The Role of Metallothionein in Oxidative Stress
Abstract
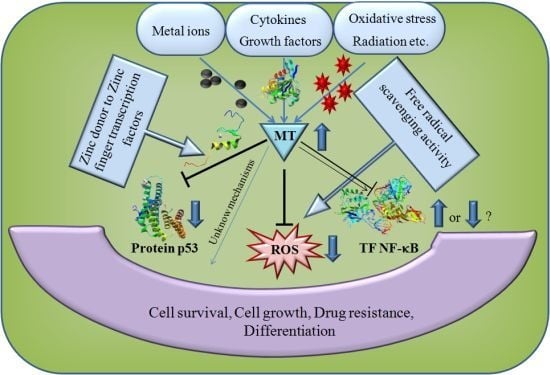
:1. Introduction
2. Metallothioneins
3. Zinc as Signaling Compound and Antioxidant
4. Zinc and MT
5. The Role of MT in Cancer and Apoptosis
6. Antioxidant Function of MT
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Oxygen free-radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine—Some problems and concepts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1986, 246, 501–514. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas, E. Biochemistry of oxygen-toxicity. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1989, 58, 79–110. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Telser, J. Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Mol. Cell. Biochem 2004, 266, 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Biasi, F.; Chiarpotto, E. Oxidative stress and cell signalling. Curr. Med. Chem 2004, 11, 1163–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B. Antioxidants in human health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr 1996, 16, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge, J.M.C.; Halliwell, B. Comments on review of free-radicals in biology and medicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med 1992, 12, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Niki, E. Free radicals in biology and medicine: Good, unexpected, and uninvited friends. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2010, 49, S2. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free-Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Clarendon Press: Gloucestershire, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, M.; Kim, S.J. Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and their functional correlations in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neural Transm 2012, 119, 891–910. [Google Scholar]
- Pourova, J.; Kottova, M.; Voprsalova, M.; Pour, M. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in normal physiological processes. Acta Physiol 2010, 198, 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Vasak, M. Advances in metallothionein structure and functions. J. Trace Elements Med Biol 2005, 19, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, G.; Krebs, B. Metallothioneins: Zinc, cadmium, mercury, and copper thiolates and selenolates mimicking protein active site features—Structural aspects and biological implications. Chem. Rev 2004, 104, 801–824. [Google Scholar]
- Coyle, P.; Philcox, J.C.; Carey, L.C.; Rofe, A.M. Metallothionein: The multipurpose protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2002, 59, 627–647. [Google Scholar]
- Margoshes, M.; Vallee, B.L. A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1957, 79, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar]
- Kagi, J.H.R.; Schaffer, A. Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 8509–8515. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Isart, N.; Vasak, M. Advances in the structure and chemistry of metallothioneins. J. Inorg. Biochem 2002, 88, 388–396. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.R.; Cousins, R.J. Metallothionein expression in animals: A physiological perspective on function. J. Nutr 2000, 130, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Diwan, B.A. Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2009, 238, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, D.M.; Cherian, M.G. Toxicological significance of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol 1991, 205, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kagi, J.H.R. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol 1991, 205, 613–626. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, C.F.; Savas, M.M.; Petering, D.H. Ligand substitution and sulfhydryl reactivity of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol 1991, 205, 401–414. [Google Scholar]
- Karin, M.; Cathala, G.; Nguyenhuu, M.C. Expression and regulation of a human metallothionein gene carried on an autonomously replicating shuttle vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 4040–4044. [Google Scholar]
- Enger, M.D.; Tesmer, J.G.; Travis, G.L.; Barham, S.S. Clonal variation of cadmium response in human-tumor cell-lines. Am. J. Phys 1986, 250, C256–C263. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Iszard, M.B.; Andrews, G.K.; Palmiter, R.D.; Klaassen, C.D. Transgenic mice that overexpress metallothionein-I are protected from cadmium lethality and hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 1995, 135, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, B.A.; Kelly, E.J.; Quaife, C.J.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Targeted disruption of metallothionein-I and metallothionein-II genes increases sensitivity to cadmium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 584–588. [Google Scholar]
