Spontaneous Reaction of Oleacein and Oleocanthal with Primary Amines: A Biochemical Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
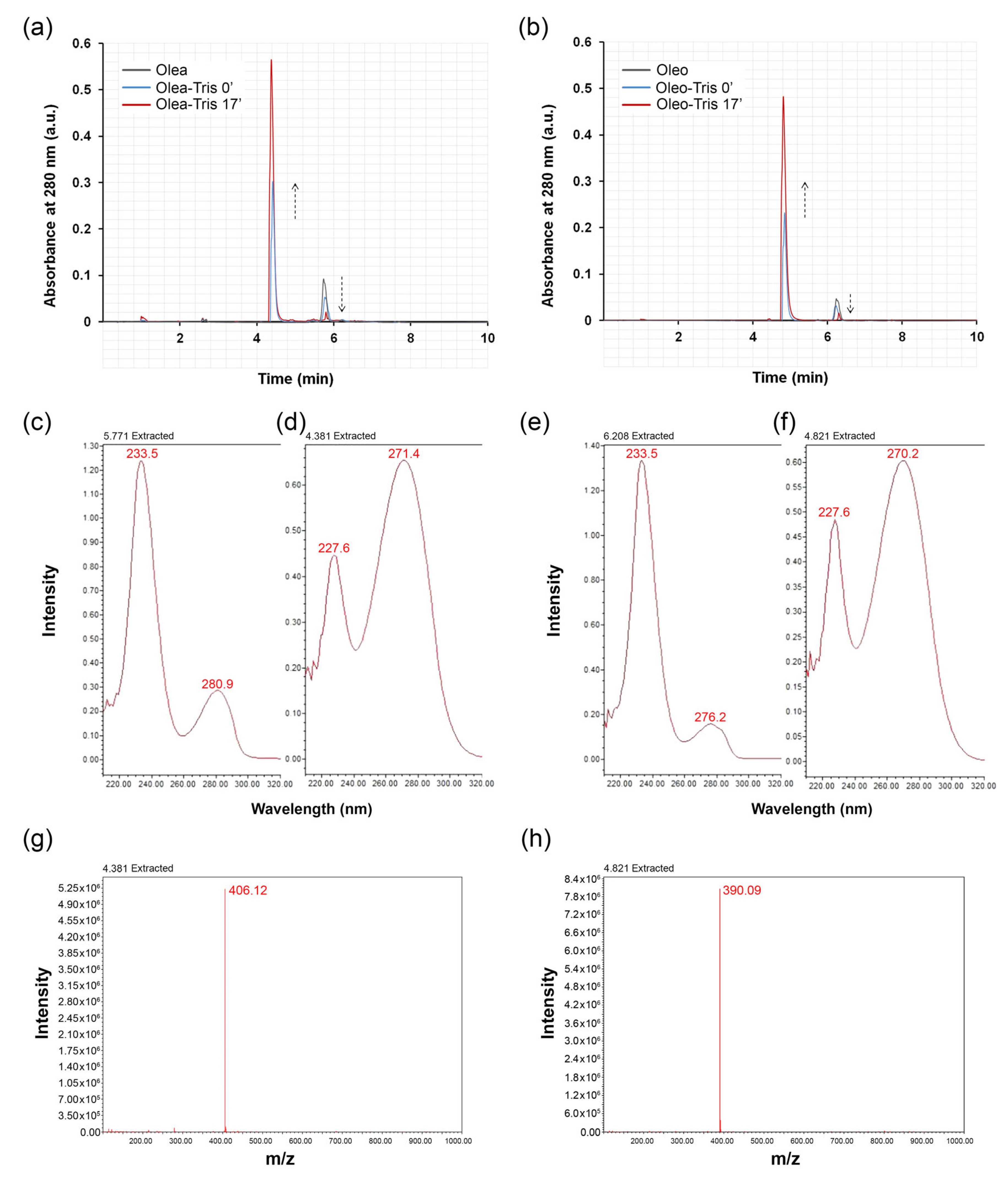
2.1. Adduct Formation and Structural Characterization
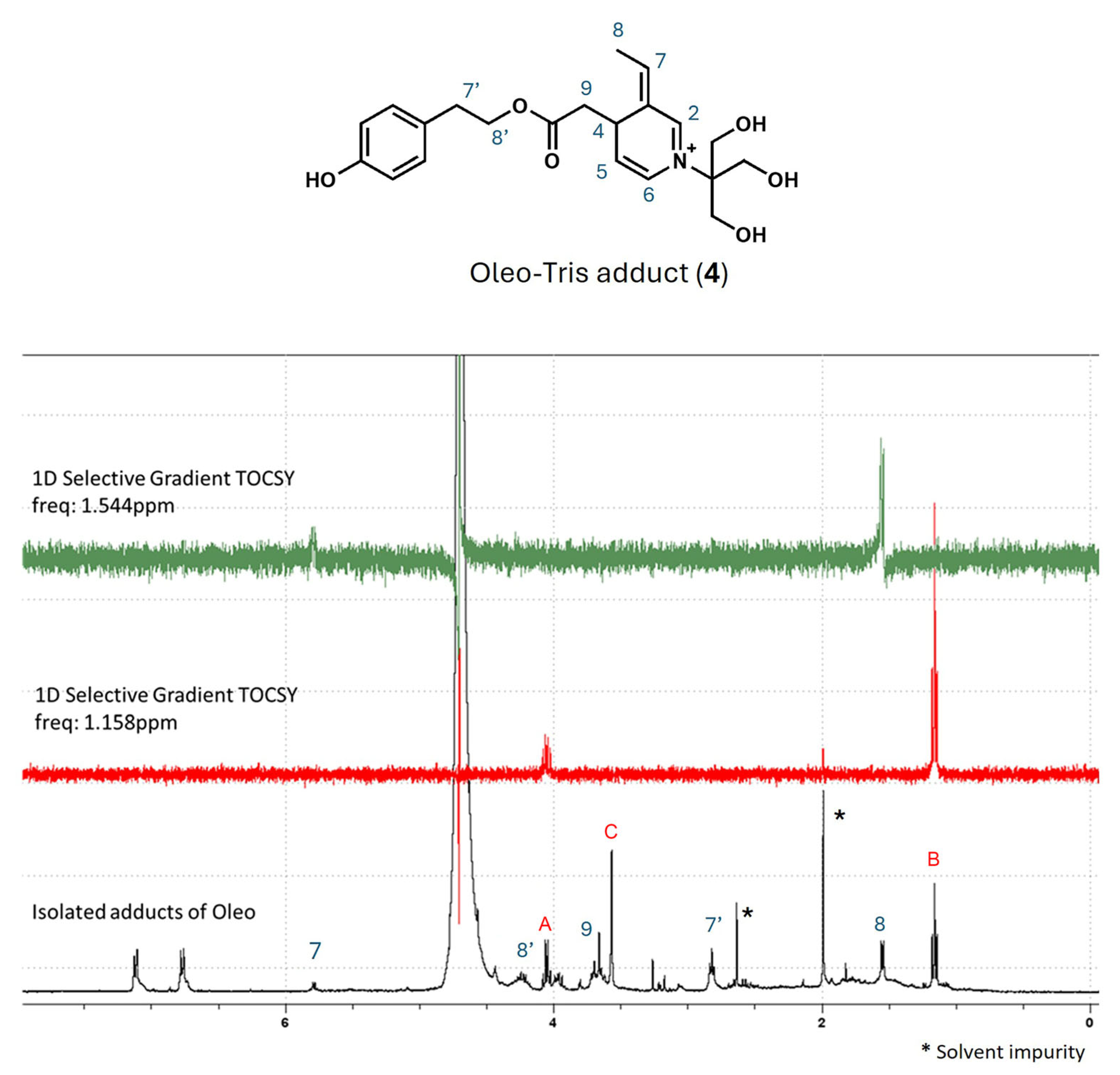
2.2. Investigation on the Structure of Olea-/Oleo-Tris Adducts: High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HR-MS) and 1H-NMR Analyses
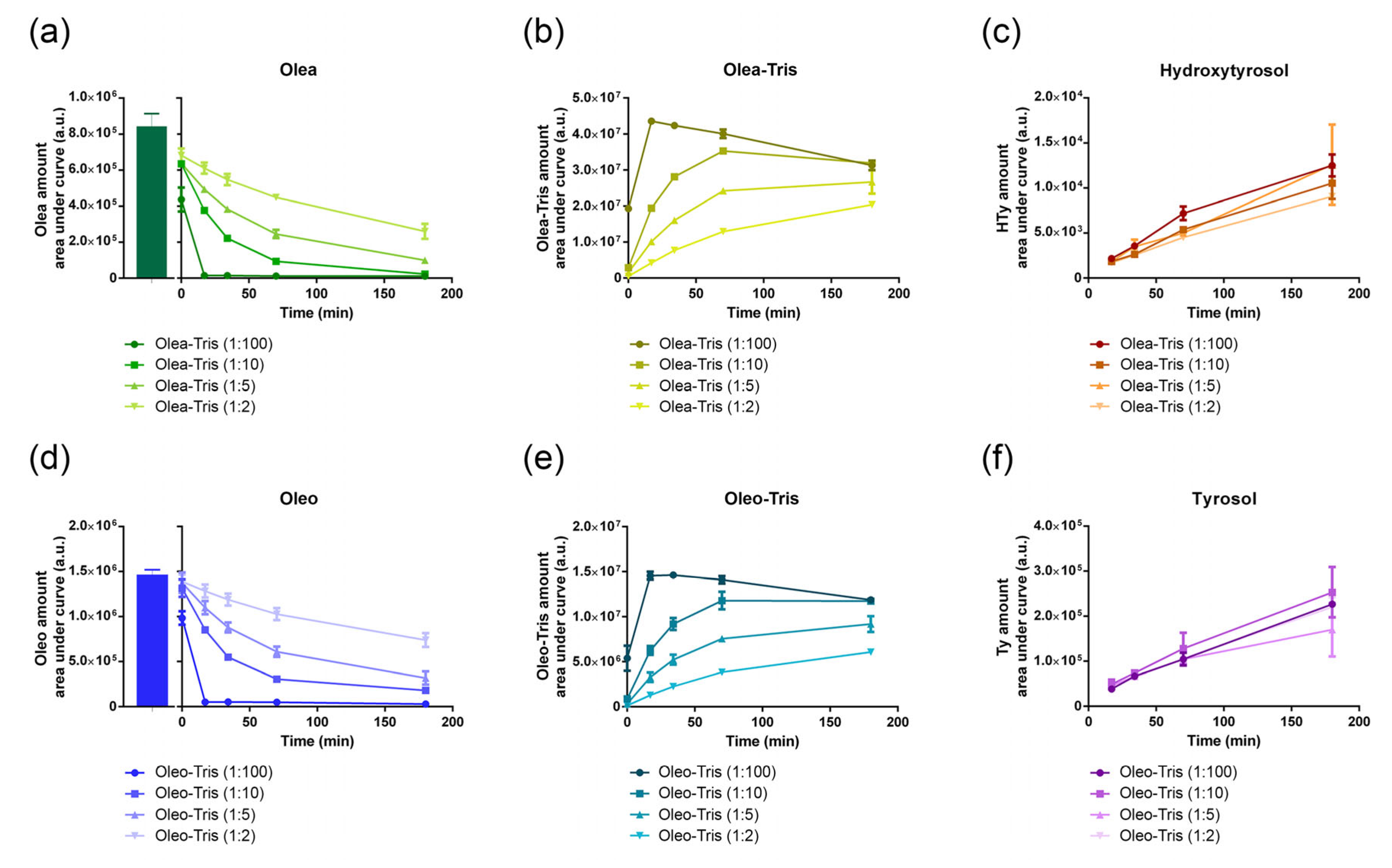
2.3. Kinetics of Adduct Formation and Their Stability
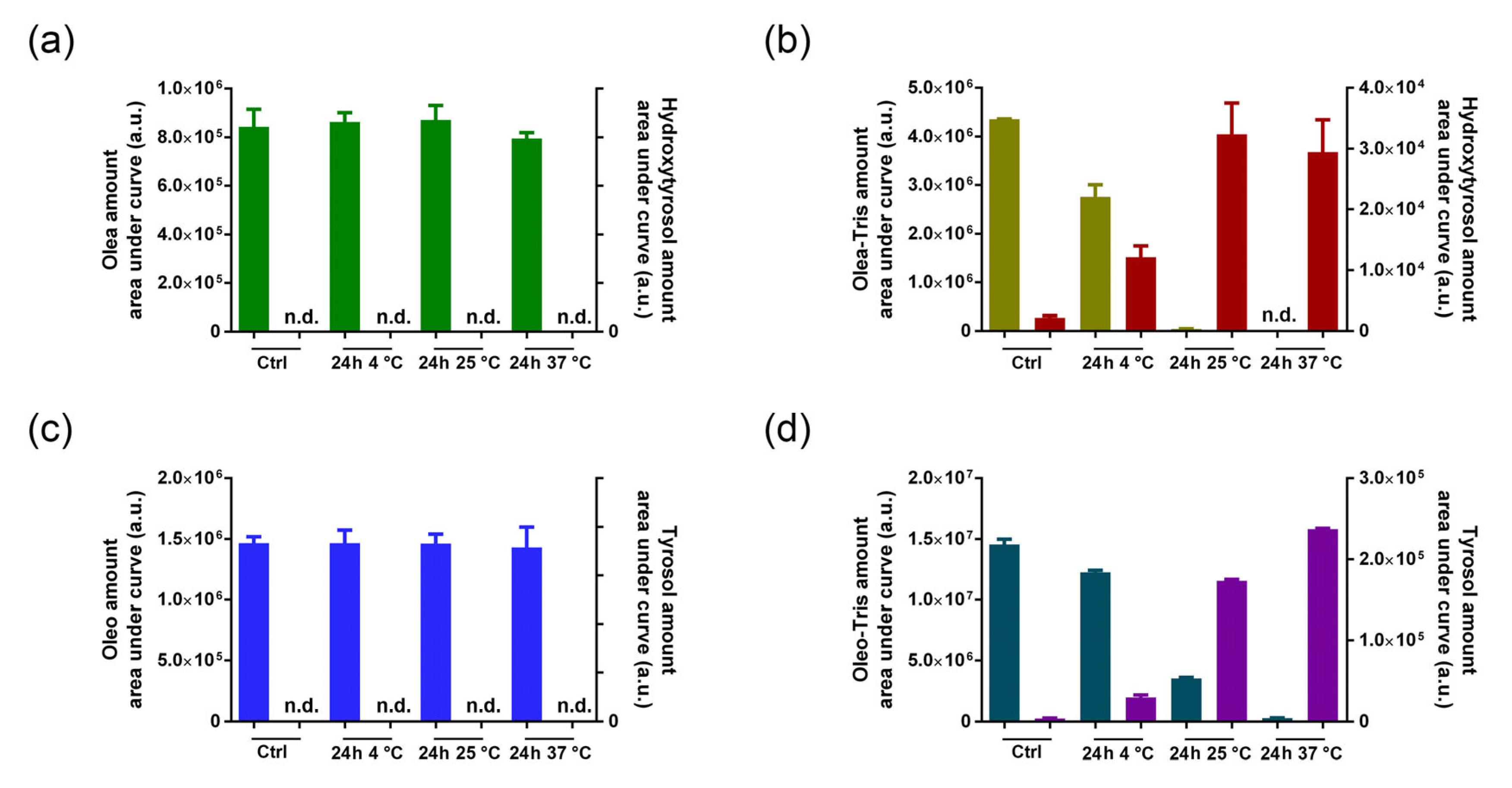
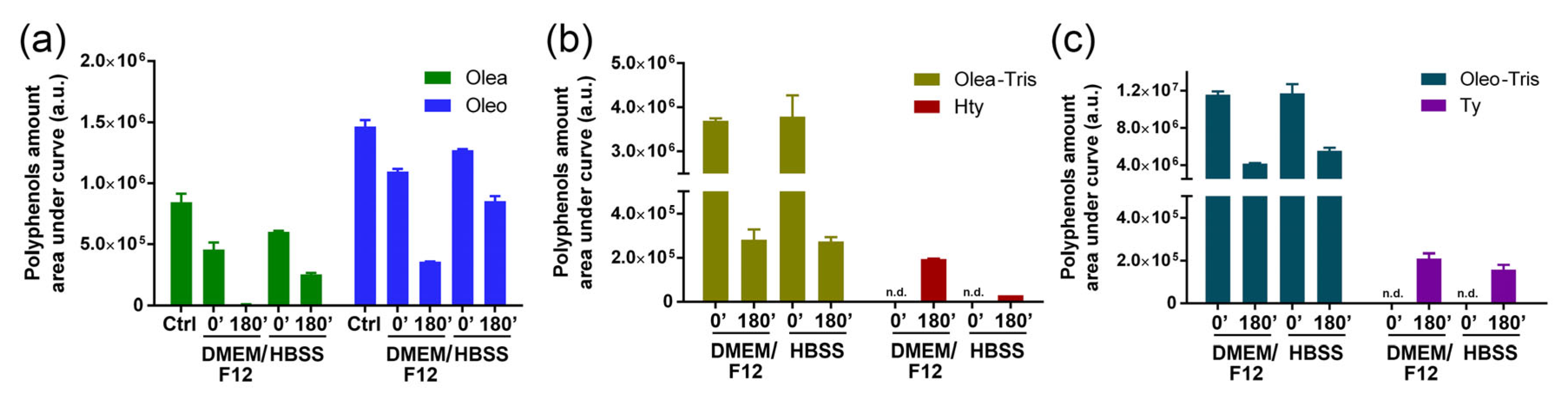
2.4. Stability of Olea, Oleo, and Their Respective Adducts in Cell Culture Medium
2.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Olea, Oleo, and Their Respective Adducts
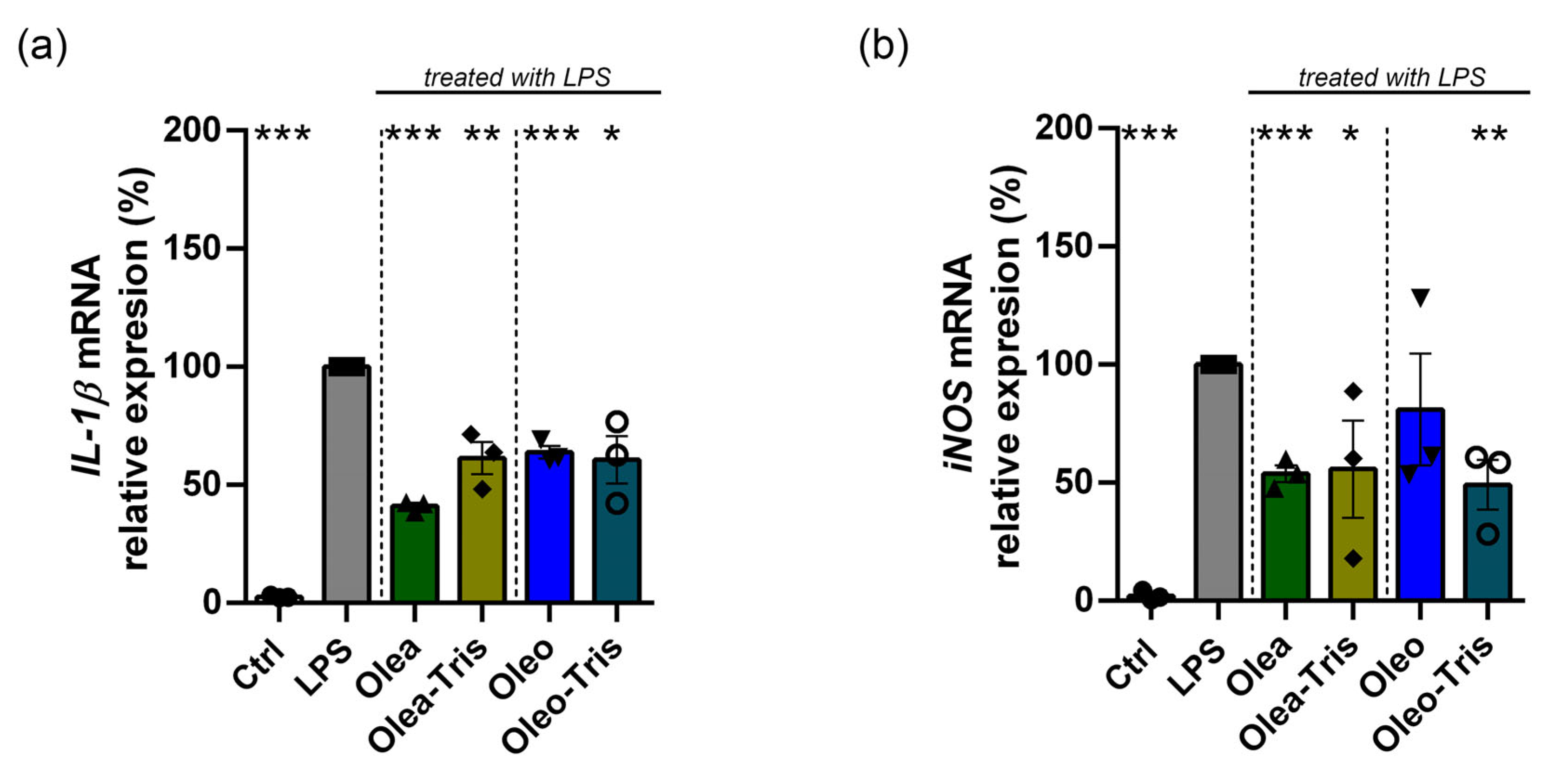
2.6. Biological Activity of Olea, Oleo, and Their Respective Adducts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials Used
4.2. Adduct Formation and Chromatographic Analysis
4.3. High-Resolution MS and NMR Analysis
4.4. DPPH Assay
4.5. ABTS Assay
4.6. Biological Experiment on BV-2 Cell Line
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucciantini, M.; Leri, M.; Nardiello, P.; Casamenti, F.; Stefani, M. Olive Polyphenols: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigacci, S.; Stefani, M. Nutraceutical