Potential Antibacterial Activity of Carvacrol-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Nanoparticles against Microbial Biofilm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
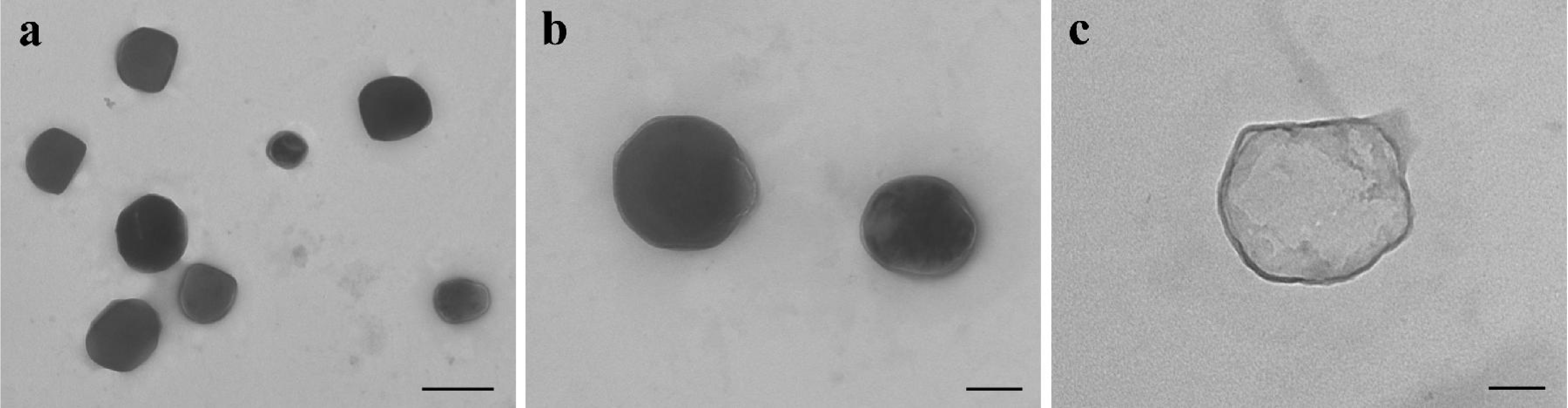
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Car.-Nps
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release
2.3. Biofilm Growth and Rheological Tests
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Nanocapsules
3.3. Characterization of Car.-Nps
3.4. Preparation and Analysis of Car.-Nps by T.E.M
3.5. Determination of Car. Loading
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release
3.7. Biofilm Preparation
3.8. Rheological Tests
3.9. Data analysis and Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Lawrence, JR; Korber, DR; Hoyle, BD; Costerton, JW; Caldwell, DE. Optical sectioning of microbial biofilms. J. Bacteriol 1991, 173, 6558–6567. [Google Scholar]
- De Beer, D; Stoodley, P; Roe, F; Lewandowski, Z. Effects of biofilm structures on oxygen distribution and mass transport. Biotechnol. Bioeng 1994, 43, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, W; Veeh, R; Shirtliff, M; Pasmore, M; Post, C; Ehrlich, G. The application of biofilm science to the study and control of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Invest 2003, 112, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy, LR; Burns, JL; Lory, S; Lewis, K. Emergence of pseudomonas aeruginosa strains producing high levels of persister cells in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Bacteriol 2010, 192, 6191–6199. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnsholt, T; Jensen, PØ; Fiandaca, MJ; Pedersen, J; Hansen, CR; Andersen, CB; Pressler, T; Givskov, M; Høiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in the Respiratory Tract of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol 2009, 44, 547–558. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, AR; Leid, JG; Hunsaker, D. Bacterial biofilms on the sinus mucosa of human subjects with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Catalanotti, P; Lanza, M; Del Prete, A; Lucido, M; Catania, MR; Gallè, F; Boggia, D; Perfetto, B; Rossano, F. Slime-producing Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus in acute bacterial conjunctivitis in soft contact lens wearers. New Microbiol 2005, 28, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Passerini, L; Lam, K; Costerton, JW; King, EG. Biofilms on indwelling vascular catheters. Crit. Care Med 1992, 20, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Pople, IK; Bayston, R; Hayward, RD. Infection of cerebrospinal fluid shunts in infants: a study of etiological factors. J. Neurosurg 1992, 77, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Okajima, Y; Kobayakawa, S; Tsuji, A; Tochikubo, T. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis on intraocular lens material. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 2006, 47, 2971–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Gristina, AG; Oga, M; Webb, LX; Hobgood, CD. Adherent bacterial colonization in the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis. Science 1985, 228, 990–993. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, JL; Patel, R. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N. Engl. J. Med 2009, 361, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, SM; Foster, JM; Emerson, J; Burns, JL. Clinically feasible biofilm susceptibility assay for isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol 2004, 42, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Høiby, N; Bjarnsholt, T; Givskov, M; Molin, S; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar]
- Keren, I; Kaldalu, N; Spoering, A; Wang, Y; Lewis, K. Persister cells and tolerance to antimicrobials. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2004, 230, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Balaban, NQ; Merrin, J; Chait, R; Kowalik, L; Leibler, S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science 2004, 305, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Driffield, K; Miller, K; Bostock, M; O’Neill, AJ; Chopra, I. Increased mutability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2008, 61, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Bagge, N; Hentzer, M; Andersen, JB; Ciofu, O; Givskov, M; Hoiby, N. Dynamics and spatial distribution of β-lactamase expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2004, 48, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, RJW; Skandamis, PN; Coote, PJ; Nychas, GJE. A study of the minimum inhibitory