Biomarkers in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy
Abstract
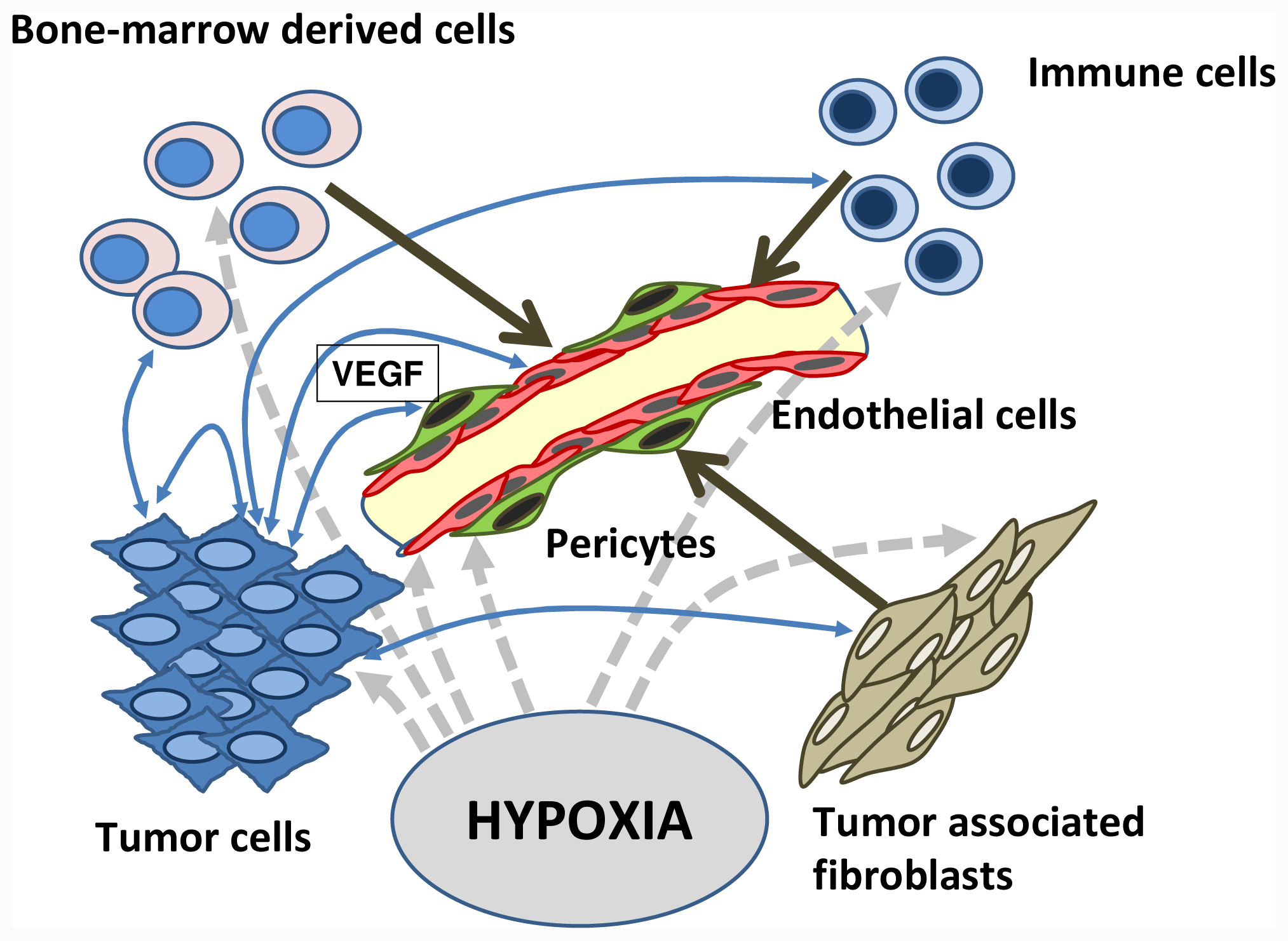
:1. Introduction
2. Tissue Sampling/Tissue Biomarker
3. Blood Soluble Markers
4. EPC
5. Imaging Techniques
5.1. DCE-MRI
5.2. Ultrasound
6. Biomarkers under Anti-Angiogenic Therapies
6.1. Anti-Angiogenic Therapies
6.2. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
6.3. Sorafenib
6.4. Cediranib
6.5. Sunitinib
6.6. Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibodies
Bevacizumab
7. Conclusions
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nature Med 1995, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Medinger, M; Skoda, R; Gratwohl, A; Theocharides, A; Buser, A; Heim, D; Dirnhofer, S; Tichelli, A; Tzankov, A. Angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor-/receptor expression in myeloproliferative neoplasms: correlation with clinical parameters and JAK2- V617F mutational status. Br. J. Haematol 2009, 146, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Medinger, M; Fischer, N; Tzankov, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor-related pathways in hemato-lymphoid malignancies. J. Oncol 2010, 2010, 729725. [Google Scholar]
- Medinger, M; Mross, K. Clinical trials with anti-angiogenic agents in hematological malignancies. J. Angiogenes. Res 2010, 2, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Lyden, D; Hattori, K; Dias, S; Costa, C; Blaikie, P; Butros, L; Chadburn, A; Heissig, B; Marks, W; Witte, L; et al. Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nature Med 2001, 7, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Rafii, S; Lyden, D; Benezra, R; Hattori, K; Heissig, B. Vascular and haematopoietic stem cells: novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy? Nat. Rev Cancer 2002, 2, 826–835. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, BA; Diaz, LA; Polyak, K; Meszler, L; Romans, K; Guinan, EC; Antin, JH; Myerson, D; Hamilton, SR; Vogelstein, B; Kinzler, KW; Lengauer, C. Contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells to human tumor vasculature. Nature Med 2005, 11, 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N; Gerber, HP; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nature Med 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, KJ; Li, B; Winer, J; Armanini, M; Gillett, N; Phillips, HS; Ferrara, N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar]
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Medinger, M; Drevs, J. Receptor tyrosine kinases and anticancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des 2005, 11, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz, H; Fehrenbacher, L; Novotny, W; Cartwright, T; Hainsworth, J; Heim, W; Berlin, J; Baron, A; Griffing, S; Holmgren, E; Ferrara, N; Fyfe, G; Rogers, B; Ross, R; Kabbinavar, F. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 2004, 350, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki, D; Itin, A; Soffer, D; Keshet, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 1992, 359, 843–845. [Google Scholar]
- Dor, Y; Porat, R; Keshet, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular adjustments to perturbations in oxygen homeostasis. Amer. J. Physiol 2001, 280, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Ryuto, M; Ono, M; Izumi, H; Yoshida, S; Weich, HA; Kohno, K; Kuwano, M. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha in human glioma cells. Possible roles of SP-1. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 28220–28228. [Google Scholar]