Properties of Olive Oil Polyphenols. An Itinerary from Cultured Cells through Animal Models to Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Morató, J.; Xicota, L.; Fitó, M.; Farré, M.; Dierssen, M.; De La Torre, R. Potential Role of Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 4655–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servili, M.; Esposto, S.; Fabiani, R.; Urbani, S.; Taticchi, A.; Mariucci, F.; Selvaggini, R.; Montedoro, G.F. Phenolic Compounds in Olive Oil: Antioxidant, Health and Organoleptic Activities According to Their Chemical Structure. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón, M.L.; Montoya, T.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M. Potential Protective Role Exerted by Secoiridoids from Olea Europaea l. in Cancer, Cardiovascular, Neurodegenerative, Aging-Related, and Immunoinflammatory Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Costa, M.; Videira, R.A.; Andrade, P.B.; Paiva-Martins, F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Olive Oil Polyphenols—The Role of Oleacein and Its Metabolites. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Barbalace, M.C.; Hrelia, S. Bioactivity of Olive Oil Phenols in Neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, S.; Mattioli, R.; Di Risola, D.; Mosca, L.; Di Pietro, M.; Sessa, R. Olea Europaea L-Derived Secoiridoids: Beneficial Health Effects and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 254, 108595. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Castellón, J.; López-Yerena, A.; Rinaldi de Alvarenga, J.F.; Romero del Castillo-Alba, J.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Health-Promoting Properties of Oleocanthal and Oleacein: Two Secoiridoids from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2532–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, K.L.; Chin, K.Y. The Biological Activities of Oleocanthal from a Molecular Perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Salsano, J.E.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Doccini, S.; et al. The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and Mirna Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating Nf-Κb Activation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Usman, M.; Patil, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C. A Review on Management of Cardiovascular Diseases by Olive Polyphenols. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4639–4655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rigacci, S. Olive Oil Phenols as Promising Multi-Targeting Agents Against Alzheimer’s