Maternal Phylogeny of a Newly-Found Yak Population in China
Abstract
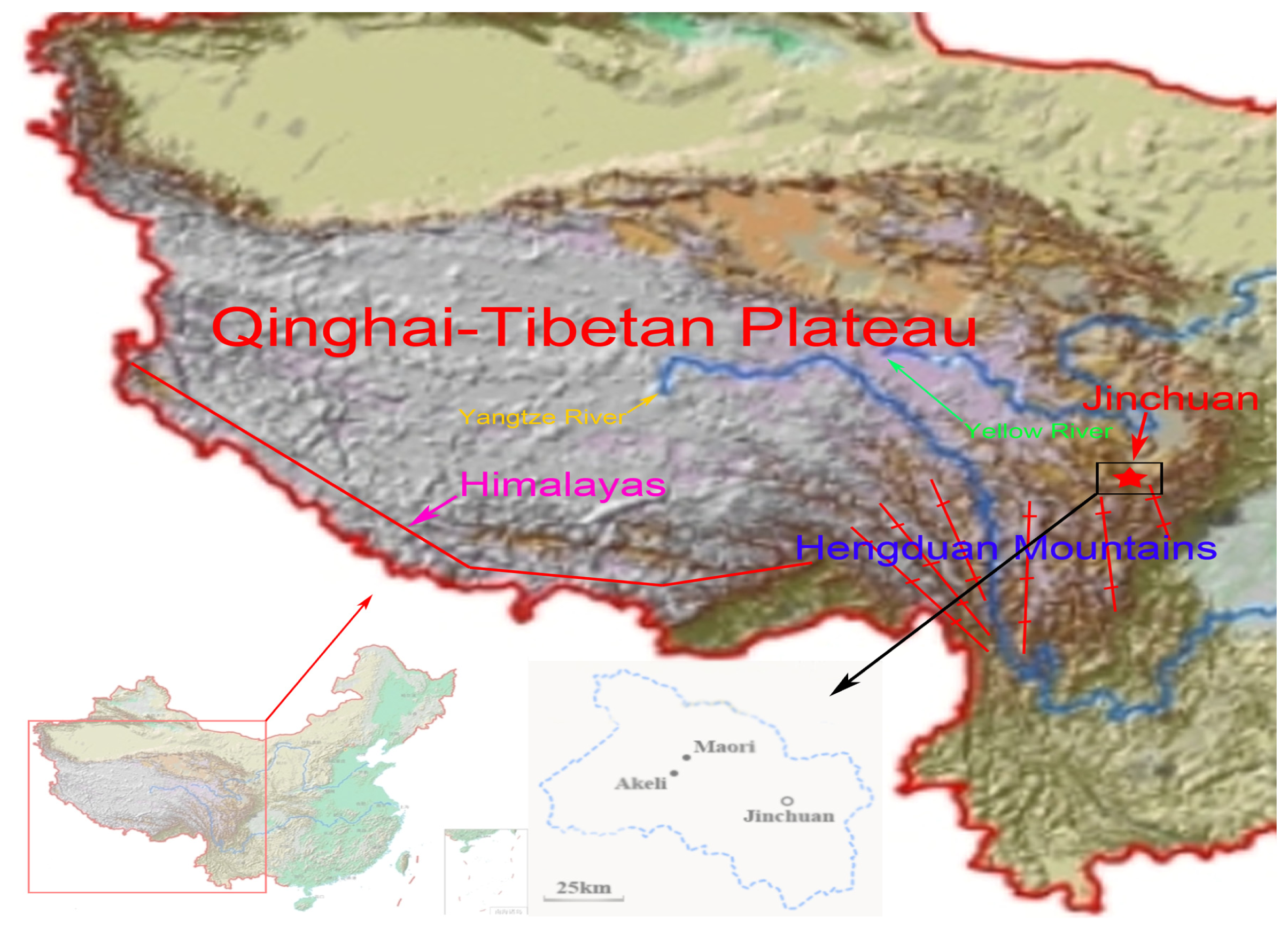
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Nucleotide and Haplotype Diversity
2.2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2.2.1. Phylogeny Inferred from mtDNA Control Region
2.2.2.2. Phylogeny Inferred from Coding Regions of Mitochondrial Genomic Sequences
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
3.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
3.3. Nucleotide and Haplotype Diversity
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Miller, D.J.; Harris, R.B.; Cai, C.Q. Wild yak and Their Conservation in the Tibetan Plateau. Proceedings of the First International Congress on Yak, Lanzhou, China, 1–6 August 1994; Southwest University for Nationalities: Chengdu, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, G.; Han, J.L.; Long, R.J. The Yak, 2nd ed; Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Bangkok, Thailand, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Wu, C. Complete sequence of the yak (Bos grunniens) mitochondrial genome and its evolutionary relationship with other ruminants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol 2007, 42, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.X.; Li, L. Study on the Relation between Yak Performance and Ecological Protection. Proceedings of the Fourth International Congress on Yak, Chengdu, China, 9–26 September 2004.