- Pertovaara, L; Kaipainen, A; Mustonen, T; Orpana, A; Ferrara, N; Saksela, O; Alitalo, K. Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 6271–6274. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin, WG, Jr. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein and clear cell renal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res 2007, 13, 680–682. [Google Scholar]
- Gille, H; Kowalski, J; Li, B; LeCouter, J; Moffat, B; Zioncheck, TF; Pelletier, N; Ferrara, N. Analysis of biological effects and signaling properties of Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) and KDR (VEGFR-2). A reassessment using novel receptor-specific vascular endothelial growth factor mutants. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, K; Dias, S; Heissig, B; Hackett, NR; Lyden, D; Tateno, M; Hicklin, DJ; Zhu, Z; Witte, L; Crystal, RG; Moore, MA; Rafii, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 stimulate postnatal hematopoiesis by recruitment of vasculogenic and hematopoietic stem cells. J. Exp. Med 2001, 193, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy, WT; Richter, L; Frutiger, Y; Grogan, TM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 728–733. [Google Scholar]
- Autiero, M; Luttun, A; Tjwa, M; Carmeliet, P. Placental growth factor and its receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1: novel targets for stimulation of ischemic tissue revascularization and inhibition of angiogenic and inflammatory disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost 2003, 1, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N; Kerbel, RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, LM. The role of neuropilins in cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther 2006, 5, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Soker, S; Takashima, S; Miao, HQ; Neufeld, G; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 1998, 92, 735–745. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, T; Tokunaga, T; Hatanaka, H; Kijima, H; Yamazaki, H; Abe, Y; Osamura, Y; Inoue, H; Ueyama, Y; Nakamura, M. Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, J; Wick, W; Weller, M. Human malignant glioma cells express semaphorins and their receptors, neuropilins and plexins. Glia 2003, 42, 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, MJ; Van Buren, G; Dallas, NA; Xia, L; Wang, X; Yang, AD; Somcio, RJ; Lin, YG; Lim, S; Fan, F; et al. Therapeutic targeting of neuropilin-2 on colorectal carcinoma cells implanted in the murine liver. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst 2008, 100, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Dallas, NA; Gray, MJ; Xia, L; Fan, F; van Buren, G; Gaur, P; Samuel, S; Lim, SJ; Arumugam, T; Ramachandran, V; Wang, H; Ellis, LM. Neuropilin-2-mediated tumor growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 8052–8060. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q; Chanthery, Y; Liang, WC; Stawicki, S; Mak, J; Rathore, N; Tong, RK; Kowalski, J; Yee, SF; Pacheco, G; et al. Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Dempke, WC; Zippel, R. Brivanib, a novel dual VEGF-R2/bFGF-R inhibitor. Anticancer Res 2010, 30, 4477–4483. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, Y. Angiopoietins. Rec. Res. Cancer Res 2010, 180, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mita, AC; Takimoto, CH; Mita, M; Tolcher, A; Sankhala, K; Sarantopoulos, J; Valdivieso, M; Wood, L; Rasmussen, E; Sun, YN; et al. Phase 1 study of AMG 386, a selective angiopoietin 1/2-neutralizing peptibody, in combination with chemotherapy in adults with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res 2010, 16, 3044–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, SI; Pietras, K. ALK1 as an emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer. Blood 2011, 117, 6999–7006. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Schneider, V. The use of vascular biomarkers and imaging studies in the early clinical development of anti-tumor agents targeting angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med 2006, 260, 517–529. [Google Scholar]
- Jubb, AM; Hurwitz, HI; Bai, W; Holmgren, EB; Tobin, P; Guerrero, AS; Kabbinavar, F; Holden, SN; Novotny, WF; Frantz, GD; Hillan, KJ; Koeppen, H. Impact of vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression, thrombospondin-2 expression, and microvessel density on the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2006, 24, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sessa, C; Guibal, A; Del Conte, G; Ruegg, C. Biomarkers of angiogenesis for the development of antiangiogenic therapies in oncology: tools or decorations? Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol 2008, 5, 378–391. [Google Scholar]
- Wedam, SB; Low, JA; Yang, SX; Chow, CK; Choyke, P; Danforth, D; Hewitt, SM; Berman, A; Steinberg, SM; Liewehr, DJ; et al. Antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of bevacizumab in patients with inflammatory and locally advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2006, 24, 769–777. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Alfa, GK; Schwartz, L; Ricci, S; Amadori, D; Santoro, A; Figer, A; De Greve, J; Douillard, JY; Lathia, C; Schwartz, B; et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol 2006, 24, 4293–4300. [Google Scholar]
- Antonescu, CR; Yoshida, A; Guo, T; Chang, NE; Zhang, L; Agaram, NP; Qin, LX; Brennan, MF; Singer, S; Maki, RG. KDR activating mutations in human angiosarcomas are sensitive to specific kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 7175–7179. [Google Scholar]
- Pircher, A; Ploner, F; Popper, H; Hilbe, W. Rationale of a relaunch of gefitinib in Caucasian non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2010, 69, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, BP; Radovich, M; Miller, KD. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor genetic variability in cancer. Clin. Cancer. Res 2009, 15, 5297–5302. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, BP; Wang, M; Radovich, M; Sledge, GW; Badve, S; Thor, A; Flockhart, DA; Hancock, B; Davidson, N; Gralow, J; et al. ECOG 2100. Association of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 genetic polymorphisms with outcome in a trial of paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel plus bevacizumab in advanced breast cancer: ECOG 2100. J. Clin. Oncol 2008, 26, 4672–4678. [Google Scholar]
- Rini, BI; Cohen, DP; Lu, D; Chen, I; Hariharan, S; Gore, ME; Figlin, RA; Baum, MS; Motzer, RJ. Hypertension (HTN) as a Biomarker of Efficacy in Patients (pts) with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC) Treated with Sunitinib, ACSO 2010 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium Abstract No. 312; American Society of Clinical Oncology, San Francisco, CA, USA; 2010.
