Characterization and Purification of Polydisperse Reconstituted Lipoproteins and Nanolipoprotein Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
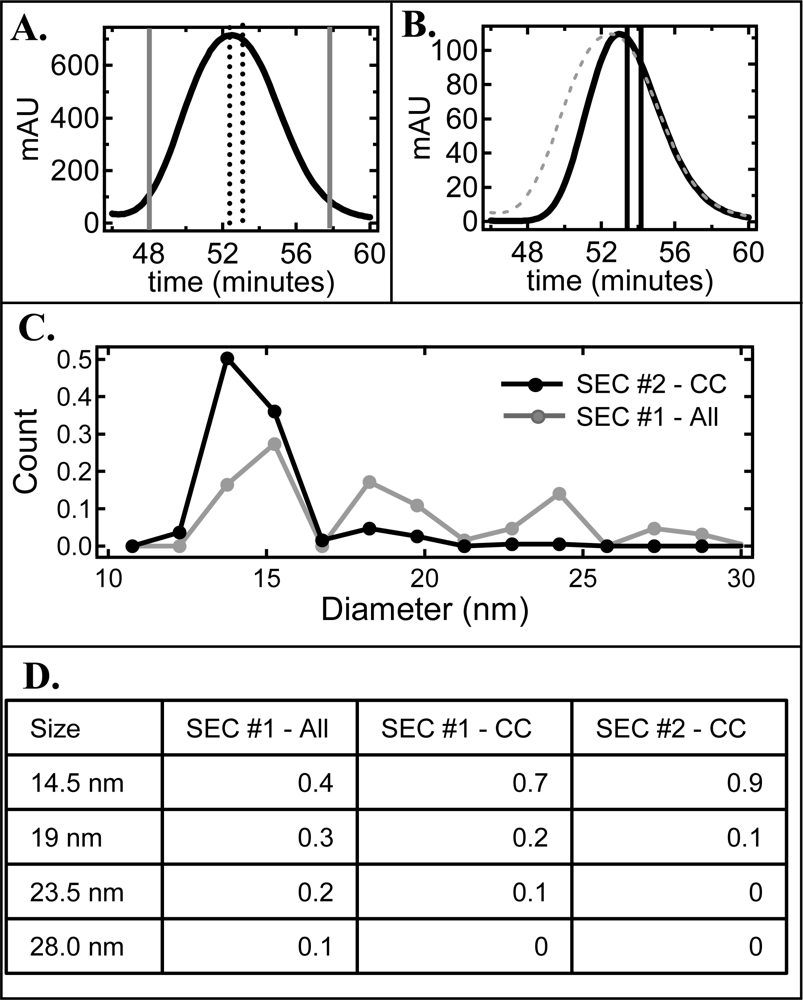
2.1. Effect of cholate on NLP separation by SEC and native gel electrophoresis
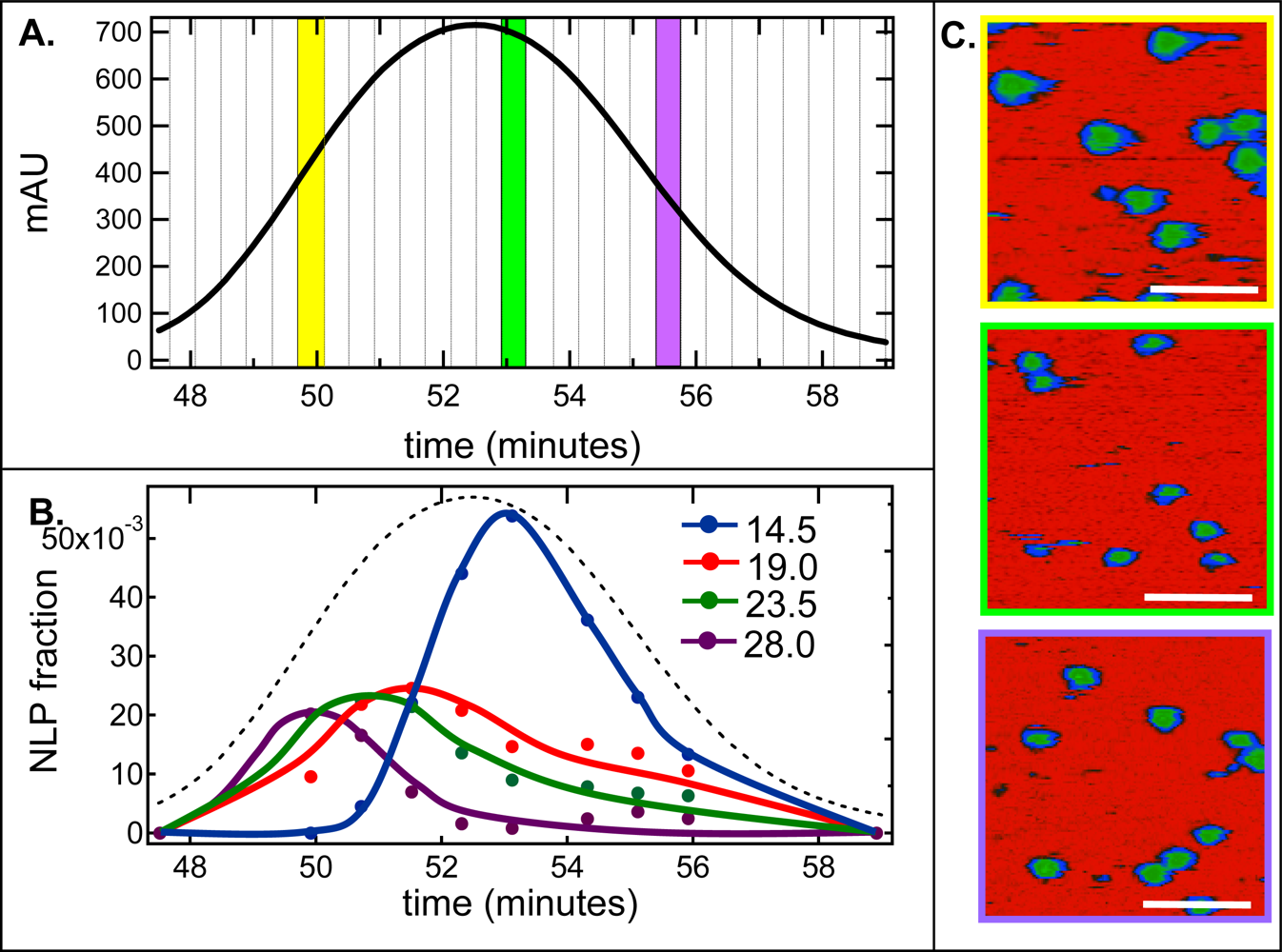
2.2. De-convolution of the single NLP peak
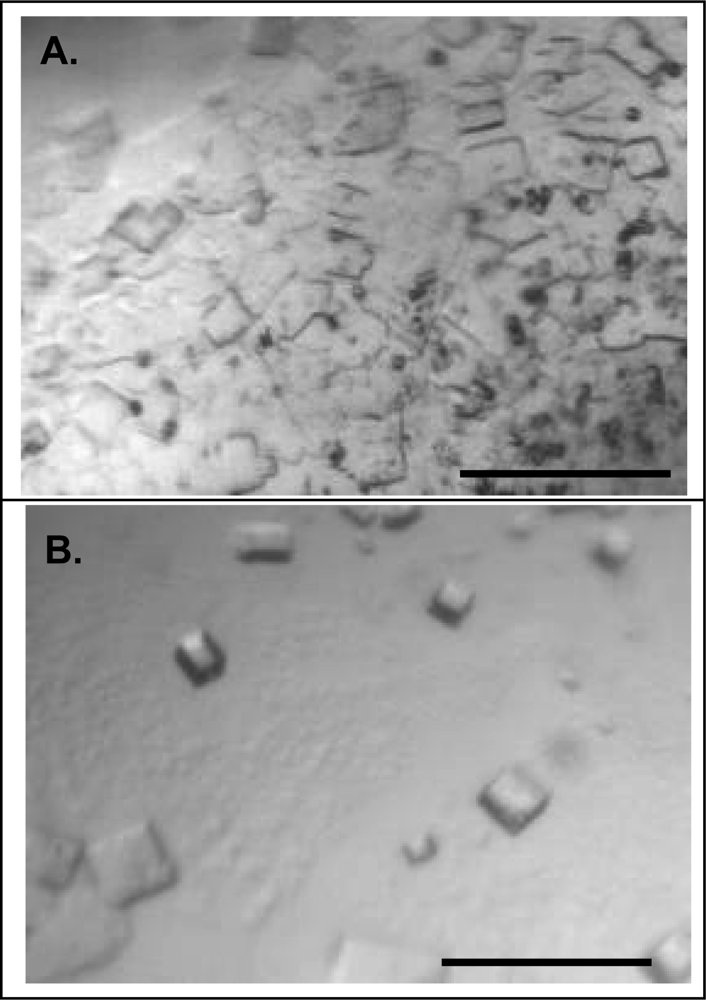
2.3. Effect of homogeneity on NLP crystallization
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. apoE422K protein production
3.3. Nanolipoprotein particle (NLP) formation
3.4. Atomic force microscopy (AFM)
3.5. Crystallization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Garda, HA; Arrese, EL; Soulages, JL. Structure of apolipophorin-III in discoidal lipoproteins - Interhelical distances in the lipid-bound state and conformational change upon binding to lipid. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 19773–19782. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, A. Reconstitution of high-density-lipoproteins. Meth. Enzymology 1986, 128, 553–582. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, JH; Krul, ES; Jonas, A. Structure of Apolipoprotein-a-I in 3 homogeneous, reconstituted high-density-lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem 1990, 265, 20037–20043. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, A; Sweeny, SA; Herbert, PN. Discoidal complexes of A and C apolipoproteins with lipids and their reactions with lecithin - cholesterol acyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem 1984, 259, 6369–6375. [Google Scholar]
- Zorich, N; Jonas, A; Pownall, HJ. Activation of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase by human apolipoprotein-E in discoidal complexes with lipids. J. Biol. Chem 1985, 260, 8831–8837. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B; Morrow, JA; Weisgraber, KH. Reorganization of the four-helix bundle of human apolipoprotein E in binding to phospholipid. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 20775–20781. [Google Scholar]
- Hatters, DM; Peters-Libeu, CA; Weisgraber, KH. Apolipoprotein E structure: Insights into function. Trends Biochem. Sci 2006, 31, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Gursky, O; Ranjana; Gantz, DL. Complex of human apolipoprotein C-1 with phospholipid: Thermodynamic or kinetic stability? Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7373–7384. [Google Scholar]
