Reinforcement Effect of CaCl2 on Cementation Performance of Solid-Waste-Based Cementitious Materials for Fine Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of CaCl2 Content on Cementing Performance of SWCMs for Fine Tailings
2.2. Effect of CaCl2 on the Hydration Properties of SWCMs
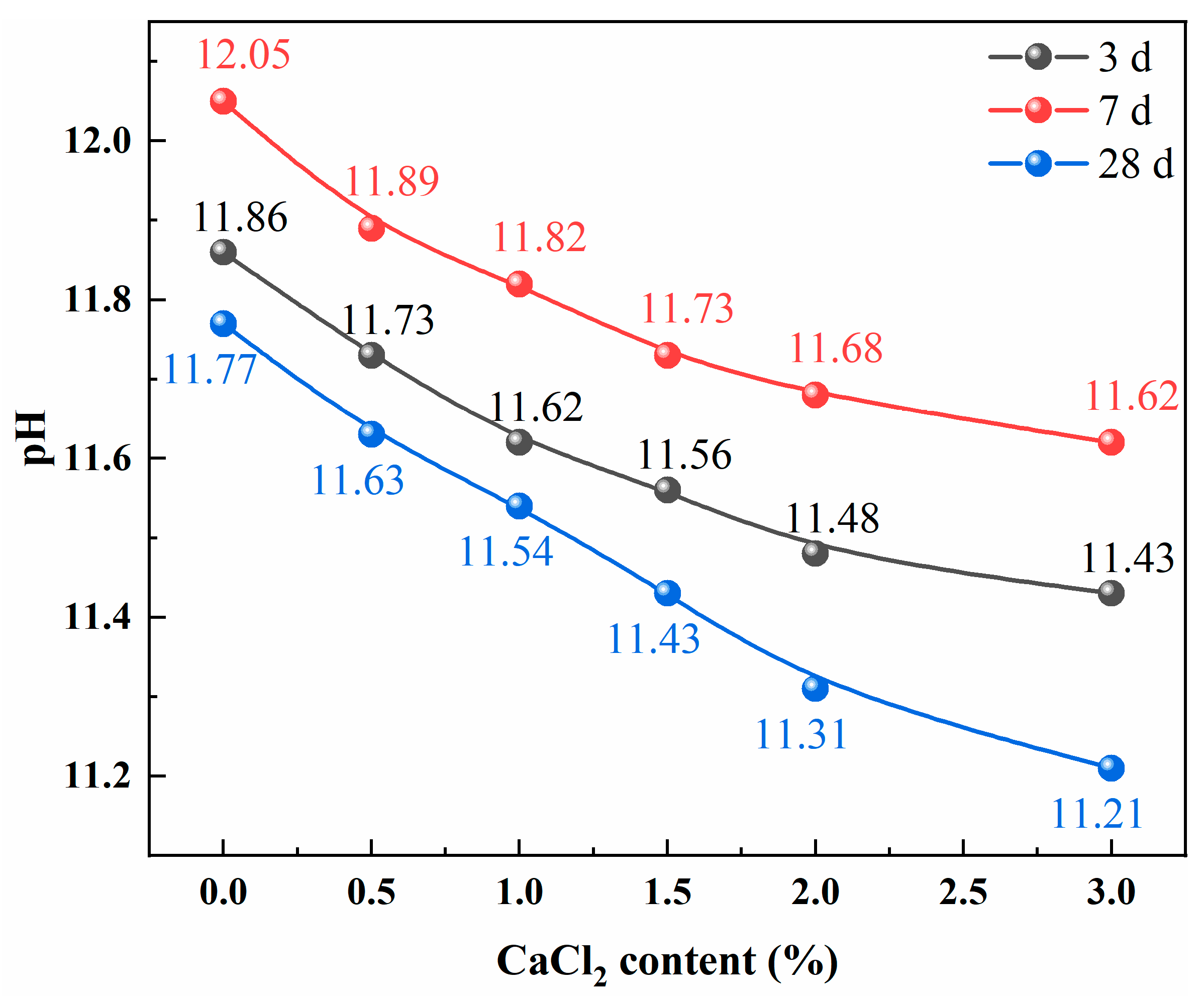
2.2.1. pH of the Pore Solution of SWCMs
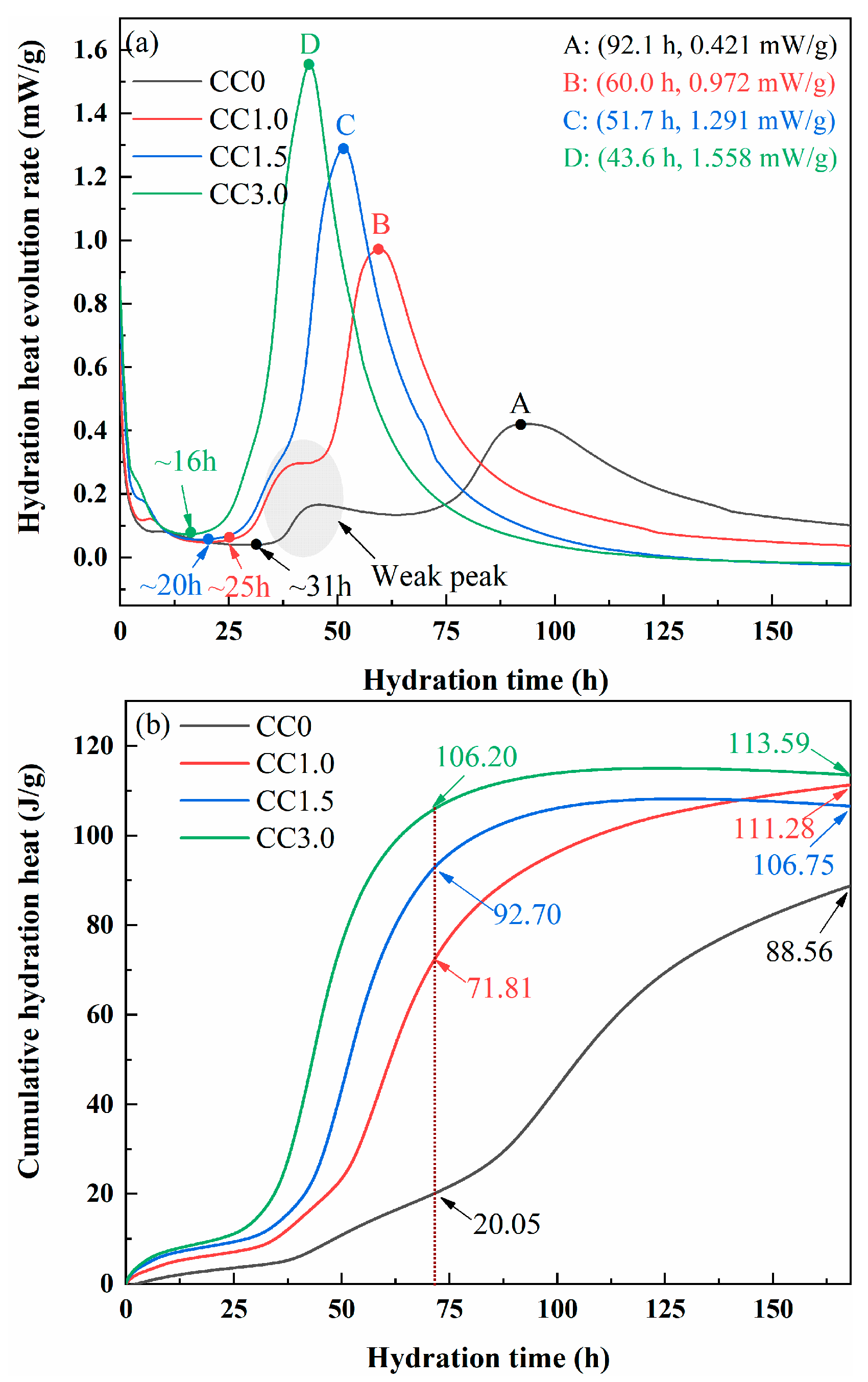
2.2.2. Hydration Heats of SWCMs
2.2.3. Hydration Products of SWCMs
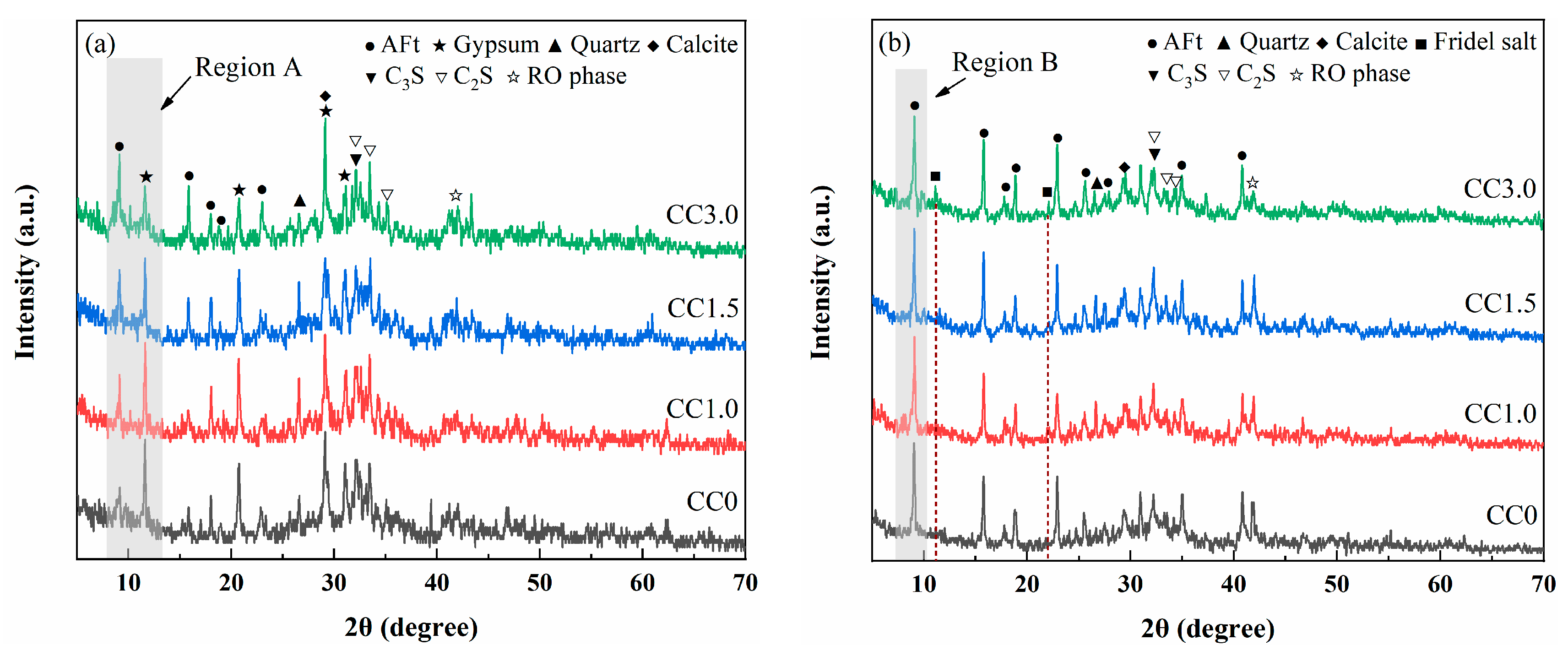
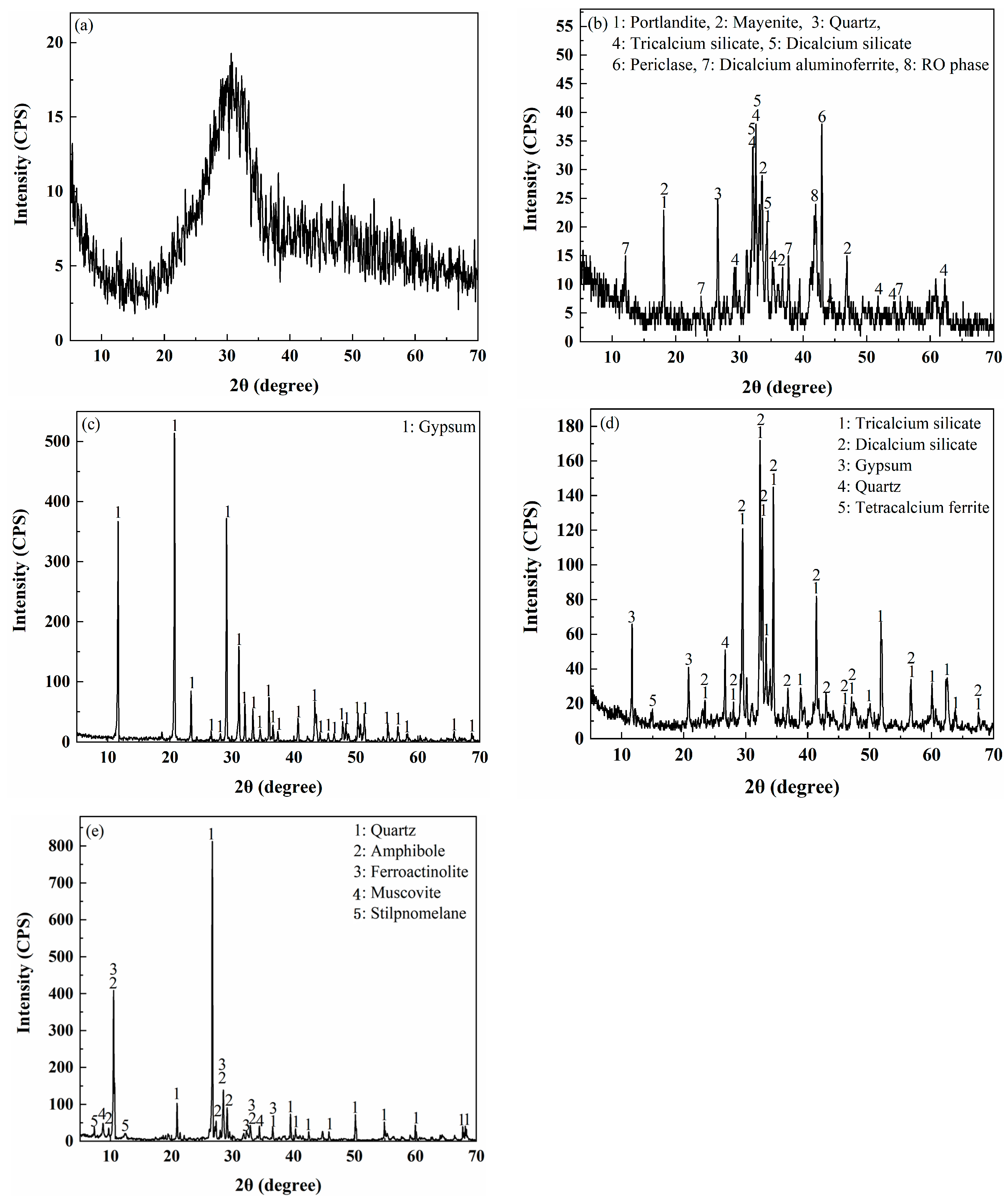
XRD Analysis
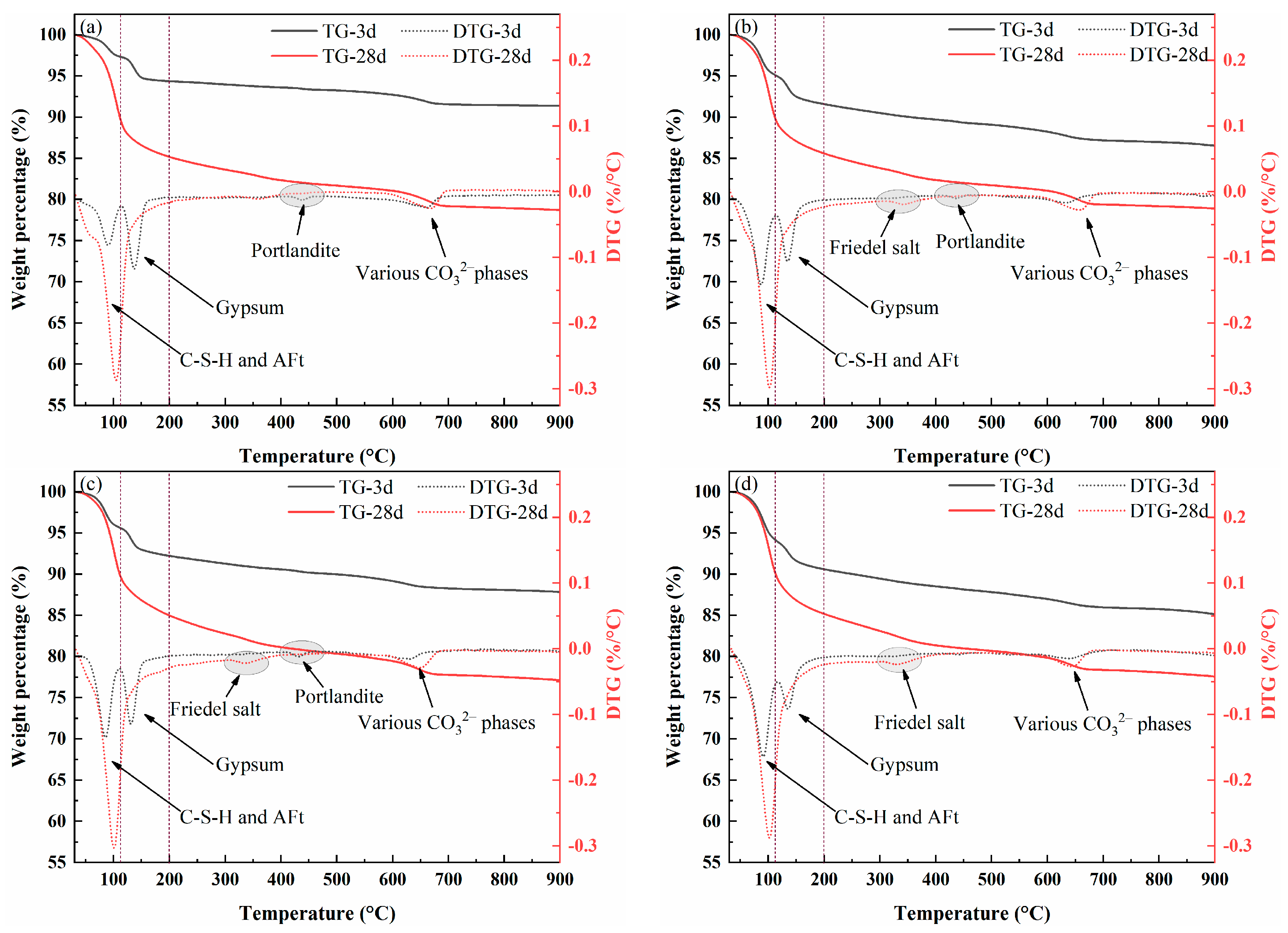
TG-DTG Analysis
SEM-EDS Analysis
2.3. Microstructural Analysis of Cemented Fine Tailings Backfill
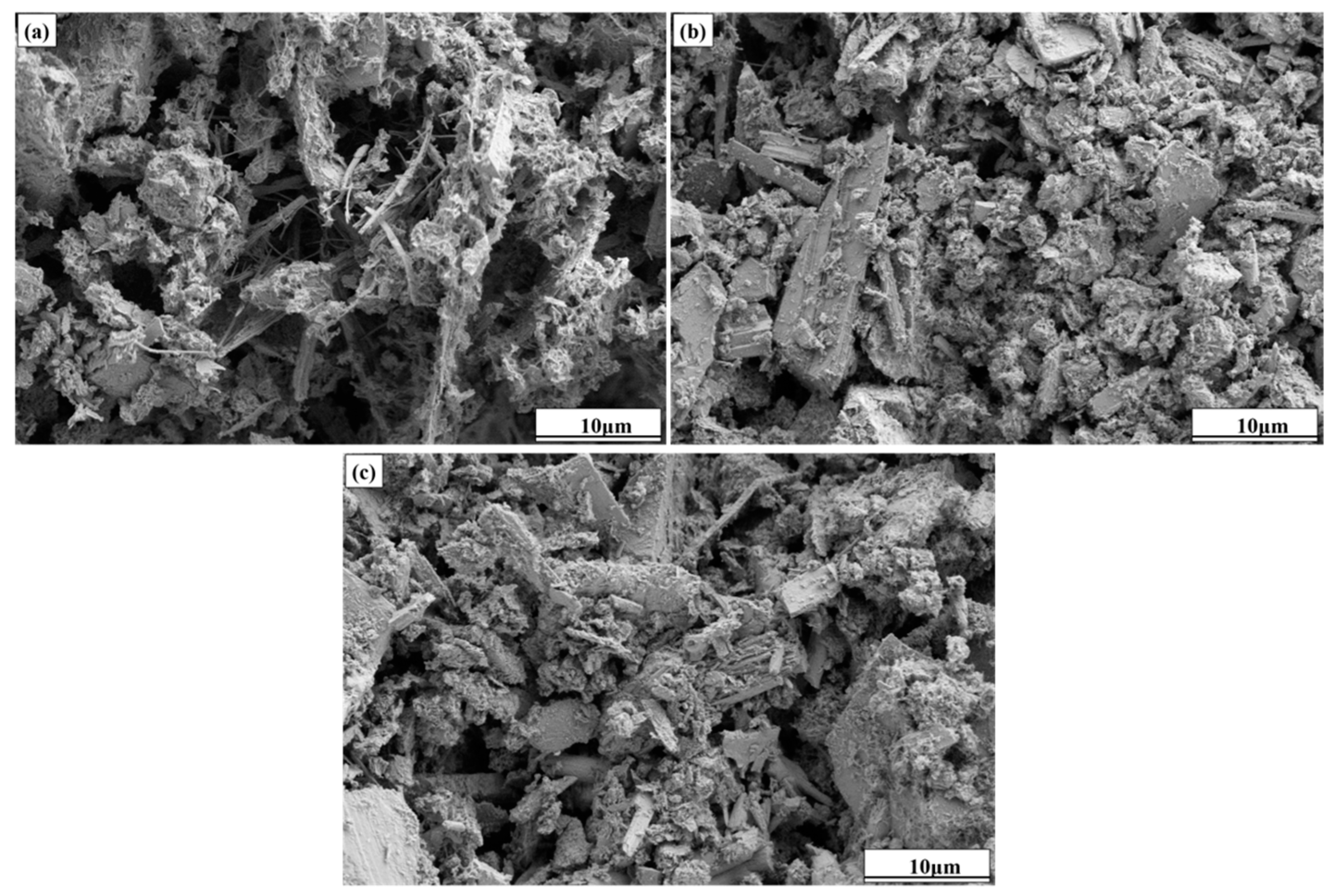
2.3.1. Microscopic Morphology Analysis
2.3.2. Pore Structure Analysis
3. Experimental Materials and Methods
3.1. Characterization of Experimental Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Cemented Tailings Backfills
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of Pastes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.L.; Du, G.J.; Zhang, M.; Du, J.L.; Gao, J.Y. Problems and Suggestions of Comprehensive Utilization Industrail of Tailings. Mod. Min. 2022, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wen, X.C.; Zhou, J.W.; Lu, Z.; Li, X.Y.; Yan, B. A critical review on the migration and transformation processes of heavy metal contamination in lead-zinc tailings of China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.H.; Li, J.C.; Liu, H.B.; Jiao, H.Z.; Yin, S.H.; Chen, X.M.; Yu, Y. Systematic review of mixing technology for recycling waste tailings as cemented paste backfill in mines in China. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.; Vilarinho, I.; Capela, M.N.; Caetano, A.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.L.; Seabra, M.P. Waste-Based One-Part Alkali Activated Materials. Materials 2021, 14, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. Cemented paste backfill for mineral tailings management: Review and future perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2019, 144, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edraki, M.; Baumgartl, T.; Manlapig, E.; Bradshaw, D.; Franks, D.M.; Moran, C.J. Designing mine tailings for better environmental, social and economic outcomes: A review of alternative approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hane, I.; Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Maqsoud, A. Laboratory Characterization of Cemented Tailings Paste Containing Crushed Waste Rocks for Improved Compressive Strength Development. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Ouellet, S. Experimental characterization of the influence of tailings fineness and density on the quality of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q. A strength prediction model using artificial intelligence for recycling waste tailings as cemented paste backfill. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Shao, Y.; Wu, A.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. A systematic review of paste technology in metal mines for cleaner production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fall, M. Strength and self-desiccation of slag-cemented paste backfill at early ages: Link to initial sulphate concentration. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihangir, F.; Akyol, Y. Mechanical, hydrological and microstructural assessment of the durability of cemented paste backfill containing alkali-activated slag. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2018, 32, 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Gan, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J. Additivity effect on properties of cemented ultra-fine tailings backfill containing sodium silicate and calcium chloride. Minerals 2024, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Meng, Z.; Gao, T.; Dong, S.; Ni, P.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, K. Optimization of proportions of alkali-activated slag-flyash-based cemented tailings backfill and its strength characteristics and microstructure under combined action of dry-wet and freeze-thaw cycles. Materials 2024, 17, 4945. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Kang, M. Recycling multisource industrial waste residues as green binder for cemented ultrafine tailings backfill: Hydration kinetics, mechanical properties, and solidification mechanism. Powder Technol. 2024, 441, 119799. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, J. Effects of Early Strength Accelerators on the Strength of Filling Body Comprised of Consolidated Powder and Mixed Aggregate. Met. Min. 2020, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Koohestani, B.; Darban, A.K.; Mokhtari, P. A comparison between the influence of superplasticizer and organosilanes on different properties of cemented paste backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Mishra, D.P.; Singh, P.; Mishra, K.; Mandal, S.K.; Ghosh, C.N.; Kumar, R.; Mandal, P.K. Utilization of mill tailings, fly ash and slag as mine paste backfill material: Review and future perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125120. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, T.; Blask, O.; Stephan, D. Acceleration of cement hydration-A review of the working mechanisms, effects on setting time, and compressive strength development of accelerating admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, C. Accelerators for normal concrete: A critical review on hydration, microstructure and properties of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104762. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; He, T.; Wan, S.; Chang, N.; Ma, X.; Qiu, H. Study on the effect of supplementary cementitious materials on the volume stability of mortar mixed with laboratory-made high-content fluorine-type accelerator. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sohn, D.; Jennings, H.M.; Mason, T.O. Hydration of alkali-activated ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jennings, H.M. Pore solution chemistry of alkali-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pan, X. Effects of Steel Slag on Mechanical Properties and Mechanism of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04019348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T. In-depth insight into the cementitious synergistic effect of steel slag and red mud on the properties of composite cementitious materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, Z.; Pang, B. Strength Development of Cemented Paste Backfill with CaCl2 and NaCl in Above-Zero Underground Environments. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 5927–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Suraneni, P.; Weiss, J. Flexural strength reduction of cement pastes exposed to CaCl2 solutions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 86, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, P.; Zhang, B.; Huan, C.; Guo, L.; Yang, Q.; Song, K.I. Study on hydration reaction and structure evolution of cemented paste backfill in early-age based on resistivity and hydration heat. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cui, M.