Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity
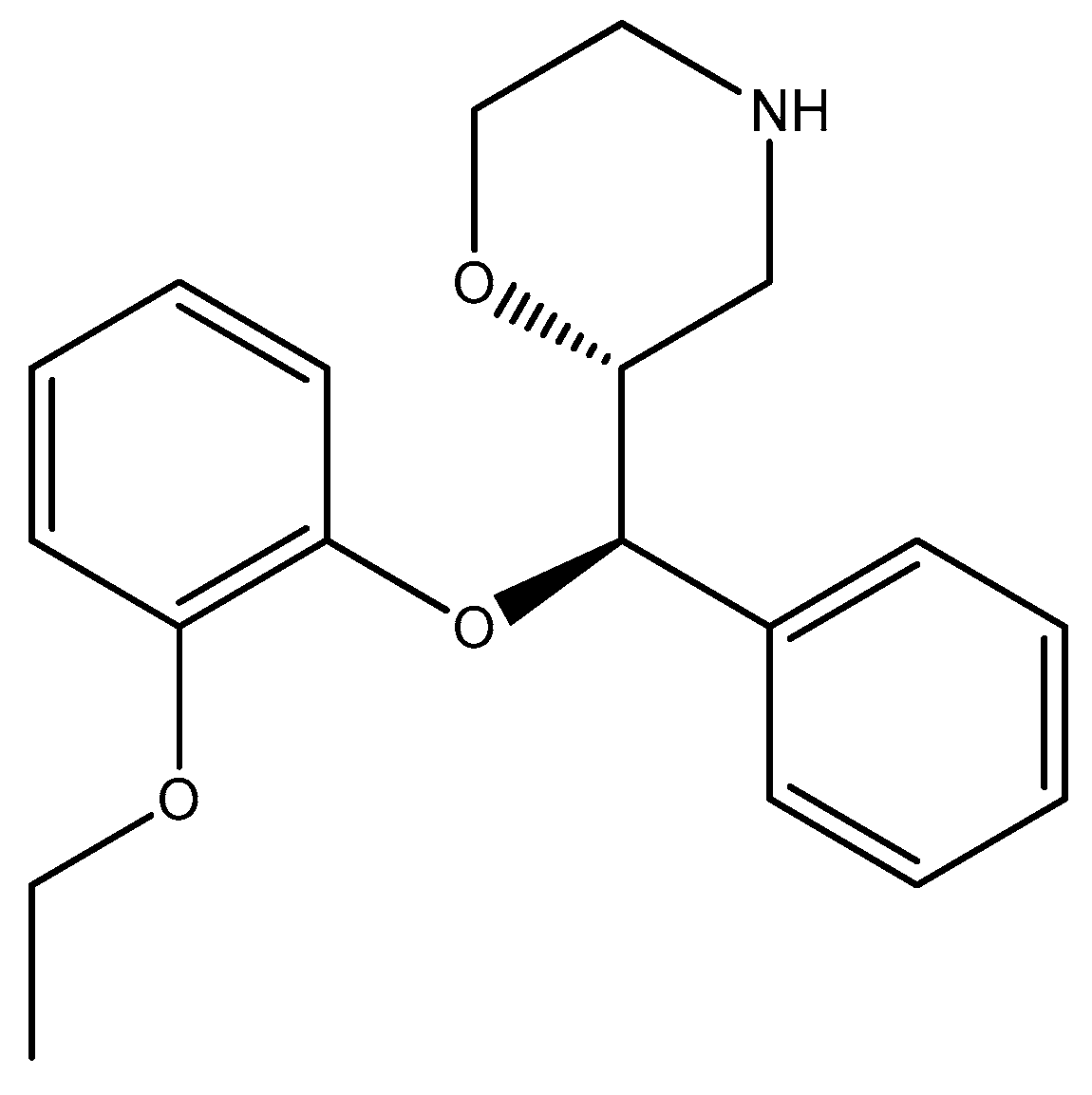
2.1. Morpholine Moiety
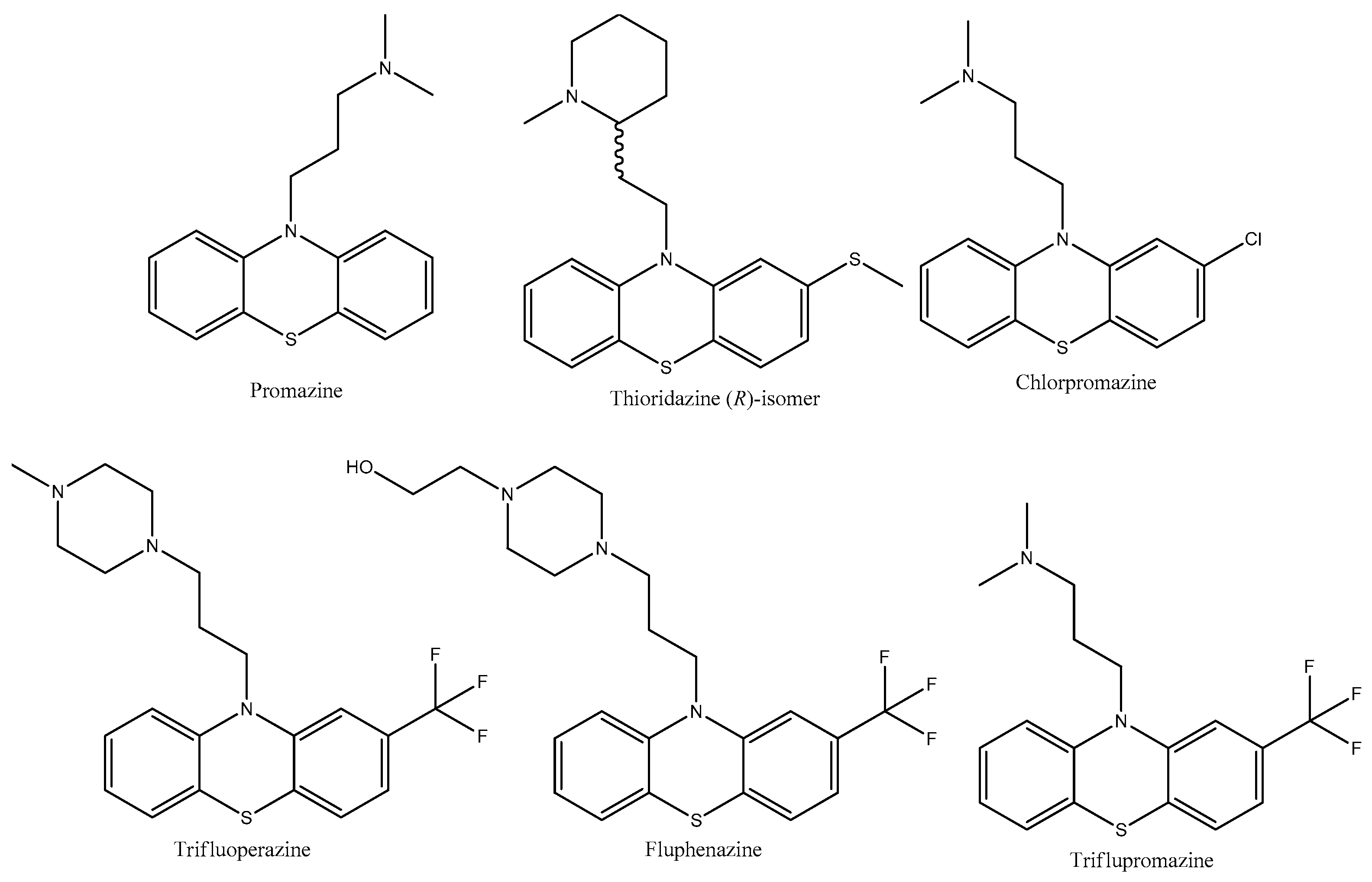
2.2. Thiomorpholine Moiety
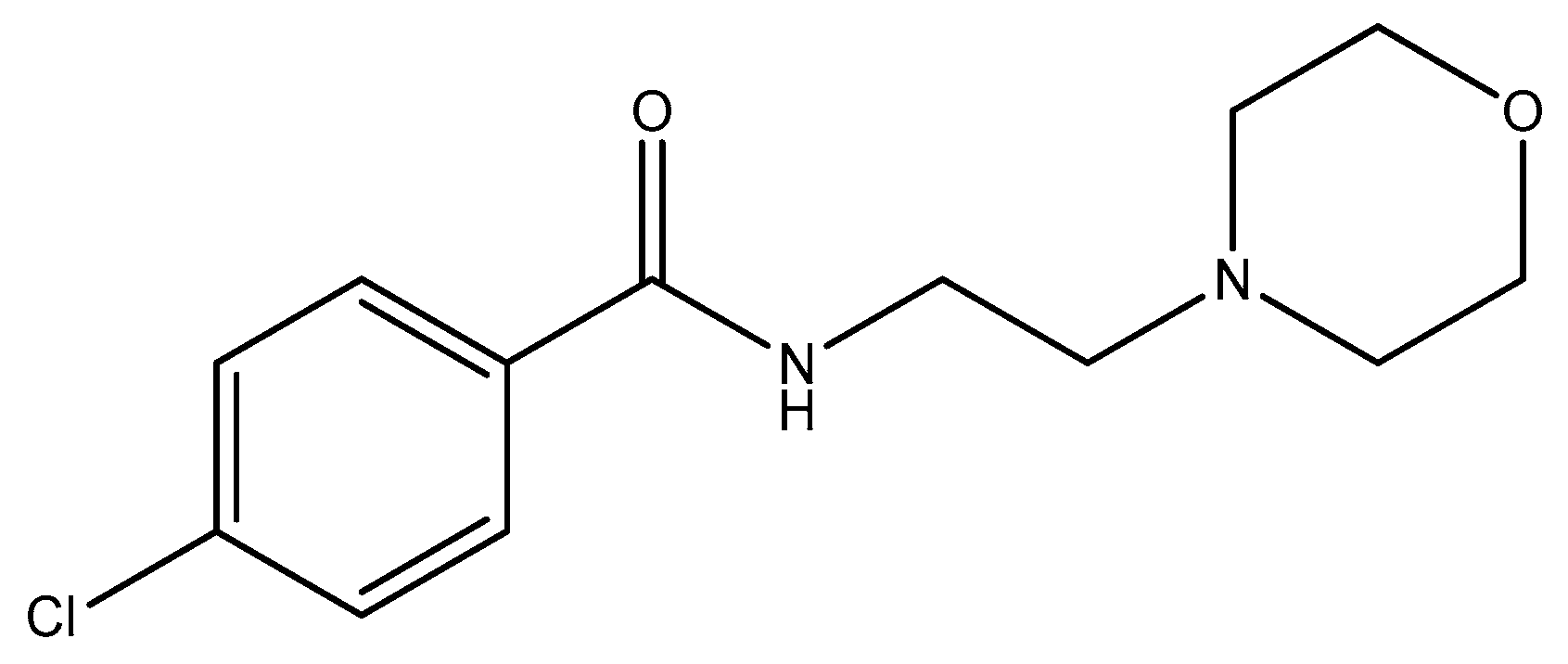
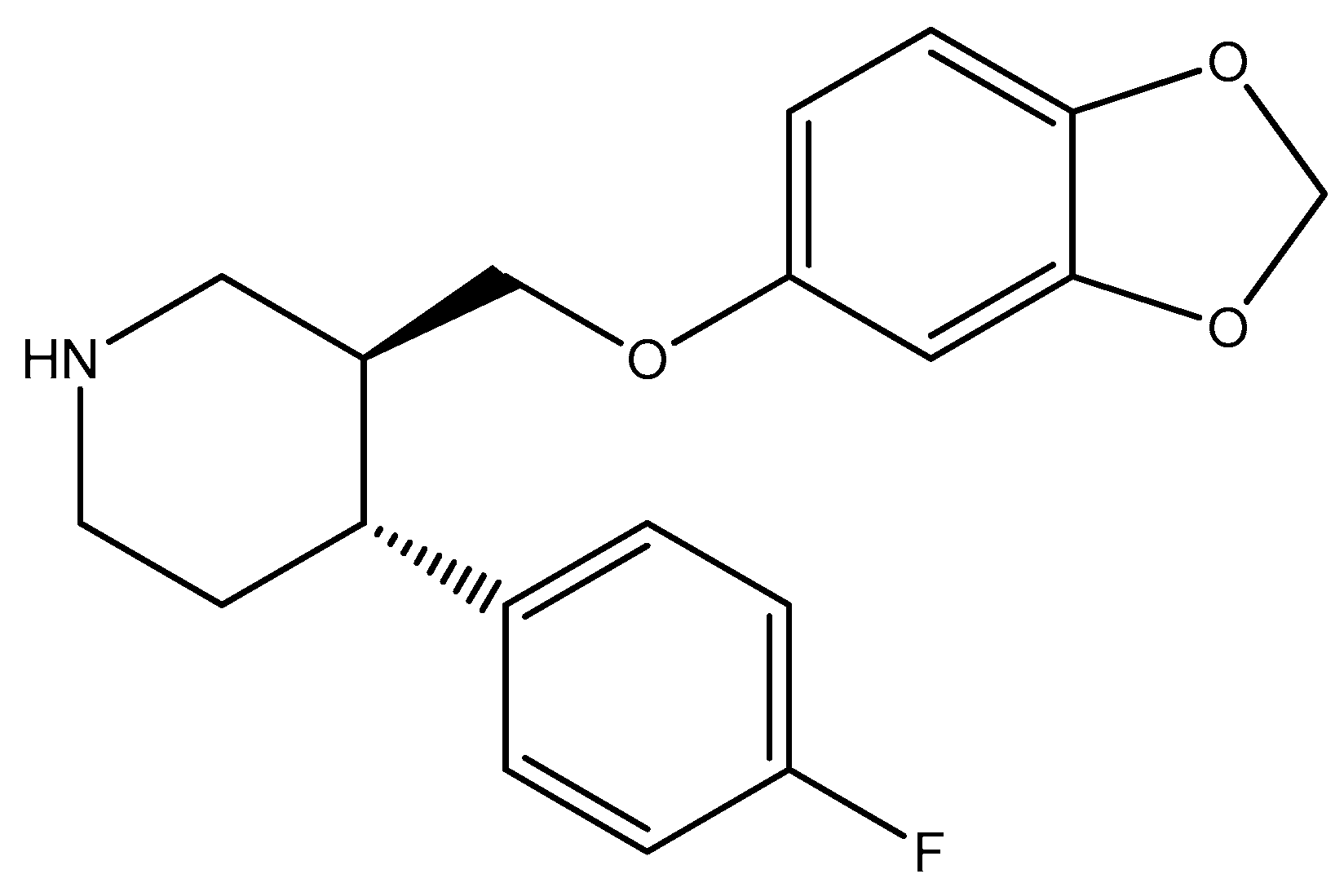
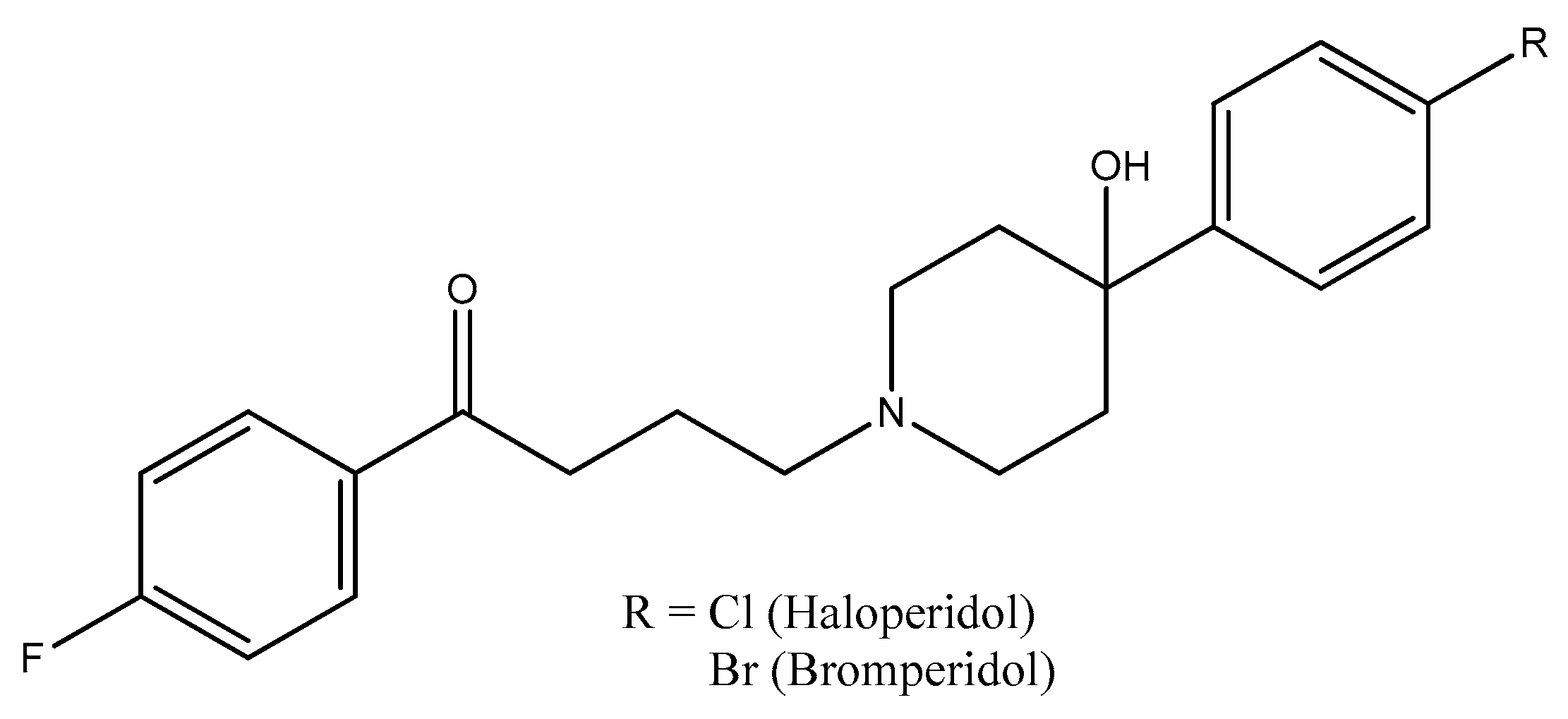
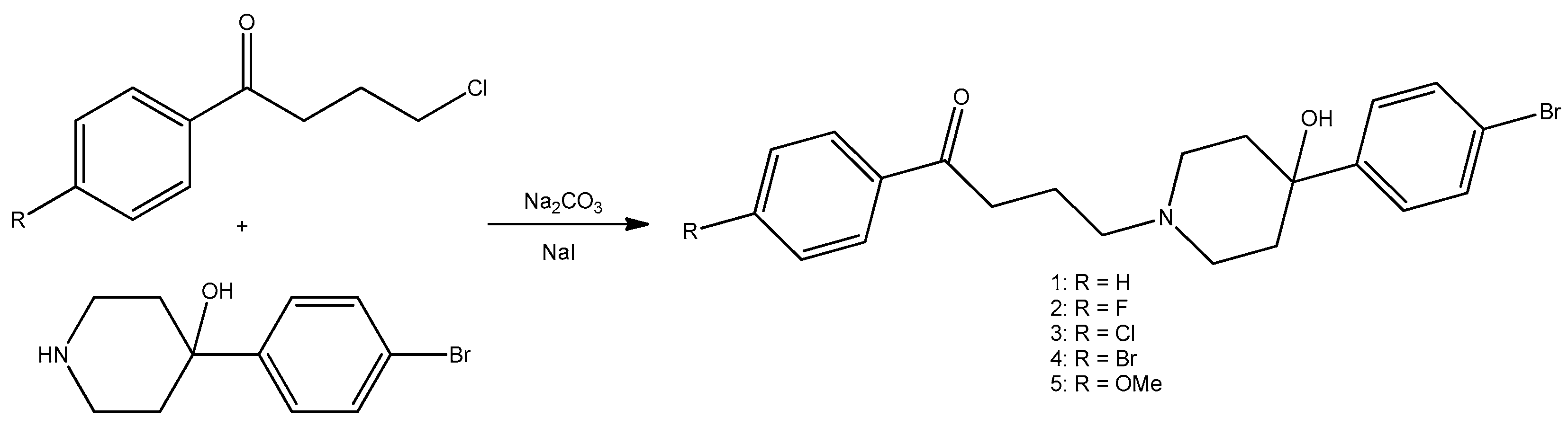
2.3. Piperidine Moiety
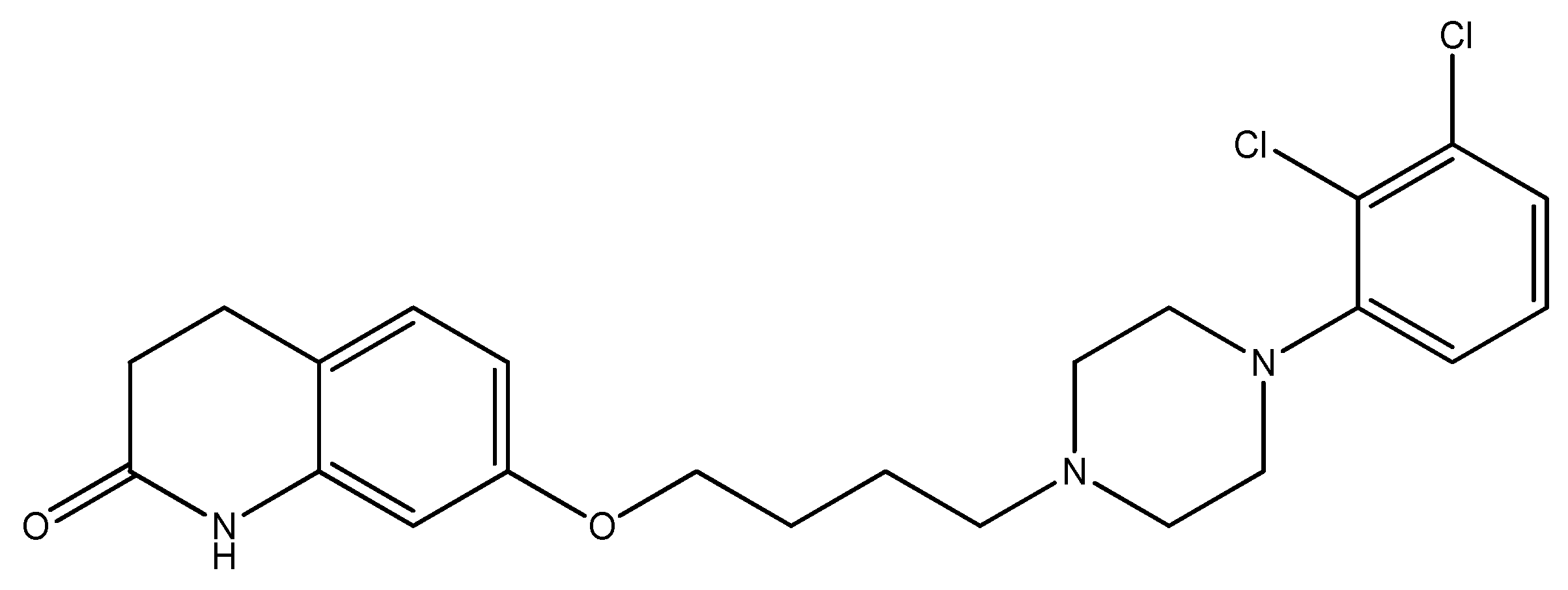
2.4. Piperazine Moiety
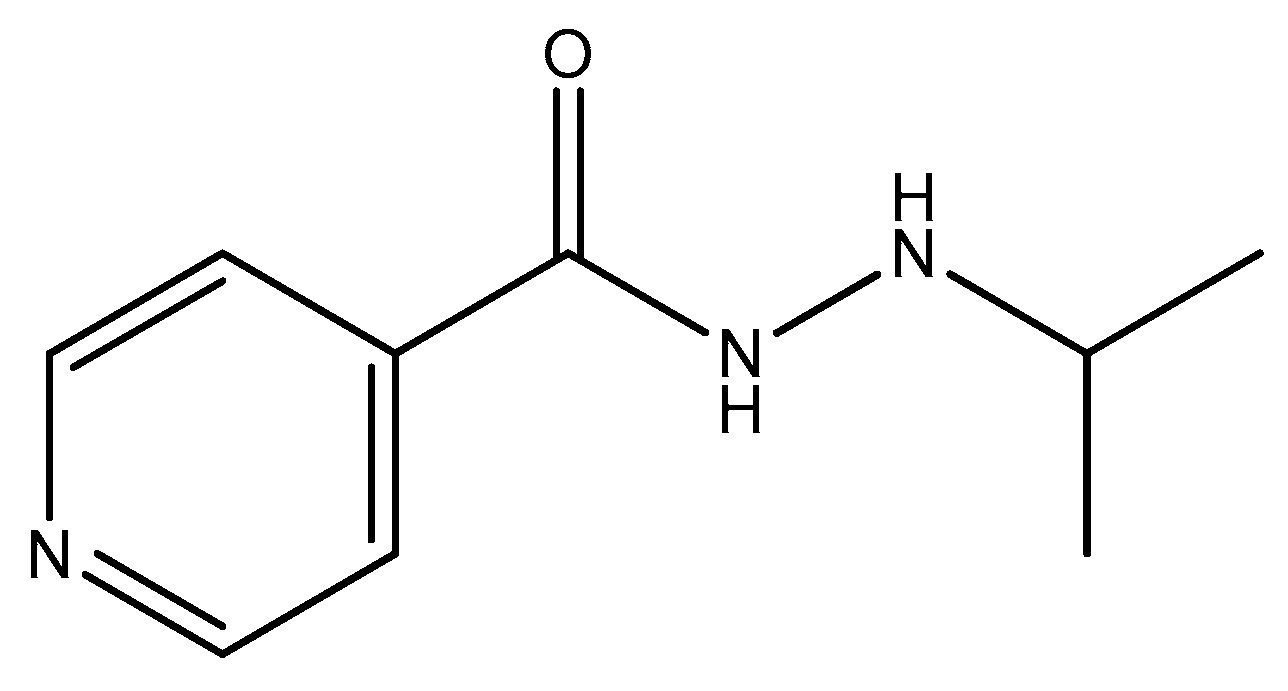
2.5. Pyridine Moiety
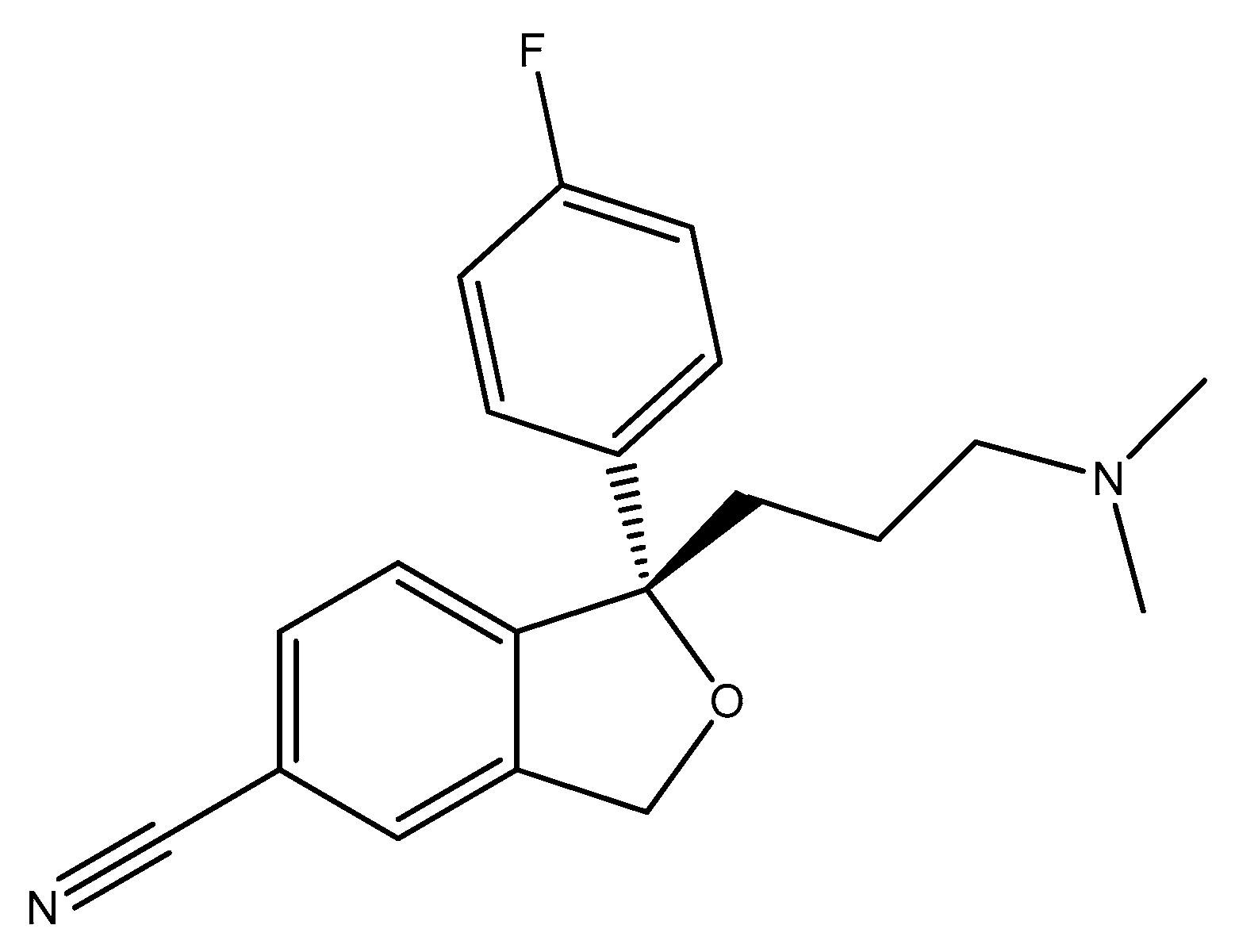
2.6. Seven-Membered Heterocycles
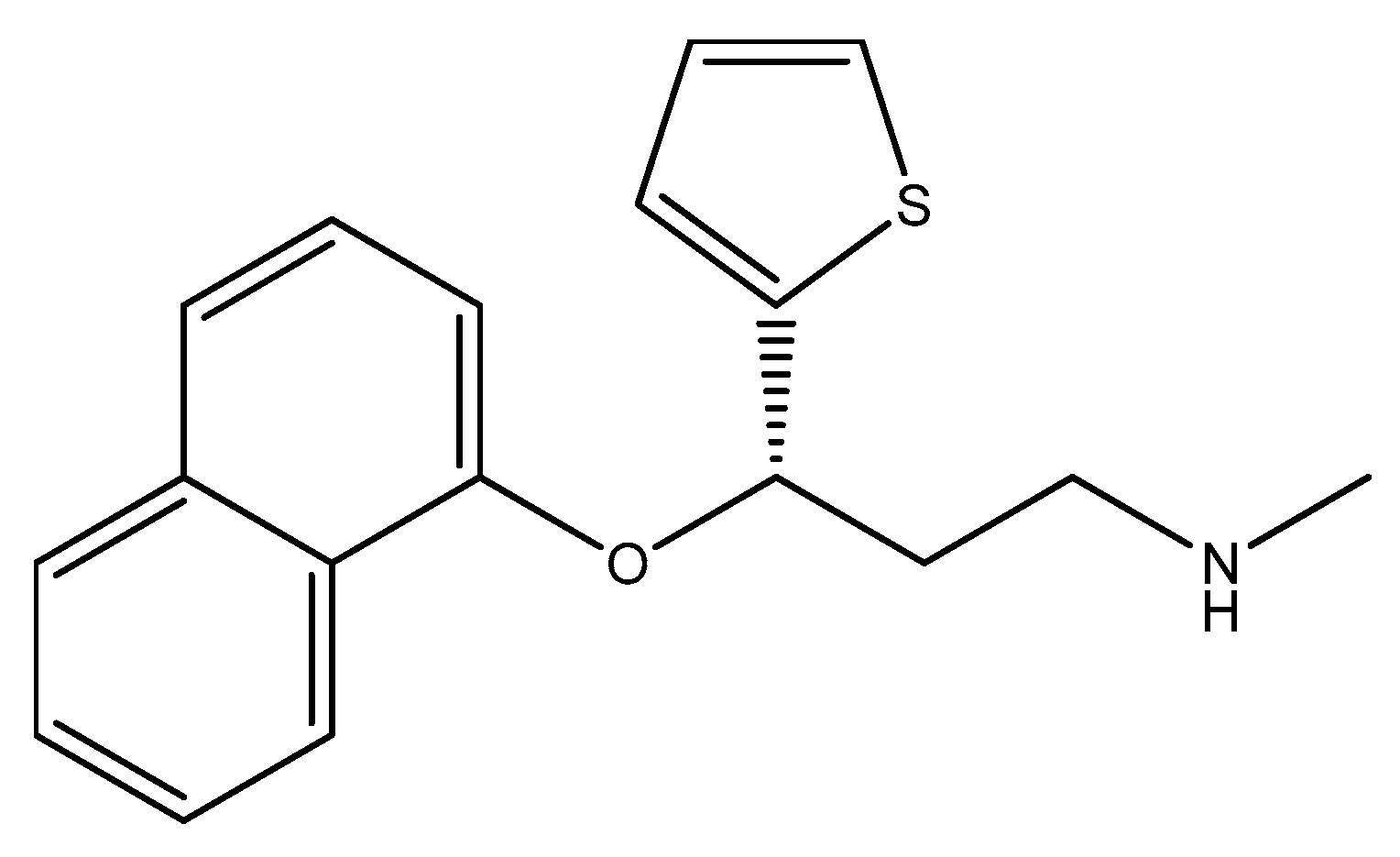
2.7. Five-Membered Heterocycles
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clapp, M.; Aurora, N.; Herrera, L.; Bhatia, M.; Wilen, E.; Wakefield, S. Gut microbiota’s effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin. Pract. 2017, 157, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Regulation of Neurotransmitters by the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Cognition in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.G.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, D.D.; Wu, S.X.; Huang, S.Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Yang, Z.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Anxiety, Depression, and Other Mental Disorders as Well as the Protective Effects of Dietary Components. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Del Valle, C.; Fernández, J.; Solá, E.; Montoya-Castilla, I.; Morillas, C.; Bañuls, C. Association between gut microbiota and psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1215674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, G.; Bachtel, G.; Sugden, S.G. Gut microbiota, nutrition, and mental health. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1337889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelberer, M.M.; Buchanan, K.L.; Klein, M.E.; Barth, B.B.; Montoya, M.M.; Shen, X.; Bohórquez, D.V. A gut-brain neural circuit for nutrient sensory transduction. Science 2018, 361, eaat5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanote, J.; Correa Rojo, A.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Ertaylan, G. Systematic identification of the role of gut microbiota in mental disorders: A TwinsUK cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Hu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, J. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation from Healthy Donors Reduced Alcohol-induced Anxiety and Depression in an Animal Model of Chronic Alcohol Exposure. Chin. J. Physiol. 2018, 61, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chang, L.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Hashimoto, K. A role of the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve in depression-like phenotypes in mice after fecal microbiota transplantation from Chrna7 knock-out mice with depression-like phenotypes. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Celniker, S.E.; Xia, Y.; Mao, J.-H.; Snijders, A.M.; Chang, H. Gut microbiome partially mediates and coordinates the effects of genetics on anxiety-like behavior in Collaborative Cross mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrioaie, I.-M.; Duhaniuc, A.; Nastase, E.V.; Iancu, L.S.; Luncă, C.; Trofin, F.; Anton-Păduraru, D.