Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
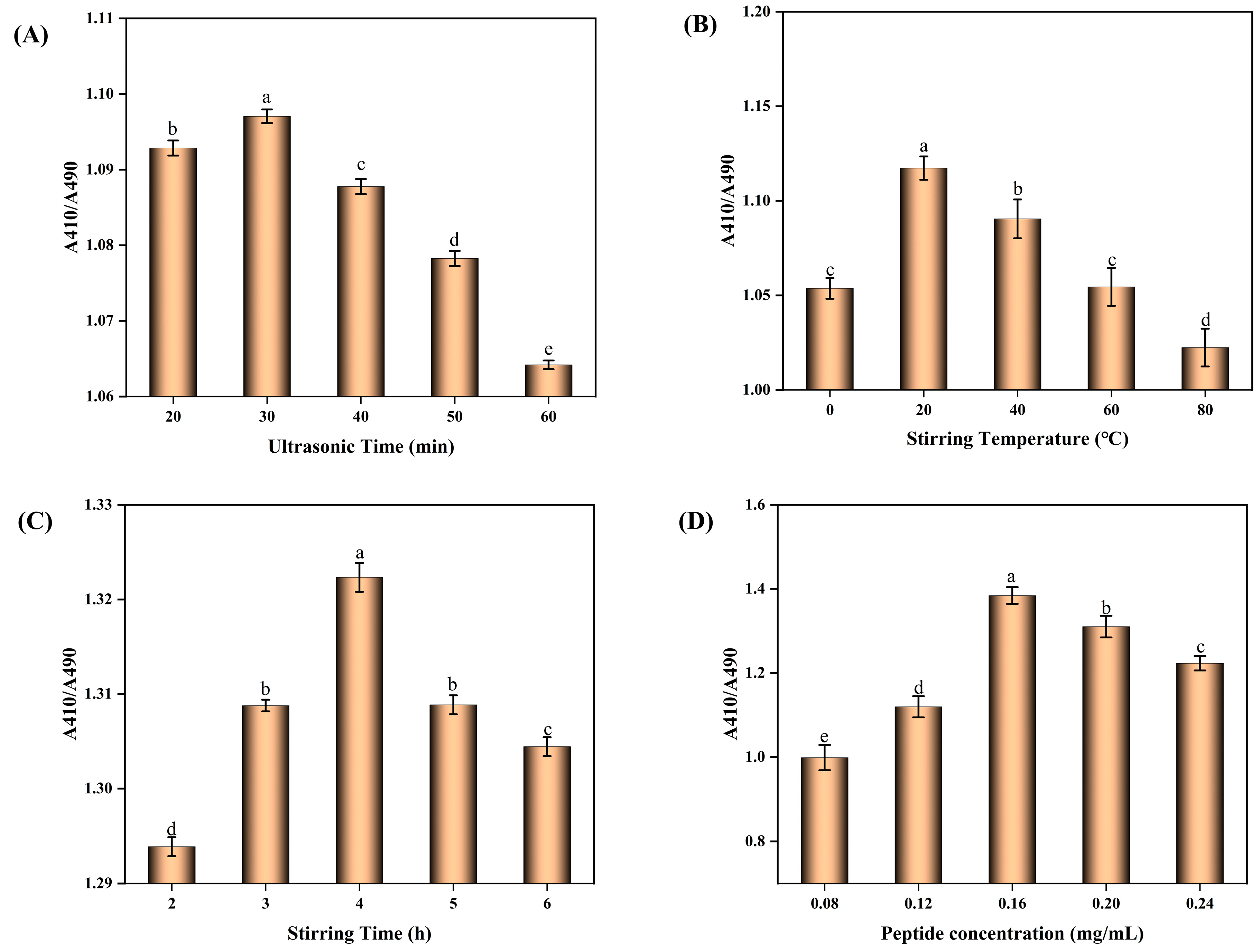
2.1. Optimal Conditions for the Preparation of BBPP-SeNPs
2.1.1. Dual-Wavelength Method
2.1.2. Conditions for the Synthesis of BBPP-SeNPs
2.2. Characterization Results of BBPP-SeNPs
2.2.1. FTIR Infrared Spectral Analysis
2.2.2. Particle Size Analysis and Z-Potential Analysis
2.2.3. SEM, TEM Analysis
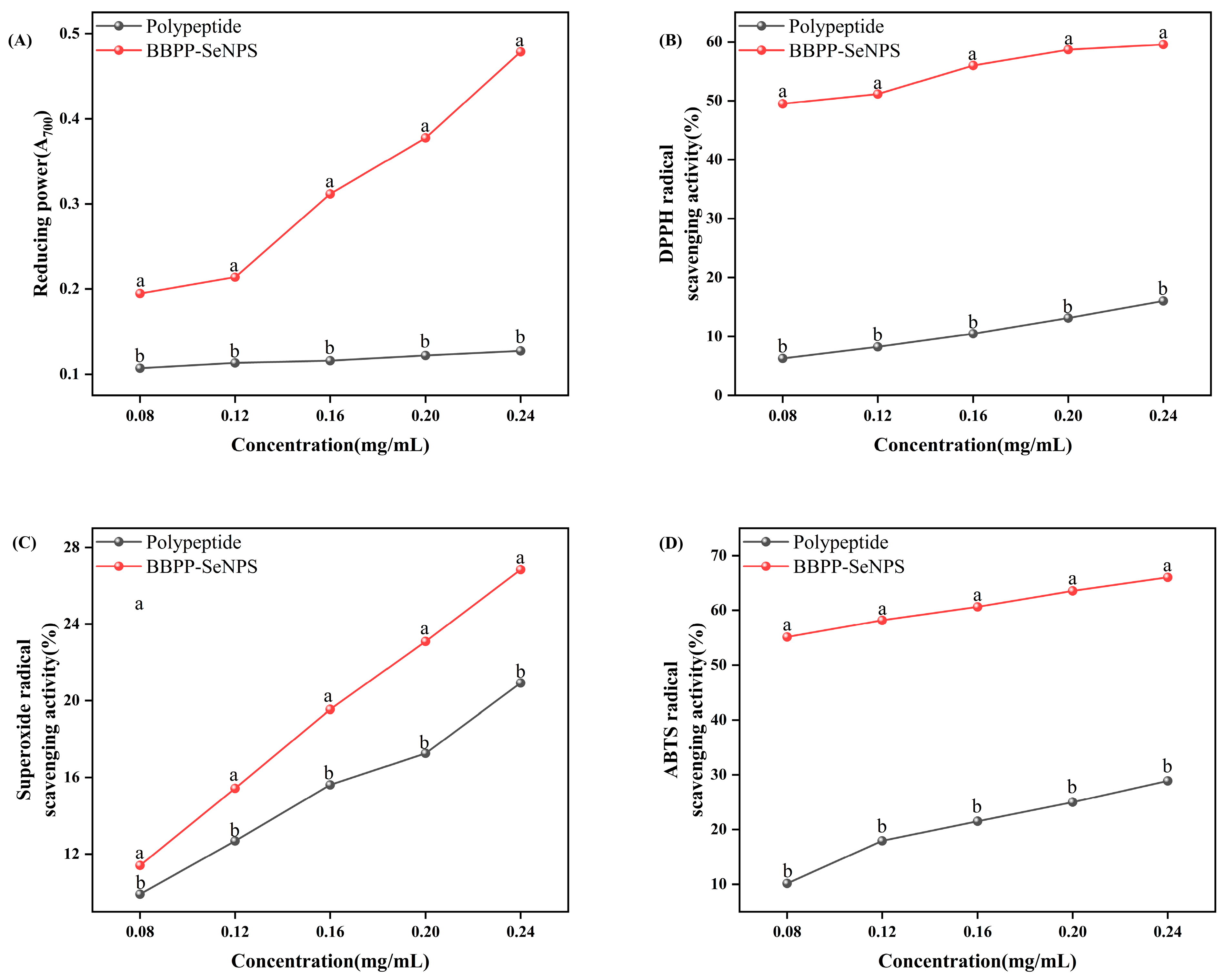
2.3. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.4. Inhibition of Tyrosine by BBPP-SeNPs
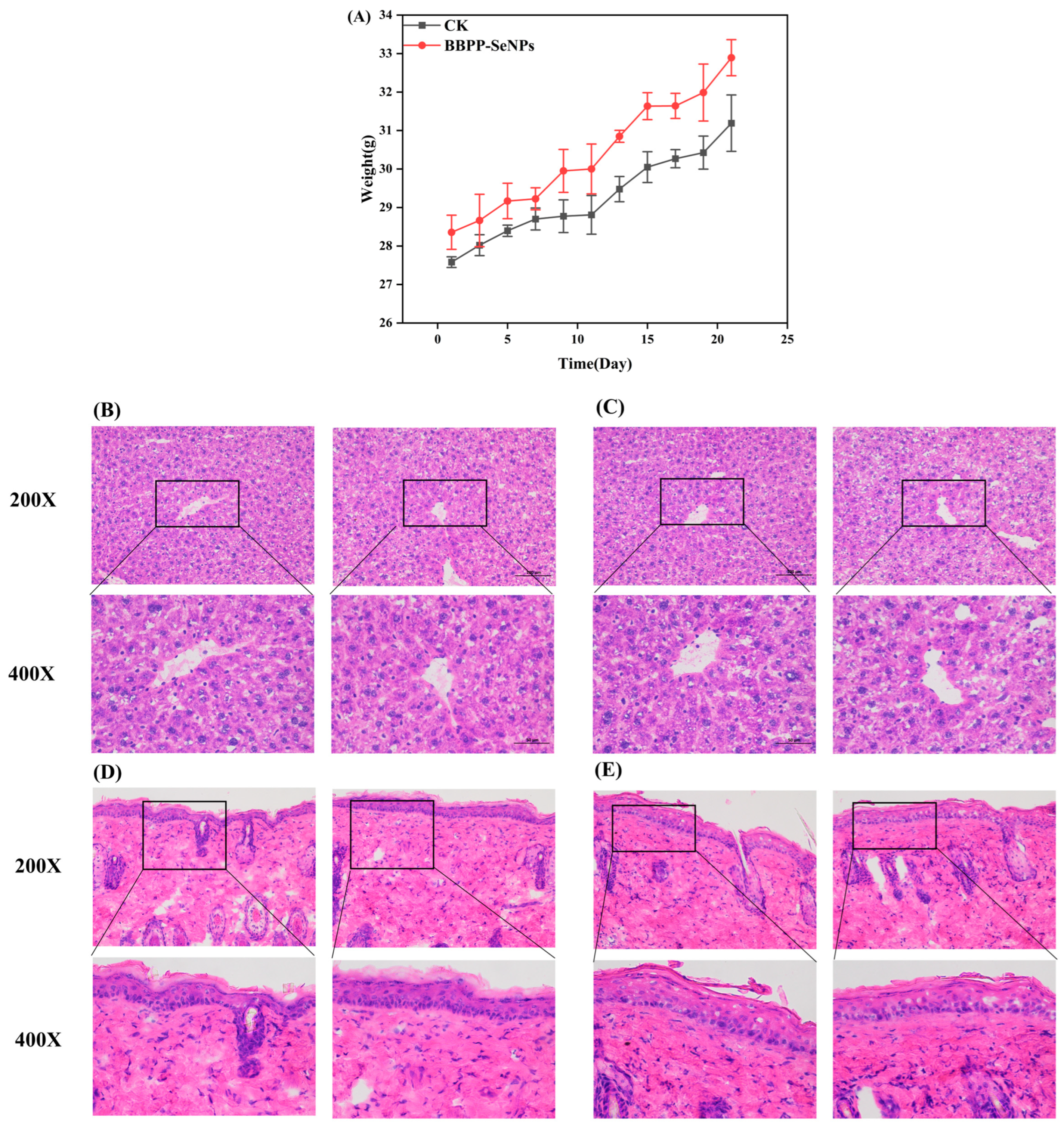
2.5. Experimental Results from the Mouse Models
2.5.1. Skin Whitening Experiment
2.5.2. Toxicity Experiment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Reagents
4.1. Extraction of Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide
4.2. Preparation of BBPP-SeNPs
4.3. Characterization Method of BBPP-SeNPs
4.3.1. Fourier Infrared Spectrum Analysis
4.3.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
4.3.3. TEM and SEM Scan Analysis
4.4. Determination of Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
4.4.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging
4.4.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging
4.4.3. Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging
4.4.4. Reducing Power
4.5. Determination of Whitening Ability In Vitro
4.6. Experimental Methodology in Mouse Models
4.6.1. Animal Ethics Committee Statement
4.6.2. Experimental Methodology for Skin Whitening
Grouping and Modeling in Skin Whitening
Administration in Skin Whitening
Brightness Variation
Slice Observation
4.6.3. Experimental Methodology for Toxicity
Grouping and Modeling in Toxicity
Administration in Toxicity
Weight and Biopsy
4.7. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nag, S.; Kar, S.; Mishra, S.; Stany, B.; Seelan, A.; Mohanto, S.; Haryini S, S.; Kamaraj, C.; Subramaniyan, V. Unveiling green synthesis and biomedical theranostic paradigms of selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)- A State-of-the-Art comprehensive update. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 662, 124535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Sun, L.; Ding, Z.-C.; Yan, J.