- Petrlova, J.; Potesil, D.; Mikelova, R.; Blastik, O.; Adam, V.; Trnkova, L.; Jelen, F.; Prusa, R.; Kukacka, J.; Kizek, R. Attomole voltammetric determination of metallothionein. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5112–5119. [Google Scholar]
- Simpkins, C.O. Metallothionein in human disease. Cell. Mol. Biol 2000, 46, 465–488. [Google Scholar]
- Hamer, D.H. Metallothionein—An Overview. Mar. Environ. Res 1988, 24, 171–171. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, B.A.; Quaife, C.J.; Erickson, J.C.; Kelly, E.J.; Froelick, G.J.; Zambrowicz, B.P.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Metallothionein-III is expressed in neurons that sequester zinc in synaptic vesicles. J. Neurosci 1994, 14, 5844–5857. [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt, P.; Denizeau, F. Metallothionein in physiological and physiopathological processes. Drug Metab. Rev 1997, 29, 261–307. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, P.F.; Davison, B.L.; Stuart, G.W.; Wilkie, T.M.; Norstedt, G.; Palmiter, R.D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein-I and metallothionein-II genes. Mol. Cell. Biol 1984, 4, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt, P.; Seguin, C. Expression of the gene encoding metallothionein-3 in organs of the reproductive system. DNA Cell. Biol 1998, 17, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, Y.; Takio, K.; Titani, K.; Ihara, Y.; Tomonaga, M. The growth inhibitory factor that is deficient in the Alzheimers-disease brain is a 68-amino acid metallothionein-like protein. Neuron 1991, 7, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Quaife, C.J.; Findley, S.D.; Erickson, J.C.; Froelick, G.J.; Kelly, E.J.; Zambrowicz, B.P.; Palmiter, R.D. Induction of a new metallothionein isoform (Mt-Iv) occurs during differentiation of stratified squamous epithelia. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 7250–7259. [Google Scholar]
- Moleirinho, A.; Carneiro, J.; Matthiesen, R.; Silva, R.M.; Amorim, A.; Azevedo, L. Gains, losses and changes of function after gene duplication: Study of the metallothionein family. PLoS One 2011, 6, e18487. [Google Scholar]
- Vallee, B.L. The function of metallothionein. Neurochem. Int 1995, 27, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.P.; Ho, E. Zinc and its role in age-related inflammation and immune dysfunction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res 2012, 56, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and human health: An update. Arch. Toxicol 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.K.; Rahman, I. Environmental toxicity, redox signaling and lung inflammation: The role of glutathione. Mol. Aspects Med 2009, 30, 60–76. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, R.B.; Costello, L.C. The important role of the apoptotic effects of zinc in the development of cancers. J. Cell. Biochem 2009, 106, 750–757. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, R.S. The role of zinc in growth and cell proliferation. J. Nutr 2000, 130, 1500S–1508S. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc—An overview. Nutrition 1995, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Oteiza, P.I. Zinc and the modulation of redox homeostasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2012, 53, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. Cytotoxic/tumor suppressor role of zinc for the treatment of cancer: An enigma and an opportunity. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther 2012, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Carraway, R.E.; Dobner, P.R. Zinc pyrithione induces ERK- and PKC-dependent necrosis distinct from TPEN-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 544–557. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.L.; Yang, M.W.; Liang, D.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, L. Cell apoptosis induced by zinc deficiency in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem 2012, 361, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kambe, T.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Nagao, M. Overview of mammalian zinc transporters. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2004, 61, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hogstrand, C.; Kille, P.; Nicholson, R.I.; Taylor, K.M. Zinc transporters and cancer: A potential role for ZIP7 as a hub for tyrosine kinase activation. Trends Mol. Med 2009, 15, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hathout, Y.; Fabris, D.; Fenselau, C. Stoichiometry in zinc ion transfer from metallothionein to zinc finger peptides. Int. J. Mass Spectrom 2001, 204, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, L.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Franklin, R.B.; Kennedy, M.C. Zinc inhibition of mitochondrial aconitase and its importance in citrate metabolism of prostate epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 28875–28881. [Google Scholar]
