A Proline-Based Neuraminidase Inhibitor: DFT Studies on the Zwitterion Conformation, Stability and Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Functional Groups on Zwitterion Stabilities
2.2. Conformational Analysis of BL
2.2.1. In the absence of water (n = 0)
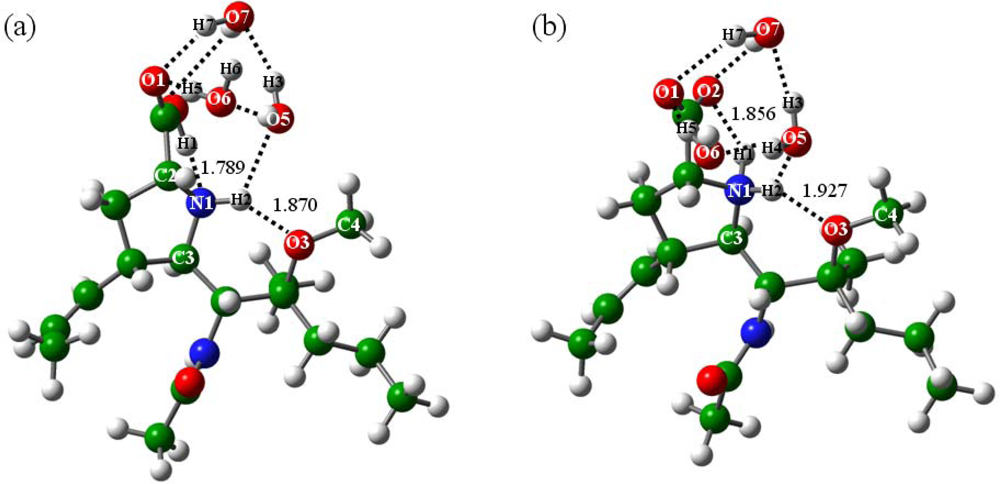
2.2.2. With addition of water molecules
2.3. Formation of the Zwitterionic Isomer of BL
3. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Neumann, G; Noda, T; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine–origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, C; Kanyalkar, M; Joshi, M; Coutinho, E; Srivastava, S. Probing molecular level interaction of oseltamivir with H5N1-NA and model membranes by molecular docking, multinuclear NMR and DSC methods. Biochimica. Et. Biophysica. Acta (BBA)–Biomembranes 2009, 1788, 484–494. [Google Scholar]
- Moscona, A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza. N. Engl. J. Med 2005, 353, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar]
- von Itzstein, M. The war against influenza: Discovery and development of sialidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov 2007, 6, 967–974. [Google Scholar]
- Beigel, J; Bray, M. Current and future antiviral therapy of severe seasonal and avian influenza. Antivir. Res 2008, 78, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Moscona, A. Medical management of influenza infection. Annu. Rev. Med 2008, 59, 397–413. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, P; Small, I; Smith, J; Suter, P; Dutkowski, R. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and its potential for use in the event of an influenza pandemic. J Antimicrob Chemother 2005, 55(Suppl. S1), i5–i21. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization.
- Gubareva, LV; Kaiser, L; Hayden, FG. Influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitors. Lancet 2000, 355, 827–835. [Google Scholar]
- Garman, E; Laver, G. Controlling influenza by inhibiting the virus’s neuraminidase. Curr. Drug. Targets 2004, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, RJ; Haire, LF; Stevens, DJ; Collins, PJ; Lin, YP; Blackburn, GM; Hay, AJ; Gamblin, SJ; Skehel, JJ. The structure of H5N1 avian influenza neuraminidase suggests new opportunities for drug design. Nature 2006, 443, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi, M; Asaoka, N; Sakai, T; Ohuchi, R. Roles of neuraminidase in the initial stage of influenza virus infection. Microbes. Infect 2006, 8, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Colman, PM; Varghese, JN; Laver, WG. Structure of the catalytic and antigenic sites in influenza virus neuraminidase. Nature 1983, 303, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- von Itzstein, M; Wu, WY; Kok, GB; Pegg, MS; Dyason, JC; Jin, B; van Phan, T; Smythe, ML; White, HF; Oliver, SW. Rational design of potent sialidase–based inhibitors of influenza virus replication. Nature 1993, 363, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Colman, PM. Influenza virus neuraminidase: Structure, antibodies, and inhibitors. Protein Sci 1994, 3, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Kati, WM; Montgomery, D; Carrick, R; Gubareva, L; Maring, C; McDaniel, K; Steffy, K; Molla, A; Hayden, F; Kempf, D; Kohlbrenner, W. In vitro characterization of A-315675, a highly potent inhibitor of A and B strain influenza virus neuraminidases and influenza virus replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2002, 46, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian, S; Bayrakdarian, M; Luo, X. Total synthesis of A-315675: A potent inhibitor of influenza neuraminidase. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 4716–4721. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, Y; Nehme, B; Baz, M; Boivin, G. Activity of the neuraminidase inhibitor A-315675 against oseltamivir–resistant influenza neuraminidases of N1 and N2 subtypes. Antivir. Res 2008, 77, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, ZW; Yang, G; Zu, YG; Fu, YJ; Zhou, LJ. The conformational analysis and proton transfer of the neuraminidase inhibitors: A theoretical study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, RH; McMahon, TB. Stabilization of the zwitterionic structure of proline by an alkylammonium ion in the gas phase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2007, 46, 3668–3671. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G; Zu, YG; Fu, YJ; Zhou, LJ; Zhu, RX; Liu, CB. Assembly and stabilization of multi–amino acid zwitterions by the Zn(II) ion: A computational exploration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 4899–4906. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, L; Murray, CW; Hartshorn, MJ; Tickle, IJ; Verdonk, ML. Sensitivity of molecular docking to induced fit effects in influenza virus neuraminidase. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2002, 16, 855–869. [Google Scholar]