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Lyu, X. Alkali-hydrothermal activation of mine tailings to prepare one-part geopolymer: Activation mechanism, workability, strength, and hydration reaction. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 30407–30417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ni, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, D. Hydration mechanism and orthogonal optimisation of mix proportion for steel slag–slag-based clinker-free prefabricated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 117036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalamurugan, J.; Kumar, V.G.; Padmapriya, R.; Raja, V.K.B. Recent applications of steel slag in construction industry. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 2865–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Shi, C.; Pan, S.Y. Characteristics of steel slags and their use in cement and concrete—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ni, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Hitch, M.; Pascual, R. Carbonation of steel slag and gypsum for building materials and associated reaction mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 125, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, X.; Wang, J. Synthesis of nanoparticles from slag and their enhancement effect on hydration properties of CaO/CaSO4-activated slag binder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103586. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Kunther, W.; Gijbels, K.; Samyn, P.; Carvelli, V.; Illikainen, M.; Kinnunen, P. On the retardation mechanisms of citric acid in ettringite-based binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106315. [Google Scholar]
- Poupelloz, E.; Gauffinet, S.; Nonat, A. Study of nucleation and growth processes of ettringite in diluted conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 127, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traetteberg, A.U.D.; Grattan-Bellew, P.E. Hydration of 3CaO·Al2O3 and 3CaO·Al2O3 + Gypsum With and Without CaCl2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1975, 58, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, W.S.; Jeong, Y.; Yoon, S.; Jeon, D.; Jun, Y.; Oh, J.E. Effects of CaCl2 on hydration and properties of lime(CaO)-activated slag/fly ash binder. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 84, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wan, X.; Han, X.; Ren, J.; Luo, J.; Yu, Q. Solidification of chloride ions in alkali-activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126219. [Google Scholar]