-T.; Dorneanu, O.-S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Psychiatric Disorders. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Mu, C.L.; Farzi, A.; Zhu, W.Y. Tryptophan metabolism: A link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, M.; Rowatt, E.; Harrison, K. The production of acetylcholine by a strain of Lactobacillus plantarum with an addendum on the isolation of acetylcholine as a salt of hexanitrodiphenylamine. Microbiology 1947, 1, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Misawa, H.; Moriwaki, Y.; Fujii, Y.X.; Fujii, T.; Horiuchi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Imanaka, T.; Kamekura, M. Ubiquitous expression of acetylcholine and its biological functions in life forms without nervous systems. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 2206–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Park, A.J.; Sinclair, D.; Khoshdel, A.; Lu, J.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.A.; Fahnestock, M.; Moine, D.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Ahuja, V.; Paul, J. Dysregulation of GABAergic signalling contributes in the pathogenesis of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsgaard Bendtsen, K.M.; Krych, L.; Sørensen, D.B.; Pang, W.; Nielsen, D.S.; Josefsen, K.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, A.K. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Correlated to Grid Floor Induced Stress and Behavior in the BALB/c Mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyte, M.; Li, W.; Opitz, N.; Gaykema, R.P.; Goehler, L.E. Induction of anxiety-like behavior in mice during the initial stages of infection with the agent of murine colonic hyperplasia Citrobacter rodentium. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 89, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.M.; Kassam, Z.; Bercik, P. The adoptive transfer of behavioral phenotype via the intestinal microbiota: Experimental evidence and clinical implications. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, M.; Zhao, J.H.; Ruan, B. Altered gut microbiota profile in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 104, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Meng, C.; Li, L.; Feng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Han, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, W.; Figeys, D.; et al. Positive mood-related gut microbiota in a long-term closed environment: A multiomics study based on the “Lunar Palace 365” experiment. Microbiome 2023, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kretzschmar, B.; Herold, S.; Nau, R.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Schütze, S.; Bähr, M.; Hein, K. Beneficial effect of chronic Staphylococcus aureus infection in a model of multiple sclerosis is mediated through the secretion of extracellular adherence protein. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, W.E.; Wang, B.; Sukhum, K.V.; D’Souza, A.W.; Hink, T.; Cass, C.; Seiler, S.; Reske, K.A.; Coon, C.; Dubberke, E.R.; et al. Acute and persistent effects of commonly used antibiotics on the gut microbiome and resistome in healthy adults. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Bustos Fernandez, L.