- Luikart, G.; Gielly, L.; Excoffier, L.; Vigne, J.D.; Bouvet, J.; Taberlet, P. Multiple maternal origins and weak phylogeographic structure in domestic goats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5927–5932. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrosa, S.; Uzun, M.; Arranz, J.J.; Gutierrez-Gil, B.; San Primitivo, F.; Bayon, Y. Evidence of three maternal lineages in Near Eastern sheep supporting multiple domestication events. Proc. Biol. Sci 2005, 272, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Achilli, A.; Bonfiglio, S.; Olivieri, A.; Malusa, A.; Pala, M.; Kashani, B.H.; Perego, U.A.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Liotta, L.; Semino, O.; et al. The multifaceted origin of taurine cattle reflected by the mitochondrial genome. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5753. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Lei, C. Matrilineal genetic inter-introgression of Bos taurus and Bos indicus in China. Livest. Sci 2010, 128, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lin, B.Z.; Baig, M.; Mitra, B.; Lopes, R.J.; Santos, A.M.; Magee, D.A.; Azevedo, M.; Tarroso, P.; Sasazaki, S.; et al. Zebu cattle are an exclusive legacy of the South Asia neolithic. Mol. Biol. Evol 2010, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.J.; Liu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, X.W.; Yao, Y.G. Genetic diversity and origin of Chinese cattle revealed by mtDNA D-loop sequence variation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol 2006, 38, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.C.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.P. Polymorphism in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of yak (Bos grunniens). Biochem. Genet 2002, 40, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Yao, Y.G. Mitochondrial DNA sequence diversity and origin of Chinese domestic yak. Anim. Genet 2007, 38, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Savolainen, P.; Su, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J. Origin of mitochondrial DNA diversity of domestic yaks. BMC Evol. Biol 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Su, J.; Yonezawa, T.; Yu, Y.; Guo, S.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Vila, C.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Phylogeographical analyses of domestic and wild yaks based on mitochondrial DNA: New data and reappraisal. J. Biogeogr 2010, 37, 2332–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.P.; Qiu, H. Genetic diversity and divergence in Chinese yak (Bos grunniens) populations inferred from blood protein electrophoresis. Biochem. Genet 1997, 35, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X.; Chen, W.S.; Xue, M.; Wang, Z.G.; Chang, H.; Han, X.; Liao, X.J.; Wang, D.L. Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of Chinese yak breeds (Bos grunniens) using microsatellite markers. J. Genet. Genomics 2008, 35, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Eperon, I.C.; Sanger, F.; Young, I.G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J. Mol. Biol 1982, 156, 683–717. [Google Scholar]