Disease; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Darakjian, L.I.; Rigakou, A.; Brannen, A.; Qusa, M.H.; Tasiakou, N.; Diamantakos, P.; Reed, M.N.; Panizzi, P.; Boersma, M.D.; Melliou, E.; et al. Spontaneous in Vitro and in Vivo Interaction of (-)-Oleocanthal with Glycine in Biological Fluids: Novel Pharmacokinetic Markers. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS for Profiling the Distribution of Oleacein and Its Metabolites in Rat Tissues. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Mols, R.; Augustijns, P.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. Absorption and Intestinal Metabolic Profile of Oleocanthal in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikou, T.; Karampetsou, K.V.; Koutsoni, O.S.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Dotsika, E.; Halabalaki, M. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism Investigation of Oleocanthal. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Risola, D.; Mattioli, R.; Federico, R.; Pascarella, G.; Fontana, M.; Dainese, E.; Dufrusine, B.; Ciogli, A.; Gasparrini, F.; Morea, V.; et al. Green Synthesis and Two-Step Chromatographic Separation of Thiocanthal and Thiocanthol: Two Novel Biologically Active Sulfur Derivatives of Oleocanthal and Oleacein from Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikou, T.; Sakavitsi, M.E.; Kalampokis, E.; Halabalaki, M. Metabolism and Bioavailability of Olive Bioactive Constituents Based on In Vitro, In Vivo and Human Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, S.; Komada, H.; Yonekura, L.; Sato, A.; Nishiwaki, H.; Tamura, H. Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion by Freely Moving Rats of 3,4-DHPEA-EDA and Related Polyphenols from Olive Fruits (Olea Europaea). J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 2016, 9104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Corona, G.; Debnam, E.S.; Oruna-Concha, M.J.; Vauzour, D.; Gordon, M.H.; Spencer, J.P.E. Absorption and Metabolism of Olive Oil Secoiridoids in the Small Intestine. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.; Romero, M.P.; Macià, A.; Saha, S.; Furniss, C.S.M.; Kroon, P.A.; Motilva, M.J. Digestion Stability and Evaluation of the Metabolism and Transport of Olive Oil Phenols in the Human Small-Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2/TC7 Cell Line. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsano, J.E.; Digiacomo, M.; Cuffaro, D.; Bertini, S.; Macchia, M. Content Variations in Oleocanthalic Acid and Other Phenolic Compounds in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil during Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, A.; Gómez, R.; Sperry, J.; Conde, J.; Bianco, G.; Meli, R.