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinemerem Nwobodo, D.; Ugwu, M.C.; Oliseloke Anie, C.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Chinedu Ikem, J.; Victor Chigozie, U.; Saki, M. Antibiotic resistance: The challenges and some emerging strategies for tackling a global menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Chait, Y.; Mottawea, W.; Tompkins, T.A.; Hammami, R. Unravelling the antimicrobial action of antidepressants on gut commensal microbes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ding, P.; Lu, J.; Mao, L.; Ngiam, L.; Yuan, Z.; Engelstädter, J.; Schembri, M.A.; Guo, J. Antidepressants can induce mutation and enhance persistence toward multiple antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2208344120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepede, G.; Corbo, M.; Fiori, F.; Martinotti, G. Reboxetine in clinical practice: A review. Clin. Ter. 2012, 163, e255–e262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalaycı, S.; Demirci, S.; Sahin, F. Antimicrobial Properties of Various Psychotropic Drugs Against Broad Range Microorganisms. Curr. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.I.; Alhuwaydi, A.M.; Taha, A.E.; Abouelkheir, M. Anti-Candidal Activity of Reboxetine and Sertraline Antidepressants: Effects on Pre-Formed Biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lass-Flörl, C.; Dierich, M.P.; Fuchs, D.; Semenitz, E.; Jenewein, I.; Ledochowski, M. Antifungal properties of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors against Aspergillus species in vitro. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.J.; Mattingly, G.W.; Jain, R.; O’Neal, W. Current and future nonstimulants in the treatment of pediatric ADHD: Monoamine reuptake inhibitors, receptor modulators, and multimodal agents. CNS Spectr. 2022, 27, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, R.; Leigh, T.; Rao, B.S.; Todd, A.H. Optical isomers of 2-(2-ethoxyphenoxymethyl)tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine (viloxazine) and related compounds. Med. Chem. 1976, 19, 1074–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.; Benfield, P. Moclobemide: An update of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1996, 52, 450–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C. Promazine. In X Pharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, S.M.; Fariba, K.A.; Saadabadi, A. Thioridazine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK459140/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Mann, S.K.; Marwaha, R. Chlorpromazine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553079/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Davis, C. Trifluoperazine. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Mansi, K.; Haynes, E.; Adams, C.E.; Sampson, S.; Furtado, V.A. Trifluoperazine versus placebo for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 1, CD010226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, H.E.; Almerie, M.Q.; Sampson, S.J. Fluphenazine (oral) versus placebo for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD006352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, H.; Saulnier, P.; Ramadan, A.A.; Cassisa, V.; Guillet, C.; Eveillard, M.; Umerska, A. Antibacterial activity of