- Arnason, U.; Gullberg, A.; Widegren, B. The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial DNA of the fin whale, Balaenoptera physalus. J. Mol. Evol 1991, 33, 556–568. [Google Scholar]
- Arnason, U.; Johnsson, E. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the harbor seal, Phoca vitulina. J. Mol. Evol 1992, 34, 493–505. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Arnason, U. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the horse, Equus caballus: Extensive heteroplasmy of the control region. Gene 1994, 148, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Gullberg, A.; Arnason, U. The complete mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of the donkey and mtDNA comparisons among four closely related mammalian species-pairs. J. Mol. Evol 1996, 43, 438–446. [Google Scholar]
- Gissi, C.; Gullberg, A.; Arnason, U. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus. Genomics 1998, 50, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hiendleder, S.; Lewalski, H.; Wassmuth, R.; Janke, A. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the domestic sheep (Ovis aries) and comparison with the other major ovine haplotype. J. Mol. Evol 1998, 47, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Chang, L.C.; Cheng, I.C.; Mao, S.J.; Huang, M.C. Complete nucleotide sequence of pig (Sus scrofa) mitochondrial genome and dating evolutionary divergence within Artiodactyla. Gene 1999, 236, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Nishibori, M.; Hanazono, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsudzuki, M.; Yasue, H. Complete nucleotide sequence of mitochondrial DNA in White Leghorn and White Plymouth Rock chickens. Anim. Sci. J 2003, 74, 437–439. [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen, P.; Zhang, Y.P.; Luo, J.; Lundeberg, J.; Leitner, T. Genetic evidence for an East Asian origin of domestic dogs. Science 2002, 298, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, A.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, C. Performance of criteria for selecting evolutionary models in phylogenetics: A comprehensive study based on simulated datasets. BMC Evol. Biol 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar]






| Breed or population | N | H | Hd ± SD | Pi ± SD | A | B | Nc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinchuan | 23 | 13 | 0.925 ± 0.035 | 0.02035 ± 0.00225 | 3 | ||
| Tianzhu | 21 | 9 | 0.829 ± 0.066 | 0.00997 ± 0.00281 | 7 | 0.333333 | 4 |
| Gannan | 7 | 5 | 0.905 ± 0.103 | 0.01857 ± 0.00529 | 3 | 0.428571 | 7 |
| Datong | 31 | 19 | 0.942 ± 0.030 | 0.01582 ± 0.00271 | 13 | 0.419355 | 2 |
| Huanhu | 61 | 18 | 0.800 ± 0.048 | 0.01218 ± 0.00206 | 9 | 0.147541 | 5 |
| Plateau | 88 | 30 | 0.911 ± 0.017 | 0.01393 ± 0.00167 | 48 | 0.545455 | 14 |
| Jiali | 42 | 21 | 0.912 ± 0.031 | 0.01593 ± 0.00222 | 21 | 0.500000 | 1 |
| Sibu | 12 | 8 | 0.909 ± 0.065 | 0.01923 ± 0.00288 | 4 | 0.333333 | 2 |
| Pali | 40 | 19 | 0.933 ± 0.021 | 0.01733 ± 0.00220 | 19 | 0.475000 | 4 |
| Maiwa | 23 | 14 | 0.925 ± 0.041 | 0.01856 ± 0.00280 | 12 | 0.521739 | 6 |
| Jiulong | 12 | 8 | 0.924 ± 0.057 | 0.01403 ± 0.00477 | 5 | 0.416667 | 2 |