- Coffey, R.N.T.; Watson, R.W.G.; Hegarty, N.J.; O'Neill, A.; Gibbons, N.; Brady, H.R.; Fitzpatrick, J.M. Thiol-Mediated apoptosis in prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer 2000, 88, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.; Liang, J.Y.; Li, T.L.; Guan, Z.X.; Zou, J.; Franklin, R.B.; Costello, L.C. Zinc induces mitochondria apoptogenesis in prostate cells. Mol. Urol 2000, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, L.C.; Fenselau, C.C.; Franklin, R.B. Evidence for operation of the direct zinc ligand exchange mechanism for trafficking, transport, and reactivity of zinc in mammalian cells. J. Inorg. Biochem 2011, 105, 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Vallee, B.L.; Falchuk, K.H. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol. Rev 1993, 73, 79–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gumulec, J.; Masarik, M.; Krizkova, S.; Adam, V.; Hubalek, J.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Kizek, R. Insight to Physiology and pathology of zinc(II) ions and their actions in breast and prostate carcinoma. Curr. Med. Chem 2011, 18, 5041–5051. [Google Scholar]
- Aimo, L.; Cherr, G.N.; Oteiza, P.I. Low extracellular zinc increases neuronal oxidant production through nadph oxidase and nitric oxide synthase activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2010, 48, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima-Yuasa, A.; Umeda, K.; Olikita, T.; Kennedy, D.O.; Nishiguchi, S.; Matsui-Yuasa, I. Role of reactive oxygen species in zinc deficiency-induced hepatic stellate cell activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2005, 39, 631–640. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, A.; Roth, H.P.; Kirchgessner, M. Supplementation with vitamin C, vitamin E or beta-carotene influences osmotic fragility and oxidative damage of erythrocytes of zinc-deficient rats. J. Nutr 1997, 127, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Oteiza, P.I.; Olin, K.L.; Fraga, C.G.; Keen, C.L. Zinc-Deficiency causes oxidative damage to proteins, lipids and DNA in rat testes. J. Nutr 1995, 125, 823–829. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhao, H.B.; Wang, Q.S.; Pan, Y.C. Comparative analysis of MTF-1 binding sites between human and mouse. Mamm. Genome 2010, 21, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, G.K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression by oxidative stress and metal ions. Biochem. Pharmacol 2000, 59, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Soltaninassab, S.R.; Sekhar, K.R.; Meredith, M.J.; Freeman, M.L. Multi-faceted regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. J. Cell. Physiol 2000, 182, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cortese, M.M.; Suschek, C.V.; Wetzel, W.; Kroncke, K.D.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. Zinc protects endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide via Nrf2-dependent stimulation of glutathione biosynthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2008, 44, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook, G.L.; Mayer, M.L. Micromolar concentrations of Zn2+ antagonize NMDA and GABA responses of hippocampal-neurons. Nature 1987, 328, 640–643. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Li, Y. Coordination dynamics of zinc in proteins. Chem. Rev 2009, 109, 4682–4707. [Google Scholar]
- Zitka, O.; Kukacka, J.; Krizkova, S.; Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Masarik, M.; Prusa, R.; Kizek, R. Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr. Med. Chem 2010, 17, 3751–3768. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Imanishi, M.; Futaki, S.; Sugiura, Y. Alpha-Helical linker of an artificial 6-zinc finger peptide contributes to selective DNA binding to a discontinuous recognition sequence. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 8517–8524. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, S.S.; Majumdar, I.; Grishin, N.V. Structural classification of zinc fingers. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31, 532–550. [Google Scholar]