- Wientzek, M; Kay, CM; Oikawa, K; Ryan, RO. Binding of insect apolipophorin-Iii to dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles - Evidence for a conformational change. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 4605–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Herscovitz, H; Hadzopouloucladaras, M; Walsh, MT; Cladaras, C; Zannis, VI; Small, DM. Expression, secretion, and lipid-binding characterization of the N-terminal 17-percent of apolipoprotein-B. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7313–7317. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette, CD; Richard, L; Benner, WH; Pesavento, JB; Cappuccio, JA; Walsworth, VL; Kuhn, EA; Corzett, M; Chromy, BA; Segelke, BW; Coleman, MA; Bench, G; Hoeprich, PD, Jr; Sulchek, TA. Quantifying Size Distributions of Nanolipoprotein Particles (NLPs) with single particle analysis and Molecular Dynamic (MD) simulations. J. Lipid Res 2008, 49, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Chromy, BA; Arroyo, E; Blanchette, CD; Bench, G; Benner, H; Cappuccio, JA; Coleman, MA; Henderson, PT; Hinz, AK; Kuhn, EA; Pesavento, JB; Segelke, BW; Sulchek, TA; Tarasow, T; Walsworth, VL; Hoeprich, PD. Different apolipoproteins impact nanolipoprotein particle formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 14348–14354. [Google Scholar]
- Bayburt, TH; Sligar, SG. Self-assembly of single integral membrane proteins into soluble nanoscale phospholipid bilayers. Protein Sci 2003, 12, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Bayburt, TH; Grinkova, YV; Sligar, SG. Assembly of single bacteriorhodopsin trimers in bilayer nanodiscs. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2006, 450, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, IG; Grinkova, YV; Lazarides, AA; Sligar, SG. Directed self-assembly of monodisperse phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs with controlled size. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar]
- Bayburt, TH; Grinkova, YV; Sligar, SG. Self-assembly of discoidal phospholipid bilayer nanoparticles with membrane scaffold proteins. Nano Lett 2002, 2, 853–856. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y; Kijac, AZ; Sligar, SG; Rienstra, CM. Structural analysis of nanoscale self-assembled discoidal lipid bilayers by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Biophys. J 2006, 91, 3819–3828. [Google Scholar]
- Boldog, T; Grimme, S; Li, M; Sligar, SG; Hazelbauer, GL. Nanodiscs separate chemoreceptor oligomeric states and reveal their signaling properties. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11509–11514. [Google Scholar]
