Radioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of One-Year and Seven-Year White Tea Extracts Against 137Cs Radiation-Induced Cell Damage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
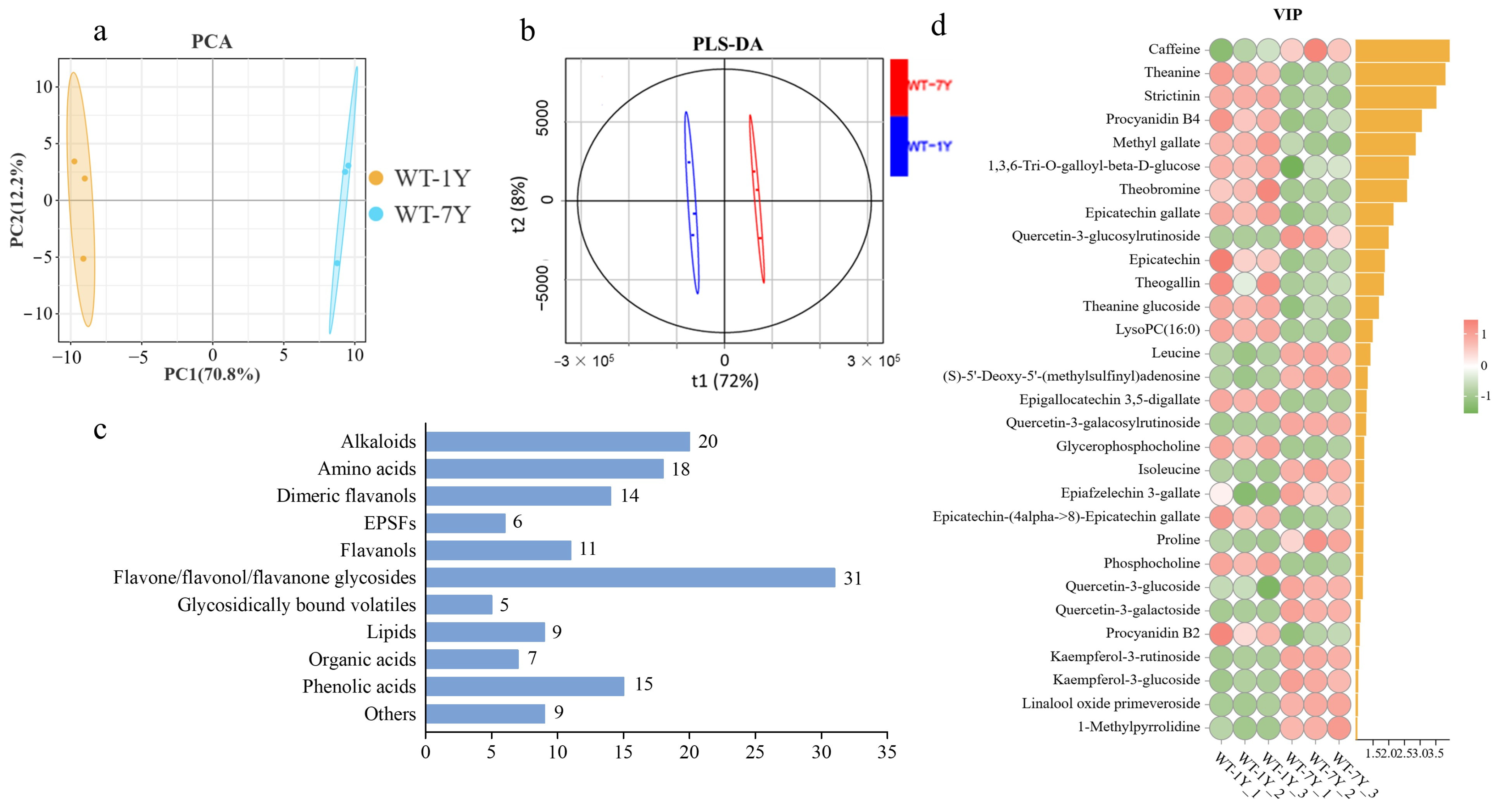
2.1. Metabolite Differences Between WT-1Y and WT-7Y
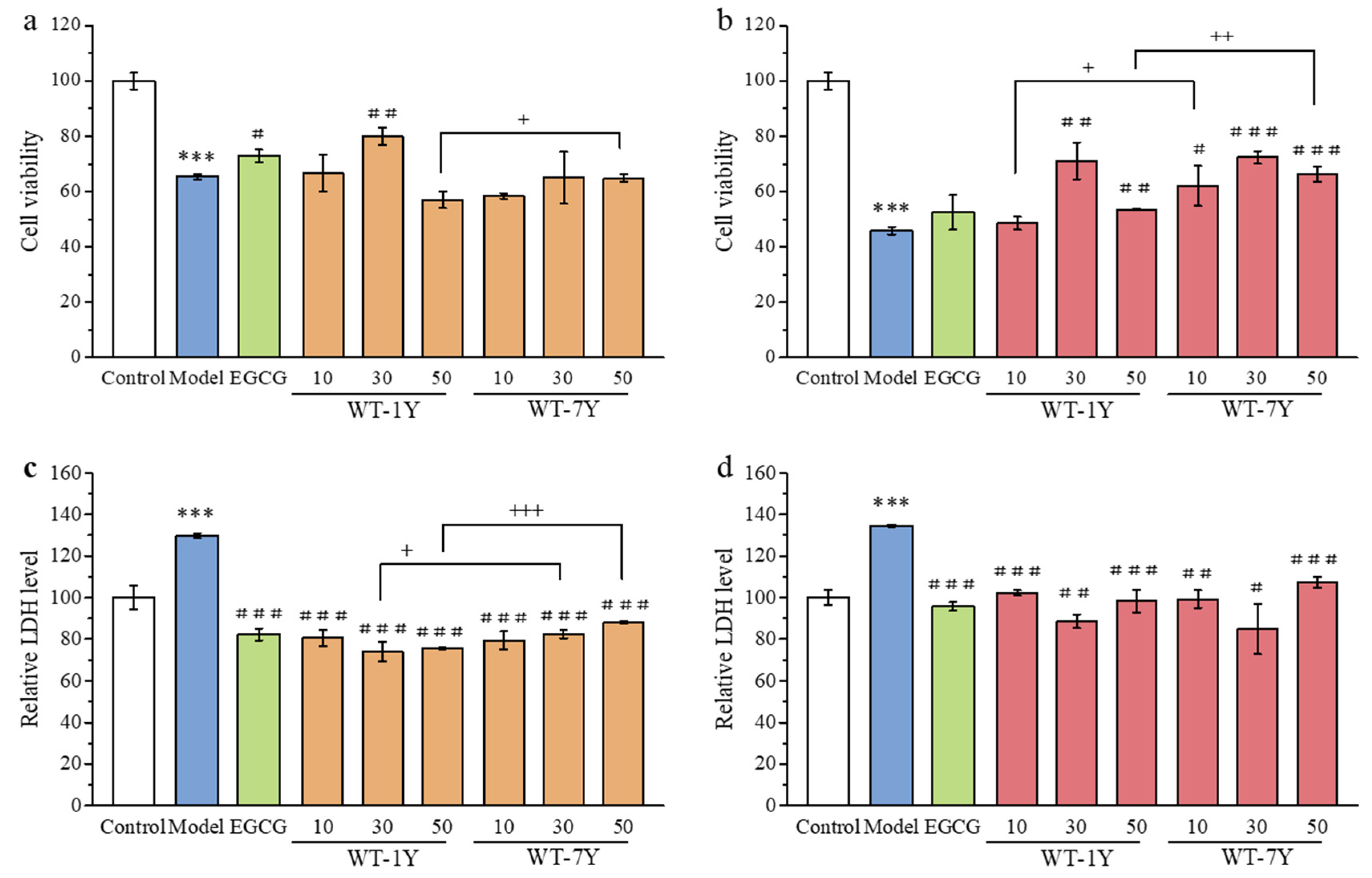
2.2. WT-1Y and WT-7Y Extracts Reduce Radiation-Induced Cytotoxicity
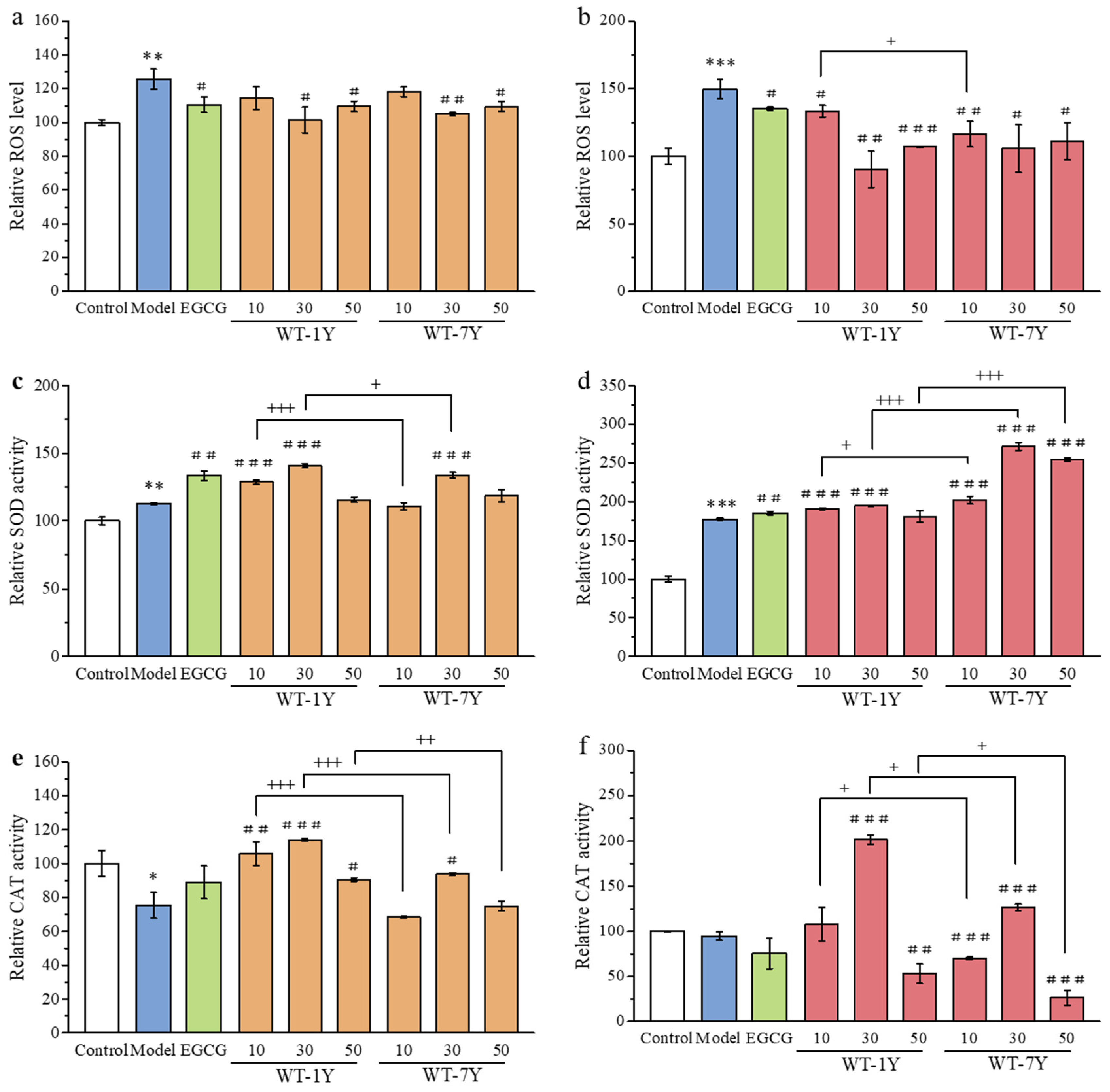
2.3. WT-1Y and WT-7Y Extracts Rebalance the Radiation-Induced Changes in Intracellular ROS, SOD, and CAT Levels
2.4. WT-1Y and WT-7Y Extracts Maintain the Integrity of Cellular Ultrastructure
2.5. WT-1Y and WT-7Y Inhibit Radiation-Induced Activation of p53 and Caspase-3
2.6. Analysis of the Correlation Between the Level of Intracellular Indexes and Metabolite Contents of WT-1Y and WT-7Y
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of White Tea Sample
4.3. Nontargeted Metabolomics Analysis
4.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.5. Cell Viability Measurement
4.6. ROS Level Detection
4.7. Antioxidant Enzyme Detection
4.8. Ultrastructure Analysis of Cell
4.9. Immunological Fluorescence Assay
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mouri, G.; Golosov, V.; Shiiba, M.; Hori, T. Assessment of the caesium-137 flux adsorbed to suspended sediment in a reservoir in the contaminated fukushima region in japan. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Ohba, R.; Oura, M.; Kato, S. Study on long-term radiation exposure analysis after the fukushima dai-ichi nuclear power plant accident: Validation of the eu long-term radiation exposure model (ermin). J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballin, U.; Sause, A. Radiocasium in fishery products. In Radioactivity in Humans and the Environment, Proceedings of the 30th Annual Meeting of the Fachverband-fur-Strahlenschutz in Conjunction with the Osterreichischer-Verband-fur-Strahlenschutz, 28 September–2 October 1998; Winter, M., Henrichs, K., Doerfel, H., Eds.; TUeV-Verlag: Koeln, Germany, 1998; pp. 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Beia, S.; Burcea, M.; Beia, V.E. Studies on the degree of radioactive contamination of poultry eggs. Sci. Pap.-Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2015, 15, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, H.; Bo, X.C.; Chen, H.B. Ionizing radiation damage and repair from 3d-genomic perspective. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameziane-El-Hassani, R.; Boufraqech, M.; Lagente-Chevallier, O.; Weyemi, U.; Talbot, M.; Métivier, D.; Courtin, F.; Bidart, J.M.; El Mzibri, M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Role of H2O2 in ret/ptc1 chromosomal rearrangement produced by ionizing radiation in human thyroid cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebicki, J.M.; Nauser, T. Initiation and prevention of biological damage by radiation-generated protein radicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouky, O.; Ding, N.; Zhou, G. Targeted and non-targeted effects of ionizing radiation. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovici, G.M.; Cascone, M.G.; Huber, T.; Chierici, A.; Gaudio, P.; de Souza, S.O.; D’Errico, F.; Malizia, A. Cytogenetic bio-dosimetry techniques in the detection of dicentric chromosomes induced by ionizing radiation: A review. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagetia, G.C. Radioprotective potential of plants and herbs against the effects of ionizing radiation. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Shukla, S.K.; Kumar, I.P.; Namita, I.; Afrin, F.; Sharma, R.K. Radioprotective properties of apple polyphenols: An in vitro study. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 288, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, T.G.; Nair, C.; Janardhanan, K.K. Enhancement of repair of radiation induced dna strand breaks in human cells by Ganoderma mushroom polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Mitchell, J.B.; Bursill, C.A.; Sowers, A.L.; Thetford, A.; Cook, J.A.; van Reyk, D.M.; Davies, M.J. The nitroxide radical tempol prevents obesity, hyperlipidaemia, elevation of inflammatory cytokines, and modulates atherosclerotic plaque composition in apoe−/− mice. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Cai, X.H.; Zhang, W.B.; Li, Y.N.; Qiu, P.Y.; Lu, D.D.; He, X.Y. Flavonoids of Rosa roxburghii tratt exhibit radioprotection and anti-apoptosis properties via the bcl-2(ca2+)/caspase-3/parp-1 pathway. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 1125–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohian, F.; Shanei, A.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Hejazi, S.H.; Moradi, M.T. The radioprotective effect of resveratrol against genotoxicity induced by γ-irradiation in mice blood lymphocytes. Dose-Response 2017, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.F.; Engelhardt, U.H.; Lin, Z.; Kaiser, N.; Maiwald, B. Flavonoids, phenolic acids, alkaloids and theanine in different types of authentic chinese white tea samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 57, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söhle, J.; Knott, A.; Holtzmann, U.; Siegner, R.; Grönniger, E.; Schepky, A.; Gallinat, S.; Wenck, H.; Stäb, F.; Winnefeld, M. White tea extract induces lipolytic activity and inhibits adipogenesis in human subcutaneous (pre)-adipocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Effects of the aqueous extract of white tea (Camellia sinensis) in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes model of rats. