Automated Determination of Ammonium at Nanomolar Levels in Seawater by Coupling Lab-in-Syringe with Highly Sensitive Light-Emitting-Diode-Induced Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
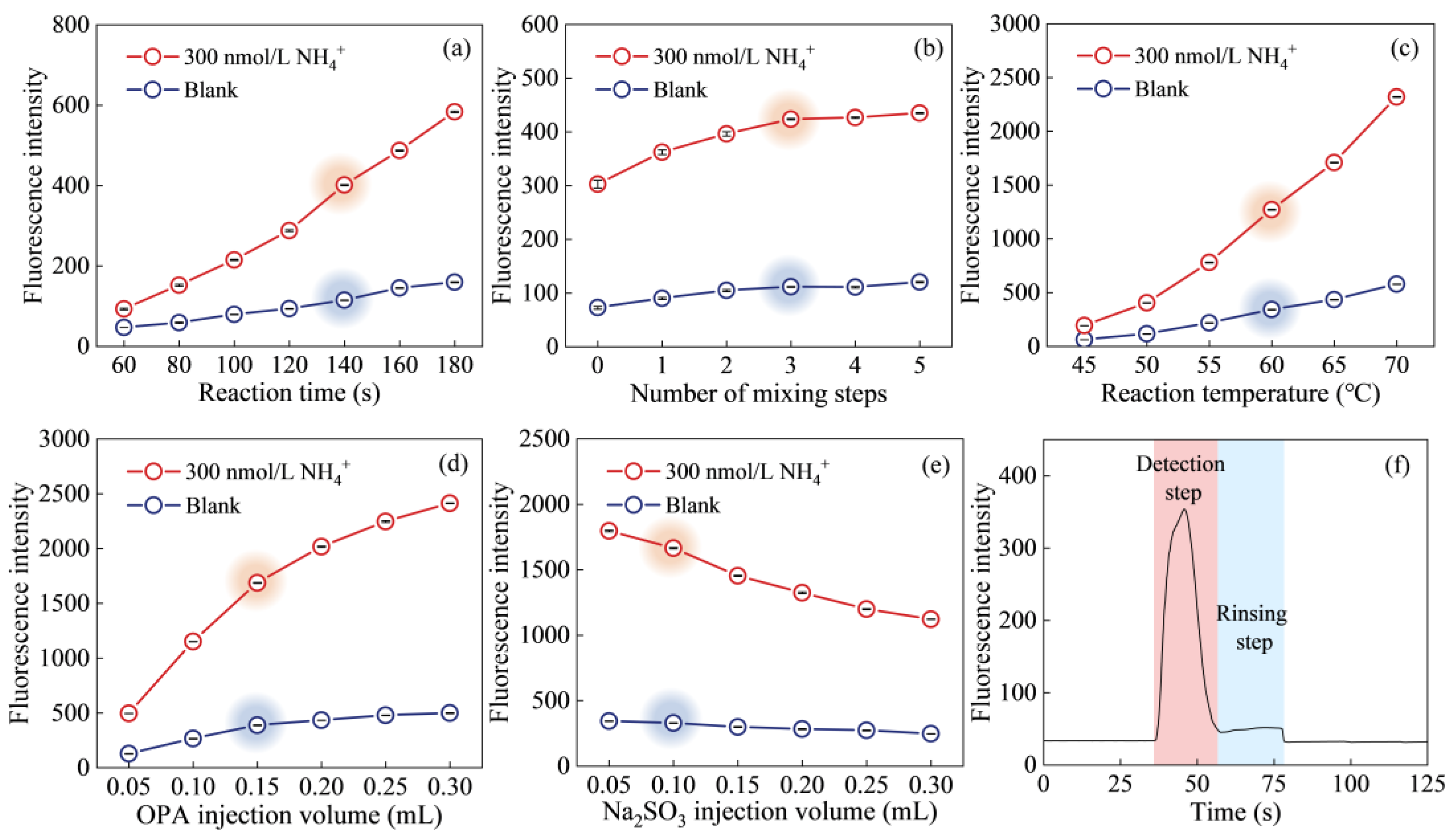
2.1. Parameter Optimization
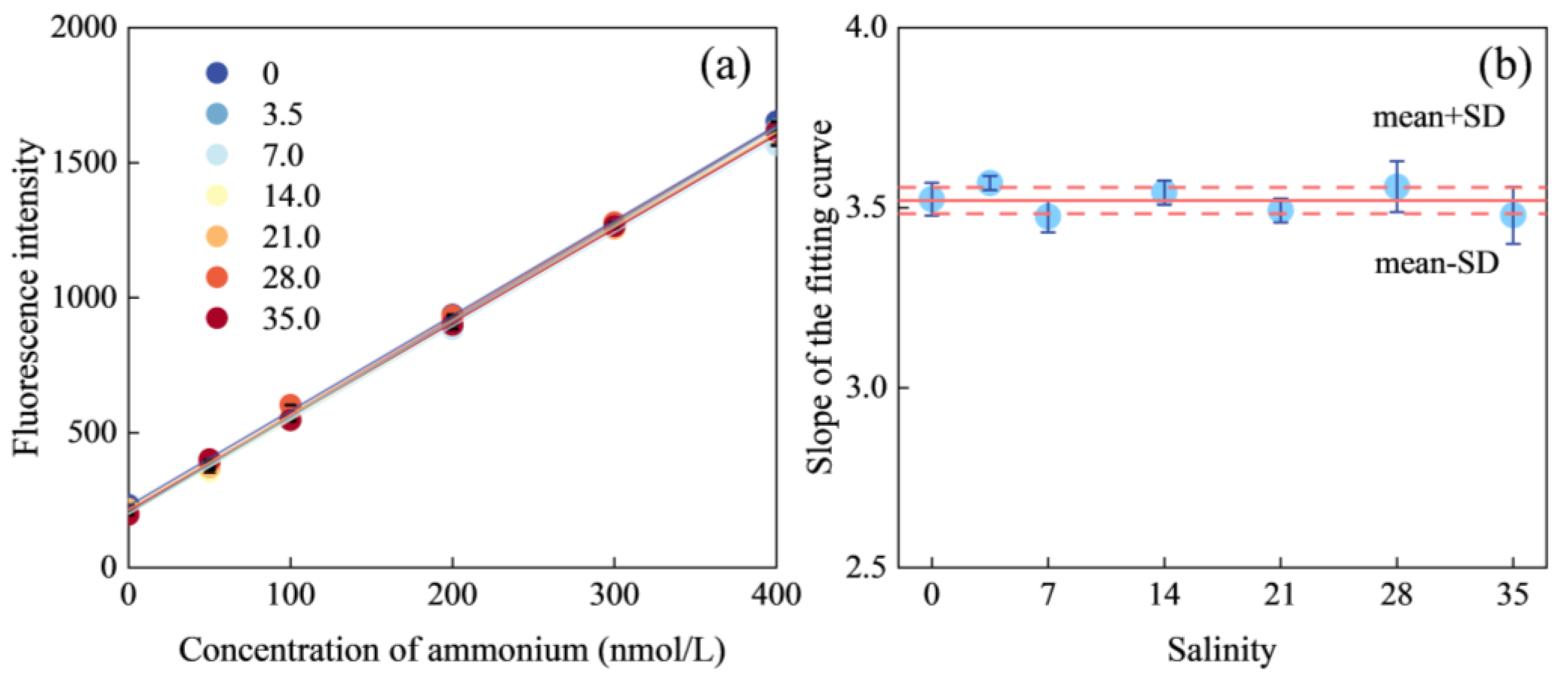
2.2. Seawater Matrix Effect
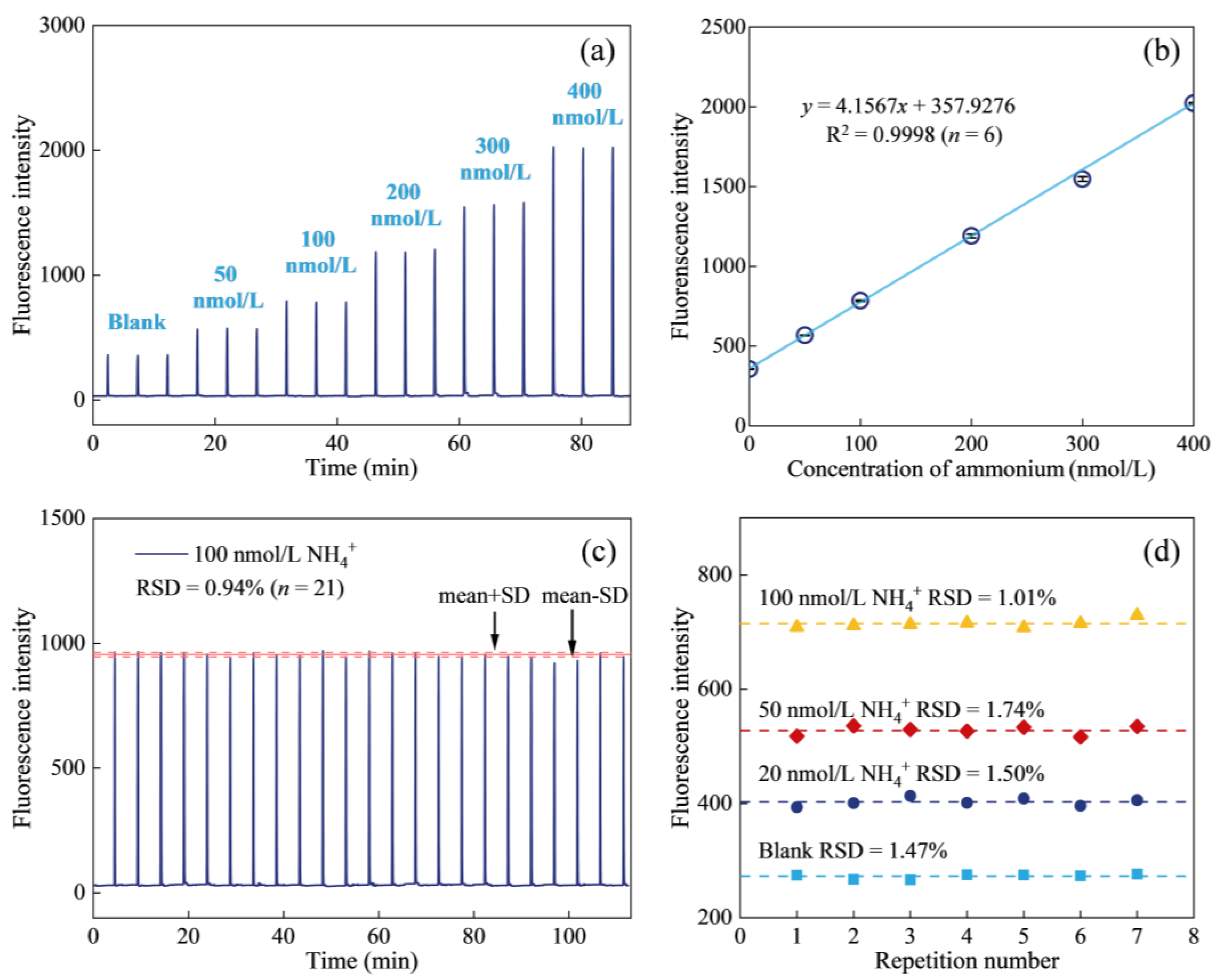
2.3. Analytical Figures of Merit
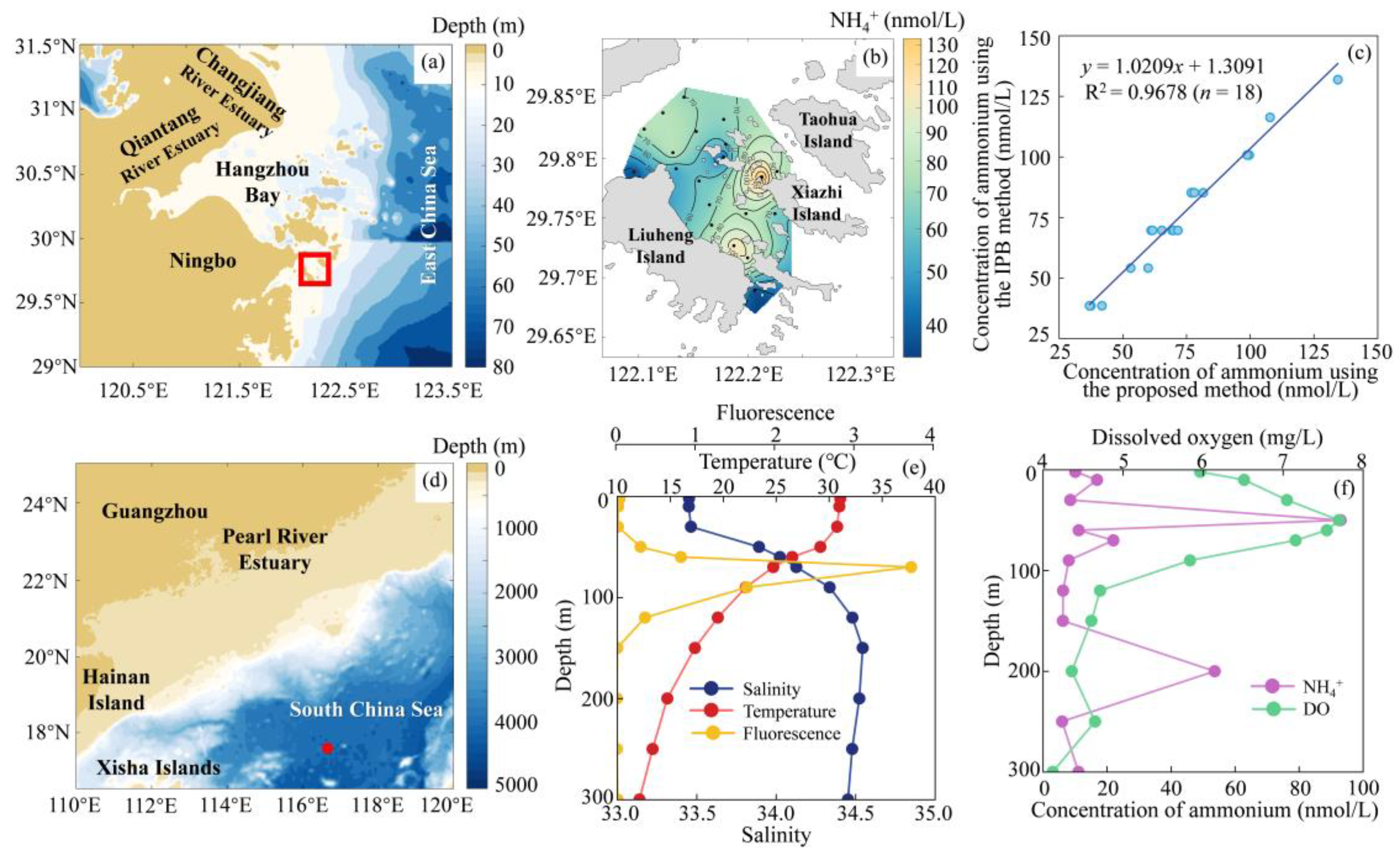
2.4. Validation of the Method
2.5. Field Application
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
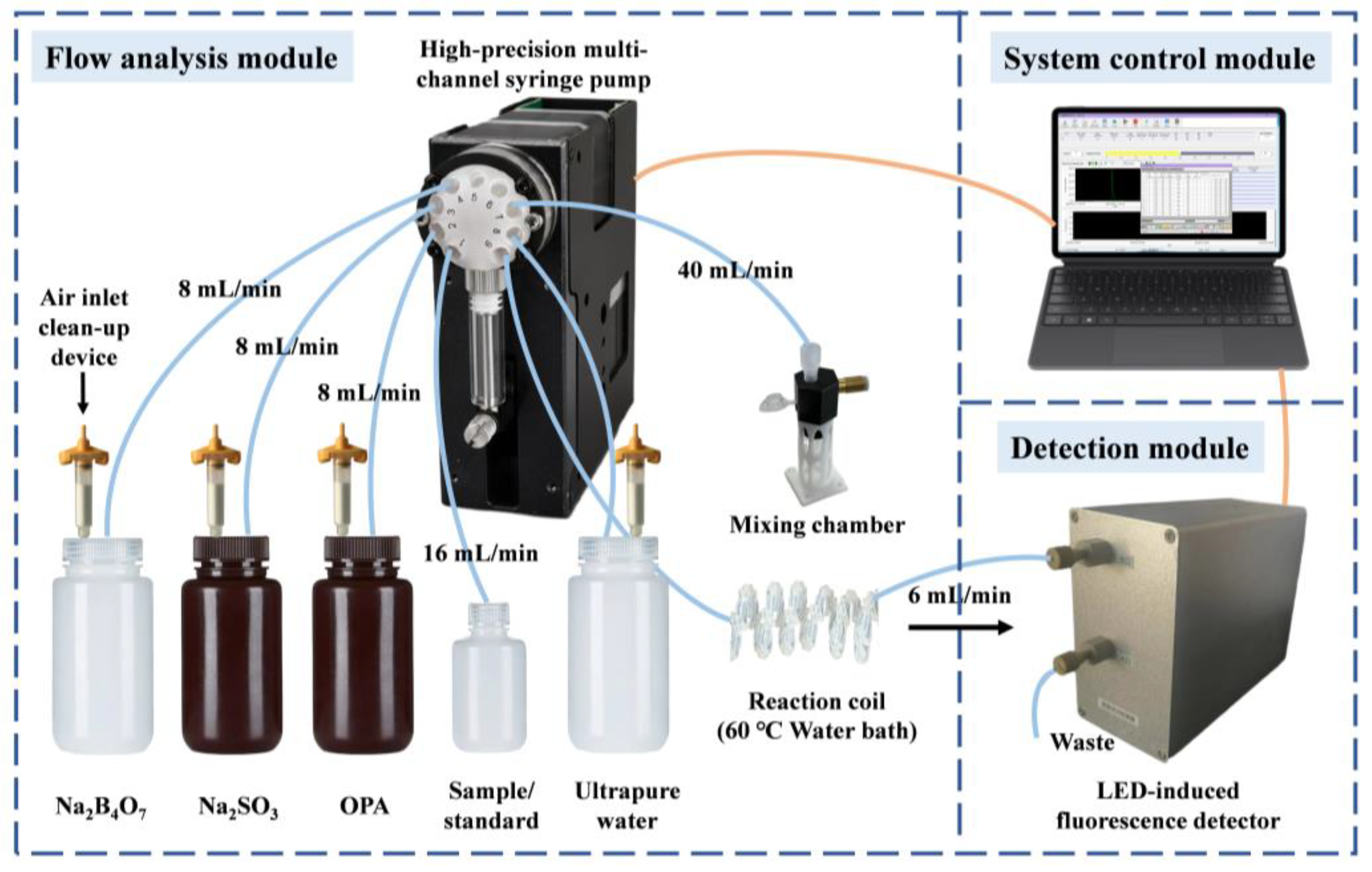
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Analytical Procedure
3.4. Sample Collection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPB | Indophenol blue |
| OPA | o-phthalaldehyde |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| LIS | Lab-in-syringe |
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
| LNSW | Low-nutrient seawater |
| CFA | Continuous flow analysis |
| FIA | Flow injection analysis |
| SIA | Sequential injection analysis |
| rFIA | Reverse flow injection analysis |
| ABA | Autonomous batch analyzer |
| NDA | Naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxaldehyde |
References