| Bazhou | 33 | 7 | 0.822 ± 0.035 | 0.00579 ± 0.00039 | 21 | 0.636364 | 0 |
| Zhongdian | 9 | 7 | 0.917 ± 0.092 | 0.02210 ± 0.00385 | 4 | 0.444444 | 1 |
| wild | 55 | 30 | 0.961 ± 0.012 | 0.02207 ± 0.00111 | 9 | 0.163636 | 23 |
| unclear | 6 | 3 | |||||
| Gansu unclear | 8 | ||||||
| Sichuan unclear | 5 | ||||||
| Total | 476 | 77 |
| Lineages | Clades | The haplotypes shared by Jinchuan and other yaks | The number of individuals from different populations harbored in the haplotypes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage I | A | H6 | 4JC, 1ZD, 7PL, 2HH, 7TZ, 1GL, 19P, 7BZ, 3SB, 11JL, 7DT, 3MW, 3JL, 6W, 2SU |
| H14, H18, H57 | 3JC, 6PL, 5HH, 19P, 4BZ, 7JL, 4DT, 9MW, 2JL, 4GU | ||
| B | H35 | 2JC, 1GL, 1P, 10BZ, 1JL | |
| Lineage II | C | H8 | 5JC, 3ZD, 6PL, 2HH, 1GL, 9P, 1SB, 2JL, 2DT, 2MW, 1GU |
| H5 | 1JC, 4W |
| PCR primer set | Primer name | Sequence(5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st pair | F1 | AAATGACGAAAGTGACCCTA |
| R1 | TAGGGCTCCGATTAGTGCGT | |
| F1F06 | AGAAAGTACCGCAAGGGA | |
| R1R06 | ATGAGCGATAGAGTGATTTGAC | |
| 2nd pair | F2 | CCTACGTGATCTGAGTTCAG |
| R2 | TGAGCCCATTGATGAGACAG | |
| F2F08 | CAAACATGGCTAATCCTCC | |
| R2R08 | GGAGTAATAGTACGGCGGTG | |
| F2F09 | AACCCACGAGCTACAGAA | |
| F2F10 | CATCCTAATCCTCGCCACT | |
| 3rd pair | F3 | TCTACTATTTGGAGCCTGGG |
| R3 | ACGAAATGTCAGTATCAGGC | |
| F3F30 | GAGCTATAATGTCAATCGGA | |
| R3R30 | TATTAAGAGGGCGGATAGAG | |
| F3F31 | TTTCAAGCCAACACCATAAC | |
| 4th pair | F4 | AAGCCCTTGACCCCTTACAG |
| R4 | TCGTGTAAAGGAAGGTGAGA | |
| F4F02 | TTTGACTTTTCCTCTATGTTTC | |
| R4R02 | GAGTATTAGGAAGTTTAGGGATC | |
| 5th pair | F5 | CAAACGGACCTAAAATCACT |
| R5 | GTGTATTGCTAGGAATAGGC | |
| F5F04 | AATCTTCCAACTACCCGCTCTA | |
| R5R04 | AGTTATTGTAACTGGGTGGTCT | |
| 6th pair | F6 | AGAAAACCCTACGAAACCAA |
| R6 | CTTTCATCGTTCCCTTGCGG | |
| F6F06 | CAGGCTCCAACAATCCAA | |
| R6R06 | ATCGGCTGTTGTAGGGTC | |
| F6F08 | GGGGATGCTTGGACTCAG | |
| F6F07 | TGTAAAGAGCCTCACCAGTA |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mipam, T.D.; Wen, Y.; Fu, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Ai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zou, D. Maternal Phylogeny of a Newly-Found Yak Population in China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11455-11470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911455
Mipam TD, Wen Y, Fu C, Li S, Zhao H, Ai Y, Li L, Zhang L, Zou D. Maternal Phylogeny of a Newly-Found Yak Population in China. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):11455-11470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911455
Chicago/Turabian StyleMipam, Tserang Donko, Yongli Wen, Changxiu Fu, Shanrong Li, Hongwen Zhao, Yi Ai, Lu Li, Lei Zhang, and Deqiang Zou. 2012. "Maternal Phylogeny of a Newly-Found Yak Population in China" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 11455-11470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911455
APA StyleMipam, T. D., Wen, Y., Fu, C., Li, S., Zhao, H., Ai, Y., Li, L., Zhang, L., & Zou, D. (2012). Maternal Phylogeny of a Newly-Found Yak Population in China. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(9), 11455-11470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911455