concentration and mode of action of oregano essential oil, thymol and carvacrol. J. Appl. Microbiol 2001, 91, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Nostro, A; Sudano Roccaro, A; Bisignano, G; Marino, A; Cannatelli, MA; Pizzimenti, FC; Cioni, PL; Procopio, F; Blanco, AR. Effects of oregano, carvacrol and thymol on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. J. Med. Microbiol 2007, 56, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Nostro, A; Marino, A; Blanco, AR; Cellini, L; Di Giulio, M; Pizzimenti, F; Sudano Roccaro, A; Bisognano, G. In vitro activity of carvacrol against staphylococcal preformed biofilm by liquid and vapour contact. J. Med. Microbiol 2009, 58, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, HM; Sohn, M; Al-Ghananeem, A; DeLuca, PP. Materials for pharmaceutical dosage forms: Molecular pharmaceutics and controlled release drug delivery aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2010, 11, 3298–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Suk, JS; Lai, SK; Wang, YY; Ensign, LM; Zeitlin, PL; Boyle, MP; Hanes, J. The penetration of fresh undiluted sputum expectorated by cystic fibrosis patients by non-adhesive polymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, BC; Dawson, M; Lai, SK; Wang, YY; Suk, JS; Yang, M; Zeitlin, P; Boyle, MP; Fu, J; Hanes, J. Biodegradable polymer nanoparticles that rapidly penetrate the human mucus barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19268–19273. [Google Scholar]
- Meers, P; Neville, M; Malinin, V; Scotto, AW; Sardaryan, G; Kurumunda, R; Mackinson, GJ; Fisher, S; Perkins, WR. Biofilm penetration, triggered release and in vivo activity of inhaled liposomal amikacin in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth 2008, 61, 859–868. [Google Scholar]
- Cheow, WS; Chang, MW; Hadinoto, K. Antibacterial efficacy of inhalable levofloxacin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles against E. coli biofilm cells: The effect of antibiotic release profile. Pharm. Res 2010, 27, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Keawchaoon, L; Yoksan, R. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release study of carvacrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 84, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J; Shive, M. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 1997, 28, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Towler, BW; Rupp, CJ; Cunningham, AB; Stoodley, P. Viscoelastic properties of a mixed culture biofilm from rheometer creep analysis. Biofouling 2003, 19, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, SG; Wyllie, SG; Markham, JL; Leach, D. The role of structure and molecular properties of terpenoids in determining their antimicrobial activity. Flavour Fragr. J 1999, 14, 322–332. [Google Scholar]
- Stoodley, P; Lewandowski, Z; Boyle, JD; Lappin-Scott, HM. Structural deformation of bacterial biofilms caused by short-term fluctuations in fluid shear: an in situ investigation of biofilm rheology. Biotechnol. Bioeng 1999, 65, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Stoodley, P; Cargo, R; Rupp, CJ; Wilson, S; Klapper, I. Biofilm material properties as related to shear- induced deformation and detachment phenomena. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2002, 29, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Korstgens, V; Flemming, HC; Wingender, J; Borchard, W. Uniaxial compression measurement device for investigation of the mechanical stability of biofilms. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, I; Rupp, CJ; Cargo, B; Purvedorj, R; Stoodley, P. Viscoelastic fluid description of bacterial biofilm material properties. Biotechnol. Bioeng 2002, 80, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, T; Winston, M; Rupp, CJ; Klapper, I; Stoodley, P. Commonality of elastic relaxation times in biofilms. Phys. Rev. Lett 2004, 93, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, AM; Winston, M; Rupp, CJ; Stoodley, P. Rheology of biofilms formed from the dental plaque pathogen Streptococcus mutans. Biofilms 2004, 1, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, CJ; Fux, CA; Stoodley, P. Viscoelasticity of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in response to fluid shear allows resistance to detachment and facilitates rolling migration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2005, 71, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Towler, BW; Cunningham, A; Stoodley, P; McKittrick, L. Amodel of fluid–biofilm interaction using a Burger material law. Biotechnol. Bioeng 2007, 96, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Yarwood, JM; Paquette, KM; Tikh, IB; Volper, EM; Greenberg, EP. Generation of virulence factor variants in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Bacteriol 2007, 189, 7961–7967. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, HA; Hutton, JF; Walters, K. Linear viscoelasticity. In An Introduction to Rheology, 1st Ed; Barnes, HA, Hutton, JF, Walters, K, Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V; Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 3, pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, K. Persister cells. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 2010, 64, 357–372. [Google Scholar]
- Dalleau, S; Cateau, E; Bergès, T; Berjeaud, JM; Imbert, C. In vitro activity of terpenes against Candida biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Houari, A; Picard, J; Habarou, H; Galas, L; Vaudry, H; Heim, V; Di Martino, P. Rheology of biofilms formed at the surface of NF membranes in a drinking water production unit. Biofouling 2008, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Fessi, H; Puisieux, F; Devissaguet, JP; Ammoury, N; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer depositino following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, J; Nakada, Y; Sakurai, K; Nakamura, T; Takahashi, Y. Preparation of nanoparticles consisted of poly(l-lactide)–poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(L-lactide) and their evaluation in vitro. Int. J. Pharm 1999, 185, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Verger, MLL; Fluckiger, L; Kim, YI; Hoffman, M; Maincent, P. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles containing an antihypertensive agent. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 1998, 46, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stefano, A; D’Aurizio, E; Trubiani, O; Grande, R; Di Campli, E; Di Giulio, M; Di Bartolomeo, S; Sozio, P; Iannitelli, A; Nostro, A; Cellini, L. Viscoelastic properties of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis mono-microbial biofilms. Microb. Biotechnol 2009, 2, 634–641. [Google Scholar]


| Particle size (nm) | Polydispersity | Zeta potential (mV) | DL% | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 209.8 ± 7.2 | 0.260 ± 0.013 | −18.99 ± 3.01 | 21 | 26 |
| Sample | LVR (Pa) | η0 (Pa s) | Je0 (Pa−1) | λ (min) | G′ (Pa)1 | G″ (Pa)1 | τy (Pa)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bio | 1–10 | (1.1 ± 0.2) × 106 | (1.1 ± 0.3) × 10 −3 | 21.9 ± 6.2 | (1.3 ± 0.3) × 103 | (1.3 ± 0.5) × 102 | (2.3 ± 0.3) × 102 |
| Bio + Car. | 1–10 | (6.9 ± 0.6) × 105a | (2.5 ± 0.5) × 10 −3 | 21.6 ± 4.4 | (9.3 ± 1.5) × 102 | (0.9 ± 0.1) × 102 | (1.5 ± 0.5) × 102 |
| Bio + Car.-Np | 1–10 | (5.5 ± 1.7) × 105a | (7.9 ± 2.8) × 10 −3a,b | 25.5 ± 7.3 | (6.1 ± 1.2) × 102a | (0.6 ± 0.1) × 102a | (1.3 ± 0.6) × 102 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannitelli, A.; Grande, R.; Stefano, A.D.; Giulio, M.D.; Sozio, P.; Bessa, L.J.; Laserra, S.; Paolini, C.; Protasi, F.; Cellini, L. Potential Antibacterial Activity of Carvacrol-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Nanoparticles against Microbial Biofilm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5039-5051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12085039
Iannitelli A, Grande R, Stefano AD, Giulio MD, Sozio P, Bessa LJ, Laserra S, Paolini C, Protasi F, Cellini L. Potential Antibacterial Activity of Carvacrol-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Nanoparticles against Microbial Biofilm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(8):5039-5051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12085039
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannitelli, Antonio, Rossella Grande, Antonio Di Stefano, Mara Di Giulio, Piera Sozio, Lucinda Janete Bessa, Sara Laserra, Cecilia Paolini, Feliciano Protasi, and Luigina Cellini. 2011. "Potential Antibacterial Activity of Carvacrol-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Nanoparticles against Microbial Biofilm" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 8: 5039-5051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12085039
APA StyleIannitelli, A., Grande, R., Stefano, A. D., Giulio, M. D., Sozio, P., Bessa, L. J., Laserra, S., Paolini, C., Protasi, F., & Cellini, L. (2011). Potential Antibacterial Activity of Carvacrol-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Nanoparticles against Microbial Biofilm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(8), 5039-5051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12085039