- Dahlberg, SE; Sandler, AB; Brahmer, JR; Schiller, JH; Johnson, DH. Clinical course of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients experiencing hypertension during treatment with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel on ECOG 4599. J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Maitland, ML; Bakris, GL; Black, HR; Chen, HX; Durand, JB; Elliott, WJ; Ivy, SP; Leier, CV; Lindenfeld, J; Liu, G; et al. Cardiovascular Toxicities Panel, Convened by the Angiogenesis Task Force of the National Cancer Institute Investigational Drug Steering Committee. Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 2010, 102, 596–604. [Google Scholar]
- Ebos, JM; Lee, CR; Kerbel, RS. Tumor and host-mediated pathways of resistance and disease progression in response to antiangiogenic therapy. Clin. Cancer. Res 2009, 15, 5020–5025. [Google Scholar]
- Cascone, T; Herynk, MH; Xu, L; Du, Z; Kadara, H; Nilsson, MB; Oborn, CJ; Park, YY; Erez, B; Jacoby, JJ; et al. Upregulated stromal EGFR and vascular remodeling in mouse xenograft models of angiogenesis inhibitor-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Invest 2011, 121, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, LM; Hicklin, DJ. Pathways mediating resistance to vascular endothelial growth factortargeted therapy. Clin. Cancer. Res 2008, 14, 6371–6375. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, F; Wu, X; Malik, AK; Zhong, C; Baldwin, ME; Schanz, S; Fuh, G; Gerber, HP; Ferrara, N. Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nat. Biotechnol 2007, 25, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, F; Zhong, C; Wu, X; Yu, L; Ferrara, N. Role of myeloid cells in tumor angiogenesis and growth. Trends Cell. Biol 2008, 18, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mollay, C; Wechselberger, C; Mignogna, G; Negri, L; Melchiorri, P; Barra, D; Kreil, G. Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1999, 374, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, F; Wu, X; Qu, X; Kowanetz, M; Yu, L; Tan, M; Meng, YG; Ferrara, N. G-CSFinitiated myeloid cell mobilization and angiogenesis mediate tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF therapy in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6742–6747. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, F; Wu, X; Zhong, C; Yu, L; Liang, XH; Yao, J; Blanchard, D; Bais, C; Peale, FV; van Bruggen, N; et al. Bv8 regulates myeloid-cell-dependent tumour angiogenesis. Nature 2007, 450, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Jubb, AM; Miller, KD; Rugo, HS; Harris, AL; Chen, D; Reimann, JD; Cobleigh, MA; Schmidt, M; Langmuir, VK; Hillan, KJ; Chen, DS; Koeppen, H. Impact of exploratory biomarkers on the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer. Res 2011, 17, 372–381. [Google Scholar]
- Dowlati, A; Gray, R; Sandler, AB; Schiller, JH; Johnson, DH. Cell adhesion molecules, vascular endothelial growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab—an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Clin. Cancer. Res 2008, 14, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Kopetz, S; Hoff, PM; Morris, JS; Wolff, RA; Eng, C; Glover, KY; Adinin, R; Overman, MJ; Valero, V; Wen, S; et al. Phase II trial of infusional fluorouracil, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: efficacy and circulating angiogenic biomarkers associated with therapeutic resistance. J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan, EO; Lin, HY; Kim, ES; Yan, S; Du, DZ; McKee, KS; Tran, HT; Lee, JJ; Ryan, AJ; Langmuir, P; et al. Distinct patterns of cytokine and angiogenic factor modulation and markers of benefit for vandetanib and/or chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Norden-Zfoni, A; Desai, J; Manola, J; Beaudry, P; Force, J; Maki, R; Folkman, J; Bello, C; Baum, C; DePrimo, SE; Shalinsky, DR; Demetri, GD; Heymach, JV. Blood-based biomarkers of SU11248 activity and clinical outcome in patients with metastatic imatinibresistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Clin. Cancer. Res 2007, 13, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolinakos, PG; Altorki, N; Yankelevitz, D; Tran, HT; Yan, S; Rajagopalan, D; Bordogna, W; Ottesen, LH; Heymach, JV. Plasma cytokine and angiogenic factor profiling identifies markers associated with tumor shrinkage in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with pazopanib. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, P; Burlini, A; Pruneri, G; Goldhirsch, A; Martinelli, G; Bertolini, F. Resting and activated endothelial cells are increased in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Blood 2001, 97, 3658–3661. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, P; Calleri, A; Cassi, C; Gobbi, A; Capillo, M; Pruneri, G; Martinelli, G; Bertolini, F. Circulating endothelial cells as a novel marker of angiogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2003, 522, 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Goon, PK; Lip, GY; Stonelake, PS; Blann, AD. Circulating endothelial cells and circulating progenitor cells in breast cancer: relationship to endothelial damage/dysfunction/apoptosis, clinicopathologic factors, and the Nottingham Prognostic Index. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 771–779. [Google Scholar]
- Farace, F; Massard, C; Borghi, E; Bidart, JM; Soria, JC. Vascular disrupting therapy-induced mobilization of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Ann. Oncol 2007, 18, 1421–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Ronzoni, M; Manzoni, M; Mariucci, S; Loupakis, F; Brugnatelli, S; Bencardino, K; Rovati, B; Tinelli, C; Falcone, A; Villa, E; Danova, M. Circulating endothelial cells and endothelial progenitors as predictive markers of clinical response to bevacizumab-based first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer patients. Ann. Oncol 2010, 21, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar]
- Dellapasqua, S; Bertolini, F; Bagnardi, V; Campagnoli, E; Scarano, E; Torrisi, R; Shaked, Y; Mancuso, P; Goldhirsch, A; Rocca, A; Pietri, E; Colleoni, M. Metronomic cyclophosphamide and capecitabine combined with bevacizumab in advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2008, 26, 4899–4905. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, F; Shaked, Y; Mancuso, P; Kerbel, RS. The multifaceted circulating endothelial cell in cancer: towards marker and target identification. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 835–845. [Google Scholar]
- Shaked, Y; Henke, E; Roodhart, JM; Mancuso, P; Langenberg, MH; Colleoni, M; Daenen, LG; Man, S; Xu, P; Emmenegger, U; et al. Rapid chemotherapy-induced acute endothelial progenitor cell mobilization: implications for antiangiogenic drugs as chemosensitizing agents. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, B; Thomas, AL; Drevs, J; Hennig, J; Buchert, M; Jivan, A; Horsfield, MA; Mross, K; Ball, HA; Lee, L; et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker for the pharmacological response of PTK787/ZK 222584, an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, in patients with advanced colorectal cancer and liver metastases: results from two phase I studies. J. Clin. Oncol 2003, 21, 3955–3964. [Google Scholar]
- Mross, K; Fasol, U; Frost, A; Benkelmann, R; Kuhlmann, J; Büchert, M; Unger, C; Blum, H; Hennig, J; Milenkova, TP; Tessier, J; Krebs, AD; Ryan, AJ; Fischer, R. DCE-MRI assessment of the effect of vandetanib on tumor vasculature in patients with advanced colorectal cancer and liver metastases: a randomized phase I study. J. Angiogenes. Res 2009, 1, 5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, JP; Jackson, A; Parker, GJ; Jayson, GC. DCE-MRI biomarkers in the clinical evaluation of antiangiogenic and vascular disrupting agents. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mross, K; Stefanic, M; Gmehling, D; Frost, A; Baas, F; Unger, C; Strecker, R; Henning, J; Gaschler-Markefski, B; Stopfer, P; et al. Phase I study of the angiogenesis inhibitor BIBF 1120 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer. Res 2010, 16, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Medinger, M; Mross, K; Fuxius, S; Hennig, J; Buechert, M; Thomas, A; Unger, C; Chen, BL; Lebwohl, D; Laurent, D. A phase IA, open-label, dose-escalating study of PTK787/ZK 222584 administered orally on a continuous dosing schedule in patients with advanced cancer. Anticancer Res 2010, 30, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Siegert, P; Medinger, M; Mross, K; Strecker, R; Zirrgiebel, U; Harder, J; Blum, H; Robertson, J; Jürgensmeier, JM; et al. Phase I clinical study of AZD2171, an oral vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol 2007, 25, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Müller-Driver, R; Wittig, C; Fuxius, S; Esser, N; Hugenschmidt, H; Konerding, MA; Allegrini, PR; Wood, J; Hennig, J; Unger, C; Marmé, D. PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, affects the anatomy of the tumor vascular bed and the functional vascular properties as detected by dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Hofmannm, I; Hugenschmidt, H; Wittig, C; Madjar, H; Müller, M; Wood, J; Martiny-Baron, G; Unger, C; Marmé, D. Effects of PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, on primary tumor, metastasis, vessel density, and blood flow in a murine renal cell carcinoma model. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 4819–4824. [Google Scholar]
