, G.; Siejak, P.; Polewski, K.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J. Cold Pressed Oil from Japanese Quince Seeds (Chaenomeles japonica): Characterization Using DSC, Spectroscopic, and Monolayer Data. Molecules 2025, 30, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030477
Kamińska W, Neunert G, Siejak P, Polewski K, Tomaszewska-Gras J. Cold Pressed Oil from Japanese Quince Seeds (Chaenomeles japonica): Characterization Using DSC, Spectroscopic, and Monolayer Data. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030477
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamińska, Wiktoria, Grażyna Neunert, Przemysław Siejak, Krzysztof Polewski, and Jolanta Tomaszewska-Gras. 2025. "Cold Pressed Oil from Japanese Quince Seeds (Chaenomeles japonica): Characterization Using DSC, Spectroscopic, and Monolayer Data" Molecules 30, no. 3: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030477
APA StyleKamińska, W., Neunert, G., Siejak, P., Polewski, K., & Tomaszewska-Gras, J. (2025). Cold Pressed Oil from Japanese Quince Seeds (Chaenomeles japonica): Characterization Using DSC, Spectroscopic, and Monolayer Data. Molecules, 30(3), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030477












