Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases
Abstract
:1. Definition of disease and objectives of the review
2. Phenotypic variability of human prion disease
2.1. Variability of the prion protein
2.2. The spectrum of human prion diseases
2.3. Etiological classification
2.4. Summary of major clinical presentations
2.5. Neuropathology of human prion diseases
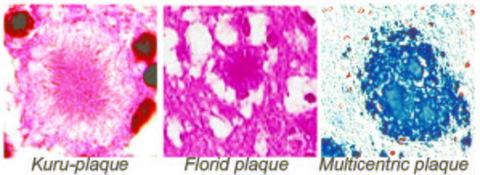
2.5.1. Classical histopathology
2.5.2. PrP immunostaining patterns
2.5.3. Other proteins in prion diseases
2.6. The concept of strains
2.7. Genetic background of human prion diseases
2.8. Molecular classification of human prion diseases
3. Neuronal degeneration in prion disease
3.1. Pathways of prion transport
3.2. Cell death pathways in prion disease
4. Summary
- PrP exists in different and overlapping forms in diseased and non-diseased brains; however, abundant disease-associated PrP together with tissue pathology characterizes prion diseases and associates with transmissibility.
- Different etiological forms of prion disease differ in pathogenesis, which has implications for public health, clinical differential diagnosis, research, spread of infectivity within the body, and also therapeutic approaches.
- In diseased brain PrP is the major protein that deposits mainly extracellularly in the brain; however, other proteins associated with other neurodegenerative disorders, in particular hyperphosphorylated tau, amyloid-beta, and alpha-synuclein may be deposited as well. The exact interactions of these proteins await clarification.
- Mutations of the PRNP are associated with genetic forms; however the polymorphism at codon 129 has a crucial influence on phenotype and susceptibility and may have implications for other non-prion disorders.
- The codon 129 polymorphism in combination with the Western blot pattern of PrP after proteinase K digestion remains as a basis for molecular subtyping of sCJD. This represents strains in human prion disease.
- Tissue damage may result from several parallel, interacting or subsequent pathways that involve cellular systems associated with synapses, protein processing, oxidative stress, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Acknowledgments
References
- Westergard, L; Christensen, HM; Harris, DA. The cellular prion protein (PrP(C)): Its physiological function and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 629–644. [Google Scholar]
- Caughey, B; Baron, GS. Prions and their partners in crime. Nature 2006, 443, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, SB. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar]
- Safar, J; Wille, H; Itri, V; Groth, D; Serban, H; Torchia, M; Cohen, FE; Prusiner, SB. Eight prion strains have PrP(Sc) molecules with different conformations. Nat. Med 1998, 4, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Tzaban, S; Friedlander, G; Schonberger, O; Horonchik, L; Yedidia, Y; Shaked, G; Gabizon, R; Taraboulos, A. Protease-sensitive scrapie prion protein in aggregates of heterogeneous sizes. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12868–12875. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, JR; Raymond, GJ; Hughson, AG; Race, RE; Sim, VL; Hayes, SF; Caughey, B. The most infectious prion protein particles. Nature 2005, 437, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti, P; Dong, Z; Yuan, J; Xiao, X; Zheng, M; Alshekhlee, A; Castellani, R; Cohen, M; Barria, MA; Gonzalez-Romero, D; Belay, ED; Schonberger, LB; Marder, K; Harris, C; Burke, JR; Montine, T; Wisniewski, T; Dickson, DW; Soto, C; Hulette, CM; Mastrianni, JA; Kong, Q; Zou, WQ. A novel human disease with abnormal prion protein sensitive to protease. Ann. Neurol 2008, 63, 697–708. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J; Xiao, X; McGeehan, J; Dong, Z; Cali, I; Fujioka, H; Kong, Q; Kneale, G; Gambetti, P; Zou, WQ. Insoluble aggregates and protease-resistant conformers of prion protein in uninfected human brains. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 34848–34858. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, WQ; Gambetti, P. Prion: The chameleon protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2007, 64, 3266–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Legname, G; Baskakov, IV; Nguyen, HO; Riesner, D; Cohen, FE; DeArmond, SJ; Prusiner, SB. Synthetic mammalian prions. Science 2004, 305, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Bueler, H; Aguzzi, A; Sailer, A; Greiner, RA; Autenried, P; Aguet, M; Weissmann, C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell 1993, 73, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Budka, H; Aguzzi, A; Brown, P; Brucher, JM; Bugiani, O; Gullotta, F; Haltia, M; Hauw, JJ; Ironside, JW; Jellinger, K; et al. Neuropathological diagnostic criteria for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases). Brain Pathol 1995, 5, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO manual for surveillance of human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies including variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; WHO: Geneva, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Will, RG. Acquired prion disease: iatrogenic CJD, variant CJD, kuru. Br. Med. Bull 2003, 66, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Puopolo, M; Ladogana, A; Pocchiari, M; Budka, H; van Duijn, C; Collins, SJ; Boyd, A; Giulivi, A; Coulthart, M; Delasnerie-Laupretre, N; Brandel, JP; Zerr, I; Kretzschmar, HA; de Pedro-Cuesta, J; Calero-Lara, M; Glatzel, M; Aguzzi, A; Bishop, M; Knight, R; Belay, G; Will, R; Mitrova, E. Genetic prion disease: The EUROCJD experience. Hum. Genet 2005, 118, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Trabattoni, G; Hainfellner, JA; Ironside, JW; Knight, RS; Budka, H. Mutations of the prion protein gene phenotypic spectrum. J. Neurol 2002, 249, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, MD; Knight, RS; Will, RG. First hundred cases of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Retrospective case note review of early psychiatric and neurological features. BMJ 2002, 324, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti, B; Dlouhy, SR; Giaccone, G; Bugiani, O; Frangione, B; Farlow, MR; Tagliavini, F. Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease and the Indiana kindred. Brain Pathol 1995, 5, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Montagna, P; Gambetti, P; Cortelli, P; Lugaresi, E. Familial and sporadic fatal insomnia. Lancet Neurol 2003, 2, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Budka, H. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). Arch Virol Suppl 2000, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ironside, JW; McCardle, L; Horsburgh, A; Lim, Z; Head, MW. Pathological diagnosis of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Apmis 2002, 110, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Head, MW; Hegyi, I; Bunn, TJ; Flicker, H; Hainfellner, JA; McCardle, L; Laszlo, L; Jarius, C; Ironside, JW; Budka, H. Immunohistochemistry for the prion protein: Comparison of different monoclonal antibodies in human prion disease subtypes. Brain Pathol 2002, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti, B; Piccardo, P; Spillantini, MG; Ichimiya, Y; Porro, M; Perini, F; Kitamoto, T; Tateishi, J; Seiler, C; Frangione, B; Bugiani, O; Giaccone, G; Prelli, F; Goedert, M; Dlouhy, SR; Tagliavini, F. Vascular variant of prion protein cerebral amyloidosis with tau-positive neurofibrillary tangles: The phenotype of the stop codon 145 mutation in PRNP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Paquet, C; Privat, N; Kaci, R; Polivka, M; Dupont, O; Haik, S; Laplanche, JL; Hauw, JJ; Gray, F. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy with co-localization of prion protein and beta-amyloid in an 85-year-old patient with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol 2008, 116, 567–573. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, JG; Escaig-Haye, F; Grigoriev, V. Ultrastructural localization of prion proteins: Physiological and pathological implications. Microsc. Res. Tech 2000, 50, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Preusser, M; Strohschneider, M; Budka, H. Subcellular localization of disease-associated prion protein in the human brain. Am. J. Pathol 2005, 166, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Glatzel, M; Abela, E; Maissen, M; Aguzzi, A. Extraneural pathologic prion protein in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. N. Engl. J. Med 2003, 349, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Hainfellner, JA; Budka, H. Disease associated prion protein may deposit in the peripheral nervous system in human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Acta Neuropathol 1999, 98, 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Peden, AH; Ironside, JW. Review: Pathology of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Folia Neuropathol 2004, 42(Suppl A), 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Peden, AH; Ritchie, DL; Head, MW; Ironside, JW. Detection and localization of PrPSc in the skeletal muscle of patients with variant, iatrogenic, and sporadic forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am. J. Pathol 2006, 168, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Peden, AH; Ritchie, DL; Uddin, HP; Dean, AF; Schiller, KA; Head, MW; Ironside, JW. Abnormal prion