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, P.; Tiano, L.; Padella, L.; Bacchetti, T.; Customu, C.; Kay, A.; Damiani, E. Antioxidant activity of white, green and black tea obtained from the same tea cultivar. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghaalipour, F.; Kanthimathi, M.S.; Sanusi, J.; Rajarajeswaran, J. White tea (Camellia sinensis) inhibits proliferation of the colon cancer cell line, ht-29, activates caspases and protects dna of normal cells against oxidative damage. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, E.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; He, P.; Youying, T. He inhibitory role and mechanism of white tea extracts on pulmonary fibrosis induced by nano-sized SiO2 in rats. J. Tea Sci. 2020, 40, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, H.; Cai, M.; Kim, E.; Liu, X.; He, P.; Youying, T. Improvement of white tea on cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in mice. J. Tea Sci. 2020, 40, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.; Jeong, W. Cellular defensive mechanisms of tea polyphenols: Structure-activity relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, C.; López-Jiménez, J.A.; Pérez-Llamas, F.; Guardiola, F.A.; Esteban, M.A.; Arnao, M.B.; Zamora, S. Long-term intake of white tea prevents oxidative damage caused by adriamycin in kidney of rats. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2016, 96, 3079–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berilli, P.; Fanaro, G.B.; Santos, J.P.; Reyes, F.; Iglesias, A.H.; Reis, M.; Cazarin, C.; Marostica, M.R. White tea modulates antioxidant defense of endurance-trained rats. Curr. Res. Physiol. 2022, 5, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.D.; Tan, J.F.; Lu, M.L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, P.L.; Peng, Q.H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, D.C.; Hu, Z.Y.; et al. Metabolomics investigation reveals that 8-c n-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinone-substituted flavan-3-ols are potential marker compounds of stored white teas. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 7209–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, M.J.; Jin, S.; Wang, S.Y.; Yue, W.J.; Zhang, L.X.; Ye, N.X. Macro-composition quantification combined with metabolomics analysis uncovered key dynamic chemical changes of aging white tea. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkasiewicz, A.; Dorociak, M.; Stach, K.; Szelachowski, P.; Tabola, R.; Augoff, K. The usefulness of lactate dehydrogenase measurements in current oncological practice. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, P.; Lippi, G.; Maffulli, N. Biochemical markers of muscular damage. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flameng, W.; Borgers, M.; Daenen, W.; Stalpaert, G. Ultrastructural and cytochemical correlates of myocardial protection by cardiac hypothermia in man. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1980, 79, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cao, J.J.; Liu, P.; Guo, D.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Y.; Rahman, K. Protective role of tea polyphenols in combination against radiation-induced haematopoietic and biochemical alterations in mice. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.W.; Ge, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, Q.; Wu, C.H.; Yu, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.L.; Zou, J. Tea polyphenol attenuates oxidative stress-induced degeneration of intervertebral discs by regulating the keap1/nrf2/are pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6684147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Song, J.L.; Yi, R.K.; Li, G.J.; Sun, P.; Park, K.Y.; Suo, H.Y. Comparison of antioxidative effects of insect tea and its raw tea (kuding tea) polyphenols in kunming mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. P53: 800 million years of evolution and 40 years of discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Assanelli, D.; Bianchi, R. Effects of acute caffeine administration on nos and bax/bcl2 expression in the myocardium of rat. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumari, A.; Gulati, A.; Padwad, Y.; Sharma, R. Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses premature senescence of preadipocytes by inhibition of pi3k/akt/mtor pathway and induces senescent cell death by regulation of bax/bcl-2 pathway. Biogerontology 2019, 20, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.D.; Qu, L.Z.; Dai, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.L.; Feng, Y.L.; Chen, X.J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; et al. Structural insight into the molecular mechanism of p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Jang, J.S.; Jo, S.K.; Kim, S.H. Modification of gamma-radiation response in mice by green tea polyphenols. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, H.; Mahé, M.M.; Derkinderen, P.; Bach-Ngohou, K.; Neunlist, M.; Lardeux, B. The omega-6 fatty acid derivative 15-deoxy-δ12,14-prostaglandin j2 is involved in neuroprotection by enteric glial cells against oxidative stress. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scola, G.; Conte, D.; Spada, P.; Dani, C.; Vanderlinde, R.; Funchal, C.; Salvador, M. Flavan-3-ol compounds from wine wastes with in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. Dietary flavonoids: Role of (-)-epicatechin and related procyanidins in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.; Fernandes, V.C.; Araújo, P.