Integral Kinetic Model for Studying Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as Affected by Cholesterol During Heating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Changes of Quercetin during Heating with and without Cholesterol
2.2. Peroxidation and Epoxidation of Cholesterol during Heating
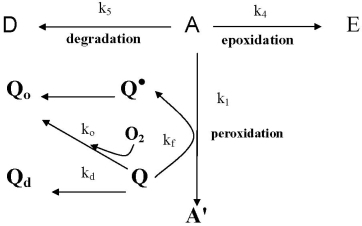
2.3. Kinetic Studies of Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as well as Cholesterol Hydroperoxide Formation
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Heating of Quercetin with or without Cholesterol
3.4. Extraction and Purification of Cholesterol and COPs
3.5. Extraction and Purification of Quercetin
3.6. HPLC Analysis of Quercetin
3.7. TLC Analysis of COPs
3.8. HPLC Analysis of COPs
3.9. Kinetic Analysis of COPs and Quercetin
4. Conclusions
References
- Hertog, MGL; Hollman, PCH; Katan, MB. Content of potentially anticarcinogenic flavonoids of 28 vegetables and 9 fruits commonly in the Netherlands. J. Agric. Food Chem 1992, 40, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Miean, KH; Mohamed, S. Flavonoids (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Hopia, A; Heinonen, M. Antioxidant activity of flavonol aglycones and their glycosides in methyl linoleate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 1999, 76, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Das, NP; Pereira, TA. Effects of flavonoids on thermal autoxidation of palm oil: Structure-activity relationships. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 1990, 67, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, DP; Rossiter, JT. Buttriss, J, Saltmarsh, M, Eds.; Quercetin and rutin (quercetin 3-O-rhamnosylglucoside) thermal degradation in aqueous media under alkaline condition. In Functional Foods-Claims and Evidence; Royal Society of Chemistry Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 216–238. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, DP; Rossiter, JT. Heat-induced, metal-catalyzed oxidative degradation of quercetin and rutin (quercetin 3-o-rhamnosylglucoside) in aqueous model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem 2000, 48, 3830–3838. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, S; Garrido, A; Sanhueza, J; Loyola, LA; Morales, G; Leighton, F; Valenzuela, A. Flavonoids as stabilizers of fish oil: An alternative to synthetic antioxidants. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 1993, 70, 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Pekkarinen, SS; Heinonen, IM; Hopia, AI. Flavonoids quercetin, myricetin, kaemferol and (+)-catechin as antioxidants in methyl linoleate. J. Sci. Food Agric 2000, 79, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G; Guan, L; Sun, J; Chen, ZY. Oxidation of cholesterol and β-sitosterol and prevention by natural antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem 2009, 57, 9284–9292. [Google Scholar]
- Maerker, G. Cholesterol autoxidation-current status. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 1987, 64, 388–392. [Google Scholar]
- Paniangvait, P; King, AJ; Jones, AD; German, BG. Cholesterol oxides in foods of animal origin. J. Food Sci 1995, 60, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, JT; Wang, HC; Chen, BH. Kinetic model of the cholesterol oxidation during heating. J. Agric. Food Chem 1998, 46, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, JT; Huang, DY; Chen, BH. Kinetic study of the cholesterol oxidation as inhibited by stearylamine during heating. J. Agric. Food Chem 2004, 52, 7132–7138. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G; Sun, J; Liang, Y; Yang, C; Chen, ZY. Interaction of fatty acids with oxidation of cholesterol and β-sitosterol. Food Chem 2010, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfaouz, MM; Kummerow, FA. Cholesterol-rich diets have different effects on lipid peroxidation, cholesterol oxides, and antioxidant enzymes in rats and rabbits. J. Nutr. Biochem 2000, 11, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Leonarduzzi, G; Sottero, B; Poli, G. Oxidized products of cholesterol: Dietary and metabolic origin and proatherosclerotic effects (review). J. Nutr. Biochem 2002, 13, 700–710. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, JT; Hsu, DJ; Chen, BH. Kinetic model for studying the effect of quercetin on cholesterol oxidation during heating. J. Agric. Food Chem 2006, 54, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, LL. Cholesterol autoxidation 1981–1986. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1987, 44, 87–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, WA; Cornicelli, JA; Devall, LJ; Tait, B; Trivedi, BK; Witiak, DT; Wu, MA. Rapid screening test to determine the antioxidant potencies of natural and synthetic antioxidants. J. Org. Chem 1993, 58, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar]
- Foti, M; Ruberto, G. Kinetic solvent effects on phenolic antioxidants determined by spectrophotometric measurements. J. Agric. Food Chem 2001, 49, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Foti, M; Piattelli, M; Baratta, MT; Ruberto, G. Flavonoids, coumarins, and cinnamic acids as antioxidants in a micellar system. Structure-activity relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem 1996, 44, 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ozilgen, S; Ozilgen, M. Kinetic model of lipid oxidation in foods. J. Food Sci 1990, 55, 498–536. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, LL; Hill, FL. Detection of sterol hydroperoxides on thin layer chromatoplates by means of the wurster dyes. J. Chromatogr 1972, 66, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- SAS, SAS Procedures and SAS/Graph User’s Guide; Version 9.1.3 Foundation. Software Release 9.1 (TS1M3 DSCS3054) of the SAS System for Microsoft windows XP Professional; SAS Institute, Inc: Cary, NC, USA, 1999.