protein in the pituitary in sporadic and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Gen. Virol 2007, 88, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Heikenwälder, M; Kurrer, MO; Margalith, I; Kranich, J; Zeller, N; Haybaeck, J; Polymenidou, M; Matter, M; Bremer, J; Jackson, WS; Lindquist, S; Sigurdson, CJ; Aguzzi, A. Lymphotoxin-dependent prion replication in inflammatory stromal cells of granulomas. Immunity 2008, 29, 998–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Heikenwälder, M; Zeller, N; Seeger, H; Prinz, M; Klohn, PC; Schwarz, P; Ruddle, NH; Weissmann, C; Aguzzi, A. Chronic lymphocytic inflammation specifies the organ tropism of prions. Science 2005, 307, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Kalev, O; Gelpi, E; Haberler, C; Wanschitz, J; Strohschneider, M; Molnar, MJ; Laszlo, L; Budka, H. The prion protein in human neuromuscular diseases. J. Pathol 2004, 204, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ligios, C; Sigurdson, CJ; Santucciu, C; Carcassola, G; Manco, G; Basagni, M; Maestrale, C; Cancedda, MG; Madau, L; Aguzzi, A. PrPSc in mammary glands of sheep affected by scrapie and mastitis. Nat. Med 2005, 11, 1137–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Seeger, H; Heikenwälder, M; Zeller, N; Kranich, J; Schwarz, P; Gaspert, A; Seifert, B; Miele, G; Aguzzi, A. Coincident scrapie infection and nephritis lead to urinary prion excretion. Science 2005, 310, 324–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Lindeck-Pozza, E; Chimelli, L; Araujo, AQ; Gabbai, AA; Ströbel, T; Glatzel, M; Aguzzi, A; Budka, H. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and inclusion body myositis: Abundant disease-associated prion protein in muscle. Ann. Neurol 2004, 55, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Levi, Y; Ovadia, H; Höftberger, R; Einstein, O; Abramsky, O; Budka, H; Gabizon, R. Fatal neurological disease in scrapie-infected mice induced for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Virol 2007, 81, 9942–9949. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Budka, H. Protein-based neuropathology and molecular classification of human neurodegenerative diseases. In Protein Folding and Misfolding: Neurodegenerative Diseases; Ovadi, J, Orosz, F, Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 251–272. [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone, G; Mangieri, M; Capobianco, R; Limido, L; Hauw, JJ; Haik, S; Fociani, P; Bugiani, O; Tagliavini, F. Tauopathy in human and experimental variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar]
- Sikorska, B; Liberski, PP; Sobow, T; Budka, H; Ironside, JW. Ultrastructural study of florid plaques in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A comparison with amyloid plaques in kuru, sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 2009, 35, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, XF; Dong, CF; Zhang, J; Wan, YZ; Li, F; Huang, YX; Han, L; Shan, B; Gao, C; Han, J; Dong, XP. Human tau protein forms complex with PrP and some GSS- and fCJD-related PrP mutants possess stronger binding activities with tau in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biochem 2008, 310, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Zerbi, P; Voigtländer, T; Strohschneider, M; Trabattoni, G; Hainfellner, JA; Budka, H. The prion protein in human neurodegenerative disorders. Neurosci. Lett 2002, 329, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Parkin, ET; Watt, NT; Hussain, I; Eckman, EA; Eckman, CB; Manson, JC; Baybutt, HN; Turner, AJ; Hooper, NM. Cellular prion protein regulates beta-secretase cleavage of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11062–11067. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtländer, T; Klöppel, S; Birner, P; Jarius, C; Flicker, H; Verghese-Nikolakaki, S; Sklaviadis, T; Guentchev, M; Budka, H. Marked increase of neuronal prion protein immunoreactivity in Alzheimer’s disease and human prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol 2001, 101, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Haik, S; Privat, N; Adjou, KT; Sazdovitch, V; Dormont, D; Duyckaerts, C; Hauw, JJ. Alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive deposits in human and animal prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol 2002, 103, 516–520. [Google Scholar]