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Smith, A.B.; Gualillo, O. Effect of Oleocanthal and Its Derivatives on Inflammatory Response Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in a Murine Chondrocyte Cell Line. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanucci, V.; García-Viñuales, S.; Tempra, C.; Bernini, R.; Zarrelli, A.; Lolicato, F.; Milardi, D.; Di Fabio, G. Modulating Aβ Aggregation by Tyrosol-Based Ligands: The Crucial Role of the Catechol Moiety. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 265, 106434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sperry, J.B.; Crowe, A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Smith, A.B.; Lee, V.M.Y. Inhibition of Tau Fibrillization by Oleocanthal via Reaction with the Amino Groups of Tau. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-García, R.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Montoya, T.; Alcarranza, M.; Ortega-Vidal, J.; Altarejos, J.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirmi, S.; Maugeri, A.; Russo, C.; Musumeci, L.; Navarra, M.; Lombardo, G.E. Oleacein Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by the Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Miranda, B.; Gallardo, I.; Melliou, E.; Cabero, I.; Álvarez, Y.; Magiatis, P.; Hernández, M.; Nieto, M.L. Oleacein Attenuates the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Both Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakasugi, D.; Kondo, S.; Ferdousi, F.; Mizuno, S.; Yada, A.; Tominaga, K.; Takahashi, S.; Isoda, H. A Rare Olive Compound Oleacein Functions as a TrkB Agonist and Mitigates Neuroinflammation Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Castejón, M.L.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón de-la-Lastra, C. Oleocanthal Modulates LPS-Induced Murine Peritoneal Macrophages Activation via Regulation of Inflammasome, Nrf-2/HO-1, and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5552–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, I.; Ortíz-Flores, R.; Badía, R.; García-Borrego, A.; García-Fernández, M.; Lara, E.; Martín-Montañez, E.; García-Serrano, S.; Valdés, S.; Gonzalo, M.; et al. Rich Oleocanthal and Oleacein Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Inflammatory and Antioxidant Status in People with Obesity and Prediabetes. The APRIL Study: A Randomised, Controlled Crossover Study. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HBSS (Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution) Preparation and Recipe; AAT Bioquest, Inc.: Pleasanton, CA, USA, 2024.