- Tofts, PS. Modeling tracer kinetics in dynamic Gd-DTPA MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Medinger, M; Esser, N; Soltau, J; Lehmann, KM; Konerding, MA; Wolloscheck, T; Ryan, AJ; Drevs, J. Antitumor effect of the vascular-disrupting agent ZD6126 in a murine renal cell carcinoma model. Int. J. Oncol 2011, 38, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Mross, K; Drevs, J; Müller, M; Medinger, M; Marmé, D; Hennig, J; Morgan, B; Lebwohl, D; Masson, E; Ho, YY; Günther, C; Laurent, D; Unger, C. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of PTK/ZK, a multiple VEGF receptor inhibitor, in patients with liver metastases from solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Soltau, J; Drevs, J. Mode of action and clinical impact of VEGF signaling inhibitors. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther 2009, 9, 649–662. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, RJ; Rajan, A; Force, J; Lopez-Chavez, A; Keen, C; Cao, L; Yu, Y; Choyke, P; Turkbey, B; Raffeld, M; et al. Evaluation of KRAS mutations, angiogenic biomarkers, and DCE-MRI in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer receiving sorafenib. Clin. Cancer. Res 2011, 17, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Maitland, ML; Kasza, KE; Karrison, T; Moshier, K; Sit, L; Black, HR; Undevia, SD; Stadler, WM; Elliott, WJ; Ratain, MJ. Ambulatory monitoring detects sorafenib-induced blood pressure elevations on the first day of treatment. Clin. Cancer Res 2009, 15, 6250–6257. [Google Scholar]
- Wedge, SR; Kendrew, J; Hennequin, LF; Valentine, PJ; Barry, ST; Brave, SR; Smith, NR; James, NH; Dukes, M; Curwen, JO; et al. AZD2171: a highly potent, orally bioavailable, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 4389–4400. [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler, W; Mesters, R; Heuser, M; Ehninger, G; Berdel, WE; Zirrgiebel, U; Robertson, JD; Puchalski, TA; Collins, B; Jürgensmeier, JM; Serve, H. An open-label, Phase I study of cediranib (RECENTIN) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res 2010, 34, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg, MH; van Herpen, CM; De Bono, J; Schellens, JH; Unger, C; Hoekman, K; Blum, HE; Fiedler, W; Drevs, J; Le Maulf, F; Fielding, A; Robertson, J; Voest, EE. Effective strategies for management of hypertension after vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibition therapy: results from a phase II randomized, factorial, double-blind study of Cediranib in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol 2009, 27, 6152–6159. [Google Scholar]
- Motzer, RJ; Hutson, TE; Tomczak, P; Michaelson, MD; Bukowski, RM; Rixe, O; Oudard, S; Negrier, S; Szczylik, C; Kim, ST; et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renalcell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med 2007, 356, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, E; Dahan, L; Raoul, JL; Bang, YJ; Borbath, I; Lombard-Bohas, C; Valle, J; Metrakos, P; Smith, D; Vinik, A; et al. Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 501–513. [Google Scholar]
- Demetri, GD; van Oosterom, AT; Garrett, CR; Blackstein, ME; Shah, MH; Verweij, J; McArthur, G; Judson, IR; Heinrich, MC; Morgan, JA; et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Gracia, JL; Prior, C; Guillén-Grima, F; Segura, V; Gonzalez, A; Panizo, A; Melero, I; Grande-Pulido, E; Gurpide, A; Gil-Bazo, I; Calvo, A. Identification of TNF-alpha and MMP-9 as potential baseline predictive serum markers of sunitinib activity in patients with renal cell carcinoma using a human cytokine array. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Farace, F; Gross-Goupil, M; Tournay, E; Taylor, M; Vimond, N; Jacques, N; Billiot, F; Mauguen, A; Hill, C; Escudier, B. Levels of circulating CD45(dim)CD34(+)VEGFR2(+) progenitor cells correlate with outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Paule, B; Bastien, L; Deslandes, E; Cussenot, O; Podgorniak, MP; Allory, Y; Naïmi, B; Porcher, R; de La Taille, A; Menashi, S; Calvo, F; Mourah, S. Soluble isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor are predictors of response to sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinomas. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10715. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, AX; Sahani, DV; Duda, DG; di Tomaso, E; Ancukiewicz, M; Catalano, OA; Sindhwani, V; Blaszkowsky, LS; Yoon, SS; Lahdenranta, J; et al. Efficacy, safety, and potential biomarkers of sunitinib monotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol 2009, 27, 3027–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Presta, LG; Chen, H; O’Connor, SJ; Chisholm, V; Meng, YG; Krummen, L; Winkler, M; Ferrara, N. Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other disorders. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 4593–4599. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, A; Gray, R; Perry, MC; Brahmer, J; Schiller, JH; Dowlati, A; Lilenbaum, R; Johnson, DH. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 2006, 355, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K; Wang, M; Gralow, J; Dickler, M; Cobleigh, M; Perez, EA; Shenkier, T; Cella, D; Davidson, NE. Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 2007, 357, 2666–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Jubb, AM; Harris, AL. Biomarkers to predict the clinical efficacy of bevacizumab in cancer. Lancet Oncol 2010, 11, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Österlund, P; Soveri, LM; Isoniemi, H; Poussa, T; Alanko, T; Bono, P. Hypertension and overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Rini, BI; Halabi, S; Rosenberg, JE; Stadler, WM; Vaena, DA; Archer, L; Atkins, JN; Picus, J; Czaykowski, P; Dutcher, J; Small, EJ. Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa versus interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results of CALGB 90206. J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz, H; Douglas, PS; Middleton, JP; Sledge, GW; Johnson, DH; Reardon, DA; Chen, D; Rosen, O. Analysis of early hypertension (HTN) and clinical outcome with bevacizumab (BV). J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Drevs, J; Zirrgiebel, U; Schmidt-Gersbach, CI; Mross, K; Medinger, M; Lee, L; Pinheiro, J; Wood, J; Thomas, AL; Unger, C; Henry, A; Steward, WP; Laurent, D; Lebwohl, D; Dugan, M; Marmé, D. Soluble markers for the assessment of biological activity with PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer from two phase I trials. Ann. Oncol 2005, 16, 558–565. [Google Scholar]
- Loupakis, F; Cremolini, C; Fioravanti, A; Orlandi, P; Salvatore, L; Masi, G; Di Desidero, T; Canu, B; Schirripa, M; Frumento, P; et al. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacogenetic angiogenesis-related markers of first-line FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab schedule in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Baar, J; Silverman, P; Lyons, J; Fu, P; Abdul-Karim, F; Ziats, N; Wasman, J; Hartman, P; Jesberger, J; Dumadag, L; et al. A vasculature-targeting regimen of preoperative docetaxel with or without bevacizumab for locally advanced breast cancer: impact on angiogenic biomarkers. Clin. Cancer Res 2009, 15, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar]

© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pircher, A.; Hilbe, W.; Heidegger, I.; Drevs, J.; Tichelli, A.; Medinger, M. Biomarkers in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 7077-7099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12107077
Pircher A, Hilbe W, Heidegger I, Drevs J, Tichelli A, Medinger M. Biomarkers in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(10):7077-7099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12107077
Chicago/Turabian StylePircher, Andreas, Wolfgang Hilbe, Isabel Heidegger, Joachim Drevs, André Tichelli, and Michael Medinger. 2011. "Biomarkers in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 10: 7077-7099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12107077
APA StylePircher, A., Hilbe, W., Heidegger, I., Drevs, J., Tichelli, A., & Medinger, M. (2011). Biomarkers in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(10), 7077-7099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12107077