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Synthesis, characterisation and antioxidant features of procyanidin b4 and malvidin-3-glucoside stearic acid derivatives. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.F.; Zhao, J.W.; Yu, H.L.; Zhu, J.J. Relationship between neuroprotective effects and structure of procyanidins. Molecules 2022, 27, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, K.; Fujii, K.; Anzai, K.; Ozawa, T. In vivo monitoring of hydroxyl radical generation caused by x-ray irradiation of rats using the spin trapping/epr technique. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Pranata, R.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, P.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Tzen, J.; Chen, R.J. Alleviation of hyperuricemia by strictinin in aml12 mouse hepatocytes treated with xanthine and in mice treated with potassium oxonate. Biology 2023, 12, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzen, J. Strictinin: A key ingredient of tea. Molecules 2023, 28, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.G.; Jia, L.N.; Shen, Y.; Ohmura, A.; Kitanaka, S. Inhibitory effects of constituents from Euphorbia lunulata on differentiation of 3t3-l1 cells and nitric oxide production in raw264.7 cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 8305–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.M.; Chuang, H.C.; Wu, C.H.; Yen, G.C. Cytoprotective effects of phenolic acids on methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis in neuro-2a cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlcek, J.; Jurikova, T.; Skrovankova, S.; Sochor, J. Quercetin and its anti-allergic immune response. Molecules 2016, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Pişkin, Ö.; Baş, Y.; Aydın, B.G.; Can, M.; Elmas, Ö.; Büyükuysal, Ç. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on radiation-induced brain injury in rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalingam, K.B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Ramdas, P.; Haleagrahara, N. Quercetin glycosides induced neuroprotection by changes in the gene expression in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 55, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, D.P.; Li, Z.Y.; Qi, B.; He, L.; Yu, Y.; Yin, W.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Lin, L. Radiotherapy induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the atm and smad pathways. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.G.; Lee, B.H.; Jung, S.H.; Oh, S.H. Role of autophagy in chemoresistance: Regulation of the atm-mediated dna-damage signaling pathway through activation of dna-pkcs and parp-1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Feng, X.; Pan, Y.; Gong, S.; Fan, F.