- Cappuccio, JA; Blanchette, CD; Sulchek, TA; Arroyo, ES; Kralj, JM; Hinz, AK; Kuhn, EA; Chromy, BA; Segelke, BW; Rothschild, KJ; Fletcher, JE; Katzen, F; Peterson, TC; Kudlicki, WA; Bench, G; Hoeprich, PD; Coleman, MA. Cell-free co-expression of functional membrane proteins and apolipoprotein, forming soluble nanolipoprotein particles. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2008, 7, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar]
- Schneeweis, LA; Koppaka, V; Lund-Katz, S; Phillips, MC; Axelsen, PH. Structural analysis of lipoprotein E particles. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 12525–12534. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, CD; King, WC; Applegate, KR; Forte, T; Glomset, JA; Norum, KR; Gjone, E. Characterization of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoproteins in familial lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. J. Lipid Res 1980, 21, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, A; Kezdy, KE; Wald, JH. Defined apolipoprotein a-I conformations in reconstituted high-density lipoprotein disks. J. Biol. Chem 1989, 264, 4818–4824. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, JW; Jonas, A; Sligar, SG. Imaging and manipulation of high-density lipoproteins. Biophys. J 1997, 73, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, AY; Freddolino, PL; Sligar, SG; Schulten, K. Disassembly of nanodiscs with cholate. Nano Lett 2007, 7, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, A; Drengler, SM; Patterson, BW. 2 Types of complexes formed by the interaction of apolipoprotein a-I with vesicles of l-alpha-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem 1980, 255, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette, CG; Jones, JL; Ng, TC; Kercret, H; Chung, BH; Segrest, JP. Structural studies of apolipoprotein-a-I phosphatidylcholine recombinants by high-field proton NMR, nondenaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis, and electron-microscopy. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L; Chen, JG; Mishra, VK; Kurtz, JA; Cao, DF; Klon, AE; Harvey, SC; Anantharamaiah, GM; Segrest, JP. Double belt structure of discoidal high density lipoproteins: Molecular basis for size heterogeneity. J. Mol. Biol 2004, 343, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman, S; Gantz, DL; Gursky, O. Kinetic stabilization and fusion of apolipoprotein A-2: DMPC disks: Comparison with apoA-1 and apoC-1. Biophys. J 2005, 88, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P; Giddings, JC. Isolation and measurement of colloids in human plasma by membrane-selective flow field-flow fractionation: Lipoproteins and pharmaceutical colloids. J. Pharm. Sci 1996, 85, 895–898. [Google Scholar]