- Zakira, U.; Zheng, K.; Xie, N.; Birgisson, B. Development of high-strength geopolymers from red mud and blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of superabsorbent polymer introduction on properties of alkali-activated slag mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127541. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Lyu, X. Synthesis and optimization of green one-part geopolymer from mine tailings and slag: Calcium carbide residue and soda residue as supplementary alkali sources. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129013. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, L.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Dissolution processes, hydrolysis and condensation reactions during geopolymer synthesis: Part I—Low Si/Al ratio systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, C.K.; Lukey, G.C.; Van Deventer, J.S. The coexistence of geopolymeric gel and calcium silicate hydrate at the early stage of alkaline activation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, P.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Sirivivatnanon, V. Kinetics of geopolymerisation: The role of Al2O3 and SiO2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 512–518. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Lyu, X. Variation in Polymerization Degree of C-A-S-H Gels and Its Role in Strength Development of Alkali-activated Slag Binders. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2021, 36, 871–879. [Google Scholar]
- Makaratat, N.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Namarak, C.; Sata, V. Effects of binder and CaCl2 contents on the strength of calcium carbide residue-fly ash concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.J.; Day, R.L. Pozzolanic reaction in the presence of chemical activators: Part II—Reaction products and mechanism. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Qiao, C.; Wu, W.; Hu, Y. Activation of Yellow River sediment by calcium chloride/oxalic acid system and study of mechanical properties. Concrete 2022, 6, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 17671–2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- HJ 962-2018; Soil–Determination of pH–Potentiometry. China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2018.