- Adjou, KT; Allix, S; Ouidja, MO; Backer, S; Couquet, C; Cornuejols, MJ; Deslys, JP; Brugere, H; Brugere-Picoux, J; El-Hachimi, KH. Alpha-synuclein accumulates in the brain of scrapie-affected sheep and goats. J. Comp. Pathol 2007, 137, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, AM; Powell, C; Webb, TE; Linehan, JM; Collinge, J; Brandner, S. Lack of TAR-DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) pathology in human prion diseases. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 2008, 34, 446–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ironside, JW; McCardle, L; Hayward, PA; Bell, JE. Ubiquitin immunocytochemistry in human spongiform encephalopathies. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 1993, 19, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, SC; Brown, DR; Whiteman, M; Li, R; Pan, T; Perry, G; Wisniewski, T; Sy, MS; Wong, BS. Prion protein is ubiquitinated after developing protease resistance in the brains of scrapie-infected mice. J. Pathol 2004, 203, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Alafuzoff, I; Al-Sarraj, S; Arzberger, T; Bogdanovic, N; Capellari, S; Ferrer, I; Gelpi, E; Kovari, V; Kretzschmar, H; Nagy, Z; Parchi, P; Seilhean, D; Soininen, H; Troakes, C; Budka, H. Mixed brain pathologies in dementia: The BrainNet Europe consortium experience. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord 2008, 26, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hainfellner, JA; Wanschitz, J; Jellinger, K; Liberski, PP; Gullotta, F; Budka, H. Coexistence of Alzheimer-type neuropathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol 1998, 96, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, J; Clarke, AR. A general model of prion strains and their pathogenicity. Science 2007, 318, 930–936. [Google Scholar]
- Parchi, P; Giese, A; Capellari, S; Brown, P; Schulz-Schaeffer, W; Windl, O; Zerr, I; Budka, H; Kopp, N; Piccardo, P; Poser, S; Rojiani, A; Streichemberger, N; Julien, J; Vital, C; Ghetti, B; Gambetti, P; Kretzschmar, H. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, A; Heikenwälder, M; Polymenidou, M. Insights into prion strains and neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol 2007, 8, 552–561. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, J. Molecular neurology of prion disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 906–919. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, LG; Brown, P; McCombie, WR; Goldgaber, D; Swergold, GD; Wills, PR; Cervenakova, L; Baron, H; Gibbs, CJ, Jr; Gajdusek, DC. Transmissible familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with five, seven, and eight extra octapeptide coding repeats in the PRNP gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10926–10930. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, SB. The prion diseases. Brain Pathol 1998, 8, 499–513. [Google Scholar]
- Vital, C; Gray, F; Vital, A; Ferrer, X; Julien, J. Prion disease with octapeptide repeat insertion. Clin. Exp. Pathol 1999, 47, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, S; Higuchi, J; Shin, RW; Tateishi, J; Kitamoto, T. Protective prion protein polymorphisms against sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1998, 351, 419. [Google Scholar]
- Alperovitch, A; Zerr, I; Pocchiari, M; Mitrova, E; de Pedro Cuesta, J; Hegyi, I; Collins, S; Kretzschmar, H; van Duijn, C; Will, RG. Codon 129 prion protein genotype and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1999, 353, 1673–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Pocchiari, M; Puopolo, M; Croes, EA; Budka, H; Gelpi, E; Collins, S; Lewis, V; Sutcliffe, T; Guilivi, A; Delasnerie-Laupretre, N; Brandel, JP; Alperovitch, A; Zerr, I; Poser, S; Kretzschmar, HA; Ladogana, A; Rietvald, I; Mitrova, E; Martinez-Martin, P; de Pedro-Cuesta, J; Glatzel, M; Aguzzi, A; Cooper, S; Mackenzie, J; van Duijn, CM; Will, RG. Predictors of survival in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Brain 2004, 127, 2348–2359. [Google Scholar]
- Will, RG; Alperovitch, A; Poser, S; Pocchiari, M; Hofman, A; Mitrova, E; de Silva, R; D’Alessandro, M; Delasnerie-Laupretre, N; Zerr, I; van Duijn, C. Descriptive epidemiology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in six European countries, 1993–1995. EU Collaborative Study Group for CJD. Ann. Neurol 1998, 43, 763–767. [Google Scholar]
- Windl, O; Dempster, M; Estibeiro, JP; Lathe, R; de Silva, R; Esmonde, T; Will, R; Springbett, A; Campbell, TA; Sidle, KC; Palmer, MS; Collinge, J. Genetic basis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the United Kingdom: A systematic analysis of predisposing mutations and allelic variation in the PRNP gene. Hum. Genet 1996, 98, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Windl, O; Giese, A; Schulz-Schaeffer, W; Zerr, I; Skworc, K; Arendt, S; Oberdieck, C; Bodemer, M; Poser, S; Kretzschmar, HA. Molecular genetics of human prion diseases in Germany. Hum. Genet 1999, 105, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Doh-ura, K; Kitamoto, T; Sakaki, Y; Tateishi, J. CJD discrepancy. Nature 1991, 353, 801–802. [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti, P; Parchi, P; Petersen, RB; Chen, SG; Lugaresi, E. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Clinical, pathological and molecular features. Brain Pathol 1995, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, LG; Petersen, RB; Tabaton, M; Brown, P; LeBlanc, AC; Montagna, P; Cortelli, P; Julien, J; Vital, C; Pendelbury, WW; et al. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Disease phenotype determined by a DNA polymorphism. Science 1992, 258, 806–808. [Google Scholar]