- Posewitz, M.C.; Wilcox, D.E. Properties of the SP1 zinc-finger-3 peptide-coordination chemistry, redox reactions, and metal-binding competition with metallothionein. Chem. Res. Toxicol 1995, 8, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Shaw, C.F.; Petering, D.H. Interprotein metal exchange between transcription factor IIIa and apo-metallothionein. J. Inorg. Biochem 2004, 98, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- CanoGauci, D.F.; Sarkar, B. Reversible zinc exchange between metallothionein and the estrogen receptor zinc finger. FEBS Lett 1996, 386, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Heuchel, R.; Schaffner, W.; Kagi, J.H.R. Thionein (apometallothionein) can modulate DNA-binding and transcriptional activation by zinc finger containing factor-SP1. FEBS Lett 1991, 279, 310–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Vallee, B.L.; Kagi, J.H.R. Zinc transfer from transcription factor-IIIA fingers to thionein clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9984–9988. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Larsen, K.S.; Vallee, B.L. Coordination dynamics of biological zinc “clusters” in metallothioneins and in the DNA-binding domain of the transcription factor Gal4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Roesijadi, G.; Bogumil, R.; Vasak, M.; Kagi, J.H.R. Modulation of DNA binding of a tramtrack zinc finger peptide by the metallothionein-thionein conjugate pair. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 17425–17432. [Google Scholar]
- Kroncke, K.D.; Klotz, L.O. Zinc fingers as biologic redox switches? Antioxid. Redox Signal 2009, 11, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W. Metallothionein disulfide interactions, oxidative stress, and the mobilization of cellular zinc. Neurochem. Int 1995, 27, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, C.; Maret, W.; Vallee, B.L. Control of zinc transfer between thionein, metallothionein, and zinc proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3489–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.J.; Maret, W.; Vallee, B.L. The glutathione redox couple modulates zinc transfer from metallothionein to zinc-depleted sorbitol dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W. Oxidative metal release from metallothionein via zinc thiol-disulfide interchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kroncke, K.D.; Fehsel, K.; Schmidt, T.; Zenke, F.T.; Dasting, I.; Wesener, J.R.; Bettermann, H.; Breunig, K.D.; Kolbbachofen, V. Nitric-oxide destroys zinc-sulfur clusters inducing zinc release from metallothionein and inhibition of the zinc finger-type yeast transcription activator LAC9. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1994, 200, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- St Croix, C.M.; Wasserloos, K.J.; Dineley, K.E.; Reynolds, I.J.; Levitan, E.S.; Pitt, B.R. Nitric oxide-induced changes in intracellular zinc homeostasis are mediated by metallothionein/thionein. Am. J. Physiol 2002, 282, L185–L192. [Google Scholar]
- Spahl, D.U.; Berendji-Grun, D.; Suschek, C.V.; Kolb-Bachofen, V.; Kroncke, K.D. Regulation of zinc homeostasis by inducible NO synthase-derived NO: Nuclear translocation and intranuclear metallothionein Zn2+ release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13952–13957. [Google Scholar]
- Malaiyandi, L.M.; Dineley, K.E.; Reynolds, I.J. Divergent consequences arise from metallothionein overexpression in astrocytes: Zinc buffering and oxidant-induced zinc release. Glia 2004, 45, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, L.L.; Gandley, R.E.; Han, W.P.; Wasserloos, K.; Stitt, M.; Kanai, A.J.; McLaughlin, M.K.; Pitt, B.R.; Levitan, E.S. Role of metallothionein in nitric oxide signaling as revealed by a green fluorescent fusion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W. Zinc and sulfur: A critical biological partnership. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Vallee, B.L. Thiolate ligands in metallothionein confer redox activity on zinc clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3478–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W. Redox biochemistry of mammalian metallothioneins. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem 2011, 16, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, M.G.; Jayasurya, A.; Bay, B.H. Metallothioneins in human tumors and potential roles in carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res 2003, 533, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadi, M.; Leuschen, M.P.; ElRefaey, H.; Hamada, F.M.; Rojas, P. The antioxidant properties of zinc and metallothionein. Neurochem. Int 1996, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J. Metallothionein redox cycle and function. Exp. Biol. Med 2006, 231, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Bremner, I. Oxygen free-radicals and metallothionein. Free Radic. Biol. Med 1993, 14, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Iszard, M.B.; Liu, J.; Klassen, C.D. Effect of several metallothionein inducers on oxidative stress defense mechanisms in rats. Toxicology 1995, 104, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Aschner, M.; Conklin, D.R.; Yao, C.P.; Allen, J.W.; Tan, K.H. Induction of astrocyte metallothioneins (MTs) by zinc confers resistance against the acute cytotoxic effects of methylmercury on cell swelling, Na+ uptake, and K+ release. Brain Res 1998, 813, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Namdarghanbari, M.; Wobig, W.; Krezoski, S.; Tabatabai, N.M.; Petering, D.H. Mammalian metallothionein in toxicology, cancer, and cancer chemotherapy. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem 2011, 16, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Koropatnick, J.; Cherian, M.G. Metallothionein protects DNA from copper-induced but not iron-induced cleavage in vitro. Chem. Biol. Interact 1995, 96, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, K.; Nishimura, N.; Suzuki, J.S.; Tohyama, C.; Naganuma, A.; Satoh, M. Role of metallothionein as a protective factor against radiation carcinogenesis. J. Toxicol. Sci 2008, 33, 651–655. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, M.A.; Lazo, J.S.; Yalowich, J.C.; Allen, W.P.; Whitmore, M.; Bergonia, H.A.; Tzeng, E.; Billiar, T.R.; Robbins, P.D.; Lancaster, J.R.; et al. Metallothionein protects against the cytotoxic and DNA-damaging effects of nitric-oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4452–4456. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Rusnak, J.M.; Hoyt, D.G.; Settineri, C.E.; Pitt, B.R.; Lazo, J.S. Enhanced apoptosis in metallothionein null cells. Mol. Pharmacol 1997, 52, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X.; Zheng, J.M.; Xu, A.M.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, S.H. Downregulated expression of metallothionein and its clinicopathological significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res 2007, 37, 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Fraker, P.J.; King, L.E. A distinct role for apoptosis in the changes in lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis created by deficiencies in zinc. FASEB J 2001, 15, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Yu, H.X.; Wang, C.J.; Sun, L.H.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.Z.; Xiao, Q.Y.; Han, D.B.; Saiyin, H.; Zhu, J.D.; et al. Metallothionein MT1M is a tumor suppressor of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.W.; Fan, J.W.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, M.X.; Wen, Y.G.; Li, D.W.; Zhou, C.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Q.; Tang, H.M.; et al. Downregulation of Metallothionein 1F, a putative oncosuppressor, by loss of heterozygosity in colon cancer tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 918–926. [Google Scholar]
- Faller, W.J.; Rafferty, M.; Hegarty, S.; Gremel, G.; Ryan, D.; Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M.; Dervan, P.A.; Gallagher, W.M. Metallothionein 1E is methylated in malignant melanoma and increases sensitivity to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Melanoma Res 2010, 20, 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, S. Molecular functions of metallothionein and its role in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol 2012, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dutsch-Wicherek, M.; Sikora, J.; Tomaszewska, R. The possible biological role of metallothionein in apoptosis. Front. Biosci 2008, 13, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, H.M.; Woods, G.M.; Bennett, B.; Chung, R.S. The two faces of metallothionein in carcinogenesis: Photoprotection against UVR-induced cancer and promotion of tumour survival. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci 2010, 9, 586–596. [Google Scholar]
- Chaabane, W.; User, S.D.; El-Gazzah, M.; Jaksik, R.; Sajjadi, E.; Rzeszowska-Wolny, J.; Los, M.J. Autophagy, apoptosis, mitoptosis and necrosis: Interdependence between those pathways and effects on cancer. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp 2013, 61, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell. Prolif 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, R.; Kumar, D.; Li, T.M.; Singal, P.K. Metallothioneins, oxidative stress and the cardiovascular system. Toxicology 2000, 155, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie, A.H. Apoptosis: An overview. Br. Med. Bull 1997, 53, 451–465. [Google Scholar]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: Enemies within. Science 1998, 281, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie, A.H.; Bellamy, C.O.C.; Bubb, V.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Corbet, S.; Curtis, L.; Harrison, D.J.; Hooper, M.L.; Toft, N.; Webb, S.; et al. Apoptosis and carcinogenesis. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, D.K.; Chadha, V.D. Zinc: A promising agent in dietary chemoprevention of cancer. Indian J. Med. Res 2010, 132, 676–682. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, W.G.; Fraker, P.J. Preferential induction of apoptosis in mouse CD4(+)CD8(+)alphabeta- tcr(lo)CD3-epsilon(lo) thymocytes by zinc. J. Cell. Physiol 1995, 164, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, D.