- Fornabaio, M; Cozzini, P; Mozzarelli, A; Abraham, DJ; Kellogg, GE. Simple, intuitive calculations of free energy of binding for protein–ligand complexes. 2. Computational titration and pH effects in molecular models of neuraminidase–inhibitor complexes. J. Med. Chem 2003, 46, 4487–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, P; Bryce, RA. Molecular dynamics and free energy analysis of neuraminidase–ligand interactions. Protein Sci 2004, 13, 946–957. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M; Yu, K; Liu, H; Luo, X; Chen, K; Zhu, W; Jiang, H. QSAR analyses on avian influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitors using CoMFA, CoMSIA, and HQSAR. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2006, 20, 549–566. [Google Scholar]
- Barillari, C; Taylor, J; Viner, R; Essex, JW. Classification of water molecules in protein binding sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K; Zimmerman, DM; Chung-Phillips, A; Cassady, C. Experimental and ab initio studies of the gas–phase basicities of polyglycines. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1993, 115, 10812–10822. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D; Rauk, A; Armstrong, DA. Radicals and ions of glycine: An ab initio study of the structures and gas–phase thermochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1995, 117, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K; Chung-Phillips, A. Conformers of gaseous protonated glycine. J. Comput. Chem 1998, 19, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, M; Skurski, P; Simons, J. Dipole–bound anions of glycine based on the zwitterion and neutral structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2000, 122, 10159–10162. [Google Scholar]
- Skurski, P; Rak, J; Simons, J; Gutowski, M. Quasidegeneracy of zwitterionic and canonical tautomers of arginine solvated by an excess electron. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2001, 123, 11073–11074. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, T; Russo, N; Toscano, M. Interaction of Li+, Na+, and K+ with the proline amino acid. Complexation modes, potential energy profiles, and metal ion affinities. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, SJ; Zheng, WJ; Radisic, D; Bowern, KH, Jr. The stabilization of arginine’s zwitterion by dipole–binding of an excess electron. J. Chem. Phys 2005, 122, 091103. [Google Scholar]
- Kass, SR. Zwitterion–dianion complexes and anion–anion clusters with negative dissociation energies. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2005, 127, 13098–13099. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G; Zu, YG; Liu, CB; Fu, YJ; Zhou, LJ. Stabilization of amino acid zwitterions with varieties of anionic species: The intrinsic mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 7104–7110. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G; Zhou, LJ; Liu, CB. Glycine canonical and zwitterionic isomers within zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10399–10402. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, JH; Gordon, MS. On the number of water molecules necessary to stabilize the glycine zwitterion. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1995, 117, 8159–8170. [Google Scholar]