- Poulter, M; Baker, HF; Frith, CD; Leach, M; Lofthouse, R; Ridley, RM; Shah, T; Owen, F; Collinge, J; Brown, J; et al. Inherited prion disease with 144 base pair gene insertion. 1. Genealogical and molecular studies. Brain 1992, 115, 675–685. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, ER; Rezek, K; Escorsi-Rosset, S; Landemberger, MC; Castro, RM; Valadao, MN; Guarnieri, R; Velasco, TR; Terra-Bustamante, VC; Bianchin, MM; Wichert-Ana, L; Alexandre, V, Jr; Brentani, RR; Martins, VR; Sakamoto, AC; Walz, R. Cognitive performance of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy is not associated with human prion protein gene variant allele at codons 129 and 171. Epilepsy Behav 2006, 8, 635–642. [Google Scholar]
- Combarros, O; Sanchez-Guerra, M; Llorca, J; Alvarez-Arcaya, A; Berciano, J; Pena, N; Fernandez-Viadero, C. Polymorphism at codon 129 of the prion protein gene is not associated with sporadic AD. Neurology 2000, 55, 593–595. [Google Scholar]
- Del Bo, R; Scarlato, M; Ghezzi, S; Martinelli-Boneschi, F; Fenoglio, C; Galimberti, G; Galbiati, S; Virgilio, R; Galimberti, D; Ferrarese, C; Scarpini, E; Bresolin, N; Comi, GP. Is M129V of PRNP gene associated with Alzheimer’s disease? A case-control study and a meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging 2006, 27, 770 e1–770 e5. [Google Scholar]
- Dermaut, B; Croes, EA; Rademakers, R; Van den Broeck, M; Cruts, M; Hofman, A; van Duijn, CM; Van Broeckhoven, C. PRNP Val129 homozygosity increases risk for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol 2003, 53, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo, T; Sakasegawa, Y; Asada, T; Kinoshita, T; Goto, Y; Kimura, H; Mizusawa, H; Hachiya, NS; Kaneko, K. Absence of association between codon 129/219 polymorphisms of the prion protein gene and Alzheimer’s disease in Japan. Ann. Neurol 2003, 54, 553–554. [Google Scholar]
- Plazzi, G; Montagna, P; Beelke, M; Nobili, L; De Carli, F; Cortelli, P; Vandi, S; Avoni, P; Tinuper, P; Gambetti, P; Lugaresi, E; Ferrillo, F. Does the prion protein gene 129 codon polymorphism influence sleep? Evidence from a fatal familial insomnia kindred. Clin. Neurophysiol 2002, 113, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Riemenschneider, M; Klopp, N; Xiang, W; Wagenpfeil, S; Vollmert, C; Muller, U; Forstl, H; Illig, T; Kretzschmar, H; Kurz, A. Prion protein codon 129 polymorphism and risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2004, 63, 364–366. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer, JD; Mead, S; Omar, R; Poulter, M; Warren, JD; Collinge, J; Rossor, MN. Prion protein (PRNP) genotypes in frontotemporal lobar degeneration syndromes. Ann. Neurol 2006, 60, 616. [Google Scholar]
- Rujescu, D; Meisenzahl, EM; Giegling, I; Kirner, A; Leinsinger, G; Hegerl, U; Hahn, K; Moller, HJ. Methionine homozygosity at codon 129 in the prion protein is associated with white matter reduction and enlargement of CSF compartments in healthy volunteers and schizophrenic patients. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, MT; Su, YC; Chen, YH; Chen, CH. Lack of evidence to support the association of the human prion gene with schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Makrinou, E; Collinge, J; Antoniou, M. Genomic characterization of the human prion protein (PrP) gene locus. Mamm. Genome 2002, 13, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Genoud, N; Behrens, A; Miele, G; Robay, D; Heppner, FL; Freigang, S; Aguzzi, A. Disruption of Doppel prevents neurodegeneration in mice with extensive Prnp deletions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4198–4203. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Premzl, M; Sangiorgio, L; Strumbo, B; Marshall Graves, JA; Simonic, T; Gready, JE. Shadoo, a new protein highly conserved from fish to mammals and with similarity to prion protein. Gene 2003, 314, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Amouyel, P; Vidal, O; Launay, JM; Laplanche, JL. The apolipoprotein E alleles as major susceptibility factors for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. The French Research Group on Epidemiology of Human Spongiform Encephalopathies. Lancet 1994, 344, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering-Brown, SM; Mann, DM; Owen, F; Ironside, JW; de Silva, R; Roberts, DA; Balderson, DJ; Cooper, PN. Allelic variations in apolipoprotein E and prion protein genotype related to plaque formation and age of onset in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci. Lett 1995, 187, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Van Everbroeck, B; Croes, EA; Pals, P; Dermaut, B; Jansen, G; van Duijn, CM; Cruts, M; Van Broeckhoven, C; Martin, JJ; Cras, P. Influence of the prion protein and the apolipoprotein E genotype on the Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease phenotype. Neurosci. Lett 2001, 313, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, S; Beck, J; Dickinson, A; Fisher, EM; Collinge, J. Examination of the human prion protein-like gene doppel for genetic susceptibility to sporadic and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci. Lett 2000, 290, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Plamont, MA; Chasseigneaux, S; Delasnerie-Laupretre, N; Beaudry, P; Peoc’h, K; Laplanche, JL. Variation at the ADAM10 gene locus is not associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci. Lett 2003, 344, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, JE; Baybutt, HN; Everington, D; Will, RG; Ironside, JW; Manson, JC. PRNP contains both intronic and upstream regulatory regions that may influence susceptibility to Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. Gene 2002, 288, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, MT; Kovacs, GG; Sanchez-Juan, P; Knight, RS. Cathepsin D SNP associated with increased risk of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. BMC Med. Genet 2008, 9, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, J; Sidle, KC; Meads, J; Ironside, J; Hill, AF. Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the aetiology of ‘new variant’ CJD. Nature 1996, 383, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, WJ; Giese, A; Windl, O; Kretzschmar, HA. Polymorphism at codon 129 of the prion protein gene determines cerebellar pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Clin. Neuropathol 1996, 15, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Ironside, JW; Ritchie, DL; Head, MW. Phenotypic variability in human prion diseases. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 2005, 31, 565–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, AF; Joiner, S; Wadsworth, JD; Sidle, KC; Bell, JE; Budka, H; Ironside, JW; Collinge, J. Molecular classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 2003, 126, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Cali, I; Castellani, R; Yuan, J; Al-Shekhlee, A; Cohen, ML; Xiao, X; Moleres, FJ; Parchi, P; Zou, WQ; Gambetti, P. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease revisited. Brain 2006, 129, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar]
- Puoti, G; Giaccone, G; Rossi, G; Canciani, B; Bugiani, O; Tagliavini, F. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: co-occurrence of different types of PrP(Sc) in the same brain. Neurology 1999, 53, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Head, MW; Bunn, TJ; Bishop, MT; McLoughlin, V; Lowrie, S; McKimmie, CS; Williams, MC; McCardle, L; MacKenzie, J; Knight, R; Will, RG; Ironside, JW. Prion protein heterogeneity in sporadic but not variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: UK cases 1991–2002. Ann. Neurol 2004, 55, 851–859. [Google Scholar]
- Polymenidou, M; Stoeck, K; Glatzel, M; Vey, M; Bellon, A; Aguzzi, A. Coexistence of multiple PrPSc types in individuals with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet Neurol 2005, 4, 805–814. [Google Scholar]
- Yull, HM; Ritchie, DL; Langeveld, JP; van Zijderveld, FG; Bruce, ME; Ironside, JW; Head, MW. Detection of type 1 prion protein in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am. J. Pathol 2006, 168, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Notari, S; Capellari, S; Langeveld, J; Giese, A; Strammiello, R; Gambetti, P; Kretzschmar, HA; Parchi, P. A refined method for molecular typing reveals that co-occurrence of PrP(Sc) types in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is not the rule. Lab. Invest 2007, 87, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, AF; Joiner, S; Beck, JA; Campbell, TA; Dickinson, A; Poulter, M; Wadsworth, JD; Collinge, J. Distinct glycoform ratios of protease resistant prion protein associated with PRNP point mutations. Brain 2006, 129, 676–685. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti, B; Piccardo, P; Frangione, B; Bugiani, O; Giaccone, G; Young, K; Prelli, F; Farlow, MR; Dlouhy, SR; Tagliavini, F. Prion protein amyloidosis. Brain Pathol 1996, 6, 127–145. [Google Scholar]