antipsychotic agents, their association with lipid nanocapsules and its impact on the properties of the nanocarriers and on antibacterial activity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, T.; Jørgensen, N.S.; Holmer, I.; Kromann, S.; Sheikhsamani, E.; Permin, A.; Svenningsen, S.W.; Christensen, J.B.; Olsen, R.H. A Novel Promazine Derivative Shows High in vitro and in vivo Antimicrobial Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 560798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrynchuk, N.; Vrynchanu, N. Antibacterial properties of thioridazine. Farmatsevtychnyi Zhurnal 2019, 4, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, N.K.; Pinn, M.L.; Zhao, M.; Rudek, M.A.; Karakousis, P.C. Thioridazine lacks bactericidal activity in an animal model of extracellular tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.Ø.; Klitgaard, J.K.; Christensen, J.B.; Kallipolitis, B.H.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Kaatz, G.W.; Plenge, P.; Fey, S.J.; Kristiansen, J.E. Comparison of Antibacterial Activity of (–) Thioridazine and Racemic Thioridazine in Staphylococcus aureus. Am. J. Bioavailab. Bioequiv. 2018, 1, 001–009. [Google Scholar]
- Ordway, D.; Viveiros, M.; Leandro, C.; Jorge Arroz, M.; Molnar, J.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Amaral, L. Chlorpromazine has intracellular killing activity against phagocytosed Staphylococcus aureus at clinical concentrations. J. Infect. Chemother. 2002, 8, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistorescu, S.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Udrea, A.-M.; Simon, Á.; Pascu, M.L.; Chifiriuc, M.-C. Laser-Irradiated Chlorpromazine as a Potent Anti-Biofilm Agent for Coating of Biomedical Devices. Coatings 2020, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozar, T.; Nastasa, V.; Stoicu, A.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Popa, M.; Kamerzan, C.; Pascu, M.L. In vitro antimicrobial efficacy of laser exposed chlorpromazine against Gram-positive bacteria in planktonic and biofilm growth state. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, T.; Staicu, A.; Pascu, A.I.; Radu, E.; Stoicu, A.; Nastasa, V.V.; Dinache, A.C.; Boni, M.; Amaral, L.; Pascu, M.L. Characterization of mixtures of compounds produced in chlorpromazine aqueous solutions by ultraviolet laser irradiation: Their applications in antimicrobial assays. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 20, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, R.; Ganguly, K.; Dastidar, S.G.; Chakrabarty, A.N. Trifluoperazine: A broad spectrum bactericide especially active on staphylococci and vibrios. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastidar, S.G.; Debnath, S.; Mazumdar, K.; Ganguly, K.; Chakrabarty, A.N. Triflupromazine: A microbicide non-antibiotic compound. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2004, 51, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastidar, S.G.; Chaudhury, A.; Annadurai, S.; Roy, S.; Mookerjee, M.; Chakrabarty, A.N. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial action of fluphenazine. J. Chemother. 