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y. Evolution of the fluorometric method for the measurement of ammonium/ammonia in natural waters: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 171, 117519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, D.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Jin, H.; Ran, L. Development of analytical methods for ammonium determination in seawater over the last two decades. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Ciais, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; et al. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, H.J.; Sinha, A.K.; Nawata, C.M.; Blust, R.; Wood, C.M.; De Boeck, G. Differential responses in ammonia excretion, sodium fluxes and gill permeability explain different sensitivities to acute high environmental ammonia in three freshwater teleosts. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Detection methods of ammonia nitrogen in water: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Rea, G.; Severini, L.; Cerri, L.; Leo, G.; Paialunga, E.; Mantegazza, P.; Mazzuca, C.; Micheli, L. Expanding the circularity of plastic and biochar materials by developing alternative low environmental footprint sensors. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 6774–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.R.; Rees, A.P.; Joint, I. Ammonium regeneration and nitrification rates in the oligotrophic Atlantic Ocean: Implications for new production estimates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, J.A.; Devol, A.H.; Deutsch, C. New developments in the marine nitrogen cycle. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ward, B.B.; Sigman, D.M. Global nitrogen cycle: Critical enzymes, organisms, and processes for nitrogen budgets and dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5308–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.S. Microfluorometric method to measure ammonium in natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1978, 23, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Dasgupta, P.K. Fluorometric measurement of aqueous ammonium ion in a flow injection system. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornthammarong, N.; Zhang, J.Z. Shipboard fluorometric flow analyzer for high-resolution underway measurement of ammonium in seawater. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J.; Feng, S. A sensitive flow-batch system for on board determination of ultra-trace ammonium in seawater: Method development and shipboard application. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 794, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y. Review of separation methods for the determination of ammonium/ammonia in natural water. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 27, e00098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Guo, Q.; Hu, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q. A novel analytical method for trace ammonium in freshwater and seawater using 4-methoxyphthalaldehyde as fluorescent reagent. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 387207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y.; Pan, Y. Toward sensitive determination of ammonium in field: A novel fluorescent probe, 4, 5-dimethoxyphthalaldehyde along with a hand-held portable laser diode fluorometer. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2018, 276, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornthammarong, N.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ortner, P.B.; Stamates, J.; Shoemaker, M.; Kindel, M.W. A portable analyser for the measurement of ammonium in marine waters. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminot, A.; Kérouel, R.; Birot, D. A flow injection-fluorometric method for the determination of ammonium in fresh and saline waters with a view to in situ analyses. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šraj, L.O.C.; Almeida, M.I.G.; McKelvie, I.D.; Kolev, S.D. Determination of trace levels of ammonia in marine waters using a simple environmentally-friendly ammonia (SEA) analyser. Mar. Chem. 2017, 194, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Schroeder, F. Using sequential injection analysis to improve system and data reliability of online methods: Determination of ammonium and phosphate in coastal waters. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2007, 2007, 49535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornthammarong, N.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ortner, P.B. An autonomous batch analyzer for the determination of trace ammonium in natural waters using fluorometric detection. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, B.; Solich, P. The automation technique Lab-in-Syringe: A practical guide. Molecules 2020, 25, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Shu, H.; Lin, K.; Chen, N.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, D.; Ma, J. High-frequency underway analysis of ammonium in coastal waters using an integrated syringe-pump-based environmental-water analyzer (iSEA). Talanta 2019, 195, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C.; Xu, J.; Liang, Y. A novel and rapid approach to fluorescent automated Lab-In-Syringe sensing of ammonium. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakisikli, G.; Anthemidis, A.N. Automatic pressure-assisted dual-headspace gas-liquid microextraction. Lab-in-syringe platform for membraneless gas separation of ammonia coupled with fluorimetric sequential injection analysis. Anal. Chem. Acta 2018, 1033, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Bakker, K.; Van Ooijen, J.; Ossebaar, S.; Woodward, E.M.S. Report from an International Nutrient Workshop Focusing on Phosphate Analysis; Yang Yang: Fukushima, Japan, 2015; 78p, Available online: https://plymsea.ac.uk/id/eprint/6678 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Bey, S.K.A.K.; Connelly, D.P.; Legiret, F.E.; Harris, A.J.; Mowlem, M.C. A high-resolution analyser for the measurement of ammonium in oligotrophic seawater. Ocean Dynam. 2011, 61, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, B.; Duarte, C.M.; Cerda, V. A miniature and field-applicable multipumping flow analyzer for ammonium monitoring in seawater with fluorescence detection. Talanta 2011, 85, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.R. The Development of a Fluorescence-Based Reverse Flow Injection Analysis (rFIA) Method for Quantifying Ammonium at Nanomolar Concentrations in Oligotrophic Seawater. Master’s Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2015. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/etd/5892 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, Y. Ammonium determination by merging-zone flow injection analysis and a naphthalene-based fluorescent probe. Talanta 2023, 256, 124274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia-Freshwater; U.S. EPA, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 40–52.