-K. Preparation, characterization, and antioxidant capacities of selenium nanoparticles stabilized using polysaccharide–protein complexes from Corbicula fluminea. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Liu, Q.; Zou, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Construction of selenium nanoparticles/β-glucan composites for enhancement of the antitumor activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gu, Q.; Shu, J. Research progress on toxicity of selenium and its hygienic standard. LaborMed 1993, 02, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G.F.; Garbisu, C.; Yee, B.C.; Yee, A.; Buchanan, B.B. Bioavailability of selenium accumulated by selenite-reducing bacteria. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 52, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: Comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.N. Synthesis, Physicochemical Characteristics and Bioactivity of Selenium Nanosystem Stablized by Chitosan. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L. Preparation and Properties of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bacterial Cellulose Mask. Master’s Thesis, Henan University, Kaifeng, China, 2024. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27114/d.cnki.ghnau.2024.001507 (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Hu, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Traditional Uses, Origins, Chemistry and Pharmacology of Bombyx batryticatus: A Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Shi, L.-C.; Yao, H.; Song, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-L. Identification of Bombyx batryticatus based on DNA barcoding technology. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2016, 51, 1784–1790. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16438/j.0513-4870.2016-0215 (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Z.; Shi, L. Structural elucidation and in vitro antitumor activity of a novel oligosaccharide from Bombyx batryticatus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Yuan, X.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Antiepileptic Effects of Protein-Rich Extract from Bombyx batryticatus on Mice and Its Protective Effects against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells via Regulating PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7897584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yang, X.