- Fiorentino, F.; Bolla, J.R. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Dynamics and Interactions of the LPS Translocon LptDE. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2548, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ascorbic Acid | Olea | Oleo | Olea-Tris | Oleo-Tris | Olea 24 h | Oleo 24 h | Olea-Tris 24 h | Oleo-Tris 24 h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH mean ± SD | 34.00 ± 0.56 | 60.00 ± 4.70 | 5456 ± 1296 | 60.00 ± 2.80 | 331.00 ± 51.00 | 86.00 ± 32.00 | 5541 ± 1503 | 265.00 ± 77.00 | 6303.00 ± 151.00 |
| ABTS·+ mean ± SD | 6.00 ± 0.95 | 43.00 ± 2.60 | 92.00 ± 16.00 | 37.00 ± 2.30 | 4.60 ± 0.46 | 45.00 ± 8.70 | 105.00 ± 3.00 | 59.00 ± 16.00 | 5.60 ± 0.28 |
| Time | % Water + 0.1% Formic Acid | % Methanol + 0.1% Formic Acid |
|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 98 | 2 |
| 1 min | 98 | 2 |
| 6 min | 45 | 55 |
| 10 min | 20 | 80 |
| 10.5 min | 0 | 100 |
| 12.5 min | 0 | 100 |
| 12.7 min | 98 | 2 |
| 17 min | 98 | 2 |
| Target | Forward | Tm (°C) | Reverse | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPS27A | AGA GGC TGA TCT TTG CTG GT | 59 | ACC AGA TGA AGG GTG GAC TC | 59 |
| IL-1β | TTC GTG AAT GAG CAG ACA GC | 59 | CCA TGG TTT CTT GTG ACC CT | 58 |
| iNOS | GCA AGA GAG TGC TGT TCC AG | 60 | CCT GAA CGT AGA CCT TGG GT | 59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Risola, D.; Laurenti, D.; Ferraro, F.; Ciogli, A.; Manetto, S.; Gazzilli, Y.; Federico, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L.; Mattioli, R. Spontaneous Reaction of Oleacein and Oleocanthal with Primary Amines: A Biochemical Perspective. Molecules 2025, 30, 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071645
Di Risola D, Laurenti D, Ferraro F, Ciogli A, Manetto S, Gazzilli Y, Federico R, Francioso A, Mosca L, Mattioli R. Spontaneous Reaction of Oleacein and Oleocanthal with Primary Amines: A Biochemical Perspective. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071645
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Risola, Daniel, Davide Laurenti, Francesca Ferraro, Alessia Ciogli, Simone Manetto, Yuri Gazzilli, Rodolfo Federico, Antonio Francioso, Luciana Mosca, and Roberto Mattioli. 2025. "Spontaneous Reaction of Oleacein and Oleocanthal with Primary Amines: A Biochemical Perspective" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071645
APA StyleDi Risola, D., Laurenti, D., Ferraro, F., Ciogli, A., Manetto, S., Gazzilli, Y., Federico, R., Francioso, A., Mosca, L., & Mattioli, R. (2025). Spontaneous Reaction of Oleacein and Oleocanthal with Primary Amines: A Biochemical Perspective. Molecules, 30(7), 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071645