- Peters-Libeu, CA; Newhouse, Y; Hall, SC; Witkowska, HE; Weisgraber, KH. Apolipoprotein E*dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine particles are ellipsoidal in solution. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Segelke, BW. Efficiency analysis of sampling protocols used in protein crystallization screening. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 232, 553–562. [Google Scholar]
- Fraunhofer, W; Winter, G. The use of asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation in pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 2004, 58, 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, B; Zattoni, A; Reschiglian, P; Moon, MH; Mirasoli, M; Michelini, E; Roda, A. Field-flow fractionation in bioanalysis: A review of recent trends. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 635, 132–143. [Google Scholar]

© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanchette, C.D.; Segelke, B.W.; Fischer, N.; Corzett, M.H.; Kuhn, E.A.; Cappuccio, J.A.; Benner, W.H.; Coleman, M.A.; Chromy, B.A.; Bench, G.; et al. Characterization and Purification of Polydisperse Reconstituted Lipoproteins and Nanolipoprotein Particles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2958-2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10072958
Blanchette CD, Segelke BW, Fischer N, Corzett MH, Kuhn EA, Cappuccio JA, Benner WH, Coleman MA, Chromy BA, Bench G, et al. Characterization and Purification of Polydisperse Reconstituted Lipoproteins and Nanolipoprotein Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2009; 10(7):2958-2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10072958
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanchette, Craig D., Brent W. Segelke, Nicholas Fischer, Michele H. Corzett, Edward A. Kuhn, Jenny A. Cappuccio, William Henry Benner, Matthew A. Coleman, Brett A. Chromy, Graham Bench, and et al. 2009. "Characterization and Purification of Polydisperse Reconstituted Lipoproteins and Nanolipoprotein Particles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 10, no. 7: 2958-2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10072958
APA StyleBlanchette, C. D., Segelke, B. W., Fischer, N., Corzett, M. H., Kuhn, E. A., Cappuccio, J. A., Benner, W. H., Coleman, M. A., Chromy, B. A., Bench, G., Hoeprich, P. D., & Sulchek, T. A. (2009). Characterization and Purification of Polydisperse Reconstituted Lipoproteins and Nanolipoprotein Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10(7), 2958-2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10072958