-Q.; Su, D.-X.; He, S.; Tan, J.-C.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Yuan, Y. Development structure characterization and stability of food grade selenium nanoparticles stabilized by tilapia polypeptides. J. Food Eng. 2020, 275, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Peng, Q.; Li, Q.; Bi, Y.; Kong, F.; Wang, Z.; Tan, S. Synthesis, characterization; biological activity, and in vitro digestion of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by Antarctic ice microalgae polypeptide. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 141, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Ren, D.F. Preparation and characterization of selenium nanoparticles decorated by Spirulina platensis polysaccharide. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Tan, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, H.; Su, L.; He, Z.; Ma, Q.; Dong, S.; Ramachandran, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Effects of Schisandra chinensis Polysaccharide-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles on Intestinal Injury in Mice. Animals 2023, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, W.; Yang, X.-Q.; Su, D.-X.; He, S.; Nag, A.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Yuan, Y. Development, characterization and in vitro bile salts binding capacity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by soybean polypeptides. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Polypeptide nano-Se targeting inflammation and theranostic rheumatoid arthritis by anti-angiogenic and NO activating AMPK signaling pathway. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3497–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Kalagatur, N.K. Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles From Emblica officinalis Fruit Extract and Exploring Its Biopotential Applications: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Lin, Y.; Mao, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Construction, characterization, antioxidant activity and effects on properties in vitro digestion of selenium nanoparticles decorated with Cyperus esculentus polysaccharides. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.B.; Elahi, I.; Sardar, N.; Ghaffar, O.; Ali, H.; Alsubki, R.A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Attia, K.A.; Abushady, A.M. Exploring Non-Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized from Gymnema sylvestre and Cinnamon cassia Extracts for Herbal Nanomedicine. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 192, 106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.-J.; Ye, X.-G.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Lin, X.-R.; Li, B. Preparation and Characterization of Complexes of Tea Polysaccharide-selenium Nanoparticles. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 225–231+144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Cao, Y.-H.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.-W.; Si, W.-Y. Analysis and stability evaluation of tea polyphenols, free amino acids and vitamin C in four kinds of tea beverages. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Javed, M.R.; Ali, K.; Saleem, M.; Manzoor, M.F.; Farhan, M.; Mugabi, R.; Sharma, A. Gulzar Ahmad Nayik. Microwave-sonication synergistic extraction of dairy waste proteins: A review of green approach for dairy waste proteins valorization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 111, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Noman, A.; Zhang, C.; Al-Dalali, S.; Abed, S.M. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the enzymolysis of hybrid sturgeon (Huso dauricus × Acipenser schrenckii) protein and the structural, functional, and antioxidant properties of hydrolysates. LWT 2023, 188, 115421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, S.; Su, D.; Ye, M.; Zeng, Q.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis, characterization of tuna polypeptide selenium nanoparticle, and its immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects in vivo. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Tian, Y. Preparation of nano-selenium by sodium carboxymethyl cellulose template method. J. Funct. Mater. 2004, 2, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant Determinations by the Use of a Stable Free Radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.H.; Wang, L. Effect of Ultrasonic Technology on the Processing Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Protein in Oat. J. Xuzhou Inst. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 37, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.Y.; Feng, H.Y.; Lin, X.; Ying, X.Y.; Ling, W.X.; Tao, Z. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Porphyra haitanensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Mao, S.; Xu, Q. Preparation and structure identification of antioxidant peptides from mixed fermentation of Fructus Ligustris. Chin. Food Addit. 2025, 36, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Kang, M.K.; Yoon, D.; Kang, D.; Park, Y.; et al. Highly potent anti-melanogenic effect of 2-thiobenzothiazole derivatives through nanomolar tyrosinase activity inhibition. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 150, 107586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Teng, B.; McRae, J.M. Valonea Tannin: Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity, Structural Elucidation and Insights into the Inhibition Mechanism. Molecules 2021, 26, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.C.; Fang, C.W.; Suhail, M.; Vu, Q.L.; Chuang, C.H.; Wu, P.C. Improved skin permeability and whitening effect of catechin-loaded transfersomes through topical delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Group. | V (Sample Solution)/mL | V (PBS)/mL | V (Tyrosinase)/mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| A2 | 0.5 | 2 | 0 |
| A3 | 0 | 2 | 0.5 |
| A4 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, Y.; Peng, C.; Weihong, L.; Cuiping, F.; Xiaowen, W.; Qiling, W. Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability. Molecules 2025, 30, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051153
Ning Y, Peng C, Weihong L, Cuiping F, Xiaowen W, Qiling W. Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051153
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Yang, Chen Peng, Li Weihong, Feng Cuiping, Wang Xiaowen, and Wang Qiling. 2025. "Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051153
APA StyleNing, Y., Peng, C., Weihong, L., Cuiping, F., Xiaowen, W., & Qiling, W. (2025). Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability. Molecules, 30(5), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051153