- Nourooz-Zadeh, J. Determination of autoxidation products from free or total cholesterol: A new multistep enrichment methodology including the enzymatic release of esterified cholesterol. J. Agric. Food Chem 1990, 38, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Maerker, G; Bunick, FJ. Cholesterol oxides: Isolation and determination of some cholesterol oxidation products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 1986, 63, 767–771. [Google Scholar]







| Heating time (min) | COPs (%)a | |
|---|---|---|
| Controlb | Quercetinb | |
| 0 | 0.08 ± 0.00 A,a | 0.07 ± 0.00 A,b |
| 5 | 0.18 ± 0.01 A,a | 0.09 ± 0.00 A,b |
| 10 | 0.94 ± 0.01 B,a | 0.16 ± 0.01 A,b |
| 30 | 5.94 ± 0.05 C,a | 0.51 ± 0.00 B,b |
| 60 | 15.4 ± 0.3D,a | 2.05 ± 0.03 C,b |
| 90 | 30.9 ± 0.5E,a | 7.77 ± 0.06 D,b |
| 120 | —c | 24.4 ± 0.4 E |
| Heating time (min) | Cholesterol (%) a | |
|---|---|---|
| Control b | Quercetin b | |
| 0 | 97.9 ± 0.6 A,a | 96.9 ± 0.3 A,a |
| 5 | 93.2 ± 1.05 B,a | 95.7 ± 0.2 A,b |
| 10 | 87.5 ± 0.4 C,a | 94.1 ± 0.1 A,b |
| 30 | 69.0 ± 1.0 D,a | 86.4 ± 0.1 B,b |
| 60 | 64.2 ± 0.9 E,a | 80.5 ± 0.3 C,b |
| 90 | 66.4 ± 0.7 E,a | 77.1 ± 0.5 D,b |
| 120 | —c | 77.4 ± 2.4 D |
| Treatment | Rate equations a | k (h−1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 0.253 ± 0.027 | 0.94 | |
| Oxygen | 0.868 ± 0.019 | 0.99 | |
| Oxygen and Cholesterol | 7.17 ± 0.67 | 0.91 |
| Rate equations a | Reactions | C b | Qu b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k (h−1) | r2 | k (h−1) | r2 | ||
| Free radical chain | 488.2 ± 0.2 | 1.00 | 1.8×10−4 ± 0.1×10−4 | 0.94 | |
| Epoxidation | 4240.8 ± 344.7 | 0.89 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.82 | |
| Degradation | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 0.99 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.99 | |
| Free radical chain | —c | — | 3.28 ± 0.00 | 0.94 | |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chien, J.-T.; Hsu, D.-J.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.-H. Integral Kinetic Model for Studying Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as Affected by Cholesterol During Heating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2805-2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11082805
Chien J-T, Hsu D-J, Inbaraj BS, Chen B-H. Integral Kinetic Model for Studying Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as Affected by Cholesterol During Heating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2010; 11(8):2805-2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11082805
Chicago/Turabian StyleChien, John-Tung, Da-Jung Hsu, Baskaran Stephen Inbaraj, and Bing-Huei Chen. 2010. "Integral Kinetic Model for Studying Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as Affected by Cholesterol During Heating" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 11, no. 8: 2805-2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11082805
APA StyleChien, J.-T., Hsu, D.-J., Inbaraj, B. S., & Chen, B.-H. (2010). Integral Kinetic Model for Studying Quercetin Degradation and Oxidation as Affected by Cholesterol During Heating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 11(8), 2805-2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11082805