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. Recent advances on white tea: Manufacturing, compositions, aging characteristics and bioactivities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.; Zhan, J.; Ho, C. Focusing on the recent progress of tea polyphenol chemistry and perspectives. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.M.; Uddin, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.K. [6]-gingerol prevents gamma radiation-induced cell damage in hepg2 cells. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 305, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Dai, W.D.; Xiong, M.F.; Gao, J.J.; Zhou, H.J.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.L. Metabolomics investigation of the chemical variations in white teas with different producing areas and storage durations. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Warusawitharana, H.K.; Liu, X.H.; Tu, Y.Y. The prevention role of theaflavin-3,3′-digallate in angiotensin ii induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy via can-nfat signal pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.Y.; Cai, F.Z.; Li, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yu, M.J.; Chen, S.K.; Lu, J.J.; Hu, C.H. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes involve in oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury and mitochondrial dysfunction under diquat exposing. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 3906–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, C.; Cai, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z. Radioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of One-Year and Seven-Year White Tea Extracts Against 137Cs Radiation-Induced Cell Damage. Molecules 2025, 30, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071448
Xia C, Cai M, Lu Y, Wang B, Xu L, Wang K, Liu Z. Radioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of One-Year and Seven-Year White Tea Extracts Against 137Cs Radiation-Induced Cell Damage. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071448
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Chen, Meisheng Cai, Yanting Lu, Bingkui Wang, Linglin Xu, Kaixi Wang, and Zhonghua Liu. 2025. "Radioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of One-Year and Seven-Year White Tea Extracts Against 137Cs Radiation-Induced Cell Damage" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071448
APA StyleXia, C., Cai, M., Lu, Y., Wang, B., Xu, L., Wang, K., & Liu, Z. (2025). Radioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of One-Year and Seven-Year White Tea Extracts Against 137Cs Radiation-Induced Cell Damage. Molecules, 30(7), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071448