- Geng, X.; Wu, D.; Guan, Y. A compact and highly sensitive light-emitting diode-induced fluorescence detector for capillary flow systems. Talanta 2012, 88, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Shi, M.; Ning, H.; Feng, C.; Guan, Y. A compact and low-cost laser induced fluorescence detector with silicon based photodetector assembly for capillary flow systems. Talanta 2018, 182, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | Ref. | Chemistry | Technique | LOD (nmol/L) | Linear Range (μmol/L) | Precision (% RSD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | [13] | OPA–sulfite with HCHO | CFA or FIA | 1.1 | 0.1–12 | 2.2 (200 nmol/L); 6.7 (1 nmol/L) |
| 2011 | [28] | OPA–sulfite | CFA | <5 | 0.05–25 | 1–4 (5 nmol/L-25 μmol/L) |
| 2011 | [29] | OPA–sulfite | Multi-pumping flow analysis | 13 | Up to 16 | <2 (5 μmol/L) |
| 2011 | [22] | OPA–sulfite with HCHO | Modified SIA (termed as ABA) | 1 | 0.005–25 | 0.6 (200 nmol/L) |
| 2013 | [18] | OPA–sulfite with HCHO | Modified ABA with a portable detector | 10 | 0.05–10 | 3 (2 μmol/L) |
| 2015 | [30] | OPA–sulfite with HCHO | rFIA | 1.1 | Up to 1 | 2.4 (1 μmol/L) |
| 2023 | [31] | NDA–sulfite | Merging-zone flow injection | 45 | 0.045–6 | 3.68 (1.5 μmol/L) |
| 2024 | [25] | M2OPA–sulfite with HCHO | LIS | 9.04 (25 °C) 15.11 (50 °C) | 0.015–0.6 | 1.21 (25 °C, 50 nmol/L) 3.26 (50 °C, 50 nmol/L) |
| This method | OPA–sulfite with HCHO | LIS | 0.9 | Up to 0.4 | 0.94 (100 nmol/L) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J. Automated Determination of Ammonium at Nanomolar Levels in Seawater by Coupling Lab-in-Syringe with Highly Sensitive Light-Emitting-Diode-Induced Fluorescence Detection. Molecules 2025, 30, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061288
Guo X, Li H, Shen Y, Lu Y, Zhu Y, Chen J. Automated Determination of Ammonium at Nanomolar Levels in Seawater by Coupling Lab-in-Syringe with Highly Sensitive Light-Emitting-Diode-Induced Fluorescence Detection. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061288
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaochen, Hongliang Li, Yue Shen, Yangyang Lu, Yong Zhu, and Jianfang Chen. 2025. "Automated Determination of Ammonium at Nanomolar Levels in Seawater by Coupling Lab-in-Syringe with Highly Sensitive Light-Emitting-Diode-Induced Fluorescence Detection" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061288
APA StyleGuo, X., Li, H., Shen, Y., Lu, Y., Zhu, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Automated Determination of Ammonium at Nanomolar Levels in Seawater by Coupling Lab-in-Syringe with Highly Sensitive Light-Emitting-Diode-Induced Fluorescence Detection. Molecules, 30(6), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061288