1995, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M.; Molnar, J. Antimicrobial activity of phenothiazines. In Vivo 2004, 18, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Nowaczyk, J.; Fijałkowski, Ł.; Nowaczyk, A. Paroxetine—Overview of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa Silva, R.A.; da Silva, C.R.; de Andrade Neto, J.B.; da Silva, A.R.; Campos, R.S.; Sampaio, L.S.; do Nascimento, F.B.S.A.; da Silva Gaspar, B.; da Cruz Fonseca, S.G.; Josino, M.A.A.; et al. In vitro anti-Candida activity of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors against fluconazole-resistant strains and their activity against biofilm-forming isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Ennis, C.L.; Hartooni, N.; Johnson, A.D.; Lohse, M.B. A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, a proton pump inhibitor, and two calcium channel blockers inhibit candida albicans biofilms. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekintaş, Y.; Temel, A.; Ateş, A.; Eraç, B.; Metin, D.Y.; Hilmioğlu Polat, S.; Hoşgör Limoncu, M. Antifungal and antibiofilm activities of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors alone and in combination with fluconazole. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 17, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foletto, V.S.; Serafin, M.B.; Bottega, A.; da Rosa, T.F.; Machado, C.d.S.; Coelho, S.S.; Hörner, R. Repositioning of fluoxetine and paroxetine: Study of potential antibacterial activity and its combination with ciprofloxacin. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, V.P.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Barbosa, A.D.; Moreira, L.E.; Sá, L.G.; Silva, C.R.; Neto, J.B.; Silva, J.; Marinho, E.S.; Santos, H.S.; et al. Antibacterial activity of paroxetine against Staphylococcus aureus and possible mechanisms of action. Future Microbiol. 2023, 18, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.H.; Santos, M.H.d.M.; Scandorieiro, S.; Gonçalves, B.C.; Vespero, E.C.; Perugini, M.R.E.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors: Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPEE Bacteria and Mechanisms of Action. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberca, L.N.; Sbaraglini, M.L.; Balcazar, D.; Fraccaroli, L.; Carrillo, C.; Medeiros, A.; Benitez, D.; Comini, M.; Talevi, A. Discovery of novel polyamine analogs with anti-protozoal activity by computer-guided drug repositioning. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, R.; Ward, A. Haloperidol decanoate. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in psychosis. Drugs 1987, 33, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinsky, B.; McGuire, J.L.; Niemegeers, C.J.; Janssen, P.A.; Weintraub, H.S.; McKenzie, B.E. Bromperidol, a new butyrophenone neuroleptic: A review. Psychopharmacology 1982, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianou, M.; Kulesskiy, E.; Lopes, J.P.; Granlund, M.; Wennerberg, K.; Urban, C.F. Antifungal application of nonantifungal drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramón-García, S.; Ng, C.; Anderson, H.; Chao, J.D.; Zheng, X.; Pfeifer, T.; Av-Gay, Y.; Roberge, M.; Thompson, C.J. Synergistic drug combinations for tuberculosis therapy identified by a novel high-throughput screen. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3861–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, H.M.D.E.S.; Brandão, L.B.S.; de Melo, T.R.; Ferreira, S.B. Anti-Bacterial Perspective of Non-Antibiotic Drugs. Med. Sci. Forum 2022, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.J.; Tsai, C.N.; Johnson, J.W.; French, S.; Elhenawy, W.; Porwollik, S.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.; McClelland, M.; Magolan, J.; Coombes, B.K.; et al. A macrophage-based screen identifies antibacterial compounds selective for intracellular Salmonella typhimurium. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldara, M.; Marmiroli, N. Antimicrobial Properties of Antidepressants and Antipsychotics—Possibilities and Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, S.Y.L.; Garzan, A.; Dennis, E.K.; Shrestha, S.K.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Repurposing antipsychotic drugs into antifungal agents: Synergistic combinations of azoles and bromperidol derivatives in the treatment of various fungal infections. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelmach, A.; Guzek, K.; Rożnowska, A.; Najbar, I.; Sadakierska-Chudy, A. Antipsychotic drug-aripiprazole against schizophrenia, its therapeutic and metabolic effects associated with gene polymorphisms. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmi, M.; Bodini, L.; Cocozza, S.; Seeman, M.V.; Vieta, E.; Dragioti, E.; Carvalho, A.F.; Fusar-Poli, P. Aripiprazole monotherapy as transdiagnostic intervention for the treatment of mental disorders: An umbrella review according to TRANSD criteria. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 41, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Aripiprazole repurposed as an inhibitor of biofilm formation and sterol biosynthesis in multidrug-resistant Candida albicans. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, R.A.; Eckhardt, S.B. Iproniazid. In Drug Discovery; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluger, N.W. Using Isoniazid More Safely and More Effectively: The Time Is Now. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timbrell, J. Principles of Biochemical Toxicology, 4th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, C.; Claude, P.; Tuatay, H.; Rubin, E.H. Iproniazid in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Dis. Chest 1954, 25, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.A.; Leinonen, E.V. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001, 7, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukavishnikov, G.; Leonova, L.; Kasyanov, E.; Leonov, V.; Neznanov, N.; Mazo, G. Antimicrobial activity of antidepressants on normal gut microbiota: Results of the in vitro study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1132127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukavishnikov, G.; Leonova, L.; Kasyanov, E.; Leonov, V.; Mazo, G. P. 0603 The antimicrobial effects of mirtazapine and fluvoxamine: Results of the pilot experiment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 53, S442–S443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.J.; Saadabadi, A. Trazodone. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Salsburg, L.P. Investigating the Effects of Trazodone on the Gut Microbiome of Shelter Dogs. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Almasi, A.; Patel, P.; Meza, C.E. Doxepin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Caldara, M.; Marmiroli, N. Tricyclic antidepressants inhibit Candida albicans growth and biofilm formation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazehkand, M.N. The effect of doxepin on Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Cell Sci. Mut. 2018, 2, 33–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.L.; Evans, R.L. Evaluation of amoxapine. Clin. Pharm. 1982, 1, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.A.; Fitts, E.C.; Kirtley, M.L.; Ponnusamy, D.; Peniche, A.G.; Dann, S.M.; Motin, V.L.; Chauhan, S.; Rosenzweig, J.A.; Sha, J.; et al. New role for FDA-approved drugs in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3717–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burin, R.; Shah, D.H. Phenelzine and Amoxapine Inhibit Tyramine and d-Glucuronic Acid Catabolism in Clinically Significant Salmonella in A Serotype-Independent Manner. Pathogens 2021, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sha, J.; Strong, E.; Chopra, A.K.; Lee, S. FDA-Approved Amoxapine Effectively Promotes Macrophage Control of Mycobacteria by Inducing Autophagy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0250922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, J.S.; Rosani, A.; Saadabadi, A. Desipramine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470581/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Fayez, R.; Gupta, V. Imipramine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Molnár, J.; Béládi, I.; Holland, I.B. The plasmid curing action of imipramine in Escherichia coli K12. Gen. Res. 1978, 31, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
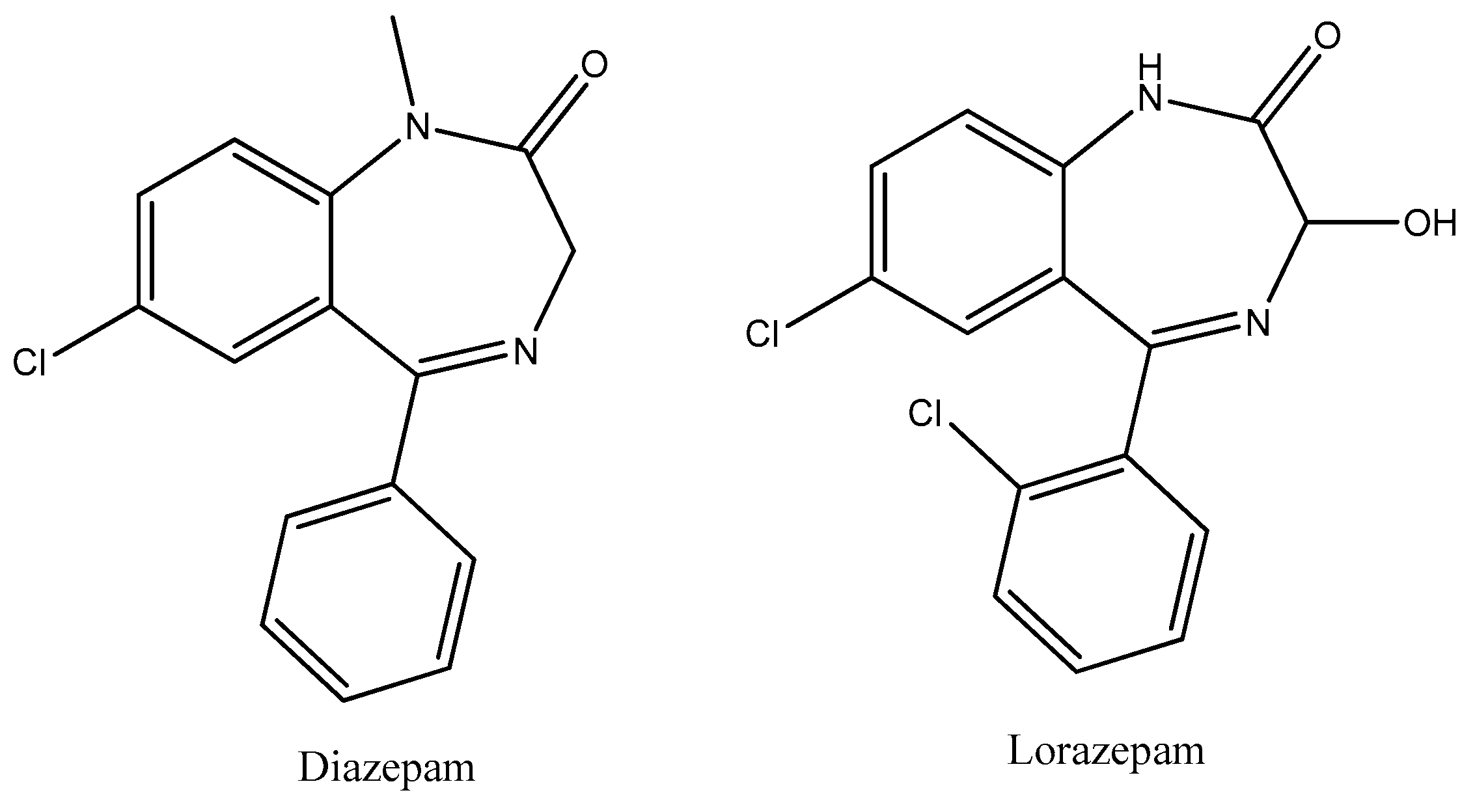
- Calcaterra, N.E.; Barrow, J.C. Classics in chemical neuroscience: Diazepam (valium). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiasi, N.; Bhansali, R.K.; Marwaha, R. Lorazepam. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532890/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Kathwate, G.H.; Shinde, R.B.; Karuppayil, S.M. Antiepileptic drugs inhibit growth, dimorphism, and biofilm mode of growth in human pathogen Candida albicans. Assay. Drug Dev. Technol. 2015, 13, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, D.C.; Ferreira-Pereira, A. Insights on the anticandidal activity of non-antifungal drugs. J. Mycol. Med. 2019, 29, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvêncio da Silva, L.; Dias Barroso, F.D.; Vieira, L.S.; Carlos Mota, D.R.; da Silva Firmino, B.K.; Rocha da Silva, C.; de Farias Cabral, V.P.; Cândido, T.M.; Sá, L.G.D.A.V.; Barbosa da Silva, W.M.; et al. Diazepam’s antifungal activity in fluconazole-resistant Candida spp. and biofilm inhibition in C. albicans: Evaluation of the relationship with the proteins ALS3 and SAP5. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rosa, T.F.; Serafin, M.B.; Foletto, V.S.; Franco, L.N.; de Paula, B.R.; Fuchs, L.B.; Calegari, L.; Hörner, R. Repositioning of Benzodiazepine Drugs and Synergistic Effect with Ciprofloxacin Against ESKAPE Pathogens. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
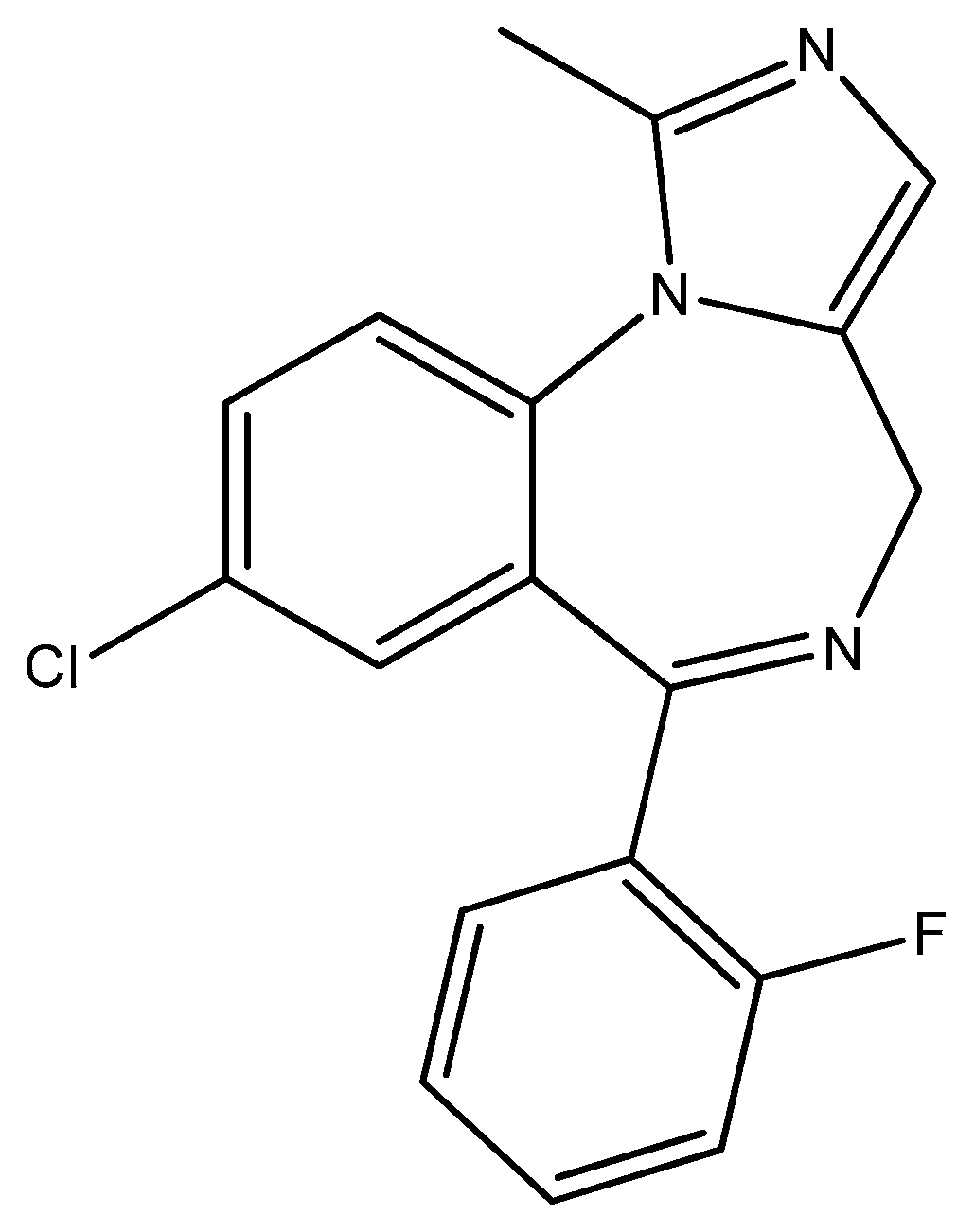