- Piccardo, P; Dlouhy, SR; Lievens, PM; Young, K; Bird, TD; Nochlin, D; Dickson, DW; Vinters, HV; Zimmerman, TR; Mackenzie, IR; Kish, SJ; Ang, LC; De Carli, C; Pocchiari, M; Brown, P; Gibbs, CJ, Jr; Gajdusek, DC; Bugiani, O; Ironside, J; Tagliavini, F; Ghetti, B. Phenotypic variability of Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease is associated with prion protein heterogeneity. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 1998, 57, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Budka, H. Prion diseases: From protein to cell pathology. Am. J. Pathol 2008, 172, 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Beekes, M; McBride, PA. The spread of prions through the body in naturally acquired transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. FEBS J 2007, 274, 588–605. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, MA; Frigg, R; Flechsig, E; Raeber, AJ; Kalinke, U; Bluethmann, H; Bootz, F; Suter, M; Zinkernagel, RM; Aguzzi, A. A crucial role for B cells in neuroinvasive scrapie. Nature 1997, 390, 687–690. [Google Scholar]
- Montrasio, F; Frigg, R; Glatzel, M; Klein, MA; Mackay, F; Aguzzi, A; Weissmann, C. Impaired prion replication in spleens of mice lacking functional follicular dendritic cells. Science 2000, 288, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Kunzi, V; Glatzel, M; Nakano, MY; Greber, UF; Van Leuven, F; Aguzzi, A. Unhampered prion neuroinvasion despite impaired fast axonal transport in transgenic mice overexpressing four-repeat tau. J. Neurosci 2002, 22, 7471–7477. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, JR. What is the basis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy induced neurodegeneration and can it be repaired? Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 2002, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikura, N; Clever, JL; Bouzamondo-Bernstein, E; Samayoa, E; Prusiner, SB; Huang, EJ; DeArmond, SJ. Notch-1 activation and dendritic atrophy in prion disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Unterberger, U; Voigtländer, T; Budka, H. Pathogenesis of prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol 2005, 109, 32–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, PP; Sikorska, B; Bratosiewicz-Wasik, J; Gajdusek, DC; Brown, P. Neuronal cell death in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases) revisited: From apoptosis to autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol 2004, 36, 2473–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Guentchev, M; Hainfellner, JA; Trabattoni, GR; Budka, H. Distribution of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in brain correlates with hippocampal and temporal cortical pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 1997, 56, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen, M; Messenger, MJ; Klohn, PC; Brandner, S; Wadsworth, JD; Collinge, J; Tabrizi, SJ. Disease-related prion protein forms aggresomes in neuronal cells leading to caspase activation and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 38851–38861. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen, M; Deriziotis, P; Dimcheff, DE; Jackson, GS; Ovaa, H; Naumann, H; Clarke, AR; van Leeuwen, FW; Menendez-Benito, V; Dantuma, NP; Portis, JL; Collinge, J; Tabrizi, SJ. Disease-Associated Prion Protein Oligomers Inhibit the 26S Proteasome. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Adori, C; Kovacs, GG; Low, P; Molnar, K; Gorbea, C; Fellinger, E; Budka, H; Mayer, RJ; Laszlo, L. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in Creutzfeldt-Jakob and Alzheimer disease: Intracellular redistribution of components correlates with neuronal vulnerability. Neurobiol. Dis 2005, 19, 427–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Kurucz, I; Budka, H; Adori, C; Muller, F; Acs, P; Klöppel, S; Schatzl, HM; Mayer, RJ; Laszlo, L. Prominent stress response of Purkinje cells in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol. Dis 2001, 8, 881–889. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, AD; Hutter, G; Jackson, WS; Heppner, FL; Borkowski, AW; King, OD; Raymond, GJ; Aguzzi, A; Lindquist, S. Heat shock factor 1 regulates lifespan as distinct from disease onset in prion disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13626–13631. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, AR; Jackson, GS; Collinge, J. The molecular biology of prion propagation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci 2001, 356, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Porto-Carreiro, I; Fevrier, B; Paquet, S; Vilette, D; Raposo, G. Prions and exosomes: From PrPc trafficking to PrPsc propagation. Blood Cells Mol. Dis 2005, 35, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Gelpi, E; Ströbel, T; Ricken, G; Nyengaard, JR; Bernheimer, H; Budka, H. Involvement of the endosomal-lysosomal system correlates with regional pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 2007, 66, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Rambold, AS; Muller, V; Ron, U; Ben-Tal, N; Winklhofer, KF; Tatzelt, J. Stress-protective signalling of prion protein is corrupted by scrapie prions. EMBO J 2008, 27, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A; Piccardo, P; Barmada, SJ; Ghetti, B; Harris, DA. Prion protein with an octapeptide insertion has impaired neuroprotective activity in transgenic mice. EMBO J 2007, 26, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro, B; Trifilo, M; Race, R; Meade-White, K; Teng, C; LaCasse, R; Raymond, L; Favara, C; Baron, G; Priola, S; Caughey, B; Masliah, E; Oldstone, M. Anchorless prion protein results in infectious amyloid disease without clinical scrapie. Science 2005, 308, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Mallucci, GR; White, MD; Farmer, M; Dickinson, A; Khatun, H; Powell, AD; Brandner, S; Jefferys, JG; Collinge, J. Targeting cellular prion protein reverses early cognitive deficits and neurophysiological dysfunction in prion-infected mice. Neuron 2007, 53, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Tatzelt, J; Schatzl, HM. Molecular basis of cerebral neurodegeneration in prion diseases. FEBS J 2007, 274, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, NS; Yonkovich, JL; Hegde, RS. Protection from cytosolic prion protein toxicity by modulation of protein translocation. EMBO J 2004, 23, 4550–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Rambold, AS; Miesbauer, M; Rapaport, D; Bartke, T; Baier, M; Winklhofer, KF; Tatzelt, J. Association of Bcl-2 with misfolded prion protein is linked to the toxic potential of cytosolic PrP. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 3356–3368. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, GG; Gasque, P; Ströbel, T; Lindeck-Pozza, E; Strohschneider, M; Ironside, JW; Budka, H; Guentchev, M. Complement activation in human prion disease. Neurobiol. Dis 2004, 15, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mabbott, NA; Bruce, ME. Complement component C5 is not involved in scrapie pathogenesis. Immunobiology 2004, 209, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Unterberger, U; Höftberger, R; Gelpi, E; Flicker, H; Budka, H; Voigtländer, T. Endoplasmic reticulum stress features are prominent in Alzheimer disease but not in prion diseases in vivo. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 2006, 65, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hetz, C; Lee, AH; Gonzalez-Romero, D; Thielen, P; Castilla, J; Soto, C; Glimcher, LH. Unfolded protein response transcription factor XBP-1 does not influence prion replication or pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Riemer, C; Schultz, J; Burwinkel, M; Schwarz, A; Mok, SW; Gultner, S; Bamme, T; Norley, S; van Landeghem, F; Lu, B; Gerard, C; Baier, M. Accelerated prion replication in, but prolonged survival times of, prion-infected CXCR3-/- mice. J. Virol 2008, 82, 12464–12471. [Google Scholar]
- Tamguney, G; Giles, K; Glidden, DV; Lessard, P; Wille, H; Tremblay, P; Groth, DF; Yehiely, F; Korth, C; Moore, RC; Tatzelt, J; Rubinstein, E; Boucheix, C; Yang, X; Stanley, P; Lisanti, MP; Dwek, RA; Rudd, PM; Moskovitz, J; Epstein, CJ; Cruz, TD; Kuziel, WA; Maeda, N; Sap, J; Ashe, KH; Carlson, GA; Tesseur, I; Wyss-Coray, T; Mucke, L; Weisgraber, KH; Mahley, RW; Cohen, FE; Prusiner, SB. Genes contributing to prion pathogenesis. J. Gen. Virol 2008, 89, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar]



© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/). This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacs, G.G.; Budka, H. Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 976-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10030976
Kovacs GG, Budka H. Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2009; 10(3):976-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10030976
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacs, Gabor G., and Herbert Budka. 2009. "Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 10, no. 3: 976-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10030976
APA StyleKovacs, G. G., & Budka, H. (2009). Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10(3), 976-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10030976