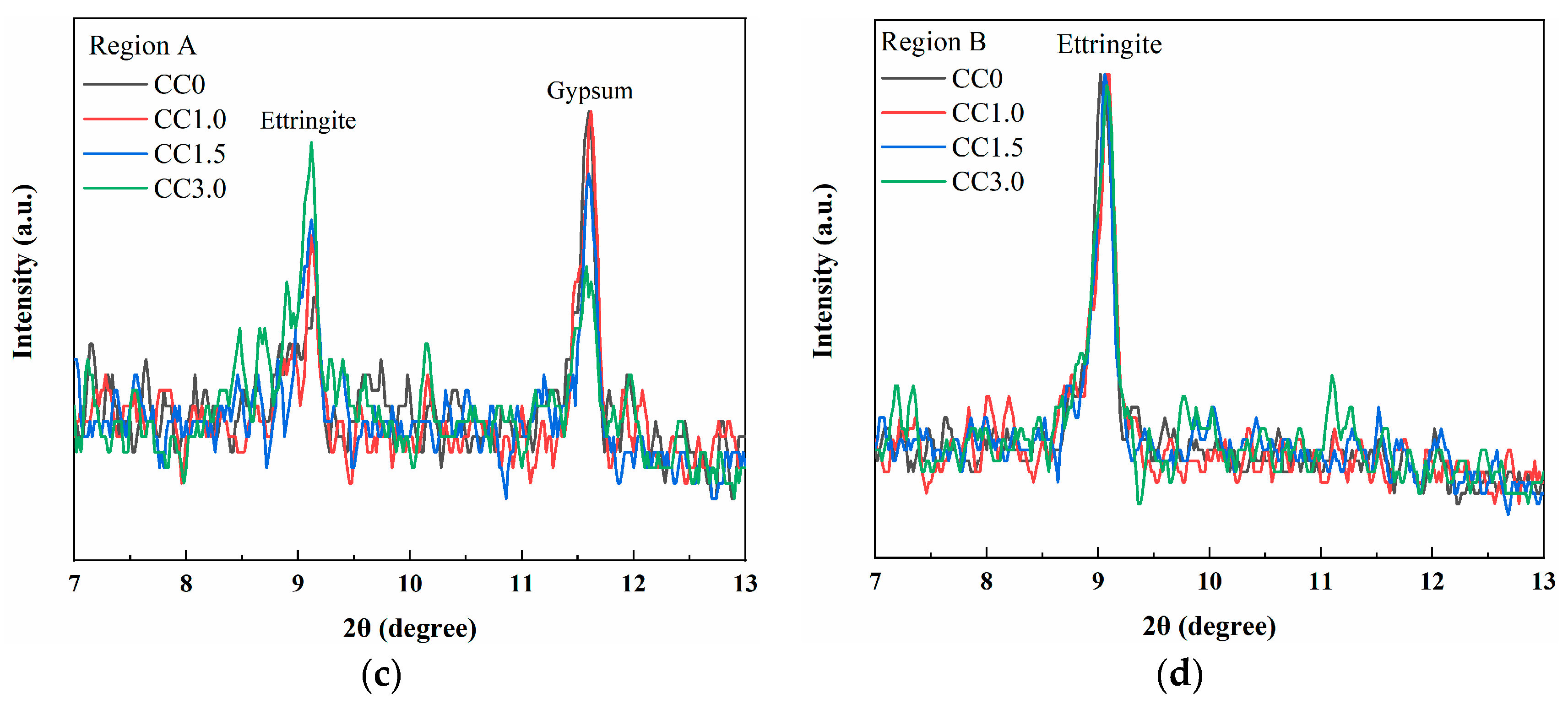
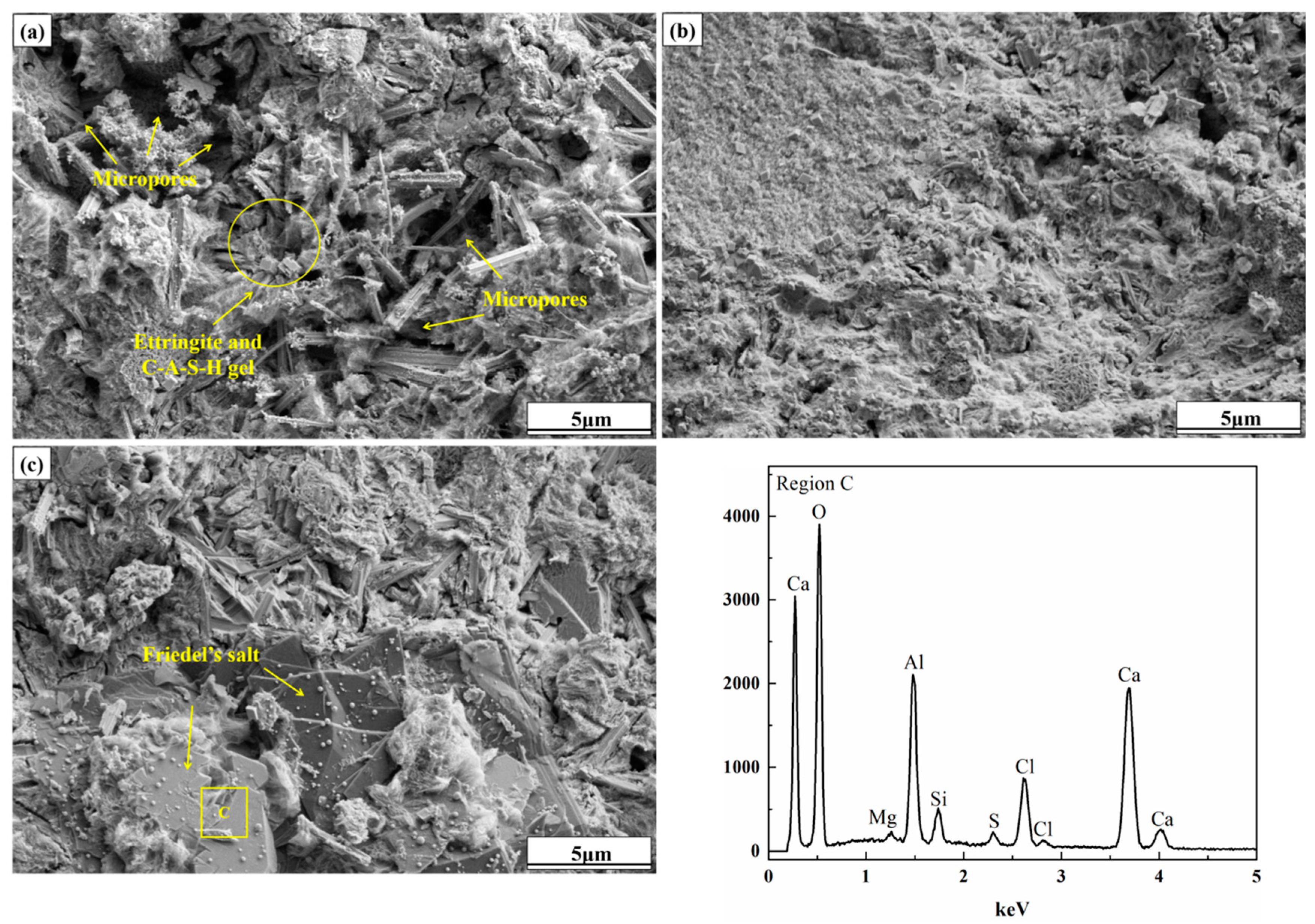

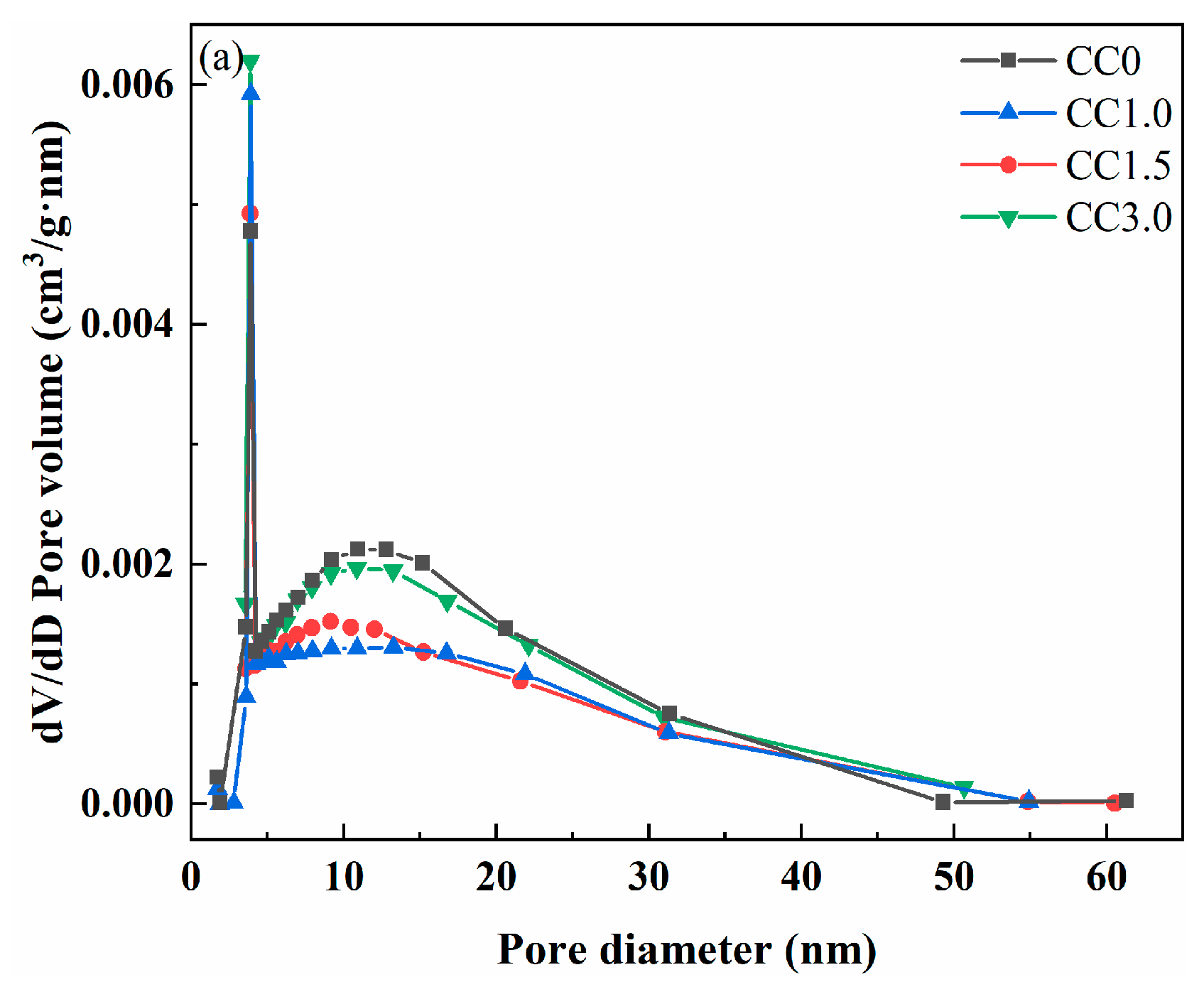
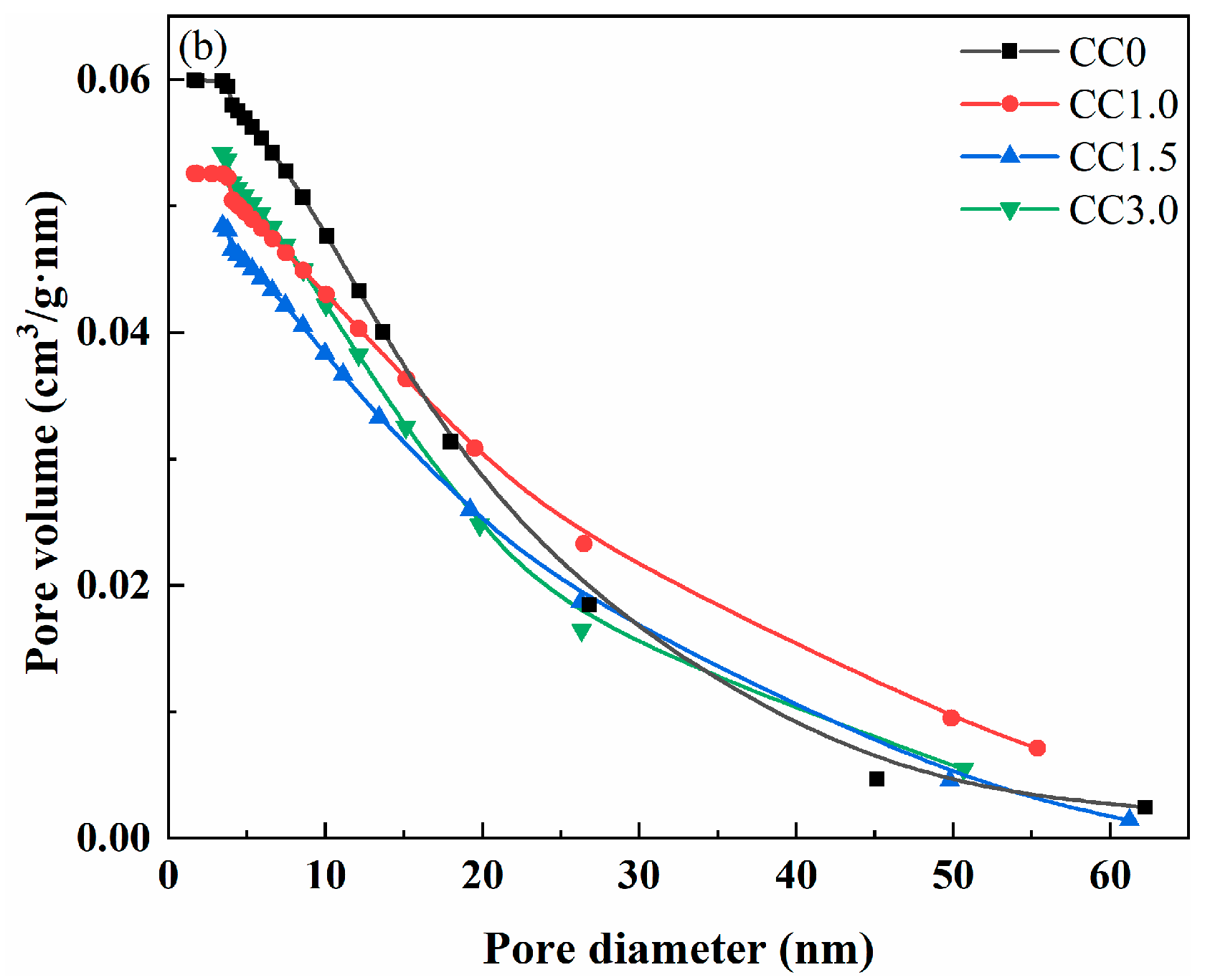
| Hydration Age | Hydration Products | Weight Loss | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC0 | CC1.0 | CC1.5 | CC3.0 | ||
| 3 days | C-S-H and AFt | 3.04 | 4.67 | 5.17 | 6.21 |
| CaSO4·2H2O | 3.24 | 3.19 | 2.81 | 2.51 | |
| Ca(OH)2 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0 | |
| Carbonate | 1.60 | 1.58 | 1.68 | 1.45 | |
| 28 days | C-S-H and AFt | 10.15 | 12.23 | 12.58 | 11.78 |
| CaSO4·2H2O | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Friedel salt | 0 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 0.89 | |
| Ca(OH)2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Carbonate | 2.44 | 2.37 | 2.29 | 2.26 | |