- Lingamchetty, T.N.; Hosseini, S.A.; Saadabadi, A. Midazolam. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537321/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Keleş, G.T.; Kurutepe, S.; Tok, D.; Gazi, H.; Dinç, G. Comparison of antimicrobial effects of dexmedetomidine and etomidate-lipuro with those of propofol and midazolam. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2006, 23, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocatürk, Ö.; Dönmez Özkan, H.; Poyrazoğlu Çoban, E.; Bıyık, H. Antimicrobial Effects of Dexmedetomidine and Midazolam in Bicarbonate Buffer: An in vitro Study. Cerrahpasa Med. J. 2019, 43, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoglu, H.; Kulah, C.; Turan, I. Antimicrobial effects of two anaesthetic agents: Dexmedetomidine and midazolam. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2008, 36, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, M.A.; da Silva, C.R.; de A Neto, J.B.; Sá, L.G.D.A.; Nascimento, F.B.D.; Barroso, D.D.; da Silva, L.J.; Cândido, T.M.; Leitão, A.C.; Barbosa, A.D.; et al. Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity In Vitro of Midazolam Against Fluconazole-Resistant Candida spp. Isolates. Future Microbiol. 2021, 16, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSilva, P.; Fenton, M.; Rathbone, J. Zotepine for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD001948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezchlibnyk-Butler, K.; Aleksic, I.; Kennedy, S.H. Citalopram—A review of pharmacological and clinical effects. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2000, 25, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.M.; Subhan, F.; Ahmed, J.; Khan, A.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Syed, N.; Ullah, I.; Hussain, S.N. Citalopram and venlafaxine differentially augments antimicrobial properties of antibiotics. Acta Pol. Pharm.-Drug Res. 2015, 72, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Landy, K.; Rosani, A.; Estevez, R. Escitalopram. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Dhaliwal, J.S.; Spurling, B.C.; Molla, M. Duloxetine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).


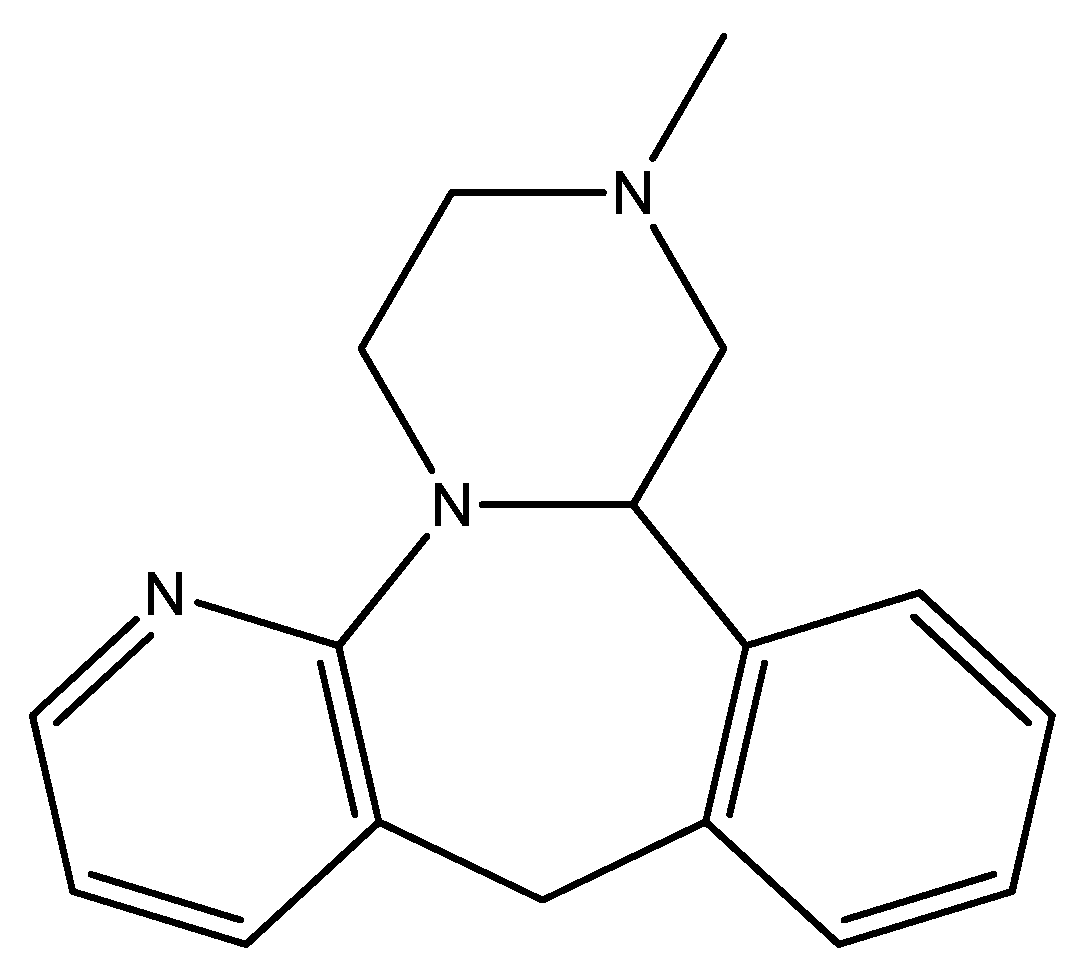
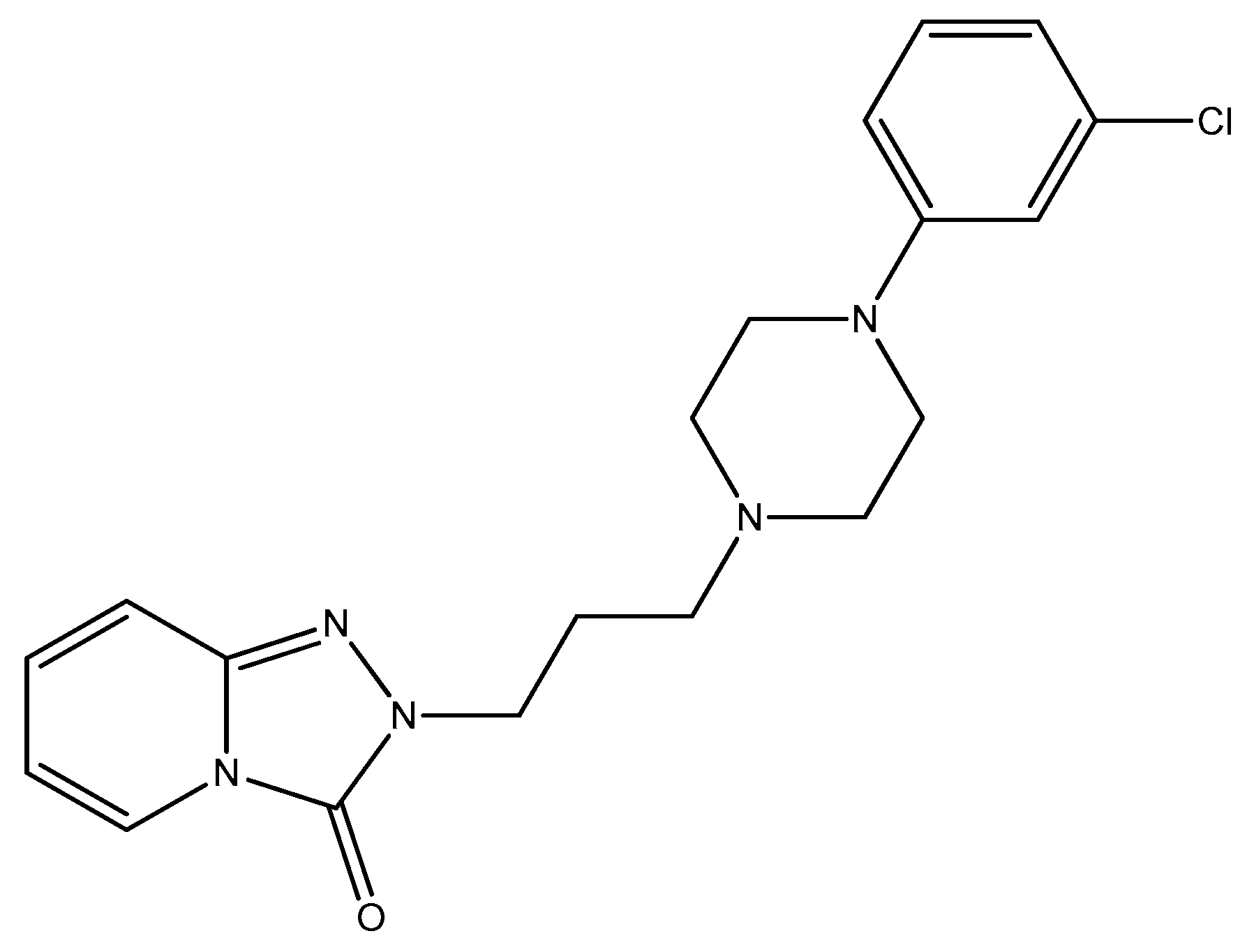

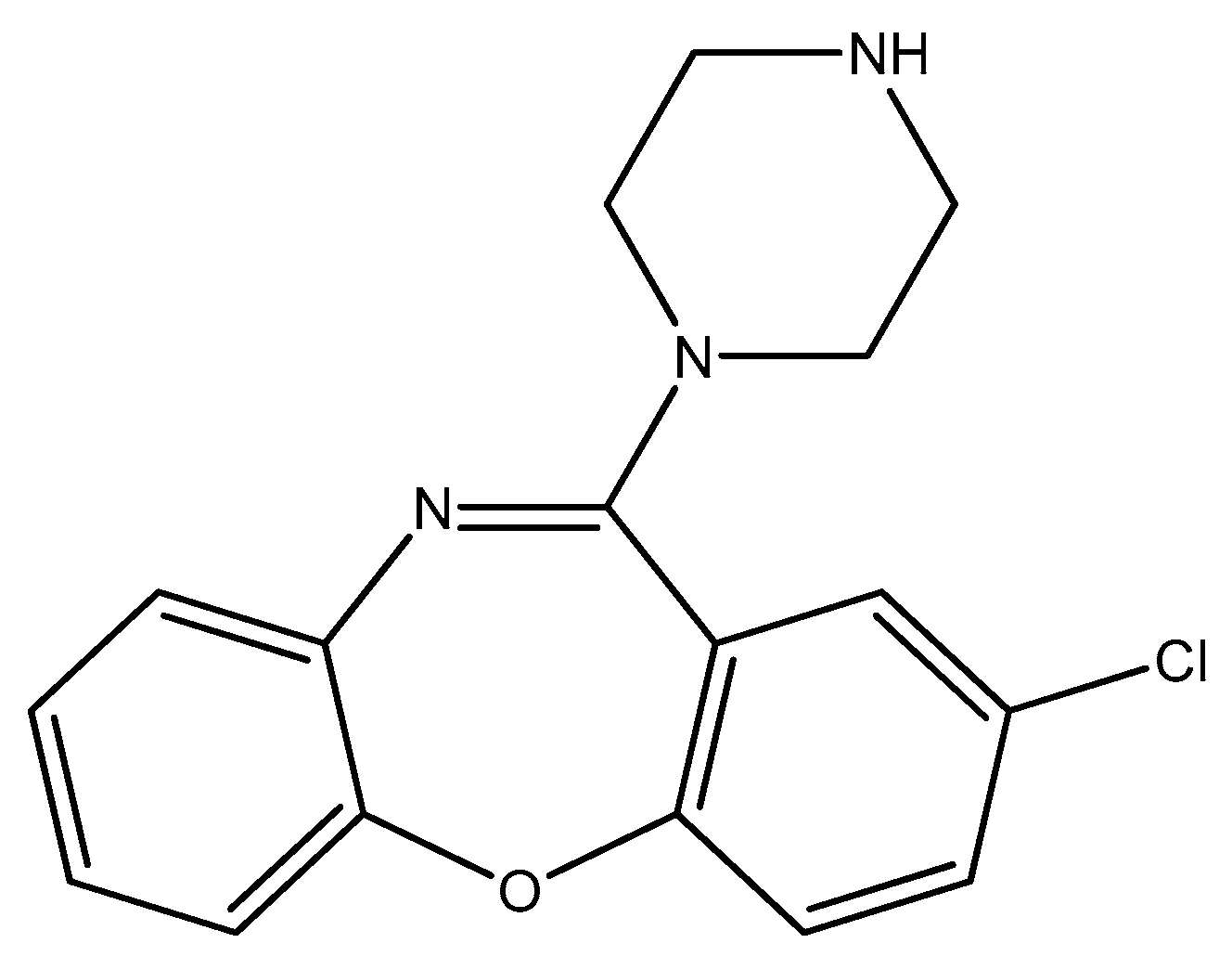
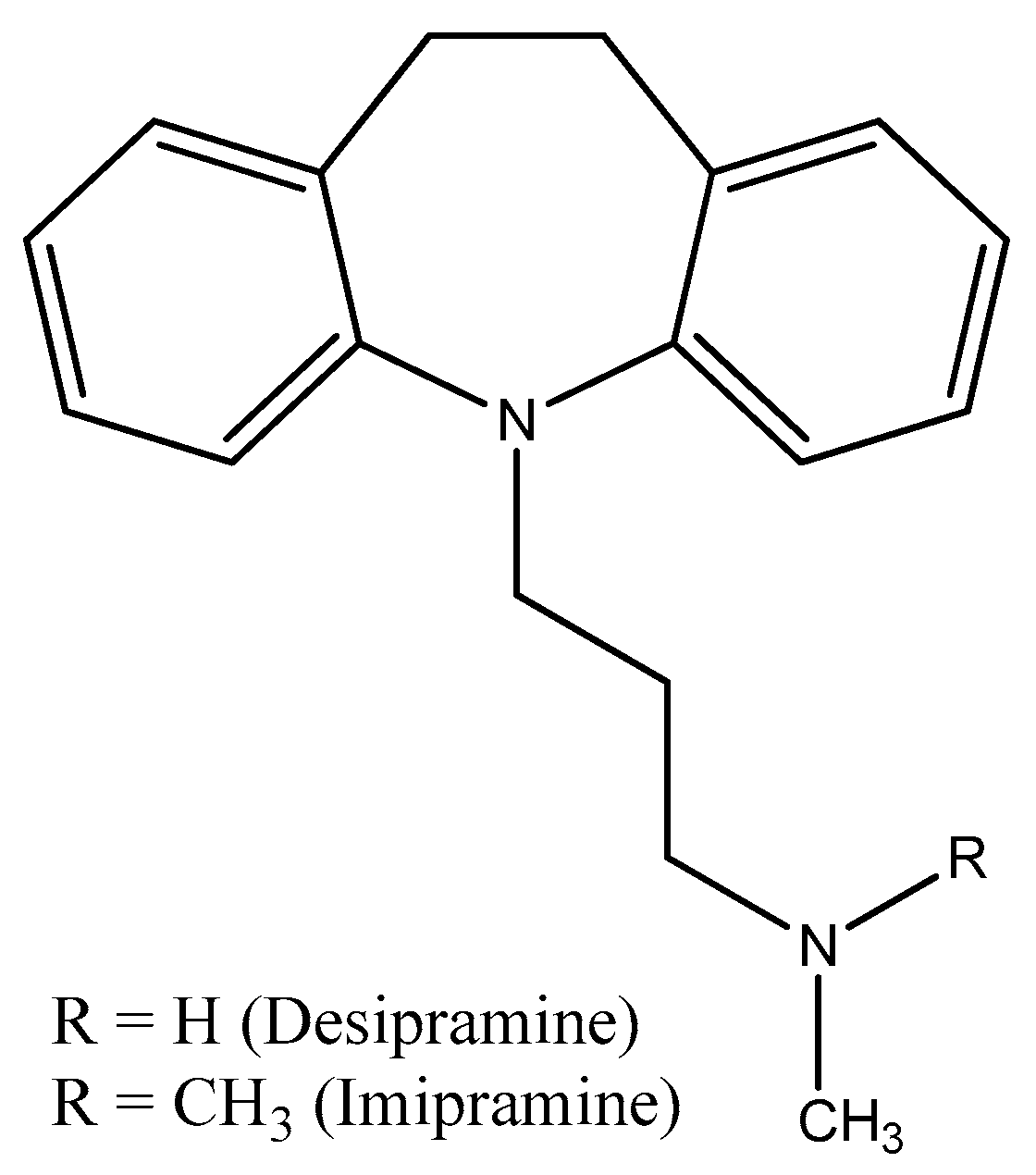
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zolotareva, D.; Zazybin, A.; Belyankova, Y.; Bayazit, S.; Dauletbakov, A.; Seilkhanov, T.; Kemelbekov, U.; Aydemir, M. Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity. Molecules 2025, 30, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051102
Zolotareva D, Zazybin A, Belyankova Y, Bayazit S, Dauletbakov A, Seilkhanov T, Kemelbekov U, Aydemir M. Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051102
Chicago/Turabian StyleZolotareva, Darya, Alexey Zazybin, Yelizaveta Belyankova, Sarah Bayazit, Anuar Dauletbakov, Tulegen Seilkhanov, Ulan Kemelbekov, and Murat Aydemir. 2025. "Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051102
APA StyleZolotareva, D., Zazybin, A., Belyankova, Y., Bayazit, S., Dauletbakov, A., Seilkhanov, T., Kemelbekov, U., & Aydemir, M. (2025). Heterocyclic Antidepressants with Antimicrobial and Fungicide Activity. Molecules, 30(5), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051102