- Yamabe, S; Ono, N; Tsuchida, N. Molecular interactions between glycine and H2O affording the zwitterion. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 7915–7922. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, A; Sahu, PK; Lee, SL. Many–body interaction in glycine–(water)3 complex using density functional theory method. J. Chem. Phys 2004, 120, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kapitán, J; Baumruk, V; Kopecký, V, Jr; Pohl, R; Bouř, P. Proline zwitterion dynamics in solution, glass, and crystalline state. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 13451–13462. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, MF; Prell, JS; Saykally, RJ; Williams, ER. One water molecule stabilizes the cationized arginine zwitterion. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 13544–13553. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, SX; Sun, X; Cao, R; Yang, JL. Thermal stabilities of the microhydrated zwitterionic glycine: A kinetics and dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 480–483. [Google Scholar]
- Sapse, AM; Levy, LM; Daniels, SB; Erickson, BW. The gamma turn: Ab initio calculations on proline and N-acetylproline amide. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1987, 109, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanian, SG; Reva, ID; Radchenko, ED; Adamowicz, L. Conformers of nonionized proline. Matrix–isolation infrared and post–hartree–fock ab initio study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 10664–10072. [Google Scholar]
- Czinki, E; Csásázr, AG. Conformers of gaseous proline. Chem. Eur. J 2003, 9, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, WD; Czinki, E; Csásázr, AG. Molecular structure of proline. Chem. Eur. J 2004, 10, 4512–4517. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, KM; Park, SW; Jeon, IS; Lee, BR; Ahn, DS; Lee, S. Computational study of proline–water cluster. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 2005, 26, 909–912. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G; Wu, XM; Zu, YG; Liu, CB; Fu, YJ; Zhou, LJ. Proton transfer at the carboxylic sites of amino acids: A single water molecule catalyzed process. Int. J. Quantum Chem 2009, 109, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, MJ; Trucks, GW; Schlegel, HB; Scuseria, GE; Robb, MA; Cheeseman, JR; Montgomery, JA; Vreven, T, Jr; Kudin, KN; Burant, JC; Millam, JM; Iyengar, SS; Tomasi, J; Barone, V; Mennucci, B; Cossi, M; Scalmani, G; Rega, N; Petersson, GA; Nakatsuji, H; Hada, M; Ehara, M; Toyota, K; Fukuda, R; Hasegawa, J; Ishida, M; Nakajima, T; Honda, Y; Kitao, O; Nakai, H; Klene, M; Li, X; Knox, JE; Hratchian, HP; Cross, JB; Adamo, C; Jaramillo, J; Gomperts, R; Stratmann, RE; Yazyev, O; Austin, AJ; Cammi, R; Pomelli, C; Ochterski, JW; Ayala, PY; Morokuma, K; Voth, GA; Salvador, P; Dannenberg, JJ; Zakrzewski, VG; Dapprich, S; Daniels, AD; Strain, MC; Farkas, O; Malick, DK; Rabuck, AD; Raghavachari, K; Foresman, JB; Ortiz, JV; Cui, Q; Baboul, AG; Clifford, S; Cioslowski, J; Stefanov, BB; Liu, G; Liashenko, A; Piskorz, P; Komaromi, I; Martin, RL; Fox, DJ; Keith, T; Al-Laham, MA; Peng, CY; Nanayakkara, A; Challacombe, MP; Gill, MW; Johnson, B; Chen, W; Wong, MW; Gonzalez, C; Pople, JA. Gaussian 03; , Revision D01; Gaussian, Inc: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, AD. A multicenter numerical integration scheme for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys 1988, 88, 2547–2551. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C; Yang, W; Parr, RG. Development of the colle–salvetti correlation–energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar]






© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.-W.; Wu, X.-M.; Zhou, L.-J.; Yang, G. A Proline-Based Neuraminidase Inhibitor: DFT Studies on the Zwitterion Conformation, Stability and Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3918-3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093918
Yang Z-W, Wu X-M, Zhou L-J, Yang G. A Proline-Based Neuraminidase Inhibitor: DFT Studies on the Zwitterion Conformation, Stability and Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2009; 10(9):3918-3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093918
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhi-Wei, Xiao-Min Wu, Li-Jun Zhou, and Gang Yang. 2009. "A Proline-Based Neuraminidase Inhibitor: DFT Studies on the Zwitterion Conformation, Stability and Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 10, no. 9: 3918-3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093918
APA StyleYang, Z.-W., Wu, X.-M., Zhou, L.-J., & Yang, G. (2009). A Proline-Based Neuraminidase Inhibitor: DFT Studies on the Zwitterion Conformation, Stability and Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10(9), 3918-3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093918