| Sample | CC0 | CC1.0 | CC1.5 | CC3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.060 | 0.052 | 0.048 | 0.054 |
| Average pore diameter (nm) | 14.160 | 13.559 | 12.499 | 13.246 |
| Components | Slag | SS | DG | OPC | MTs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 33.16 | 16.70 | 0.82 | 25.46 | 61.95 |
| Al2O3 | 16.31 | 5.94 | 0.97 | 11.98 | 6.34 |
| CaO | 38.86 | 40.38 | 41.81 | 49.60 | 4.05 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.36 | 19.66 | 0.22 | 3.72 | 23.18 |
| MgO | 8.37 | 8.04 | 0.77 | 3.61 | 2.85 |
| MnO2 | 0.67 | 3.01 | - | - | - |
| Na2O | 0.71 | - | 0.25 | - | 0.61 |
| K2O | - | - | - | 0.91 | - |
| SO3 | 1.25 | 0.75 | 54.17 | 3.46 | 1.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Wu, Y. Reinforcement Effect of CaCl2 on Cementation Performance of Solid-Waste-Based Cementitious Materials for Fine Tailings. Molecules 2025, 30, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071520
Liu Q, Wu Y. Reinforcement Effect of CaCl2 on Cementation Performance of Solid-Waste-Based Cementitious Materials for Fine Tailings. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071520
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qing, and Yanan Wu. 2025. "Reinforcement Effect of CaCl2 on Cementation Performance of Solid-Waste-Based Cementitious Materials for Fine Tailings" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071520
APA StyleLiu, Q., & Wu, Y. (2025). Reinforcement Effect of CaCl2 on Cementation Performance of Solid-Waste-Based Cementitious Materials for Fine Tailings. Molecules, 30(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071520