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Stennicke, H.R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Duriez, P.; Poirier, G.G.; Hannun, Y.A. Zinc is a potent inhibitor of the apoptotic protease, caspase-3—A novel target for zinc in the inhibition of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 18530–18533. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidou, M.; Maravelias, C.; Dona, A.; Spiliopoulou, C. Zinc: A multipurpose trace element. Arch. Toxicol 2006, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Seve, M.; Chimienti, F.; Favier, A. Role of intracellular zinc in programmed cell death. Pathol. Biol 2002, 50, 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.Z.; Cherian, M.G. Potential role of p53 on metallothionein induction in human epithelial breast cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Meplan, C.; Verhaegh, G.; Richard, M.J.; Hainaut, P. Metal ions as regulators of the conformation and function of the tumour suppressor protein p53: Implications for carcinogenesis. Proc. Nutr. Soc 1999, 58, 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Meplan, C.; Richard, M.J.; Hainaut, P. Metalloregulation of the tumor suppressor protein p53: zinc mediates the renaturation of p53 after exposure to metal chelators in vitro and in intact cells. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5227–5236. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Jacob, C.; Vallee, B.L.; Fischer, E.H. Inhibitory sites in enzymes: Zinc removal and reactivation by thionein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1936–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, E.S.; Kondo, Y.; Watkins, S.C.; Hoyt, D.G.; Lazo, J.S. Nucleophilic distribution of metallothionein in human tumor cells. Exp. Cell. Res 1996, 224, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinska-Mosson, M.; Milnerowicz, H.; Rabczynski, J.; Milnerowicz, S. Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein and p53 protein in pancreatic serous cystadenomas. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp 2009, 57, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, S.V.; Silveira, J.B.; Machado, V.D.; De-Paula, A.M.B.; Loyola, A.M.; de Aguiar, M.C.F. Expression of metallothionein and p53 antigens are correlated in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2009, 29, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, A.S. Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappa B. J. Clin. Invest 2001, 107, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Karin, M.; Cao, Y.X.; Greten, F.R.; Li, Z.W. NF-Kappa B in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-kappa B antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Guttridge, D.C.; Mayo, M.W.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-kappa B induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol 1999, 19, 5923–5929. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.X.; Ao, Z.H.; Prasad, K.V.S.; Wu, R.L.; Schlossman, S.F. IEX-1L, an apoptosis inhibitor involved in NF-kappa B-mediated cell survival. Science 1998, 281, 998–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Butcher, H.L.; Kennette, W.A.; Collins, O.; Zalups, R.K.; Koropatnick, J. Metallothionein mediates the level and activity of nuclear factor kappa B in murine fibroblasts. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therapeutics 2004, 310, 589–598. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Ahn, Y.S. Zinc-Induced NF-kappa B inhibition can be modulated by changes in the intracellular metallothionein level. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2003, 190, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Agrawal, K.C. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B: Potential role in metallothionein-mediated mitogenic response. Cancer Res 1998, 58, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cusack, J.C.; Liu, R.; Baldwin, A.S. Control of inducible chemoresistance: Enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappa B. Nat. Med 1999, 5, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Itoh, N.; Kawasaki, A.; Tanaka, J.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, K. Zinc-induced activation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter is mediated by metallothionein and nuclear factor-kappa B. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2001, 173, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Vasak, M. Possible role for metallothionein in protection against radiation-induced oxidative stress—Kinetics and mechanism of its reaction with superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 827, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, J.; Deruiter, N. Inhibition of hydroxyl-radical-generated DNA-degradation by metallothionein. Toxicol. Lett 1989, 47, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Klein, J.B.; Kang, Y.J. Metallothionein inhibits peroxynitrite-induced DNA and lipoprotein damage. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 38957–38960. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, M.A.; Lazo, J.S.; Yalowich, J.C.; Reynolds, I.; Kagan, V.E.; Tyurin, V.; Kim, Y.M.; Watkins, S.C.; Pitt, B.R. Cytoplasmic metallothionein overexpression protects NIH 3T3 cells from tert-butyl hydroperoxide toxicity. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 15238–15243. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.H.; Yang, C.L. Mechanism of gentamicin-nephrotoxicity in rats and the protective effect of zinc-induced metallothionein synthesis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 1994, 9, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.L.; Du, X.H.; Zhao, J.H.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.X. Zinc-Induced metallothionein synthesis could protect from gentamicin-nephrotoxicity in suspended proximal tubules of rats. Renal Fail 1994, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, B.A.; Eneman, J.D.; Gong, Q.; DurieuxLu, C.C. Increased oxidant resistance of alveolar epithelial type II cells. Isolated from rats following repeated exposure to cadmium aerosols. Toxicol. Lett 1995, 81, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, M.; Kondo, Y.; Mita, M.; Nakagawa, I.; Naganuma, A.; Imura, N. Prevention of carcinogenicity of anticancer drugs by metallothionein induction. Cancer Res 1993, 53, 4767–4768. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, M.; Naganuma, A.; Imura, N. Effect of preinduction of metallothionein on paraquat toxicity in mice. Arch. Toxicol 1992, 66, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada, A.R.; Byrnes, R.W.; Krezoski, S.O.; Petering, D.H. Direct reaction of H2O2 with sulfhydryl groups in HL-60 cells: Zinc-metallothionein and other sites. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1996, 334, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Chubatsu, L.S.; Meneghini, R. Metallothionein protects DNA from oxidative damage. Biochem. J 1993, 291, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, D.; Onosaka, S.; Cherian, M.G. Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in cell-nucleus and cytoplasm of rat-liver and kidney. Toxicology 1982, 24, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, W.W.; Vallee, B.L. Cell-Cycle regulation of metallothionein in human colonic-cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression. Prog. Nucl. Res. Mol. Biol 2001, 66, 357–384. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujikawa, K.; Imai, T.; Kakutani, M.; Kayamori, Y.; Mimura, T.; Otaki, N.; Kimura, M.; Fukuyama, R.; Shimizu, N. Localization of metallothionein in nuclei of growing primary cultured adult-rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 1991, 283, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Ibata, K.; Suzuki, K.T. Role of metallothionein in the cell cycle: Protection against the retardation of cell proliferation by endogenous reactive oxygen species. J. Health Sci 2004, 50, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Synchronized generation of reactive oxygen species with the cell cycle. Life Sci 2004, 75, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Nuclear trafficking of metallothionein requires oxidation of a cytosolic partner. J. Cell. Physiol 2005, 202, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Ogra, Y.; Onishi, S.; Kajiwara, A.; Hara, A.; Suzuki, K.T. Enhancement of nuclear localization of metallothionein by nitric oxide. J. Health Sci 2008, 54, 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Eckschlager, T.; Adam, V.; Hrabeta, J.; Figova, K.; Kizek, R. Metallothioneins and cancer. Curr. Protein Peptide Sci 2009, 10, 360–375. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M. Dose-Dependent increases in metallothionein synthesis in the lung and liver of paraquat-treated rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 1991, 107, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Sasaki, M.; Hojo, H. Antioxidative roles of metallothionein and manganese superoxide-dismutase induced by tumor-necrosis-factor-alpha and interleukin-6. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1995, 316, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Takeda, Y.; Kondoh, S.; Hayashi, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Aono, K. Increased metallothionein content in rat-liver and kidney following X-irradiation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 1986, 85, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Koropatnick, J.; Leibbrandt, M.; Cherian, M.G. Organ-specific metallothionein induction in mice by X-irradiation. Radiat. Res 1989, 119, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, K.; Satoh, M.; Muraoka, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Oida, M.; Shimizu, H. Induction of metallothionein synthesis in transplanted murine tumors by X-irradiation. Radiat. Res 1995, 143, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, J.; Tajima, Y.; Karasawa, M. Promotion of radioresistance by metallothionein induction prior to irradiation. Environ. Res 1987, 43, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, J. Metallothionein induction—A measure of radioprotective action. Health Phys 1988, 55, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kimler, B.F.; Liu, Y.P.; Klaassen, C.D. Metallothionein-I transgenic mice are not protected from gamma-radiation. Toxicol. Lett 1999, 104, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.H.; Zhou, Z.X.; Kang, Y.J. Attenuation of doxorubicin chronic toxicity in metallothionein-overexpressing transgenic mouse heart. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 3382–3387. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.C.; Sun, X.H. Antiapoptotic effect and inhibition of ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in metallothionein-overexpressing transigenic mice. Am. J. Pathol 2003, 163, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.X.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.H.; Wang, L.P.; Zhou, Z.X.; Kang, Y.J. Inhibition of superoxide generation and associated nitrosative damage is involved in metallothionein prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Zhou, Z.X.; Saari, J.T.; Kang, Y.J. Alcohol-Induced myocardial fibrosis in metallothionein-null mice—Prevention by zinc supplementation. Am. J. Pathol 2005, 167, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Merten, K.E.; Feng, W.K.; Zhang, L.; Pierce, W.; Cai, J.; Klein, J.B.; Kang, Y.J. Modulation of cytochrome c oxidase-Va is possibly involved in metallothionein protection from doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2005, 315, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.H.; Li, X.K.; Hein, D.W.; Xiang, X.L.; Marshall, J.P.; Prabhu, S.D.; Cai, L. Metallothionein suppresses angiotensin II-Induced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation, nitrosative stress, apoptosis, and pathological remodeling in the diabetic heart. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2008, 52, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, D.; Yepiskoposyan, H.; Selvaraj, A.; Balamurugan, K.; Rajaram, R.; Simons, A.; Multhaup, G.; Mettler, S.; Vardanyan, A.; Georgiev, O.; et al. A family knockout of all four Drosophila metallothioneins reveals a central role in copper homeostasis and detoxification. Mol. Cell. Biol 2006, 26, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar]
- Krizkova, S.; Ryvolova, M.; Hrabeta, J.; Adam, V.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Kizek, R. Metallothioneins and zinc in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Drug Metab. Rev 2012, 44, 287–301. [Google Scholar]




| Reactive Oxygen Species | Reactive Nitrogen Species | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free Radicals | Other Substances | Free Radicals | Other Substances | ||||
| Superoxide anion radical | O2•− | Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 | Nitric oxide radical | NO• | Peroxynitrite | ONOO− |
| Hydroxyl radical | HO• | Hypochlorous acid | HOCl | Nitric dioxide radical | NO2• | Nitrites | NO2− |
| Alkoxyl radical | RO• | Ozone | O3 | Nitrates | NO3− | ||
| Peroxyl radical | ROO• | Singlet oxygen | 1O2 | Nitrosyl | NO+ | ||
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Nejdl, L.; Gumulec, J.; Zitka, O.; Masarik, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. The Role of Metallothionein in Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6044-6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14036044
Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Nejdl L, Gumulec J, Zitka O, Masarik M, Eckschlager T, Stiborova M, Adam V, Kizek R. The Role of Metallothionein in Oxidative Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(3):6044-6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14036044
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuttkay-Nedecky, Branislav, Lukas Nejdl, Jaromir Gumulec, Ondrej Zitka, Michal Masarik, Tomas Eckschlager, Marie Stiborova, Vojtech Adam, and Rene Kizek. 2013. "The Role of Metallothionein in Oxidative Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 3: 6044-6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14036044
APA StyleRuttkay-Nedecky, B., Nejdl, L., Gumulec, J., Zitka, O., Masarik, M., Eckschlager, T., Stiborova, M., Adam, V., & Kizek, R. (2013). The Role of Metallothionein in Oxidative Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(3), 6044-6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14036044